Text
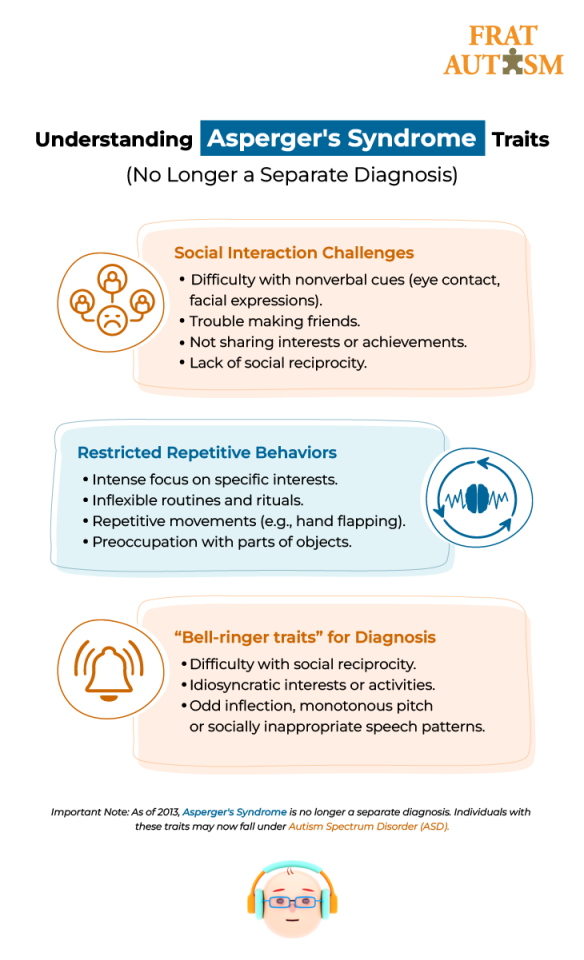
What is Asperger’s Syndrome?
What is Asperger’s Syndrome?
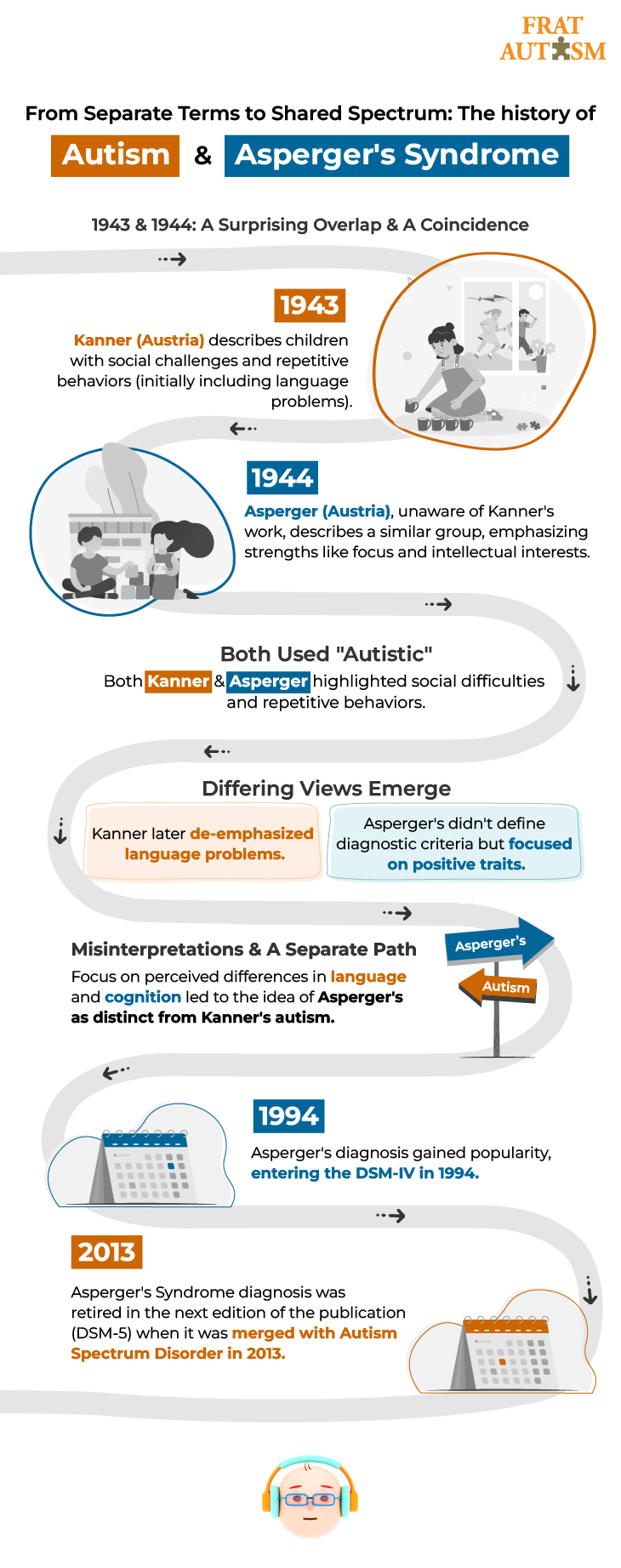
In the past, Asperger’s Syndrome was seen as a milder version of autism, or a way of being autistic with stronger cognitive skills. People diagnosed with Asperger’s were thought to experience autistic traits that were less severe or closer to those seen in neurotypical individuals.
The syndrome was named after the Austrian pediatrician Hans Asperger, who, in 1944, described children in his care who struggled to form friendships, did not understand others’ gestures or feelings, engaged in one-sided conversations about their favorite interests, and were clumsy.
Asperger’s was first introduced into the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) in 1994 and was retired in the next edition of this publication, the DSM-5 in 2013, when it became a part of the Autism Spectrum Disorder.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding ABA Therapy: A Key to Unlocking Potential in Children with Autism
What is ABA Therapy?
ABA therapy, which stands for Applied Behavior Analysis, is a way of learning that focuses on rewarding positive behaviors and helping people reduce challenging behaviors or develop new skills.
Sometimes, behaviors can become too frequent or intense, causing difficulties in daily life. These are often called ‘challenging behaviors’ and can include things like tantrums, meltdowns, repetitive actions, or difficulty following instructions.
ABA therapy can be particularly helpful in addressing these challenges. ABA therapists work closely with individuals and their families to identify these specific challenging behaviors. They then develop a personalized plan to address them. This plan often involves positive reinforcement for desired behaviors, alongside strategies to reduce the occurrence of challenging ones.
In some cases, ABA therapy may be combined with other approaches like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to achieve even greater results.
This blog post will delve deeper into the principles of ABA therapy, explore its benefits, and answer common questions parents may have.
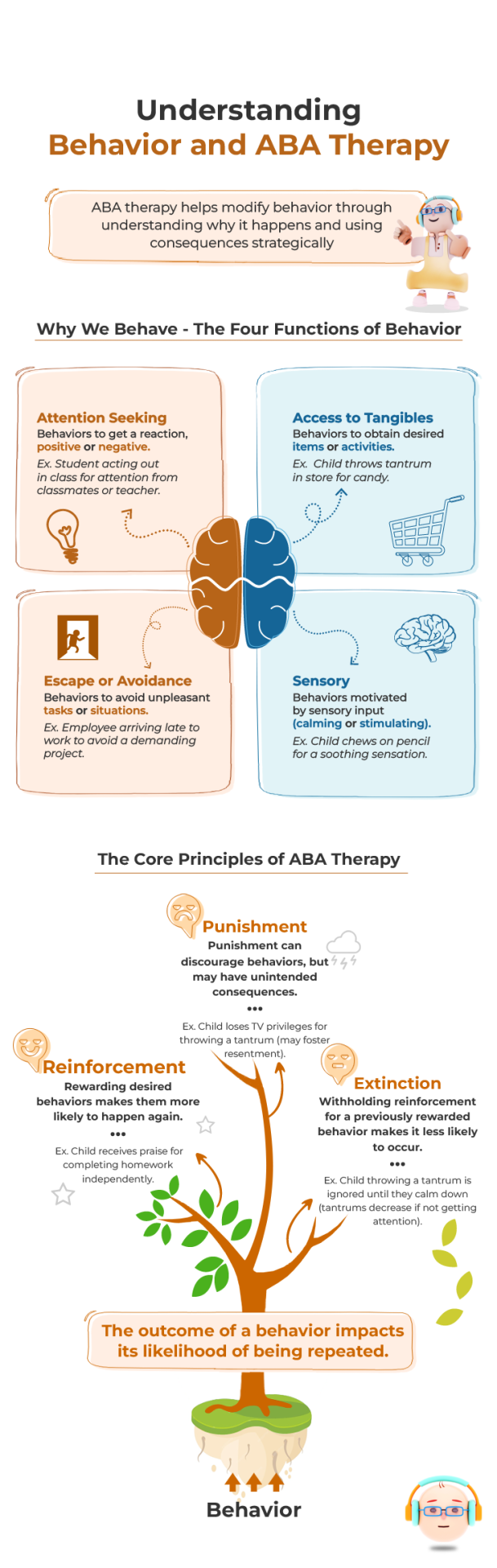
Understanding ABA therapy
Have you ever wondered why children act the way they do? Understanding the reasons behind behaviors is crucial, especially when it comes to modifying them. In ABA therapy, this initial step involves identifying the function of a particular behavior. This essentially means figuring out what the child is trying to achieve through their actions.
Understanding Why We Behave: The Four Functions of Behavior
Here are four main categories that encompass most behaviors:
Access to Attention: Sometimes, behaviors are simply a cry for attention. Imagine a student who starts acting out in class. They might be craving the acknowledgement of their peers or the teacher’s intervention.
Example: A toddler throws a tantrum in the grocery store because his/her parents refuse to buy him/her candy. The tantrum might be a way to get the parent’s attention and potentially change their mind.
Access to Tangibles: This function is all about getting something desired. A classic example is a child who throws a fit in the checkout line, demanding a specific toy. If the parent gives in to stop the scene, the child learns that this behavior leads to the desired outcome.
Example: A teenager cleans their room meticulously only when they know it will result in getting permission to go to a party.
Access to Escape: Sometimes, behaviors are a way to avoid something unpleasant. This could be a boring task, a reprimand, or even a specific activity. Imagine a child who suddenly complains of stomach pain right before bedtime to avoid going to sleep.
Example: An employee starts arriving late to work consistently to escape a particularly demanding project they’ve been assigned.
Sensory: Our nervous system can also influence behavior. Certain actions might provide a calming or stimulating sensation that the person seeks out. Fidgeting, nail-biting, or rocking back and forth can all be examples of sensory-seeking behaviors.
Example: A child chews on their pencil in class not because they’re hungry, but because the chewing provides a soothing sensation for their nervous system.
The Core Principles of ABA Therapy: Understanding How We Learn
Now that we understand the “why” behind behaviors, let’s explore the core principles of ABA therapy that inform how these behaviors can be modified. These principles all revolve around the concept of consequences and their impact on future behavior.
Behavior is controlled by consequences: The actions we take are heavily influenced by the outcome. If a behavior consistently leads to a positive outcome (reinforcement), it’s more likely to be repeated. Conversely, if a behavior leads to an undesirable outcome (punishment) or no outcome at all (extinction), it’s less likely to be repeated in the future.
Reinforcement (reward) increases or strengthens behavior: Positive reinforcement is a key tool in ABA therapy. When a desired behavior occurs, it’s followed by a reward, making it more likely to happen again in the future.
Example: A child who completes their homework without being reminded receives praise from the parent, strengthening the behavior of completing homework independently.
Punishment decreases or weakens behavior: Punishment can be used to discourage unwanted behaviors. However, it’s important to note that punishment can also have unintended consequences, such as fostering resentment or fear. ABA therapy often utilizes positive reinforcement techniques as a more effective long-term strategy.
Example: A child who throws a tantrum might lose the privilege of watching their favorite TV show for a short period. The goal is to discourage tantrums in the future.
Extinction is the process of withholding reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior: When a behavior no longer leads to a desired outcome (previously reinforcing consequence), it’s likely to decrease in frequency.
Example: A child who throws a tantrum to get attention might be ignored by the parent until he/she calms down. Over time, if the tantrums no longer get a reaction, they’re likely to decrease.
1 note
·
View note
Text
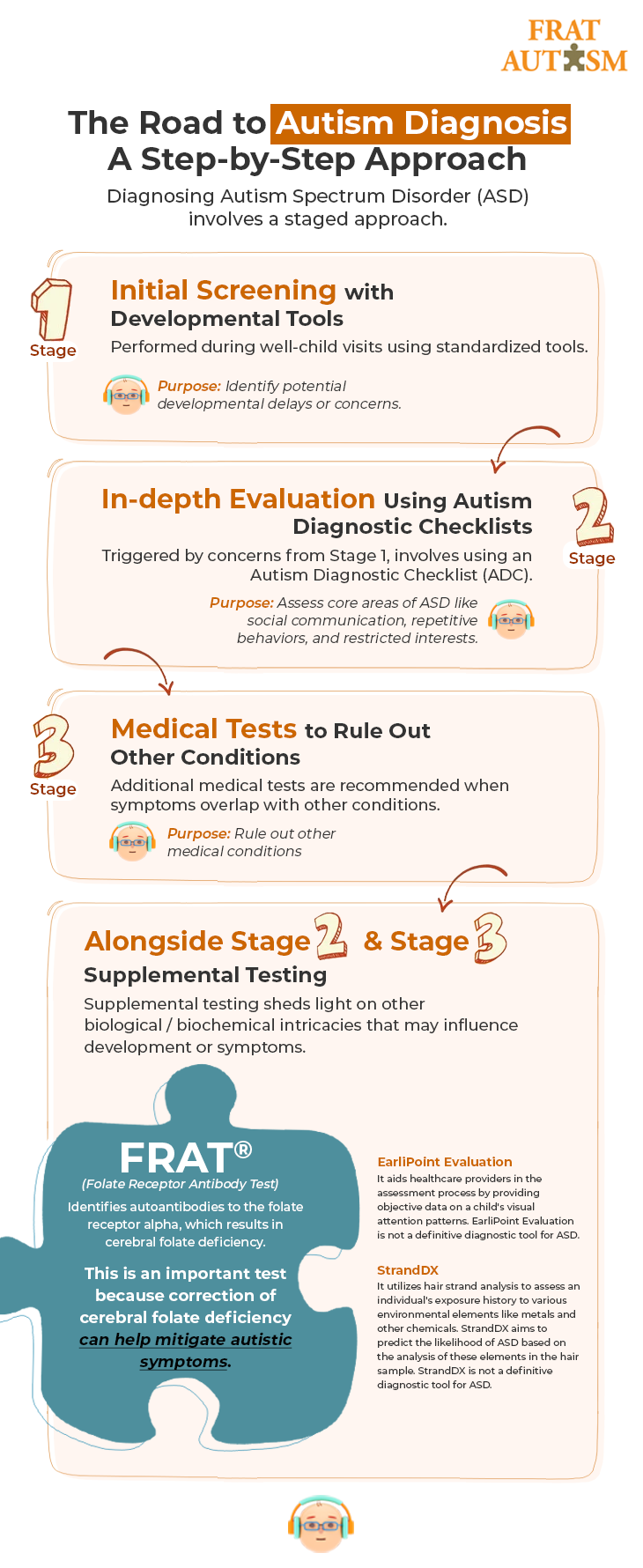
How is Autism Diagnosed?
Introduction:
The journey of diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a multifaceted process that involves careful observation, evaluation, and collaboration with healthcare professionals. Unlike straightforward medical tests, diagnosing ASD requires a comprehensive approach due to the spectrum's varied manifestations. This blog explores the intricate steps involved in diagnosing ASD, shedding light on the complexities parents may encounter along the way.
To uncover the detailed process of diagnosing ASD, check the image below.
0 notes
Text
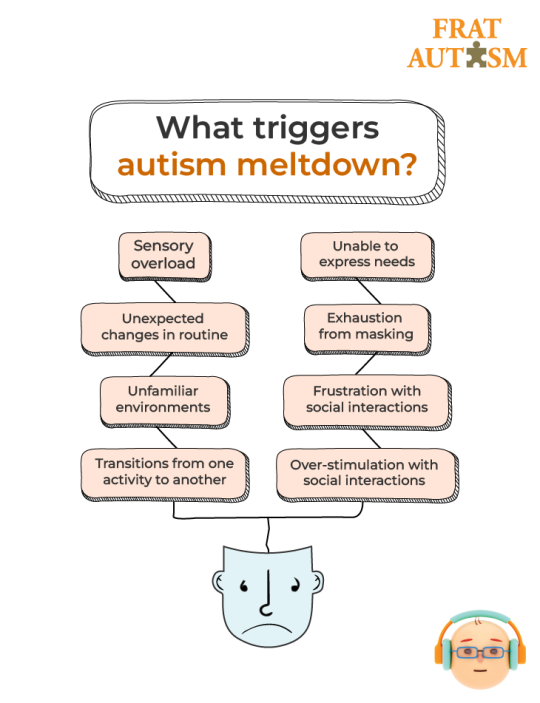
Autism Meltdown: A Guide For Everyone
Introduction:
Navigating autism meltdowns can be a challenging journey for both individuals on the spectrum and their caregivers. Understanding the nuances of these meltdowns, from triggers to supportive strategies, is key to providing effective assistance. In this blog, we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of autism meltdowns, shedding light on their differences from tantrums and offering insights into prevention and support.
To delve deeper into the world of autism meltdowns, check the image below.
0 notes
Text
Navigating the Spectrum: The 3 Autism Levels Explained
Introduction:
Understanding autism can be overwhelming, especially when faced with the complexities of support levels. But fear not, as we embark on a journey to demystify this spectrum. Today, we delve into the three levels of autism, shedding light on the nuances of each. Join us in unraveling this narrative of support, empowerment, and individuality.
To know more, check the image below.

#asd#autism#autism spectrum disorder#frat#fratnow#autism levels#levels of autism#autism level 2#autism level 1#autism level 3#asd level 1#asd level 2#asd level 3
0 notes
Text
Understanding the What, Why and How of Autism Masking
What is Autism Masking?
Autism masking, also called autism camouflaging or autism neurodivergent masking, describes the conscious or subconscious effort by autistic people to suppress their autistic traits and behaviors to appear neurotypical i.e. non-autistic.
Autism masking is a coping mechanism used by individuals with autism to hide their autism symptoms to either fit into or better navigate social situations.

What Does Autism Masking Look Like?
Imagine you’re playing dress-up. You put on a costume, maybe a superhero cape or a pirate hat, to fit in with the game. That is kind of what “masking” is in autism. Some autistic people act differently in social situations than they do naturally, like wearing a “social costume” to fit in.
But underneath that costume are their autistic traits, their unique way of thinking and experiencing the world. It’s like their superpowers! This table shows some differences between these “superpowers” and the “costume” some people choose to wear:
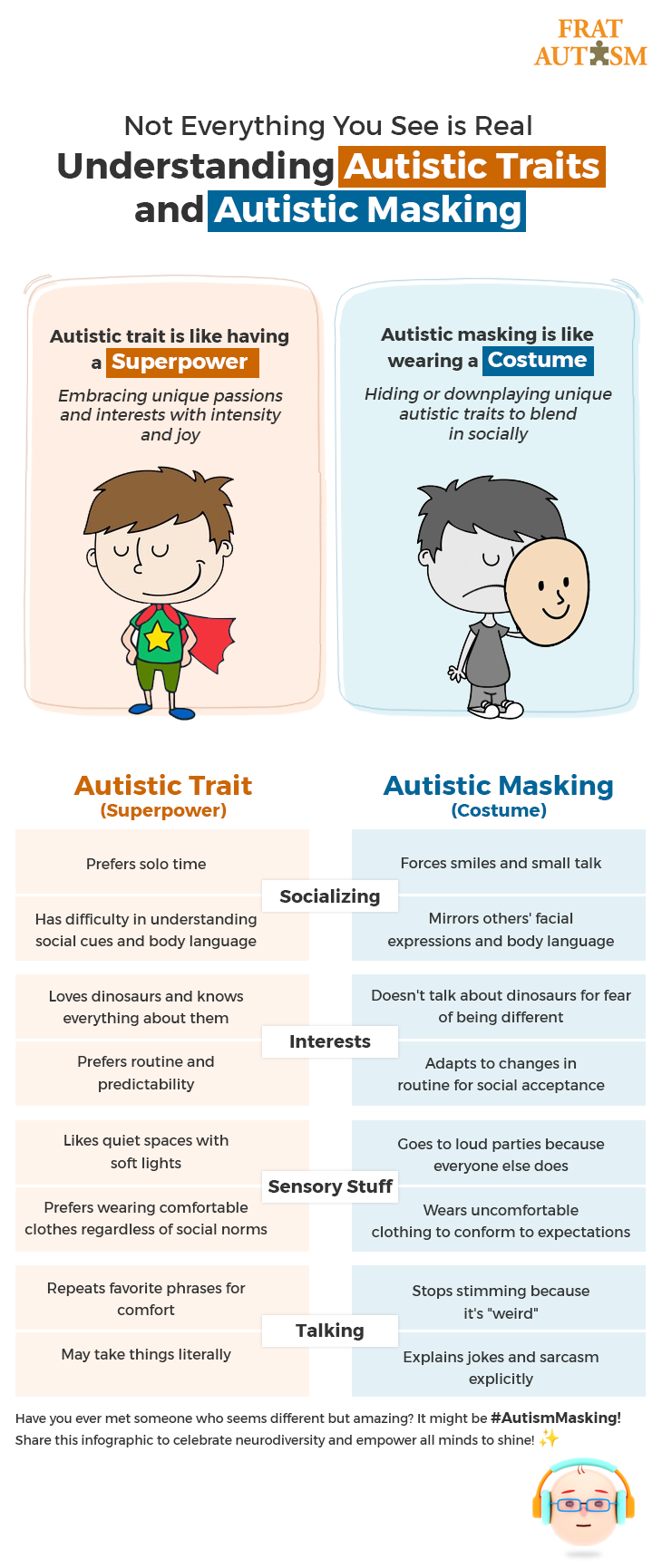
Remember, not every autistic individual wears a costume all the time, and the costume can look different for each person. The most important thing is to be kind and understanding of everyone, no matter what “costume” they wear!
Why Do Autistic People Mask?
Imagine living in a world where your natural way of interacting, processing information, and experiencing joy makes you stand out. Imagine the subtle (and sometimes not-so-subtle) cues that tell you you’re “different,” that your unique perspective isn’t always welcome. This, unfortunately, is the reality for many autistic individuals who engage in masking, a complex phenomenon where they adapt their behavior to conform to social expectations.
The core driver behind masking lies in the universal human desire for belonging and acceptance. We are innately wired to connect with others, and rejection stings deeply. Autistic individuals, unfortunately, often face social rejection due to their neurodivergent traits. Stimming behaviors, sensory sensitivities, and even blunt honesty can be misconstrued as “weird” or “inappropriate” by neurotypical individuals, leading to ostracism and bullying. To navigate this challenging social landscape, many autistic individuals choose to mask their natural behaviors.
Understanding why autistic people mask is crucial for building a more inclusive and accepting world. By recognizing the inherent desire for connection and the challenges faced due to neurodivergence, we can create spaces where autistic individuals feel safe to express themselves authentically, without fear of rejection or judgment.

Is Autistic Masking Good?
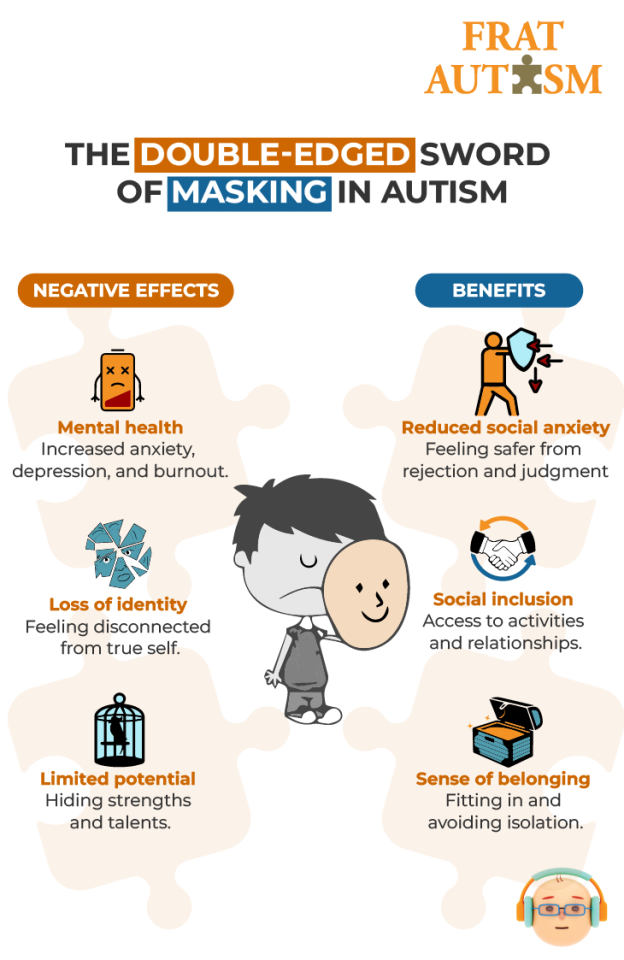
It’s crucial to remember that masking is not a choice but a coping mechanism. While masking can offer some short-term relief from social anxieties, it comes at a significant cost.
Mental Health Impact: Masking can be mentally and emotionally draining, leading to anxiety, depression, and burnout. Suppressing one’s authentic self for extended periods can take a toll on self-esteem and well-being.
On Stress & Anxiety: The 2019 study on Understanding the Reasons, Contexts and Costs of Camouflaging for Autistic Adults[1] revealed higher stress and anxiety in people who masked autistic traits frequently compared to those who masked less often.
On Depression: In 2018, research (Experiences of Autism Acceptance and Mental Health in Autistic Adults)[2] revealed that autistic adults who masked their traits more often were more likely to experience depression and feel socially ostracized.
Exhaustion: A 2016 NIH study[3] found that autistic women who masked their traits to conform to neurotypical expectations reported feeling exhausted by the constant effort.
Loss of Identity: Masking can create a disconnect between an individual’s true self and the persona they present to the world. This can lead to feelings of inauthenticity and confusion about one’s identity.
Limited Potential: Masking can prevent autistic individuals from fully expressing their unique strengths and talents. By hiding their true selves, they may miss opportunities to connect with others who share their interests and perspectives.
Perpetuating Stereotypes: Masking reinforces the idea that there is only one “right” way to be social, further marginalizing autistic individuals and their unique experiences.
1 note
·
View note
Text
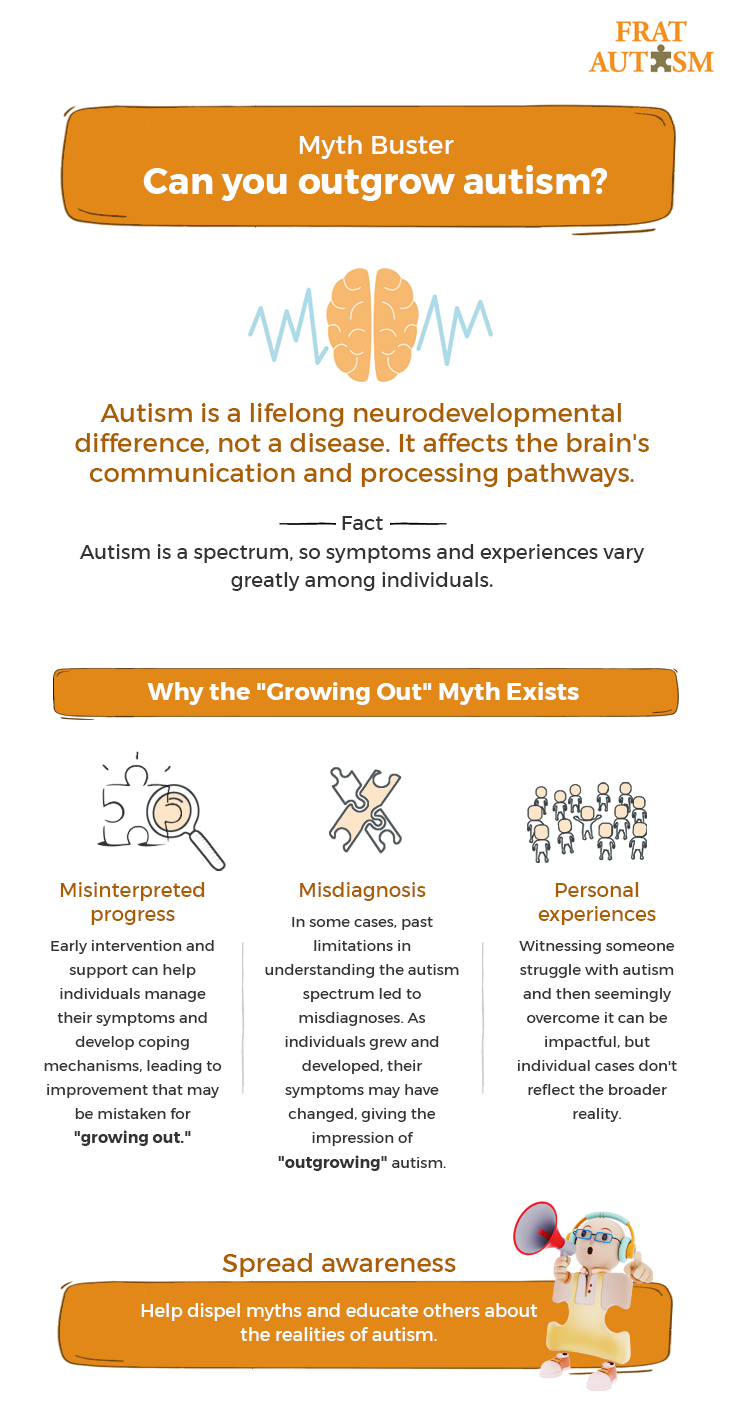
Can Autism Go Away?
Introduction:
Autism is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that persists throughout a person's lifetime, with no known cure. While some may believe it can vanish with age, the reality is far more nuanced. Autism manifests uniquely in each individual, with a spectrum of challenges and strengths. Early intervention and tailored therapies play a pivotal role in supporting individuals on the autism spectrum.
To learn more about the complexities of autism and the role of early intervention, explore the detailed information provided below.
To delve deeper into the subject, refer to the attached image.
#asd#autism#autism spectrum disorder#frat#fratnow#ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder)#autism awareness#autism acceptance#autism support#autism community#AutismAwarenessMonth
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Guide to Speech Delay and Autism: Types, Red Flags, Impact and the Power of Early Intervention
Introduction:
Meet John, an eight-year-old bursting with knowledge about dinosaurs yet struggling to express his own needs and desires. John's journey is a glimpse into the world of speech delay in autism — a world filled with complexities, challenges, and untapped potential.
In this blog, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of speech delay in autism, exploring its nuances and shedding light on the critical role of early intervention. Join us as we uncover the layers of communication barriers and discover pathways to empowerment for children like John.
To learn more about John's story and delve deeper into the complexities of speech delay in autism, check the image below:
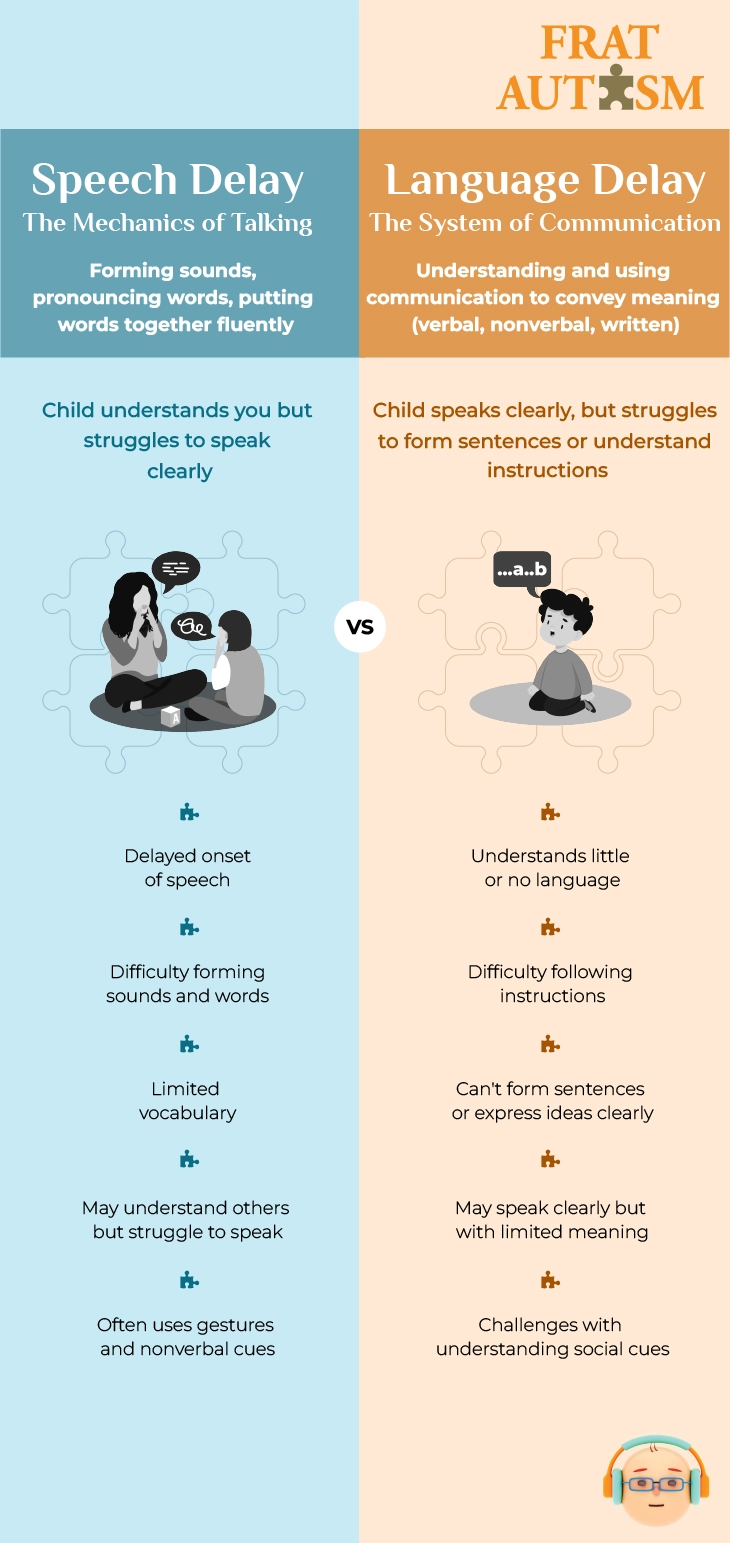
#asd#autism#autism spectrum disorder#frat#fratnow#speech delay#speech development#speech delay in autism
0 notes
Text
Echolalia in Autism: Causes, Types, Reasons, Treatment and Support
Introduction:
Echolalia, the charming repetition of words or phrases, holds a captivating mystery within the world of children, especially those navigating the realm of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). While often misconstrued, echolalia is far more than mere echoes—it's a nuanced form of communication, a pathway to understanding, and a key to unlocking the intricate world of language development in children.
Curious to delve deeper into the layers of echolalia and its significance in the lives of children? Discover the intricacies, functions, and impacts of echolalia in autism, and uncover the unseen threads that weave through the fabric of communication.
To know more, check the image below:
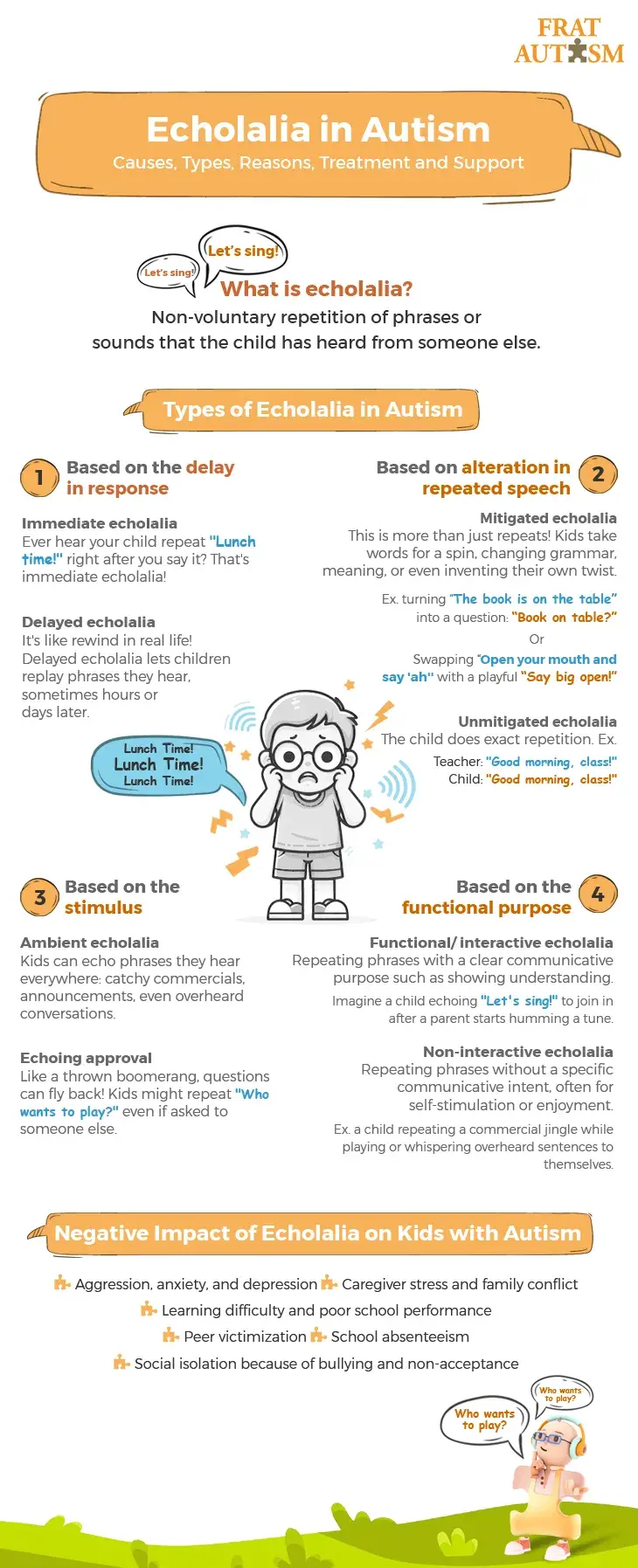
1 note
·
View note
Text
From Triggers to Strategies: Understanding and Navigating Autism Wandering

Introduction:
In December 2017, the Noel family's world took an unexpected turn when four-year-old Chelsea, diagnosed with autism and non-verbal, embarked on a wandering journey that left her family in a state of fear and uncertainty. Chelsea's story is unfortunately not unique, shedding light on the challenges faced by autistic children and the profound impact of wandering on their families. In this blog, we delve into the intricate world of autism wandering, exploring triggers, challenges, and strategies to ensure the safety of these extraordinary children.
Understanding Autism Wandering: Autism wandering refers to the tendency of autistic individuals to leave safe spaces, exposing themselves to potential dangers. This behavior poses significant risks, and Chelsea's story underscores the urgency of addressing this issue.
Triggers and Challenges: Autism wandering can be triggered by various factors, including destination-driven motives, escape from overwhelming situations, or other sensory-related challenges. Understanding these triggers is crucial for devising effective safety measures.
Safety Concerns and Impact on Families: While the world may be a playground for autistic individuals, statistics reveal the overshadowing risks associated with wandering. Chelsea's story highlights not only the potential dangers for the child but also the emotional toll on caregivers.
Prevention Strategies: Building a bridge of safety is essential to empower both parents and children in navigating the challenges of autism wandering. This blog offers practical strategies, including key supervision techniques, understanding triggers, teaching safety measures, and utilizing technology for enhanced safety.
Responding to Wandering Instances: In moments of crisis, staying calm and taking immediate steps are paramount. This blog provides a comprehensive guide on responding to wandering instances, from alerting local authorities to prioritizing safety zones.
Conclusion and Support: Wandering is a complex issue, but hope and proactive action can pave the way for greater safety and freedom. Embrace the strategies outlined in this blog, tailored to the unique needs of each child. Remember, you are not alone on this journey.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Low-Functioning Autism: Definition, Therapies, Comorbidities & FAQs

Introduction:
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that manifests differently in each individual, leading to a diverse range of strengths and challenges. The terms "low-functioning" and "high-functioning" autism, while commonly used, can be misleading and stigmatizing. It's important to understand that these terms lack official medical recognition within the current diagnostic framework.
Understanding "Low-Functioning" Autism: The term "low-functioning autism" is not an official medical diagnosis, but it is often used colloquially to describe individuals with ASD who face significant challenges in communication, social interaction, and behavior. However, this term is considered outdated and misleading due to its potential to oversimplify and stigmatize the diverse experiences of individuals on the autism spectrum.
Symptoms and Therapies: Individuals with severe autism may exhibit a range of symptoms, including severe language deficits, sensory challenges, repetitive behaviors, and behavioral problems. Therapeutic interventions, such as Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC), speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, sensory integration therapy, and Applied Behavioral Analysis (ABA), can be tailored to address specific needs.
Comorbid Conditions: Children with severe autism may have comorbid conditions, including skin allergies, asthma, food allergies, ear infections, headaches, gastrointestinal problems, and sleep disorders. Some genetic and neurological disorders are also more prevalent in individuals with ASD.
Importance of Early Intervention: Early intervention is crucial for individuals with low-functioning autism, offering significant improvements in communication, social interaction, and behavior. Early support empowers both individuals and their caregivers to navigate challenges effectively.
Managing Challenging Behaviors: Challenging behaviors in individuals with low-functioning autism require careful management. Identifying triggers, using visual supports, addressing sensory needs, reinforcing positive behavior, and implementing comprehensive behavior plans are key strategies.
Support for Families and Caregivers: Families and caregivers play a vital role in the well-being of individuals with low-functioning autism. Respite care and support groups provide avenues for relaxation, rejuvenation, and connection with others facing similar challenges.

2 notes
·
View notes