#Linear Actuators
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Unlocking Precision and Power: A Guide to Hydraulic Servo Actuators
Introduction: In the realm of automation and motion control, hydraulic servo actuators reign supreme for their unmatched blend of raw power and exceptional precision. These marvels of engineering combine the potent force of hydraulics with the meticulous control of electronic systems. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of hydraulic servo actuators, exploring their inner workings,…
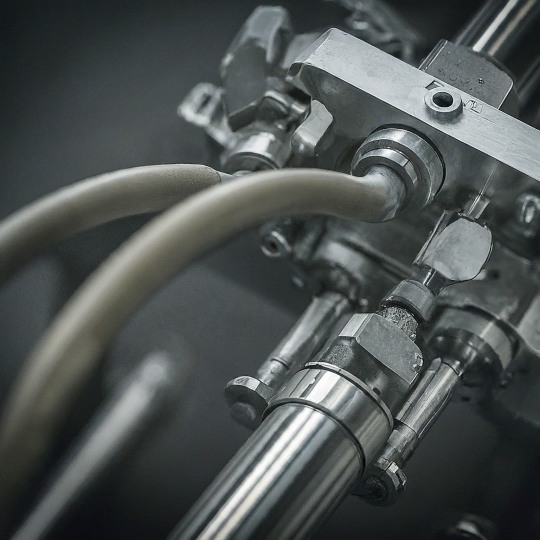
View On WordPress
#Electrohydraulic Actuators#Feedback Mechanisms#Flight Control Systems#High Force Applications#Hydraulic servo actuators#Industrial automation#Linear Actuators#Motion Control Systems#Proportional Valves#Robotics#Rotary Actuators
0 notes
Text
V-Slot Linear Actuator Solutions
V-Slot Linear Actuator Solutions
Linear Actuators Simplified Linear actuators are mechanical or electronic devices that convert energy into motion. It is used to control or move a mechanism, system, or process. Linear actuators are crucial components in various applications such as simple devices like household appliances, complex industrial systems and robotics. In a world driven by automation and efficiency, linear actuators…
View On WordPress
#Ball Screw Actuator#Belt Actuator#Gantry#Lead Screw#Linear Actuators#Linear Motion#Rack Pinion#V-Slot Actuator#V-Slot Linear Actuator#V-Slot Linear Motion
1 note
·
View note
Text
god i really do need to work on the mechanical goggles while im energetic
#at least just to get a functional prototype#proof of concept and all#i need light sensors and figure out is linear actuators or servos would work better#i think servos would react faster but the motion i need is back and forth#ig i could turn rotation into linear motion through gears but thats a lotta failure points
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Practices for Installing Pneumatic Linear Actuators
Understanding the Importance of Proper Installation
Installing pneumatic linear actuators correctly is critical to ensuring optimal performance, long service life, and overall system reliability. While these devices are designed to be robust and durable, poor installation can lead to premature failure, erratic movement, or even damage to connected equipment. By following best practices during the setup process, engineers and maintenance teams can minimize downtime and enhance safety in automation systems.

Start with a Thorough Pre-Installation Inspection
Before beginning the installation process, it is essential to conduct a comprehensive inspection of the actuator and surrounding components. This includes checking for visible damage, contamination, or signs of wear on the actuator, cylinder barrel, piston rod, seals, and mounting interfaces. Ensure that all required fittings, brackets, and mounting hardware are available and in good condition. Additionally, verify that the actuator type and size match the application specifications, including stroke length, bore size, and pressure rating. It’s also important to check the air supply for cleanliness and consistency, as contaminated air can cause seal degradation and premature wear.
Ensure Proper Mounting and Alignment
One of the most crucial aspects of installing a pneumatic linear actuator is achieving correct alignment between the actuator and the load it will move. Misalignment can create side loads, which place undue stress on the actuator’s internal components and bearings, leading to reduced efficiency and eventual failure. The actuator should be mounted securely to a rigid surface using the correct type of mounting configuration—whether it’s a foot mount, flange mount, or trunnion mount—depending on the application. During installation, care must be taken to ensure that the piston rod moves in a straight, unobstructed line. If the actuator is coupled to a load, the coupling must be properly aligned and allow for slight misalignments or axial movement if necessary.
Connect Pneumatic Lines Carefully
Once the actuator is mounted and aligned, the pneumatic lines should be connected to the appropriate ports on the cylinder end caps. Care must be taken to prevent cross-threading and to ensure leak-free connections. Use clean, dry compressed air and make sure the supply pressure matches the actuator’s rated operating range. Flow control valves should be installed close to the actuator to provide precise control over the speed of extension and retraction. Where applicable, quick exhaust valves and cushioning mechanisms should be included to improve performance and reduce mechanical stress during rapid movements. It’s also a good idea to include manual shut-off valves or pressure regulators to allow safe maintenance and system tuning.
Test and Adjust for Optimal Performance
After mechanical and pneumatic connections have been completed, the actuator should be tested under normal operating conditions. Start with a low-pressure test to verify movement and check for leaks. Gradually increase pressure to the desired operating level while monitoring actuator response, speed, and stroke length. If the actuator is equipped with adjustable cushions, fine-tune them to minimize end-of-stroke impact and noise. Sensors or switches, if used, should be calibrated and tested to ensure accurate position feedback or limit detection. It’s important to allow the actuator to complete several full cycles during testing to confirm smooth and consistent operation.
Implement a Routine Maintenance Plan
Proper installation sets the stage for reliable operation, but long-term performance depends on regular maintenance. After installation, the actuator should be periodically inspected for leaks, unusual noise, or wear. Air filters and lubricators in the pneumatic system must be checked and maintained to keep the air supply clean and at the correct pressure. Lubrication, if required, should follow the manufacturer's recommendations. Documenting installation parameters and test results can also aid future troubleshooting and system optimization.
Conclusion
Installing a pneumatic linear actuator may seem straightforward, but attention to detail and adherence to best practices can make a significant difference in performance and longevity. From pre-installation checks and precise alignment to careful air line connections and thorough testing, each step plays a role in ensuring the actuator functions as intended. By investing time in proper installation and following up with regular maintenance, operators can maximize uptime, reduce repair costs, and achieve smoother, more efficient automation in their processes.
0 notes
Text
Linear Actuator Market to Witness Comprehensive Growth by 2032
Allied Market Research, titled, “Linear Actuator Market Size By Operation Mechanism and End Use Industry: Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast, 2023-2032", the linear actuator market was valued at $17.4 billion in 2022, and is estimated to reach $31.2 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2023 to 2032.
The linear actuator is a device that creates motion in a straight line. It transfers energy, which can be in any of the different forms like electricity, propulsion or pneumatics, into a linear motion. This motion is typically used to push or pull something, lift or lower loads, or position them with high precision.
Linear actuators offer several advantages. They provide precise control over movement, can maintain a position with power off, and can be designed for high force and long-life operation. It may be used in a number of industries, from machines that function valves or gates to purchaser digital goods which includes alter desks and automatic window openers.
Innovation maintained in linear actuators, which is aimed at enhancing performance, reducing length and integrating more advanced functions including sensors for comments and Internet of Things connectivity. These advances have enabled linear actuators to be extra adaptable, green and capable of characteristic in quite a few environments.
The growth in integration of linear actuators in smart homes and office systems is a key factor fueling the growth of the linear actuator market. The role of linear actuators becomes more crucial in facilitating these automatic adjustments as the shift toward automated and intelligent environments intensifies. They are utilized in a range of functions, including the movement of windows, doors, and adjustable ergonomic furniture, all aimed at improving comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency. The versatility and exactness provided by linear actuators make them perfectly suited for such tasks, with their ability to be remotely controlled and customized for specific operations. Consequently, the escalating demand for intelligent, automated solutions in residential and commercial spaces is a major contributor to the expansion of the market for linear actuators, driven by the need for precise and dependable motion control systems.

However, technological obsolescence, due to rapid technological advancements, is a significant restraint for the linear actuator market. Linear actuators can become outdated in a short period as technology evolves quickly. For example, a linear actuator developed with current technology might soon be outclassed by a newer model with enhanced efficiency, precision, or integration capabilities. The rapid pace of innovation will make it difficult for consumers to invest in the current models because they are afraid that their investments may soon be outdated. In view of the need to continuously innovate and update products in order for them to compete, manufacturers are also facing a challenge that requires significant long term investment. This pressure on the market to keep pace with technological developments could hinder growth if both manufacturers and consumers are forced to face changes that have implications for their longevity and relevance of linear actuator technologies.
Innovations in actuator technology present a significant opportunity in the linear actuator market, as developing new, more efficient, and cost-effective technologies can greatly enhance product offerings. For instance, the introduction of brushless DC motors in linear actuators represents such an innovation. These motors offer higher efficiency, lower maintenance requirements, and longer lifespans compared to traditional brushed motors. In applications such as solar panel tracking systems, these innovative actuators ensure more reliable and energy efficient operation, reducing overall costs and improving system performance. The linear actuator market is expected to meet evolving demands with more sustainable and effective solutions, driving growth and competitiveness in various industrial sectors by embracing such advancements.
The most important role in industrial automation systems is played by the actuator linear technology. These actuator linear devices are known for their precise and controlled linear movements, which make them indispensable in applications such as production equipment or robotics. Unprecedented reliability is offered by the actuator linear systems, which ensure safe and efficient operation in different sectors with a view to further improving productivity.
Linear actuator market sizes continued to expand, in line with the rapid linear actuator market growth of a strong and increasing linear actuator market demand for these devices from different industrial sectors. It is clear that companies are actively competing for a larger linear actuator market share through their use of emerging linear actuator market trends on the market, as demonstrated by our recent linear actuator market analysis of the market. The integration of innovative technologies and features into linear actuators is a notable linear actuator market trend, enhancing their appeal and functionality. With the continued automation of industrial processes and the growing need for precision control, the linear actuator market is poised for sustained growth in the foreseeable future.
The linear actuator market is segmented on the basis of operation mechanism, end use industry, and region. By operation mechanism, the market is divided into electric linear actuators, pneumatic linear actuators, hydraulic linear actuators, and others. On the basis of end use industry, the market is fragmented into automotive, construction, energy and mining, healthcare, and others. On the basis of region, the market is analyzed across North America (the U.S., Canada, and Mexico), Europe (the UK, Germany, France, and rest of Europe), Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India, South Korea, and rest of Asia-Pacific) and LAMEA (Latin America, Middle East, and Africa).
Key Findings of the Study
In terms of operation mechanism, the electric segment was the highest revenue contributor in the market, with $7,319.44 million in 2022, and is estimated to reach $14,162.07 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 6.88%.
By end use industry, the automotive segment was the highest revenue contributor in the market, with $5,612.17 million in 2022, and is estimated to reach $10,894.57 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 6.92%.
By region, Asia-Pacific was the highest revenue contributor, accounting for $6,239.75 million in 2022, and is estimated to reach $12,186.61 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 6.98%.
The linear actuator market key players profiled in the report include Bosch Rexroth AG, Emerson Electric Co., HepcoMotion Ltd., Kollmorgen Corporation, LINAK, Oriental Motor Co., Ltd., Parker Hannifin Corporation, Rockwell Automation, Thomson Industries, Inc., Tolomatic, Inc. The market players have adopted various strategies, such as product launches, expansion, new product development, geographical expansion, and product upgrade/development strategies to expand their foothold in the linear actuator industry.
0 notes
Text
Discover Tecnik Valves' multiple spring pneumatic actuators—compact, field-reversible, and engineered for high thrust and precise control in throttling, modulating, and on-off applications across industrial processes.
#Multiple spring actuators#pneumatic actuators#high-thrust actuators#Tecnik Valves#linear valve actuators#industrial valve automation#field-reversible actuators#diaphragm actuators#control valve actuators#compact actuator design
0 notes
Text
maybe i should invest in a nice keyboard and be done with it
#ny laptop has ghosting issues and it pisses me OFF#my only alternative is a shitty goodmans “gaming” keyboard my dad got at currys for like ten quid#which. it is impossible to use for anything other than maybe typing if you have headphones on#its loud in a bad way. and it feels like shit#its so tough to press the keys down#i was using it to play vivid/stasis because ghosting issues forced me to#AND I CANT HEAR#i cant hear anything over the keys themselves#and the physical feedback of pushing the key is so delayed from the actuation point that im going to explode someone#i keep losing combo because the hitsounds‚ keypress noises‚ and actual input points are all at different times and i cant keep track of shit#ill get a nice cheap-ish low profile with linears or some shit and just. be free
1 note
·
View note
Text
Hydraulic And Electric Linear Actuators Market projected to reach $118.2 billion by 2032
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Global Actuators Market is experiencing significant expansion, projected to grow from USD 67.7 billion in 2024 to USD 94.8 billion by 2029, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.0%. This growth is fueled by rapid urbanization, industrialization, and the increasing demand for automation across diverse industries. Within this thriving market, linear actuators stand out as a key component, playing a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency, precision, and safety. In this blog, we’ll explore what linear actuators are, how they function, and how they contribute to the larger actuators market.
The operation of a Linear Actuator Market depends on its specific type, but the fundamental concept involves converting input energy into linear displacement. Here’s a breakdown of the primary types of linear actuators and how they function:
Electric Linear Actuators: These are powered by an electric motor. When the motor runs, it rotates a screw or lead screw, which pushes or pulls a piston, resulting in linear motion.
Hydraulic Linear Actuators: These use hydraulic fluid pressure to drive a piston forward or backward. The pressure applied to the fluid creates movement, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Pneumatic Linear Actuators: These rely on compressed air to create movement. The compressed air enters a cylinder, moving a piston in the desired direction and allowing for rapid, precise linear motion.
Each type of linear actuator offers unique advantages, with electric actuators favored for precise control, hydraulic actuators for heavy loads, and pneumatic actuators for fast movement in lighter applications.
#Linear Actuators Market#Linear Actuators Market Market#Linear Actuators Market Industry#Global Linear Actuators Market Market#Linear Actuators Market Market Companies#Linear Actuators Market Market Size#Linear Actuators Market Market Share#Linear Actuators Market Market Growth#Linear Actuators Market Market Statistics
0 notes
Text
Valves, Actuators and Positioners Market - Forecast(2024 - 2030)
Global Valves Market generated revenue of about $60.56 billion in 2017 growing with CAGR of 3.60% during the forecast period i.e. 2018-2023. APAC occupied the major market share in the valves market generating total revenue of $20.67 billion in 2017.
Request Sample
What is Valves, Actuators and Positioners Market?
Valves is a control units when electrically energy is passed the valves either shut off or it allows the fluid flow. The actuator takes the form of an electromagnet. When energized, a magnetic field builds up which pulls a plunger or pivoted armature against the action of a spring. When de-energized, the plunger or pivoted armature is returned to its original position by the spring action. Valves, actuators and positioners are segmented based on the type in which there are two way valves, three way valves. Two way valves are shut-off valves with one inlet port and one outlet port whereas the three way valves are provided with a three port connections and two valve seats one valve seal always remains open and the other closed in the de-energized mode. When the coil is energized the mode reverses.
What are the major applications for Valves, Actuators and Positioners Market?
The major applications of valves, actuators and positioners includes in many industries such as aerospace and defense, automobiles, oil and gas, water and waste water treatment, agriculture, mining, paper and pulp and many more. In aerospace and defense valves are used in fuel systems, cockpit locks whereas in automobiles used in gear box and air conditioner systems.
Inquiry Before Buying
Market Research and Market Trends of Valves, Actuators and Positioners Market:
In recent years the gas over oil pipeline actuators are provided with ELB units for line break monitoring. This ELB will enable the operator to monitor the running condition of the gas pipeline and the open, close status of the valves. ELB is provided with an array of programmable alarm and alert indication which can help the operator to close the appropriate valves and solve the problem.
For the connection of valves, number of wire are used by which it has become difficult to connect appropriately. To solve this problem of connection consolidated solenoid wiring is used into a single collective connection on the valve manifold. This method will significantly reduce the cost and complexity as the valve manifold can be moved out of the control cabinet to the point-of-use application located near the pneumatic process which will reduce the delayed responses in operation.
Emerson has acquired Pentairs valves to enhance their portfolio globally in many sectors like chemical, power, refining, mining and Oil and Gas. This acquisition promises long term growth opportunities and provides their customers with appropriate solutions to their toughest challenges.
Who are the Major Players in Valves, Actuators and Positioners Market?
The companies referred in the market research report includes iScaler Ltd., CloudFlare Inc., ChinacacheÂ, Internap Corporation, MaxCDN, Fastly Inc.and more than 10 other companies.
Schedule a Call
What is our report scope?
The report incorporates in-depth assessment of the competitive landscape, product market sizing, product benchmarking, market trends, product developments, financial analysis, strategic analysis and so on to gauge the impact forces and potential opportunities of the market. Apart from this the report also includes a study of major developments in the market such as product launches, agreements, acquisitions, collaborations, mergers and so on to comprehend the prevailing market dynamics at present and its impact during the forecast period 2018-2023.
All our reports are customizable to your company needs to a certain extent, we do provide 20 free consulting hours along with purchase of each report, and this will allow you to request any additional data to customize the report to your needs.
Buy Now
Key Takeaways from this Report
Evaluate market potential through analyzing growth rates (CAGR %), Volume (Units) and Value ($M) data given at country level – for product types, end use applications and by different industry verticals.
Understand the different dynamics influencing the market – key driving factors, challenges and hidden opportunities.
Get in-depth insights on your competitor performance – market shares, strategies, financial benchmarking, product benchmarking, SWOT and more.
Analyze the sales and distribution channels across key geographies to improve top-line revenues.
Understand the industry supply chain with a deep-dive on the value augmentation at each step, in order to optimize value and bring efficiencies in your processes.
Get a quick outlook on the market entropy – M&A’s, deals, partnerships, product launches of all key players for the past 4 years.
Evaluate the supply-demand gaps, import-export statistics and regulatory landscape for more than top 20 countries globally for the market.
#valves market size#actuators market size#positioners market size#pneumatic#hydraulic actuator#linear actuator#hydraulic cylinder#sprinkler#motor#valve positioners#water treatment#agriculture#mining#fuel systems#cockpit locks
0 notes
Text
Mastering Machine Control: A Guide to Limit Switch Sensors in Sharjah, Dubai, UAE (Including Roller Plunger and Linear Limit Switches)
Limit switch sensors are the silent guardians of industrial automation in Sharjah, Dubai, and across the UAE. These unassuming devices play a critical role in ensuring machinery operates efficiently and safely. But with various types and functionalities, choosing the right limit switch can feel overwhelming. This article serves as your guide to navigating the world of limit switch sensors in the UAE, focusing on roller plunger and linear limit switch options.
Understanding Limit Switch Sensors:
At its core, a limit switch sensor detects the position or movement of an object and triggers an electrical response. This allows machines to automate tasks, prevent collisions, and activate specific functions based on object presence or absence.
Types of Limit Switch Actuators:
The "trigger" for a limit switch comes from the actuator, a component that interacts with the machine to activate the switch. Common actuator types in Sharjah, Dubai, and the UAE include:
Basic Levers: Simple and cost-effective for basic on/off control.
Fork Levers: Designed to straddle objects for precise detection.
Roller Lifters: Ideal for detecting the presence or absence of materials.
Focus on Roller Plunger Limit Switches:
A popular choice for precise positioning applications, roller plunger limit switches feature a spring-loaded roller that presses a plunger to activate the switch. This design offers several advantages:
High Versatility: Roller plungers can detect a wide range of objects, making them adaptable to various applications.
Precise Control: The spring-loaded mechanism allows for accurate detection of object presence or absence.
Durability: Roller plungers are often built tough to withstand harsh industrial environments.
Linear Limit Switches for Long Travel Detection:
Linear limit switches excel in applications requiring detection over extended distances. These switches have a long, linear actuator that activates the switch upon reaching a specific position. Here's what makes them valuable:
Ideal for Long Strokes: Linear switches are perfect for conveyor systems, material handling equipment, and other applications with long travel distances.
Compact Design: Despite their long actuator travel, linear limit switches can have a surprisingly compact housing, saving valuable space.
Variety of Actuators: Linear switches come with diverse actuator options, such as rods, slides, and fork-style attachments, catering to specific detection needs.
Finding the Right Limit Switch Solution in Sharjah, Dubai, and the UAE
With a vast selection of limit switch sensors and actuators available in Sharjah, Dubai, and the UAE, choosing the right combination can feel daunting. However, by understanding your application's requirements, such as travel distance, object type, and desired level of precision, you can narrow down your options. Additionally, consulting with local automation specialists can ensure you find the perfect limit switch solution for your needs in the UAE.
Keywords: Limit Switch Sensor, Roller Plunger Limit Switch, Linear Limit Switch, Limit Switch Actuator, Sharjah, Dubai, UAE
#Limit Switch Sensor#Roller Limit Switch Types#Limit Switch Plunger Type#Roller Plunger Limit Switch#Linear Limit Switch#Limit Switch Actuator
0 notes
Text
The Power of Hydraulics: A Comprehensive Guide to Hydraulic Cylinders, Linear Actuators, and Their Applications
Introduction: The world around us is driven by motion, and hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in generating that motion. These powerful workhorses are the backbone of countless machines, from construction equipment to factory assembly lines. But how exactly do hydraulic cylinders function, and what makes them so versatile? This comprehensive guide will delve into the fascinating world of…

View On WordPress
#Displacement#Double-Acting Cylinder#Force#Hydraulic cylinders#Hydraulic Fluid#Linear Actuator#Piston#pressure#Rod Seal#Single-Acting Cylinder#Telescopic Cylinder
0 notes
Text
Enhancing Efficiency with Pneumatic Linear Actuators in Manufacturing

In the competitive world of manufacturing, efficiency is a defining factor for success. Companies continually seek ways to optimize their operations, reduce downtime, and improve product quality—all while maintaining cost-effectiveness. One of the technologies that contribute significantly to achieving these goals is the pneumatic linear actuator. These devices play a critical role in automating tasks that require precise linear motion, helping manufacturers streamline processes and increase productivity without the need for overly complex or expensive systems.
Role of Pneumatic Actuators in Automation
Pneumatic linear actuators are widely used in manufacturing environments to perform essential tasks such as pushing, pulling, lifting, clamping, or positioning parts during assembly and production. They function by using compressed air to move a piston within a cylinder, translating air pressure into linear mechanical motion. This straightforward principle allows for fast, repetitive movement that is highly suitable for applications where reliability and speed are crucial. Because they do not rely on electricity to generate movement, pneumatic actuators are especially valuable in areas where electrical components might pose safety risks or where air power is more readily available.
Increasing Production Speed and Accuracy
One of the biggest advantages of incorporating pneumatic linear actuators into manufacturing systems is their ability to significantly increase production speed. These actuators operate quickly and with consistent force, making them ideal for repetitive tasks such as stamping, labeling, or pushing components down a conveyor line. When configured properly, pneumatic systems can cycle rapidly with minimal lag time, reducing the duration of each production cycle and allowing more units to be processed within the same timeframe. At the same time, their consistent output contributes to greater accuracy and uniformity, which is vital for maintaining high product standards across large volumes.
Reducing Operational Costs
Efficiency in manufacturing isn’t solely about speed—it’s also about cost control. Pneumatic linear actuators offer a cost-effective solution for automation because of their relatively low initial investment and minimal maintenance requirements. Compared to other motion systems like electric or hydraulic actuators, pneumatic options are often more affordable to install and easier to integrate into existing workflows. Since compressed air is already commonly used in many manufacturing facilities, leveraging that existing infrastructure further reduces setup costs. Additionally, pneumatic systems are known for their durability, and with routine maintenance, they can deliver long-term performance with minimal downtime.
Adapting to Harsh and Demanding Environments
Manufacturing floors are not always ideal environments for sensitive electronic equipment. Dust, moisture, vibrations, and extreme temperatures are common in industrial settings, and they can compromise more delicate automation solutions. Pneumatic linear actuators are particularly well-suited to these conditions. Their robust construction and minimal reliance on electronics make them highly durable and resilient in challenging environments. This reliability helps maintain uptime and reduces the risk of failure, supporting continuous production with fewer interruptions.
Flexibility and Scalability in Manufacturing Systems
Modern manufacturing requires flexible systems that can be adapted to different products, processes, and production volumes. Pneumatic linear actuators offer that flexibility. They come in a variety of sizes, force outputs, and stroke lengths, allowing manufacturers to select the exact configuration needed for a specific task. Whether it's a small component in an electronics assembly line or a heavy-duty actuator used in automotive fabrication, pneumatic solutions can be scaled to meet different demands. Additionally, they can be easily reconfigured or relocated within a production line, making them ideal for facilities that frequently adjust layouts or product lines.
Supporting Lean and Sustainable Operations
Efficiency in today’s manufacturing landscape also includes minimizing waste and environmental impact. Pneumatic systems support lean manufacturing principles by helping eliminate unnecessary motion, reducing overproduction, and streamlining repetitive tasks. Their clean operation—free from lubricants or complex cooling systems—also reduces environmental hazards and simplifies compliance with safety and sustainability standards. When combined with proper control systems and air management, pneumatic actuators can be part of a greener, more sustainable production process.
Conclusion
Pneumatic linear actuators are more than just motion devices—they are strategic tools that enhance the efficiency, flexibility, and reliability of manufacturing systems. By enabling faster production, reducing operational costs, and adapting to the rigorous demands of industrial environments, these actuators have become essential in modern manufacturing. As industries continue to seek smarter, more efficient ways to automate and produce, pneumatic actuators remain a trusted solution that delivers consistent results with simplicity and strength.
0 notes
Text
Small servo motors are compact electromechanical devices designed to provide precise control over angular or linear motion. Unlike conventional motors, servo motors are equipped with feedback mechanisms such as encoders, enabling accurate positioning and velocity control. These motors are characterized by their high torque-to-volume ratio, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Efficiency of Pneumatic Linear Actuators in Industrial Automation

Introduction
Pneumatic Linear Actuators Pneumatic linear actuators are crucial components in industrial automation systems, providing reliable and efficient motion control. These actuators utilize compressed air to generate linear motion, making them suitable for various applications across industries such as manufacturing, automotive, packaging, and more. Understanding their efficiency is vital for optimizing productivity and minimizing energy consumption in automated processes and for more details click here Pneumatic Linear Actuator.
Operating Principles and Mechanisms
Pneumatic linear actuators operate based on the principle of converting compressed air energy into linear motion. They typically consist of a piston enclosed within a cylinder, with air pressure applied to one side of the piston to create movement. This simple yet effective mechanism allows for precise control over the actuator's extension and retraction, making them ideal for tasks requiring repetitive and accurate motion.
Efficiency Metrics and Performance Factors
Efficiency in pneumatic linear actuators is evaluated based on several metrics, including speed, force output, energy consumption, and reliability. Factors such as air pressure, cylinder size, and valve design significantly influence their performance. Optimizing these parameters ensures maximum efficiency while minimizing operational costs and downtime. Additionally, advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques contribute to enhancing the overall efficiency and longevity of pneumatic actuators.
Applications in Industrial Automation
Pneumatic linear actuators find widespread use in various industrial automation applications, ranging from simple pick-and-place operations to complex assembly processes. Their fast response times, high force output, and suitability for harsh environments make them indispensable in industries where reliability and productivity are paramount. Examples include material handling, machine loading, robotic arm movements, and conveyor systems.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite their numerous advantages, pneumatic linear actuators face challenges such as air leakage, friction, and limited speed control. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development efforts focused on improving sealing technologies, reducing internal friction, and enhancing control algorithms. Moreover, the integration of smart sensors and predictive maintenance techniques holds promise for further optimizing the efficiency and reliability of pneumatic actuation systems in the future.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Several case studies demonstrate the successful implementation of pneumatic linear actuators in industrial automation settings. For instance, a manufacturing plant achieved significant cost savings and productivity improvements by replacing hydraulic actuators with pneumatic ones due to their lower maintenance requirements and faster response times. Similarly, an automotive assembly line utilized pneumatic actuators for precise positioning of components, resulting in higher throughput and assembly accuracy.
Conclusion and Outlook
In conclusion, pneumatic linear actuators play a crucial role in driving efficiency and productivity in industrial automation applications. By understanding their operating principles, optimizing performance factors, and addressing challenges, manufacturers can maximize the benefits of these versatile actuation systems. Continued innovation and integration of advanced technologies will further enhance the efficiency and reliability of pneumatic linear actuators, ensuring their continued relevance in the evolving landscape of industrial automation.
0 notes
Text

Transform your vehicle with top-tier auto accessories available at MyPushcart! Conveniently shop online and explore our diverse range of high-quality accessories, including car security systems, turnkey products, and remote start kits, to enhance your driving experience. Visit our website and order now for a seamless shopping experience.
1 note
·
View note