Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Security Everywhere
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/uptick-in-ransomware-mobile/
Uptick in Ransomware, Mobile Banking Malware
There is an increase in mobile banking malware threats from 2018 to 2019. Ransomware was much more prevalent in the first half of 2019. Threat actors attacks have stopped numerous organisations worldwide from operating normally. Usually, after a ransom attack, there will be a silent sequence of bot infections.
The majority of attacks used older vulnerabilities that were registered in 2017 and earlier, and some were even seven years old.
This year there was many sextortion scams and business email compromises.
Furthermore, there is a rise in attacks targeting resources and sensitive data in public cloud environments. Cloud crypto-mining campaigns were able to evade basic cloud security products, and abused vulnerable Docker hosts and shut down competitors’ crypto-mining campaigns operating in the cloud.
0 notes
Text
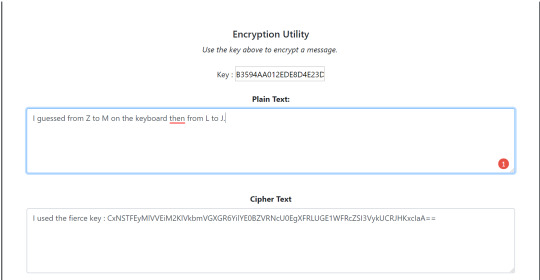
Coincidence Index
“ Index of Coincidence is a cryptanalysis technique studying the probability of finding repeating letters in an encrypted text. “ from https://www.dcode.fr/index-coincidence
http://alexbarter.com/statistics/index-of-coincidence/
To figure out the index of coincidence use this formula:
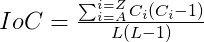
If a letter does not appear more than once then the index of coincidence will be 0 because when Ci is 1 or 0, Ci x (Ci – 1) = 0 and when the numerator is 0 the whole fraction is 0.
0 notes
Text
Claude Shannon
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Claude_Shannon
https://www.itsoc.org/about/shannon
Claude Eldwood Shannon is born on April 30, 1916, in the US and died on February 24, 2001. He was at the age of 84 when he died. He attended MIT ( Massachusetts Institute of Technology) and the University of Michigan. He is a mathematician, electrical engineer, and cryptographer. He is well known for his founding of digital circuit design theory (1937) and information theory with a landmark paper, A Mathematical Theory of Communication (1948).
0 notes
Text
Identifying unknown ciphers
http://practicalcryptography.com/cryptanalysis/text-characterisation/identifying-unknown-ciphers/
Classes of Cipher Algorithms
Transposition ciphers - changing the positions of the characters. Such as Railfence, Columnar Transposition, route ciphers.
Monoalphabetic substitution ciphers - replacing each letter with another such as simple substitution, caesar.
Polyalphabetic ciphers - more than one letter can replace another letter depending on their position such as Vigenere, Beaufort, Enigma, etc.
Polygraphic Substitution ciphers - groups of characters are replaced such as foursquare.
Other types - bifid, trifid, ADFGVX, Straddle checkerboard.
0 notes
Text
Practical Activites
Simple Crypto
I knew there was something about the position of the numbers 3 4 4 1. I couldn’t figure it out what it was. My friend hinted me to read them in columns. Putting the 3 4 4 1 into columns allowed me to realise how to solve the crypto. I put each text separated by space underneath the previous and from there I read the flag from the first column to the next.

Shredding Analysis
What I looked at was the author’s name, and the headline (each word began with capital letters).
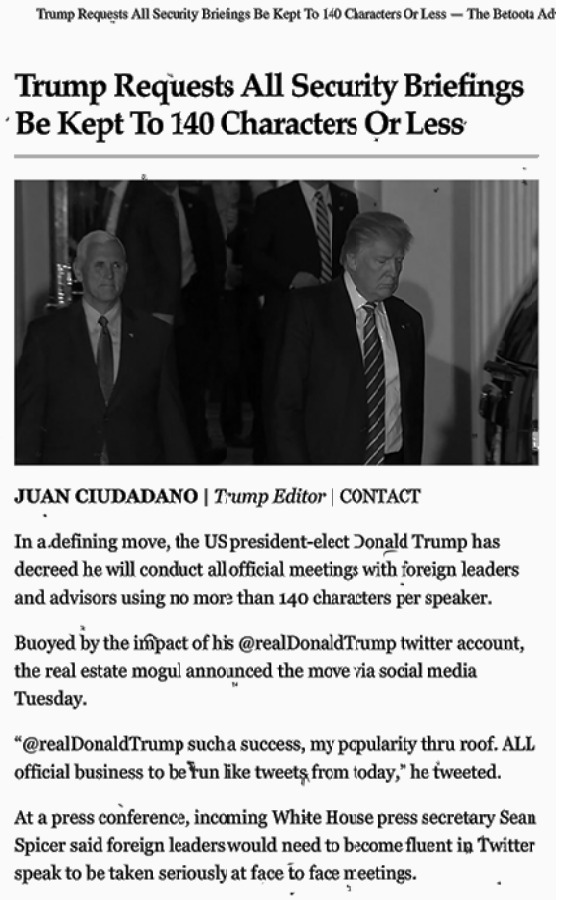
Dumpster Dive
There was a lot of information on the tags and receipts.


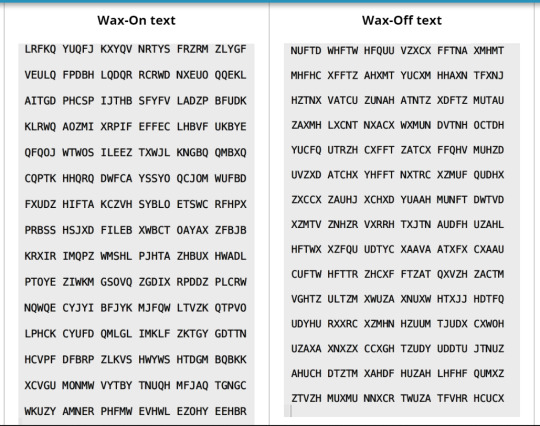
Coincidence Index
Wax on had less coincidence than wax off. My conclusion was that the wax off text is the mono-alphabetic substitution cipher and/or transposition cipher.

Merkle puzzles

Trump Phishing
Dear Donald, There was a suspicious login to your Facebook account. Please confirm this is you by clicking on this link: [insert link]
Log in: Saturday, 12th June, 14:21:11 IP Address: 266.55.121.923 Location: Australia Kind Regards, Facebook Security Team
Note: Please do not reply to this email as it was automatically generated. Email Phishing: Puppy Love
I got rejected on several attempts. The reply was all the same.

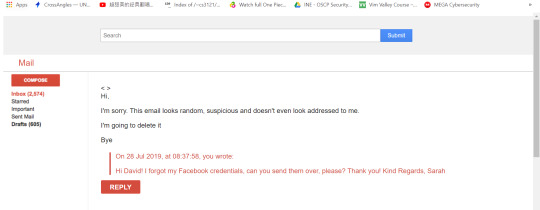
I had no success.
0 notes
Text
WriteUp for Something Awesome Project
Something Awesome proposal: https://superbobthebuilderfan.tumblr.com/post/185628975027/something-awesome-proposal-hackthebox
OBJECTIVES
Categories I plan to explore are Crypto, or Stego, or Pwn, or Web, or Misc, or Forensics, or Mobile. The aim was to complete one or more challenges in the categories I chose to explore. In achieving my aim I would have learned various hacking techniques, practical hacking skillsets, and developed my skills in hacking.
PLANNED
I chose to explore Crypto, Misc, Stego, and Pwn (Pwn is extension work)
Get invite code for hackthebox.eu, explore hackthebox’s environment and restrictions as a non-VIP member, research about ciphers and encryption types + Setup/explore programs/tools and the environment for digital forensics and penetration testing and CTF’s (Kali Linux) + Complete one or more challenges in the above-stated categories.
ACTUAL
I was able to get the invite code, I explored hackthebox’s environment and restrictions as a guest member, studied many various ciphers and encryption types, successfully dual-booted Windows and Kali Linux, explored preinstalled programs/tools and the environment. Furthermore, I managed to complete one or more challenges in all chosen categories except Pwn. Pwn will be completed in Week 9 as declared in my Something Awesome proposal blog (link is at the very top).
WHAT I LEARNT
Invite code, environment, ciphers, encryptions, crypto
Week 2-3
https://superbobthebuilderfan.tumblr.com/search/week3%20somethingawesome
Refer to the above link to see the completed challenges and goals for week 2-3.
In week 2, I obtained the invite code and didn’t blog about it until week3. It was easy because I have done something similar to this before such as hacking the game Cookie Clicker and Clicker Heros.
I learnt:
how to make POST request via terminal by typing curl -XPOST [INSERT URL].
about hackthebox’s environment such as where the discussion forums are, settings page, my profile page, how to check my progress, where the challenges are, where the pen-testing labs are, where the pen-testing machines are
many new ciphers and encryptions, the most unique one I discovered was Fernet (symmetric encryption)
Kali Linux, penetration and digital forensics tools, CTFs tools
Week 4
https://superbobthebuilderfan.tumblr.com/search/week4%20somethingawesome
Refer to the above link to see completed goals for week 4.
I learnt:
how to dual boot 2 OS’s on one laptop
commands such as netdiscover, nmap, gobuster
tools such as Burpe Suite, BruteSpray, Hashcat, John the Ripper and many more for password attacks
tools for sniffing and spoofing such as Wireshark, bettercap, Wifi Honey
tools for hardware hacking such as android-sdk, apktool, Arduino
tools for information gathering such as arp-scan, Xplico, InTrace, iSMTP
tools for vulnerability analysis such as Oscanner, Powerfuzzer, sfuzz
tools for wireless attacks such as Airbase-ng, Aircrack-ng, Fern Wifi Cracker
tools for web applications such as DirBuster, fimap, FunkLoad
forensic tools such as Binwalk, bulk-extractor, Capstone
stress testing tools such as DHCPig, FunkLoad, iaxflood
reverse engineering tools such as apktool, dex2jar, diStorm3, edb-debugger
reporting tools such as CaseFile, cherrytree, CutyCapt
hardware hacking tools such as android-sdk, apktool, Arduino
I learnt about the existence of those tools and their purposes and their usage and tested them out, but not all of them.
Misc
Week 5-6
https://superbobthebuilderfan.tumblr.com/search/week5%20somethingawesome
Refer to the above link to see completed challenges for week 5-6.
I learnt:
To pay attention to details because I have attempted one that is similar. It was under the same programming language category “Esteroic programming language” in week 3. The previous was Brainfuck, this one is Piet and malbolge. The whole list of Esteroic programming languages https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Esoteric_programming_language
Steganography
How to extract zip folders in terminal: extract [INSERT ZIP FOLDER NAME]
How to solve steganography using steghide extract -sf [INSERT FILE NAME], which is a command-line tool
Base64 encryption can be done twice
Renaming files to the correct format is good practice
How to base64 decode once and twice in terminal: base64 --decode [INSERT FILE NAME] | base64 --decode
How to check file properties in terminal: file [INSERT FILE NAME]
ls -R and fcrackzip -v -u -D -p [inputfilepath] [path to the file/folder wanted to crack] command
How to fix "E : Unable to Locate Package" Error In Kali Linux
Application of pdfcrack tool
Stego
Week 7-8
Part 1 (week7): https://superbobthebuilderfan.tumblr.com/post/186443678597/htb-stego-da-vinci
Part 2 (week8): https://superbobthebuilderfan.tumblr.com/post/186443681237/htb-stego-davinci
Refer to the above link to see completed challenges for week 7-8.
I learnt:
strings and binwalk command, the rest of the knowledge required had already been acquired from previous challenges such as steghide and base64
OVERVIEW OF MY EXPERIENCES FOR THE PROJECT
As a first-timer in the field of CTFs and I am surprised I could solve more than one challenge in each chosen category. I feel like I have achieved my objectives for the Something Awesome project as I have learnt hacking techniques and skills, both technical, and theoretical, and problem-solving skills. The skillset I have learnt would potentially be useful for completing future CTFs and as a security major computer science student. I did my best to be on schedule and if not, I would extend myself by doing another challenge whenever I am ahead of schedule. I am satisfied with the amount of effort I put in from the beginning (Week 2) of this project to now (Week 8).
0 notes
Text
Week 8 Tutorial
Heap spraying
Heap spraying is scattering shell code everywhere in the heap, with nops. Wherever you are in the heap, the shellcode will run.
Something Awesome (SA) Presentation:
Corebooting Laptop:
UEFI - boots faster and more modern features for security
BIOS - is basic input/output system, it handles initialisation of software
Alice’s GIPA Request:
UNSW student notebook contained terrorist plans and got in trouble with the police. Apparently, the evidence was planted.
RNG (random number generator):
Millisecond
Square root
Real-time changes
Memory address
Combination
Android Forensics
Used FTK imager to analyse images stored on a phone
Able to restore deleted images (only a few was restored in full, some of the images were cut off)
Used Autopsy to extract SMS from the database.
Bill Barr decryption
Kris’ wifi scam
Kris set up a wifi access point where it takes in any usernames and passwords and still allows you to connect to it. The username and password that is inputted would be hashed. So Kris ran it with John the Ripper and was able to get the passwords in plaintexts.
Don’t trust wifi networks, not even your own.
0 notes
Text
Week 8 Evening Lecture
Extended lecture - Privacy
Signing up something online means we forfeit our information.
Google map’s timeline keeps a record of your location over a period of time, based on GPS data.
About 4 layers of aluminum foil, or a Faraday bag, can be used to block signals such as WiFi, Bluetooth, and mobile networks.
Methods of Prevention
Simple and accessible, but less effective
Use DuckDuckGo as it doesn’t use cookies, or share your IP address
Don’t be logged in to any account that can reveal your real identity
Use a VPN because it masks your IP address, but how can you know you can trust the VPN itself?
Heavier
Onion Routing
- Diverts requests around many nodes
- Each node adds/removes a layer of encryption using a symmetric key
- The client has all of the keys
VPN can be used to can get you cheaper plane tickets by changing your location.
Extended lecture - Digital Forensics
Recovery/Investigation of material found on digital devices.
TWO Types of personnel
Technicians - gather evidence at crime scenes
Examiners - specialists in an area of digital evidence
Stages of a Digital Forensics Investigation
Acquisition/Imaging - capture an image of the drive
Analysis - keyword searches, recover deleted files
Reporting - evidence used to construct events/actions, layman report written
Types of forensics
Computer forensics - memory/data
Mobile device - phone
Network forensics - router, switches, packet captures
Database forensics
Video/Audio forensics - movie files, audio recorded on the phone
Steganography
Tooling
EnCase, Autopsy/Sleuth Kit, FTK Imager, File, Strings, Xxd, Foremost, Binwalk, mmls
Drives and Partitioning (FAT32)
FAT stands for File Allocation Tables
The FAT record stores the status of each cluster (bad region, allocated, unallocated) on the drive
Where do deleted files go?
The name of the file is changed to (0xe5)[file_name].
Buckland’s Lecture
Three Mile Island
Nuclear reactor disaster - end of 1978.
UNSW security
Identify critical assets and protect them
Assume you’ll be breached and set it up so that it doesn’t matter
Don’t keep data that isn’t needed anymore
0 notes
Text
Week 8 Morning Lecture
Root cause analysis
When something goes wrong. What is the root cause?
1. Human error Accidents - last person who touched it gets blamed Bad management - never suggested by the company
2. Culture - we don't have the right culture - no individual is responsible - no blame (or everyone to blame) Spend money on education program - but this does anything Hard to change the culture
Human weakness: dishonesty Honesty - commander in cheat humans lie and cheat Trump - may be lying to himself e.g. believed lots of people were at his inauguration
Signing honor calculations effect. Test - do a bunch of complex questions Say how many you got right Signing honor code at the start of the test had more impact than at the end - if they left it on, the students were more honest (lower reported average score) Stanford & Princeton Princeton - honor code shoved in your face - plays, songs
no difference
Having children - telling them something is bad e.g. jaywalking encourages you not to do it. Lies - Santa, the tooth fairy ruin childhood
Limited focus - torch in a dark room
Torch in dark room We only focus on some things - limited focus Human Subject to misdirection Humans should focus on what's logically important, but we focus on what's psychologically salient
Social engineers magicians. The trick works because they're focused on something else e.g. talking, gestures, explosions, timing Your object is to make things you don't want people to notice look natural
If the situation is complex, a torch is useless
Modes of problem-solving
Similarity matching - match present situation with things that happened in the past and treat them similarly. Don't need to think much. Frequency gambling - if you're unsure which pattern to match, pick the one that you've used most commonly in the past. e.g. hear a lion - run straight away We're just trying to match a pattern quickly
Accidents vs attacks
Physics puzzles/problems - asked for physics postgrads and what happens next? Random people, both got it wrong Textbook questions - physics postgrads got them all right (past experience) Real-world - harder Accident US attack - intent
Attack - someone tries to make it go wrong Programming for security - programming the devil's computer - assume everything is against you.
Train sets - trains run around track picking things up, drop off, gets money. But on collision, everyone loses. Shift focus from money -> safety
Marshmallow game - raising tower, highest wins Everyone panics at "1 minute to go" no one tests - distracted by height We can get away with accidents but not security Pickpockets Talk - Apollo Robbins We're often blind to things close to us
Some evidence confirms our theory, some oppose it Confirmation bias - ignore things that don't match your theory
Richard - map Kept thinking he was right - "there's a mountain on the map, that small hill looks right"
"Those factors which lead to and sustain wishful thinking rather than wise thinking"
Satisficing - just trying to get something to be "good enough" bounded rationality - we have a pool of attention trickling out
People prefer positive statements Overriding tendencies to verify generalisations rather than falsify them
Group think syndrome - the way you act in a group
Powerful men all in a room - dumb plan, but people all agreed with the plan - don't want to ruin the harmony - want to fit in the group
Some guy said the plan was stupid, wrote a letter to JFK> He then joined the group, said nothing, and regretted.
A powerful man invites you for dinner, everyone laughs at a bad joke - you subconsciously laugh too mitigation - mistakes by human error should have a small impact
Many trivial things add up to cause a bigger problem human error, mechanical failure, environment, design of a system, procedures used None of the above caused the accident systemic failure
Just culture - try to work out what can be improved instead of blaming
Good design
- coherent, each component has one job - low complexity - low coupling - free to change one without breaking anything
Needed to write a program that isn't brittle - easy to modify - good design - new features - small changes
good security - resilient tight coupling - buses and taxis (a common mode of failure) Cassandra - given the gift to always know the future, then it was changed so no one believed him
Reflection - Upon reflection, we can determine what went wrong, but when it comes to being in the present moment it is hard to tell what the main issues were. We struggle to identify dangers because of our limited focus and its complexity.
Checkhov gun - in movies, the gun on the wall is always the murder weapon
Simplification - belief that events only have one cause
When recounting we simplify the story, exaggerate salient details and leave out parts we think is unimportant, leading to a warped and biased version of the original.
Hindsight bias - an event similar to a previous one has happened we will expect a similar result
Latent error - an error whose effect is not seen until later. An example, to have a visible error 2 components need to fail because one component might be covering up for another.
Automatic safety devices - triggered automatically. An example of a possible problem is that pilots or operators are losing their skills in manual control and it is relied on as the last line of defense in a disaster, this means they are likely to make mistakes during a disaster.
HOMEWORK: LEARN ABOUT Chenobyl, Bhopal or Challenger disasters (IN EXAM)
0 notes
Video
tumblr
Week 8 presentation video - one CTF from something awesome
0 notes
Text
HTB - Stego (DaVinci)
Challenge 1 continued:
strings command are used to determine the contents of and to extract text from binary files (i.e., non-text files). http://www.linfo.org/strings.html
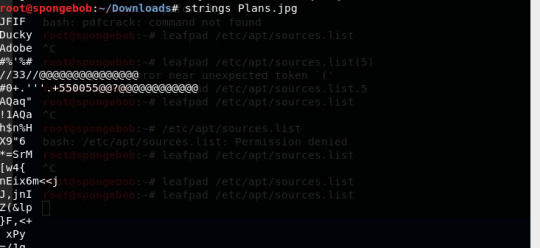
At the end of the output is a youtube URL:
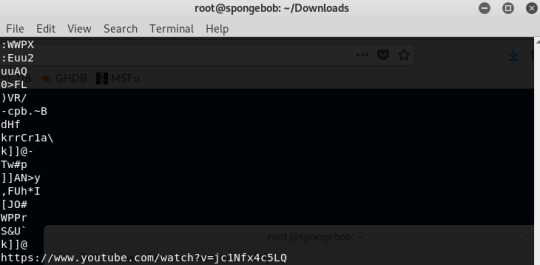
This is where the URL leads to:

Binwalk is a tool for searching a given binary image for embedded files and executable code. https://tools.kali.org/forensics/binwalk
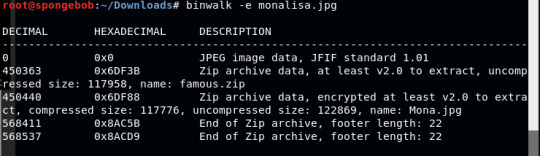
What the flag -e means:
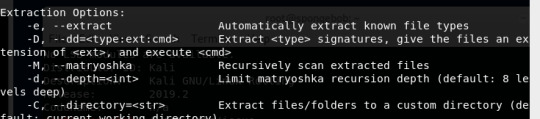
The extracted file is the folder highlighted in blue:
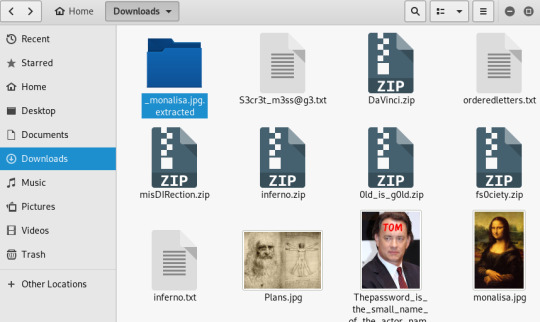
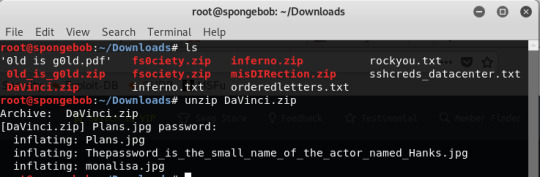
Inside the folder were 2 zip files. I tried a few times and eventually got the password, and it inflated Mona.jpg
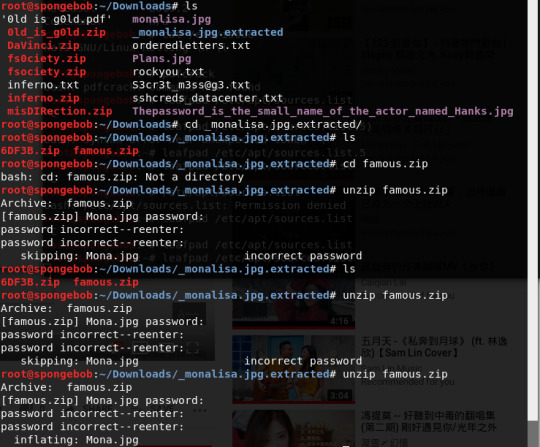
Used steghide to see if there’s any concealed message in the picture. The password is Guernica, which is the first word of the title of the youtube video above.
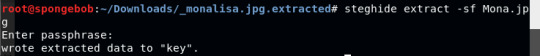
Since extracted data was written to key I ran cat on key.txt

This is base64 as we have seen many times. Since it’s in a file I ran the base64 -d command.
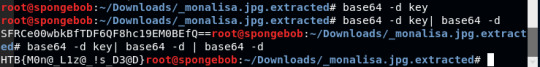
I had to run base64 -d 3 times, because after the first it was still encoded in base64 and after the second time it was also still encoded in base64. Again we only need to look and see that there’s an equal sign at the end for padding, hence it is encoded in base64. I had a laugh because there was a doubly base64 encoded text in previous challenges from another category and now this one is thricely base64 encoded.
The flag is: HTB{M0n@_L1z@_!s_D3@D}
0 notes
Text
HTB - Stego (Da Vinci)
Challenge 1 (difficulty level: brainfuck)
3 images inflated after unzipping DaVinci.zip
The 3 images are shown below:

It is obvious it is steganography because there will be concealed message/s in the picture hence I used steghide

I ran cat to see what is contained in the file:

The highlighted part is an MD5 hash. So I used an MD5 decoder.

It found: leonardo
I am currently stuck here...
0 notes
Text
Week 7 Tutorial
COMP6443 - Webapps COMP6445 - Forensics COMP6447 - Binary Exploitation and Reverse Engineering
Building stuff - use up-to-date frameworks to secure against common vulnerabilities - open source
Format string vulnerabilities printf("%s\n", "hello"); printf("hello");
This is not vulnerable: input = read(stdin); printf('%s\n', input); It will read the first thing as a string and print that out
This is vulnerable: input = read(stdin); printf(input);
printf('%d\n', var); // integer printf('%x\n', var); // hexadecimals
printf('%s\n', var); // var (the argument will be push on the stack first
printf('%3$d\n', var); // this will pop the next 3 bytes off the stack and gets 3rd int - can be useful if you use the same variable twice
%x %x %1$x - first and thrid use first arg
printf('%n\n') // how many bytes it has already printed until it sees %n
printf('abcd%n \n') - store 4 on the stack printf('abcd%n\n', &var) - store 4 in var abcd%nefg%n - 4, 7
printf('abcd%2$n\n') - stores 4 in the 2nd thing on the stack
Take hex for desired return address, turn into decimal, then use that number of characters.
Case Study: Surveillance Debate
Points for
It is required to gather information to catch criminals. Higher-level of surveillance means more information can be gathered in a short amount of time, making it a lot easier.
Cybercrimes are hard to detect if data is not mass collected.
Points against
Many crimes can be solved without excessive surveillance, by discovering and reporting them. This is how it has been in the past.
The government must not have full access to everything, because they can potentially become corrupt. We may have a government governing with good intentions now, but it may change in the future.
There is a single point of failure due to the centralisation of data.
Points in common
needed to counter the threat of terrorism, cybercrimes and crimes
0 notes
Text
Security Everywhere
https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/sky-customers-urged-to-reset/
Sky Customers Urged to Reset Passwords
Sky customers were told to reset their passwords because of a credential cyber-attack using an automated process, which would cause a high number of failed log-in attempts if users did not use the same password across multiple accounts.
The intruder obtained a list of usernames and passwords (‘credentials’) from external sources illegitimately and runs an automated program on various online services. If the credentials are still valid, it will allow the intruder to successfully take control of that account.
In response, Sky has locked affected accounts. The customer would need to call them and follow the steps they would provide.
Possible actions people can take to keep their account safe:
use password managers
use two-factor authentications
update password regularly
change similar passwords used on other accounts
0 notes
Text
Week 7 Evening Lecture
Extended seminar - Bug Bounties
port 91 on a printer; nmap used on it can make the printers go wild CTF websites: -pwnable -hackthebox -root-me -overthewire Extended - Bug bounty HackerOne Hacker101 Good fuzzing software - afl command + s on mac on boot makes you root rm -/var/db/.apples Find a bug, tell the company Where to start Hunting? Crowd-sourced BUg BOunty Website
Make a report and submit it Public and private bug bounty websites - private - generally better pay but harder to get in Scope - assets the company want you to test Out of scope Tips learn web app principles Look for wider scope and less competition - less likely to find duplicates Look for assets which have changed frequently - problems may occur in integration Look for publicly disclosed reports PROCESS 1. Find a suitable program 2. review the scope 3. Find target via recon - what software/tools you need 4. Hit the target and find a vulnerability 5. Write a report 6. Submit to company FUZZING Automated process of providing varying input - behaviour Mutation based - the user provides sample input "fuzzer "mutates" input to create a new input Generation based Fuzzing is effective because they are capable of testing many things, compared to human testing e.g. afl, SSL connection take input from fuzzer ->bit flips, byte flips, havoc
heartbleed bug: memcpy(bp, pl, payload) pl-> if this is to high, too much gets copied (buffer overflow)
fix: checks payload length
Mac demo Command + s during boot, -works if you haven't enabled Filevault (harddrive encryption) Removed file that tells the kernel the setup is done Restart-new setup - make new root user reset the password of other users Look at slides, do fuzzing tutorial
Extended seminar 2 - Pentesting - Authorised simulated cyberattack on a computer system to evaluate the security - Full risk, assessment - strengths, and weaknesses repercussing of an attack Data breach, ransomware Importance - discover vulnerability before attackers do - test security controls (firewalls, IPS, IDS) Same attack method as hackers Practical uses of pentesting Coverage Stages 1. Recon - gather intelligence 2. Planning - exploits 3. Exploitation 4. Post exploitation - establish persistence Tools nmap - open-source network scanner exploring networks, perform security scans, networks audit, finding open ports on a remote machine open ports - vulnerable to listening Kali - Linux distribution with many pen-testing tools for e.g. Info gathering, reverse engineering, exploitation tools METASPLOIT - antivirus will go crazy if you install this GOBUSTER - used to brute force URLs (directories and files) in websites and DNS subdomains web crawl
WordPress - logging in with username admin and an incorrect password, and WordPress says user ‘admin’ exists
Richard Buckland’s Lecture
Diffie Hellman doesn’t give authentication. It gives a shared secret that provides confidentiality.
It is easy to authenticate someone if you have a shared secret, but it is hard without.
Man in the middle
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Man-in-the-middle_attack
Bob sends his public key to Alice. Mallory (man in the middle) intercepts. Mallory pretending to be Bob sends her own public key instead of Bob’s to Alice.
Alice encrypts her message with Mallory’s public key thinking it is Bob’s and sends to Bob. Mallory intercepts this. Decrypts with a private key and possibly alters the message if she wants. She then encrypts it with Bob’s public key and sends it to Bob.
Here Bob and Alice think they are communicating with each other, but in actual fact, they are talking to Mallory and she is being the man in the middle passing on their messages, potentially changing them.
There is a need to make sure that 2 individuals are actually using each other’s key.
Web of trust
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_of_trust
This is a concept used in PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) to establish authenticity of the binding between a public key and its owner.
The system is similar to user ratings. It uses a decentralised trust model of Public Key Infrastructure. It doesn’t rely on Certificate Authorities or any similar hierarchy.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_key_infrastructure
Secure way of communicating online is provided by SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) (old) and TLS (Transport Layer Security).
It binds public keys to a domain name (not a person) like a passport.
The bindings are signed by a Certificate Authorities (CA) to show that the public key actually belongs to that entity.
Browsers with a padlock at the top on the left mean that the website has a certificate, which indicates that the person who owns the site has this key. It is not necessarily true that the website is absolutely safe.
PKI solves the man in the middle problem.
Registration Authorities
If someone shonky is a CA, they can sign other shonky websites. In the old days, anyone who paid Netscape could become a CA. This mean “www.gooogle.com” can be set up and have the CA to sign it (gets paid) and potentially conduct phishing.
0 notes
Text
Week 7 Morning Lecture
Week 7 -"Under construction" Midsem worst answered questions q5, 10 5. 10 digit pin launch code known by the president. What are you most worried about? - It could be brute-forced ~33 bits security - What if they wanted to launch but they couldn't? - Single point of failure - take out president, they can't launch.
10. Merkle puzzles, what encryption to use? Want a code that can be broken easily by a good guy, but a bad guy needs more work (but they may have more powerful tech) "answer": RSA 64 - easier to crack than RSA 2048 (encrypter using public key)
Bad: RSA with a public key, if you solve one puzzle, it helps with others - key is the same
Proof of liveness- like a challenge question/responses - proof that the other person is still there, able to respond/react
Earthquake in California, someone attacked by a dog Diffie Hellman - for sharing a secret when you are not near each other 2 people on different sides of the world - need to share a secret Uses exponentiation (5^3)^7 =...125 (a^b)^c = a^(b*c) (5^7)^3 = ...125 = (a^c)^b Use mod to get smaller numbers. Richard->Saeed "lets use 5 as a base" Each pick a secret number Richard picks 7, 5^7 = 78125 Richard says "78125" Saeed picks 3, says "125" Using big numbers makes it hard to go back. Richard uses 125^7 = ...125 ->mod1000 Saed does 78125^3 = ...125 ->mod1000 The secret is the same number Public only knows a, a^b, a^c - hard to get a^(b*c) 7^R -> 78125 -> 3^5 125^7 <- 125 <- 125^7 = ...125 mod1000
Crack de Chevalier - a castle with defense in depth
Sieging people forged a letter to surrender? - fell due to humans - social engineering vulnerability - a potential weakness exploit - uses vulnerability bug - problem
Memory corruption - changes memory causing program to have differently - changes control
Buffer overflow stack - FILO, used when functions are called currently operating function on top heap - used when the amount of space required is not known at compile time (dynamic) Most people focus on protecting the stack, but not the heap
Integer overflow - integers have a fixed amount of space keep adding until it overflows - it wraps around and becomes small again e.g. password with length counter - may try to fit large password in a tiny buffer. Format String vulnerabilities Google hacking - googling if there is an exploit for a line of code printf - format string old: printf("%s\n", "hello world") everyone would write printf("hello world\n") name <- enter your name printf(name) - problem: what if there's a special character printf("Richard%s") - for %s, it will look at the next argument in the stack and print it out "%x %x %x %x" - gets the stack in hexadecimal can get functions such as login - passwords "%n" - print command writes to memory ^ hard to do an attack Swiss cheese analogy of safety - lots of holes. Slice them up and shuffle them - usually, other layers cover the holes But sometimes the holes line up - analogous to finding vulnerabilities
0 notes
Text
HTB - Misc (misDIRection)
Challenge 6 (difficulty level: brainfuck)
This is what I got when I unzipped the misDIRection zip file.
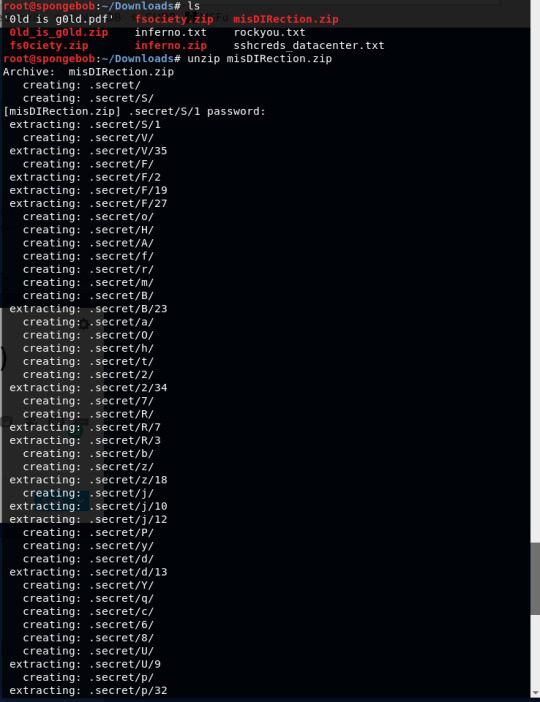
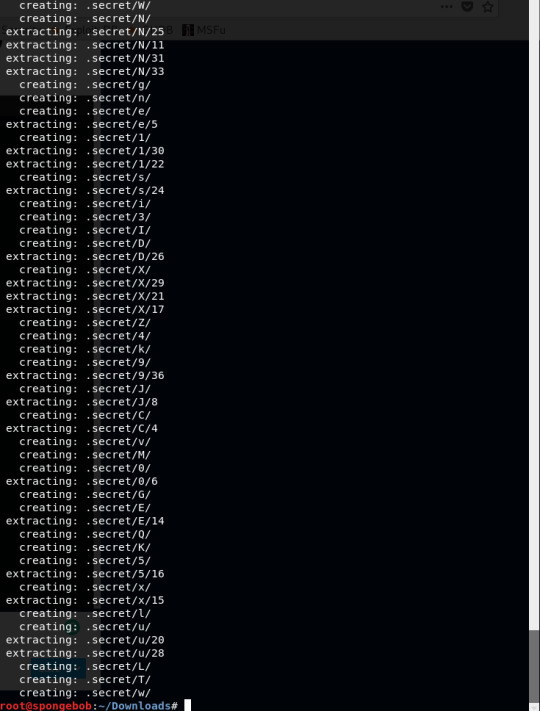
The interesting thing was after all those files were created after extraction there seem to be no changes in the Downloads file when I do ls.
So I decided to do ls -a to see all the files including the invisible ones because there are the .secret/[filename] I can see being created.
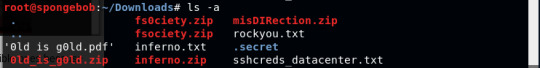
After cd into .secret directory and running the ls command this is what I see:
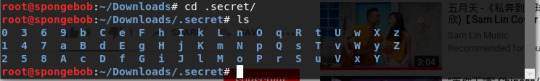
I thought they were files initially then I realised they were also directories.
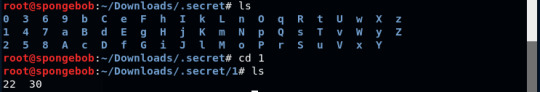
I ran ls -R
This explains what the -R do. I ran the ls --help command.
This is the output of ls -R.
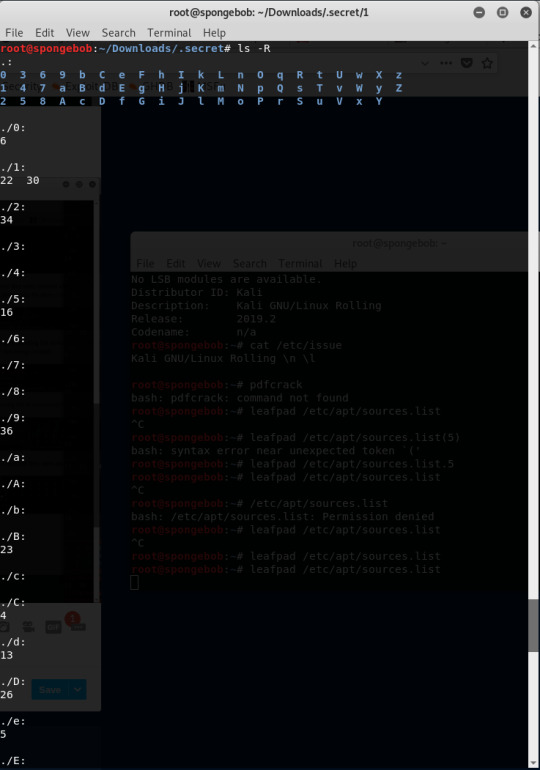
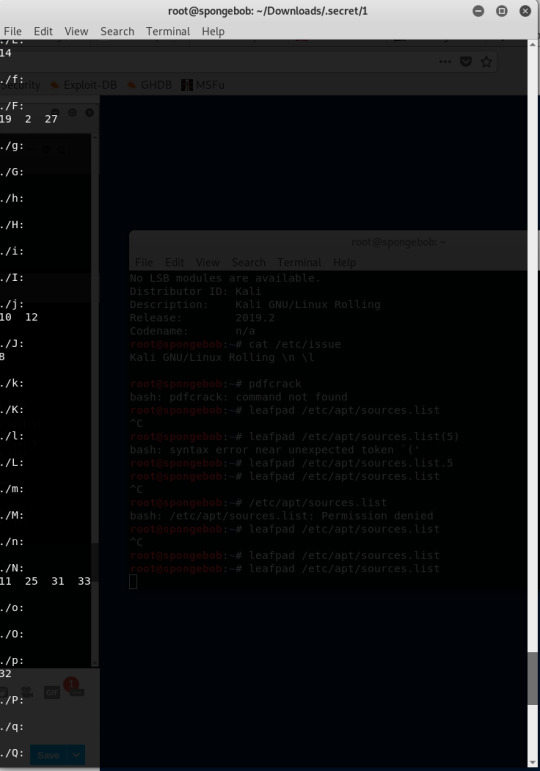
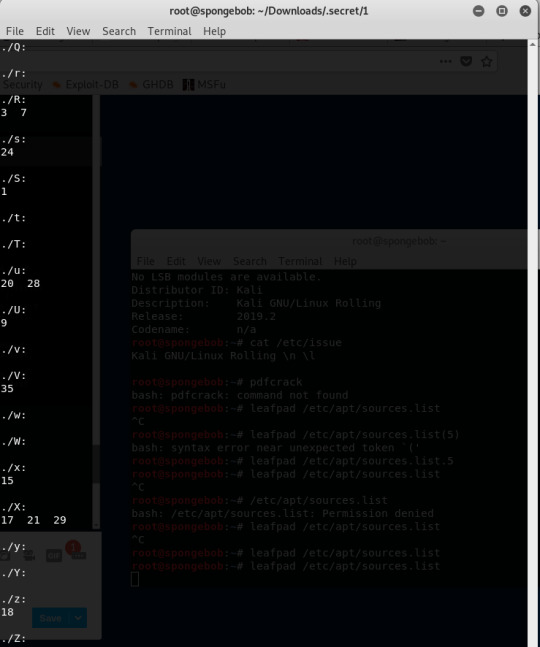
I rearranged the letters in accordance with the numbers in ascending order manually and wrote it to a file named orderedletters.txt
Then I cat the file to make sure what I typed is saved. I used a base64 --decode command on orderedletters.txt because it is a mix of upper and lower case letters and numbers, it just has no paddings and that means no equal sign at the end. Also, base64 is the most commonly used encoder.
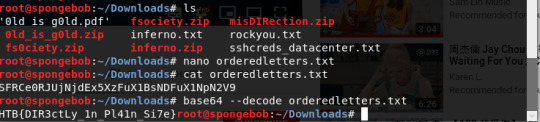
The flag is: HTB{DIR3ctLy_1n_Pl41n_Si7e}
0 notes