#Datamatrix
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Bulgari Sets A New Record (Again) For The World's Thinnest Watch With The New Octo Finissimo Ultra
A Mere 0.05mm Later, and the New Ultra Supplants Richard Mille's 2022 Efforts and Also Claims the Record as World's Thinnest Chronometer-Certified Watch.
— Danny Milton | April 08, 2024

World's thinnest watch 2024, the Octo Finissimo Ultra Cosc by Bulgari. Bulgari has developed the thinnest mechanical watch ever produced
I remember it like it was just yesterday. Richard Mille came out absolutely nowhere delivering a watch in partnership with Ferrari that snatched the throne as the world's thinnest watch, beating out the then-recently (like four months recently) released Bulgari Octo Finissimo Ultra by a mere 0.05mm.
We wrote pretty extensively about the Bulgari upon its release in March 2022, especially considering it not only held the thinness record at the time, but also featured a QR code for an NFT (remember those?) on the dial. The Ferrari then came roaring in with the new record and an engineering achievement, having built the movement into the case rather than going the route Bulgari went, using the caseback as a mainplate for the movement. And so, since July 2022, RM has held the record. That changes today.

The Bulgari Octo Finissimo Ultra returns and is thinner than ever – literally. As of today, the new Ultra boasts a thickness of 1.7mm, beating the RM by another .05mm. And just like RM delivered its record-setting watch with a bit of flare via the architecture, here Bulgari is raising the stakes by COSC-certifying the new Ultra, thereby making it not just the thinnest watch ever made, but also the thinnest chronometer-certified watch ever made. By my count, that's two records (though I am not sure anyone was waiting on the latter).
Of course, this should come as no surprise, as the attainment of records has been core to the Octo Finissimo line since its creation and has been a key factor in its meteoric rise as a collection that now stands shoulder to shoulder with the likes of AP and Patek in its class (integrated bracelet sports watches).

And no matter where you stand on the need to have these records or their importance in the larger scheme of things, you can't deny the fact that Bulgari and Octo Finissimo achieved records for the thinnest tourbillon, minute repeater, self-winding watch, self-winding tourbillon, chronograph GMT, tourbillon chronograph, and perpetual calendar.
And while they may have lost the throne for the thinnest watch, full stop, for a brief period, the brand is back on top. And can add a "COSC-certified" wristwatch" to the above list. So now we know the new Ultra is the standard by which all thin watches (and thin chronometers) are to be measured. What about the watch itself? Well first off, for a complete breakdown of the original Ultra, much of which applies to this watch, I implore you to give this story a read.

Of course, the high-level points are the titanium case and the use of the caseback as a mainplate for the movement. And that caseback needed to be made of an especially hard and dense material: tungsten carbide. One hundred and seventy components of this manually wound movement are assembled and built into the watch. On the previous Ultra, as noted above, there was a QR code on the ratchet, which has now been changed to a Datamatrix, allowing the owner to experience the full details of the Ultra through photo, video, and advanced data.
Making this a COSC-certified movement added complexity to the assembly and construction of this ultra-thin watch but the caseback, used in the previous iteration, still provided enough stability for the now thinner watch. And that's because it was not the movement or the architecture that served as the area where the new thinness was achieved.

No, that would be the sapphire crystal. According to Bulgari the case was reworked to "optimize" the crystal. A careful meticulous process allows the engineers to do away with one-tenth of a millimeter necessary to achieve the record.
But it gets more interesting still, as Bulgari has made it even easier to set this piece. You quite literally place it in a dedicated case with a digital readout. Bulgari describes it as having a dedicated watchmaker at home, noting in its press release that once the watch is in the case, "the desired time is then programmed, and the adjustment cycle launched at the touch of a button. In a matter of seconds, the watch is perfectly adjusted and wound with impeccable precision." That is pretty damn cool.

This new record-breaker will be in a set of 20 pieces and will cost $529,000. In addition, Bulgari is also releasing an Octo Finissimo Ultra in platinum. It boasts the same 1.80mm thickness as the previous Ultra, which is now also a record for a platinum watch. No small deal for sure. One thing is certain, Bulgari has not lost its competitive edge and we'll have to wait and see which records are still left to beat.

The Basics:
Brand: Bulgari
Model: Octo Finissimo Ultra
Diameter: 40mm
Thickness: 1.7mm
Case Material: Titanium
Strap/Bracelet: Bracelet

The Movement:
Caliber: BVL 180
Functions: Hours Minutes Regulator Display
Thickness: 1.5mm
Power Reserve: 50 Hours
Winding: Hand-winding
Frequency: 4Hz
Chronometer Certified: Yes

The release marks Bulgari's ninth record for watch thinness
Pricing & Availability:
Price: $529,000
Availability: TBD
Limited Edition: Yes, 20 Pieces
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Generate Barcode in Adobe

Learn how to generate barcodes in SAP Adobe Forms with this step-by-step tutorial. This part of our SAP Adobe Form series covers barcode integration, barcode object configuration, and dynamic barcode generation using ABAP. Discover how to use barcode types like Code 128, QR code, and DataMatrix in Adobe LiveCycle Designer. Perfect for SAP ABAP developers and form designers looking to automate document processing, improve data accuracy, and streamline logistics using barcode-enabled forms in S/4HANA and ECC environments.
0 notes
Audio
(via Stream Young Thug, Ryoji Ikeda - Data.matrix, Halftime (.cutspace Edit) by wingless雪noise | Listen online for free on SoundCloud)
1 note
·
View note
Text
„Die Lesbarkeit von Produktetiketten – vor allem im Bereich Frische und Ultrafrische – ist eine echte Herausforderung. Darum haben wir uns jetzt gemeinsam mit GS1 Austria gekümmert“, berichtet Martin Sednik, Senior Department Manager MDM & Spacemanagement bei METRO Österreich.
„Ursprünglich war vorgesehen, am GS1-128 bzw. EAN-13 Strichcode festzuhalten und hier die bestehende Strichcodequalität zu verbessern. Doch bald war klar: Der GS1 DataMatrix ist die logischere Antwort“, fasst Christian Lauer, Leiter des Rückverfolgbarkeitsservices GS1 Trace bei GS1 Austria, den Projektstart kurz zusammen.
0 notes
Text
Machine Learning in Action By Peter Harrington This article, based on chapter 7 of Machine Learning in Action, shows how to use the Adaboost algorithm to create a decision stump that makes a decision on one feature only. A decision stump is a very simple decision tree. We are going to create a decision stump that makes a decision on one feature only. It’s a tree with only one split, so it’s a stump. While we are building the Adaboost code, we are going to work with a really simple data set to make sure we have everything straight. You can create a new file called adaboost.py and add the following code: def loadSimpData(): datMat = matrix([[ 1. , 2.1], [ 2. , 1.1], [ 1.3, 1. ], [ 1. , 1. ], [ 2. , 1. ]]) classLabels = [1.0, 1.0, -1.0, -1.0, 1.0] return datMat,classLabels You can see this data in figure 1. Try choosing one value on one axis that totally separates the circles from the squares. It’s not possible. This is the famous 45 problem that decision trees are notorious for. Adaboost will need to use multiple decision stumps to properly classify this data set. By using multiple decision stumps, we will be able to build a classifier to completely classify the data. Figure 1 Simple data used to check the Adaboost building functions. It is not possible to choose one threshold on one axis that separates the squares from the circles. Adaboost will need to combine multiple decision stumps to classify this set without an error. You can load the data set and class labels by typing in: >>> import adaboost >>> datMat,classLabels=adaboost.loadSimpData() Now that we have the data set loaded, we can create a few functions to build our decision stump. Enter the code from listing 1 into adaboost.py and save the file. Listing 1 Decision stump-generating functions def stumpClassify(dataMatrix,dimen,threshVal,threshIneq): retArray = ones((shape(dataMatrix)[0],1)) if threshIneq == 'lt': retArray[dataMatrix[:,dimen] threshVal] = -1.0 return retArray def buildStump(dataArr,classLabels,D): dataMatrix = mat(dataArr); labelMat = mat(classLabels).T m,n = shape(dataMatrix) numSteps = 10.0; bestStump = ; bestClasEst = mat(zeros((m,1))) minError = inf for i in range(n): rangeMin = dataMatrix[:,i].min(); rangeMax = dataMatrix[:,i].max(); stepSize = (rangeMax-rangeMin)/numSteps for j in range(-1,int(numSteps)+1): for inequal in ['lt', 'gt']: threshVal = (rangeMin + float(j) * stepSize) predictedVals = stumpClassify(dataMatrix,i,threshVal,inequal) errArr = mat(ones((m,1))) errArr[predictedVals == labelMat] = 0 weightedError = D.T*errArr #print "split: dim %d, thresh %.2f, thresh ineqal: %s, the weighted error is %.3f" % (i, threshVal, inequal, weightedError) if weightedError < minError: minError = weightedError bestClasEst = predictedVals.copy() bestStump['dim'] = i bestStump['thresh'] = threshVal bestStump['ineq'] = inequal return bestStump,minError,bestClasEst The code in listing 1 contains two functions. The first function, stumpClassify(), simply performs a threshold comparison to classify data. Everything on one side of the threshold is thrown into class -1, and everything on the other side is thrown into class +1. This is done using array filtering by first setting the return array to all 1s, then setting values that do not meet the inequality to -1. We can make this comparison on any feature in the data set, and we can also switch the inequality from greater than to less than. The next function, buildStump(), will iterate over all of the possible inputs to stumpClassify() and find the best decision stump for our data set. Best here will be with respect to the data weight vector D. We’ll see how this is done in a little bit.
The function starts out by making sure the data input data is in the proper format for matrix math. Then, it creates an empty dictionary called bestStump, which we will use to store the classifier information corresponding to the best choice of a decision stump given this weight vector D. The variable, numSteps, will be used to iterate over the possible values of the features. We also initialize the variable minError to positive infinity; this variable is used in finding the minimum possible error later. The main portion of the code is three nested for loops. The first one goes over all the features in our data set. We are considering numeric values and we calculate the minimum and maximum to see how large our step size should be. Then, the next for loop loops over these values. It might make sense to set the threshold outside of the extremes of our range, so there are actually two extra steps outside of the range. The last for loop toggles our inequality between greater than and less than. Inside the nested three for loops, we call stumpClassify() with the data set and our three loop variables. stumpClassify() returns its class prediction based on these loop variables. We next create the column vector errArr, which contains a 1 for any value in predictedVals that is not equal to the actual class in labelMat. We multiply these errors by the weights in D and sum the results to give us a single number, weightedError. This is the line where Adaboost interacts with the classifier. We are evaluating our classifier based on the weights D, not on another error measure. If you want to use another classifier, you would need to include this calculation to define the best classifier for D. We next print out all the values. This line can be commented out later, but it is helpful in understanding how this function works. Last, we compare the error to our known minimum error, and if the error is below it, we save this decision stump in our dictionary bestStump. The dictionary, the error, and the class estimates are all returned to the Adaboost algorithm. To see this in action, enter the following in the Python shell: >>> D = mat(ones((5,1))/5) >>> adaboost.buildStump(datMat,classLabels,D) split: dim 0, thresh 0.90, thresh ineqal: lt, the weighted error is 0.400 split: dim 0, thresh 0.90, thresh ineqal: gt, the weighted error is 0.600 split: dim 0, thresh 1.00, thresh ineqal: lt, the weighted error is 0.400 split: dim 0, thresh 1.00, thresh ineqal: gt, the weighted error is 0.600 . . split: dim 1, thresh 2.10, thresh ineqal: lt, the weighted error is 0.600 split: dim 1, thresh 2.10, thresh ineqal: gt, the weighted error is 0.400 ('dim': 0, 'ineq': 'lt', 'thresh': 1.3, matrix([[ 0.2]]), array([[-1.], [ 1.], [-1.], [-1.], [ 1.]])) As buildStump iterates over all of the possible values you can see the output, and finally you can see the dictionary returned. Summary We built a decision stump classifier, which is a single node decision tree, and applied the Adaboost algorithm. Here are some other Manning titles you might be interested in: The Quick Python Book, Second EditionVernon L. Ceder Real-World Functional ProgrammingTomas Petricek with Jon Skeet Hadoop in ActionChuck Lam
0 notes
Text
gs1 barcode
Understanding GS1 Barcodes: The Standard for Global Product Identification
In today's interconnected world of commerce, efficient product identification and seamless supply chain management are essential for businesses of all sizes. GS1 barcodes serve as the global standard for uniquely identifying products, assets, and locations, ensuring consistency and accuracy across industries worldwide. This article explores the fundamentals of GS1 barcodes, their types, and why they are critical for businesses operating in a global marketplace.
What is GS1?
GS1 (Global Standards One) is a non-profit organization that develops and maintains global standards for supply chains. Established in 1974, GS1 is best known for introducing the Universal Product Code (UPC), the world's first barcode. Today, GS1 standards are used in over 100 countries, enabling businesses to identify, capture, and share information seamlessly.
Key GS1 Functions:
Provide unique identification numbers for products, assets, and locations.
Ensure barcode consistency across global markets.
Facilitate efficient supply chain management and data sharing.
What is a GS1 Barcode?
A GS1 barcode is a machine-readable symbol used to represent a GS1 identification number. This number uniquely identifies products, locations, shipments, or assets in a standardized format, ensuring seamless communication between businesses, retailers, and consumers.
Each GS1 barcode contains:
GTIN (Global Trade Item Number): A unique product identifier.
Company Prefix: A unique code assigned to the brand owner.
Product Code: A unique number for each product variant.
Check Digit: Ensures barcode accuracy during scanning.
Types of GS1 Barcodes
GS1 offers a variety of barcode formats tailored for different uses across industries.
1. UPC (Universal Product Code)
Commonly used in retail stores worldwide.
Contains 12 digits (GTIN-12).
Ideal for point-of-sale (POS) scanning.
2. EAN (European Article Number)
Widely used in Europe and globally.
Contains 13 digits (GTIN-13).
Compatible with retail and POS systems.
3. GS1-128
Used for logistics and shipping labels.
Can encode batch numbers, expiration dates, and other data.
Improves traceability in the supply chain.
4. DataMatrix
A 2D barcode used in healthcare and manufacturing.
Stores large amounts of data in a small space.
Ideal for tracking medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
5. QR Code (Quick Response Code)
Used in marketing, payments, and digital product information.
Can store URLs, text, or serial numbers.
Scannable using smartphones.
6. GS1 Digital Link
Connects physical products to digital content via barcodes.
Enables customers to access product information, promotions, and manuals online.
Why Use GS1 Barcodes?
GS1 barcodes offer several advantages for businesses across different sectors:
Global Recognition: Accepted worldwide in retail, logistics, and healthcare.
Accuracy: Minimize errors during scanning and data entry.
Efficiency: Streamline inventory management and reduce manual processes.
Traceability: Enable end-to-end product tracking across the supply chain.
Transparency: Provide detailed product information to consumers.
Regulatory Compliance: Meet international standards and regulations.
How to Get a GS1 Barcode?
Register with GS1: Start by creating an account with your local GS1 organization.
Obtain a GS1 Company Prefix: This prefix uniquely identifies your brand.
Assign GTINs: Allocate a Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) to each product.
Generate Barcodes: Use GS1-approved tools to create your barcode.
Print and Apply: Ensure high-quality printing for clear scanning.
GS1 in Different Industries
1. Retail:
Accurate product identification at point-of-sale terminals.
Better inventory control and stock management.
2. Healthcare:
Tracking of medical equipment and medications.
Enhancing patient safety with precise identification.
3. Logistics:
Real-time tracking of shipments and parcels.
Better warehouse management and order fulfillment.
4. E-commerce:
Simplify product catalog management.
Ensure compatibility across online marketplaces.
5. Food and Beverage:
Track ingredients and final products through supply chain transparency.
Ensure product authenticity and reduce counterfeiting.
Benefits of GS1 Barcodes
Global Standards Compliance: Recognized worldwide for cross-border trade.
Supply Chain Optimization: Enhances logistics and warehouse efficiency.
Reduced Errors: Lowers the risk of manual data entry mistakes.
Enhanced Customer Trust: Accurate product information boosts credibility.
Cost-Effective: Saves time and resources in manual tracking systems.
Challenges in Implementing GS1 Barcodes
While GS1 barcodes offer numerous advantages, businesses may face challenges:
Initial Setup Costs: Registering and obtaining GS1 licenses may require investment.
Training Needs: Staff must be trained to handle barcode systems efficiently.
Printing Quality: Poor-quality barcode printing can affect scanner accuracy.
The Future of GS1 Barcodes
The GS1 system continues to evolve with advancements in technology:
Integration with IoT (Internet of Things): Enabling smarter supply chain solutions.
Blockchain Technology: Enhancing traceability and data transparency.
AI and Machine Learning: Improving demand forecasting and inventory management.
GS1 Digital Link: Bridging physical products with the digital world through scannable links.
Conclusion
GS1 barcodes are more than just a series of lines and numbers—they represent a global standard for efficiency, traceability, and accuracy. Whether you're a small business or a multinational corporation, adopting GS1 barcodes ensures your products are identified correctly, tracked seamlessly, and meet global compliance standards.
Investing in GS1 barcode standards is not just a business decision; it’s a step towards global competitiveness and customer trust.
0 notes
Text
Enhance Your Marking Precision with Electric Dot Peen Markers
In today's competitive manufacturing industry, precision, efficiency, and durability in product identification are crucial for maintaining quality and traceability. One of the most effective tools for achieving these goals is the Electric Dot Peen Marker. This advanced marking system offers manufacturers a reliable and cost-effective solution for permanent marking on a wide range of materials. Let's dive into why the Electric Dot Peen Marker is a must-have for industries that prioritize precision and durability in their product marking.

What is an Electric Dot Peen Marker?
An Electric Dot Peen Marker is a marking machine that creates permanent marks on materials by striking the surface with a carbide or tungsten stylus. The stylus moves in a controlled pattern, creating a series of closely spaced dots that form text, numbers, logos, or even complex codes like DataMatrix. This marking process does not require any additional consumables like ink or chemicals, making it both environmentally friendly and economical.
Key Benefits of Electric Dot Peen Markers
High Precision: Electric Dot Peen Markers deliver exceptional marking accuracy. They can mark detailed, small characters and symbols with clarity, ensuring that each product is traceable throughout its life cycle. This level of precision is particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing, where part identification must remain readable even after years of use.
Versatility: These markers are compatible with a variety of materials, from soft plastics to hard metals like steel and aluminum. The ability to mark diverse surfaces makes Electric Dot Peen Markers a versatile tool for manufacturers across different sectors.
Durability and Permanence: The marks created by an Electric Dot Peen Marker are highly durable, resisting wear, corrosion, and even exposure to extreme conditions. This permanence ensures long-term traceability and compliance with regulatory standards.
Low Maintenance and Cost-Efficiency: Since these machines operate without the need for air compressors or external power sources like their pneumatic counterparts, they are more cost-efficient and require minimal maintenance. They also eliminate the need for consumables, which reduces operating costs over time.
Customizability: With Electric Dot Peen Markers, manufacturers can easily customize the marking depth, speed, and style to fit their specific needs. Whether you need deep marks for rugged environments or surface marks for delicate components, these machines can handle it all.
Why Choose an Electric Dot Peen Marker?
Industries that rely on precision marking, such as automotive, electronics, medical, and aerospace, will find that Electric Dot Peen Markers offer unmatched reliability and efficiency. With their ability to produce clear, permanent marks on virtually any material, they help ensure that parts and products remain traceable and compliant with industry standards. Furthermore, the low operational costs make these systems an excellent long-term investment for any production facility.
Conclusion
As manufacturers continue to seek out efficient and sustainable solutions for product marking, the Electric Dot Peen Marker stands out as a top choice. With its precision, versatility, and low operating costs, this marking system is ideal for businesses looking to improve the quality, durability, and traceability of their products.
To learn more about Electric Dot Peen Markers and explore available options, visit CNMarking's Electric Dot Peen Marker page today!
0 notes
Text
HAAAI!! i got bored and made a small little cryptography puzzle
I decided to call it Three Layer Pie it does not contain anything about pies :< i choose this name because i thought it was cool. ANYWAYS To those who are interested in trying to crack it, (its not very good), this is my first time trying to make a cryptography puzzle There are some prerequisites unless you wanna have a really annoying time. * The Ability to write and run python or some other programming language * Knowledge of some basic encoding schemes J29LfV9hDHMEPIEPIERyuvhagwno6yuU-cGdqNZy17P_8D6Qof7jXuzkfQmHwtx6LTRc7zZa_RBIEPIEPIGFVEPIEPIFPSrIl33PY3ME-cZZKYMxMkR_e1hKgcXqEBYSKDYYQoFI4s9KDgh3lERwoPIEPIEPIQCDEPIEPIEP3NtT7QFd7IH__0HyvdquPIEPlSgSnjwEPIFJyufSuvIEPPefzqfyEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIEPIgqaVm3k0gG4qOeNJKCVGQcX6vgs3Z3hsQmfDFzDJGDZmyt3UlXK3FkPIEPIEPIEvIEPIEPIEPJaPIEPIEPIEPKw3jR2I6jqgXsWdtYGS6NIzVAchMMvjvOaMweDYHyuN6higtZmWviYEPIEPIEPIEXvDPVLNIEPImKDhTDUPIESx1DJl1EPIEZtZKZZJIEPI7ZKk1ZFIEPIEPIEPIEVIFoJUPKIzICPPWEqszSkQ389QgZpMPYX__WIkfKVlqT_4vNGdAMwej_xI-OxYmPJ_-MQeERJaPW_gPKEPIEPIb4lIEPIEPIHWrO7jfpiMkD_ktTyZUYUP_XdzBoKZVXL__OGQ1ZUEkE_8IEPIEPIE__lIEPIEPIH__PIEPIEPIT_8PIEPIEPI__aPIEPIEPL__EPIEPIEPX_8Y29SjK9oHWT=
DO NOT READ PAST THIS POINT UNLESS YOU WANT SPOILERS
IF YOUR STUCK THE FIRST STAGE IS

that image is there just to overwrite the thumbnail when you copy the link to this post A VIGENERE CYPHER All further hints will be encoded in base64 Stage 2: VGhlIFNlY29uZCBTdGFnZSBpcyBiaW5hcnkgYmFzZTY0IA== Stage 3: dGhlIHRoaXJkIHN0YWdlIGFuZCBmaW5hbCBzdGFnZSBpcyBhbG90IGhhcmRlcgppdHMgYSBibGFjayBhbmQgd2hpdGUgYmluYXJ5IGltYWdlIHdoZXJlIGVhY2ggMSBvciAwIHR1cm5zIGludG8gYSBwaXhlbCwgaWxsIGxlYXZlIGl0IHRvIHlvdSB0byBmaWd1cmUgb3V0IHRoZSByZXNvbHV0aW9u
So i wanna give like a huge shoutout to the people at Checking Boxes, while i havent joined the discord myself the 1000x1000 image thing was a huge inspiration to me for creating a 64x64 Image

I suppose we can start breaking down on the top and bottom are some strings

this is so when you get to the point of figuring out its binary you know youre on the right track
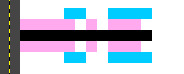
I really wanted to put in a trans flag into my thingy but that's not possible because its a black and white image so i figured what if we wrote out the colors in hex 0cf fae fff fae 0cf

Next

the datamatrix qr code, it just links to my website

Im a really really big fan of toki pona and rain world so i figured id write out mi olin mute e toki pona and put a slugcat next to it
and thats everything :3

THANKS FOR READING AND OR SOLVING!
0 notes
Text
VeryUtils JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK for Web and Mobile Apps.
VeryUtils JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK for Web and Mobile Apps

The VeryUtils JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK is a powerful tool that enables real-time localization and decoding of barcodes and QR codes directly in web browsers on mobile or laptop devices. With just a few lines of JavaScript code, you can transform any camera-equipped device into a reliable barcode scanner, making it an ideal solution for both web and app development.
Designed for Developers, Built for Users This SDK is crafted with developers in mind while ensuring a seamless user experience. It provides enterprise-level features without the significant development effort typically required for such capabilities.
Turn Web Apps into Barcode Scanning Machines Empower your users with the ability to scan up to 20 barcodes per second with 99% accuracy, even in challenging conditions such as damaged codes or low light. All of this is achievable within the browser, making it highly accessible for users.
Performance-Optimized Features in One Library The VeryUtils JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK combines user-friendly components with ultra-fast decoding capabilities. You can easily customize features to meet your business requirements:
User Guidance: Enhanced user experience with visual aids, audio, and haptic feedback to assist in the scanning process.
Multiple Barcode Support: Efficiently batch scan barcodes quickly and accurately, streamlining operations.
Deploy Anywhere: Compatible with public websites and internal-only private networks, offering flexible deployment options.
Work Offline: Progressive Web App (PWA) support allows users to work with minimal or no internet connectivity, ensuring a smooth experience even in low-connectivity environments.
A JavaScript Barcode Scanner You Don't Have to Worry About Leveraging WebAssembly technology, our JavaScript library provides users with an enterprise-ready barcode scanner without the need for any setup or app downloads. Key advantages include:
No Setup Required: Users can start scanning immediately, without the hassle of installations.
Best-in-Class Security: The SDK adheres to stringent security and privacy compliance standards, ensuring data safety.
Continuous Updates: Benefit from ongoing feature enhancements and performance improvements.
Exceptional Recognition Rate and Accuracy The VeryUtils JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK boasts industry-leading accuracy with its advanced barcode detection algorithm. It includes Optical Character Recognition (OCR) capabilities and camera-enhancing functionality, ensuring optimal scanning performance.
Unmatched Speed When Decoding from Video Streams Experience unparalleled speed, with the capability to scan over 500 barcodes per minute—significantly faster than other solutions in the market.
A Full-Capability Barcode Web SDK This SDK supports comprehensive barcode and QR code scanning from any image files, captured images, or real-time scanning. It is optimized for various challenging scenarios:
Optimized for QR and DataMatrix Codes: Employs advanced techniques to decode difficult QR codes and DataMatrix symbols, including those that are wrinkled, glared, or missing borders.
Decode from Images and Video Streams: Capable of processing barcodes from diverse inputs, such as images, base64 strings, raw image data, and importantly, video streams.
✅ Supported Symbologies and Barcodes
Linear Barcodes (1D) Code 11, Code 39 (including Code 39 Extended), Code 93, Code 128, UCC 128, 2 of 5 Interleaved, Codabar, Patch Code, Pharmacode, EAN-8, EAN-13, UPC-A, UPC-E, Add 2, Add 5, GS1 DataBar/RSS-14, GS1 DataBar/RSS Limited, GS1 DataBar/RSS Expanded, GS1 DataBar/RSS Expanded Stacked
2D Barcodes PDF417 (including Compact PDF417), Data Matrix, QR Code (including Micro QR Code)
Postal Codes PostNet, Planet, RM4SCC, Australia Post, Intelligent Mail Barcode (IMB)
With the VeryUtils JavaScript Barcode Scanner SDK, you can effortlessly integrate robust barcode scanning capabilities into your web applications and mobile apps, providing users with a fast, accurate, and secure scanning experience.
0 notes
Text
Laser Marking Machine
In the bustling halls of modern industry, where efficiency meets innovation, there exists a silent architect – the Laser Marking Machine. Often overlooked but omnipresent, these machines wield a profound influence, shaping the very fabric of manufacturing processes. In this exploration, we unveil the hidden intricacies of laser marking technology and illuminate its transformative role in industrial evolution.

The Symphony of Precision: Imagine a symphony where every note is meticulously crafted, every harmony perfectly orchestrated. Such is the essence of laser marking machines – masters of precision in a cacophony of manufacturing. With surgical precision, lasers etch intricate designs, alphanumeric codes, and identifiers onto a myriad of materials, ensuring flawless execution and unrivaled clarity. From aerospace components to medical devices, the symphony of precision resonates across industries, setting the standard for quality and reliability.
A Tapestry of Traceability: At the heart of every product lies a story waiting to be told – a journey from conception to consumption. Laser marking machines imbue each component with a unique identity, weaving a tapestry of traceability that spans continents and lifetimes. Through serialized codes, QR tags, and DataMatrix symbols, manufacturers can trace the origin, history, and authenticity of every item, safeguarding against counterfeiting and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. In this digital age, where transparency reigns supreme, laser marking serves as the guardian of integrity and trust.
The Canvas of Creativity: In the hands of artisans, laser marking machines transcend utility, becoming instruments of creativity and expression. From bespoke artworks to personalized mementos, lasers transform mundane objects into cherished artifacts, imbuing them with meaning and significance. Whether it's engraving heartfelt messages on wedding bands or embellishing corporate gifts with company logos, the canvas of creativity knows no bounds. With lasers as their brush and imagination as their guide, artisans breathe life into every mark, leaving an indelible impression on hearts and minds.
Harmony in Sustainability: In a world grappling with environmental challenges, laser marking machines emerge as champions of sustainability, harmonizing efficiency with eco-consciousness. Unlike traditional methods that rely on chemical etchants and consumables, lasers operate with surgical precision, generating minimal waste and emissions. By embracing clean, contactless technology, manufacturers can reduce their environmental footprint, comply with stringent regulations, and meet the demands of eco-conscious consumers. In the symphony of sustainability, laser marking machines play a vital role, conducting harmony amidst chaos.
Conclusion:
As the curtain falls on our exploration of laser marking machines, one truth resonates clearly – they are the silent architects shaping the future of industry. From precision marking and traceability to creativity and sustainability, these unsung heroes embody the essence of innovation and progress. As we navigate the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, let us recognize and celebrate the profound impact of laser marking machines – the silent architects of our industrial renaissance.
0 notes
Text
OKAY new update:

going off the image posted to the instagram account that i mentioned above, the discord found that the number of i's DID matter, and used the acount of them in each row to come up with some numbers.
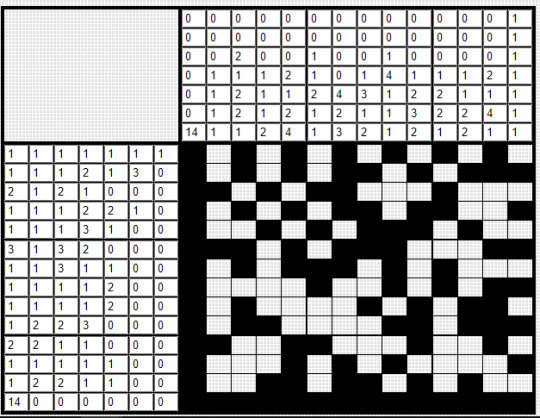
they used this to then create a nonogram (a logic puzzle that operates based off the number of filled-in and blank squares in each row and column; notably one of cellbit's favorite types of logic puzzles).
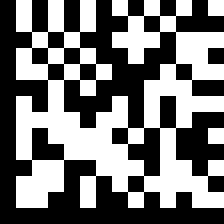
turning the nonogram into a datamatrix got this image ^ which upon scanning got the word "viisil," or "path" in estonian (so it looks like estonian IS relevant to the arg, so that "see.ootab.mind" ("it waits/it is waiting for me") gathered from the pawprints earlier likely is important, though how it factors in we don't know yet).
next, going to http://oth3r.site/viisil got another mega link, this time getting us an audio file titled "10.mp3" that consisted of two minutes of what appears to be the sound of someone walking through the woods.

looking at the metadata on the file shows a comment that reads "curvas sequere," or "follow the curves." i would guess this has something to do with the loop image from above and the binary in the pawprints, but i haven't seen anything definitive come from this yet.
and, finally, a note from cellbit:
"A general note: No puzzle or clues directly reference or have a connection with the characters and events of the Ordem RPG series."
so, basically, don't make connections based off story elements or character attributes, as they won't be tied to the ARG in a way that requires knowing the story to solve it.
Enigma do Medo ARG

okay so! so far cellbit's discord has found a few things aside from what was tweeted (^^), as they knew to look elsewhere to find more clues.


this led them to find two images, one from the nuuvem page and one from the steam page. you can see a dog (lupi) and a girl (mia) in them respectively.

which then led to a christmas image ordem tweeted at one point-- and it's very glaring that the two images that led here included mia and lupi but not veríssimo. adds to the whole element of him being missing.
they're also working on a few things with numbers hidden in the cracks of the images, but right now these are the biggest updates and most solid leads! ill keep updating periodically 🩵🩵
234 notes
·
View notes
Photo

El Sistema de Estándares #GS1 fue diseñado en torno a varios elementos, incluidas las Claves de Identificación GS1. Estas claves identifican cualquier objeto, ubicación, paciente o cuidador para que los interesados puedan acceder a la información a través de un simple escaneo. Las claves de identificación que se muestran en la siguiente imagen son: GLN: (Global Location Number) Número de ubicación global GIAI: (Global Individual Asset Identifier) Identificador Global de Bienes Individuales GRAI: (Global Returnable Asset Identifier) Identificador Global de Bienes Retornables GSRN: (Global Service Relation Number) Número de relación de servicio global GTIN: (Global Trade Item Number) Número global de artículo comercial El soporte de datos utilizado es el GS1 #DataMatrix #gs1healthcare #gs1standards #gs1patientsafety #gs1algeria #healthcaresector https://www.instagram.com/p/CkMKZu1Pum6/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
0 notes
Photo

GS1 barcode, starting with prefix 890, provides unambiguous and universal identification to your products.
The unique product code could then be encoded to various barcode forms – liner barcode, QR code, Datamatrix , etc., based on the requirement to enable instant capture of product information.
#Get a Barcode#QR Code#Datamatrix#apply for barcode#barcode for products#GS1 barcode#Why GS1 india#register for barcode#barcode registration#sell online
0 notes
Text
Barcode
Understanding Barcodes: The Key to Modern Inventory and Retail Management
Barcodes have become an indispensable part of our daily lives, revolutionizing how products are tracked, managed, and sold globally. From retail stores to warehouses, and healthcare facilities to logistics operations, barcodes simplify product identification, improve inventory accuracy, and enhance operational efficiency. This article dives into the fundamentals of barcodes, their types, uses, and why they remain a critical tool in modern business operations.
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable format using a combination of parallel lines, spaces, or dots. Scanners or mobile devices equipped with barcode readers decode this data and convert it into readable information, such as product details, pricing, or inventory levels.
Barcodes primarily consist of two elements:
Black Bars (or Patterns): Represent data.
White Spaces: Separate the black bars for clarity.
Each barcode contains a unique identifier that links to a database, providing details about the product, including its price, stock status, and origin.
History of Barcodes
The concept of barcoding was introduced in the 1940s by Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver. However, it wasn’t until 1974 that the first barcode was scanned on a Wrigley’s gum pack in an Ohio supermarket, marking the beginning of a technological revolution in retail and inventory management.
Types of Barcodes
There are two primary categories of barcodes: 1D (Linear Barcodes) and 2D Barcodes.
1. 1D (Linear) Barcodes:
These are the traditional barcodes with vertical black and white lines. Examples include:
UPC (Universal Product Code): Commonly used in retail stores.
EAN (European Article Number): International retail barcode.
Code 39: Used in manufacturing and military applications.
Code 128: Often found in logistics and shipping.
2. 2D Barcodes:
These barcodes store more data in both horizontal and vertical patterns. Examples include:
QR Codes (Quick Response Codes): Used in marketing, payments, and product information.
DataMatrix Codes: Common in healthcare and electronics.
PDF417: Found in shipping labels and ID cards.
How Do Barcodes Work?
Barcode Creation: A unique identification number is encoded into a barcode format.
Printing: The barcode is printed on labels or product packaging.
Scanning: A barcode scanner reads the black and white patterns.
Decoding: The scanner translates the barcode into digital data.
Database Lookup: The system retrieves product or asset details from the database.
This seamless process ensures accurate and instant information retrieval, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
Applications of Barcodes
Barcodes are widely used across various industries:
1. Retail:
Quick and accurate billing at checkout counters.
Improved inventory management and stock tracking.
2. Healthcare:
Tracking patient medications.
Managing medical equipment and supplies.
3. Logistics and Warehousing:
Real-time tracking of shipments.
Efficient warehouse inventory control.
4. Manufacturing:
Monitoring production lines.
Ensuring quality control through traceability.
5. Event Management:
Ticket scanning for concerts, sports events, and conferences.
Benefits of Barcodes
Accuracy: Reduces human errors in data entry.
Speed: Speeds up processes like billing, inventory checks, and shipping.
Cost-Effective: Affordable technology with significant ROI.
Inventory Control: Real-time visibility into stock levels.
Improved Traceability: Enhances product tracking across supply chains.
Data Insights: Provides accurate data for business analysis and forecasting.
Barcode Scanning Technology
Barcode scanners are devices designed to read and decode barcode information. Common types include:
Laser Scanners: Fast and accurate, commonly used in retail.
CCD Scanners (Charge-Coupled Device): Best for short-range scanning.
2D Image Scanners: Can read both 1D and 2D barcodes.
Mobile Scanners: Smartphones with barcode scanner apps for flexible use.
Barcodes vs RFID
While barcodes are widely used, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is emerging as an alternative technology.
Feature
Barcode
RFID
Cost
Low
Higher
Range
Short-range scanning
Long-range reading
Line of Sight
Required
Not required
Data Storage
Limited
Extensive
Both technologies have their advantages, but barcodes remain the preferred choice for cost-sensitive applications.
Challenges with Barcodes
Despite their advantages, barcodes face certain challenges:
Damage or Smudging: Barcodes may become unreadable if damaged.
Limited Data Storage: 1D barcodes can only store minimal information.
Dependency on Line of Sight: Direct scanning is necessary.
The Future of Barcodes
The future of barcoding technology is promising:
Smart Barcodes: Embedded with enhanced data storage.
Integration with IoT (Internet of Things): Enabling smarter inventory systems.
AI Integration: Improving predictive analytics for supply chains.
Blockchain Integration: Ensuring immutable traceability records.
With the rise of e-commerce and digital logistics, barcodes are evolving to meet the demands of modern supply chains.
How to Get a Barcode for Your Business
Register with GS1: GS1 is the global authority for barcode standards.
Obtain a GTIN (Global Trade Item Number): A unique identifier for your product.
Generate the Barcode: Use GS1-approved barcode creation tools.
Print and Apply: Ensure high-quality printing for accurate scanning.
Investing in barcoding systems ensures smooth operations and enhances scalability for businesses of all sizes.
Conclusion
Barcodes are far more than black lines on product packaging—they are a gateway to efficiency, accuracy, and global connectivity. From simplifying retail checkouts to ensuring supply chain transparency, barcodes have proven their value across industries.
As technology continues to advance, barcodes remain a cornerstone of effective product identification and data management, offering unparalleled benefits in a world driven by speed and precision.
0 notes
Video
youtube
XT6201Hospital DPM Code Engraving Scalpel Direct Part Mark 2D Barcode Sc...https://xtiot.en.alibaba.com/product/62206428652-814898484/XT6201_Wine_Bottle_Code_OCR_Passport_Scanner_ID_Card_Barcode_Scanner_Manufacturers.html?spm=a2700.icbuShop.41413.15.7c336da0k11M0G
0 notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes