MIDAO Directory Services provides the world’s best legal & regulatory frameworks for web3, crypto, and DAOs.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
DAO Service: Revolutionize Your Business Operations
Thinking about changing how your business works? You might want to make things more efficient, open, and independent. A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is a blockchain-based system. It lets organizations run without needing a single boss.
This setup means decisions can be made more democratically and your business can be more stable. Using such a system can make your business run smoother and safer. It also helps in building a culture of openness.
In this article, we'll dive into how a dao service can help your business.
Understanding DAO Services and Their Business Impact
DAO services use blockchain governance and smart contracts to change how we manage organizations. They make sure decisions are clear, safe, and can't be altered.
Smart contracts are key to DAO platforms. They make rules and actions happen automatically. This cuts down on the need for middlemen and lowers the chance of mistakes. It helps businesses act fast and make smart choices.
Using a DAO service can make your organization more efficient and effective. This lets you create a company that's quick to adapt, responsive, and full of new ideas. It's perfect for today's fast-changing business world.
How to Implement a DAO Service in Your Business
Adding a DAO service to your business can change how things work. It brings in decentralization and makes things more open. To do this, you need a clear plan.
Identifying Suitable Business Processes
First, find out which parts of your business can use decentralization. Look at how smart contracts and blockchain can make things better.
Preparing Your Team for Decentralized Governance
After picking the right areas, get your team ready for DAO. Teach them about DAO and how it makes decisions more open and fair.
Popular DAO Platforms Comparison
Look at DAO platforms like Aragon or DAOstack. See which one fits your business best. Think about how well they scale, their security, and how easy they are to use.
Configuring Smart Contracts for Your Needs
Setting up smart contracts is key for your DAO. Make sure they match your business needs and work well.
Establishing Voting Mechanisms
It's important to have a fair voting system. Pick a crypto voting system that fits your DAO's values and is safe.
Creating Transparent Decision-Making Processes
Make sure decisions are clear and open. This builds trust and responsibility in your team. Make sure everyone has the info they need to decide well.
By following these steps, you can add a DAO service to your business. This will improve how you manage your digital organization and use DAO solutions.
Conclusion
Exploring DAO services shows they can change how your business works. They bring transparency, efficiency, and freedom. By using DAO tech right, your company can be more flexible and quick to respond.
Looking to make the switch? Dao consulting services can help. They make sure your transition goes smoothly. This way, you avoid mistakes and get the most out of decentralized governance.
Adopting a DAO service opens up new opportunities for your business. It helps you succeed in a changing world. By using DAO services, you'll stay ahead of the game.
0 notes
Text
Blockchain Regulation Around the World
Blockchain technology has moved beyond cryptocurrency speculation and become part of the broader financial, technological, and governmental sectors. As its applications expand, countries are taking varied approaches to regulate how blockchain is used, especially in areas like finance, data handling, and consumer protection. There is no single global standard for blockchain regulation, and governments differ in how strict or supportive they are.
Contrasting Approaches
Some countries have opted for a clear and structured legal framework, while others remain cautious or inconsistent.
European Union: The EU has taken one of the most organized approaches. Its Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation was approved in 2023 and is set to come into force in stages through 2025. MiCA is designed to create a single set of rules for crypto-assets across all member states. It focuses on stablecoins, licensing requirements, and protections against market manipulation. By creating a harmonized structure, the EU aims to reduce regulatory confusion and increase consumer trust.
United States: In contrast, the United States still lacks a unified federal framework for blockchain and crypto-assets. Regulatory oversight is split between multiple agencies like the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), the CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission), and the IRS. As a result, companies and investors face uncertainty, particularly when it comes to determining whether a digital asset is considered a security or a commodity. Recent enforcement actions have made it clear that the U.S. is willing to regulate through litigation while Congress debates more comprehensive laws.
China: The Chinese government has taken a strict stance. Cryptocurrency trading and mining are banned, and platforms offering related services have been shut down or forced to move operations elsewhere. However, China has been actively developing its own central bank digital currency (CBDC), known as the digital yuan. This reflects a preference for state-controlled innovation while suppressing private-sector initiatives that could threaten financial stability or capital controls.
Japan and South Korea: Both countries have introduced relatively clear rules after experiencing major crypto-related incidents, such as exchange hacks. Japan was one of the first major economies to license crypto exchanges and require anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. South Korea also tightened regulations around identity verification and exchange registration. While not overly restrictive, these rules aim to balance innovation with user protection.
El Salvador: In a high-profile move, El Salvador adopted Bitcoin as legal tender in 2021. This made headlines globally, but the policy has drawn criticism from international financial institutions. Critics argue it exposes the country to volatility and other financial risks, while supporters say it encourages innovation and financial inclusion. Regardless of opinions, El Salvador’s decision highlights how blockchain regulation can also be used to attract global attention or reshape national financial policy.
Marshall Islands: The Marshall Islands has taken a unique approach by developing its own blockchain-based currency, the Sovereign (SOV). Intended to circulate alongside the U.S. dollar, the SOV is designed to operate on a public blockchain, with built-in identity and compliance features. The project faced criticism from global financial bodies, including the International Monetary Fund, due to concerns about monetary stability and regulatory readiness. Still, the Marshall Islands’ decision reflects how smaller nations may use blockchain as a way to assert financial autonomy or explore new models of digital governance, for example like MIDAO LLC, providing blockchain regulatory services and located in the Marshall Islands.
The Outlook
Global regulation of blockchain technology continues to be inconsistent. While some regions have implemented well-defined laws, others rely on outdated financial frameworks or case-by-case enforcement. There is a growing recognition that some coordination will be needed, especially as blockchain-based financial services cross borders.
International bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) have issued guidelines, particularly concerning AML and counter-terrorism financing, but these are not binding. Enforcement still depends on national governments.
For companies operating in this space, understanding the local rules in each market is non-negotiable. The patchwork nature of global regulation creates legal risk and increases the complexity of cross-border projects.
Blockchain is no longer a fringe concept. It is being integrated into financial markets, supply chains, digital identity systems, and public sector initiatives. Regulation is playing catch-up, but with growing pressure from both industry and consumers, more countries are moving from vague statements to clear rules.
0 notes
Text
The Benefits of Implementing a DAO for Startups in 2025
Setting up a DAO for startups brings a fresh approach to business organization. Companies worldwide now seek better ways to manage their operations, and decentralized structures offer clear advantages over traditional models.
This shift toward DAOs marks a genuine change in how new businesses think about management and growth. The move toward decentralized systems comes from a real need to make business operations more open and efficient.

What Makes DAOs Work for New Companies
A DAO changes everything about how startups handle their daily operations. Instead of old-school management chains, these organizations use smart contracts and blockchain systems. This means everyone involved can see what's happening and take part in making decisions.
The transparency helps build trust between team members, investors, and customers.
Small teams find DAOs particularly helpful because they remove many common business headaches. No more endless email chains about simple decisions or confusion about who approved what.
Everything gets recorded and tracked automatically, saving time and preventing misunderstandings.
Key Elements That Drive Success
Building Blocks
Clear voting systems
Fair reward sharing
Open decision making
Simple fund management
Quick response tools
Community input channels
Progress tracking methods
Technical Needs
Security measures
Payment processing
Member tracking
Resource planning
Growth monitoring
Integration options
Backup systems
Real Value for Growing Companies
When startups adopt DAO structures, they cut down on paperwork and speed up decisions. Teams work better together because everyone knows their role and can see how their work affects the company. Money moves faster, and there's less waste in day-to-day operations.
The automated nature of DAOs helps prevent many common startup problems.
No more questions about where the money went or who made what decision. The blockchain records everything, creating a clear trail anyone can check. This transparency makes it easier to spot and fix problems before they grow too big.
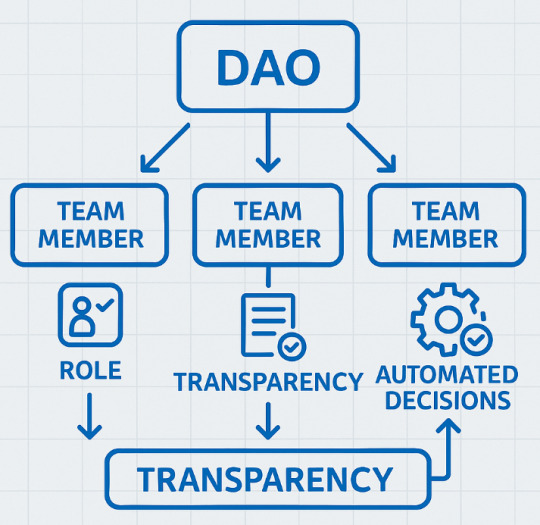
Money Matters
New companies often have trouble dealing with investors and sharing ownership. DAOs make this simpler by using digital tokens and straightforward rules about who owns what.
This helps startups raise money without getting tangled in complicated legal arrangements.
Investors appreciate knowing exactly where their money goes and having a real say in important decisions. The clear rules and automatic enforcement of agreements through smart contracts reduce the risk of disputes and make everyone feel more secure about their investment.
Different Ways to Use DAOs
Tech companies might use DAOs to decide what products to build next. Marketing firms could use them to pick projects and share resources. Service companies find them helpful for managing client money and paying workers on time.
Manufacturing startups use DAOs to manage their supply chains more effectively. Creative agencies apply them to project selection and resource sharing. Even traditional businesses find ways to use DAO principles to improve their operations and decision-making processes.
Working with Communities
DAOs help startups stay close to their customers. People who use the product or service can suggest changes and vote on new features. This creates a strong bond between the company and its users, leading to better products and more loyal customers.
The community aspect goes beyond just getting feedback. Users often become passionate supporters who spread the word about products they help shape. This organic growth through community involvement often works better than traditional marketing approaches.
Getting Started with a DAO
Starting a DAO takes good planning and clear goals. Companies need to think about what they want to achieve and how they'll make decisions together. The rules they set up should help the business grow while keeping things running smoothly.
Early choices about voting rights and governance significantly affect how well the DAO works. Teams should consider how to balance quick decision-making with fair representation. Getting these basics right makes everything else work better.
Following the Rules
Laws about DAOs keep changing as more companies use them. Smart startups work with experts who understand these rules. Many countries now accept DAOs as real businesses, making it easier to operate legally.
The regulatory environment varies by region, but most places now recognize the value of decentralized organizations. Staying informed about these rules helps companies avoid problems and take advantage of new opportunities as they arise.
Tracking Growth and Success
Companies using DAOs can easily see how well they're doing. They track things like member participation, decision quality, and how quickly work gets done. This information helps them improve how they operate.
Regular monitoring shows what works and what needs adjustment. Teams can spot trends early and make changes before small issues become big problems. The transparency of DAO systems makes this kind of tracking natural and simple.

Making Changes When Needed
Markets change all the time, but DAOs help startups adjust quickly. Members can suggest and approve changes when needed, helping the company stay competitive and meet new challenges. This flexibility gives DAO-based startups an edge over more rigid traditional structures.
Looking Ahead
More startups consider DAOs each month as better tools become available. Small teams can now set up DAOs without spending too much money or needing deep technical knowledge. This makes it possible for more companies to try this new way of working.
The technology behind DAOs keeps improving, making them easier to use and more powerful. New features come out regularly, helping companies do more with their decentralized systems. These improvements make DAOs more attractive to different types of businesses.
Mixing Old and New
Some startups combine DAO features with regular business practices. This gives them the best of both worlds - they get the benefits of decentralized decision-making while keeping some familiar ways of working that their partners understand.
This hybrid approach helps companies transition smoothly to more decentralized operations. They can move at their own pace, adding DAO features as team members and partners get comfortable with the new ways of working.
The Road Forward
DAOs represent a real change in how startups can run their businesses. They make it easier to work together, share information, and keep everyone involved in the company's success. The growth of DAO for startups shows how business practices continue to evolve with technology.
As tools get better and more people understand how DAOs work, they'll become an even more common choice for new businesses.
The key lies in setting them up thoughtfully and making sure everyone knows how to participate effectively. When done right, a DAO gives startups the tools they need to grow and succeed in today's markets.
The future looks bright for companies willing to try new approaches. DAOs offer a path to more efficient, transparent, and fair business operations. Those who take the time to understand and implement them well stand to gain significant advantages in their markets.
#DAO for Startups#DAO Adoption#Business Growth with DAO#DAO Technology#Blockchain for Startups#Web3 Startup Solutions
0 notes
Text
Understanding DAO Crypto: The Intersection of Decentralized Finance and Governance
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have become one of the most compelling innovations in the blockchain and cryptocurrency space. By combining blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature with cryptocurrency’s financial mechanisms, DAO crypto represents a new model of governance, financial management, and organizational structure. Unlike traditional organizations, DAOs operate without centralized control, and their members, often through the use of crypto tokens, are empowered to make decisions and manage operations autonomously.

What is DAO Crypto?
DAO crypto refers to the integration of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) with cryptocurrencies, where blockchain-based smart contracts govern the organization’s operations and financial processes. At its core, a DAO crypto combines the decentralized decision-making model of a DAO with the utility of cryptocurrency tokens for governance, transactions, and rewards.
In a DAO, participants use cryptocurrency tokens to vote on important decisions, propose changes, and manage assets. These tokens not only serve as a voting mechanism but also represent ownership or a stake in the DAO, making participants financially incentivized to ensure the organization's success. Cryptocurrency tokens are also used to distribute rewards, manage operational costs, and facilitate peer-to-peer transactions within the DAO.
0 notes
Text
Challenges in DAO Operations: Overcoming Obstacles in Decentralized Governance
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in organizational governance. They promise to disrupt traditional corporate structures by using blockchain technology to decentralize decision-making, allowing communities to govern themselves autonomously without the need for intermediaries. Despite their many advantages—such as transparency, inclusivity, and decentralization—DAOs face numerous challenges in their operations. These challenges can significantly impact their success, scalability, and long-term sustainability.

1. Governance and Decision-Making Inefficiencies
A cornerstone of any DAO is its decentralized governance model, where decisions are made collectively by token holders through voting. While this system is designed to be inclusive and transparent, it can lead to inefficiencies when scaling up.
Challenges:
Slow Decision-Making: As the number of participants in a DAO grows, the process of gathering votes and making decisions can become sluggish. This is especially problematic when quick action is required, such as in the case of security breaches or market changes.
Voter Apathy: Many DAO participants are passive voters, meaning only a small subset of active members influence decisions. This can lead to the governance process being controlled by a few individuals, undermining the decentralized ethos.
Sybil Attacks: In some cases, bad actors may manipulate the voting process by creating multiple fake identities to influence the outcome of votes, distorting the democratic process.
Solutions:
Quadratic Voting: To prevent large token holders from dominating decisions, DAOs can implement quadratic voting, which reduces the influence of whales and ensures a more equitable distribution of voting power.
Delegated Voting: Allowing participants to delegate their voting power to trusted representatives or experts can streamline the decision-making process, ensuring that votes are cast more efficiently and with greater expertise.
Thresholds for Proposals: Setting a minimum threshold for participation (e.g., requiring a certain percentage of the total token supply to vote) can help mitigate voter apathy and ensure that decisions reflect the interests of a broader community.
2. Security Risks and Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
DAOs rely heavily on smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. While smart contracts offer a high degree of automation and efficiency, they are not immune to bugs, exploits, and hacking attempts. The very autonomy of DAOs makes them prime targets for malicious actors.
Challenges:
Coding Errors and Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts are written in code, which can contain bugs or security flaws that may be exploited by hackers. Even minor coding errors can lead to substantial financial losses.
Hacking and Exploits: Given that DAOs often hold significant amounts of funds in their treasury, they are attractive targets for cybercriminals. A breach can undermine the DAO’s credibility and stability.
Lack of Upgradeability: Many DAOs operate on immutable smart contracts, meaning that once deployed, they cannot be changed. If a vulnerability is discovered after the contract is live, the DAO may struggle to patch it or deploy fixes.
Solutions:
Regular Audits and Penetration Testing: Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing of smart contracts can identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Third-party audits by reputable firms can provide an additional layer of security.
Bug Bounty Programs: To incentivize the community to identify potential weaknesses, DAOs can launch bug bounty programs, rewarding security researchers for finding vulnerabilities.
Upgradeable Contracts and Governance: DAOs can design their smart contracts to be upgradeable, allowing for modifications to be made if a bug or security vulnerability is discovered. However, this introduces a level of centralized control, so it must be done with caution.
3. Legal and Regulatory Uncertainty
DAOs operate in a gray area within the legal landscape. The regulatory environment surrounding blockchain technology, decentralized finance (DeFi), and DAOs remains uncertain in many jurisdictions. This creates challenges related to compliance, taxation, and legal recognition.
Challenges:
Lack of Legal Framework: Many countries have not yet developed clear legal frameworks for DAOs, leading to confusion around their status. In some cases, DAOs may not be recognized as legal entities, which can create issues when attempting to enter into contracts or raise funds.
Jurisdictional Issues: DAOs are borderless by design, which complicates matters of jurisdiction. If a legal dispute arises, it may be unclear which laws govern the DAO’s operations, especially if its members are spread across multiple countries.
Regulatory Scrutiny: As the popularity of DAOs grows, they are increasingly under the radar of financial regulators. Issues such as securities laws, anti-money laundering (AML), and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations can present significant challenges for DAOs, especially those operating in the DeFi space.
Solutions:
Legal Compliance and DAO Jurisdictions: DAOs can engage with legal experts to navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance. In some jurisdictions, DAOs are able to operate as decentralized limited liability companies (LLCs) or similar structures that offer legal recognition while maintaining decentralization.
Collaborating with Regulators: Engaging with regulators early on and proactively complying with emerging regulations can help mitigate the risk of future legal issues.
Creating Clear Governance Guidelines: By establishing clear governance frameworks and rules for participation, DAOs can increase their legitimacy and improve their standing in the eyes of regulators.
4. Scalability and Resource Management
As DAOs grow, they face scalability challenges that can affect their operations, including how resources are managed, distributed, and used. A small DAO with a few participants may have no trouble organizing and executing decisions, but as the DAO scales up, this becomes more difficult.
Challenges:
Coordination Issues: As more members join, coordinating activities and ensuring that everyone’s voice is heard can become increasingly challenging. Larger DAOs can become fragmented, with different factions pushing for conflicting goals.
Resource Allocation: In large DAOs, efficiently allocating funds and resources becomes more complex. Without a clear structure for resource distribution, there can be inefficiencies, waste, or even mismanagement of funds.
Overwhelming Proposals: With a larger community, the volume of proposals can overwhelm the decision-making process, leading to delays and potentially undermining the DAO’s effectiveness.
Solutions:
Modular Structures and Sub-DAOs: One approach to scalability is to implement modular structures or create sub-DAOs that focus on specific tasks or projects. This allows for more efficient resource management and delegation of decision-making.
Automated Proposal Systems: Using automated systems to manage proposals and votes can help streamline decision-making, ensuring that the process remains manageable even as the DAO grows.
Clear Resource Management Frameworks: Establishing transparent and efficient frameworks for resource allocation can ensure that funds are distributed based on community consensus and align with the DAO’s goals.
5. Member Engagement and Participation
One of the greatest challenges for DAOs is maintaining member engagement over time. While participation may be high at the outset, it can dwindle as the novelty wears off, leaving the DAO vulnerable to inaction or governance by a small, disengaged group of active participants.
Challenges:
Voter Apathy: Apathy is a common problem in DAOs, where many members may hold governance tokens but fail to participate in voting or governance activities.
Lack of Incentives: Without proper incentives, members may lose interest and stop contributing to the DAO’s growth or success.
Fragmentation and Divisiveness: In larger DAOs, different groups may form, each with their own agenda. This can lead to fragmentation and a lack of alignment, making it harder to achieve the DAO’s long-term goals.
Solutions:
Incentive Programs: Offering incentives, such as token rewards or other benefits, can help encourage active participation. Staking and governance rewards can be tied to engagement to create a more participatory environment.
Community Building and Communication: DAOs can invest in building a strong community by providing clear communication, holding regular discussions, and offering a space for members to collaborate.
Inclusive Decision-Making: Ensuring that all members feel their voices are heard and that their contributions are valued can help maintain engagement and reduce the risk of divisiveness.
Conclusion
While DAOs offer a unique and transformative approach to organizational governance, they come with a set of operational challenges that must be addressed for long-term success. From governance inefficiencies and security risks to legal uncertainty and scalability issues, overcoming these obstacles requires careful planning, innovative solutions, and continuous adaptation.
By focusing on governance structures, security practices, legal compliance, member engagement, and scalability, DAOs can address these challenges and build sustainable, decentralized organizations that thrive in the digital age. As the DAO ecosystem continues to mature, it is likely that new tools, frameworks, and best practices will emerge to help DAOs operate more effectively and navigate the complexities of decentralized governance.
0 notes
Text
DAO Tools: Empowering Decentralized Governance and Collaboration
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are unique communities that run without traditional centralized management or hierarchies. Instead, they rely on blockchain technology, smart contracts, and a variety of software platforms to facilitate transparent decision-making, streamline operations, and coordinate community members around shared goals. As DAOs have gained popularity, a diverse ecosystem of “DAO tools” has emerged, helping these organizations stay organized, compliant, and effective. By leveraging these tools, DAOs can manage their treasuries, run governance votes, engage participants, and measure their performance in a decentralized, trust-minimized environment.

The Role of DAO Tools
DAOs face complex challenges: coordinating a global community, enforcing governance rules embedded in code, distributing funds, and scaling decision-making processes. DAO tools are designed to help them meet these challenges head-on. These tools typically include a range of software solutions—from user-friendly interfaces that let members submit proposals and vote, to more specialized analytics dashboards that track on-chain activity, treasury health, and community engagement. In essence, DAO tools provide a comprehensive toolkit that merges transparency, efficiency, and security with the flexibility needed to accommodate each DAO’s unique mission.
Types of DAO Tools
Governance Platforms: Governance platforms are at the heart of most DAOs. They provide user interfaces that allow members to propose changes, initiatives, or investments and then vote on them according to predefined governance rules. Popular solutions like Snapshot and Aragon offer simple and secure voting mechanisms, while more advanced frameworks might integrate on-chain execution to automatically implement approved proposals.
Treasury Management and Accounting Solutions: Managing and securing community funds is a fundamental aspect of running a DAO. Treasury tools help automate payroll, grants, and revenue distributions, ensuring that funds move only when authorized by DAO members. Services like Gnosis Safe create secure multisignature wallets, while specialized DAO accounting platforms can provide financial reporting, expense tracking, and even compliance solutions tailored to a decentralized environment.
Communication and Collaboration Tools: While the blockchain provides the fundamental infrastructure for trust, off-chain communication is still crucial. DAOs often use platforms like Discord, Discourse, or specialized DAO forums to discuss proposals, share updates, and gather community feedback. Some DAO tooling providers are building integrated collaboration hubs that combine document management, proposal drafting templates, and real-time chat, reducing fragmentation and making it easier for members to stay informed.
Analytics and Insights Dashboards: Keeping track of a DAO’s health can be challenging, especially as it scales and conducts complex activities. Analytics tools provide real-time insights into treasury allocations, voting patterns, token distributions, and member engagement. Platforms like DeepDAO aggregate data across multiple blockchains, giving stakeholders a clear view into how a DAO is growing, how its proposals evolve, and which participants are most active.
On-Chain Identity and Reputation Systems: One of the key hurdles for DAOs is balancing pseudonymity with accountability. Identity and reputation tools (like BrightID or Proof-of-Personhood solutions) help ensure that one person does not create multiple accounts to influence voting unfairly. Reputation scoring systems can also reward active, constructive members and enhance the quality of governance decisions.
Development Frameworks and Protocol Toolkits: Technical contributors often rely on developer-focused DAO tools, including smart contract libraries, testing frameworks, and templates for deploying new DAO structures. Tools such as OpenZeppelin and Hardhat streamline the process of writing, testing, and upgrading contracts, reducing development overhead and security risks.
Choosing the Right DAO Tools
Selecting the right toolset depends on the DAO’s mission, complexity, and stage of development. For instance, a small, early-stage DAO might focus on simple governance and secure treasury solutions. A well-established DAO that manages a large treasury and complex operations might need advanced analytics, compliance integrations, and more granular access control systems. Additionally, DAOs can experiment with multiple tools and migrate as better solutions emerge, reflecting the dynamic and evolving nature of Web3 technology.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Security is paramount. Since DAOs control significant capital and have reputations at stake, the tools they use must be battle-tested, audited, and continuously improved. Many DAO tool developers invest heavily in code audits, bug bounties, and community review processes. On the compliance front, as DAOs navigate emerging regulations, there is a growing class of tools designed to help them understand and adhere to local laws. This might include tax reporting tools, identity verification solutions, or legal wrappers that give DAOs a recognized status in certain jurisdictions.
The Future of DAO Tools
As the DAO ecosystem matures, we can expect a more seamless integration of the various tool categories. In the future, DAOs may access “all-in-one” platforms where governance, treasury management, analytics, and compliance modules integrate into a unified dashboard. Interoperability standards will likely emerge, enabling DAOs to plug and play tools without lock-in or complicated migrations. Advancements in zero-knowledge proofs, decentralized identity systems, and cross-chain bridges will further enhance the capabilities and user experience of DAO tools, making it easier for anyone, anywhere, to participate meaningfully in decentralized governance.
Conclusion
DAO tools serve as the backbone of modern decentralized organizations, providing essential support for governance, treasury management, communication, analytics, and compliance. In a world where DAOs transcend traditional boundaries—geographically, legally, and operationally—these tools empower communities to operate with transparency, fairness, and efficiency. As the DAO landscape continues to evolve, so too will the ecosystem of tools that foster innovation, trust, and collective success.
0 notes
Text
Marshall Islands Public Companies: An In-Depth Overview
The Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI), situated in the heart of the Pacific Ocean, has established itself as a prominent hub for international business, particularly through its favorable corporate laws and strategic advantages. Public companies incorporated in the Marshall Islands benefit from a robust legal framework, tax incentives, and a reputation for reliability and efficiency.
Understanding Public Companies in the Marshall Islands
A public company in the Marshall Islands is a legal entity that offers its shares to the general public, typically through a stock exchange or other public trading platforms. These companies are governed by the Marshall Islands Business Corporation Act (BCA), which provides a flexible and business-friendly environment conducive to various types of enterprises, including those aiming to access international capital markets.
Public companies in the Marshall Islands are often chosen by businesses seeking to leverage the jurisdiction's advantageous regulatory landscape, which combines minimal bureaucracy with strong legal protections. The RMI's corporate laws are designed to attract international investors by offering simplicity in incorporation, confidentiality for shareholders, and favorable tax conditions.
Benefits of Incorporating as a Public Company in the Marshall Islands
Incorporating a public company in the Marshall Islands offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive choice for businesses worldwide. One of the primary benefits is the jurisdiction's favorable tax regime. The Marshall Islands imposes no corporate income tax, capital gains tax, or withholding tax on dividends, interest, or royalties. This tax neutrality is a significant draw for companies aiming to maximize their profitability and minimize tax liabilities.
Additionally, the Marshall Islands provides a streamlined and efficient incorporation process. Establishing a public company is straightforward, with minimal capital requirements and no restrictions on the nationality or residency of directors and shareholders. This flexibility allows businesses to operate without the constraints often encountered in other jurisdictions.
Confidentiality is another key advantage. The Marshall Islands does not mandate the disclosure of shareholders' identities, offering a level of privacy that is highly valued by international investors and businesses. This anonymity, coupled with strong legal protections, ensures that the interests of shareholders and directors are safeguarded.
Furthermore, the Marshall Islands is renowned for its robust legal system, which is based on English common law principles. The jurisdiction's commitment to upholding the rule of law and providing a stable legal environment instills confidence among investors and business owners alike.
Legal Framework and Regulatory Environment
The legal framework governing public companies in the Marshall Islands is primarily outlined in the Business Corporation Act (BCA). The BCA provides comprehensive regulations that govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of public companies, ensuring that businesses operate within a clear and predictable legal structure.
Public companies must adhere to certain governance standards, including the appointment of a board of directors responsible for overseeing the company's strategic direction and ensuring compliance with legal obligations. While the BCA does not impose stringent reporting requirements, public companies are encouraged to maintain transparent and accurate financial records to foster trust and credibility among investors.
Regulatory oversight in the Marshall Islands is designed to balance business flexibility with necessary safeguards. The Registrar of Corporations oversees the registration and regulation of public companies, ensuring that entities comply with statutory requirements and maintain good standing within the jurisdiction.
Moreover, the Marshall Islands is a member of various international organizations and adheres to global standards related to anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT). Public companies must comply with these international standards, ensuring that their operations are transparent and legally compliant on a global scale.
Incorporation Process for Public Companies
Forming a public company in the Marshall Islands involves several key steps, each designed to facilitate a smooth and efficient incorporation process.
1. Name Reservation: The first step is to choose a unique name for the company and reserve it with the Registrar of Corporations. The name must comply with the naming conventions outlined in the BCA, avoiding prohibited words and ensuring distinctiveness.
2. Submission of Incorporation Documents: The company must submit the necessary incorporation documents, including the Articles of Incorporation, which outline the company's structure, purpose, and governance framework. These documents must be filed with the Registrar of Corporations along with the required fees.
3. Appointment of Directors and Officers: A public company must appoint a board of directors who will oversee the company's operations and strategic direction. While the BCA does not require directors to be residents of the Marshall Islands, appointing knowledgeable and experienced individuals is crucial for effective governance.
4. Issuance of Shares: Public companies must issue shares to their initial shareholders, establishing the foundation for public trading. The BCA provides flexibility in determining the number and classes of shares, allowing companies to tailor their capital structure to meet their specific needs.
5. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: After incorporation, public companies must comply with ongoing regulatory requirements, including maintaining accurate records, holding annual general meetings, and adhering to international AML and CFT standards.
6. Listing on a Stock Exchange (Optional): While not mandatory, public companies may choose to list their shares on international stock exchanges to access a broader investor base and enhance their market presence.
Practical Considerations for Operating Public Companies
Operating a public company in the Marshall Islands entails several practical considerations that businesses must address to ensure compliance and operational efficiency.
Corporate Governance: Effective corporate governance is essential for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the long-term success of the company. Public companies should establish clear governance policies, including the roles and responsibilities of directors and officers, conflict of interest policies, and mechanisms for shareholder engagement.
Financial Management: Maintaining robust financial management practices is crucial for public companies. Accurate bookkeeping, regular financial reporting, and transparent auditing processes help uphold the company's integrity and facilitate informed decision-making.
Legal Compliance: Staying abreast of legal and regulatory changes is vital for ongoing compliance. Public companies should engage legal counsel familiar with Marshall Islands corporate law to navigate any legal complexities and ensure adherence to statutory obligations.
Investor Relations: Building and maintaining strong relationships with investors is a key aspect of operating a public company. Transparent communication, regular updates on company performance, and responsiveness to investor inquiries foster trust and encourage continued investment.
Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks is essential for the stability and growth of public companies. This includes implementing comprehensive risk management strategies, securing adequate insurance coverage, and establishing contingency plans for potential disruptions.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Marshall Islands offers a conducive environment for public companies, businesses must be aware of certain challenges and considerations.
Reputation and Perception: The Marshall Islands, like some other offshore jurisdictions, may face perceptions related to tax avoidance and lack of transparency. Public companies must proactively demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices, regulatory compliance, and transparency to build and maintain a positive reputation.
Access to Local Markets: The Marshall Islands is a relatively small market, and public companies primarily benefit from its favorable incorporation laws rather than local consumer bases. Companies should consider their global strategies and target markets when incorporating in the Marshall Islands.
Legal and Regulatory Changes: The global regulatory landscape is continually evolving, particularly concerning offshore jurisdictions. Public companies must stay informed about changes in international regulations, such as those related to tax transparency and corporate governance, to remain compliant and avoid potential legal issues.
Operational Costs: While the Marshall Islands offers competitive incorporation fees, companies must consider other operational costs, such as legal services, accounting, and compliance measures. Balancing these costs with the benefits of incorporation is essential for sustainable business operations.
Future Outlook
The future of public companies in the Marshall Islands appears promising, driven by ongoing advancements in international business practices and the increasing integration of digital technologies. As global businesses seek flexible and tax-efficient jurisdictions, the Marshall Islands is well-positioned to attract a diverse array of public companies.
Technological Integration: The adoption of blockchain and digital technologies can enhance transparency, security, and efficiency for public companies. Embracing these technologies can further solidify the Marshall Islands' reputation as a forward-thinking jurisdiction.
Sustainable Practices: With growing emphasis on sustainability and corporate social responsibility, public companies in the Marshall Islands can leverage their international presence to promote environmentally and socially responsible practices, appealing to a broader range of investors and stakeholders.
Expansion of Legal Frameworks: The Marshall Islands may continue to refine and expand its legal frameworks to accommodate emerging business models and international standards, ensuring that it remains an attractive destination for public companies.
Conclusion
Incorporating a public company in the Marshall Islands offers a blend of legal advantages, tax benefits, and operational flexibility that appeals to international businesses. The jurisdiction's business-friendly environment, combined with robust legal protections and minimal regulatory burdens, makes it a strategic choice for companies aiming to access global capital markets and optimize their financial operations.
However, businesses must carefully navigate the legal and regulatory landscape, uphold high standards of corporate governance, and proactively manage their reputations to fully capitalize on the benefits of incorporation in the Marshall Islands. As the global business environment continues to evolve, the Marshall Islands is poised to remain a key player in facilitating the growth and success of public companies worldwide.
0 notes
Text
MIDAO Customer Spotlight: MetaDAO
MetaDAO is revolutionizing organizational governance by embracing "futarchy," a model that allows markets, rather than leaders or voters, to drive decision-making. This innovative approach is based on the idea that speculative markets can outperform traditional decision-making methods in various contexts. MetaDAO utilizes decentralized principles and blockchain technology to automate decisions, placing trust in market outcomes. With a focus on transparency and community involvement, MetaDAO aims to create a sustainable governance model that aligns with its ambitious vision, supported by legal structures like the Marshall Islands DAO framework.
Read More
0 notes
Text
Unlocking Collaboration: The Rise of DAO Partner Programs in the Web3 Ecosystem
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain and decentralized technologies, collaboration is key to driving innovation and adoption. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are at the forefront of this movement, leveraging collective decision-making and smart contracts to operate without centralized control. As the Web3 ecosystem expands, DAO Partner Programs and Web3 Partner Programs are emerging as pivotal mechanisms for fostering strategic alliances, sharing resources, and accelerating growth.

The Importance of Partnerships in the DAO Ecosystem
DAOs represent a paradigm shift in how organizations are structured and governed. By utilizing blockchain technology, DAOs enable participants to have a direct say in the organization's direction, creating a more democratic and transparent model. However, the decentralized nature of DAOs also presents challenges, particularly when it comes to scaling operations and reaching wider audiences.
This is where partnerships become crucial. By collaborating with other organizations, DAOs can:
Leverage Expertise: Access specialized knowledge and skills that may not be available within the DAO.
Expand Reach: Tap into new markets and user bases through the partner's network.
Share Resources: Pool resources for mutual benefit, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Drive Innovation: Combine different technologies and ideas to create novel solutions.
Understanding DAO Partner Programs
A DAO Partner Program is a structured initiative designed to facilitate collaboration between a DAO and external entities, such as other DAOs, traditional businesses, or individual contributors. These programs outline the terms of partnership, areas of cooperation, and the mutual benefits expected from the alliance.
Key Features of DAO Partner Programs
Transparent Governance: Decisions regarding partnerships are made collectively by DAO members through voting mechanisms.
Smart Contract Agreements: Partnerships are often codified through smart contracts that automatically enforce the terms of collaboration.
Token Incentives: Partners may receive tokens that grant them certain rights or rewards within the DAO ecosystem.
Community Engagement: Partner programs often involve joint community events, co-marketing efforts, and shared platforms for communication.
The Role of Web3 Partner Programs
The Web3 Partner Program concept extends beyond DAOs to encompass the broader decentralized internet movement. Web3 aims to create a more open, secure, and user-centric internet by leveraging blockchain and decentralized technologies. Web3 Partner Programs are initiatives that encourage collaboration among developers, startups, enterprises, and DAOs to build and promote Web3 solutions.
Benefits of Web3 Partner Programs
Interoperability: Facilitates the integration of different blockchain networks and protocols.
Resource Sharing: Provides access to development tools, funding opportunities, and technical support.
Market Expansion: Helps participants reach global audiences by leveraging the collective networks of all partners.
Educational Opportunities: Offers training and workshops to enhance skills and knowledge about Web3 technologies.
Examples of Successful DAO and Web3 Partnerships
1. Uniswap Grants Program
Uniswap, a leading decentralized exchange, has a DAO Partner Program that funds projects contributing to the Uniswap ecosystem. By partnering with developers and organizations, Uniswap accelerates the development of new features and integrations, enhancing its platform's utility.
2. Gitcoin and Ethereum Foundation
Gitcoin, a platform for open-source bounties, collaborates with the Ethereum Foundation through a Web3 Partner Program. This partnership supports developers working on Ethereum-based projects, fostering innovation and growth within the Ethereum ecosystem.
3. Chainlink and Filecoin Collaboration
Chainlink and Filecoin entered a strategic partnership to combine decentralized oracle services with decentralized storage solutions. This collaboration exemplifies how DAO Partner Programs can bring together different technologies to create more robust and versatile applications.
How to Participate in DAO and Web3 Partner Programs
Organizations or individuals interested in joining a DAO Partner Program or Web3 Partner Program can follow these general steps:
Identify Alignment: Ensure that your goals and values align with those of the DAO or Web3 organization.
Engage with the Community: Participate in forums, attend virtual events, and connect with existing members.
Submit a Proposal: Many DAOs require a formal proposal outlining the partnership's scope, benefits, and implementation plan.
Participate in Governance: Be prepared to engage in the DAO's governance processes, including voting and discussions.
Leverage Resources: Take advantage of the tools, support, and networks provided through the partner program.
The Future of DAO Partnering in Web3
As the decentralized ecosystem matures, the role of partnerships will become increasingly significant. DAO Partner Programs and Web3 Partner Programs offer structured ways to collaborate, driving innovation and expanding the reach of decentralized technologies. By fostering a culture of cooperation, DAOs and Web3 organizations can overcome common challenges, such as scalability and adoption barriers, paving the way for a more decentralized and equitable digital future.
Conclusion
Partnerships are the lifeblood of innovation in the decentralized world. DAO Partner Programs and Web3 Partner Programs serve as catalysts for collaboration, enabling organizations to pool resources, share expertise, and co-create solutions that push the boundaries of what's possible. As more entities recognize the value of these programs, we can expect to see a proliferation of strategic alliances that will shape the future of the Web3 ecosystem.
0 notes
Text
Web3 Banking: The Future of Decentralized Finance
The evolution of the internet from Web1, a read-only environment, to Web2, where users could both read and create content, has been transformative. However, the dawn of Web3 is set to change the landscape even further, particularly when it comes to financial services. Web3 banking represents a decentralized, permissionless, and trustless financial system that operates on blockchain technology, offering an alternative to traditional banking methods.

What Is Web3 Banking?
Web3 banking refers to financial services built on decentralized networks that leverage blockchain technology and smart contracts. Unlike traditional banks that are centralized and controlled by financial institutions, Web3 banking is decentralized, meaning it operates without intermediaries or central authorities.
Web3 banking is part of the broader Web3 movement, which seeks to give users more control over their data, digital assets, and interactions by using cryptographic technologies. In the context of finance, Web3 banking allows individuals to hold, trade, and manage assets in a decentralized manner, often using cryptocurrency wallets instead of traditional bank accounts.
Key Components of Web3 Banking
Cryptocurrencies: Digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum are at the core of Web3 banking. They act as mediums of exchange and store of value, offering an alternative to fiat currencies.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance): DeFi platforms offer decentralized versions of traditional financial services such as lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. These platforms use smart contracts to automate transactions and eliminate the need for banks or financial institutions.
Blockchain Technology: At the foundation of Web3 banking is blockchain, a distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This ensures transparency, security, and immutability of transactions.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts where the terms are encoded into the blockchain. These contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries and automatically execute transactions when predefined conditions are met.
Decentralized Identity: Web3 banking allows users to retain control of their identities and personal information. Using decentralized identities, users can access financial services without revealing unnecessary personal data, enhancing privacy and security.
Benefits of Web3 Banking
1. Decentralization
One of the core principles of Web3 banking is decentralization. Unlike traditional banks, which are centralized and controlled by a handful of financial institutions, Web3 banking operates across a decentralized network of computers. This allows for a more transparent and democratized system where users have direct control over their assets and data.
2. Financial Inclusion
Web3 banking has the potential to bring financial services to the billions of people around the world who are unbanked or underbanked. Traditional banking systems often exclude individuals who lack access to identification, credit history, or stable infrastructure. With Web3 banking, all you need is an internet connection and a cryptocurrency wallet, providing financial services to anyone, anywhere.
3. Lower Fees and Faster Transactions
In traditional banking, intermediaries such as banks, payment processors, and remittance companies charge fees for processing transactions. These fees can be high, particularly for cross-border payments. Web3 banking eliminates the need for intermediaries, significantly reducing transaction fees and enabling near-instantaneous transfers, even across international borders.
4. Enhanced Privacy and Security
Web3 banking allows users to maintain control over their data through decentralized identities and cryptographic encryption. Unlike traditional banks that store customer data in centralized databases (which are prone to breaches), Web3 banking operates on a blockchain, making it highly secure. Users don’t have to provide sensitive personal information to third parties, reducing the risk of identity theft or data breaches.
5. Transparency and Trustlessness
In Web3 banking, all transactions are recorded on a public ledger (blockchain), which ensures transparency. This system is also “trustless,” meaning users don’t need to rely on a central authority or institution to facilitate transactions. Instead, smart contracts automate processes, ensuring that agreed-upon terms are executed without human intervention.
How Web3 Banking Differs from Traditional Banking
1. Centralization vs. Decentralization
Traditional banking relies on central authorities like banks or government-regulated financial institutions to manage transactions, hold funds, and provide services. In contrast, Web3 banking is decentralized, with no single entity controlling the system. Instead, a network of nodes maintains the blockchain and ensures the integrity of the system.
2. Intermediaries vs. Direct Control
In traditional banking, intermediaries like banks, payment processors, and clearinghouses facilitate transactions. These intermediaries are responsible for ensuring the legitimacy of transactions and providing a trusted network for the transfer of funds. Web3 banking eliminates intermediaries, allowing users to have direct control over their assets using decentralized wallets and smart contracts.
3. Accessibility and Inclusivity
Traditional banking systems require identification, credit scores, and access to specific financial institutions. In contrast, Web3 banking is open to anyone with an internet connection, offering financial inclusion to the unbanked and underbanked populations.
4. Privacy and Data Ownership
In traditional banking, users must provide personal information to banks and financial institutions, which store it in centralized databases. Web3 banking shifts the power of data ownership to the individual. Using decentralized identities, users control their own data and only share it when absolutely necessary.
The Future of Web3 Banking
Web3 banking is still in its infancy, but its potential to disrupt traditional banking is immense. As decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to grow, we will likely see more sophisticated financial services that rival or even surpass those offered by traditional banks. These could include decentralized savings accounts, lending platforms, and even decentralized insurance products.
Regulation will be a key factor in the future development of Web3 banking. While the decentralized nature of Web3 is one of its strengths, governments and financial regulators may impose rules that could shape the future of the space. However, as more users and institutions embrace Web3 technologies, it’s clear that the financial world is on the cusp of a significant transformation.
Conclusion
Web3 banking represents a paradigm shift in how financial services are delivered and accessed. By leveraging blockchain, smart contracts, and decentralized networks, Web3 banking offers a more transparent, inclusive, and secure alternative to traditional banking systems. As the Web3 ecosystem continues to evolve, we are likely to see further innovation in decentralized finance, making financial services more accessible and efficient for everyone.
The future of banking is decentralized, and Web3 banking is leading the way.
0 notes
Text
DAO Structure: A New Paradigm in Organizational Management

In the evolving landscape of organizational management, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a groundbreaking shift from traditional hierarchical structures. DAOs leverage blockchain technology to create a decentralized, transparent, and autonomous framework, enabling members to participate in decision-making processes directly. This structure contrasts sharply with conventional organizations, which rely on centralized authority and rigid top-down control.
What is a DAO?
A DAO, or Decentralized Autonomous Organization, is a collective governed by smart contracts on a blockchain. Unlike traditional organizations where decisions are made by a central authority or a board of directors, DAOs empower their members to vote on key issues, from project funding to governance changes. This democratized approach ensures that every member has a say, and decisions are made based on the majority’s preference.
How Does a DAO Work?
DAOs operate through a series of smart contracts — self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically enforce rules and execute decisions based on the outcomes of votes cast by the DAO’s members.
For example, if a proposal is made to allocate funds to a new project, members vote on the proposal. Once a consensus is reached, the smart contract executes the decision without needing further approval from a central authority. This process is not only efficient but also reduces the risk of human error and corruption.
Key Advantages of DAO Structure
Transparency: Since all transactions and decisions are recorded on the blockchain, DAOs offer unparalleled transparency. Every member can see how decisions are made and funds are allocated, fostering trust within the organization.
Decentralization: In a DAO, no single entity holds control. Power is distributed among all members, reducing the risk of manipulation or corruption by a central authority.
Autonomy: DAOs operate independently of human intervention. Once the rules are set in the smart contracts, they execute automatically, making the organization truly autonomous.
Global Participation: DAOs enable people from around the world to participate in decision-making processes. This global reach can bring diverse perspectives and solutions to the table, enriching the organization’s strategies and outcomes.
Challenges Facing DAOs
While the DAO structure offers many advantages, it is not without challenges. Some of the primary concerns include:
Legal Uncertainty: As a relatively new concept, DAOs operate in a legal grey area. Many jurisdictions have yet to establish clear regulations for decentralized organizations, which can lead to legal complications.
Security Risks: Since DAOs rely on smart contracts, they are vulnerable to coding errors or security breaches. A single flaw in the contract code can lead to significant financial losses or exploitation by malicious actors.
Coordination: Decentralization can sometimes make decision-making slow, especially if members are not actively participating or if there is no clear consensus.
DAO vs. Traditional Organizations
The most significant difference between DAOs and traditional organizations lies in their governance structure. Traditional organizations operate on a hierarchical model, where decisions are made by a select few at the top of the pyramid. In contrast, DAOs function on a flat structure, where every member has an equal say in decision-making.
This difference leads to contrasting operational dynamics. Traditional organizations often have clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and accountability. In contrast, DAOs rely on collective decision-making, which can lead to innovative solutions but may also result in slower decision processes due to the need for consensus.
For a more in-depth comparison between DAO structures and traditional organizations, and to understand which might be better suited for your needs, you can refer to this detailed blog post on DAO Structure vs. Traditional Organizations.
Conclusion
DAOs are redefining what it means to be an organization in the digital age. By decentralizing control, enhancing transparency, and empowering global participation, DAOs offer a compelling alternative to traditional corporate structures. However, like any innovation, they come with challenges that need to be addressed. As technology and legal frameworks evolve, DAOs are likely to become a more prevalent and robust option for organizing collective efforts and resources.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur looking to start a new venture or a member of an existing organization considering a shift to a more decentralized model, understanding the nuances of DAO structures is crucial. Embracing this new paradigm could unlock new opportunities for innovation, inclusivity, and efficiency in organizational management.
0 notes
Text
Understanding DAO Organizations: The Future of Decentralized Governance

In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain and cryptocurrency, DAO organizations, or Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, have emerged as a groundbreaking concept. These entities leverage the power of blockchain technology to create a new form of governance that is decentralized, transparent, and driven by code. But what exactly are DAO organizations, and why are they garnering so much attention? Let’s delve into the intricacies of DAOs and explore their potential impact on the future of organizational governance.
What is a DAO?
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is an organization represented by rules encoded as a computer program that is transparent, controlled by organization members, and not influenced by a central government. DAOs are typically based on blockchain technology, most notably the Ethereum blockchain, which enables the creation of smart contracts. These smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Key Characteristics of DAO Organizations
Decentralization: Unlike traditional organizations, DAOs operate without a central authority. Decision-making power is distributed among all members, ensuring that no single entity has complete control.
Autonomy: DAOs function autonomously based on pre-programmed rules. Once the smart contracts are deployed on the blockchain, they can execute transactions and make decisions without human intervention.
Transparency: All transactions and rules within a DAO are recorded on a public blockchain. This ensures complete transparency and allows members to verify the organization’s activities.
Governance by Consensus: DAOs use consensus mechanisms to make decisions. Members typically vote on proposals, and the outcome is determined by the majority. This democratic process ensures that all voices are heard.
How Do DAOs Work?
The operation of a DAO is governed by smart contracts. These contracts define the rules of the organization and the mechanisms for decision-making. When a DAO is launched, its creators deploy the smart contracts on a blockchain and issue tokens to members. These tokens often represent voting power, and members use them to participate in the governance of the DAO.
For example, if a DAO wants to fund a new project, a proposal is created and members vote on it. If the proposal receives enough votes, the smart contract executes the transaction, transferring funds to the project. This process eliminates the need for intermediaries and ensures that decisions are made collectively.
Advantages of DAO Organizations
Efficiency: DAOs streamline decision-making processes by eliminating the need for intermediaries. This can lead to faster and more efficient operations.
Cost-Effectiveness: By removing intermediaries, DAOs can reduce operational costs. There is no need for managers, board members, or other traditional roles that typically require salaries.
Global Participation: DAOs are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, allowing for global participation. This inclusivity can lead to a more diverse and innovative organization.
Immutable Governance: Once deployed, the rules of a DAO cannot be changed without consensus. This ensures that the organization operates predictably and according to agreed-upon rules.
Challenges and Risks
Despite their potential, DAOs are not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is security. Since DAOs operate on code, they are susceptible to bugs and vulnerabilities. The infamous hack of The DAO in 2016, which resulted in the loss of $50 million worth of Ethereum, highlighted the importance of robust security measures.
Additionally, the legal status of DAOs is still unclear in many jurisdictions. As decentralized entities, they do not fit neatly into existing legal frameworks, which can lead to regulatory uncertainty.
The Future of DAOs
The concept of DAO organizations is still in its infancy, but the potential is immense. As blockchain technology continues to mature, we can expect DAOs to become more prevalent and sophisticated. They offer a new paradigm for organizational governance that is transparent, efficient, and democratic.
In the coming years, we may see DAOs revolutionize various industries, from finance to social organizations, by providing a model for decentralized, autonomous governance. As with any emerging technology, there will be hurdles to overcome, but the promise of DAOs is too significant to ignore.
Conclusion
DAO organizations represent a bold step towards decentralizing governance and creating more transparent and efficient systems. While challenges remain, the potential benefits make DAOs a compelling innovation in the world of blockchain and beyond. As we continue to explore and refine this concept, DAOs could very well become the standard for organizational governance in the digital age.
0 notes
Text
DAO Development Company: Empowering Decentralization with Cutting-Edge Solutions

In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have emerged as a revolutionary concept, enabling decentralized decision-making and governance. A DAO development company plays a pivotal role in this transformation by offering specialized services that empower organizations to harness the full potential of decentralization. This article delves into the significance of DAO development companies, their services, and the impact they have on various industries.
Understanding DAOs
What is a DAO?
A Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) is an organization represented by rules encoded as a computer program, controlled by its members, and not influenced by a central government. DAOs operate on blockchain technology, ensuring transparency, security, and automation of processes. The core principle of a DAO is to provide a decentralized framework for decision-making, where stakeholders have a direct say in the governance and operations of the organization.
The Rise of DAOs
The concept of DAOs gained significant traction with the advent of blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum, which provided the infrastructure to create smart contracts. These smart contracts automate various functions of a DAO, from voting to financial transactions, ensuring that all actions are transparent and tamper-proof. The rise of DAOs marks a shift towards a more democratic and inclusive approach to organizational governance.
The Role of a DAO Development Company
Expertise in Blockchain Technology
DAO development companies are at the forefront of blockchain innovation, offering expertise in creating and managing decentralized systems. Their knowledge spans across various blockchain platforms, enabling them to develop robust and scalable DAOs tailored to the specific needs of their clients.
Custom DAO Development
One of the primary services offered by DAO development companies is custom DAO development. This involves understanding the unique requirements of an organization and building a DAO from the ground up. From defining the governance model to implementing smart contracts, these companies ensure that the DAO aligns with the client’s vision and goals.
Smart Contract Development
Smart contracts are the backbone of any DAO, automating processes and ensuring transparency. DAO development companies specialize in writing, testing, and deploying smart contracts that govern the operations of the DAO. These contracts are designed to be secure, efficient, and easy to audit, providing a solid foundation for the DAO’s activities.
Integration and Migration Services
For existing organizations looking to transition to a DAO model, development companies offer integration and migration services. This involves integrating existing systems with the DAO framework and migrating data and processes to the blockchain. These services ensure a smooth transition, minimizing disruptions to the organization’s operations.
Security and Compliance
Security is a critical concern in the world of blockchain and DAOs. DAO development companies prioritize security, implementing robust measures to protect the DAO from vulnerabilities and attacks. Additionally, they ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards, providing peace of mind to stakeholders.
Impact of DAOs on Various Industries
Finance and DeFi
DAOs are transforming the finance sector by enabling decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. These platforms operate without intermediaries, providing more transparent and efficient financial services. DAO development companies are instrumental in creating DeFi platforms that offer lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services in a decentralized manner.
Governance and Voting
In the realm of governance, DAOs provide a transparent and democratic approach to decision-making. They are being adopted by various organizations, from non-profits to corporations, to facilitate fair and inclusive voting processes. DAO development companies help these organizations implement voting mechanisms that are secure and verifiable.
Supply Chain Management
DAOs are also making waves in supply chain management by providing a decentralized approach to tracking and verifying the movement of goods. This transparency reduces fraud, enhances efficiency, and builds trust among stakeholders. DAO development companies develop supply chain DAOs that offer real-time tracking and immutable records.
Content Creation and Distribution
The content creation and distribution industry is leveraging DAOs to provide fair compensation and recognition to creators. DAOs enable decentralized platforms where content creators can directly interact with their audience and receive payments without intermediaries. DAO development companies design these platforms to ensure transparency and fairness.
Conclusion
The rise of DAOs signifies a new era of decentralized governance and operations. DAO development companies are at the heart of this revolution, providing the expertise and services necessary to build and maintain robust DAOs. Their contributions are not only transforming individual organizations but also reshaping entire industries. As the world continues to embrace decentralization, the role of DAO development companies will become increasingly pivotal in driving innovation and growth.
0 notes
Text
MoonDAO: To the Moon!
MoonDAO is one of over a hundred DAOs that recently chose to domicile in the Marshall Islands to help them achieve their goals. Here’s an overview of what MoonDAO is and why they chose the Marshall Islands. This is part 3 of a series telling our customer’s stories.

MoonDAO: The Internet’s Space Program
MoonDAO began with a simple goal: to send someone to space through the crowd-sourced power of the internet, using ETH, the Ethereum Network’s native currency. In a one-month campaign in January 2022, MoonDAO raised 2,612 ETH from over 2,000 contributors, amounting to $8.3 million at the time. Shortly after, they purchased two seats on a Blue Origin rocket. By August 2022, just eight months after its inception, MoonDAO sent its first astronaut to space through a democratic vote by its members.
Read more about MoonDAO.
0 notes
Text
Marshall Islands Enhances Legislation to Boost DAOs Legal Status, Accelerates Registration and Provides Immunity

MIDAO, a public-private partnership between the Marshall Islands and MIDAO Directory Services, serves as the registrar’s office extension for DAOs and Web 3. Adam Miller claims that the updated Act is the most comprehensive law for DAOs worldwide, providing a blueprint for DAO regulations. Since recognizing DAOs as legal entities in 2022, the Marshall Islands has incorporated nearly 100 DAOs under its original act of 2021.
The revised law offers several benefits for DAOs, including faster registration times capped at 30 days (previously 30–60 days), and immunity for DAOs from being held accountable for the use of any open-source software they create. Additionally, most governance tokens will not be classified as securities unless they offer economic rights beyond potential financial gain.
To establish a DAO in the Marshall Islands, one must visit MIDAO.org and hire MIDAO as a registered agent. The Act also legitimizes Series DAO LLCs, which are often used to segregate assets and liabilities in sub-DAO structures.
The unique status of the Marshall Islands allows it to make these advancements without being subject to U.S. federal laws, while still maintaining access to U.S. services such as the U.S. Postal Services, Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and the U.S Military.
For more details, you can visit the original article on Binance: Marshall Islands Enhances Legislation to Boost DAOs Legal Status, Accelerates Registration and Provides Immunity.
0 notes
Text
Marshall Islands and Crypto: Best Place for DAOs Amid New Global Regulatory Crackdown

Legal Recognition of DAOs: In December 2022, the Marshall Islands became the first country to legally recognize DAOs. This was further strengthened in October 2023 with amendments to streamline the process.
DAOs and Regulatory Challenges: DAOs, which are organizations that operate on blockchain principles and smart contracts, face regulatory uncertainties. They are largely unregulated and have been subject to scrutiny by bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
Marshall Islands’ Unique Position: Amidst regulatory uncertainties in the U.S. and other countries, the Marshall Islands is positioning itself as a favorable destination for DAOs. The country’s amended legislation aims to provide a comprehensive legal framework for DAOs, including faster registration times, liability protections, and non-classification of most governance tokens as securities.
Setting up a DAO in the Marshall Islands: The process of setting up a DAO in the Marshall Islands is facilitated by registered agents like MIDAO and can be done remotely without the need for a local office or law firm.
The article suggests that while larger countries are still figuring out how to regulate DAOs, the Marshall Islands is taking a proactive approach by offering legal protections and a streamlined process, positioning itself as a leading jurisdiction for DAO creation.
0 notes
Text
Announcing Rise’s Partnership with MIDAO
Today marks a monumental chapter in the world of Web3-native organizations. Rise, known for its dedication to streamlining crypto <> fiat payroll and compliance operations for decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), is excited to announce its partnership with MIDAO, the exclusive registered agent for the revolutionary DAO LLC legal entity in the Marshall Islands.
This partnership is not just a collaboration; it’s a leap towards revolutionizing Web3 legislation. Since early 2022, the Marshall Islands, an idyllic nation in the Pacific Ocean, has been the epicenter of innovative Web3 law. Together with MIDAO, they have crafted what is arguably the most advanced legal structure for Web3 entities — the DAO LLC. This landmark legislation allows organizations to incorporate blockchain-based governance directly into their legal framework, providing the benefits of corporate personhood, tax optimization, and crucially, limited liability protection for their members.
The significance of this partnership cannot be overstated. For the first time, emerging DAOs within the Rise network will have access to a legal entity tailor-made for their unique needs. Rise’s commitment to aiding DAOs in all facets of business, including payroll and compliance, meshes seamlessly with MIDAO’s legal expertise. Together, they stand as a beacon for organizations navigating the complex legal and regulatory Web3 terrain.
The recent amendment to the DAO Act of 2022 by the Marshall Islands, carried out in close cooperation with MIDAO, underscores this commitment to innovation. This historic move simplifies the DAO incorporation process, further cementing the Marshall Islands as a global vanguard for Web3 legal entities. MIDAO’s role as the gatekeeper for these entities ensures that a broad spectrum of Web3 organizations can now establish their DAO LLC or Series DAO LLC with ease, enjoying the benefits of a legal framework that understands their distinctive needs.
Read more about Rise’s Partnership with MIDAO
0 notes