#1824-1898
Text
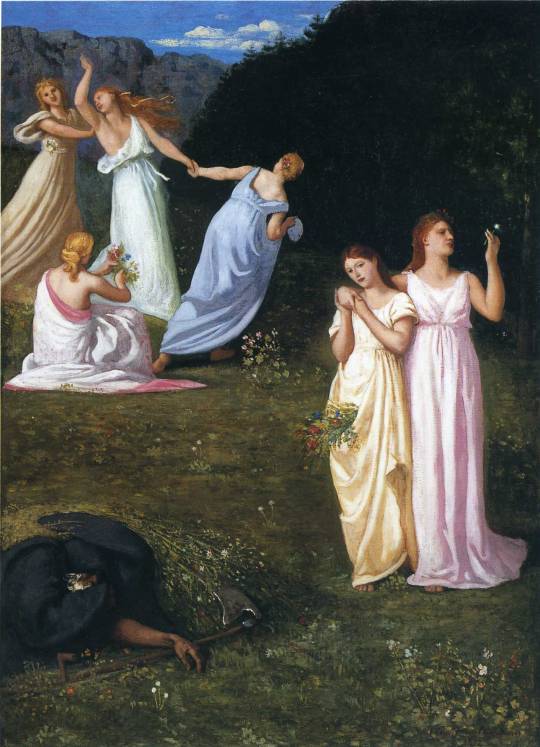

Death and the Maidens by Pierre Puvis de Chavannes (1824 - 1898)
637 notes
·
View notes
Text
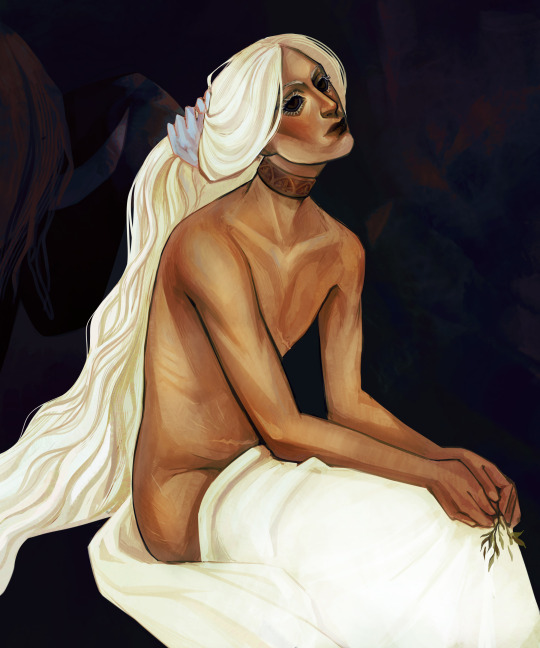

The Toilette by Pierre Puvis de Chavannes (1824 - 1898)
#homage#fear and hunger nosramus#nosramus#enki ankarian#fear and hunger enki#fear and hunger fanart#fear and hunger#artists on tumblr#art#illustration#digital drawing#fanart
572 notes
·
View notes
Text



Eugène Boudin (French, 1824--1898)
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Market at Trouville by Eugene Boudin (1824 - 1898)
194 notes
·
View notes
Text
What it meant to "do geology" in Hutton's time was to apply lessons of textual hermeneutics usually reserved for scripture [...] to the landscape. Geology was itself textual. Rocks were marks made by invisible processes that could be deciphered. Doing geology was a kind of reading, then, which existed in a dialectical relationship with writing. In The Theory of the Earth from 1788, Hutton wrote a new history of the earth as a [...] system [...]. Only a few kilometers away from Hutton’s unconformity [the geological site at Isle of Arran in Scotland that inspired his writing], [...] stands the remains of the Shell bitumen refinery [closed since 1986] as it sinks into the Atlantic Ocean. [...] As Hutton thought, being in a place is a hermeneutic practice. [...] [T]he Shell refinery at Ardrossan is a ruin of that machine, one whose great material derangements have defined the world since Hutton. [...]
The Shell Transport and Trading Company [now the well-known global oil company] was created in the Netherlands East Indies in 1897. The company’s first oil wells and refineries were in east Borneo [...]. The oil was taken by puncturing wells into subterranean deposits of a Bornean or Sumatran landscape, and then transported into an ever-expanding global network of oil depots at ports [...] at Singapore, then Chennai, and through the Suez Canal and into the Mediterranean. [...] The oil in these networks were Bornean and Sumatran landscapes on the move. Combustion engines burnt those landscapes. Machinery was lubricated by them. They illuminated the night as candlelight. [...] The Dutch East Indies was the new land of untapped promise in that multi-polar world of capitalist competition. British and Dutch colonial prospectors scoured the forests, rivers, and coasts of Borneo [...]. Marcus Samuel, the British founder of the Shell Transport and Trading Company, as his biographer [...] put it, was “mesmerized by oil, and by the vision of commanding oil all along the line from production to distribution, from the bowels of the earth to the laps of the Orient.” [...]
---
Shell emerged from a Victorian era fascination with shells.
In the 1830s, Marcus Samuel Sr. created a seashell import business in Houndsditch, London. The shells were used for decorating the covers of curio boxes. Sometimes, the boxes also contained miniature sculptures, also made from shells, of food and foliage, hybridizing oceanic and terrestrial life forms. Wealthy shell enthusiasts would sometimes apply shells to grottos attached to their houses. As British merchant vessels expanded into east Asia after the dissolution of the East India Company’s monopoly on trade in 1833, and the establishment of ports at Singapore and Hong Kong in 1824 and 1842, the import of exotic shells expanded.
Seashells from east Asia represented the oceanic expanse of British imperialism and a way to bring distant places near, not only the horizontal networks of the empire but also its oceanic depths.
---
The fashion for shells was also about telling new histories. The presence of shells, the pecten, or scallop, was a familiar bivalve icon in cultures on the northern edge of the Mediterranean. Aphrodite, for example, was said to have emerged from a scallop shell. Minerva was associated with scallops. Niches in public buildings and fountains in the Roman empire often contained scallop motifs. St. James, the patron saint of Spain, was represented by a scallop shell [...]. The pecten motif circulated throughout medieval European coats of arms, even in Britain. In 1898, when the Gallery of Palaeontology, Comparative Anatomy, and Anthropology was opened in Paris’s Museum of Natural History - only two years after the first test well was drilled in Borneo at the Black Spot - the building’s architect, Ferdinand Dutert, ornamented the entrance with pecten shell reliefs. In effect, Dutert designed the building so that one entered through scallop shells and into the galleries where George Cuvier’s vision of the evolution of life forms was displayed [...]. But it was also a symbol for the transition between an aquatic form of life and terrestrial animals. Perhaps it is apposite that the scallop is structured by a hinge which allows its two valves to rotate. [...] Pectens also thrive in the between space of shallow coastal waters that connects land with the depths of the ocean. [...] They flourish in architectural imagery, in the mind, and as the logo of one of the largest ever fossil fuel companies. [...]
---
In the 1890s, Marcus Samuel Jr. transitioned from his father’s business selling imported seashells to petroleum.
When he adopted the name Shell Transport and Trading Company in 1897, Samuel would likely have known that the natural history of bivalves was entwined with the natural history of fossil fuels. Bivalves underwent an impressive period of diversification in the Carboniferous period, a period that was first named by William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822 to identify coal bearing strata. In other words, the same period in earth’s history that produced the Black Spot that Samuel’s engineers were seeking to extract from Dayak land was also the period that produced the pecten shells that he named his company after. Even the black fossilized leaves that miners regularly encountered in coal seams sometimes contained fossilized bivalve shells.
The Shell logo was a materialized cosmology, or [...] a cosmogram.
Cosmograms are objects that attempt to represent the order of the cosmos; they are snapshots of what is. The pecten’s effectiveness as a cosmogram was its pivot, to hinge, between spaces and times: it brought the deep history of the earth into the present; the Black Spot with Mediterranean imaginaries of the bivalve; the subterranean space of liquid oil with the surface. The history of the earth was made legible as an energetic, even a pyrotechnical force. The pecten represented fire, illumination, and certainly, power. [...] If coal required tunnelling, smashing, and breaking the ground, petroleum was piped liquid that streamed through a drilled hole. [...] In 1899, Samuel presented a paper to the Society of Arts in which he outlined his vision of “liquid fuel.” [...] Ardrossan is a ruin of that fantasy of a free flowing fossil fuel world. [...] At Ardrossan, that liquid cosmology is disintegrating.
---
All text above by: Adam Bobbette. "Shells and Shell". e-flux Architecture (Accumulation series). November 2023. At: e-flux dot com slash architecture/accumulation/553455/shells-and-shell/ [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me. Presented here for commentary, teaching, criticisms purposes.]
65 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Claude Monet
Claude Monet (1840-1926) was a French impressionist painter who transformed modern art with his emphasis on light brushstrokes, bright colours, and uncluttered nature. Famed for his landscapes and series of paintings that captured the same view in different momentary atmospheric conditions, Monet is heralded as one of the greatest and most influential artists of all time.
Early Life
Oscar-Claude Monet was born in Paris on 14 November 1840. The job of Monet's father, Claude-Adolphe, is not known except that it was a humble one and that the family often struggled financially. In 1845, the Monets moved to Le Havre on the northern coast of France where Claude-Adolphe worked in his brother-in-law's thriving wholesale grocery business. Oscar-Claude's favourite subject at school was art, and, fascinated by the boats in the busy harbour, he often sketched them. From 15, he made money by selling caricatures, some of which were displayed in a local shop window each Sunday, which became a minor local attraction. Monet's aunt, Marie-Jeanne Lecadre, was an amateur painter and she encouraged Oscar-Claude, introducing him to the artist Amand Gautier (1825-1894).
Another artistic influence was the landscape painter Eugène Boudin (1824-1898) and the pair went painting together en plein air (outdoors), as opposed to the traditional method of painting in the studio. Still only 17, Monet produced his first outdoor painting, View from Rouelles, in 1858. Monet later described the experience:
Boudin put up his easel and set to work…for me it was like the rending of a veil; I understood; I grasped what painting could be…my destiny as a painter opened up before me. If I have indeed become a painter; I owe it to Eugène Boudin…Gradually my eyes were opened and I understood nature.
(Hodge, 15)
In April 1859, Monet gathered together his savings from his caricatures sales and went to study art in Paris. He enrolled in the unconventional Académie Suisse and started to make friends with artists like Camille Pissarro (1830-1903) and Paul Cézanne (1839-1906). More caricatures helped eke out his savings.
In June 1861, Monet's studies were rudely interrupted by conscription into the French army. Joining the African Light Cavalry, he was shipped off to Algeria. The bright colours of North Africa left a lasting impression on the young artist, who continued to sketch when he could. Then, after contracting typhoid in 1862, Monet was invalided back home. Six months later, Aunt Marie-Jeanne bought her nephew out of the army. Now 22, he dropped the Oscar from his name and began to paint again. It was at Le Havre that Monet met the Dutch artist Johan Barthold Jongkind (1819-1891), whose work he already admired for its broad and bold brushstrokes and which captured effects of the weather on seascapes. As Monet noted, Jongkind "became from this moment, my true master; and it is to him that I owe the final development of my painter's eye" (Hodge, 19).
Continue reading...
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

Eugène Boudin (1824-1898) - Étude de ciel
Pastel on blue paper. Executed c.1860s.
5.9 x 9 inches, 15 x 23 cm. Estimate: £20,000-30,000.
Sold Christie's, London, 8 March 2024 for £201,600 incl B.P.
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

Franz Xaver Winterhalter (German, 1805-1873)
Princess Francisca of Brazil, 1844
Palace of Versailles
Dona Francisca (2 August 1824 – 27 March 1898) was a princess of the Empire of Brazil (as daughter of Emperor Dom Pedro I, who also reigned as King Dom Pedro IV of Portugal, and his first wife Maria Leopoldina of Habsburg), who became Princess of Joinville upon marrying François d’Orléans, son of the French king Louis Philippe I.
#real people#princess#royalty#royal#Franz Xaver Winterhalter#German#German art#Germany#1844#1800s#art#fine art#european art#classical art#europe#european#fine arts#oil painting#europa#female portrait#female#portrait#brunette#woman#black eyes#Winterhalter#world history#historical art#historical painting#Habsburg
29 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rotterdam, Le Pont de Bourse painted by Eugene Boudin (1824 - 1898)
#art#art history#artwork#cityscape#culture#history#museums#painting#vintage#eugene boudin#urban#buildings
97 notes
·
View notes
Photo
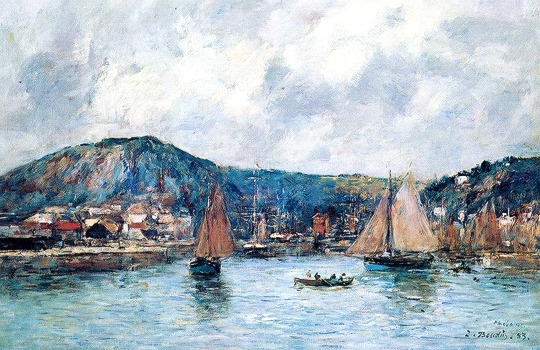

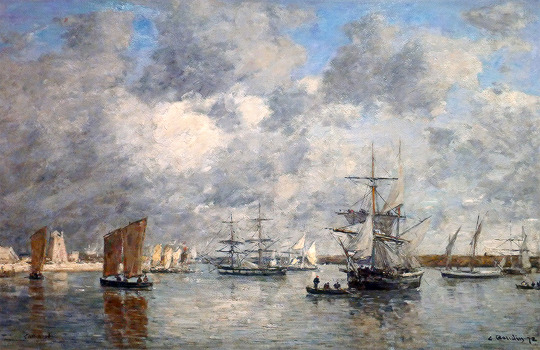
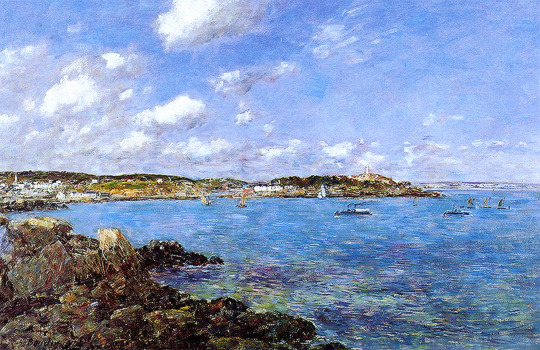
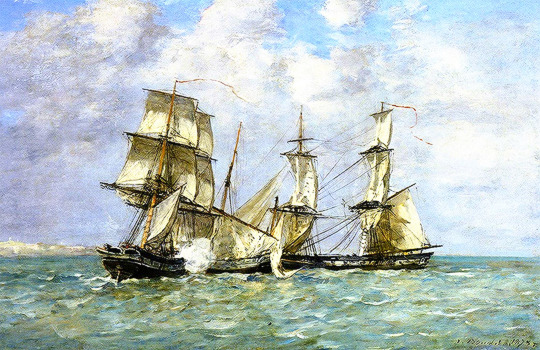
Eugene Boudin (1824 - 1898)
Cherbourg (1883)
Douarnenez, the Shore and the Bay (1897)
Harbour at Camaret (1872)
The Bay of Douarnenez (1897)
The Capture of the 'Petit Rodeur' (1878)
#artedit#art history#french painter#impressionism#marine art#19th century#xix century#eugene boudin#paintings#painting#art#mine
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
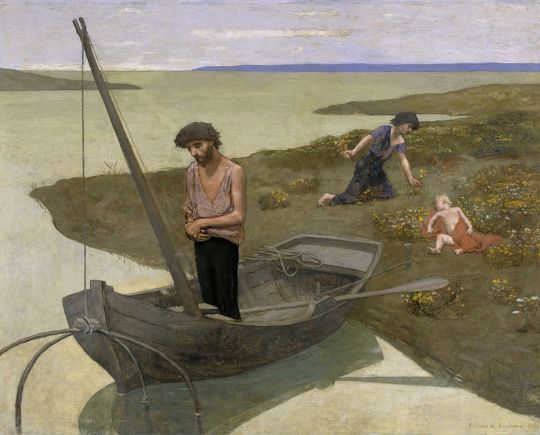

Pierre Puvis de Chavannes (1824-1898)
"The Poor Fisherman" (1881)
Oil on canvas
Located in the Musée d'Orsay, Paris, France
#paintings#art#artwork#genre painting#genre scene#pierre puvis de chavannes#oil on canvas#fine art#musée d’orsay#musee d'orsay#museum#art gallery#french artist#poverty#poor#family#struggling#1880s#late 1800s#late 19th century
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
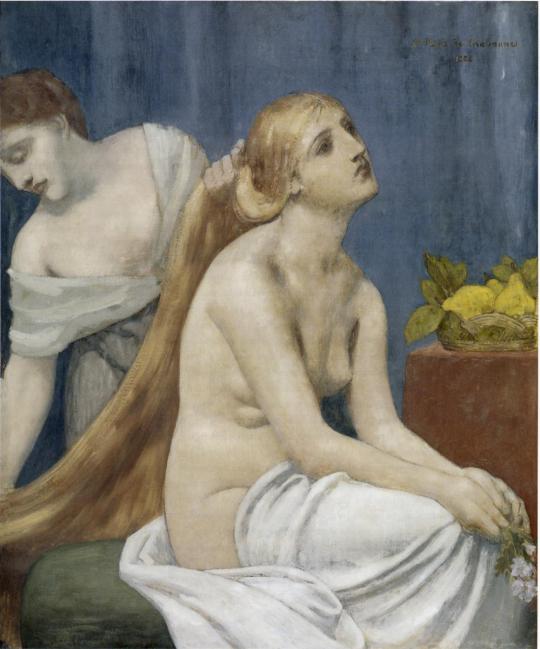

The Toilette by Pierre Puvis de Chavannes (1824 - 1898)
883 notes
·
View notes
Text
HAPPY BLACK HISTORY MONTH! 🤎🤎🤎
For Day 2, I wanted to give a list of black inventors and their inventions. Due to the whitewashing of history, many people don’t know about the revolutionary inventions that black people created. Some inventions were stolen by white inventors and patented so that these black inventors never got credit or revenue. There were also many instances of discrimination that didn’t allow black inventors to patent their inventions; they were often asked for extensive proof and sometimes, their inventions were destroyed and the ideas were given to white inventors to take credit for instead. Thankfully, that isn’t the case anymore and black inventors have ingrained themselves into history books and text. Let us look at some of the inventions that make life today much easier.
Michael Croslin(1933-1989): Blood Pulse and Monitoring Device
Frederick McKinley Jones(1893-1961): Roof Mounted Refrigeration for Vehicles
Garrett Morgan(1877-1963): Gas Mask and 3 Light Traffic Signal
Sarah Boone(1847-1904): Improved Ironing Board
Mary Van Brittan Brown(1922-1999): Home Camera Security System
Alexander Miles: Automatic Elevator Doors
Henry Brown(1800s):Safe Deposit Box
Alfred L. Cralle(1866-1920): Ice Cream Scoop
Lyda Newman(1898): Synthetic Hairbrush
Doctor Shirley Jackson: Breakthroughs in scientific research that allowed others to create call waiting, Caller ID, the portable fax and many others
Albert Richardson(1894): Casket Lowering System
Doctor Patricia Bath(1986): Invented Laser Probe that revolutionized cataract and other eyes surgeries, even restoring the sight of many individuals
George Crum(1824-1914): Potato Chips
Charles Drew(1904-1950): Blood Banks
David N. Crosthwait(1898-1976): Heating System
These are just a few of the hundreds of things black people have invented and so many of them are used to make life easier and better. So we thank all of these inventors for what they endured and the study they set forth to give us not only simple luxuries and pleasures but also advancements in medicine and science.
THANK YOU BLACK INVENTORS AND SCIENTISTS🤎🤎🤎🤎
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
Who do you consider to have been some of the most important / formative mayors of New York?
This is a great question, and actually rather difficult to answer, because for the longest time both Tammany Hall and the Whig/Republican machine tended to prefer mayors who were dull but reliable non-entities. Starting in 1824, NYC was divided into wards that elected Aldermen and Assistant Aldermen to the Board of Aldermen and the Board of Assistants, who together made up the bicameral Common Council. This led to a system whereby the real political action was shunted to the local level, where the ward's Aldermen and the ward boss (and his precinct bosses) ran the show.
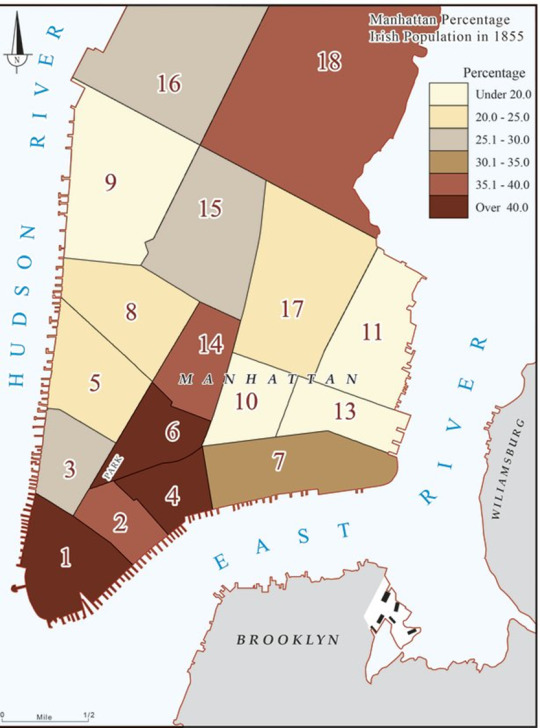
The downfall of Boss Tweed led to some reforms, with the bicameral Common Council replaced by a unicameral Board of Aldermen who were elected from larger State Senate districts or at-large, as part of the Whig Party's drive to dilute the power of Tammany's Irish Catholic voting base. This would change somewhat when the five boroughs were consolidated into Greater New York in 1898, which added the borough presidents and the Board of Estimate into the mix, and then again in 1901 and so forth.
However, the overall trend was a weak mayor system where real political power was fairly evenly distributed between aldermen (who were not only the city's legislatures but were also represented on the Board of Estimate through their President), the borough presidents, the mayor, and the comptroller.
So the major players in NYC politics tended not to be mayors:

Dewitt Clinton was incredibly transformational, but despite serving three terms as mayor his real mark on New York was as governor where he was the driving force behind the construction of the Erie Canal.
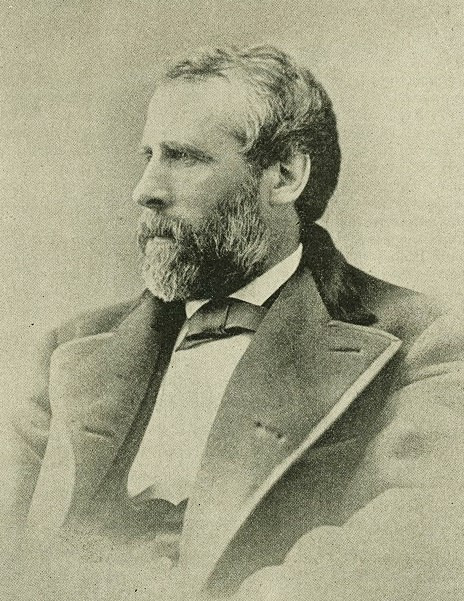

Andrew Haswell Green, the "Father of Greater New York," was responsible for the creation of Central Park, the New York Public Library, the Bronx Zoo, The Museum of Natural History, the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Riverside, Morningside, and Fort Washington Parks, Columbus Circle, and the consolidation of Greater New York - but he never served as mayor. The original Robert Moses, Green's political power came from his leadership of the Central Park Commission, the Greater New York Commission, a six-year stint in the Comptroller's office, and his position on a number of NGOs.
But if we're talking transformative mayors, there is one name that rises above all the rest: Fiorello goddamn LaGuardia.

There had been other reform mayors before him - Seth Low had established the Civil Service, John P. Mitchel brought scientific management to city government - but none of them had ever been able to get re-elected. Unlike the wealthy WASP reformers, LaGuardia knew how to beat Tammany at the ethnic politics game. Tammany's strength had always been in the Irish wards of the city, and while they had tried to divide-and-rule by promoting the naturalization of Russian and Polish Jews in return for them voting for Irish-American politicians in the Lower East Side while noticably neglecting the naturalization of Italians, the emergence of second-generation Jewish and Italian voters meant that this strategy had run its course.
Born to a Sephardic mother from Trieste and a lapsed Catholic father from southern Italy, Fiorello had an astonishing knack for transcending ethnic political boundaries in New York City - he spoke Italian, German, Yiddish, and Croatian, but he was also a progressive Republican and Episcopalian (which meant he could speak middle-class WASP too). LaGuardia won the 1933 mayoral election by bringing together a Fusion coalition that brought middle class German-American Republicans together with Italians and Jews, a coalition that he would expand in 1936 by bringing socialists, unions, and black voters together into the American Labor Party.
Over his twelve years as Mayor, LaGuardia was almost pathologically active (in a way that's oddly reminiscent of Henry II), transforming almost every aspect of New York City:
Jobs for the Unemployed:
LaGuardia's immediate mission as mayor was to fight the Great Depression that had had left a third of the City unemployed. He did this by forming an enduring alliance with FDR in which the New Deal would provide NYC with unpredecented level of federal support in exchange for NYC becoming the New Deal's model city - the first of the "Little New Deals." In his first hundred days in office, LaGuardia convinced FDR to give New York City a full 20% of the Civil Works Administration's work relief budget. This put 200,000 New Yorkers back to work - and this would only be the beginning of New York City's experiments with direct job creation.
As part of Fiorello LaGuardia's "Little New Deal," LaGuardia's new Parks Department employed 70,000 workers - paid for by CWA and later WPA money - to rebuild New York City's parks, constructing the Central Park Zoo and 60 playgrounds in the first year.
When the New Deal created the Works Progress Administration in 1935, LaGuardia once again lobbied FDR to put NYC first in line. This culminated in some 700,000 New Yorkers - a tenth of the city's entire population - getting jobs through the WPA and other New Deal programs. Together with the Parks Department, LaGuardia and Robert Moses would mobilize this workforce to completely transform the city.
Public Works:
This is where we have to discuss Fiorello LaGuardia's fateful decision to make Robert Moses his master builder. While Moses was in the process of becoming the "Power Broker" before LaGuardia - he had already been made president of the Long Island State Park Commission and chairman of the New York State Council of Parks - LaGuardia enabled his ascent to the heights of power by making him Parks Commissioner, Commissioner and then Chairman of the Triborough Bridge Authority, Commissioner of the NYC Planning Commission, and Chairman of the Emergency Public Works Commission.
The pact between them was simple: LaGuardia would give Moses the public appointments he needed to consolidate public works across the city and would steer New Deal public works money through Moses' agencies, and in exchange Moses would be LaGuardia's master builder with a mandate to "build it quickly and build it well." This was not an easy task, because Robert Moses was a political enemy of FDR and FDR tried to bar him from being given any WPA or PWA funding, but the mayor was able to persuade Roosevelt that it was more important that LaGuardia's proposed $1 billion public works program for NYC be carried at speed and administered efficiently.
As LaGuardia's workhorse, Moses would oversee almost all of NYC's public works, including the West Side Highway, the future FDR Drive, the Brooklyn Battery Tunnel, the Triborough Bridge, the LaGuardia and future JFK Airports, and Jones Beach Park, among others. LaGuardia would also construct the Sixth Avenue Subway line, the Queens-Midtown Tunnel and the Lincoln Tunnel without Moses (who was completely uninterested in mass transit and who always preferred bridges to tunnels).
In addition to these major projects, LaGuardia with and without Moses built the city's first municipal power plants, 37 sewage treatment plants, 9 fire houses, 142 elementary schools and 22 high schools, half of NYC's then-23 municipal hospitals, eight District Health Centers to provide preventative, specialized, and public health immunization care, and the first 14 of the City's public housing projects.
City Government:
To dismantle Tammany's patronage system, he began to massively expand the civil service to eliminate patronage jobs, and then when Tammany beat him on a government reform bill in 1934, he simply kept pushing. He pushed through the LaGuardia Reform Charter of 1938 that abolished the Tammany-dominated Board of Aldermen and replaced it with a City Council elected by Single Transferrable Vote, established the Board of Estimate as a central administrative body with powers over the city budget, public contracts, franchises, and land use - crippling Tammany's ability to raise money through graft and kickbacks.
To transform New York City into a "strong mayor" model, he undertook a campaign of transforming independent agencies scattered across the five boroughs into a system of unified citywide departments or public authorities that answered directly to the mayor and gave him unprecedented state capacity. In 1934, he formed the Parks Department and the New York City Housing Authority; in 1936 he formed the Department of Buildings and the City Planning Commission; in 1938, he restructured the Department of Welfare to run the city's social welfare programs and a massively expanded public hospital system; in 1940, he took over the IRT (operating the 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6), and the BMT and IND (operating the A, B, C, D, E, F, G, J, L, M, N, Q, R, W, and Z lines), unifying the NYC subway system for the first time.
To deal with police corruption, LaGuardia appointed Lewis Valentine to purge the NYPD so that the mayor could use it (and Thomas Dewey) in a crusade against the mafia's gambling, racketeering, and vice operations. This marked a rare period of honesty and effectiveness in the NYPD, although after WWII the system of protection rackets and mafia corruption would eventually re-establish itself.
Ironically, this exhaustive list of accomplishments really made it hard for later mayors to distinguish themselves, because mostly their task was completing, managing, or mis-managing the system that LaGuardia had built. After LaGuardia I would say that Robert Wagner Jr. (established public sector collective bargaining, created CUNY, Lincoln Center, Shakespeare in the Park, and dealt the killing blow to Tammany) and John Lindsay (see my previous post, but chiefly scatter-site housing, the civilian complaint review board, and the Knapp Commission on police corruption) are on my list of formative mayors.
After them, there have been long-serving mayors and good mayors, but unfortunately not the two combined.
#history#historical analysis#nyc history#nyc mayor#fiorello laguardia#tammany hall#urban history#urban studies#urban politics#political machines#new deal#robert moses#infrastructure
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Port of Landerneau - Finistere by Eugene Boudin (1824 - 1898)
159 notes
·
View notes
Text

"The Reader", by Pierre Puvis de Chavannes (1824-1898). French painter. Private Collection. oil on canvas
201 notes
·
View notes