#CAN BUS TCP/IP Converter
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
CAN BUS Haberleşme Çözümleri - GelecekBT
#can 2.0#CAN BUS#CAN OPEN#CAN FD#CAN BUS FIBER CONVERTER#CAN BUS TCP/IP Converter#canbus rs232#canbus rs485#canbus usb converter
1 note
·
View note
Text
Computer Networking Devices And Its Functions

Networking devices are electronic devices that allow multiple computer devices to communicate, interact, and share information, such as desktops, mobile phones, laptop computers, printers, and others. There are various types of networks, such as a star, bus, and mesh network, among others; networking devices function as nodes and help connect devices in such a network.
A Techbox7 protocol in a computer network determines how different devices communicate with one another; these protocols include TCP, IP, DHCP, FTP, and others. Furthermore, data is transferred within a network via data packets; due to the massive amount of data transmitted over a network, we require devices that facilitate easy communication and data flow. Network devices manage the flow of data packets and aid in the transmission of data from the source to the destination within and between networks. A network management system aids in the management of multiple networks; it also manages the operation of various software and hardware devices present in the network.
Networking devices help to connect inter-network and intra-network devices in a network. RJ45 and NIC cards are examples of devices that allow connecting inter-network devices. Switches, routers, and hubs, on the other hand, help to connect intra-network devices.
The following are the most common networking devices:
A Tech box 7 repeater is a networking device that receives a signal, amplifies it, and retransmits it with increased signal power. This is done because the power of a signal degrades over long distances. A repeater, which operates in the network's physical layer, helps the signal travel longer distances (such as 100 metres). Network hubs are the most basic networking devices; they also serve as repeaters, amplifying signals that travel long distances. It can handle both analogue and digital data. When it receives analogue data, it transmits it as a signal, and when it receives digital data, it transmits it as data packets. It is not an intelligent device that performs packet filtering; instead, it transmits whatever data it receives to all connected devices. Active Hub- It acts as a repeater, cleaning and amplifying the signal so that it can travel long distances.
The Tech box7 wiring from other nodes and power supplies of an active hub is collected and retransmitted without amplification by a passive hub.
Intelligent Hub- Using admin access, this hub can monitor network traffic and configure all of its ports. It is an intelligent network device that aids in remote network management.
Bridge: A bridge connects two or more networks. It subdivides a large network into smaller networks and allows communication between these smaller networks. The bridge's function is to store and transfer data frames using Media Access Control (MAC) addresses; it identifies the MAC addresses of the devices and sends the frames to them. It does not, unlike hubs, transfer frames to all connected devices. It receives data packets known as 'frames,' identifies the address, and sends them only to specific devices. It makes use of a bridge table for this purpose. The bridge table contains information about the LAN addresses of computers and other bridges. This aids in the transfer of frames to these devices.
Cable operators and telephone companies typically use modems. They convert the incoming digital signal to analogue and send it out. It retransforms analogue signals into digital signals at the receiver end and assists the computer in interpreting the digital version of the signal. A serial line transports digital data from the model to the computer or from the modem to the computer (RS 232) Routers are intelligent networking devices that can store data packets for connected networks and transmit them using packet filtering. They allow packets to be sent across a large network of connected computers. Border routers aid in the translation of LAN to WAN framing because LAN and WAN use different protocols. A router, like a bridge, divides a large network into smaller networks and allows data to be transferred between them; it also transfers data between multiple routers in these smaller networks. If the destination address is unavailable, the intelligent device knows where to request.
Tech box 7’s range of Routers.
Network switches are multiport devices that allow multiple systems to communicate while revealing less information about the nodes in a network. They can see the data packets' destination hardware address and send them to the correct destination. Because of its ability to switch virtual circuits, a switch improves network security and efficiency. Virtual circuits are invisible to network monitors, providing security. When used properly, it outperforms routers and hubs.
Techbox 7’s range of Switches.
Access Points: This term usually refers to a wireless device, but it can also refer to a wired device. It can function as a bridge connecting wired devices or as a router transmitting data between devices. Wireless Access Points (WAPs) are devices that combine a transmitter and a receiver (transceiver) to form a wireless network (WLAN). Access points are network devices that include an antenna, transmitter, or adaptor. To connect WLANs and a wired Ethernet LAN, APs use the wireless infrastructure network mode. They also have a lot of ports, so you can expand the network to accommodate more clients. Depending on the size of the network, multiple access points can be used to provide better coverage. Additional APs can be used to extend the range of wireless networks.
Gateways: Gateways can operate at multiple network layers. It connects two networks; gateways receive data, interpret it, and send it to another system. Gateways translate two networking protocols: Open System Interconnection (OSI) and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). As a result, gateways connect two or more independent networks, each with its own routing algorithms, protocols, topology, domain name service, and network administration procedures and rules. A gateway is a router with additional translation capabilities that can perform almost all of the functions of a router.
A network should be closely monitored for security and to ensure that devices and data transfer within the network are not redundant and are operating at peak efficiency. Any issues or bugs in a network should be resolved as soon as possible for data security and network efficiency. It must be safeguarded against malicious attacks and other risks associated with such network devices.
Navigation after the jump
1 note
·
View note
Text
Something about Ethernet card
About the network card we all know that there are many kinds of network card, involving industrial automation, network security, optical fiber to the desktop and other applications, Ethernet card is what, what are the functions of Ethernet card, then The following small make up with you to introduce the Ethernet card.

1. What is an Ethernet card
Network card (NIC), namely network interface controller, also known as network adapter or LAN receiver, is the most basic, the most important, the most indispensable connection equipment in the computer network system. It can be said that, if there is no network card component, the computer equipment can not be interconnected. Networking is difficult.
2. Main functions of network card:
In the TCP/IP model, network CARDS work at the physical and data link levels and are mainly used to receive and send data.
1) Encapsulation and unsealing of data: it is like mailing a package, the contents of which are data, and the packaging of the package is the beginning and end of the frame.
2) Represents a fixed address: for example, when data is sent, to whom you need to send it, and from whom you receive it, it is all determined by the address.
3) Data coding and decoding: Data transmission needs to be carried on the physical medium. In the actual process, electrical signals or optical signals are transmitted, so the data need to be converted into electrical signals or optical signals.
4) Link management: Ethernet is a Shared link, so when you are sending data, if someone else is using it, there will be conflicts, so you need to check if the link state is idle when you request to send.
5) Send and receive data.
3. Historical evolution of network card

4. Classification of network CARDS
With the rapid development of computer network technology, in order to meet the needs of various environments and levels of application, different types of network CARDS appear in the market.
1) according to the type of bus, there are PCI, PCIe, USB, ISA, among which ISA/PCI bus ISA relatively early bus, which has been gradually phased out in the market, and USB interface network card is mainly used in consumer electronics, so in industrial applications, server computers are mainly used by the PCIe bus.
2) Divided by structure and form: Integrated network card (LOM), PCIe network card, Mezz card, heterosexual card, etc.
3) By bandwidth: 100Mb, 1000M, 2.5g, 10G, 25G, 40G, 50G, 100G, 200G...
4) According to the network interface, it is mainly divided into electric port (RJ45) and optical fiber port (SC, LC, etc.);
5) Divided by application: server network card, desktop network card, industrial network card, etc.
In this way, more dedicated server nic and the difference between ordinary card: compared with dedicated server level card, workstation's network is mainly used in PC, workstations, and consumer electronics products, requirements for reliability and security of the network card is not so high, but dedicated server nic needs long time and stable operation, so the server should possess special card data transmission speed, low CPU usage, higher performance and safety performance.
Small make up said so much, we basically on the Ethernet card is what have a basic understanding of it, also know that there are many kinds of network card classification, so that there is no specific good or bad network card, suitable for their own is the best, when choosing to buy network card, you can buy according to their own needs. However, quality is always the first, it is recommended that users buy network CARDS must choose a regular, with good qualifications of the manufacturers and businesses to buy, not only to ensure that you can buy authentic, more importantly, there is a guarantee of after-sales service.
0 notes
Text
Computer Network Homework Help
Help for computer network assignment | Help for computer network homework
If you are an aspiring computer engineering aspiring and are looking for help with tasks for your computer networking subject, then you may be looking for different help for offline and online tasks. However, choosing the right help that can provide you with a complete task on time is not an easy task. Here we will inform you about the different topics covered in the assignment of computer networks and finally we will give you a perfect option to select for your computer network homework help.
To provide a quick exit for your teacher with a complete understanding of the task and consequently get better grades it is important that students choose the task with different features such as professionalism, good editing skill, exclusive content and no ordeal, and so on. If you can find all these important features, then finally you need to compare the prices and topic that they can cover for the desired subject, such as computer networks. For your help in assigning computer network, all assignment experts can be a choice you can trust.
About Computer Network homework Help
The computer network is one of the most essential and interesting disciplines for students of electronics and computer engineering. This topic is at the core and provides complete information about how prevailing communication systems, such as wired and wireless communication networks. All components used, the different types of topology used and all the essential concepts relating to the technical aspects of networking with the computer are explained in detail in this subject. Different terminologies used in the computer network are mentioned below. Based on this, there are numerous assignments and projects are given to students:
In generic terms, they are divided into the form of wired, wireless, and distributed and undistributed networks.
The computer network can be defined as the set of computers also known as nodes that are connected using wires or wireless media.
The primary purpose of networking between the computer is the sharing of information and resources. With the help of the shared network, you can share resources and information. You can create files on one computer and access them on another.
There are different types of topologies, such as star, mesh, bus, and ring topologies, that are used to establish the network.
Routers, cables, distributors, network cards (internal and external), and USB are some of the necessary hardware that is used to establish a network. Network interfaces, firewall, repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, and modems are the necessary hardware that has made it possible for the Internet to function as the computer to the network.
Different protocols are used for communication on computer networks such as TCP/IP and more. We are mentioning protocols here because computer networking is a generic term that is used. However, the World Wide Web is also a type of computer network on which different servers and computers are connected on a large scale that uses the different set of algorithms and protocols to work with.
There are different types of computer networks, such as LAN, MAN, WAN, VPN, backbone network, Internet and Intranet with extranet, and so on. Let's discuss these networks in summary:
LAN means the local network of acres that is valid up to a limited area, such as in a building or in any institution.
MAN represents the metropolitan network that exists in areas such as a small town or village. The cable network used for TV broadcasting is MAN type.
WAN means area network that covers a wide area. The Internet is one of the examples of WAN.
VPN is the virtual private network that comes in the application when members of the company or group of computers form a network so that they can share the different files and other resources needed. VPN are widely used to gain access to multiple sites that are not allowed to open in a specific area or on a particular server
The Internet is the WAN or the global network, which is widely used for different applications such as search, download, upload and so on.
However, the intranet is valid only as small LAN, MAN, or VPN. It cannot be considered as WAN because not everyone can access the network. It is a private network with authorization only for some people.
Wired, wireless and exotic technologies are currently being used for communication over the computer network
When you are in high school or undergraduate school, you may have to present some of the basic concepts and their functioning in the form of attribution. However, if you are studying in higher classes, such as PG or PhD, you may have to do research on the wireless network (the most common currently) or other relevant and new concept and bring something new to your dissertation. Your computer systems-based thesis is quite complex, as you will not only have to formulate something new, but you will also have to prove it. This is where you want to get help with the computer network homework.
How can All Assignments experts help you with the help of Network Assignment?
Well, the answer is simple. We have a set of experienced professionals who are not only useful for finding unique content, but also able to offer you timely delivery of the content. You can complete your work on time. The Computer Networks project will be a piece of cake when you contact all task experts.
With the help of simple steps, you'll be able to get the best out of all task experts. Not only are we required to give you the assignments, but we guarantee to guide you with all the important concepts that have been used within it. So, what are you waiting for? Register with all task specialists now!
Popular topics students are looking to us for online help for are:
COMPUTER NETWORK HOMEWORK HELP
Advanced multicast routing models Analog data for digital signals
Campus Area Network (CAN) application layer
Data Link Layer Congestion Control Techniques
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) IEEE 802.4: Network Token Bus
IPV4 and IPV6 Internet Protocols
LAN (Local Network) Layer Network Architecture -OSI 7
Man (Metropolitan Area Network) media converters
Network Devices - Hub, Repeater, Modem Network Interface Card (NIC)
Network layer Network management and security
Network topologies and layered network and architecture networks
Router and SWITCHES PAN (Personal Area Network)
Storage Area Network (SAN) routing algorithms
Area network of the system of programming of soques
Transmission medium and topology Transport layer
WAN (Wide Area Network) WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP TECHNICAL SUPPORT Interview Questions and Answers
Technical Support interview Questions for freshers and experienced :-
1. Name some of the latest Computer Processors? Intel Pentium Quad Core, Intel I3, I5 and I7 processor are some of the latest Computer Processor. 2. What does a ‘?’ sign in device manager indicate? When this sign appears, it indicates the device is not properly installed. Such problem arises in case of brand new plug-in cards. 3. How will you cope up with a customer, who complains about a brand new printer and system, and yet failing to get a proper print copy? The first thing I will ask the customer, whether the system is properly connected with the printer. The next thing would be to check the Device Driver. Many times it happens that if you install an incorrect Device Driver, the print copy would not be clear. 4. How you keep yourself updated with the current technology? I keep myself connected with social networking sites, the first platform for any technological advancement news and also keep surfing on the latest technology on internet. 5. What are the tools that will be helpful to you in identifying the problems and solving them? Manuals, Knowledge, team-members and experience are the tools that will be helpful to trouble shoot the problem and solving them. 6. What is the expected period of an average call while dealing with the customers? The expected period of an average call would be around 2-3 minutes, sometimes less or more depending on the problem complexity. 7. Why 8085 processor is called 8 bit processor? It is called 8 bit processor as it has 8 bit ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit). 8. What is stack and can we use ROM as stack? Stack is a portion of RAM used for saving the content of the program counter and general purpose registers. ROM cannot be used as a stack, as it is not possible to write on ROM. 9. What does it mean by interrupt? To perform a particular task, interrupt is a signal send by external device to the processor. 10. What is a Microprocessor? A microprocessor is a program controlled device. It retrieves the data instructions from memory and decodes them, after decoding, it executes the instruction.

TECHNICAL SUPPORT Interview Questions 11. What is Latch? It is a temporary storage device controlled by a timing signal, which can store 1 or 0. It is a D-type flip flop storage device. 12. What is the disadvantage of microprocessor? It has a limitation on the size of the data, also most microprocessor does not support floating point operations. 13. What do you mean by DHCP? DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, it is a network protocol, and it enables the server to assign automatically, IP address to a computer. 14. What do you mean by OSI? OSI stands for open system interconnection. It is a standard description or a reference model of how message should be conveyed between any two points within a telecommunication network. It is made up of several layers and each layer provides services to the layer above. 15. What is TCP/IP? TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol or Internet protocol. It is used to connect hosts on the internet, by transferring data over the network. 16. What are RJ45 and RJ11 connectors? RJ45 connectors are used for LAN/internet connections while RJ11 connectors are used for Table cable connectors. 17. What do you mean by packaging a Microprocessor? What are the different packaging’s available? The process of packaging a microprocessor to the computer motherboard is known as a microprocessor. The different types of microprocessor’s packaging are PGA SPGA SECC LGA 18. Explain the Cache memory? What is the advantage of a processor having more cache memory? Cache memory is the memory area between Processor and Ram. If the cache memory increases, the speed of the system will also increases. 19. What is over clocking? What are the advantages of over clocking? It is a process where the computer component is forced to run at a higher clock rate. The advantages of over clocking are: Increases the CPU’s performance It is cost-saving Makes PC games and Applications to run faster 20. What is chipset? How is it different from processor and motherboard? Chipset is one of the processing devices in a computer. It is a number of integrated circuits, designed to control how information travels between other components and processor. It is a group of microchip to work as a unit to perform one or more related functions. While motherboard is where all other components like CPU, Memory, Sockets for external connectors and drives are attached. Chipset is a built in feature of Motherboard. While, processor is a main integrated circuit block, which does the function according to the instruction of a computer program. It is based on the logical, arithmetical and input/output of the system. 21. What is heat sink and what is the use in the system? To lower the temperature of a device, a heat sink component is used. It is there on the microprocessor and if it is not functioning well then the computer will shut down automatically. 22. What is Jumper and why you need it? Jumper is a metal bridge that closes an electric circuit. A jumper consists of a plastic plug that fits over a pair of protruding pins. It is used to change the board’s parameters. 23. What are the different types of DRAM? The different types of DRAM are SRAM, VRAM, SGRAM, DDR-SDRAM 24. What might be the problem when you don’t see the display? ► Power related issues ► Heat sink related issues ► CPU fan related issues ► Improper Jumper settings 25. What is SATA? SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment. It is high speed computer bus interface designed to connect the host bus adapters to mass storage devices, such as hard disk drives and optical drives. 26. A Customer running Windows XP (Home Edition) with an Antivirus application installed reports that he has downloaded a program from the internet and installed it in his computer. After installing the program, he started receiving emails from people he never knew. The Customer removed the program from his computer but he is still getting those emails. How would you help this customer? Download the most recent virus signature files and scan his computer for viruses. 27. You are configuring Power Management on your Windows XP Computer. With ACPI, Power Management should be under the exclusive contol of: The Operating System 28. Which file must be located in the root folder of the Active Partition for Dual Booting of Windows XP and Windows ME to boot? Boot.ini 29. A Customer calls and says he is unable to get online. He uses a cable connection to connect to the internet on a Windows XP Computer. You ping 127.0.0.1 on his computer and get the results that All the packets are Lost. What should you do next? Rebuild the TCP/IP Stack in the users computer 30. Very frequently, users in your office put floppy disks in the drives and forget to take them out. This results in boot-up problems and results in support requests. How would you stop this computer from looking in the A: drive for boot files first. Change the Boot Order in BIOS. 31. After Restarting your Windows XP (Professional) computer, your monitor shows a Blank, Blue screen. You remember that a new Video driver was just installed. What would be the best way to fix this problem? Restart the Computer, Keep tapping on the F8 Key to go to the Windows Advanced Options Menu and select the option “Last Known Good Configuration” and hit the key. 32. You need to Dual-Boot a computer with Windows XP and Windows Me. You need all the Partitions to be accesible from both the Operating Systems. Which File System would you use in this scenario? FAT32 33. What is the command to convert a FAT32 file system to NTFS? Would there be any loss of data? The command is: CONVERT : /fs:NTFS. There will be no effect on the data. (Data will be safe).But remember this: if you want to convert NTFS partition back to FAT32, you will have to re-format that partition and select the FAT32 file system. 34. What are the features of the Disk Defragmenter Tool in Windows XP and Windows 2000? Does the Windows XP version have any more features than the Windows 2000 version? The features of the Disk Defragmenter Tool are the same in both Windows XP and Windows 2000. They are: 1. Enhanced Analysis Functionality 2. A Compression option 3. Increased Defragmentation Option and an Automatic Defrag-Scheduling Option. 35. You are a Desktop Support Technician at EQS. One of the customers has just installed a Brand New Printer for himself. This customer calls you after some time and says that every time he tries to print something, all he gets is some garbled text. However, the printer prints the Test Page fine. What do you think is the problem here? The customer has installed an Incorrect Device Driver for the Printer. I would uninstall the driver, from the WIndows Device Manager and install the correct Device Driver for the Printer from the Disk that came with the Printer. (If the Disk is not available, I can still download the correct device driver from the manufacturer’s website) 36. If, upon Booting up a Computer, you see the error message “Keyboard Error…” What do you think could be the problem? It could be that 1. The keyboard is not attached to the PC or 2. The keyboard has failed 37. If you turn on a PC and the boot-up process halts and you get the error message “Non-System Disk or Disk Error…Replace and Press any Key when Ready…” What do you think could be the problem? A non-bootable Floppy Disk is in the Floppy-disk drive and it should be removed. 38. If, upon booting up a PC, you see a message which says “Invalid Drive Configuration..” What do you think is causing this? This problem could be due to any of the following situations: 1. The Hard-Disk cable within the System Unit is not attached to the Controller 2. The Hard Disk Drive has failed 3. The Hard Disk Drive has not been partitioned. 39. If you turn on a PC and the boot process halts and you get the error message ” C:\System32\Config file missing or Corrupt” What is this due to? The Registry Hives are corrupted. They need to be repaired. 40. A Customer complains that he keeps getting the error message “HAL.DLL missing or Corrupt”. Which file needs to be repaired/rebuilt to rectify the issue? BOOT.INI 41. You have Norton 360. When the Firewall is turned on, you are unable to browse the internet. But if you turn off the firewall, you are able to browse. What is the first thing you would do to fix this problem? Reconfigure Norton Firewall to allow Internet Explorer to access the internet. 42. Which utility is used to do a Software Clean Boot? Msconfig 43. What does a “?” sign in device manager signify? The device is not installed. ( You can refer to this article for more details). For more information on Device Manager check this article from Microsoft. 44. What is the command to start Windows System Restore from the Command Line? rstrui.exe 45. What does the term UAC stand for? UAC stands for User Access Control. For more information read this article. 46. You are a Desktop Support Technician. A user calls and complains that till yesterday he was able to view his CD drive in his computer. But today when he turned on his computer, he is not able to view the CD-ROM drive in “My Computer”. What can be done to fix this problem? Open the Windows Registery Editor and Delete the Upper and Lower Filter Keys. 47. A user calls and says that whenever he starts his computer, it boots up only in Safe Mode. There is no other error message. What would you do to fix this problem? Go to Msconfig and select Normal Mode and Restart the Computer. 48. A user complains that whenever he connects any USB 2.0 device to his computer, he gets the error message “USB device not recognized…” What could be the possible reason for this? The USB Port could be faulty. 49. A user complains that he is no longer able to hear any sound from his computer – after he downloaded some updates from the Microsoft Website. What could be the possible reason for this? The Windows Audio Service is Disabled. Enable it. 50. Mark uses Windows XP Professional and is connected to the internet directly through a DSL line. He wants to know how he could enable the filtering of packets and get rid of the harmful incomming data. What would you tell him? Enable the Firewall 51. A Customer reports that his Windows XP Professional portable computer is not able to connect to any network resource and is also not able to authenticate on the network’s Active Directory Domain. The computer was fine yesterday. No other person in the organization is facing this problem. What is the first thing you would do to fix this problem? Ask the user to Right-Click on the Network Connection icon and select “Repair” from the Menu. 52. A customer has recently upgraded from Windows 98 to Windows XP Professional. After the upgrade, it takes longer for Windows, Menus, Sub-Menus and other use interface features to open. She wants them to open faster. How can you help this customer? Use System in Control Panel and select the option “Adjust for Best Performance” in the Performance Options dialogue box. 53. You suspect that your computer is failing because of a Corrupt Master Boot Record. Which utility is the best to fix this problem? Recovery Console (By Using the fixmbr command) 54. You performed a Parallel installation of Windows XP (Home Edition) to resolve certain problems on a Customer’s Computer. After installation, the customer says she can see the previous profile folders in Documents & Settings but when she tries to open then, she gets an “Access Denied” error. What can you do to remove the “Access Denied” Problem? Boot into Safe Mode, Right-Click on the Old Profile Folder, Go to Security – Advanced and give Ownership to the new user. 55. A Customer calls in and says that her copy of Windows XP went corrupt and the previous Technician installed it again without losing any data. Now when the computer boots up, it shows a menu for a few seconds and then it boots normally.She wants to get rid of this menu. You asked her about the menu options and the customer tells you that both the options in the Menu Read the same thing – Windows XP Home. How will you fix this problem so that the Menu does not appear again? Edit the Boot.ini file and set the Timeout as 0 (Zero) or Edit the Boot.ini file and Remove the Second Option and set the Timeout as 0 (Zero) 56. What is BIOS? BIOS stands for Basic Input-Output System and is pronounced as “Bye-Ose“. The BIOS is available on all the computers. It makes sure that all the components of the computer can function together. It has information about all the hardware components in the Computer. BIOS can also be called as a Special Software that interfaces the major hardware components of a computer with the Operating System. It is usually stored in a Flash Memory Chip on the Motherboard. Some functions of BIOS: Performs a POST (Power-On Self Test) for all the different Hardware Components in the System to make sure everything is working properly. Activating other BIOS Chips on different cards installed in the computer, for example, SCSI and Graphics Cards. Provides a set of low-level suiting that the Operating System uses to interface different Hardware devices. BIOS manages things in your computer like the Keyboard, Monitor, Serial and Parallel Ports especially when the computer is Booting up. Manage the settings for Hard-disk drives, System Clock etc. Sequence of things done by the BIOS when you turn on your Computer: Check the CMOS for Custom Settings Load the interrupt Handlers and Device Drivers Initialize Registers and Power Management Perform POST (Power On Self Test) Display System Settings Determine which devices are Bootable Initialize the Bootstrap sequence 57. What are the Hardware Components of a Desktop Computer / Laptop? The Hardware Components of a Desktop Computer / Laptop are as follows: 1. The Processor (CPU) 2. Motherboard 3. RAM (Random Access Memory) 4. Power Supply – SMPS (Switch Mode Power Supply) 5. Hard-disk Drives 6. CD/DVD-ROM Drives 7. Floppy Disk Drive 8. Sound Card 9. Graphics (Display) Card 10. Keyboard 11. Mouse 12. Monitor 58. What are Hard-Disk Partitions? Partitions are used to Divide a Hard-disk drive into smaller segments as required by the user and for better management of the space in it. 59. Difference between RAM and ROM? RAM (Random Access Memory) – is used to temporarily store information that the computer is currently working on. ROM (Read Only Memory) – This is a Permanent type of memory storage used by computers for important data which never changes. (Example: BIOS) 60. What would you check if there is no sound from your computer? (Audio not working) 1. Check for cable connections 2. Check for power to the speakers 3. Check for volume control 4. Check for device drivers 61. If a Customer complains that his computer is working really slow, what are the things you would check? 1. Check if it is taking longer than usual to start up 2. Check if it is slow with one / any particular application or slow overall. 3. Check for Spyware/Malware/Virus in the computer 4. Check the available Hard-Disk Drive Space in the computer. 62. What is the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)? A Blue Screen of Death (or just a Blue Screen Error) is an indication of a Critical System Problem wherein the Computer freezes altogether and does not respond to anything. To rectify this problem, try Restarting the computer or Booting into Safe Mode. For more information, read this. 63. Why are Device Drivers required? A Device Driver (or just Driver) is a piece of software which is requied to run every Hardware Component present in the computer. 64. Name one of the latest Computer Processors (CPU) ? Intel Pentium Quad Core, Intel I3, I5, I7 processors. 65. What is Ping? Ping is a command that checks the connectivity with an IP address. For more read this article 66. What is a Data Cable? A Data Cable is a Thin Plastic band-like cable used to connect the Data-Devices like Hard-disk drives, Floppy Disk Drives, CD/DVD-ROM drives with the motherboard. Data Cables are primarily used for Data Transfer. 67. Lights on a Modem / LAN Card: Generally, there are 04 lights. They indicate the following: 1. Power Light: Shows if the device (Modem)is getting Power Supply or not. 2. Link Light: Indicates if the device is getting broadband/internet signals properly from the ISP 3. Data Light: Indicates wether the internet is working or not. 4. Connectivity Light: Indicates the Modem is connected to a PC or not. 68. Name some of the Ports available in a Computer Some of the commonly available ports in a Computer are as follows: 1. Keyboard & Mouse Ports – Also known as PS/2 ports 2. USB Ports 3. VGA Ports 4. Sound Ports 5. LAN Port – Also known as Ethernet Port 69. What does the term USB stand for? USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It allows devices to be connected or disconnected from a computer without shutting down or restarting the computer. The current version of USB is 2.0 70. What is the difference between CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) and LCD (Flat Screen Monitors)? CRT Monitors: The Monitor has a picture tube and uses a light-gun to highlight pixels on the screen. LCD Monitors: These monitors do not have a picture tube and contain a layer of liquid crystals on an Electronic Board. 71. What is an IP Address? An IP address is a unique numerical identifier of every device on a network. A typical IP address can look like this: 216.27.61.141. To detect a computer’s IP Address, go to Start – Run – Type in CMD in the Run Dialogue Box and click OK or hit – In the Command Prompt Screen that comes up, type in IPCONFIG and hit 72. What is DHCP? DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is used to generate & provide IP addresses to the computers on a network. 73. What is DNS? DNS stands for Domain Name Services – it is used to convert URLs into IP addresses and vice-versa. 74. Mention a sample computer configuration: 1. Intel Pentium Core 2 Duo – 3.0Ghz 2. 2 GB RAM 3. 300GB HDD 4. DVD Writer 5. 17 inches LCD Monitor 6. Keyboard 7. Mouse 75. Name any Five Microsoft Office Applications: 1. MS Word 2. MS Excel 3. MS Powerpoint 4. MS Access 5. MS Outlook 76. What are RJ45 and RJ11 connectors? RJ45 connectors are used for LAN/Ethernet connections and RJ11 connectors are used for Telephone Cable connections. 77. What is a Parallel Windows installation? When the first installation of Windows fails to boot for some reason, another copy of Windows is installed in teh same drive but in a different directory (so that the customer can access to and backup his old data). This is called Parallel Installation of Windows. 78. Name some of the versions of Windows XP. Windows XP Home Edition, Professional, Media Center Edition, Tablet PC Edition, Mobile 79. Difference betwen a WORKGROUP and a DOMAIN? In a Workgroup, all the computers function as Peers. But in a Domain, One computer is the Server and the others are Clients. 80. What is the difference between FAT32 and NTFS file systems? 1. NTFS allows compression and file encryption. FAT32 does not. 2. NTFS is more secure than FAT32 81. What does BOOT.INI do? Boot.ini lists all the Operating Systems present in the computer and provide information about which partitions they are located on. 82. How would you access the Recovery Console in Windows? By booting with the Windows XP CD and following the on-screen instructrions. The Recovery Console can also be installed in your computer. 83. Provide the names of a few Firewalls: Norton, McAfee, Zone Alarm etc 84. What feature of Outlook Express allows multiple customers to send and receive emails, each using a separate account? Identities 85. What are the components needed to setup a Basic Home Network? LAN Cards, LAN Cables, Router/Hub Technical Support Questions and Answers pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Ethernet Compliance Testing at Toradex
Introduction
Toradex offers robust and reliable embedded systems, which are required to work continuously in harsh environments. Ethernet is one of the most important interfaces for the Internet of Things (IoT). We will review some Ethernet standards and show you how Toradex tests for compliance with them.
After looking at the standards, we’ll describe our test configuration, test procedures, and the test results. A Colibri iMX6ULL SoM and Iris Carrier Board were used in this example, but you can use this as a model for testing custom carrier boards if that testing will be part of your verification process.

Why We Use Standards and Do Compliance Testing
Ethernet designs adhere to the IEEE 802.3 standard, which defines the Physical and Data Link layer of the seven-layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. Waveform characteristics are specified in the standard. Designing to this standard allows compatibility and interoperability with other devices, in all kinds of environments all over the world. Otherwise, transmission issues and data losses are likely to occur. Compliance testing ensures that the implementation meets the standard.
In addition to the waveform characteristics specified in the IEEE 802.3 standard, the University of New Hampshire InterOperability Laboratory (UNH-IOL) has provided standard conformance test procedures for those signals.
The documents can be found at these links:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/browse/standards/get-program/page/series?id=68
https://www.iol.unh.edu/
Ethernet Physical Layer Basics
The Ethernet standard is several thousand pages, so we’ll just cover the most important concepts and some key terminology.

Figure 1 OSI Reference Model from IEEE Standard for Ethernet
Let’s start with the physical medium. Signals typically arrive through a twisted pair copper cable to an Ethernet jack with magnetics on our Carrier Board, then continue through impedance matched differential traces on the PCB to the Ethernet PHY IC. This device converts analog signals from the medium to digital signals for the processor and vice versa.
The electrical signals first encounter the Medium Dependent Interface (MDI) of the PHY, a part of the Physical layer. Different physical media have different characteristics. In accordance with the specific kind of the media, the signals are transformed and sent to the next layer of the OSI-model, the Data Link Layer. We provide 10Base-T and 100Base-TX (Fast Ethernet) on our Colibri Modules and 1000Base-T (Gigabit) on the Apalis modules. The standardized interface between the first two OSI-layers is called Media Independent Interface (MII) and is independent of the physical layer.

Meanwhile, we are talking about the advanced backward-compatible Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII) and the next interface for the 10 Gigabit is already named as XGMII. Reduced means that there are fewer signals needed for the same standard. The xMII’s are parallel data buses. There is a supplementary serial bus for management purpose called Management Data Input/Output (MDIO). The xMII interface ends at the Media Access Control (MAC) layer. Here the well-known MAC address is used as a unique identifier. The MAC layer can be integrated with the System on Chip (SoC), like on NXP® processors. But it could be already embedded in the same IC as the PHY, which is better known as an Ethernet Controller. The Ethernet Controller IC, in turn, is connected with the SoC through a separate interface like USB or PCIe. Note that we are not looking at higher OSI layers and protocols like ARP, NDP, IP, TCP, UDP, etc., which are organized in frames and packages, because for all these protocols the electrical characteristics on the first physical levels are the same!
For now, let’s go back to the physical layer. There are 2 main characteristics of the physical link I’d like to expand on, namely, speed and duplex mode. Our modules support speeds up to 1Gbit on Apalis Modules and 100Mbit on Colibri Modules, and both half and full duplex modes. In full duplex mode of operation, PHYs on both ends of the link can communicate with each other simultaneously. For the half duplex mode, where the PHY can’t receive and transmit data at the same time, there need to use the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to avoid collisions and control the data flow.
As already described, our Apalis Modules are capable of Gigabit Ethernet, but how do the communication partners know with which speed they can send the data? An-auto negotiation procedure exists, where the linking partners set the best link trough 16ms link pulses. Please be careful with auto-negotiation settings, as there is a well-known problem of the duplex mismatch, when the linking partners are configured in a fixed way. On the electrical side of the physical layer 10Base-T and 100Base-TX use two twisted pairs while 1000Base-TX uses 4. 100Base-TX is faster than 10Base-T based on the much faster frequency of 62.5 MHz instead of 10 MHz and denser signal modulation scheme (PAM-3). 1000Base-TX uses the same frequency as 100Base-TX, but transmits across 4 twisted pairs and with a higher level of modulation (PAM-5). Finally, there is an additional feature called EEE, Energy Efficient Ethernet. The aim of this standard is to save energy.
https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/application-notes/EE-269.pdf
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duplex_mismatch
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Media-independent_interface
https://www.asix.com.tw/new_alias.php?alias=93&full=http://www.embedded.com/design/202804534
The picture below summarizes the Ethernet possibilities on the Toradex SoM approach:
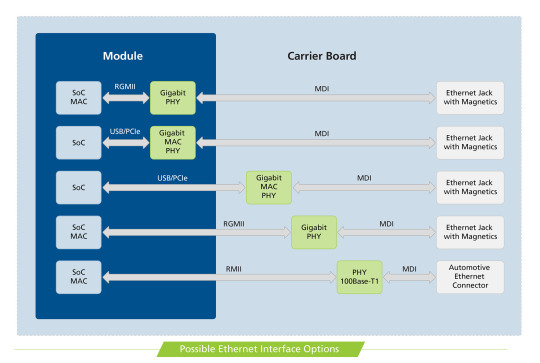
Automotive Ethernet
Before we continue to the Compliance Testing, I want to quickly let you know that I receive a lot of questions about 100Base-T1, better known as Automotive Ethernet. The customers want to know, if it is possible to connect Automotive Ethernet to a fast Ethernet PHY. The 100Base-T1 has a different physical layer specification to fulfill the requirements in a harsher automotive environment. It is not possible to connect it, but the MII is still the same! The solution is to connect the 100Base-T1 PHY to the Multimedia Independent Interface of the SoC directly. Consequently, a Module with an xMII on the Module Edge Connector must be selected! Of course, you have to design your Custom Carrier Board with a 100Base-T1 PHY. Here you can find the list of Toradex Modules which provide an xMII on the edge connector. Please note that this is not a Standard Toradex Interface and the pin assignment varies with each module.
Apalis iMX8
Colibri iMX8X
Colibri iMX7
Colibri iMX6ULL
Colibri Vybrid
Ethernet Compliance Testing for Toradex Systems

Figure 2 10Base-T Test: DOV Internal MAU Normal
After this very short overview, I want to continue with the compliance testing, where we test the electrical signals in time and voltage. The electrical signals look totally different for the 10/100/1000 Mbps and have different requirements as you can see in the oscillograms.
The tests evaluate the voltage amplitudes, jitter values, rise/fall times and other signal characteristics. For each test a defined test signal must be generated by the DUT, e.g. a continuous pseudo-random signal has to be emitted. The easiest way to test the signal requirements is to define a test mask. The signals must not intersect with the mask in order to fulfill the specification. The 10Base-T tests are very often defined through a test mask, as you can see in the first figure. I want to mention some values: The Peak Differential Output Voltage must be between 2.2 V and 2.8 V. The Differential Output Voltage Harmonics must be greater than 27 dB and all Jitter values must be smaller than 22 ns. Very interesting is the twisted-pair model for 10Base-T, which must be used for some compliance tests. With the equivalent circuit based on lumped elements, it is possible to model multiple different transmission elements with just passive components. Depending on the PHY a linking partner is needed for 10Base-T compliance tests. You can download the Test Report of Colibri iMX6ULL as an example, where you can find all tests.

Figure 3 Measured differential random 10Base-T signal without load
The interface characteristics for 100Base-TX are defined in table 2 based on the MLT-3 voltage signals with three levels. The data is encoded before with 4B5B algorithm, so a clock recovery out of the data stream is possible because a level transition is forced. For our test equipment, a pseudo-random test pattern (PRBS7) is enough for all the tests. However, some tests only trigger on defined patterns and measures only at that moment the specific values.
Table 2 Interface Characteristics 100Base-TX Characteristics Min Max Unit UTP DOV Base to Upper/Lower 950 1050 mV Signal Amplitude Symmetry 98 102 % Rise/Fall Time 3 5 ns Rise/Fall Time Symmetry 0 500 ps Duty Cycle Distortion -250 250 ps Transmit Jitter 0 1.4 ns Overshoot 0 5 %

Figure 4 Measured differential random signal 100Base-TX
The test criteria are defined in a similar manner for the 1000Base-T. I am not going to list them. For these tests an additional disturber in the form of an Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG) is needed to create the required disturbing signals with the frequency of 31.25 MHz and 20.833 MHz. In figure 5 you can see the test pattern of test mode 1 produced by the PHY. There are four different test patterns, which can be generated through PHY’s MDIO register settings. Please don’t forget that we have to perform the compliance test four times, because of the four twisted pairs.

Figure 5 Definition of Test Mode 1 Waveform 1000Base-T from IEEE Standard for Ethernet

Figure 6 Measured differential Test Mode 4 Distortion Test 1000Base-T without disturber
We have now seen some of the electrical requirements that must be fulfilled to be compliant with the interface definition. Before we have a closer look at the test equipment, I want to try and solve the most important question of this Blog: How do you generate those test signals?
Each PHY vendor has a custom method to modify the necessary register settings to enter the test modes. That is often not publicly available, and you must ask your PHY vendor. A very good example is Microchip, who has provided all information about Ethernet Compliance in one document since last year. These are the Ethernet PHYs, which we use in our modules, KSZ8041 and KSZ9031. I also want to share a document from TI with you, just as a further example. If you are looking for a new Ethernet PHY and want to do Ethernet Compliance Testing, please ask your vendor for detailed information about the register settings in advance!
http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/AppNotes/AN2686-Ethernet-Compliance-Test-10BASET-100BASETX-1000BASET.pdf
http://www.ti.com/lit/an/snla239a/snla239a.pdf
Test Equipment
As depicted above, we must measure some picoseconds precisely. For that we need very good tooling. You should use an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 1 GHz and memory of 4MS or greater. Usually you need a test fixture, which transforms the Ethernet signals from an Ethernet Jack to the oscilloscope input channels. That is why we work closely with Teledyne LeCroy. We have a great collaboration on a technical level. We use a high-end oscilloscope from the WaveMaster series with appropriate hardware and software tools. Of course, there is equipment from other vendors available like Tektronix, Rhode&Schwarz, Keysight and others.
Quotation from Mr. Hofferbert, specialist at Teledyne LeCroy:
“Teledyne LeCroy is a leading manufacturer of digital storage oscilloscopes (DSO). With modern DSOs it is possible to perform qualification measurements. Toradex uses appropriate equipment from Teledyne LeCroy to test the design of Ethernet PHYs. With the combination of our QualiPHY Software and latest oscilloscopes, a semi-automatic test has been implemented to test the physical level of the Ethernet PHYs according to the IEEE 802.3 specification. This measurement solution allows the development engineers at Toradex to test and resolve issues with signal integrity in an early development stage of their embedded systems. Toradex is very interested in using the measurement equipment as efficiently as possible. If there are any uncertainties or measurement deviation, we work together to quickly solve these issues and provide our expertise in measurement application.” Gregor Hofferbert, Teledyne LeCroy
www.teledynelecroy.com
http://cdn.teledynelecroy.com/files/manuals/qualiphyenetmanual.pdf
Conclusion
After performing a compliance test, we can create a compliance report to verify our PCB design. As you can see in the test report from Teledyne LeCroy, the Colibri iMX6ULL with Iris Carrier Board is compliant with 10Base-T and 100Base-TX standard. So, we are sure that our implementation will work with other compliant systems. We can share with confidence our PCB implementation of the Ethernet Interface with our customers. You can find the Carrier Board Design Guides here: https://developer.toradex.com/carrier-board-design
We also share our Carrier Boards Designs as Altium Designer projects for free with our customers. We provide a lot of help through our community channel as well: https://www.toradex.com/community
We started to implement and provide our testing SW in our latest BSP. We adopt the existing drivers to be easily run with our modules to perform Compliance Tests. But again be careful, for each PHY you need different SW techniques to get the test pattern. There is no simple handbook. For example: https://git.toradex.com/cgit/linux-toradex.git/commit/?h=tegra-next&id=13bd0f089ac6babeb7248fe3db4b9c19233cce3c
But issues can occur with wrong routing, bad ground layout, or inaccurate crystal circuit design. It also depends on the testing environment. Ground loops and noisy or underpowered power supplies can cause measuring errors. It is important to follow the design guides of the PHY vendors. I like the troubleshooting document provided by Intel, that you can use for the first debug consultation. There is a basic overview of failures and possible sources. Designs with too long traces, low quality magnetics or improper use of the measurement equipment can always be the source of failing the compliance test. But there are also specific errors which can be put in a strong correlation. E.g. wrong amplitude values are often caused by wrongly assembled bias resistors or issues with the centre tap circuits. Whereas too high Jitter values are due to crystal issues, impedance mismatch or bad power supply. In general, your Ethernet PHY vendor should be able to help you, probably even with a schematic or layout review.
https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/application-notes/ieee-conformance-phy-app-note.pdf
In this blog, I gave you some insights to one of the many verifications Toradex does to achieve such high-quality products. Internal testing by us and your adherence to our design guides reduces your risk to a minimum. For the highest quality, you can do your verification with your own customized carrier board, and that you follow the system engineering approach (as documented by NASA, for instance) which recommends testing in early stages to reduce risk and cost. I hope I gave you plenty of information to get started. If you need more information feel free to reach out.
#Ethernet Compliance Test#Apalis iMX8#Colibri iMX6Ull#Development Boards#NXP i.MX 8#NXP i.MX 6ULL#System on Module#Computer on Module
0 notes
Text
Juniper Publishers - Open Access Journal of Engineering Technology

Brief Industrial Networks Data Transfer Protocols Characteristics Analysis
Authored by : Vladlen Shapo
Keywords: Industrial networks; Protocols; Tunnelling; Internet; Control Networks
Abbreviations: IoT: Internet of Things; IIoT: Industrial Internet of Things; ACN: Architecture for Control Networks; AYIYA: Anything In Anything; CIP: Common Industrial Protocol; ODVA: Open Device Net Vendors Association; DNP3: Distributed Network Protocol Version 3
Opinion
During last 5-7 years in industry, at the different kinds of transport, in energetic field, etc. are very actively implementing data exchange technologies between separate devices, device groups and networks. These technologies based on Industry 4.0 (4th industrial revolution), IoT (Internet of Things), IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) concepts. In accordance with these concepts a lot of different devices became smart, possessing of own CPUs, memory and different wired and wireless interfaces for external data exchange. Some of them (like complex PLCs) allow to unite different industrial network segments, having sufficient productivity and much lower cost compared to computers [1].
From the beginning of 90th years of 20th century in industry are very popular some protocols and data transfer technologies, most known are ASi, ProfiBus, Field Bus, HART, Mod Bus, CAN, BAC and so on. But in connection with Internet development and forth coming of absolutely new challenges were created some protocols, based on TCP/IP. These protocols allow to perform remote control of complex technical systems for enhancement of control quality, decreasing response time for force majeure situations and cost for control and exploitation of such systems. Protocols ProfiNet, Mod Bus/TCP, Ethernet/IP, Ether CAT became well known; they are compatible with previous generations, but allow to solve fundamentally new tasks. But in some situations by cost/productivity ratio win protocols and technologies, which don't have wide spread, but firmly hold theirs niche. Some of them are described below.
ACN (Architecture for Control Networks) is network control protocol, initially destined for entertainment industry [2]. It has open source code and maintains some subordinate protocols (Table 1).
AYIYA (Anything In Anything) is network protocol for tunnelling between IP-networks and controlling there [3]. Very often it's used for IPv6 packets transit through the networks based on IPv4 protocol. Network security is provided with absence of addresses and content of tunnelled packets falsification possibility. At least one of two tunnel endpoints allows mobile devices connecting.
CIP (Common Industrial Protocol) is the set of standards [4], which are maintained by Open Device Net Vendors Association (ODVA). CIP extensions are CIP safety, CIP Sync and CIP Motion protocols. CIP contains full set of requirements and possibilities for complex automation systems and their subsystems development from following sides: control, information security, motion organizing, informing. Some most important protocols and industrial data transfer technologies are based on CIP as well and briefly described below.
EtherNet/IP is open industry protocol, which uses standard Ethernet chips and cable systems, based also on IEEE 802.3 standard, and serve for input/output real time data exchange and information messages in Device Net and Control Net industrial networks. CIP provides common application level between networks, which doesn't depend on media (cable system). It allows to perform direct routing CIP messages in Ether Net/IP, Control Net and Device Net networks.
Depending on application requirements EtherNet/IP network may be stand alone or combined with Device Net or Control Net networks for additional flexible information and control services realization. EtherNet/IP transfers big user, configuration and input/output data volumes in the same high speed network; tightly associates technological and corporate operations; facilitates technical maintenance expenses decreasing thanks to existing network resources and technical facilities using; allows to commercial and industrial technological levels to coexist in the same network; works with TCP/IP and HTTP protocols.
DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol, version 3) is a set of communication protocols [5], which are used for data transfer between components in automation systems. It's developed for communications between different types of equipment for data acquisition and control and described in IEEE 1815 standard. In SCADA systems DNP3 is used by SCADA master stations (control centers), Remote Terminal Units (RTU) and different Intelligent Electronic Device (IED). It uses 3 levels of OSI model (data link, transport and application) and contains Secure Authentication v5 mechanism, which allows to master or remote DNP3- system uniquely determine, that connection is established with legitimate user or host, but not with malicious user.
HART-IP (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) protocol [6] based on standard Ethernet IEEE 802.3 hardware and cable systems (twisted pair and fiber optics) and with Wi-Fi IEEE 802.11 equipment, that's why it's possible to use it with standard network switches, routers, access points, cables and connectors. It may be used in redundant mesh or ring topologies and with PoE (Power over Ethernet) power supply standard by twisted pair Possible data transfer rates are 10Mbps, 100Mbps and 1Gbps. HART network, including devices working with Wireless HART protocol, is compatible with office and industrial LAN-switches, fiber optics media converters, Wi-Fi access points and equipment. Compatibility with classic HART protocol allows to put corresponding gateways into action and to work with classic analogue 4-20mA technologies. Using IP as base interaction protocol allows HART-IP to work in the same network together with multiplicity of protocols, based on IP and Ethernet (Figure 1).
More than 60 millions devices with HART protocol supporting are installed in the world. HART over Ethernet or HART-IP widen HART accessibility in local internal industrial networks with interconnection with corporate networks and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software.
Variables and diagnostic data in HART are encapsulated in HART-IP packets. It allows to realize real time processes in existing corporate networks and to use corporate VPN (Virtual Private Networks).
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Engineering Technology please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/etoaj/index.php
To read more...Fulltext please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/etoaj/ETOAJ.MS.ID.555561.php
#Engineering Technology open access journals#Juniper Journals Reviews#Juniper publisher journals#Juniper publishers#Open Access Journals#Peer Review Journals
0 notes
Photo

Bảng mạch thế hệ mới của Pyboard nhỏ hơn Raspberry Pi Zero và được tối ưu hóa cho Python
about 150 words - 2 minutes read
Ace-in-the-Hole của Pyboard D là dòng bảng mạch nhỏ, với công suất thấp có bo mạch chạy MicroPython - phiên bản cấp thấp của Python 3.4 được tùy chỉnh để chạy trên các bộ vi điều khiển công suất thấp chỉ với 16KB RAM.
Với dòng D này, Pyboard đã sử dụng MicroPython (tương tự Python) như hệ điều hành chính thay cho Linux.
Pyboard D-Series có kích thước nhỏ hơn cả Raspberry Pi Zero và PocketBeagle. Tuy nhiên, giá của nó cũng cao hơn đáng kể, ở mức £43,80 (~ $58), so với Raspberry Pi Zero W $10 và PocketBeagle $25.
Ace-in-the-Hole của Pyboard D hứa hẹn trong tương lai sẽ hỗ trợ phần mềm tương thích cho Wi-Fi và Bluetooth vốn đã được tích hợp sẵn trên bo mạch.
Source: https://tek.io/2ustFYt
Thông số kỹ thuật:
nguyên bản tiếng Anh để tránh sai sót liên quan tới kỹ thuật
STM32F722IEK microcontroller
216 MHz Cortex M7 CPU with single-precision hardware floating point
512KiB internal flash ROM and 256KiB internal RAM
2MiB external QSPI flash with execute capabilities to extend internal flash
Additional 2MiB external QSPI flash for user filesystem and storage
Integrated, high-performance WiFi and Bluetooth 4.1 (classic and BLE) via Murata 1DX module (with CYW4343)
TCP/IP and Bluetooth stacks run on the main microcontroller, fully customisable
On-board fractal chip antenna for WiFi and Bluetooth
uFL connector for attaching external antenna, selectable via RF switch
Micro USB connector for power and serial communication
Micro SD card slot, supporting standard and high capacity SD cards
Real time clock with highly accurate pre-calibrated external oscillator
Physical electrical connectivity via 24 through holes, and a 40+40 pin mezzanine bus connector
46 independent GPIO, with 24 available via through holes
Additional 11 GPIO shared with SD card, USB, USR button, BT audio
2x I2Cs, 4x UARTs, 3x SPIs, 1x CAN interfaces
3x 12-bit analog to digital converters (ADC), available on 16 independent pins
2x 12-bit digital to analog converters (DAC), available on 2 independent pins
1x 3-colour RGB LED
1 reset and 1 user button
On-board 3.3V LDO voltage regulator to supply main microcontroller
Additional, user switchable, on-board 3.3V LDO voltage regulator to power SD card and external components
Dimensions: 33.5mm x 23.8mm
2 mounting points
Custom DFU bootloader for easy upgrading of firmware
0 notes
Text
Mainframe Integration: Use an Event Mesh to Extract Real-Time Events From Systems of Record
Mainframe technology is still considered a powerhouse when it comes to Systems of Record (SoR) and bulk data processing like statistics and transaction processing, but as peripheral systems are moving away from mainframe, real-time integration is becoming more important.
Hybrid cloud, microservices, reducing high capital investment, the need for cloud scale, etc. are accelerating the migration of systems out of the mainframe. CIOs and CTOs are realizing that incremental modernization will need a coexistence strategy with mainframe. Systems like statement generation are being moved out, but still require real-time integration with mainframe.
The Challenges of Mainframe SoR, SoE, and SoI Integration
Organizations continue to run a lot of critical workloads, especially Systems of Record on z/OS-based mainframe technology. When it comes to high-speed transaction processing, mainframes simply have no competition in terms of speed, the volume of transactions they can handle, and cost-effectiveness. That’s why banks still lean on mainframes for their core operations. Many customer interactions, such as credit card and ATM transactions, are carried out through high volume, real-time, online transaction processing (OLTP).
Engagement between companies and their customers continues to become a major component of the customer experience. While data about customers is useful, data about their engagement with a company adds a whole new layer. Organizations invest in Systems of Engagement (SoE) to manage this – to facilitate the customer journey across multiple touch points and providing a seamless experience. SoE workloads are generally highly parallel, with each individual interaction being of low value.
Systems of Engagement must interact in real-time with Systems of Record (SoR), which act as the source of truth and as custodians of critical business data. SoR are mostly transactional, highly stateful, and demand absolute consistency and transactional integrity, regardless of the value of an individual transaction. The state of an airline seat, for example, must be exact and must show consistency for every querying entity.
Systems of Intelligence (SoI) complete the picture by performance tracking and predictions based on artificial intelligence (AI). Organizations generally want to avoid converting the SoR where possible, but still need to be able to extract real-time events from the SoR for building the inference engines and to develop analytics and artificial intelligence models. Machine learning is often used to train and improve the models.
Architecturally, collection and aggregation interfaces have always been a problem in software design. In the case of SoE and SoR, one must interface front-end SoE (a highly variable and unpredictable event stream) to back-end SoR (originally architected for a more deterministic and serialized environment). Tight coupling between the two layers nullifies the benefits of nimbleness and agility that SoE offers.
An Event Mesh Facilitates Integration
An event mesh facilitates the integration between mainframe SoR, SoE, and SoI – creating a highly scalable and distributed architecture. The loosely coupled approach supported by the event mesh solves the ‘impedance mismatch’ across the layers.
An event mesh is a configurable and dynamic infrastructure layer for distributing events among decoupled applications, cloud services and devices. It enables event communications to be governed, flexible, reliable, and fast. An event mesh is created and enabled through a network of interconnected event brokers.
In other words, an event mesh is an architecture layer that allows events from one application to be dynamically routed and received by any other application no matter where these applications are deployed (no cloud, private cloud, public cloud). This layer is composed of a network of event brokers.
The generic capabilities of an event mesh include:
A network of interconnected event brokers that can be deployed in any cloud, PaaS, or non-cloud environment.
Dynamic distribution of events so that event consumers can receive events from any event producer, no matter where the producer and consumer are attached to the mesh, without the need for configuration of event routing
z/OS Mainframe Integration Options
z/OS provides a few options mainframe technology integration with external systems. In the section below, some of the commonly used patterns are listed. These include:
CICS SOAP/JSON WebServices
ESB/Adapter
z/OS Connect
z/OS with Event Mesh
CICS SOAP/JSON WebServices
CICS supports integration of applications using web services and offers two approaches: rapid deployment using an opinionated approach with least amount of programming or a flexible model using code to customize the web service application. Either way, application programs running in CICS can participate in a heterogeneous web services environment as service requesters, service providers, or both. This model also supports CICS as a JSON server, with the limitation of only supporting POST method.
CICS support for SOAP Webservices conforms to open standards, including SOAP 1.1 & 1.2, HTTP 1.1, WSDL 1.1 and 2.0 and JSON. These capabilities have been available since CICS v3.1 and have been continuously enhanced.
Support of open protocols allows CICS WebServices to be seamlessly connected to the event mesh without a need for a third-party adapter.
ESB/Adapter
Traditional enterprise service bus (ESB) technology will integrate with z/OS by leveraging an adapter. At a very minimum, apart from transport level integration, the adapter is required to do character-set translation as well as convert from mainframe COBOL message structures. Mainframe are big-endian systems and use EBCDIC character sets. This contrasts with little-endian Intel-based systems running ASCII and UTF-8. There is also a need to do message transformation.
The message structures in COMMAREA used by CICS programs are in COBOL COPYBOOK formats, and this must be converted to an open message format like XML or JSON. This implies that the adapter is tightly coupled with the z/OS program and any change in copybook needs to be done simultaneously on z/OS and the ESB adapter.
The transport between the Adapter and the z/OS is either an MQ Channel or raw TCP/IP.
In this approach, mainframe still uses a proprietary connector, and open protocol is available from the ESB/Adapter. In this model, the connectivity to the event mesh leverages the adapter.
While all leading integration products have these adapters, modern enterprises are now moving towards leveraging the native WebServices/JSON support available natively on the mainframes. This further reduces the reliance on ESBs and accelerates the journey to microservices.
z/OS Connect
z/OS Connect is IBM’s premiere technology for implementing JSON Services and APIs in CICS. z/OS Connect is the entry level low-cost option, and z/OS Connect EE is a separate IBM product and offers a richer RESTful API support.
z/OS Connect EE provides a RESTful API interface to z/OS with a security model, the ability to map the request to the backend data requirements, and data transformation.
Support of open protocol allows z/OS Connect to be seamlessly connected to the event mesh.
z/OS with Event Mesh
Based on the above mainframe integration approaches, CICS programs on z/OS can be connected to the event mesh using REST. Since the patterns use open protocols, there is no need for additional connector frameworks; Solace can natively connect to it. The three options are shown in a single picture below. Note that while the ESB/Adapter approach is being considered, availability of WebServices should allow you to integrate without ESB as well.
The Security Layer for Mainframe Integration
Any conversation about mainframe integration with the mesh will arrive at the topic of security. Here we will provide with a few basics about the security layer that is enforced in Solace, apart from the additional controls in the z layer.
Encryption
Solace makes use of TLS 1.2 to provide transport level security between Solace PubSub+ Event Broker and the mainframe.
Authentication
Solace API can be used to use a client certificate authentication by providing valid X509v3 certificates. It also supports basic authentication by authenticating with a username and a password. These credentials can be validated against Internal user repository, corporate LDAP server or an external RADIUS server. While OAuth (typically useful for connecting third party applications ) is not supported, consuming data APIs require system-to-system authentication, and not end-user authentication.
Authorization
You can use the ACL profile and topic-to-queue mapping to define which API is invoked by any of the clients (using either RESTful or messaging APIs) and which will be authorized and dispatched to the mainframe. The administrator can also be used to define a set of IP addresses/subnets from where connection is allowed or disallowed.
Solace supports wildcards while granting access, greatly simplifying the administration. Instead of defining every API separately, the taxonomy can be used to allow permissions at a broad subtree level.
IBM’s REST implementation requires several custom HTTP headers, and Solace PubSub+ will forward the headers sent by the microservices so that the CICS program can function correctly.
A Solace PubSub+ Event Broker acts as the gateway to connect to z/OS, allowing the synchronous REST request/reply mechanism to be event-enabled and to reach across the mesh.
Summary
In summary, Solace eases mainframe integration by bringing it onto an event mesh. By doing so, the mainframe SoR and the distributed SoE and SoI layers can become totally integrated into an end-to-end, real-time, event-enabled architecture using open standards and simple, widely understood protocols.
In turn, this means that the visualization of events and the tracking (lineage) of the data that make up the event is fully transparent and more available for audit, analysis, and sharing with other systems. A further benefit is that the development and management of end-to-end events is made simpler through tools such as the Solace PubSub+ Event Portal.
The post Mainframe Integration: Use an Event Mesh to Extract Real-Time Events From Systems of Record appeared first on Solace.
Mainframe Integration: Use an Event Mesh to Extract Real-Time Events From Systems of Record published first on https://jiohow.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
HWg-PWR3/12/25 – Cổng giao tiếp Ethernet – HW Group Việt Nam
INO Measure Co., Ltd có khả năng tư vấn mua sắm, sử dụng, lắp đặt và cung cấp các thiết bị đo lường và tự động hoá. Nếu bạn có nhu cầu mua sắm hoặc cần sự hỗ trợ về kỹ thuật cho một thiết bị không được liệt kê ở đây, xin vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi.
Vui lòng liên hệ với chúng tôi– chúng tôi sẽ liên hệ lại với khách hàng bằng điện thoại hoặc email.
Lưu ý: Tham khảo ý kiến của nhân viên INO sẽ giúp bạn tiết kiệm được thời gian và chi phí khi cần mua sắm. Với sự tư vấn của chúng tôi, bạn sẽ không gặp khó khăn khi tìm hiểu về đặc tính của sản phẩm cần mua.
Features:
Connects 3 / 12 / 25 external meters equipped with the M-Bus (EN 13757-2) interface, can log 170.000 values (3 values every 15 minutes = 590 days).
Converts the consumption (e.g. from [kWh] to a currency) without a need for computer or additional software.
M2M communication protocols Modbus/TCP, SNMP and XML allow integration into more complex monitoring systems.
Connected via LAN. Configuration via built-in web server.
Sends an energy consumption report for user specified period as an e-mail attachment.
Connected meter failure or out of specified range value sends an alert by e-mail, SMS or SNMP Trap.
For Ring or SMS alarm use the HWg-Trigger software (external GSM modem required), or a HWg-SMS-GW3 gateway in the same LAN.
With the HWg-PDMS software, logged data can be exported to MS Excel.
Compatible with a range of third party SW (SCADA etc.). Examples for programmers on using the product are available in the HWg-SDK (Borland C++, MS Visual, VB, C#, PHP, JAVA and more).
List of supported (tested) accessories/meters
Applications and usage:
Remote monitoring of electricity meters in small server rooms and BTS
Monitoring of energy consumption in rented premises
Reading out energy consumption in remote or inaccessible areas
Control over energy costs
Checking for individual line overloads in three-phase wirings
Checking for undervoltage in electric wirings
Monitoring the flow of liquids
HWg-PWR 3/12/25 monitors energy consumption using standard external energy meters produced by well-known manufacturers. It is possible to mix electricity meters, water meters, gas meters etc. by different manufacturers. Depending on version, HWg-PWR supports 3, 12 or 25 external meters with the M-Bus interface (EN 13757).
HWg-PWR 3 / 12 / 25 – Energy monitoring gateway:
Sends an alarm in the event of failure or value out of a specified range (E-mail, SNMP Trap, SMS)
Logs selected values (displays graphs over the WEB interface)
8x Digital Inputs for detecting single-phase 110/230VAC outage
Converts the consumption (e.g. from [kWh] to [€]) without a computer or additional software
Periodically sends an energy consumption report for the given period as an e-mail attachment
Actively uploads data to a “portal” using the HWg-Push protocol
Advantages of using third-party M-Bus meters
Vast range of meters with the EN 13757 (M-Bus) interface to choose from. It is easy to use special-purpose meters (non-standard form factor or measured range, e.g. indirect electricity meters rated up to 1000 A).
M-Bus meters frequently provide extended information (total consumption and immediate values, voltage at different phases, power factor, etc…).
Values from certified meters can be used for billing purposes.
► Các câu hỏi, thắc mắc, thông tin liên quan đến sản phẩm từ khâu mua sắm, lựa chọn, sử dụng, cài đặt hay thay thế, vui lòng liên hệ với INO team để được hỗ trợ và tư vấn kịp thời.
► Công ty Giải pháp và Công nghệ Đo lường INO, nhà cung cấp các thiết bị đo lường và tự động hóa công nghiệp
►Web: www.ino.com.vn | Mail: [email protected]
►Tel: 028 73000184 | Hotline: 0917 496 446
►Website: http://www.ino.com.vn
Model tương tự:
Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Poseidon2 3266 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Poseidon2 3268 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Poseidon2 3468 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Poseidon2 4002 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Damocles2 1208 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Damocles2 2404 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam Damocles2 MINI Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-STE Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-STE plus Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam STE2 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-Ares 10 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-Ares 12 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-Ares14 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-PWR3/12/25 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam IP WatchDog2 Industrial Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam IP WatchDog2 Lite Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam HWg-WLD Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam I/O Controller 2 Cổng giao tiếp HW Group Việt Nam IP Relay HWg-ER02b
Calibrator http://www.calibrator.vn/hw-group/hwg-pwr3-12-25-cong-giao-tiep-ethernet-hw-group-viet-nam/
0 notes
Text
CIST 1122 Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Answers
Follow Below Link to Download Tutorial
https://homeworklance.com/downloads/cist-1122-hardware-installation-maintenance-final-exam-answers/
For More Information Visit Our Website ( https://homeworklance.com/ )
Email us At: [email protected] or [email protected]
1. A HDMI cable is generally used for what computer functions?
2. Where does one go to verify correct hardware settings in a system?
3. What connectors from a power supply should be used with a graphics expansion card?
4. What MUST be performed when installing a Video card for use?
5. What expansion slots is characterized by having an x16 speed?
6. What types of Ethernet should be used if a technician has no choice but to run cable along fluorescent lighting arrays in a suspended ceiling?
7. What laptop accessories would MOST likely be used to support multiple expansion ports?
8. What connector types is used on a CAT5 cable?
9. What can be implemented on a WAP to ensure that only certain client machines can access it?
10. Secure web traffic uses what port?
11. What features can be configured with keyboards to assist users with disabilities?
12. What features makes logical processor cores appear as physical cores to the operating system?
13. What storage media would be used to build a cost-effective RAID 5 array?
14. A network consisting of numerous geographically dispersed networks that cover a large physical distance is referred to as a ______.
15. What connections has 9-pins?
16. What wireless standards is backwards compatible with 802.11g?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
17. A technician needs to make several patch cables. What tools would the technician use to attach the RJ-45 ends to the cables?
18. What is the standard loopback address for IPv4?
19. What will provide the BEST protection against power failures and data loss?
20. What is a benefit of using ECC memory?
21. What are components of an “active” CPU cooling solution?
22. What features of a CPU socket is designed to make installation of a CPU easier?
23. What ports are commonly used to send/receive email?
24. What is an example of an IPv4 address?
25. What expansion slots can ONLY be found on a desktop computer?
26. A standard Internet mail account receives incoming messages on what ports?
27. What network devices would be MOST likely to perform Network Address Translation (NAT)?
28. What is MOST likely needed when installing a new POS thermal printer?
29. What network type’s BEST represents a network centered a city?
30. What is LEAST likely to be considered a consumer replaceable part in a laptop?
31. What is the speed limitation for CAT3 wiring?
32. What provides the LEAST network security?
33. What RAM types are compatible with PC2700 and maintain the same performance?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
34. What media types is LEAST likely to be affected by electromagnetic interference?
35. A DVI-D cable is generally used for what computer functions?
36. What PC expansion cards need to be installed so you can have hard drive performance and redundancy?
37. What is the FIRST component to transfer heat away from a processor?
38. What BEST describes the function of DNS?
39. What printers is required when carbon paper is used?
40. A technician is looking to install a 3.5 inch desktop hard drive into an external enclosure. What input interfaces would provide the fastest speed for the drive?
41. What encryption methods is considered easily broken and should be avoided when configuring wireless security?
42. What cable types has a MAXIMUM transmission rate of 100 Mb?
43. A user on a wireless network has the IP address 169.254.155.2 but cannot connect to the Internet. What should the user check on the wireless router?
44. What types of RAM is used with the current i-Series CPUs?
45. Where does one go to verify correct hardware settings in a system?
46. What types of RAM can be used in a dual channel configuration?
47. What is representative of a public class B address type?
48. What memory form factors is MOST commonly found in laptops?
49. What describes the port with 3 rows and 15 pins?
50. What BEST describes the function of DNS?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
51. What devices transmits data to only certain ports?
52. What connectors is used to connect a DSL modem to a wall outlet?
53. When unable to get an IP address from a server, what represents an APIPA address that a PC might receive?
54. What expansion slots would support the HIGHEST transfer speeds for high-end graphics cards today?
55. What media types is MOST likely to be affected by electromagnetic interference?
56. What cable types has the MAXIMUM transfer rate of 100Mbps?
57. What is referred to as the Hardware address?
58. What settings when used, is MOST likely to result in an IP address conflict on a local network?
59. What is the default subnet mask for a Class B address?
60. What encryption types is the LEAST secure?
61. A technician has just installed two memory modules on a motherboard that supports DDR3 RAM with the bus speed up to 1600 MHz. The specifications of memory are DDR3 1333 MHz for one module and DDR3 1666MHz for another. On What bus speeds will the system function?
62. The helpdesk technician has been tasked to reinstall the OS on a desktop and has already inserted the OS install disk in the CD-ROM. What would MOST likely need to be configured within the BIOS to continue reinstalling the OS?
63. What devices transmits data to only certain ports?
64. What voltages is MOST likely to be supplied from a PC power supply unit? .
65. What network types BEST represents a network centered on one individual?
66. What cable types uses a 4-wire connector?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
67. What connection types has the LONGEST transmission limitation in terms of distance?
68. What is the MAXIMUM transfer speed of USB 3.0?
69. Basic web traffic uses what port?
70. What printer types needs to have ink cartridge replaced as part of the normal maintenance cycle?
71. What printers is required when carbon paper is used?
72. Why type of protocol is “connectionless”?
73. What should be considered when building a standard PC?
74. What connectors would terminate a POTS connection?
75. What connection types is MOST likely to be used to connect an internal hard drive to a computer?
76. What allows a user to use an operating system inside an operating system?
77. What devices converts digital signals to analog ones?
78. What should a technician configure to limit access to a small office home office (SOHO) wireless network by the computer’s NIC hardware identification?
79. What level of the OSI model does TCP and UDP operate at?
80. A customer states that since the new firewall has been installed, the customer has not been able to send webmail. What ports on the firewall should be checked?
0 notes
Text
CIST 1122 Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Answers
Follow Below Link to Download Tutorial
https://homeworklance.com/downloads/cist-1122-hardware-installation-maintenance-final-exam-answers/
For More Information Visit Our Website ( https://homeworklance.com/ )
Email us At: [email protected] or [email protected]
1. A HDMI cable is generally used for what computer functions?
2. Where does one go to verify correct hardware settings in a system?
3. What connectors from a power supply should be used with a graphics expansion card?
4. What MUST be performed when installing a Video card for use?
5. What expansion slots is characterized by having an x16 speed?
6. What types of Ethernet should be used if a technician has no choice but to run cable along fluorescent lighting arrays in a suspended ceiling?
7. What laptop accessories would MOST likely be used to support multiple expansion ports?
8. What connector types is used on a CAT5 cable?
9. What can be implemented on a WAP to ensure that only certain client machines can access it?
10. Secure web traffic uses what port?
11. What features can be configured with keyboards to assist users with disabilities?
12. What features makes logical processor cores appear as physical cores to the operating system?
13. What storage media would be used to build a cost-effective RAID 5 array?
14. A network consisting of numerous geographically dispersed networks that cover a large physical distance is referred to as a ______.
15. What connections has 9-pins?
16. What wireless standards is backwards compatible with 802.11g?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
17. A technician needs to make several patch cables. What tools would the technician use to attach the RJ-45 ends to the cables?
18. What is the standard loopback address for IPv4?
19. What will provide the BEST protection against power failures and data loss?
20. What is a benefit of using ECC memory?
21. What are components of an “active” CPU cooling solution?
22. What features of a CPU socket is designed to make installation of a CPU easier?
23. What ports are commonly used to send/receive email?
24. What is an example of an IPv4 address?
25. What expansion slots can ONLY be found on a desktop computer?
26. A standard Internet mail account receives incoming messages on what ports?
27. What network devices would be MOST likely to perform Network Address Translation (NAT)?
28. What is MOST likely needed when installing a new POS thermal printer?
29. What network type’s BEST represents a network centered a city?
30. What is LEAST likely to be considered a consumer replaceable part in a laptop?
31. What is the speed limitation for CAT3 wiring?
32. What provides the LEAST network security?
33. What RAM types are compatible with PC2700 and maintain the same performance?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
34. What media types is LEAST likely to be affected by electromagnetic interference?
35. A DVI-D cable is generally used for what computer functions?
36. What PC expansion cards need to be installed so you can have hard drive performance and redundancy?
37. What is the FIRST component to transfer heat away from a processor?
38. What BEST describes the function of DNS?
39. What printers is required when carbon paper is used?
40. A technician is looking to install a 3.5 inch desktop hard drive into an external enclosure. What input interfaces would provide the fastest speed for the drive?
41. What encryption methods is considered easily broken and should be avoided when configuring wireless security?
42. What cable types has a MAXIMUM transmission rate of 100 Mb?
43. A user on a wireless network has the IP address 169.254.155.2 but cannot connect to the Internet. What should the user check on the wireless router?
44. What types of RAM is used with the current i-Series CPUs?
45. Where does one go to verify correct hardware settings in a system?
46. What types of RAM can be used in a dual channel configuration?
47. What is representative of a public class B address type?
48. What memory form factors is MOST commonly found in laptops?
49. What describes the port with 3 rows and 15 pins?
50. What BEST describes the function of DNS?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
51. What devices transmits data to only certain ports?
52. What connectors is used to connect a DSL modem to a wall outlet?
53. When unable to get an IP address from a server, what represents an APIPA address that a PC might receive?
54. What expansion slots would support the HIGHEST transfer speeds for high-end graphics cards today?
55. What media types is MOST likely to be affected by electromagnetic interference?
56. What cable types has the MAXIMUM transfer rate of 100Mbps?
57. What is referred to as the Hardware address?
58. What settings when used, is MOST likely to result in an IP address conflict on a local network?
59. What is the default subnet mask for a Class B address?
60. What encryption types is the LEAST secure?
61. A technician has just installed two memory modules on a motherboard that supports DDR3 RAM with the bus speed up to 1600 MHz. The specifications of memory are DDR3 1333 MHz for one module and DDR3 1666MHz for another. On What bus speeds will the system function?
62. The helpdesk technician has been tasked to reinstall the OS on a desktop and has already inserted the OS install disk in the CD-ROM. What would MOST likely need to be configured within the BIOS to continue reinstalling the OS?
63. What devices transmits data to only certain ports?
64. What voltages is MOST likely to be supplied from a PC power supply unit? .
65. What network types BEST represents a network centered on one individual?
66. What cable types uses a 4-wire connector?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
67. What connection types has the LONGEST transmission limitation in terms of distance?
68. What is the MAXIMUM transfer speed of USB 3.0?
69. Basic web traffic uses what port?
70. What printer types needs to have ink cartridge replaced as part of the normal maintenance cycle?
71. What printers is required when carbon paper is used?
72. Why type of protocol is “connectionless”?
73. What should be considered when building a standard PC?
74. What connectors would terminate a POTS connection?
75. What connection types is MOST likely to be used to connect an internal hard drive to a computer?
76. What allows a user to use an operating system inside an operating system?
77. What devices converts digital signals to analog ones?
78. What should a technician configure to limit access to a small office home office (SOHO) wireless network by the computer’s NIC hardware identification?
79. What level of the OSI model does TCP and UDP operate at?
80. A customer states that since the new firewall has been installed, the customer has not been able to send webmail. What ports on the firewall should be checked?
0 notes
Text
Topic 2 : IP Subnetting, Lecture 4. (Summary)
IP Address .
Its a logical numeric address that allows to input in every devices such as computer,printer,switch and router.
Not only that ,devices that part of TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) also can be used but must be in accurate/suitable network.
IP address made up of 32 binary bits.
divisible into a network portion and host portion with the help of a subnet mask.
IP address can be group with,
1) OSI Model in Network Layer..
2) TCP ( transmission control protocol) / IP (Internet addressing) which located in the Internet Layer.

Figure 1 : This is the Binary octets convert to decimal.
They are different types of IP classes , they are :
Class A- the first octet in the network portion and can be used network for 16,777,214 hosts.
Class B - Second octets in the network portion,and the network can bu used 256 or 65534 hosts.
Class C - third octets in the network portion,this 4 octet only for subnets and hosts .this network are suitable that are lower than 254 hosts.
side-note : we only used class c, because this where private company usually used.
Network mass
can aid to identify which portion belongs to the address of the network and the host.
default mass for,
class A : 255.0.0.0
class B : 255.255.0.0
class C : 255.255.255.0

Things need to understand :
bits set to 1 refer to Network ID. bits set to 0 refer to Host ID.
Subnetworks
1.) also known as subnets that is visible subdivision for IP network .
2.) subnetting is dividing a network into 2 or more.
3.) for example : subnetting can make different kinds of logical networks that exist with a single class A, class B and class C.
4.) network must have unique network ID, so every computer can be link in the same network.
5.) If we break this class A ,class B, class C into smaller subnetworks, this can create “Network of interconnecting subnetworks”
purpose of using Subnet masks
Perhaps the most recognizable aspect of subnetting is the subnet mask. Like IP addresses, a subnet mask contains four bytes (32 bits) and is often written using the same "dotted-decimal" notation.
For example, a very common subnet mask in its binary representation
11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
is typically shown in the equivalent, more readable form
255.255.255.0

Side note :
more hosts bits use for subnet masks = more subnets available
more subnet available = less host addresses available per subnet.
VLSM ( Variable Length Subnet Masks).
1.) all subnet mask will be applied in all subnets.
2.) each subnet have same number that are available for host addresses.
3.) able to use any different masks for each subnet.
4.) able the network to segment an IP address space into subnets with different sizes.
5.) breaking down of IP addresses into subnets (multiple levels) and allocating it according to the individual need on a network.

Figure 1 : Identify which one is network Address and Host Address.
How to calculate VLSM.

side note* remember the cram table.
http://www.orbit-computer-solutions.com/variable-length-subnet-mask-vlsm/
references :
Techopedia.com. (2017). 8 Steps to Understanding IP Subnetting. [online] Available at: https://www.techopedia.com/6/28587/internet/8-steps-to-understanding-ip-subnetting [Accessed 26 Apr. 2017].
#http://www.scit.wlv.ac.uk/~in8297/tools/vlsmCalculator.html
Mohan (2015). Subnetting (FLSM & VLSM) with examples. [online] Slideshare.net. Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/krishnamohanssm/subnetting-44041244 [Accessed 26 Apr. 2017].
orbit-computer-solutions.com. (2015). What is VLSM ? Explained with Examples. [online] Available at: http://www.orbit-computer-solutions.com/variable-length-subnet-mask-vlsm/ [Accessed 26 Apr. 2017].
0 notes
Text
CIST 1122 Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Answers
Follow Below Link to Download Tutorial
https://homeworklance.com/downloads/cist-1122-hardware-installation-maintenance-final-exam-answers/
For More Information Visit Our Website ( https://homeworklance.com/ )
Email us At: [email protected] or [email protected]
1. A HDMI cable is generally used for what computer functions?
2. Where does one go to verify correct hardware settings in a system?
3. What connectors from a power supply should be used with a graphics expansion card?
4. What MUST be performed when installing a Video card for use?
5. What expansion slots is characterized by having an x16 speed?
6. What types of Ethernet should be used if a technician has no choice but to run cable along fluorescent lighting arrays in a suspended ceiling?
7. What laptop accessories would MOST likely be used to support multiple expansion ports?
8. What connector types is used on a CAT5 cable?
9. What can be implemented on a WAP to ensure that only certain client machines can access it?
10. Secure web traffic uses what port?
11. What features can be configured with keyboards to assist users with disabilities?
12. What features makes logical processor cores appear as physical cores to the operating system?
13. What storage media would be used to build a cost-effective RAID 5 array?
14. A network consisting of numerous geographically dispersed networks that cover a large physical distance is referred to as a ______.
15. What connections has 9-pins?
16. What wireless standards is backwards compatible with 802.11g?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
17. A technician needs to make several patch cables. What tools would the technician use to attach the RJ-45 ends to the cables?
18. What is the standard loopback address for IPv4?
19. What will provide the BEST protection against power failures and data loss?
20. What is a benefit of using ECC memory?
21. What are components of an “active” CPU cooling solution?
22. What features of a CPU socket is designed to make installation of a CPU easier?
23. What ports are commonly used to send/receive email?
24. What is an example of an IPv4 address?
25. What expansion slots can ONLY be found on a desktop computer?
26. A standard Internet mail account receives incoming messages on what ports?
27. What network devices would be MOST likely to perform Network Address Translation (NAT)?
28. What is MOST likely needed when installing a new POS thermal printer?
29. What network type’s BEST represents a network centered a city?
30. What is LEAST likely to be considered a consumer replaceable part in a laptop?
31. What is the speed limitation for CAT3 wiring?
32. What provides the LEAST network security?
33. What RAM types are compatible with PC2700 and maintain the same performance?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
34. What media types is LEAST likely to be affected by electromagnetic interference?
35. A DVI-D cable is generally used for what computer functions?
36. What PC expansion cards need to be installed so you can have hard drive performance and redundancy?
37. What is the FIRST component to transfer heat away from a processor?
38. What BEST describes the function of DNS?
39. What printers is required when carbon paper is used?
40. A technician is looking to install a 3.5 inch desktop hard drive into an external enclosure. What input interfaces would provide the fastest speed for the drive?
41. What encryption methods is considered easily broken and should be avoided when configuring wireless security?
42. What cable types has a MAXIMUM transmission rate of 100 Mb?
43. A user on a wireless network has the IP address 169.254.155.2 but cannot connect to the Internet. What should the user check on the wireless router?
44. What types of RAM is used with the current i-Series CPUs?
45. Where does one go to verify correct hardware settings in a system?
46. What types of RAM can be used in a dual channel configuration?
47. What is representative of a public class B address type?
48. What memory form factors is MOST commonly found in laptops?
49. What describes the port with 3 rows and 15 pins?
50. What BEST describes the function of DNS?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
51. What devices transmits data to only certain ports?
52. What connectors is used to connect a DSL modem to a wall outlet?
53. When unable to get an IP address from a server, what represents an APIPA address that a PC might receive?
54. What expansion slots would support the HIGHEST transfer speeds for high-end graphics cards today?
55. What media types is MOST likely to be affected by electromagnetic interference?
56. What cable types has the MAXIMUM transfer rate of 100Mbps?
57. What is referred to as the Hardware address?
58. What settings when used, is MOST likely to result in an IP address conflict on a local network?
59. What is the default subnet mask for a Class B address?
60. What encryption types is the LEAST secure?
61. A technician has just installed two memory modules on a motherboard that supports DDR3 RAM with the bus speed up to 1600 MHz. The specifications of memory are DDR3 1333 MHz for one module and DDR3 1666MHz for another. On What bus speeds will the system function?
62. The helpdesk technician has been tasked to reinstall the OS on a desktop and has already inserted the OS install disk in the CD-ROM. What would MOST likely need to be configured within the BIOS to continue reinstalling the OS?
63. What devices transmits data to only certain ports?
64. What voltages is MOST likely to be supplied from a PC power supply unit? .
65. What network types BEST represents a network centered on one individual?
66. What cable types uses a 4-wire connector?
Hardware Installation & Maintenance Final Exam Study Guide
67. What connection types has the LONGEST transmission limitation in terms of distance?
68. What is the MAXIMUM transfer speed of USB 3.0?
69. Basic web traffic uses what port?
70. What printer types needs to have ink cartridge replaced as part of the normal maintenance cycle?
71. What printers is required when carbon paper is used?
72. Why type of protocol is “connectionless”?
73. What should be considered when building a standard PC?
74. What connectors would terminate a POTS connection?
75. What connection types is MOST likely to be used to connect an internal hard drive to a computer?
76. What allows a user to use an operating system inside an operating system?
77. What devices converts digital signals to analog ones?
78. What should a technician configure to limit access to a small office home office (SOHO) wireless network by the computer’s NIC hardware identification?
79. What level of the OSI model does TCP and UDP operate at?
80. A customer states that since the new firewall has been installed, the customer has not been able to send webmail. What ports on the firewall should be checked?
0 notes
Text
Mainframe Integration: Use an Event Mesh to Extract Real-Time Events From Systems of Record
Mainframe technology is still considered a powerhouse when it comes to Systems of Record (SoR) and bulk data processing like statistics and transaction processing, but as peripheral systems are moving away from mainframe, real-time integration is becoming more important.
Hybrid cloud, microservices, reducing high capital investment, the need for cloud scale, etc. are accelerating the migration of systems out of the mainframe. CIOs and CTOs are realizing that incremental modernization will need a coexistence strategy with mainframe. Systems like statement generation are being moved out, but still require real-time integration with mainframe.
The Challenges of Mainframe SoR, SoE, and SoI Integration
Organizations continue to run a lot of critical workloads, especially Systems of Record on z/OS-based mainframe technology. When it comes to high-speed transaction processing, mainframes simply have no competition in terms of speed, the volume of transactions they can handle, and cost-effectiveness. That’s why banks still lean on mainframes for their core operations. Many customer interactions, such as credit card and ATM transactions, are carried out through high volume, real-time, online transaction processing (OLTP).
Engagement between companies and their customers continues to become a major component of the customer experience. While data about customers is useful, data about their engagement with a company adds a whole new layer. Organizations invest in Systems of Engagement (SoE) to manage this – to facilitate the customer journey across multiple touch points and providing a seamless experience. SoE workloads are generally highly parallel, with each individual interaction being of low value.
Systems of Engagement must interact in real-time with Systems of Record (SoR), which act as the source of truth and as custodians of critical business data. SoR are mostly transactional, highly stateful, and demand absolute consistency and transactional integrity, regardless of the value of an individual transaction. The state of an airline seat, for example, must be exact and must show consistency for every querying entity.
Systems of Intelligence (SoI) complete the picture by performance tracking and predictions based on artificial intelligence (AI). Organizations generally want to avoid converting the SoR where possible, but still need to be able to extract real-time events from the SoR for building the inference engines and to develop analytics and artificial intelligence models. Machine learning is often used to train and improve the models.
Architecturally, collection and aggregation interfaces have always been a problem in software design. In the case of SoE and SoR, one must interface front-end SoE (a highly variable and unpredictable event stream) to back-end SoR (originally architected for a more deterministic and serialized environment). Tight coupling between the two layers nullifies the benefits of nimbleness and agility that SoE offers.
An Event Mesh Facilitates Integration
An event mesh facilitates the integration between mainframe SoR, SoE, and SoI – creating a highly scalable and distributed architecture. The loosely coupled approach supported by the event mesh solves the ‘impedance mismatch’ across the layers.
An event mesh is a configurable and dynamic infrastructure layer for distributing events among decoupled applications, cloud services and devices. It enables event communications to be governed, flexible, reliable, and fast. An event mesh is created and enabled through a network of interconnected event brokers.
In other words, an event mesh is an architecture layer that allows events from one application to be dynamically routed and received by any other application no matter where these applications are deployed (no cloud, private cloud, public cloud). This layer is composed of a network of event brokers.
The generic capabilities of an event mesh include:
A network of interconnected event brokers that can be deployed in any cloud, PaaS, or non-cloud environment.
Dynamic distribution of events so that event consumers can receive events from any event producer, no matter where the producer and consumer are attached to the mesh, without the need for configuration of event routing
z/OS Mainframe Integration Options
z/OS provides a few options mainframe technology integration with external systems. In the section below, some of the commonly used patterns are listed. These include:
CICS SOAP/JSON WebServices
ESB/Adapter
z/OS Connect
z/OS with Event Mesh
CICS SOAP/JSON WebServices
CICS supports integration of applications using web services and offers two approaches: rapid deployment using an opinionated approach with least amount of programming or a flexible model using code to customize the web service application. Either way, application programs running in CICS can participate in a heterogeneous web services environment as service requesters, service providers, or both. This model also supports CICS as a JSON server, with the limitation of only supporting POST method.
CICS support for SOAP Webservices conforms to open standards, including SOAP 1.1 & 1.2, HTTP 1.1, WSDL 1.1 and 2.0 and JSON. These capabilities have been available since CICS v3.1 and have been continuously enhanced.
Support of open protocols allows CICS WebServices to be seamlessly connected to the event mesh without a need for a third-party adapter.
ESB/Adapter
Traditional enterprise service bus (ESB) technology will integrate with z/OS by leveraging an adapter. At a very minimum, apart from transport level integration, the adapter is required to do character-set translation as well as convert from mainframe COBOL message structures. Mainframe are big-endian systems and use EBCDIC character sets. This contrasts with little-endian Intel-based systems running ASCII and UTF-8. There is also a need to do message transformation.
The message structures in COMMAREA used by CICS programs are in COBOL COPYBOOK formats, and this must be converted to an open message format like XML or JSON. This implies that the adapter is tightly coupled with the z/OS program and any change in copybook needs to be done simultaneously on z/OS and the ESB adapter.
The transport between the Adapter and the z/OS is either an MQ Channel or raw TCP/IP.
In this approach, mainframe still uses a proprietary connector, and open protocol is available from the ESB/Adapter. In this model, the connectivity to the event mesh leverages the adapter.
While all leading integration products have these adapters, modern enterprises are now moving towards leveraging the native WebServices/JSON support available natively on the mainframes. This further reduces the reliance on ESBs and accelerates the journey to microservices.
z/OS Connect
z/OS Connect is IBM’s premiere technology for implementing JSON Services and APIs in CICS. z/OS Connect is the entry level low-cost option, and z/OS Connect EE is a separate IBM product and offers a richer RESTful API support.
z/OS Connect EE provides a RESTful API interface to z/OS with a security model, the ability to map the request to the backend data requirements, and data transformation.
Support of open protocol allows z/OS Connect to be seamlessly connected to the event mesh.
z/OS with Event Mesh
Based on the above mainframe integration approaches, CICS programs on z/OS can be connected to the event mesh using REST. Since the patterns use open protocols, there is no need for additional connector frameworks; Solace can natively connect to it. The three options are shown in a single picture below. Note that while the ESB/Adapter approach is being considered, availability of WebServices should allow you to integrate without ESB as well.
The Security Layer for Mainframe Integration
Any conversation about mainframe integration with the mesh will arrive at the topic of security. Here we will provide with a few basics about the security layer that is enforced in Solace, apart from the additional controls in the z layer.
Encryption
Solace makes use of TLS 1.2 to provide transport level security between Solace PubSub+ Event Broker and the mainframe.
Authentication
Solace API can be used to use a client certificate authentication by providing valid X509v3 certificates. It also supports basic authentication by authenticating with a username and a password. These credentials can be validated against Internal user repository, corporate LDAP server or an external RADIUS server. While OAuth (typically useful for connecting third party applications ) is not supported, consuming data APIs require system-to-system authentication, and not end-user authentication.
Authorization
You can use the ACL profile and topic-to-queue mapping to define which API is invoked by any of the clients (using either RESTful or messaging APIs) and which will be authorized and dispatched to the mainframe. The administrator can also be used to define a set of IP addresses/subnets from where connection is allowed or disallowed.
Solace supports wildcards while granting access, greatly simplifying the administration. Instead of defining every API separately, the taxonomy can be used to allow permissions at a broad subtree level.
IBM’s REST implementation requires several custom HTTP headers, and Solace PubSub+ will forward the headers sent by the microservices so that the CICS program can function correctly.
A Solace PubSub+ Event Broker acts as the gateway to connect to z/OS, allowing the synchronous REST request/reply mechanism to be event-enabled and to reach across the mesh.
Summary
In summary, Solace eases mainframe integration by bringing it onto an event mesh. By doing so, the mainframe SoR and the distributed SoE and SoI layers can become totally integrated into an end-to-end, real-time, event-enabled architecture using open standards and simple, widely understood protocols.
In turn, this means that the visualization of events and the tracking (lineage) of the data that make up the event is fully transparent and more available for audit, analysis, and sharing with other systems. A further benefit is that the development and management of end-to-end events is made simpler through tools such as the Solace PubSub+ Event Portal.
The post Mainframe Integration: Use an Event Mesh to Extract Real-Time Events From Systems of Record appeared first on Solace.
Mainframe Integration: Use an Event Mesh to Extract Real-Time Events From Systems of Record published first on https://jiohow.tumblr.com/
0 notes