RP and references account. Current AU: Kaze and Angel: after seeing his fiance die in his arms, Prince Xander of Nohr discovers the biggest secret of the retainers Laslow, Odin and Serena. They are agents of the Ministry of Harmony from the Kalosean Government, an organism in charge of keeping the balance between alternate dimensions and preserving the story of each one of them. But, what will happen with Xander when he meets Angel, his neighbour who looks like his late fiance, Kaze?
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Note
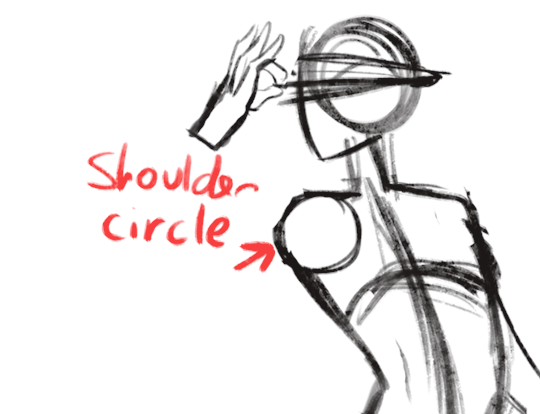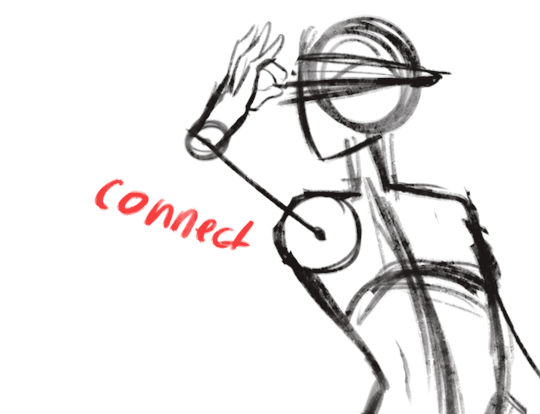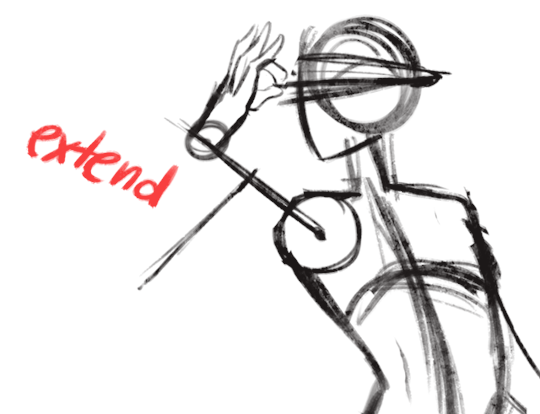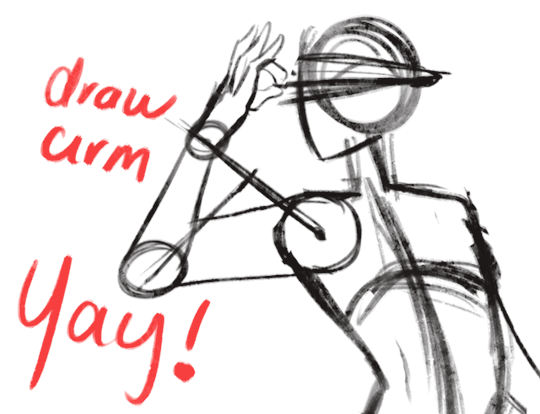
Do you have any tips on digitally shading?
u gotta be very specific anon a lot of things happen when I’m shading ;u;
but here’s a very basic walkthrough of my general process (NOT a tutorial because this doesn’t go in depth at all and I guess it’s not really useful if you’re not sure what to look for?)

1K notes
·
View notes
Text










This got big on Twitter but I never posted it here! A silly little presentation I made about drawing babies 👶
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
You know how canaries were historically brought into coal mines, because if the mine was full of carbon monoxide the canary would die first and the miners would be able to escape before they died too?
I just found the greatest thing.

This is a canary resuscitator.
When the miners notice the canary getting sick with carbon monoxide poisoning, they can close that circular hatch so no more gas gets into the canary cage, and open the valve on that oxygen tank to keep the canary breathing. In other words, they made a spacesuit for birds.
By immediately giving the canary access to clean air, the miners can save it from the poison. The bird lives. To be clear, this is not for economic purposes, this was specifically created because the miners felt bad and wanted to save the bird.
Isn’t that just the perfect demonstration of what humans are like? We started sacrificing small creatures to save ourselves, and then felt bad and spent our valuable resources on saving the critters too. Because yeah the canary was the only way to test for CO, but it’s a living creature too, dammit!
217K notes
·
View notes
Photo




http://browse.deviantart.com/art/Abdomination-How-to-draw-beef-132538271 < Source
36K notes
·
View notes
Text
✨♿Wheelchair Drawing Tutorial♿✨
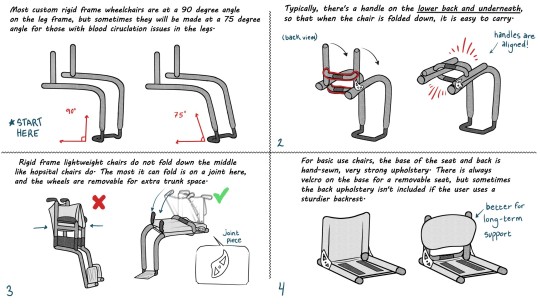
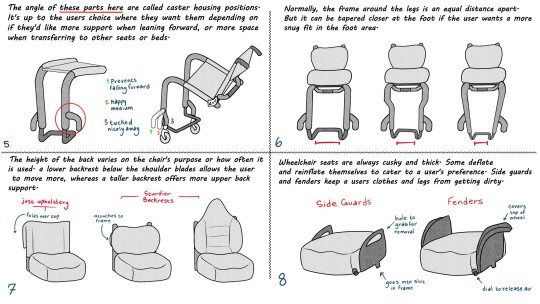


aaand it's finished! An artist's guide to custom rigid frame wheelchairs! This is completely free to use, reference, and save. Reblogs are welcome but please do not repost without permission and credit. Have fun, lovelies!
38K notes
·
View notes
Note
how do u scan your like. traditional pencil works and color them digitally? it always looks clean and good
things evolve over time and what exactly goes down depends on the piece, but heres the key shit. if u see something u happen to not understand then try google n im sure there will be info or ask me seperately
i scan at a high dpi so that they match the scale of my digital only works (600-800 dpi tho its honestly excessive) then i bring them into photoshop and use the levels editor to make whites white and blacks black and find the optimal balance of everything inbetween which varys per peice a little
if you dont have ps or a program with a levels editor or similar, brightness and contrast sliders are your next bet (raise contrast, lower brightness)


remember to also remove all saturation bcs u wont need it
i also occasionaly use liquify to fix errors. i havent needed it much lately but no shame using tools avalible to u lmao. i mightve used it here to lower Marinas leg
then i bring it into sai and with a combo of magic wand and selection tool cleanup, i select the background to erase/fill in with white (or merge onto a white layer after) and spot cleanup anything on the drawing like remaining unnessecery texture on white areas and dirt

then, the simple answer is that i set the layer to multiply then go to town coloring over if needed and below it. but ive been doing much more now to bring color out, putting it in a folder set to multiply instead, with an overlay layer inside the folder with it to color the lines and affect the color underneath it further


do flats, put them all in a folder and clip your layers for additional lighting to them and go to fucking town

also, above everything, 5-15% of this bad boy, hue change if needed

remember, these r tools, not laws. go wild babey…
u can see finished examples on my art blog @apple-cores (art shown: [x] [x])
3K notes
·
View notes
Photo


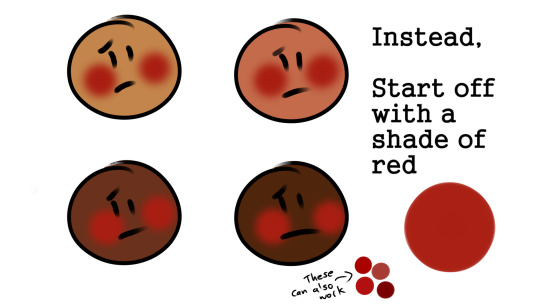



POC blush tutorial
Feel free to repost, but please credit me
61K notes
·
View notes
Text
Fantasy Guide to Architecture



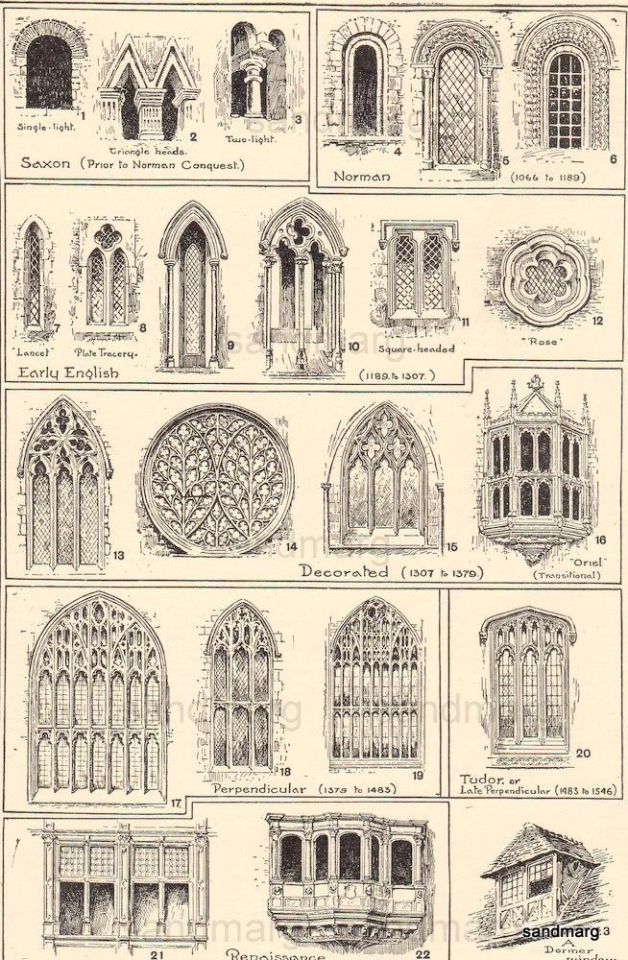


This post has been waiting on the back burner for weeks and during this time of quarantine, I have decided to tackle it. This is probably the longest post I have ever done. I is very tired and hope that I have covered everything from Ancient times to the 19th Century, that will help you guys with your worldbuilding.
Materials
What you build with can be determined by the project you intend, the terrain you build on and the availability of the material. It is one characteristic that we writers can take some some liberties with.
Granite: Granite is an stone formed of Igneous activity near a fissure of the earth or a volcano. Granites come in a wide range of colour, most commonly white, pink, or grey depending on the minerals present. Granite is hard and a durable material to build with. It can be built with without being smoothed but it looks bitchin’ and shiny all polished up.
Marble: Probably everyone’s go to materials for building grand palaces and temples. Marble is formed when great pressure is placed on limestone. Marble can be easily damaged over time by rain as the calcium in the rock dissolves with the chemicals found in rain. Marble comes in blue, white, green, black, white, red, gray and yellow. Marble is an expensive material to build with, highly sought after for the most important buildings. Marble is easy to carve and shape and polishes to a high gleam. Marble is found at converging plate boundaries.
Obsidian: Obsidian is probably one of the most popular stones mentioned in fantasy works. Obsidian is an igneous rock formed of lava cooling quickly on the earth’s surfaces. Obsidian is a very brittle and shiny stone, easy to polish but not quite a good building material but a decorative one.
Limestone: Limestone is made of fragments of marine fossils. Limestone is one of the oldest building materials. Limestone is an easy material to shape but it is easily eroded by rain which leads most limestone monuments looking weathered.
Concrete: Concrete has been around since the Romans. Concrete is formed when aggregate (crushed limstone, gravel or granite mixed with fine dust and sand) is mixed with water. Concrete can be poured into the desired shape making it a cheap and easy building material.
Brick: Brick was one of history’s most expensive materials because they took so long to make. Bricks were formed of clay, soil, sand, and lime or concrete and joined together with mortar. The facade of Hampton Court Palace is all of red brick, a statement of wealth in the times.
Glass: Glass is formed of sand heated until it hardens. Glass is an expensive material and for many years, glass could not be found in most buildings as having glass made was very expensive.
Plaster: Plaster is made from gypsum and lime mixed with water. It was used for decoration purposes and to seal walls. A little known fact, children. Castle walls were likely painted with plaster or white render on the interior.
Wattle and Daub: Wattle and daub is a building material formed of woven sticks cemented with a mixture of mud, one of the most common and popular materials throughout time.
Building terms
Arcade: An arcade is a row of arches, supported by columns.
Arch: An arch is a curved feature built to support weight often used for a window or doorway.
Mosaic: Mosaics are a design element that involves using pieces of coloured glass and fitted them together upon the floor or wall to form images.
Frescos: A design element of painting images upon wet plaster.
Buttress: A structure built to reinforce and support a wall.
Column: A column is a pillar of stone or wood built to support a ceiling. We will see more of columns later on.
Eave: Eaves are the edges of overhanging roofs built to allow eater to run off.
Vaulted Ceiling: The vaulted ceilings is a self-supporting arched ceiling, than spans over a chamber or a corridor.
Colonnade: A colonnade is a row of columns joined the entablature.
Entablature: a succession of bands laying atop the tops of columns.
Bay Window: The Bay Window is a window projecting outward from a building.
Courtyard/ Atrium/ Court: The courtyard is an open area surrounded by buildings on all sides
Dome: The dome resembles a hollow half of a sphere set atop walls as a ceiling.
Façade: the exterior side of a building
Gable: The gable is a triangular part of a roof when two intersecting roof slabs meet in the middle.
Hyphen: The hyphen is a smaller building connecting between two larger structures.
Now, let’s look at some historical building styles and their characteristics of each Architectural movement.
Classical Style
The classical style of Architecture cannot be grouped into just one period. We have five: Doric (Greek), Ionic (Greek), Corinthian (Greek), Tuscan (Roman) and Composite (Mixed).
Doric: Doric is the oldest of the orders and some argue it is the simplest. The columns of this style are set close together, without bases and carved with concave curves called flutes. The capitals (the top of the column) are plain often built with a curve at the base called an echinus and are topped by a square at the apex called an abacus. The entablature is marked by frieze of vertical channels/triglyphs. In between the channels would be detail of carved marble. The Parthenon in Athens is your best example of Doric architecture.
Ionic: The Ionic style was used for smaller buildings and the interiors. The columns had twin volutes, scroll-like designs on its capital. Between these scrolls, there was a carved curve known as an egg and in this style the entablature is much narrower and the frieze is thick with carvings. The example of Ionic Architecture is the Temple to Athena Nike at the Athens Acropolis.
Corinthian: The Corinthian style has some similarities with the Ionic order, the bases, entablature and columns almost the same but the capital is more ornate its base, column, and entablature, but its capital is far more ornate, commonly carved with depictions of acanthus leaves. The style was more slender than the others on this list, used less for bearing weight but more for decoration. Corinthian style can be found along the top levels of the Colosseum in Rome.
Tuscan: The Tuscan order shares much with the Doric order, but the columns are un-fluted and smooth. The entablature is far simpler, formed without triglyphs or guttae. The columns are capped with round capitals.
Composite: This style is mixed. It features the volutes of the Ionic order and the capitals of the Corinthian order. The volutes are larger in these columns and often more ornate. The column’s capital is rather plain. for the capital, with no consistent differences to that above or below the capital.
Islamic Architecture
Islamic architecture is the blanket term for the architectural styles of the buildings most associated with the eponymous faith. The style covers early Islamic times to the present day. Islamic Architecture has some influences from Mesopotamian, Roman, Byzantine, China and the Mongols.
Paradise garden: As gardens are an important symbol in Islam, they are very popular in most Islamic-style buildings. The paradise gardens are commonly symmetrical and often enclosed within walls. The most common style of garden is split into four rectangular with a pond or water feature at the very heart. Paradise gardens commonly have canals, fountains, ponds, pools and fruit trees as the presence of water and scent is essential to a paradise garden.
Sehan: The Sehan is a traditional courtyard. When built at a residence or any place not considered to be a religious site, the sehan is a private courtyard. The sehan will be full of flowering plants, water features snd likely surrounded by walls. The space offers shade, water and protection from summer heat. It was also an area where women might cast off their hijabs as the sehan was considered a private area and the hijab was not required. A sehan is also the term for a courtyard of a mosque. These courtyards would be surrounded by buildings on all sides, yet have no ceiling, leaving it open to the air. Sehans will feature a cleansing pool at the centre, set under a howz, a pavilion to protect the water. The courtyard is used for rituals but also a place of rest and gathering.
Hypostyle Hall: The Hypostyle is a hall, open to the sky and supported by columns leading to a reception hall off the main hall to the right.
Muqarnas : Muqarnas is a type of ornamentation within a dome or a half domed, sometimes called a “honeycomb”, or “stalactite” vaulted ceiling. This would be cast from stone, wood, brick or stucco, used to ornament the inside of a dome or cupola. Muqarnas are used to create transitions between spaces, offering a buffer between the spaces.
African Architecture
African Architecture is a very mixed bag and more structurally different and impressive than Hollywood would have you believe. Far beyond the common depictions of primitive buildings, the African nations were among the giants of their time in architecture, no style quite the same as the last but just as breathtaking.
Somali architecture: The Somali were probably had one of Africa’s most diverse and impressive architectural styles. Somali Architecture relies heavy on masonry, carving stone to shape the numerous forts, temples, mosques, royal residences, aqueducts and towers. Islamic architecture was the main inspiration for some of the details of the buildings. The Somali used sun-dried bricks, limestone and many other materials to form their impressive buildings, for example the burial monuments called taalo
Ashanti Architecture: The Ashanti style can be found in present day Ghana. The style incorporates walls of plaster formed of mud and designed with bright paint and buildings with a courtyard at the heart, not unlike another examples on this post. The Ashanti also formed their buildings of the favourite method of wattle and daub.
Afrikaner Architecture: This is probably one of the oddest architectural styles to see. Inspired by Dutch settlers (squatters), the buildings of the colony (planters/squatters) of South Africa took on a distinctive Dutch look but with an Afrikaner twist to it making it seem both familiar and strange at the same time.
Rwandan Architecture: The Rwandans commonly built of hardened clay with thatched roofs of dried grass or reeds. Mats of woven reeds carpeted the floors of royal abodes. These residences folded about a large public area known as a karubanda and were often so large that they became almost like a maze, connecting different chambers/huts of all kinds of uses be they residential or for other purposes.
Aksumite Architecture: The Aksumite was an Empire in modern day Ethiopia. The Aksumites created buildings from stone, hewn into place. One only has to look at the example of Bete Medhane Alem to see how imposing it was.
Yoruba Architecture: Yoruba Architecture was made by earth cured until it hardened enough to form into walls, or they used wattle and daub, roofed by timbers slats coated in woven grass or leaves. Each unit divided up parts of the buildings from facilities to residences, all with multiple entrances, connected together.
Igbo Architecture: The Igbo style follows some patterns of the Yoruba architecture, excepting that there are no connected walls and the spacing is not so equal. The closer a unit was to the centre, the more important inhabitants were.
Hausa architecture: Hausa Architecture was formed of monolithic walls coated in plaster. The ceilings and roof of the buildings were in the shape of small domes and early vaulted ceilings of stripped timber and laterite. Hausa Architecture features a single entrance into the building and circular walls.
Nubian Architecture: Nubia, in modern day Ethiopia, was home to the Nubians who were one of the world’s most impressive architects at the beginning of the architecture world and probably would be more talked about if it weren’t for the Egyptians building monuments only up the road. The Nubians were famous for building the speos, tall tower-like spires carved of stone. The Nubians used a variety of materials and skills to build, for example wattle and daub and mudbrick. The Kingdom of Kush, the people who took over the Nubian Empire was a fan of Egyptian works even if they didn’t like them very much. The Kushites began building pyramid-like structures such at the sight of Gebel Barkal
Egyptian Architecture: The Egyptians were the winners of most impressive buildings for s good while. Due to the fact that Egypt was short on wood, Ancient Egyptians returned to building with limestone, granite, mudbrick, sandstone which were commonly painted with bright murals of the gods along with some helpful directions to Anubis’s crib. The Egyptians are of course famous for their pyramids but lets not just sit on that bandwagon. Egyptian Architecture sported all kinds of features such as columns, piers, obelisks and carving buildings out of cliff faces as we see at Karnak. The Egyptians are cool because they mapped out their buildings in such a way to adhere to astrological movements meaning on special days if the calendar the temple or monuments were in the right place always. The Egyptians also only build residences on the east bank of the Nile River, for the opposite bank was meant for the dead. The columns of Egyptian where thicker, more bulbous and often had capitals shaped like bundles of papyrus reeds.
Chinese Architecture
Chinese Architecture is probably one of the most recognisable styles in the world. The grandness of Chinese Architecture is imposing and beautiful, as classical today as it was hundreds of years ago.
The Presence of Wood: As China is in an area where earthquakes are common, most of the buildings are were build of wood as it was easy to come across and important as the Ancient Chinese wanted a connection to nature in their homes.
Overhanging Roofs: The most famous feature of the Chinese Architectural style are the tiled roofs, set with wide eaves and upturned corners. The roofs were always tiled with ceramic to protect wood from rotting. The eaves often overhung from the building providing shade.
Symmetrical Layouts: Chinese Architecture is symmetrical. Almost every feature is in perfect balance with its other half.
Fengshui: Fengshui are philosophical principles of how to layout buildings and towns according to harmony lain out in Taoism. This ensured that the occupants in the home where kept in health, happiness, wealth and luck.
One-story: As China is troubled by earthquakes and wood is not a great material for building multi-storied buildings, most Chinese buildings only rise a single floor. Richer families might afford a second floor but the single stories compounds were the norm.
Orientation: The Ancient Chinese believed that the North Star marked out Heaven. So when building their homes and palaces, the northern section was the most important part of the house and housed the heads of the household.
Courtyards: The courtyard was the most important area for the family within the home. The courtyard or siheyuan are often built open to the sky, surrounded by verandas on each side.
Japanese Architecture
Japanese Architecture is famous for its delicacy, smooth beauty and simplistic opulence. Japanese Architecture has been one of the world’s most recognisable styles, spanning thousands of years.
Wood as a Common Material: As with the Chinese, the most popular material used by the Japanese is wood. Stone and other materials were not often used because of the presence of earthquakes. Unlike Chinese Architecture, the Japanese did not paint the wood, instead leaving it bare so show the grain.
Screens and sliding doors: The shoji and fusuma are the screens and sliding doors are used in Japanese buildings to divide chambers within the house. The screens were made of light wood and thin parchment, allowing light through the house. The screens and sliding doors were heavier when they where used to shutter off outside features.
Tatami: Tatami mats are used within Japanese households to blanket the floors. They were made of rice straw and rush straw, laid down to cushion the floor.
Verandas: It is a common feature in older Japanese buildings to see a veranda along the outside of the house. Sometimes called an engawa, it acted as an outdoor corridor, often used for resting in.
Genkan: The Genkan was a sunken space between the front door and the rest of the house. This area is meant to separate the home from the outside and is where shoes are discarded before entering.
Nature: As both the Shinto and Buddhist beliefs are great influences upon architecture, there is a strong presence of nature with the architecture. Wood is used for this reason and natural light is prevalent with in the home. The orientation is meant to reflect the best view of the world.
Indian Architecture
India is an architectural goldmine. There are dozens of styles of architecture in the country, some spanning back thousands of years, influenced by other cultures making a heady stew of different styles all as beautiful and striking as the last.
Mughal Architecture: The Mughal architecture blends influences from Islamic, Persian along with native Indian. It was popular between the 16th century -18th century when India was ruled by Mughal Emperors. The Taj Mahal is the best example of this.
Indo-Saracenic Revival Architecture: Indo Saracenic Revival mixes classical Indian architecture, Indo-Islamic architecture, neo-classical and Gothic revival of the 1800s.
Cave Architecture: The cave architecture is probably one of the oldest and most impressive styles of Indian architecture. In third century BC, monks carved temples and buildings into the rock of caves.
Rock-Cut Architecture: The Rock-cut is similar to the cave style, only that the rock cut is carved from a single hunk of natural rock, shaped into buildings and sprawling temples, all carved and set with statues.
Vesara Architecture: Vesara style prevalent in medieval period in India. It is a mixture of the Dravida and the Nagara styles. The tiers of the Vesara style are shorter than the other styles.
Dravidian Architecture: The Dravidian is the southern temple architectural style. The Kovils are an example of prime Dravidian architecture. These monuments are of carved stone, set up in a step like towers like with statues of deities and other important figures adorning them.
Kalinga Architecture: The Kalinga style is the dominant style in the eastern Indian provinces. The Kalinga style is famous for architectural stipulations, iconography and connotations and heavy depictions of legends and myths.
Sikh Architecture: Sikh architecture is probably the most intricate and popular of the styles here. Sikh architecture is famous for its soft lines and details.
Romanesque (6th -11th century/12th)
Romanesque Architecture is a span between the end of Roman Empire to the Gothic style. Taking inspiration from the Roman and Byzantine Empires, the Romanesque period incorporates many of the styles.
Rounded arches: It is here that we see the last of the rounded arches famous in the classical Roman style until the Renaissance. The rounded arches are very popular in this period especially in churches and cathedrals. The rounded arches were often set alongside each other in continuous rows with columns in between.
Details: The most common details are carved floral and foliage symbols with the stonework of the Romanesque buildings. Cable mouldings or twisted rope-like carvings would have framed doorways.
Pillars: The Romanesque columns is commonly plainer than the classical columns, with ornate captials and plain bases. Most columns from this time are rather thick and plain.
Barrel Vaults: A barrel vaulted ceiling is formed when a curved ceiling or a pair of curves (in a pointed ceiling). The ceiling looks rather like half a tunnel, completely smooth and free of ribs, stone channels to strengthen the weight of the ceiling.
Arcading: An arcade is a row of arches in a continual row, supported by columns in a colonnade. Exterior arcades acted as a sheltered passage whilst inside arcades or blind arcades, are set against the wall the arches bricked, the columns and arches protruding from the wall.
Gothic Architecture (12th Century - 16th Century)
The Gothic Architectural style is probably one of the beautiful of the styles on this list and one of most recognisable. The Gothic style is a dramatic, opposing sight and one of the easiest to describe.
Pointed arch: The Gothic style incorporates pointed arches, in the windows and doorways. The arches were likely inspired by pre-Islamic architecture in the east.
Ribbed vault: The ribbed vault of the Gothic age was constructed of pointed arches. The trick with the ribbed vaulted ceiling, is that the pointed arches and channels to bear the weight of the ceiling.
Buttresses: The flying buttress is designed to support the walls. They are similar to arches and are connected to counter-supports fixed outside the walls.
Stained-Glass Window: This is probably one of the most recognisable and beautiful of the Gothic features. They can be set in round rose windows or in the pointed arches.
Renaissance Architecture (15th Century- 17th Century)
Renaissance architecture was inspired by Ancient Roman and Greek Architecture. Renaissance Architecture is Classical on steroids but has its own flare. The Renaissance was a time for colour and grandeur.
Columns and pilasters: Roman and Greek columns were probably the greatest remix of the Renaissance period. The architecture of this period incorporated the five orders of columns are used: Tuscan, Doric, Ionic, Corinthian and Composite. The columns were used to hold up a structure, support ceilings and adorn facades. Pilasters were columns within a chamber, lining the walls for pure decoration purposes.
Arches: Arches are rounded in this period, having a more natural semi-circular shape at its apex. Arches were a favourite feature of the style, used in windows, arcades or atop columns.
Cupola: Is a small dome-like tower atop a bigger dome or a rooftop meant to allow light and air into the chamber beneath.
Vaulted Ceiling/Barrel Vault: Renaissance vaulted ceilings do not have ribs. Instead they are semi-circular in shape, resting upon a square plain rather than the Gothic preference of rectangular. The barrel vault held by its own weight and would likely be coated in plaster and painted.
Domes: The dome is the architectural feature of the Renaissance. The ceiling curves inwards as it rises, forming a bowl like shape over the chamber below. The dome’s revival can be attributed to Brunelleschi and the Herculean feat of placing a dome on the Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore. The idea was later copied by Bramante who built St. Peter’s Basilica.
Frescos: To decorate the insides of Renaissance buildings, frescos (the art of applying wet paint to plaster as it dries) were used to coat the walls and ceilings of the buildings. The finest frescos belong to Michelangelo in the Sistine Chapel.
Baroque (1625–1750)
Baroque incorporates some key features of Renaissance architecture, such as those nice columns and domes we saw earlier on. But Baroque takes that to the next level. Everything is higher, bigger, shinier, brighter and more opulent. Some key features of Baroque palaces and buildings would be:
Domes: These domes were a common feature, left over from the Renaissance period. Why throw out a perfectly good bubble roof, I ask you? But Baroque domes were of course, grander. Their interiors were were nearly always painted or gilded, so it drew the eye upwards which is basically the entire trick with Baroque buildings. Domes were not always round in this building style and Eastern European buildings in Poland and Ukraine for example sport pear-shaped domes.
Solomonic columns: Though the idea of columns have been about for years but the solomonic columns but their own twist on it. These columns spiral from beginning to end, often in a s-curved pattern.
Quadratura: Quadratura was the practice of painting the ceilings and walls of a Baroque building with trompe-l'oeil. Most real life versions of this depict angels and gods in the nude. Again this is to draw the eye up.
Mirrors: Mirrors came into popularity during this period as they were a cool way to create depth and light in a chamber. When windows faced the mirrors on the wall, it creates natural light and generally looks bitchin’. Your famous example is the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles.
Grand stairways: The grand sweeping staircases became popular in this era, often acting as the centre piece in a hall. The Baroque staircase would be large and opulent, meant for ceremonies and to smoother guests in grandeur.
Cartouche: The cartouche is a design that is created to add some 3D effect to the wall, usually oval in shape with a convex surface and edged with scrollwork. It is used commonly to outline mirrors on the wall or crest doorways just to give a little extra opulence.
Neoclassical (1750s-19th century)
The Neoclassical Period involved grand buildings inspired by the Greek orders, the most popular being the Doric. The main features of Neoclassical architecture involve the simple geometric lines, columns, smooth walls, detailing and flat planed surfaces. The bas-reliefs of the Neoclassical style are smoother and set within tablets, panels and friezes. St. Petersburg is famous for the Neoclassical styles brought in under the reign of Catherine the Great.
Greek Revival (late 18th and early 19th century)
As travel to other nations became easier in this time period, they became to get really into the Ancient Greek aesthetic. During this architectural movement they brought back the gabled roof, the columns and the entablature. The Greek Revival was more prevalent in the US after the Civil War and in Northern Europe.
Hope this helps somewhat @marril96
27K notes
·
View notes
Photo



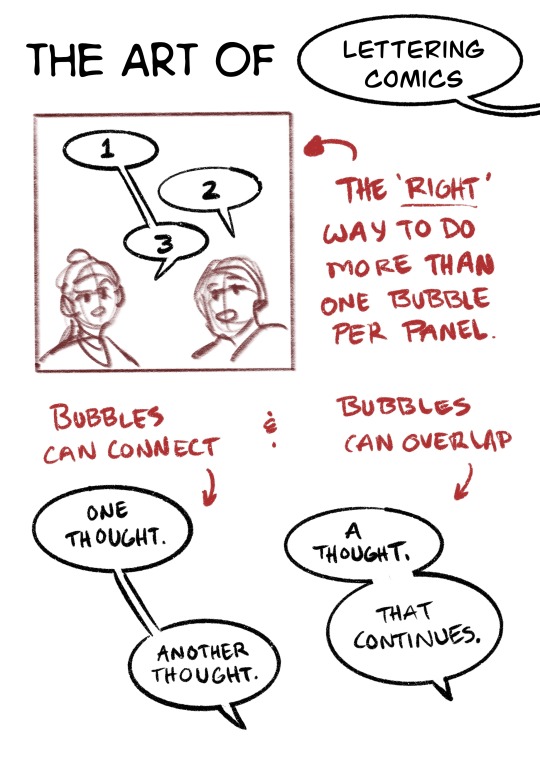




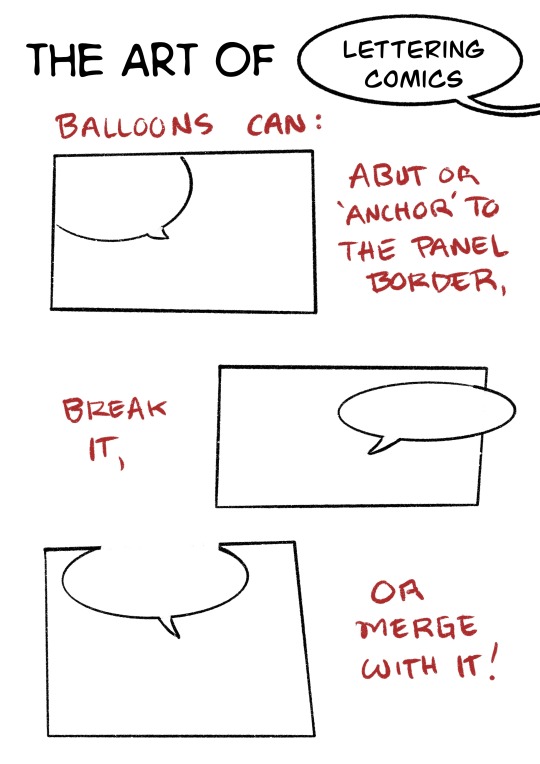
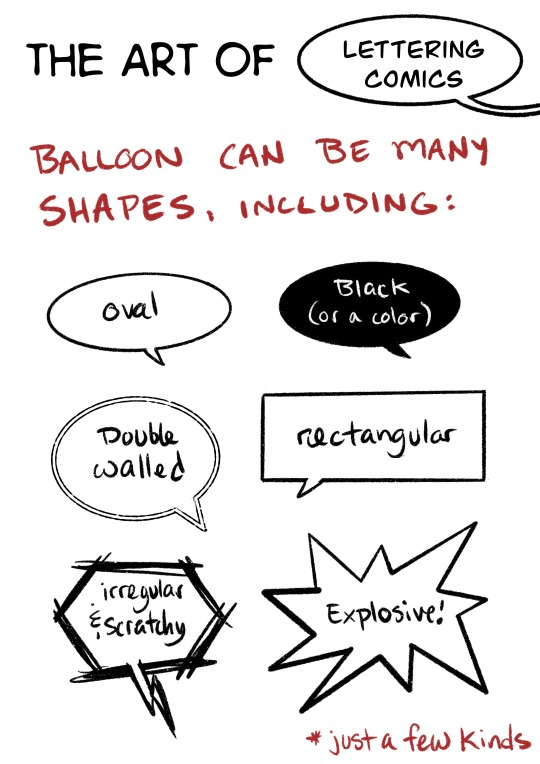
Here’s the first half of slides from my comic class on Lettering!
Rest of the slides: https://gingersnappish.tumblr.com/post/616487287636803584/the-rest-of-the-comic-lettering-slides-first
55K notes
·
View notes
Note
I love the effect on your last pokepositivity! How'd you do that TV thing?
I am veRY GLAD YOU ASK hehehe
Ok so first, you put your drawing in a folder that you merge or you open it in .png so it’s only one layer

You copy paste it three times ( you can do a ctrl z in the meanwhile to get your folder back )

then, you create three layers over each, one completely red, one completely green and one completely blue and ou put them in multiply

( you can use this if you use sai )
then you merge each one so it should look like that ( but like, keep them one on top of the other dont move them yet )

You put the two on top in the screen mode

You move them a little and add a watercolor effect !

And done !
you can play around with the layer !

( I moved the leyers too much ngl )
510 notes
·
View notes
Photo





I don’t do tutorials usually, but I get asked about this a lot! I don’t think many people have thought of it.
56K notes
·
View notes
Text
!! thank u so much! The way i draw lace is like…so time consuming but i usually use three different methods interchangeably






One of the major factors of lace is that it must maintain this very floral quality to it, which often relies on noticeable curves. Though a lot of lace contains straight lines here and there, the curves should always b the most significant!
12K notes
·
View notes
Photo


I made myself some Sai brushes for soft coloring, I thought I could share them :3
19K notes
·
View notes
Link
Medieval fashion terminology

bliaud — overgown with either long, tight sleeves or looser, elbow-length sleeves
Afficher davantage
510 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fantasy Guide to Employment: Household of a Castle
The castle does not run itself. The castle would remain a pile of stones without servants to keep it running. The guide below focuses on the private household of the lord himself, anybody who worked inside the main keep of the castle. I will be expanding outside the walls in a future post.
The Steward/Seneschal

This person was the head of the household staff. They would have the task of running things on the Lord's estate. They are the managers, so it is up to them to keep the staff in line. The steward would keep the castle accounts and keep the lord informed of all of the goings on of the lands and tenants. They would have to be educated needing to do accounts and write letters. Though the castle's Lady would be expected to do all these things, the steward served as a backup and assistant in all the tasks even representing the lord and lady when they were unavailable.
The Chamberlain

The chamberlain is the servant employed to look after the Lord's bedchamber. He would look after the Lord's clothes as well and keep track of the other servants' liveries, the official uniforms of the guards, pages and squires. This was not always the case, some larger households had a separate office but most medium seized manors and castles lumped them together. The chamberlain's main task was ensuring the lord was kept happy. He would even be the last servant a lord would see at night before he went to bed at night. They would be educated.
The Marshal

A Marshal was in charge of the stables as well as the military presence in the castle. They would oversee the household's horses, carts, wagons, and containers. He oversaw blacksmiths, horse grooms and stableboys. He also oversaw the transporting of goods. The Marshal was sometimes in charge of disciplining servants. They would likely come from a middle class background as well as having military experience and education.
The Page

A page was a young noble boy about seven years old who would be sent to serve a Lord. He would be in charge of tidying up after the lord, carrying messages to other servants and occupants of the castle and serving him at meals. Unlike others on the list, the page would not be paid. His experience was his payment as he would learn the running of a castle and manners of a lord.
The Lady's Maid
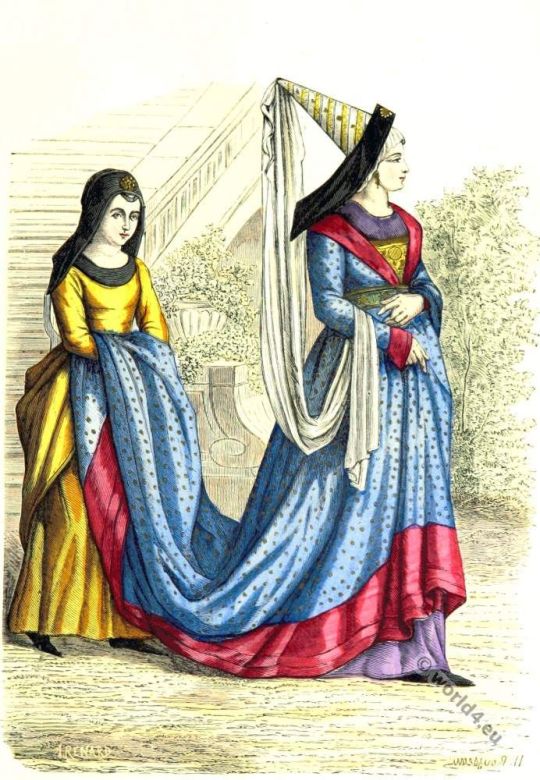

The lady's maid is be the female body attendant of the castle's noble women. She would be in charge of caring for the lady's chamber and her things. She would dress the lady and attend her wherever she would. (The lady's maid would basically do all the work a chamberlain would but you know the wage gap...)
Maidservant

A housemaid/maidservant works to clean the castle. She would be among the first to awaken every morning. Her first task would be sweeping the floors. The thing with mediaeval floors a that they were often covered with a thin layer of rushes, a kind of grass. Weekly if not daily, a maidservant would be expected to change out the rushes and scatter new ones. If it really needed it, she would scrub the stone floors which would be done with a soap called lye, made from ashes and lard. The maidservant would also be expected to go into the bedchambers when the occupants awoke. She would empty the chamberpots if need be. She would get rid of the ashes from the fire and ready the fire for later. She would make up the bed or strip it for the laundresses. She would wash anything that needed washing including furniture and ornaments.
Laundress

The laundress was responsible for the cleaning of anything made of fabric in the household. The laundress would have to fetch their own water either from the castle well or from a nearby river. They would heat the water in large vats and add lye soap (the most popular of the cleaning agents). The constant exposure to soap and hot water was physically tough on the hands of the laundresses and their backs. When the detergents were added to the water, the laundress would dump them into the vat and stir that shit like soup. To dry it they would pin it out on lines or beat the water from it. The laundress might make money by selling secrets. Since they are handling unmentionables, they knew what happened behind closed bedchamber doors or what didn't.
Nursemaid

The nursemaid was in charge of the castle's children. They would ensure the child was fed, washed and generally kept alive while the parents would either be away at court or busy with the lands. The nursemaid would be a common woman from the surrounding lands who would come in to care for a noble child in the stead of the mother who would be expected to get on with other jobs. The nursemaid would be an underlying of the noble governess, a sort of hands-off nanny.
Cook

The cook was one of the most important servants in the castle. They would have the task of overseeing the running of the kitchens and keeping supplies in order. They would likely be on call at all times. Henry VIII's cook was often woken in the night because his royal master wanted a midnight snack. The cook was a valued member of the household and would have been highly sought after if they were a very skilled cook. Cooks would have been paid a handsome wage.
Scullion

The scullion was the lowest member of staff. They would be responsible for scrubbing and cleaning the servants quarters and the kitchens. They would scrub floors with lye, scour pots with sand, sweep put the fireplace and clean up after the other servants. They were the first to rise in a castle and tasked to light all the fires in the kitchens.
Payment & Lifestyle
Within the mediaeval household, payment came from the hand of the steward. As the Lord's manager of accounts, he was in charge of paying staff.
The grander jobs in the castle such as the marshal, the chamberlain, nursemaid and lady's maid would pay better. They would have certain privileges including better bedchambers.
A nursemaid who was breastfeeding the Lord's children would be a valued member of staff. She would be fed better than the other servants.
The page would sleep in a chamber off the lord's bedchamber or sometimes at the foot of the bed. A page would wear the Lord's livery so he would be dressed on the Lord's coin.
The chamberlain would have rooms close to the lord and lady, just in case they were needed by the master in any kind of emergency.
The cook would sleep near the kitchens so they were close enough just in case they are needed in the night.
The other household servants would all sleep in chambers together. The women would sleep in one and the men would sleep in another. Nightly dalliances were frowned upon massively.
Most servants came from the surrounding lands of the castle. When the lord and his family were away at court or somewhere else, there would be a drop in employment. Everything would be cut down ex. Instead of three laundry maids, only one might stay on after the lord goes. The steward, the marshal, the chamberlain, the page, the cook, the nursemaid and the lady's maid were all important staff so their job would be permanent.
31K notes
·
View notes