Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Exploring the Efficiency of Pneumatic Linear Actuators in Industrial Automation

Introduction
Pneumatic Linear Actuators Pneumatic linear actuators are crucial components in industrial automation systems, providing reliable and efficient motion control. These actuators utilize compressed air to generate linear motion, making them suitable for various applications across industries such as manufacturing, automotive, packaging, and more. Understanding their efficiency is vital for optimizing productivity and minimizing energy consumption in automated processes and for more details click here Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
Operating Principles and Mechanisms
Pneumatic linear actuators operate based on the principle of converting compressed air energy into linear motion. They typically consist of a piston enclosed within a cylinder, with air pressure applied to one side of the piston to create movement. This simple yet effective mechanism allows for precise control over the actuator's extension and retraction, making them ideal for tasks requiring repetitive and accurate motion.
Efficiency Metrics and Performance Factors
Efficiency in pneumatic linear actuators is evaluated based on several metrics, including speed, force output, energy consumption, and reliability. Factors such as air pressure, cylinder size, and valve design significantly influence their performance. Optimizing these parameters ensures maximum efficiency while minimizing operational costs and downtime. Additionally, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques contribute to enhancing the overall efficiency and longevity of pneumatic actuators.
Applications in Industrial Automation
Pneumatic linear actuators find widespread use in various industrial automation applications, ranging from simple pick-and-place operations to complex assembly processes. Their fast response times, high force output, and suitability for harsh environments make them indispensable in industries where reliability and productivity are paramount. Examples include material handling, machine loading, robotic arm movements, and conveyor systems.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their numerous advantages, pneumatic linear actuators face challenges such as air leakage, friction, and limited speed control. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving sealing technologies, reducing internal friction, and enhancing control algorithms. Moreover, the integration of smart sensors and predictive maintenance techniques holds promise for further optimizing the efficiency and reliability of pneumatic actuation systems in the future.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Several case studies demonstrate the successful implementation of pneumatic linear actuators in industrial automation settings. For instance, a manufacturing plant achieved significant cost savings and productivity improvements by replacing hydraulic actuators with pneumatic ones due to their lower maintenance requirements and faster response times. Similarly, an automotive assembly line utilized pneumatic actuators for precise positioning of components, resulting in higher throughput and assembly accuracy.
Conclusion and Outlook
In conclusion, pneumatic linear actuators play a crucial role in driving efficiency and productivity in industrial automation applications. By understanding their operating principles, optimizing performance factors, and addressing challenges, manufacturers can maximize the benefits of these versatile actuation systems. Continued innovation and integration of advanced technologies will further enhance the efficiency and reliability of pneumatic linear actuators, ensuring their continued relevance in the evolving landscape of industrial automation.
0 notes
Text
Pushing Boundaries: How Pneumatic Linear Actuators Are Changing the Game!
In the realm of automation and robotics, pneumatic linear actuators have emerged as a groundbreaking technology, revolutionizing various industries by pushing the boundaries of what is possible. These versatile devices harness the power of compressed air to create linear motion, offering a myriad of benefits that make them an attractive choice for engineers and innovators seeking efficient and cost-effective solutions.

One of the key advantages of pneumatic linear actuators is their simplicity and reliability. Unlike complex mechanical systems, these actuators operate on a straightforward principle: the conversion of air pressure into linear motion. This simplicity translates to ease of use and maintenance, making them a preferred choice for applications where reliability is paramount. Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace are increasingly adopting pneumatic actuators to enhance the efficiency and dependability of their processes.
Efficiency is a critical factor in any industrial setting, and pneumatic linear actuator excel in this regard. They offer fast and precise movement, making them ideal for applications that demand quick response times and high-speed operations. Whether it's in assembly lines, packaging, or material handling, the speed and accuracy of pneumatic actuators contribute to increased productivity and reduced cycle times. This efficiency gains a competitive edge for businesses by optimizing their manufacturing processes.
The lightweight nature of pneumatic actuators is another game-changing aspect. In applications where weight is a crucial factor, such as robotics and aerospace, the use of lightweight components is essential for achieving optimal performance. Pneumatic actuators, being lighter than their hydraulic or electric counterparts, provide a significant advantage in these industries. This weight advantage not only enhances overall system efficiency but also contributes to energy savings.
One of the standout features of pneumatic linear actuators is their ability to operate in harsh environments. The absence of electrical components in the actuator itself makes it less susceptible to damage from dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures. This robustness is particularly valuable in industries like mining, construction, and agriculture, where equipment is often exposed to challenging conditions. Pneumatic actuators can withstand these harsh environments, ensuring reliable performance even in the toughest situations.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of pneumatic linear actuators positions them as an attractive option for budget-conscious industries. The simplicity of their design, coupled with the widespread availability of compressed air, makes them more affordable to implement and maintain compared to other actuation technologies. This cost-effectiveness extends not only to the initial investment but also to ongoing operational expenses, contributing to a favorable return on investment for businesses.
As technology continues to advance, innovations in pneumatic linear actuators are expanding their capabilities. Modern designs incorporate features such as electronic control systems, allowing for precise positioning and programmable motion profiles. These advancements enable even greater flexibility in applications, opening doors to new possibilities in industries ranging from medical devices to entertainment.
In conclusion, pneumatic linear actuators are pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in the realm of automation and robotics. Their simplicity, reliability, efficiency, lightweight design, resilience in harsh environments, and cost-effectiveness make them a preferred choice across a spectrum of industries. As technology evolves, the integration of electronic control systems further enhances their capabilities, solidifying their position as a game-changer in the world of linear motion. Whether it's speeding up manufacturing processes or navigating challenging environments, pneumatic linear actuators are indeed changing the game, setting new standards for performance and versatility.
0 notes
Text
What is a Pneumatic Actuator? Types & Applications

A pneumatic actuator is a device that converts energy from compressed air into mechanical motion. It serves as a crucial component in various industries, operating valves and mechanisms by using air pressure Pneumatic Linear Actuator. Here's an overview covering its types, workings, and applications:
1. Types of Pneumatic Actuators:
a. Pneumatic Cylinder Actuators:
Single-Acting Cylinders: These use air pressure to extend or retract the piston rod in one direction, with a spring returning it to its original position.
Double-Acting Cylinders: They utilize air pressure in both directions to extend and retract the piston, offering more control over motion.
b. Rotary Pneumatic Actuators:
Vane Actuators: These utilize vanes rotated by air pressure to create motion, typically for valves or rotary mechanisms.
Rack and Pinion Actuators: These employ a rack and pinion gear system to transform linear motion into rotary motion.
2. How Pneumatic Actuators Work:
Air Input: Compressed air enters the actuator, exerting pressure on a piston or other mechanisms, initiating motion.
Conversion of Energy: The air pressure causes movement, either extending or retracting the actuator based on the design and type.
Mechanical Motion: This mechanical motion is then utilized to control valves, move machinery, or perform other tasks within an industrial system.
3. Applications of Pneumatic Actuators:
a. Industrial Valves:
Pneumatic actuators are extensively used to control and regulate various types of industrial valves, such as gate valves, ball valves, and butterfly valves, ensuring fluid flow control in pipelines and systems.
b. Automation and Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, pneumatic actuators control robots, assembly line equipment, and various machinery, enabling precise movements and automated operations.
c. HVAC Systems:
Pneumatic actuators play a role in controlling heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, managing air flow and temperature regulation in buildings.
d. Transportation:
These actuators are employed in pneumatic brakes, door systems, and other mechanisms in vehicles, trains, and aircraft.
e. Medical and Life Sciences:
In medical devices and life science applications, pneumatic actuators aid in precise movements in equipment and devices, contributing to research and healthcare systems.
f. Packaging and Material Handling:
Pneumatic actuators are used in packaging machinery and material handling systems to manipulate and control the movement of goods in manufacturing facilities and warehouses.
g. Robotics and Control Systems:
Actuators are crucial components in robotics, providing the necessary motion control in various robotic applications, from assembly to exploratory robots.
In essence, pneumatic actuators serve as a fundamental component in numerous industries, providing controlled and precise mechanical motion through the utilization of compressed air. Their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability make them essential in controlling valves, automating systems, and facilitating various industrial operations.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Considerations when selecting a linear pneumatic actuator

To ensure the best performance and compatibility for your application, you should consider several factors when selecting a linear pneumatic actuator. We will explore the most important factors to consider when selecting a pneumatic actuator.
Force: Calculate the force required for your application. Take into account the weight of the object or the force needed to manipulate it. Make sure that the actuator can produce enough force to meet your requirements.
Stroke Length: Take into consideration the stroke length required, which is the distance that the actuator can extend and retract. Make sure that the stroke length of the actuator is aligned with the required range of motion for your application.
Speed : Determine the speed required for your application. Calculate how fast the actuator must extend and retract Pneumatic Linear Actuator. You should consider the speed and response time of the actuator to make sure it meets your speed requirements.
Environmental conditions: Determine the conditions under which the actuator is to be used. Take into account factors like temperature, humidity and exposure to contaminants or chemicals. Select an actuator suitable for your specific application's environmental conditions.
Mounting Options: Take into consideration the mounting options available and your requirements. Decide whether the actuator should be mounted horizontally or vertically. Make sure the actuator that you select has the mounting capabilities necessary to meet your requirements.
Control Options: Assess the available control options for the actuator. You should consider whether you need manual control, electric control or integration into a larger automation systems. Choose an actuator which can be easily integrated and controlled into your current setup.
Consider these factors when selecting a linear actuator for pneumatic applications. This will ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
0 notes
Text
Maintenance And Troubleshooting Tips For Pneumatic Linear Actuators

Pneumatic Linear Actuators
Pneumatic linear actuators are ingenious devices that harness the power of compressed air to convert pneumatic energy into linear motion. They consist of a series of components working together to enable precise and controlled movement.
One of the key advantages of pneumatic linear actuators is their simplicity. With fewer moving parts compared to other types of actuators, they are inherently reliable and require minimal maintenance. The straightforward design also contributes to their cost-effectiveness, making them an attractive choice for industrial automation applications.
Maintenance And Troubleshooting Tips
Proper maintenance of pneumatic linear actuators is essential to ensure their longevity and reliable performance. Here are some maintenance and troubleshooting tips to keep these actuators in optimal condition.
Regular Inspection: Perform routine visual inspections of the actuator, checking for any signs of wear, leakage, or damage. Pay attention to seals, gaskets, and connectors, and replace any worn-out components promptly.
Lubrication: Apply lubrication to moving parts and bearings according to the manufacturer's recommendations. This helps reduce friction and ensures smooth operation. Be mindful of using the correct type of lubricant suitable for pneumatic systems.
Air Filtration: Maintain a clean and efficient air filtration system to prevent contaminants from entering the actuator. Clean or replace air filters regularly to ensure proper airflow and prevent damage to internal components.
Seal Inspection: Check the integrity of seals regularly. Damaged or worn-out seals can result in air leakage and reduced performance. Replace seals as necessary to maintain optimal sealing and prevent loss of pneumatic pressure.
Troubleshooting: In the event of actuator malfunction, conduct a systematic troubleshooting process. Start by checking the air supply for proper pressure and quality. Inspect the connections and valves for any blockages or leaks. If necessary, refer to the manufacturer's documentation or consult a professional for assistance.
By following these maintenance and troubleshooting tips, you can ensure the longevity and reliable operation of pneumatic linear actuators, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
0 notes
Text
How pneumatic linear actuators work
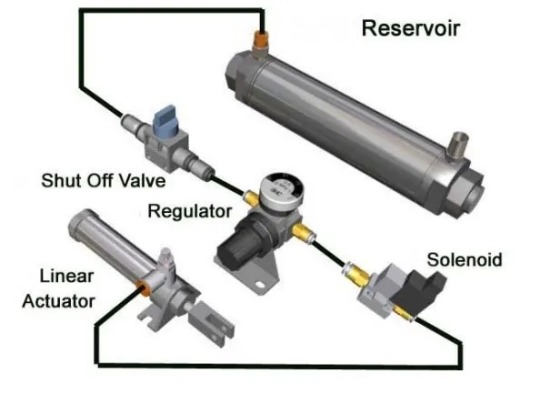
Pneumatic linear actuators are devices that convert compressed air into linear motion. They are widely used in various industrial applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and affordability. The basic principle behind their operation lies in the conversion of potential energy stored in compressed air into mechanical work.
A pneumatic linear actuator consists of several key components, including a cylinder, a piston, and valves. The cylinder is a hollow tube that houses the piston and provides a sealed environment for the movement of the piston. The piston, which is a solid cylindrical object, is positioned inside the cylinder and is connected to a rod that extends outside the actuator. The valves, located at the inlet and outlet ports of the actuator, control the flow of compressed air into and out of the cylinder Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
When compressed air is supplied to the actuator, it enters the cylinder through the inlet valve, pushing the piston and the attached rod forward. This movement is facilitated by the difference in pressure between the compressed air and the atmosphere. As the piston moves forward, the air behind it is vented through the outlet valve, allowing for continuous motion. To reverse the direction of the actuator, the flow of compressed air is redirected through the valves, causing the piston to move in the opposite direction.
Pneumatic linear actuators offer precise and controlled linear motion, making them suitable for applications that require repetitive and accurate movements. Their design allows for high-speed operation and high-force output, making them ideal for tasks such as clamping, lifting, pushing, and pulling. Furthermore, their modular nature enables easy integration into existing systems, making them a versatile choice for various industries.
In summary, pneumatic linear actuators work by converting compressed air into linear motion through the interaction of a piston, cylinder, and valves. Their simple yet effective design allows for reliable and efficient operation, making them a popular choice in industrial automation.
0 notes
Text
Advantages of using pneumatic linear actuators in industrial applications

Pneumatic linear actuators offer several advantages that make them a popular choice in industrial applications. Firstly, they provide a high force-to-weight ratio, allowing for efficient and powerful linear motion. This is particularly beneficial in applications where heavy loads need to be moved swiftly and accurately.
Secondly, pneumatic linear actuators are highly durable and can withstand harsh operating conditions. They are resistant to dust, debris, and moisture, making them suitable for use in rugged environments. This durability ensures a long lifespan and reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacement Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
Additionally, pneumatic linear actuators are known for their simplicity and ease of use. They can be easily integrated into existing systems and controlled with precision. The compressed air used to power these actuators is readily available in most industrial settings, making them a cost-effective choice.
Overall, the advantages of pneumatic linear actuators make them an attractive option for a wide range of industrial applications, including material handling, assembly lines, packaging, and robotics.
0 notes
Text
Types of pneumatic linear actuators

Pneumatic linear actuators come in a variety of types, each with its own unique features and advantages. Here are some of the most common types of pneumatic linear actuators:
Single-acting pneumatic linear actuators
Single-acting pneumatic linear actuators use air pressure to move the piston in one direction, while a spring returns the piston to its original position. These types of actuators are reliable, cost-effective, and easy to install, making them a popular choice in many industrial applications.
Double-acting pneumatic linear actuators
Double-acting pneumatic linear actuators use air pressure to move the piston in both directions, making them ideal for applications that require precise movement in both directions. They are often used in applications that require high force and speed, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
Rodless pneumatic linear actuators
Rodless pneumatic linear actuators do not have a piston rod and instead use a magnetic or mechanical connection to move the load. This design allows for a longer stroke and a smaller overall footprint, making them ideal for applications with limited space.
Compact pneumatic linear actuators
Compact pneumatic linear actuators are designed for applications that require a small footprint and low weight. They are often used in robotics and automation applications where space is at a premium.
0 notes
Text
Linear Actuator Types

Linear actuators produce straight line motions, and are therefore useful for machines that require linear movement. They are used in industrial machinery and peripherals of computers like printers and disk drives, as well as dampers and valves. Linear motion is inherent in gas or liquid cylinders. However, some equipment like the one used in DVD players requires linear motion.
Manufacturers offer a variety of linear actuators to their customers. These include:
Linear Actuators: This unit combines a ball-screw with a DC motor gearbox. The actuator comes complete and is ready to be installed in a variety of applications from medical, agricultural, and industrial.
Worm Drive Actuators - These actuators are fitted with acme screws for common use in lifting chairs and other medical equipment. They can be purchased with or without power supply, and they are UL-approved Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
Acme Screw Actuators are a combination of acme screw and DC motor gearbox in one easy-to-install unit. These linear actuators are the best choice for those who require reliable and rugged performance. These actuators are also used for ventilation, solar tracking and gardens and lawns.
VSJ Series: These actuators can be used in floor cleaning equipment, industrial machines and home healthcare equipment. These actuators are made up of acme screws that can be fitted in either DC or AC versions.
VI Series: These actuators are versatile and can be used in a variety of applications, including lawns and gardens, medical equipment, and agricultural and ATV devices. They are available in either an acme or a ball screw range and can be ordered in DC or AC depending on the task.
The VMD series Small Compact: These are very compact linear actuators. These actuators are useful in food preparation, office and automotive applications, as well as light loads.
They can be classified according not only according to market availability but also according to their mechanisms of operation. There are:
Mechanical actuators: These can be either mechanical with digital micrometer readingout or traveling screw-in roller screw actuator. These mechanical actuators can convert rotary motion into linear motion using one of the following mechanisms.
Screw: The rotating nut of an actuator is the screw shaft. This is how screw jacks, lead-screws and roller screw linear actuators work.
Cam: They work like wedges, but they have very little travel.
Wheel and Axle - Linear actuators that work according to this principle include winch, rigid chain drive, rigid chains, belt drive and winch.
Liquid under Pressure Actuators: The pressure is applied to a piston. A liquid is then conveyed to a load piston. Finally, the external load is moved. These include equipment controlled by hydraulic pumps or the hydraulic carjack.
Compressed gas actuators are similar to hydraulic actuators in principle, but use gas instead of liquid.
Piezoelectric actuators: These actuators use voltage to cause materials to expand or move outside objects.
Electro-mechanical actuators are: An electric motor replaces the handle or control knob on a mechanical actuator.
Small compact actuators: These motors are specially designed to reduce the bulk of linear actuators. They combine an actuator with a motor in the smallest possible form. Motors are made small by removing the screw and drive.
0 notes
Text
Linear Actuators - Pneumatic Linear Actuator

Linear actuators can be described as devices that convert or transform energy into motion in a linear-like manner. They are not always rotationally like electric motors. Linear actuators can be applied force to create a mechanical device that takes energy normally created by air, electricity, or liquid and transforms it into a specific form of motion. This type of motion can be used to transmit anything, from blocking, clamping or ejecting. Actuators are often used in industrial manufacturing or in other applications. They can also be used in switches, motors and pumps.
There are many types of linear actuators, but the most common is the one that's powdered with air. These linear actuators are also called the pneumatic cylinder, or the air-cylinder. These pneumatic or metal cylinders are typically made from metal and are air tight. For shifting a piston, they use compressed air energy. Pneumatic cylinders are also used in manufacturing and assembly. However, robotic grippers use linear actuators powered with compressed air to perform as close to human touch.
Linear actuators can be powered by either hydraulics or electricity. There are also hydraulic cylinders as well as electric cylinders available, just like air cylinders. These cylinders convert hydraulic or electrical energy into motion. Hydraulic cylinders are frequently used in automobiles. There are many options for linear actuators. They can be powered by a variety different sources. Solenoid valves, for example, can be powered by electricity or air. The solenoid valves are usually powered by electricity. When air is used for power, the solenoid activates.
Some linear actuators include digital readout positions and encoders. Although they resemble micrometer knobs, these are used for positioning adjustment and not measurement. Hydraulic actuators, such as hydraulic cylinders or hydraulic actuators, have a hollow cylinder with a piston in it. To achieve a controlled and precise linear displacement of the piston, both sides are de-pressurized or pressurized alternately. The piston's linear displacement is located within the cylinder or piston axis. This design is often based on hydraulic principles.
Pneumatic Linear Actuator can be used in a variety of ways. These actuators have motors that rotate the drive screw using a synchronous timing belt. Other linear actuators can use either a worm gear or direct drive. Each of these can turn the screw, so it pushes the nut drive to that screw. This pushes the rod, which in turn turns the screw in all directions. The cover tube protects the screw nut from environmental contaminants and allows for machine use without stacking. Radial thrust allows the screw's to rotate freely under load conditions and gives strength to actuators.
0 notes
Text
Converting Energy with High Performing Pneumatic Actuators

Pneumatic actuators can be used in a variety of applications and are the mainstays of expansion power and transmission power. Pneumatic systems can be used to hold a load for long periods of time. Remote control of actuators allows for automation of valves and emergency shutdown mechanisms.
Compressed Air
Pneumatic actuators convert compressed gas into mechanical motion. They are ideal for applications that don't allow for human interaction due to safety, space or location. Depending on the operating pressure, temperature, load capacity, and maximum torque, a wide variety of motion types can easily be achieved. You can achieve pushing or transmission power, and expansion power in any compressible liquid Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
Piston Style
Piston-style pneumatic actuators offer compact performance and reliability. The output pressure will increase if the rod and piston diameters are larger. These actuators are one of the most common types. They can produce strong movement and can tolerate harsh conditions such as dry and dusty environments, high humidity, and high pressure clean downs.
Double-Acting
Pneumatic actuators with double acting cylinders eliminate friction metal-to–metal. They use the force of the air to power the outstroke as well as the instroke. The exhausting back pressure can be controlled to increase speed. This valve has two ports to allow air in, one at each end of the piston and the other for closing and opening the valve. A well-designed cylinder can handle the longer strokes in certain applications, which will prevent rod buckling or bending.
Spring Return
One-acting or spring-return configurations in a pneumatic actuator mean that compressed air supply is limited to one side of the piston. Once the actuator is rotated, the energy that causes movement is transferred through one port. The valve then opens or closes and the actuator springs back to its original position.
Industry Application
Pneumatic actuators are well-suited for a wide variety of industries, including the petrochemical and refining industries, as well as water treatment, wastewater disposal and general power generation. These actuators are simple to use through automated systems and safer than other methods to generate motion. They operate air compressors and sensors, pumps, pumps, and robotics with high reliability over a long time.
High Tech Design
Pneumatic actuators are one of the easiest ways to convert compressed air into mechanical energy. Companies invest a lot of time and research into designing actuators that produce the highest output in terms force or motion.
0 notes
Text
Basics of Linear Actuators

Linear actuators are a component of motion control systems. These actuators can be powered by a variety of energy sources, including mechanical, electrical and hydraulic. The most common use of linear motion actuators is in factory automation and robotics.
There are many forms of energy that can power actuators. There are many forms of energy that can be used to power actuators, including hydraulic, pneumatic and mechanical, as well as electrical. Robotics and factory automation are a lot of use for linear actuators.
Linear motion actuators are used to convert rotational motion into linear motion. Linear actuators can be used with motors such as stepper, DC brush and induction motors. These motors can be used for different purposes depending on the application and load capacity.
A linear actuator that is equipped with an integral horsepower AC induction motor can convert large valve motions in refineries. In such cases, high speed and force are important over the actuator's move resolution and accuracy Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
The principle of operation is the basis for designing linear servo actuators. Many electro-magnetic actuators include a lead screw and nut, while others have a ball nuts and screw. Both cases have a screw that is connected to either the motor via a series of gears or the manual control knob.
Many lead screws have multiple starts. This means that there are many threads rotating on a single shaft. This allows for more adjustment between thread pitch and screw, which determines the motor's load carrying capacity and extension speed.
Manufacturers are creating integrated actuators to meet the extreme competition. They are simple, efficient, and improve their over-functionality.
Linear actuators have a higher speed, greater accuracy, and greater acceleration that other motors. These can be used to assemble machines, general purpose positions, gantry and gantry-axes. Linear stages can be used in adverse conditions to replace other potentially dangerous actuators.
For similar applications, DC actuators can also be used. They are quiet and run very smoothly. Many DC actuators on the market are waterproof. Buyers have the option to choose from a standard or a customized range of actuators, depending on their budget and needs.
1 note
·
View note