#ArrayDeque
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
📚 Comparing Java Collections: Which Data Structure Should You Use?
If you're diving into Core Java, one thing you'll definitely bump into is the Java Collections Framework. From storing a list of names to mapping users with IDs, collections are everywhere. But with all the options like List, Set, Map, and Queue—how do you know which one to pick? 🤯
Don’t worry, I’ve got you covered. Let’s break it down in simple terms, so you can make smart choices for your next Java project.
🔍 What Are Java Collections, Anyway?
The Java Collection Framework is like a big toolbox. Each tool (or data structure) helps you organize and manage your data in a specific way.
Here's the quick lowdown:
List – Ordered, allows duplicates
Set – Unordered, no duplicates
Map – Key-value pairs, keys are unique
Queue – First-In-First-Out (FIFO), or by priority
📌 When to Use What? Let’s Compare!
📝 List – Perfect for Ordered Data
Wanna keep things in order and allow duplicates? Go with a List.
Popular Types:
ArrayList – Fast for reading, not so much for deleting/inserting
LinkedList – Good for frequent insert/delete
Vector – Thread-safe but kinda slow
Stack – Classic LIFO (Last In, First Out)
Use it when:
You want to access elements by index
Duplicates are allowed
Order matters
Code Snippet:
java

🚫 Set – When You Want Only Unique Stuff
No duplicates allowed here! A Set is your go-to when you want clean, unique data.
Popular Types:
HashSet – Super fast, no order
LinkedHashSet – Keeps order
TreeSet – Sorted, but a bit slower
Use it when:
You care about uniqueness
You don’t mind the order (unless using LinkedHashSet)
You want to avoid duplication issues
Code Snippet:
java

🧭 Map – Key-Value Power Couple
Think of a Map like a dictionary. You look up values by their unique keys.
Popular Types:
HashMap – Fastest, not ordered
LinkedHashMap – Keeps insertion order
TreeMap – Sorted keys
ConcurrentHashMap – Thread-safe (great for multi-threaded apps)
Use it when:
You need to pair keys with values
You want fast data retrieval by key
Each key should be unique
Code Snippet:
java

⏳ Queue – For First-Come-First-Serve Vibes
Need to process tasks or requests in order? Use a Queue. It follows FIFO, unless you're working with priorities.
Popular Types:
LinkedList (as Queue) – Classic FIFO
PriorityQueue – Sorted based on priority
ArrayDeque – No capacity limit, faster than LinkedList
ConcurrentLinkedQueue – Thread-safe version
Use it when:
You’re dealing with task scheduling
You want elements processed in the order they come
You need to simulate real-life queues (like print jobs or tasks)
Code Snippet:
java

🧠 Cheat Sheet: Pick Your Collection Wisely

⚙️ Performance Talk: Behind the Scenes

💡 Real-Life Use Cases
Use ArrayList for menu options or dynamic lists.
Use HashSet for email lists to avoid duplicates.
Use HashMap for storing user profiles with IDs.
Use Queue for task managers or background jobs.

🚀 Final Thoughts: Choose Smart, Code Smarter
When you're working with Java Collections, there’s no one-size-fits-all. Pick your structure based on:
What kind of data you’re working with
Whether duplicates or order matter
Performance needs
The better you match the collection to your use case, the cleaner and faster your code will be. Simple as that. 💥
Got questions? Or maybe a favorite Java collection of your own? Drop a comment or reblog and let’s chat! ☕💻
If you'd like me to write a follow-up on concurrent collections, sorting algorithms, or Java 21 updates, just say the word!
✌️ Keep coding, keep learning! For More Info : Core Java Training in KPHB For UpComing Batches : https://linktr.ee/NIT_Training
#Java#CoreJava#JavaProgramming#JavaCollections#DataStructures#CodingTips#DeveloperLife#LearnJava#ProgrammingBlog#TechBlog#SoftwareEngineering#JavaTutorial#CodeNewbie#JavaList#JavaSet#JavaMap#JavaQueue#CleanCode#ObjectOrientedProgramming#BackendDevelopment#ProgrammingBasics
0 notes
Text
I have posted an article for Chinese.
0 notes
Text
Youtube Video Ideas
I want to post videos about the Java basics of: - Stack - ArrayDeque - HashMap - HashSet - LinkedHashMap - LinkedHashSet - TreeMap - TreeSet - IdentityHashMap
Do you have any ideas for more content? Any other Java class I should dive into?
My Channel: youtube.com/@DoSomeDev
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Java Collection
Java libraries are indispensable tools that streamline development by providing pre-written code for common tasks. "The Ultimate Guide to Java Libraries" explores a myriad of libraries that enhance Java programming, from handling data structures to implementing complex algorithms.
A key feature covered is collections in Java, which offer efficient ways to manage groups of objects, improving code efficiency and readability.
TpointTech is a valuable resource for developers seeking in-depth tutorials and examples on using these libraries effectively. Leveraging these libraries can significantly reduce development time and improve application performance.
Overview of Java Collections
The Java Collections Framework includes interfaces, implementations, and algorithms. The core interfaces include Collection, List, Set, Queue, and Map, each serving different purposes.
Collection Interface:
The root interface of the framework, representing a group of objects known as elements. It is extended by List, Set, and Queue interfaces.
List Interface:
An ordered collection that allows duplicate elements. Common implementations are ArrayList, LinkedList, and Vector. Lists are ideal when you need to access elements by their index.
ArrayList: Resizable array implementation, offering constant-time positional access but slower for insertion and deletion.
LinkedList: Doubly-linked list implementation, providing efficient insertion and deletion but slower access time.
Vector: Synchronized version of ArrayList, rarely used due to performance overhead.
Set Interface:
A collection that does not allow duplicate elements. It models mathematical sets and provides implementations like HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
HashSet: Uses a hash table for storage, offering constant-time performance for basic operations.
LinkedHashSet: Maintains insertion order, slightly slower than HashSet.
TreeSet: Implements the SortedSet interface, ensuring elements are in ascending order, based on their natural ordering or a specified comparator.
Queue Interface:
Designed for holding elements prior to processing, typically ordered in a FIFO (first-in-first-out) manner. Common implementations include LinkedList, PriorityQueue, and ArrayDeque.
PriorityQueue: Elements are ordered according to their natural ordering or a provided comparator, useful for creating priority-based tasks.
ArrayDeque: Resizable-array implementation of the Deque interface, providing efficient insertion and deletion from both ends.
Map Interface:
Represents a collection of key-value pairs, where each key maps to one value. Popular implementations are HashMap, LinkedHashMap, and TreeMap.
HashMap: Provides constant-time performance for basic operations, assuming a good hash function.
LinkedHashMap: Maintains a doubly-linked list of its entries, preserving the order of insertion.
TreeMap: Implements the SortedMap interface, ensuring keys are in ascending order.
Advantages of Java Collections Framework
Reduces Programming Effort: With a set of ready-made data structures and algorithms, JCF eliminates the need for developers to implement complex data structures from scratch.
Increases Program Speed and Quality: Standardized interfaces and optimized implementations ensure high performance and reliability.
Interoperability: Collections can be easily passed across APIs, reducing the complexity of integration.
Ease of Maintenance: Well-documented and widely-used classes make it easier for developers to maintain and enhance code.
Common Algorithms in JCF
Java Collections Framework includes various algorithms to perform routine tasks, such as sorting, searching, and shuffling. These algorithms are static methods in the Collections utility class.
Sorting: Collections.sort(List list), sorts the specified list into ascending order.
Shuffling: Collections.shuffle(List list), randomly permutes the elements in the list.
Searching: Collections.binarySearch(List> list, T key), performs binary search on a sorted list.
Conclusion
The Java Collections Framework is indispensable for any Java developer. It offers a standardized and efficient way to manage groups of objects, making code more robust and maintainable.
By leveraging the various interfaces and implementations, such as lists, sets, queues, and maps, developers can handle data structures effectively.
Understanding collections in Java, as detailed on resources like TpointTech, is crucial for building high-performance applications. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, mastering Java collections will significantly enhance your programming capabilities.
0 notes
Text
Коллекции?
Если коротко, то
Существует несколько типов коллекций (интерфейсов):
List - упорядоченный список. Элементы хранятся в порядке добавления, проиндексированы.
Queue - очередь. Первый пришёл - первый ушёл, то есть элементы добавляются в конец, а удаляются из начала.
Set - неупорядоченное множество. Элементы могут храниться в рандомном порядке.
Map - пара ключ-значение. Пары хранятся неупорядоченно.
У них есть реализации.
Реализации List
ArrayList - самый обычный массив. Расширяется автоматически. Может содержать элементы разных классов.
LinkedList - элементы имеют ссылки на рядом стоящие элементы. Быстрое удаление за счёт того, что элементы никуда не сдвигаются, заполняя образовавшийся пробел, как в ArrayList.
Реализации Queue
LinkedList - рассказано выше. Да, оно также реализует интерфейс Queue.
ArrayDeque - двунаправленная очередь, где элементы могут добавляться как в начало так и в конец. Также и с удалением.
PriorityQueue - элементы добавляются в сортированном порядке (по возрастанию или по алфавиту или так, как захочет разработчик)
Реализации Set
HashSet - элементы хранятся в хэш-таблице, в бакетах. Бакет каждого элемента определяется по его хэш-коду. Добавление, удаление и поиск происходят за фиксированное количество времени.
LinkedHashSet - как HashSet, но сохраняет порядок добавления элементов.
TreeSet - используется в том случает, когда элементы надо упорядочить. По умолчанию используется естественный порядок, организованный красно-чёрным деревом. (Нет, я не буду это здесь объяснять, не заставите)
LinkedList - рассказано выше. Да, оно также реализует интерфейс Queue.
ArrayDeque
Реализации Map
HashMap - то же самое что и HashSet. Использует хэш-таблицу для хранения.
TreeMap - тоже использует красно-чёрное дерево. Как и TreeSet, это достаточно медленно работающая структура для малого количества данных.
LinkedHashMap. Честно? Тяжеловато найти информацию про различия с LinkedHashSet, кроме того, что один - это Set, а второй - Map. Мда :/
А связи всего этого выглядят так
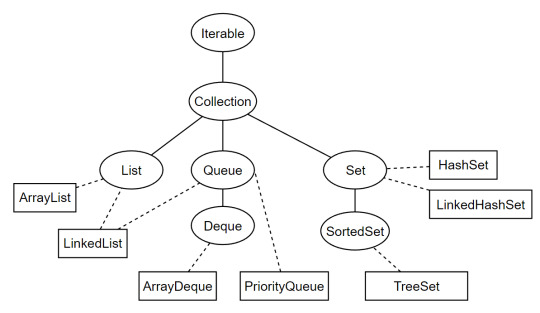
Овалы - интерфейсы; Прямоугольники - классы;
Здесь видно, что начало начал - интерфейс Iterable, ну а общий для всех интерфейс - Collection (Не путать с фреймворком Collections)
А где Map? а вот он
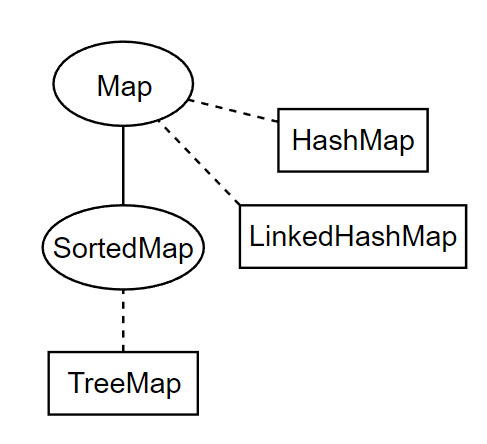
Map не наследуется от Collection - он сам по себе.
К этой теме также можно много чего добавить: устройство красно-черного дерева, работа HashSet'ов и HashMap'ов под капотом, сложность коллекций. Но это всё темы для следующих постов.
Ну, а пока надеюсь, что понятно.
#студент бормочет#List#Set#Queue#Map#ArrayList#LinkedList#ArrayDeque#PriorityOueue#HashMap#HashSet#LinkedHashMap#LinkedHashSet#TreeMap#TreeSet#как же много тегов#Коллекции
1 note
·
View note
Link
ArrayDeque (читається як аррейдек) – це клас який забезпечує двосторонню чергу. Іншими словами - це автоматично зростаючий масив, що дозволяє нам додавати або видаляти елементи з обох боків черги. ArrayDeque може бути використано як стек (LIFO, останній ввійшов - перший вийшов) або ж як черга (FIFO, перший ввійшов - перший вийшов).
0 notes
Text
The Collection Framework in Java

What is a Collection in Java?
Java collection is a single unit of objects. Before the Collections Framework, it had been hard for programmers to write down algorithms that worked for different collections. Java came with many Collection classes and Interfaces, like Vector, Stack, Hashtable, and Array.
In JDK 1.2, Java developers introduced theCollections Framework, an essential framework to help you achieve your data operations.
Why Do We Need Them?
Reduces programming effort & effort to study and use new APIs
Increases program speed and quality
Allows interoperability among unrelated APIs
Reduces effort to design new APIs
Fosters software reuse
Methods Present in the Collection Interface
NoMethodDescription1Public boolean add(E e)To insert an object in this collection.2Public boolean remove(Object element)To delete an element from the collection.3Default boolean removeIf(Predicate filter)For deleting all the elements of the collection that satisfy the specified predicate.4Public boolean retainAll(Collection c)For deleting all the elements of invoking collection except the specified collection.5Public int size()This return the total number of elements.6Publicvoid clear()This removes the total number of elements.7Publicboolean contains(Object element)It is used to search an element.8PublicIterator iterator()It returns an iterator.9PublicObject[] toArray()It converts collection into array.
Collection Framework Hierarchy
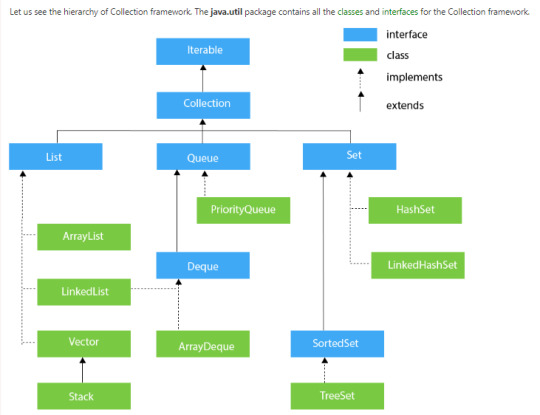
List Interface
This is the child interface of the collectioninterface. It is purely for lists of data, so we can store the ordered lists of the objects. It also allows duplicates to be stored. Many classes implement this list interface, including ArrayList, Vector, Stack, and others.
Array List
It is a class present in java. util package.
It uses a dynamic array for storing the element.
It is an array that has no size limit.
We can add or remove elements easily.
Linked List
The LinkedList class uses a doubly LinkedList to store elements. i.e., the user can add data at the initial position as well as the last position.
It allows Null insertion.
If we’d wish to perform an Insertion /Deletion operation LinkedList is preferred.
Used to implement Stacks and Queues.
Vector
Every method is synchronized.
The vector object is Thread safe.
At a time, one thread can operate on the Vector object.
Performance is low because Threads need to wait.
Stack
It is the child class of Vector.
It is based on LIFO (Last In First Out) i.e., the Element inserted in last will come first.
Queue
A queue interface, as its name suggests, upholds the FIFO (First In First Out) order much like a conventional queue line. All of the elements where the order of the elements matters will be stored in this interface. For instance, the tickets are always offered on a first-come, first-serve basis whenever we attempt to book one. As a result, the ticket is awarded to the requester who enters the queue first. There are many classes, including ArrayDeque, PriorityQueue, and others. Any of these subclasses can be used to create a queue object because they all implement the queue.
Dequeue
The queue data structure has only a very tiny modification in this case. The data structure deque, commonly referred to as a double-ended queue, allows us to add and delete pieces from both ends of the queue. ArrayDeque, which implements this interface. We can create a deque object using this class because it implements the Deque interface.
Set Interface
A set is an unordered collection of objects where it is impossible to hold duplicate values. When we want to keep unique objects and prevent object duplication, we utilize this collection. Numerous classes, including HashSet, TreeSet, LinkedHashSet, etc. implement this set interface. We can instantiate a set object with any of these subclasses because they all implement the set.
LinkedHashSet
The LinkedHashSet class extends the HashSet class.
Insertion order is preserved.
Duplicates aren’t allowed.
LinkedHashSet is non synchronized.
LinkedHashSet is the same as the HashSet except the above two differences are present.
HashSet
HashSet stores the elements by using the mechanism of Hashing.
It contains unique elements only.
This HashSet allows null values.
It doesn’t maintain insertion order. It inserted elements according to their hashcode.
It is the best approach for the search operation.
Sorted Set
The set interface and this interface are extremely similar. The only distinction is that this interface provides additional methods for maintaining the elements' order. The interface for handling data that needs to be sorted, which extends the set interface, is called the sorted set interface. TreeSet is the class that complies with this interface. This class can be used to create a SortedSet object because it implements the SortedSet interface.
TreeSet
Java TreeSet class implements the Set interface it uses a tree structure to store elements.
It contains Unique Elements.
TreeSet class access and retrieval time are quick.
It doesn’t allow null elements.
It maintains Ascending Order.
Map Interface
It is a part of the collection framework but does not implement a collection interface. A map stores the values based on the key and value Pair. Because one key cannot have numerous mappings, this interface does not support duplicate keys. In short, The key must be unique while duplicated values are allowed. The map interface is implemented by using HashMap, LinkedHashMap, and HashTable.
HashMap
Map Interface is implemented by HashMap.
HashMap stores the elements using a mechanism called Hashing.
It contains the values based on the key-value pair.
It has a unique key.
It can store a Null key and Multiple null values.
Insertion order isn’t maintained and it is based on the hash code of the keys.
HashMap is Non-Synchronized.
How to create HashMap.
LinkedHashMap
The basic data structure of LinkedHashMap is a combination of LinkedList and Hashtable.
LinkedHashMap is the same as HashMap except above difference.
HashTable
A Hashtable is an array of lists. Each list is familiar as a bucket.
A hashtable contains values based on key-value pairs.
It contains unique elements only.
The hashtable class doesn’t allow a null key as well as a value otherwise it will throw NullPointerException.
Every method is synchronized. i.e At a time one thread is allowed and the other threads are on a wait.
Performance is poor as compared to HashMap.
This blog illustrates the interfaces and classes of the java collection framework. Which is useful for java developers while writing efficient codes. This blog is intended to help you understand the concept better.
At Sanesquare Technologies, we provide end-to-end solutions for Development Services. If you have any doubts regarding java concepts and other technical topics, feel free to contact us.
0 notes
Text
The Breadth-First Search Algorithm
Graphs can be traversed in a depth-first or breadth-first manner. The first one is particularly useful when your data is a DAG (directed, acyclical graph), but both can be applied to any given kind of graph, including trees.
Consider this example:
This is a graph with 9 nodes, which I have key colored to show the depth of every layer of nodes. Hopefully this clears out the topology a bit. This graph can be represented as a 9 x 9 adjacency matrix as shown above (if you have N nodes, necessarily you need N x N size in your matrix).
The key to traversing the graph in a breadth-first manner is the implementation of two auxiliary data structures:
An N-sized array to keep track of what nodes you have already visited in your traversal, to avoid cycles when going down the graph by layers.
A queue of nodes of dynamic size, which will queue the nodes in order as you visit them, and dequeue them as you traverse down.
So in this example, you would do this, if you wished to traverse the tree starting from node 0:
Enqueue 0
Dequeue 0
Enqueue all its children, 1, 2, 3 (queue = 1, 2, 3)
Add 0 to output
Mark 0 as visited
Dequeue 1
If not visited yet, enqueue all its children, 4 and 5 (queue = 2, 3, 4, 5)
Add 1 to output
Mark 1 as visited
Dequeue 2
If not visited yet, enqueue all its children, 3 and 6 (queue = 3, 4, 5, 6) ... REPEAT UNTIL THE QUEUE IS EMPTY and all nodes have been visited
This is a sample implementation:
import java.util.Queue; import java.util.ArrayDeque; import java.util.List; import java.util.ArrayList; public class Main { public static int N = 9; public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] graph = new int[N][N]; graph[0][1] = 1; graph[0][2] = 1; graph[0][3] = 1; graph[1][4] = 1; graph[1][5] = 1; graph[2][3] = 1; graph[2][6] = 1; graph[3][7] = 1; graph[3][8] = 1; System.out.println(bfs(graph, 0).toString()); } private static List bfs(int[][] graph, int startNode) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); //visited array of N elements to avoid cycles boolean[] visited = new boolean[N]; Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(); int current = startNode; queue.add(current); visited[startNode] = true; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int currentNode = queue.poll(); result.add(currentNode); // Explore all neighbors of the current node for (int i = 0; i < graph[currentNode].length; i++) { if (graph[currentNode][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) { queue.add(i); visited[i] = true; } } } return result; } }
0 notes
Text
[100% OFF] Master Java Collection Framework
[100% OFF] Master Java Collection Framework
What you Will learn ? Collection Interfaces Types of Data Structures ArrayList Class LinkedList Class Iterator, ListIterator and Spliterator Queue and Stack ArrayDeque Class PriorityQueue Class Map Classes How Hashing Works HashMap Class LinkedHashMap Class TreeMap Class EnumMap, WeakHashMap and IdentityHashMap Classes HashSet Class LinkedHashSet Class TreeSet Class Collection…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
7 | Linked-lists
Linked-lists
The key difference between an ArrayDeque and a Doubly Linked List is that null elements can be added in the Doubly Linked List but not in the ArrayDeque. Doubly Linked List can store null elements, thus, it consumes more space. Doubly Linked List is said to be more efficient in removing elements for iteration.
We use DLList when:
> can be used in navigation systems where both front and back navigation is required
> implementing undo and redo functionality
> removing the current element in the iteration
> using null elements in a list or sequence
and use ArrayDeque when:
> saving up space

0 notes
Text
I have posted an article for Spanish.
0 notes
Text
6 | Array-Based Lists
Array-Based Lists
The lab exercise wants us to implement an ArrayDeque then it also wants us to incorporate a List interface. To be honest, I always get nervous in doing a lab exercise since I always think that its gonna be hard. [Yes I overthink so much even before doing the task HAHA]
"input.dat"— this got me crying in difficulty since its first appearance in lab exercise one. It took me a while before finding out that it was actually an input (for real) and should be read by the code that I'm about to write. I spent long hours searching the web on how to import it and I really find it difficult since I have no knowledge about Python. Python is still so foreign to me. [even c++ and c — I still need to study these languages a lot, like a lot.] Good thing that I have block mates who helped through the process and got me out of my misery in this lab exercise.
0 notes