#ILM software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

There is an aspect to Pixar, Industrial Light & Magic, and Weta that I don't think a lot of people know about. They sell their software and technology and training and workflows. Pixar movies started out largely as R&D and tech demos to help them sell software and services. Toy Story was a giant advertisement for their RenderMan software that ended up being a beloved box office success as well.
Creating The Mandalorian on The Volume was not just because it was the best technology to bring the show to life. It was also to sell The Volume to other productions. If you watch the "behind the scenes" all they talked about were those LED video walls.
They were selling something.
So, why did they do a de-aged Luke?
It's low stakes R&D in which they get paid to develop this technology. And once they get it perfected, they can sell this service or the technology behind it to others. I think Indiana Jones was ILM nearly perfecting it and the next time it is used they will pretty much have it nailed.
Perhaps this wasn't the best artistic use or implementation. But it was a stepping stone. And I think a lot of movie studios would find value in being able to cast an actor and make them any age while still maintaining the core performance.
I'm not saying this is a good or bad thing. I think it will depend on how it is done. But if you are curious as to the why, the answer is mostly technological development and money.
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Evolution of VFX: From Miniatures to Digital Magic

Visual Effects, or VFX, have completely transformed the way stories are told in film, television, and digital media. What started as simple camera tricks and miniature models has evolved into an intricate digital art form capable of bringing entire fantasy worlds to life. From early science fiction films to today’s CGI-heavy blockbusters, the journey of VFX is a fascinating story of creativity, innovation, and technological progress.
As interest in this exciting field continues to grow, many aspiring artists are enrolling in specialized training like VFX Prime Courses in Udaipur and VFX Film Making Courses in Udaipur to become part of this revolutionary industry. In this article, we’ll explore the evolution of VFX—from its humble beginnings to the digital magic we see today—and why learning VFX is more relevant than ever.
The Early Days: Optical Tricks and Miniatures
In the early 20th century, filmmakers relied on in-camera effects, matte paintings, and miniature models to create illusions. One of the earliest examples of visual effects can be found in Georges Méliès’ 1902 film A Trip to the Moon, where simple stop-motion and substitution techniques were used to produce magical transformations.
As the film industry matured, so did the complexity of visual effects. In classics like King Kong (1933) and Metropolis (1927), filmmakers used scale models, matte paintings, and rear projections to craft visually compelling scenes. These techniques laid the groundwork for future innovations.
The Golden Age of Practical Effects
By the 1970s and 1980s, practical effects had reached new heights. Visionaries like George Lucas and Steven Spielberg revolutionized VFX with films such as Star Wars and Indiana Jones. The creation of ILM (Industrial Light & Magic) introduced techniques like motion control photography, animatronics, and optical compositing.
This period also saw the rise of puppetry and physical models in iconic films like The Terminator, Alien, and Ghostbusters. These tangible effects made the impossible feel real, setting a standard for immersion in storytelling.
The Dawn of Digital Effects
The 1990s marked the beginning of the digital revolution. Terminator 2: Judgment Day (1991) and Jurassic Park (1993) introduced groundbreaking CGI, demonstrating the potential of computer-generated imagery. These films were milestones that changed the way directors and producers approached storytelling.
As CGI improved, digital effects began replacing practical ones in many areas. The Matrix (1999) popularized “bullet time,” combining digital and practical effects in a visually stunning way. By the 2000s, digital VFX became a dominant force, allowing creators to visualize anything they could imagine.
The Modern Era: Photorealism and Real-Time Rendering
Today, VFX are not just limited to films—they play a major role in television, advertising, video games, and virtual reality. Technologies like motion capture, 3D scanning, and real-time rendering (using game engines like Unreal Engine) are pushing boundaries further.
Films like Avengers: Endgame, Avatar, and The Lion King remake are examples of how digital artistry can create entire worlds and characters that feel lifelike. The use of AI and machine learning is now being explored to streamline VFX production and enhance realism.
For anyone looking to enter this dynamic field, VFX Prime Courses in Udaipur offer in-depth training on these latest technologies, preparing students for the evolving demands of the industry.
Why Understanding VFX Evolution Matters
Studying the evolution of VFX helps learners appreciate the art and science behind each frame. It’s not just about the tools—it’s about understanding how techniques have changed over time and why certain methods are still relevant today.
VFX Film Making Courses in Udaipur focus not only on software training but also on storytelling, cinematography, and integrating effects into a cohesive narrative. Students learn to respect traditional methods while mastering digital tools.
VFX Education in Udaipur: A Creative Launchpad
Udaipur is emerging as a creative hub, offering specialized programs tailored to the needs of modern visual artists. Both VFX Prime Courses in Udaipur and VFX Film Making Courses in Udaipur are designed to give aspiring artists a comprehensive understanding of VFX—from historical context to modern digital workflows.
These courses typically cover:
The history and evolution of VFX
2D and 3D compositing techniques
CGI modeling and animation
Motion capture and green screen work
Software like After Effects, Maya, Houdini, and Nuke
Project-based learning with real-world applications
With experienced mentors and hands-on training, students graduate with a portfolio that can open doors to careers in film, television, gaming, and beyond.
The Future of VFX
As technology continues to advance, the future of VFX looks incredibly promising. Virtual production—pioneered in projects like The Mandalorian—is changing the way films are shot by combining real-time environments with live-action performance. Artificial Intelligence is being used to automate tasks like rotoscoping and facial animation.
Learning these cutting-edge techniques is crucial for anyone hoping to thrive in this rapidly evolving industry. Enrolling in VFX Prime Courses in Udaipur or VFX Film Making Courses in Udaipur equips students with the skills needed to be at the forefront of this creative revolution.
Conclusion
The journey of VFX from simple camera tricks and miniature sets to today’s digital marvels is a testament to the power of innovation in storytelling. As the line between the real and the imagined continues to blur, the need for skilled VFX professionals has never been higher.
Whether you're passionate about film, gaming, or immersive experiences, now is the perfect time to explore the world of visual effects. With comprehensive and industry-aligned training like VFX Prime Courses in Udaipur and VFX Film Making Courses in Udaipur, you can begin your journey into the magical realm of digital storytelling and creative expression.
0 notes
Text
Do You Really Need a Degree to Make It in Animation & VFX? Here's the Truth

The animation and VFX industry has exploded over the past decade. From blockbuster movies to indie games, there's a massive demand for visual storytellers who can create stunning imagery and bring characters to life. But there's one question that often haunts aspiring artists: Do I really need a degree to make it in this industry?
Let’s unpack this with a realistic, human-first perspective—one that reflects what’s actually happening in studios and creative teams today.
The Degree Dilemma: Is It Still Relevant?
Traditionally, having a degree meant job security. In animation and VFX, that was once true as well. Institutions offered structured learning, networking opportunities, and a formal stamp of approval. But today, the landscape is shifting.
Studios and production houses are increasingly looking beyond degrees. They're evaluating skill, storytelling ability, software knowledge, and the strength of a demo reel. If you’re talented and can show it, that often speaks louder than any diploma.
In short, degrees can open doors—but they’re no longer the only key.
What Really Matters to Employers?
Let’s be honest: most recruiters in animation and VFX aren’t scanning your resume for a college name. They want to see what you can do. Your showreel is your portfolio, and it tells your story far better than a certificate.
Can you animate realistic motion? Can you design compelling characters or create believable particle effects? These are the questions that matter.
It’s like this: if a self-taught artist can design a mind-blowing environment using Blender, After Effects, or Houdini, they’re going to land gigs over someone with a fancy degree but average work.
That said, degrees aren’t useless. A solid curriculum can help build fundamentals. But the learning path has diversified—and for good reason.
Alternative Learning Paths That Work
Here’s the good news: there are more ways than ever to build your animation and VFX skills.
Online platforms like School of Motion, Animation Mentor, and Gnomon offer targeted, hands-on training.
Workshops and bootcamps often provide access to industry mentors and real-world projects.
Open-source tools like Krita and Blender lower the entry barrier for everyone.
Even major studios have recognized the rise of non-traditional learning. Disney, DreamWorks, and ILM have hired artists from varied backgrounds—many without formal degrees but rich in passion and portfolio.
In cities with thriving animation hubs, opportunities to upskill are more accessible than ever. For instance, if you’re looking to sharpen your skills, taking an Animation course in Hyderabad can offer the technical depth and creative exposure you need without committing to a full degree.
The AI Factor: Changing the Game (but Not the Artist)
There’s been buzz recently about AI tools generating character art or automating background creation. It’s natural to worry—will machines replace artists?
The short answer? No.
AI can support repetitive or technical tasks, like inbetweening or rotoscoping. But creativity, storytelling, emotional nuance—these are uniquely human. AI might speed up workflows, but it can’t replace the soul of the work. If anything, it frees artists to focus on the more fulfilling parts of the process.
So while it’s smart to stay updated on tech trends, don’t let them discourage you. The creative core of animation is still very much in human hands.

Real Stories, Real Success
Want some real talk? Some of the most successful animators today never followed a traditional path.
Take James Curran, a motion designer who became famous for his GIF loops. No formal degree in animation. Just relentless practice and self-initiated projects.
Or look at someone like Toniko Pantoja—he studied animation, yes, but credits his success to online communities, practice, and feedback from fellow artists.
The point is: degrees can help. But they don’t define your success. Your work, discipline, and willingness to learn do.
So, Should You Get a Degree?
Here’s a more honest answer than most career guides will give: It depends.
If you thrive in structured environments, want long-term academic depth, and can afford it—a degree might be a good fit.
If you prefer flexible learning, want to dive into real projects, or are transitioning from another career—short-term programs or self-study could be better.
Just make sure whatever path you choose builds your skills, not just your résumé.
Trends You Can’t Ignore
According to AnimationXpress, India’s animation and VFX industry is expected to cross INR 230 billion by 2025. With OTT platforms expanding and global studios outsourcing creative work, the demand for skilled artists is only growing.
This boom is not just confined to major production houses. Startups, gaming companies, and marketing agencies are all building in-house creative teams, making room for talent from all educational backgrounds.
Final Thoughts: Focus on Skill, Not Just School
At the end of the day, the animation and VFX industry celebrates creativity, not credentials.
You don’t need a degree to succeed. But you do need drive, consistency, and the ability to adapt. If you’ve got a killer reel and a hunger to learn, you’re already ahead of the curve.
And if you're in a city that's growing as a creative hub, there's no shortage of ways to grow. Programs like a 2D visualization course in Hyderabad are gaining momentum for a reason—they meet industry needs with focused, hands-on learning.
So no matter where you're starting from, the real question isn't "Do I need a degree?" It's "Am I doing the work that proves I belong here?"
0 notes
Text
Dissertation Research:
Technological Innovations Industrial Light and Magic Made that changed Cinema forever
1. 1st fully Computer generated image sequence in a feature film
Industrial Light and Magic produced the first fully computer-generated (CGI) sequence for a feature film in Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan. While most of the film’s visual effects were done using traditional techniques such as model photography and other various analog methods this 60 second scene was entire CGI which was breath-taking back then.
Among ILM's technical achievements was cinema's first entirely computer-generated sequence: the demonstration of the effects of the Genesis Device on a barren planet. The first concept for the shot took the form of a laboratory demonstration, where a rock would be placed in a chamber and turned into a flower. While Paramount appreciated the more dramatic presentation, they also wanted the simulation to be more impressive than traditional animation. . . ." (Wikipedia article on Start Trek II: The Wrath of Kahn, accessed 03-12-2012).


2. 1st fully Computer generated character for a feature film
Before becoming an independent company or being acquired by Disney, Pixar was originally a part of Lucasfilm’s computer division, where it had been since 1979. Initially called the Graphics Group, the team was responsible for the "glass man sequence," in the film Young Sherlock Holmes and this was a ground breaking invention.

Although ILM does not receive the full credit to this invention, it's mother company Lucas Films does get the credit. However this graphics group of Lucasfilms was sold to Steve Jobs in 1979 and later called it 'Pixar' animation before Disney bought it. The rendering software was called Pixar's Renderman and this is in house rende3ring software used still up to date.

0 notes
Text
Aspirations
For the past two and a half years I've been fixated on becoming proficient in as much software as possible by throwing myself into every single module. Through doing so I have a foundational understanding of which areas I would like to specialise in relation to the sort of companies/roles that interest me.

The first company that caught my eye was Passion Pictures because I'm a big fan of Robert Valley's 'Love Death and Robots' animations 'Zima Blue' and 'Ice'. In first year, I chose Valley as the animator for my first animatic and ever since then Passion Pictures has been at the back of my mind.
ILM, Dreamworks and Aardman have all created films which I loved as a kid and it would be great to see what working at these companies would be like. It's the thought of working at a company like Aardman which inspired me to take a stab at this course in the first place.
Most of my time of the course has been focused on digital animation in Maya partially because the games industry is much larger than film/TV animation. I spoke to the people at Revolution when we visited Aesthetica in York but never heard back from them when I sent out an email with my show reel. It's a small tightly knit company which only take on extra staff when necessary so I wasn't expecting a response which is why I'm aiming to apply to larger studios. My brother applied to Rebellion as a programmer but instead ended up working at Behaviour so that also sways me in the direction of games but I need to take the time to reach out to more companies as I have only tried contacting a handful with my second year reel and heard back from nobody.
Since the talk with Finn in first or second year about The Mill and Black Kite discussing his work on the Amazon advert, these companies have also been on my mind because there are a lot of opportunities in advertising and the podcast project had me rapt and carried away with different ideas so I think I might do well working on that sort of thing but I don't want to limit myself to any single area.
My main limitation is that I have gone down the 3D skill tree and I'm hoping to be an animator but I've learnt a lot of other skills which I could also see myself doing for a job.
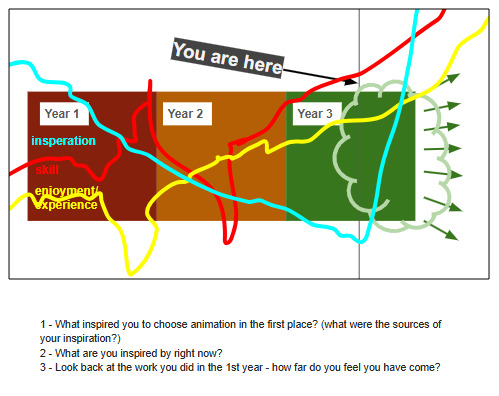
I was lulled to sleep in a Marketing lecture at Newcastle Uni trying to decipher the broken English of my lecturer at the time and found myself scrolling through Aardman's website and job postings and started to question why I was on a course that didn't challenge me. I was always fascinated by filmmaking and animation, watching my dad make home movies with my brother acting in them. I knew that I wanted to make something so I thought I'd throw myself into animation and see if any part of it stuck.
At the moment I'm watching a lot of Mike Judge's work like Idiocracy, Office Space and King of the Hill and I've finally got around to watching Arcane both of which are great but for their own reasons. I was inspired by the prospect of a chance at a role in a big company, being skilled enough to contribute on a project like Arcane or a Pixar film because I thought I would learn a lot being surrounded by people who work on those projects.
I've come a long way in understanding the animation pipeline in many of its different facets. I aim to build upon every skill I learn and challenge myself with a new technique with each project stepping from simple rigs to limbs and eyes to lip sync and full body and facial animation and in the final animation I want to have a culmination of all the different skills I've attempted so far this time with an emphasis on the acting and emotional side of things which really stood out to me when researching for my essay in the last semester.
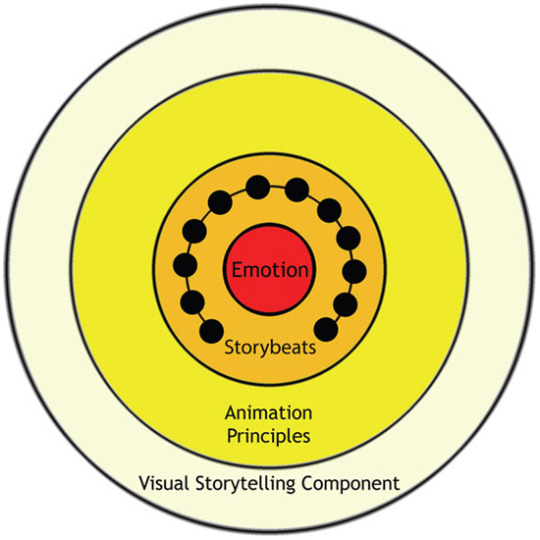
I've spent most of my time on the outer rings so far with some choppy attempts at coherent storybeats but most of my animatics are stunted by the time limit because I get carried away, make a script I like and then to reach the time limit I end up with a shell of the original idea.
youtube
I've been too focused on having a successful outcome which meets the learning objectives which has helped me do well in terms of grades but this outcome obsession stopped me from being more experimental. I want to explore the process without being so perfectionistic, I'm too set on making things perfect to the point that nothing gets made, things only get planned to the nth degree before being scrapped. This interview with Willem Dafoe gave somewhat of a freeing perspective on the creative process which flips perfectionism on its head. It's not that I'm trying to fail, its that I'm trying to abandon perfection to make room for tangible production; spending more time creating because the over-thinking is preventing me from doing anything.
0 notes
Text
Lighting is a fundamental element in modern buildings, playing a crucial role not just in visibility and aesthetics, but also in energy efficiency, safety, and occupant well-being. As buildings become more sophisticated and the demand for sustainable solutions grows, the importance of optimized lighting systems has never been greater.
In this context, Intelligent Lighting Management (ILM) has emerged as a game-changing technology. Intelligent Lighting Management refers to advanced lighting systems that use sensors, automation, and real-time data to control and optimize lighting based on occupancy, daylight availability, and other factors.
Here in this blog, we will discuss the key components of Lighting Management systems, how they work, and the specific advantages they offer to different types of buildings, from office complexes and industrial facilities to schools, hospitals, and beyond.
Understanding Intelligent Lighting Management
Intelligent Lighting Management (ILM) is a sophisticated system designed to automate and optimize lighting within a building, enhancing both energy efficiency and user comfort. Unlike traditional lighting systems, which often rely on manual adjustments and fixed settings, Intelligent Lighting Management integrates advanced technologies to create a dynamic and responsive lighting environment.
Key Features of Intelligent Lighting Management
Automation:
Intelligent Lighting Management systems automate lighting controls based on predefined rules or real-time inputs. This means lights can be adjusted automatically in response to various factors such as the time of day, occupancy, or ambient light levels.
Sensors: Sensors play a crucial role in Smart Lighting Management by providing real-time data about the environment. Occupancy sensors detect whether a room is in use and adjust lighting accordingly, while daylight sensors measure natural light levels and adjust artificial lighting to maintain consistent illumination.
Remote Control: Intelligent Lighting Management systems often include remote control capabilities, allowing users to manage lights from a central location or via mobile apps. This feature provides flexibility and convenience, enabling facility managers or building occupants to adjust lighting
Data Analytics:
Advanced Smart Lighting Management systems incorporate data analytics to track and analyze lighting usage patterns. By examining this data, users can gain insights into energy consumption, identify inefficiencies, and make informed decisions to further optimize lighting. Analytics can also help in predicting future needs and trends, contributing to ongoing improvements in energy management and operational efficiency.
Key Components of Intelligent Lighting Management
Intelligent Lighting Management (ILM) systems are built on several key components that work together to optimize lighting efficiency and enhance the overall user experience.
Sensors and Controls
Types of Sensors Used:
Occupancy Sensors:
These sensors detect the presence of people in a room or area. By monitoring movement and presence, occupancy sensors can automatically turn lights on when a room is occupied and turn them off when it’s empty
Daylight Sensors:
Daylight sensors measure the amount of natural light entering a space. They adjust artificial lighting levels based on the availability of daylight, reducing the need for electrical lighting during the day and contributing to energy savings.
Motion Sensors:
Motion sensors detect movement within a space and can be used in conjunction with occupancy sensors to provide more granular control.
How Sensors and Controls Adjust Lighting:
Sensors continuously monitor real-time conditions and send data to the lighting control system. Based on this data, the system makes automatic adjustments to lighting levels, ensuring optimal illumination while minimizing energy consumption.
Centralized Management Software
Role of Software:
Centralized management software acts as the hub of a Smart Lighting Management system, providing a user interface for monitoring, controlling, and scheduling lighting. Through this software, facility managers or building occupants can set lighting schedules, adjust settings, and create customized lighting scenes based on specific needs or events.
Data Analytics and Insights:
Intelligent Lighting Management software includes robust data analytics capabilities that track lighting usage patterns, energy consumption, and system performance. These analytics provide valuable insights into how lighting is being used, helping identify areas for improvement and opportunities for further energy savings.

Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS)
How Intelligent Lighting Management Integrates with Other Smart Building Systems:
Intelligent Lighting Management systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with other Building Management Systems (BMS), such as HVAC, security, and energy management systems.
Synergy Between Intelligent Lighting Management and Other Systems:
HVAC Integration: Intelligent Lighting Management can work in tandem with HVAC systems to optimize both lighting and climate control. For example, lighting systems can be adjusted based on HVAC settings to improve energy efficiency, such as dimming lights in areas where cooling is required or increasing lighting in spaces where heating is in use.
Security Systems Integration: When integrated with security systems, Smart Lighting Management can enhance building safety. For instance, lighting can be automatically adjusted or turned on in response to security alerts or during specific times of the day, providing better illumination in critical areas.
Energy Management Systems Integration: Intelligent Lighting Management contributes to broader energy management goals by providing detailed data on lighting energy consumption. When combined with energy management systems, Intelligent Lighting Management helps track and optimize overall energy use, contributing to reduced operational costs and improved sustainability.
OCTIOT Intelligent Lighting Management
OCTIOT Smart Lighting Management represents a significant leap forward in sustainable building practices, offering advanced solutions that optimize energy use, enhance comfort, and reduce operational costs. By integrating smart technology with efficient lighting systems, OCTIOT not only improves the functionality and longevity of lighting infrastructures but also contributes to a reduced carbon footprint. This intelligent approach to lighting ensures that spaces are illuminated in the most efficient and environmentally friendly manner possible. As we move towards a more sustainable future, OCTIOT stands at the forefront, providing innovative lighting solutions that align with the global goals of energy efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Contact us: 088600 12342
For more information: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
What is Data Lifecycle Management and Why is it Important?

Welcome! Data lifecycle management is a policy approach to manage the flow of informational data to its lifecycle. Furthermore, DLM products automate these lifecycle management processes, organising data into separate according to specified policies.
Moreover, they automate data migration from one tier to another based on those criteria. New data and data lifecycle management software that must be accessed more frequently is typically stored on faster and more expensive storage media.
In contrast, less critical data is stored on cheaper, slower media. In addition, DLM ensures the seamless flow of information throughout its lifecycle, with three main goals of data lifecycle management: confidentiality, integrity, and availability, also called the CIA triad. Lastly, DLM optimises data handling, ensuring that your information is always in the right place at the right time.
What is data lifecycle management?

Data lifecycle management (DLM) is a systematic approach to handling data from creation to deletion. Data is categorised into phases based on specific criteria and progresses through these stages as it fulfils various purposes.
Effective DLM organises data and ensures it supports critical business objectives such as security, accessibility, and customer support solutions.
As businesses face increasing risks from data breaches and system failures, robust DLM policies become indispensable. They enable organisations to prepare for and mitigate potential disasters, safeguarding their financial health and reputation.
Businesses can swiftly recover from adverse events and minimise operational disruptions by prioritising data protection and disaster recovery.
Implementing a comprehensive DLM strategy is crucial in today’s data-driven landscape, where data volumes rapidly expand and threats evolve. Proactively managing the data lifecycle enhances operational efficiency and reinforces resilience against unforeseen challenges.
Data lifecycle management vs information lifecycle management

Data lifecycle management (DLM) and information lifecycle management (ILM) are crucial to effective data management strategies. While ILM focuses on managing individual data pieces throughout their lifecycle, DLM oversees file-level data, considering factors like type, size, and age.
1. Data Lifecycle Management
Data lifecycle management (DLM) primarily deals with file-level data, encompassing management based on file characteristics such as type, size, and age. It ensures files are appropriately stored, accessed, and eventually disposed of by organisational policies and regulatory requirements.
Effective DLM can streamline workflows and enhance data security in it services project management, ensuring project data is managed efficiently throughout its lifecycle.
2. Information Lifecycle Management
ILM, sometimes used interchangeably with DLM, uniquely addresses managing individual data elements within files. It focuses on maintaining data accuracy and relevance through timely updates and ensuring compliance with data governance standards.
Phases of data lifecycle management

Data lifecycle management (DLM) encompasses several sequential phases that govern data from creation to disposal. Each phase is guided by specific policies to optimise the data’s utility throughout its lifecycle.
As businesses handle increasing volumes of data, effective DLM strategies are crucial. The phases include data creation, storage, usage, sharing, archival, and eventual disposal. Implementing DLM ensures data remains valuable and secure at every stage.
1. Data Creation
The data journey begins with its creation, sourced from various channels such as web applications, mobile devices, IoT gadgets, surveys, and more. Notably, not all data is essential for business success; new data integration should prioritise quality and relevance.
2. Data Storage
Data comes in different structures, influencing the choice of storage methods. Structured data often fits nicely into relational databases, while unstructured data finds compatibility with NoSQL databases.
Once the storage type is determined, infrastructure security is crucial, involving measures like data encryption and transformation to protect against cyber threats.
However, compliance with regulations such as GDPR is essential to avoid penalties and ensure data privacy. Business intelligence consulting services play a vital role in optimising these processes, offering expertise in data management, analytics, and strategic decision-making based on comprehensive insights derived from diverse data sources.
3. Data Sharing and Usage:
During this phase, data becomes accessible to business users. DLM enables organisations to specify who can access the data and for what purposes.
Once available, data supports various analyses, from fundamental exploratory data analysis to advanced techniques like data mining and machine learning.
These methods aid in critical business decisions and stakeholder communications. Moreover, data isn’t limited to internal use; external parties such as service providers may leverage it for activities like marketing analytics. Internally, data fuels everyday processes like dashboards, presentations, and software implementation.
4. Data Archival
Over time, data becomes less relevant for daily operations but remains crucial for potential legal or investigative needs.
A robust DLM strategy outlines when, where, and how long data should be archived. Data undergoes an archival process to ensure redundancy, allowing restoration to an active production environment when necessary.
5. Data Deletion
In the final stage, obsolete data is securely purged from records to free up storage space. Organisations delete data that exceeds retention periods or no longer serves a purpose. This step ensures data hygiene and compliance with data protection regulations.
Benefits of data lifecycle management

1. Process Improvement
Data lifecycle management (DLM) is pivotal for organisations aiming to optimise their operations.
Addressing the entire journey of data from creation to disposal, DLM ensures data integrity and reliability. This reliability becomes the bedrock for process improvement initiatives within enterprises.
By maintaining high data quality throughout its lifecycle, organisations can confidently embrace strategic initiatives. Reliable data enables informed decision-making, streamlines workflows, and enhances operational efficiency.
A robust DLM strategy not only safeguards data but also ensures that it remains a valuable asset, driving continuous improvement across all facets of the organisation.
2. Controlling Costs
In addition to process enhancement, effective DLM (Data Lifecycle Management) contributes significantly to cost management strategies and overall business growth consultancy. Organisations can venture into cost-effective solutions at each stage of the data lifecycle.
For instance, as data transitions from active to inactive phases, organisations can leverage various methods, such as archiving and data backup, to reduce storage costs. This involves transferring less-critical data to economical storage options like on-premises servers, cloud storage, or network-attached storage (NAS).
By implementing such measures, businesses can optimise their IT spending and ensure compliance with data retention policies and industry regulations.
3. Data Usability
Implementing a Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) strategy allows IT teams to establish clear policies and procedures for consistent metadata tagging. This tagging ensures that all data is easily accessible when needed, improving its usability.
By enforcing governance policies effectively, organisations can retain the value of their data for as long as necessary. Clean and well-tagged data enhances operational agility and efficiency, facilitating smoother company processes.
4. Compliance and Governance:
In every industry, specific rules dictate how long data must be retained, and a robust DLM strategy helps businesses adhere to these regulations. DLM enables organisations to manage data more efficiently and securely while ensuring compliance with privacy laws governing personal and organisational data.
Key stages of data lifecycle management

1. Collection Stage
The initial phase in data lifecycle management is data collection, where businesses accumulate information from both internal and external sources.
This stage may also be called data creation, acquisition, or entry, depending on the method of populating the database—whether through manual input or automated processes.
At Segment, we advocate prioritising the collection of first-party data derived directly from customer interactions such as on-site behaviours, app usage, and survey responses.
First-party data boasts higher accuracy than third-party purchased data, fosters trust with customers, and ensures compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, thus safeguarding future marketing and advertising strategies.
2. Storage Stage
Following data collection, the next critical step is storage. A common pitfall for businesses is dispersing data across disparate teams and data lifecycle management tools, resulting in fragmented insights into customer behaviour and overall business performance.
A practical data lifecycle management framework addresses this challenge by establishing a centralised repository and creating a unified source of truth within the organisation.
The nature of the data collected determines the appropriate storage solution; structured data, akin to information suitable for Excel sheets, should reside in relational databases or data warehouses.
3. Processing Stage
Once stored, data must undergo processing to become actionable. Data processing encompasses encryption, wrangling, and compression. Encryption involves converting human-readable data into a format decipherable only by authorised personnel, ensuring data security.
Data wrangling focuses on cleaning and transforming raw data into a structured and accessible format. Meanwhile, data compression reduces data size through restructuring or encoding, facilitating efficient storage and retrieval.
4. Analysis Stage
Data analysis involves examining processed or raw data to uncover trends and patterns. Machine learning, statistical model, and artificial intelligence are employed here.
This pivotal stage provides valuable insights into business operations and customer behaviour. For instance, it helps identify weak points in sales funnels or potential customer churn risks.
5. Deployment Stage
Also known as dissemination, the deployment stage focuses on validating, sharing, and utilising data. However, the data validation ensures the accuracy and integrity of the data structure.
Sharing involves communicating insights to stakeholders through reports, graphs, dashboards, and other visualisations.
Data usage consists of leveraging insights to drive strategic decisions and business growth. Data lifecycle management aims to democratise data, enabling various teams like marketing and product management to use insights effectively in their day-to-day operations.
6. Archiving Stage
Archiving entails moving data from active deployment environments to long-term storage. While no longer operationally critical, archived data is a resource for future reference or analysis.
However, it also poses security risks if not managed properly. Utilising secure archiving tools helps mitigate these risks by prioritising data privacy and preventing unauthorised access.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective data lifecycle management (DLM) is not merely a best practice but a critical necessity in today’s data-driven landscape.
By systematically managing data from creation to deletion, organisations ensure compliance with regulations, enhance operational efficiency and mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
Moreover, DLM facilitates strategic decision-making by providing reliable, accessible data throughout its data management lifecycle. This approach optimises resource allocation, reduces costs, and supports business continuity and resilience.
Implementing a robust DLM strategy involves defining clear policies for data handling at each stage—collection, storage, processing, analysis, deployment, and archiving.
Source: Data Lifecycle Management
0 notes
Text
AI Transforms Filmmaking: From Script to Screen
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is currently transforming the way movies are made, from the initial concept straight through to the final edits. Here's a deeper dive into how AI tools and technologies are making the filmmaking process more efficient, creative, and cutting-edge.
Revolutionizing Film Editing
Editing film can be a time-consuming part of the process. AI is here to help. Adobe Premiere Pro's Auto Reframe and DaVinci Resolve employ machine learning algorithms that not only speed up the editing but enhance the finished product. These AI tools auto-adjust framing, suggest the best cuts, and fine-tune audio quality, effectively making smart decisions that traditionally took editors hours to accomplish.
AI in editing doesn’t stop there. Tools like Audiomotion's AI-Assisted Dialogue Editing clean up and enhance audio automatically, saving precious time an improving sound quality. By reducing tedious tasks, AI software allows editors to focus more on the creative aspects of their work.
Enhancing Production Efficiency
AI steps into the production process through predictive analytics and AI-assisted scouting. ScriptBook's AI analyzes scripts to predict continuity errors before they happen, potentially saving hours in reshoots. Furthermore, Cinelytic provides AI-driven suggestions for optimal filming locations, considering factors such as costs and logistical constraints, reducing the heavy lifting in pre-production planning.
Additionally, AI uses predictive analysis to foresee potential issues in scripts, creating a smoother filming process. AI-powered platforms also help with location scouting by analyzing data like cost and weather, providing the best shooting sites effortlessly. This input drastically reduces the physical and logistical workload of production teams.
AI is turning the tide in VFX by automating intensive processes like lighting and rendering. Foundry's Katana and AI-based motion capture solutions like Rokoko's Smartsuit Pro reduce the need for extensive manual input, allowing more time for creative exploration. Also, AI-generated 'deepfakes' have emerged as a groundbreaking tool for achieving near-perfect CGI characters or effects such as de-aging.
Case Study: Disney's The Mandalorian
Showcases like Disney's The Mandalorian demonstrate AI's transformative potential in filmmaking. Using ILM's StageCraft technology, the series created unmatched dynamic environments, reducing physical set needs and associated costs significantly.
Case Study: Netflix Post-Production
Similarly, Netflix integrates AI for efficient post-production activities, automating tasks like color correction and captioning to ensure consistency and quality. These examples underscore AI's increasing role in filmmaking.
From enhanced editing to revolutionary VFX, embracing AI tools liberates creative energies and refines production workflows. As AI technologies evolve, staying updated and adaptable becomes essential for filmmakers looking to push conventional boundaries and create engaging cinema experiences.
0 notes
Text
3D Animation Studio Pioneering Innovation In Digital Storytelling In The USA
The USA has long been at the forefront of the entertainment industry, particularly in the realm of animation. With the rise of digital technologies, usa 3D animation studios in the USA have carved out a niche of extraordinary influence and creativity, setting global standards in visual effects, character design, and narrative engagement. This blog delves into the world of 3D animation in the USA, exploring the key studios, their groundbreaking work, and what makes them leaders in the digital storytelling arena.

Evolution of 3D Animation in the USA
The journey of 3D animation in the USA began in the early 1990s when the first fully computer-generated feature film, Pixar's "Toy Story," revolutionized the genre. Since then, the industry has seen exponential growth, with technological advancements enabling more complex animations and more realistic visuals. Today, 3D animation is a staple in feature films, television, video games, and virtual reality, offering audiences immersive experiences that were once unimaginable.
Leading USA 3D Animation Studios
1. Pixar Animation Studios:
Located in Emeryville, California, Pixar is synonymous with 3D animation excellence. Known for its rich storytelling and pioneering software development, Pixar continues to be a leader in the industry with award-winning films like "Finding Nemo," "Up," and "Coco."
2. DreamWorks Animation:
Another titan in the industry, DreamWorks Animation has created some of the most beloved franchises, including "Shrek," "Madagascar," and "How to Train Your Dragon." Their ability to blend humor with heartwarming narratives has earned them a special place in the hearts of viewers worldwide.
3. Industrial Light & Magic (ILM):
Founded by George Lucas in 1975, ILM has played a crucial role in the development of 3D animation techniques, especially in the realm of visual effects. While known for their work on the "Star Wars" series, their contributions to the field of animation are profound, pushing the boundaries of what 3D graphics can achieve.
4. Blue Sky Studios:
Although it was closed in 2021, Blue Sky Studios was renowned for producing "Ice Age" and "Rio." Their innovative use of 3D animation technology to create endearing characters and dynamic environments has left a lasting legacy in the industry.
Innovations and Contributions
USA 3D animation studios are not just production houses; they are hubs of innovation. Many studios develop their own proprietary software to tackle unique animation challenges. For instance, Pixar's RenderMan technology has become a fundamental tool in the industry, used widely to produce photorealistic imagery efficiently.
Furthermore, these studios often collaborate with academic institutions and technology companies to research and develop new animation techniques and tools, contributing to the industry's growth and education. Such partnerships ensure the continual evolution of animation technology, keeping the USA at the cutting edge of digital arts.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its successes, the USA 3D animation industry faces challenges such as high production costs and intense competition from studios around the world. However, these challenges also drive innovation and creativity. There is also a significant push towards inclusivity and diversity, both in storytelling and in the workforce, which is opening new avenues for cultural narratives and creative voices.
Future Trends in 3D Animation
Looking ahead, the future of 3D animation in the USA is geared towards more realistic animations, AI integration, and immersive experiences. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are becoming increasingly significant, offering new ways for audiences to experience storytelling. Moreover, with the rise of streaming platforms, there's a growing demand for high-quality animated content, ensuring that the industry's growth remains robust.
Conclusion
USA 3D animation studios have not only defined industry standards but also continue to innovate and inspire creators around the world. They blend technology with creativity to tell stories that captivate, entertain, and enlighten, making them central to the global narrative of digital media. As technology advances, these studios are well-positioned to lead the way, exploring new realms of what animation can achieve and how stories can be told. Whether you're a film buff, a budding animator, or just a fan of good storytelling, the contributions of these studios to the world of entertainment are undeniable and are set to expand even further in the coming years.
0 notes
Text
The Evolution of VFX: From Classic Films to Modern Blockbusters
The Evolution of Visual Effects (VFX) in cinema is a fascinating journey that has transformed the way stories are told on the silver screen. From the early days of practical effects to the groundbreaking digital technologies of today, VFX has played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of filmmaking, elevating storytelling to new heights and captivating audiences worldwide. Institutions like MAAC Institute have been instrumental in this evolution, providing aspiring filmmakers with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in the dynamic world of VFX. Through comprehensive programs and hands-on training, MAAC Institute prepares students to harness the power of digital tools and techniques to create stunning visual effects that push the boundaries of imagination. With MAAC Institute's guidance, the next generation of VFX artists and technicians are poised to continue the legacy of innovation and creativity in cinema for years to come.
The roots of VFX can be traced back to the earliest days of cinema, where filmmakers employed practical techniques such as matte paintings, miniatures, and stop-motion animation to create visual illusions on screen. One of the earliest examples of VFX can be seen in Georges Méliès' iconic film "A Trip to the Moon" (1902), where groundbreaking techniques such as double exposure and hand-painted color were used to bring fantastical worlds to life.
As technology advanced, so did the art of visual effects. The invention of the green screen technique in the 1930s revolutionized filmmaking, allowing filmmakers to seamlessly composite actors and sets against any backdrop imaginable. This innovation paved the way for the epic spectacles of the Golden Age of Hollywood, with films like "The Wizard of Oz" (1939) and "King Kong" (1933) pushing the boundaries of what was possible on screen.
The advent of computer-generated imagery (CGI) in the 1970s and 1980s marked a significant turning point in the evolution of VFX. With the release of films like "Star Wars" (1977) and "Tron" (1982), filmmakers began to explore the limitless possibilities of digital effects, using computers to create stunning visuals that were previously unimaginable. The development of pioneering software such as Pixar's RenderMan and Industrial Light & Magic's (ILM) proprietary tools further accelerated the growth of CGI in filmmaking.
The 1990s saw a surge in the use of CGI in blockbuster films, with groundbreaking works like "Jurassic Park" (1993) and "Terminator 2: Judgment Day" (1991) pushing the boundaries of what could be achieved with digital effects. These films showcased the power of CGI to create photorealistic creatures and environments, immersing audiences in breathtaking worlds beyond their imagination.
In the 21st century, advancements in technology have enabled filmmakers to push the boundaries of VFX even further, with films like "Avatar" (2009) and "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy (2001-2003) raising the bar for visual storytelling. These films utilized cutting-edge techniques such as performance capture and motion capture to create immersive digital worlds populated by lifelike characters and creatures.
Today, VFX plays a central role in virtually every aspect of filmmaking, from blockbuster action films to intimate dramas. The integration of VFX into filmmaking has become so seamless that audiences often don't realize the extent of the digital manipulation happening on screen. From enhancing practical effects to creating entirely digital environments, VFX artists continue to push the boundaries of what's possible, blurring the line between reality and fantasy.
Furthermore, the rise of streaming platforms and digital distribution has opened up new opportunities for VFX artists to experiment with storytelling in innovative ways. From interactive storytelling experiences to virtual reality narratives, the future of VFX holds endless possibilities for pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling even further.
In conclusion, the evolution of VFX from classic films to modern blockbusters has been nothing short of remarkable. From the early days of practical effects to the cutting-edge digital technologies of today, VFX has transformed the way stories are told on screen, captivating audiences and transporting them to worlds beyond their imagination. As technology continues to advance, the future of VFX holds endless possibilities for pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling even further, ensuring that the magic of cinema continues to captivate audiences for generations to come.
0 notes
Text
HELP NEEDED: 1997 KODAK DC120 COMPACTFLASH CARDS
i am fucking pulling my hair out over this shit this camera uses "ATA CF" cards and i have no fucking clue how to format it properly for this thing I know the following: FAT16 256MB limit (supposedly) Fixed disk requirement (supposedly) I've tried everything. 4 heads, 8 heads, 4096 bytes / sector, 1024 bytes failed; 3 other cards failed ITS JUST THIS SINGLE ONE.
I have an image of the card, and even when I put the image of that card ON THE OTHER CARDS it refuses to work. At this point, is it a hardware issue? or a software issue? PLEASE HELP. - Ilme
1 note
·
View note
Text
Maximizing Efficiency: Exploring the Power of Integrated Logistics Management and Innovative Software Solutions
In the dynamic landscape of modern supply chain management, businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to optimize their logistics operations and stay ahead of the competition. Integrated Logistics Management, coupled with advanced software solutions such as Reverse Logistics Software and Logistics Optimization Software, offers a comprehensive approach to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall efficiency. In this blog post, we'll delve into the significance of these solutions and how they can revolutionize logistics management.

1. Integrated Logistics Management
Integrated Logistics Management (ILM) is a holistic approach to managing the flow of goods and information across the entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery. Key components of ILM include:
End-to-End Visibility: ILM provides real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, enabling businesses to track shipments, monitor inventory levels, and identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
Collaboration: ILM fosters collaboration among stakeholders, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, facilitating seamless coordination and communication across the supply chain.
Optimization: By integrating various logistics functions such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory management, ILM helps businesses optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve service levels.
2. Reverse Logistics Software

Reverse Logistics Software (RLS) is a specialized solution designed to manage the reverse flow of products, materials, and information from the end consumer back to the point of origin. Key features of RLS include:
Returns Management: RLS automates the returns process, including return authorization, product evaluation, and disposition, streamlining the handling of returned goods and reducing processing times.
Repair and Refurbishment: RLS facilitates the repair and refurbishment of returned products, enabling businesses to recover value from returned items and minimize waste.
Asset Recovery: RLS helps businesses recover valuable assets from returned products, such as components or materials that can be reused or recycled, reducing disposal costs and environmental impact.
3. Logistics Optimization Software
Logistics Optimization Software (LOS) is a sophisticated tool that leverages advanced algorithms and analytics to optimize various aspects of logistics operations. Key capabilities of LOS include:
Route Optimization: LOS optimizes delivery routes to minimize transportation costs, reduce fuel consumption, and improve delivery efficiency.
Inventory Optimization: LOS analyses demand patterns and inventory levels to optimize inventory replenishment, minimize stockouts and overstocks, and improve inventory turnover.
Warehouse Optimization: LOS optimizes warehouse layout, storage locations, and picking processes to maximize space utilization, reduce labour costs, and enhance order fulfilment speed.
Conclusion
In today's highly competitive marketplace, businesses must embrace Integrated Logistics Management and leverage advanced software solutions such as Reverse Logistics Software and Logistics Optimization Software to stay agile, efficient, and responsive to changing customer demands. By adopting an integrated approach to logistics management and harnessing the power of innovative technologies, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, profitability, and sustainability in the evolving landscape of global supply chains.
For original post :- https://blague-courte.com/maximizing-efficiency-exploring-the-power-of-integrated-logistics-management-and-innovative-software-solutions
0 notes
Text
Autodesk Maya, a powerful 3D computer graphics software, has revolutionized the landscape of the creative industries. From film and television production to video game development and beyond, Maya stands as a versatile tool that empowers artists and creators to bring their visions to life
Film and Animation: Bringing Fantastical Worlds to Life
Visual Effects (VFX): Maya is a cornerstone in the creation of visual effects for blockbuster films. Studios like Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) have used Maya in films like "Star Wars: The Force Awakens" to seamlessly integrate CGI elements with live-action footage.
Animated Feature Films: Animation studios, including Pixar and DreamWorks, leverage Maya to craft stunning animated worlds. Films like "Toy Story" and "How to Train Your Dragon" showcase the software's ability to model characters, simulate physics, and render lifelike animations.
Video Game Development: Shaping Immersive Gaming Experiences
Character Design and Animation: Maya is widely employed in the gaming industry for character design and animation. Game developers utilize the software to create detailed 3D models and animations that enhance the player's immersive experience.
Environment Design: Maya's capabilities extend to the creation of expansive game environments. Whether it's a post-apocalyptic wasteland or a vibrant fantasy realm, Maya allows designers to build intricate landscapes that captivate players.



0 notes
Text
What is Virtual Production?
youtube
What is Virtual Production — Pros, Cons & Process Explained (studiobinder.com)
uses computer-generated imagery (CGI), augmented reality, motion capture, and other technologies to create realistic environments and effects on a virtual set.
Most commonly, virtual production is achieved through sets made with LED walls. This typically works by projecting images generated by a computer from the wall. These projections can be used to create sets, backgrounds, and interactive environments that appear realistic onscreen.
What is Virtual Production Used For?
Creates sets and environments quickly
Reduces the cost of traditional sets and props
Enables filmmakers to make instant adjustments
Allows for a more natural and controlled lighting setup
The main process behind virtual production is the integration of different technologies. Most commonly achieved through Unreal Engine and software such as ILM's Stagecraft.

When a live-action camera moves, the virtual environment on the LED wall shifts perspective as well, using gaming technologies to navigate a virtual landscape. The unison of movement between camera and imagery is called parallax, creating the illusion of a single physical location. Live camera tracking translates accurate camera movements into the rendering platforms where they are realized in real-time.
What is Virtual Production? A Guide to Getting Started | CG Spectrum

0 notes
Text
WHERE DOES 3D ANIMATION COME FROM?
By enrolling in the design and technology program at MAAC institute in Pune, you will have the opportunity to cultivate and enhance your creativity, problem-solving abilities, planning skills, and evaluative thinking. The program's emphasis on collaborative group projects will also enable you to develop effective communication and teamwork aptitudes. Additionally, the program will provide ample opportunities to unleash your creative potential and nurture your innate artistic abilities.
3D animation, also known as computer-generated imagery (CGI), has a fascinating and storied history that dates back several decades. The roots of 3D animation can be traced back to the early days of computer graphics and the pioneering efforts of various individuals and institutions.
The Origins:
The birth of 3D animation can be linked to the development of computer graphics in the 1960s and 1970s. Ivan Sutherland, often referred to as the "father of computer graphics," created the first computer-generated image, a simple line drawing, in 1963. This breakthrough laid the foundation for further advancements in computer-generated imagery.
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, researchers and computer scientists began exploring the potential of creating more complex images and animations using computers. One of the early milestone achievements was the short film "A Computer Animated Hand" (1972) by Ed Catmull, who would go on to co-found Pixar Animation Studios. This film showcased a 3D-rendered hand, demonstrating the possibilities of computer animation.
The Pioneering Institutions:
In the 1970s and 1980s, several institutions played a crucial role in advancing 3D animation. The University of Utah's Computer Science Department, under the leadership of Ivan Sutherland and Edwin Catmull, was at the forefront of computer graphics research. The team at the University of Utah developed groundbreaking algorithms and techniques for rendering and animating 3D objects.
In 1974, the New York Institute of Technology's Computer Graphics Lab, led by Edwin Catmull and Alexander Schure, created "Hummingbird," one of the earliest examples of a 3D-rendered character.
Industrial Light & Magic (ILM), founded by George Lucas in 1975, was instrumental in pushing the boundaries of 3D animation in the film industry. ILM's work on films like "Star Wars" and "Terminator 2: Judgment Day" showcased the potential of using 3D computer graphics for special effects and character animation.
The Rise of Pixar:
One of the most significant milestones in the history of 3D animation was the founding of Pixar in 1986. Initially a division of Lucasfilm, Pixar was later purchased by Steve Jobs in 1986 and became an independent company. Pixar's first short film, "Luxo Jr." (1986), directed by John Lasseter, marked a breakthrough in character animation. It featured the iconic Luxo desk lamp, which became Pixar's mascot, and received an Academy Award nomination.
Pixar went on to create the first feature-length 3D-animated film, "Toy Story," released in 1995, which was a massive commercial and critical success. This film heralded a new era in animation, proving that 3D animation could not only compete with traditional 2D animation but also push the boundaries of storytelling and visual creativity.
Modern Advancements:
Since the success of "Toy Story," 3D animation has become a dominant force in the animation and entertainment industry. Technological advancements have made 3D animation more accessible, allowing artists and animators to create stunning visuals with sophisticated tools and software.
Today, 3D animation is ubiquitous, found in various industries, including film, television, video games, advertising, architecture, medical visualization, and education. The evolution of 3D animation continues, with ongoing advancements in technology and artistic innovation shaping the future of this dynamic and captivating medium.
0 notes
Text
NA2SAP - SAP Data Archiving, S/4 HANA Archiving, ACDOCA Archiving, ILM with Azure Blob.
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations require robust and scalable solutions to streamline their operations, optimize productivity, and achieve sustainable growth. NA2SAP is an SAP enterprise software company that extensively provides the SAP system services such as :
S/4 HANA Archiving, ACDOCA Archiving, ILM with Azure Blob, etc.
Some additional SAP services are:
SAP Data Archiving, SAP ILM, SAP Migration, SAP Upgrade, SAP Conversion, SAP NSE, and SAP System Decommissioning.
SAP System, a global leader in enterprise software, offers a comprehensive suite of integrated solutions designed to transform businesses across industries. This article explores the key benefits and features of SAP System solutions and how they can empower organizations to stay ahead of the competition.
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Integration:
SAP System solutions such as S/4 HANA Archiving, ACDOCA Archiving, ILM with Azure Blob, etc. enable seamless integration of various business functions, such as finance, supply chain, sales, and human resources. By consolidating data and processes, organizations can eliminate silos, reduce manual errors, and enhance operational efficiency. The system’s centralized approach ensures real-time visibility, allowing businesses to make informed decisions and respond swiftly to market changes.
2. Scalability and Flexibility:
As businesses expand, their technology infrastructure needs to accommodate growth. SAP System solutions offer scalability and flexibility, enabling organizations to adapt to changing requirements. Whether it’s supporting a small startup or a multinational corporation, SAP solutions can scale up or down accordingly. This scalability ensures that the system continues to meet the evolving needs of businesses without compromising performance.
3. Streamlined Financial Management:
Financial management is critical for any organization’s success. SAP System solutions provide comprehensive tools for financial planning, accounting, and reporting. With real-time insights into financial performance, businesses can make informed decisions, manage cash flow effectively, and ensure regulatory compliance. Furthermore, automated financial processes minimize manual errors, enhance accuracy, and expedite month-end closings.
4. Optimized Supply Chain Operations:
Efficient supply chain management is vital to meet customer demands while minimizing costs. SAP System solutions offer end-to-end supply chain visibility, allowing organizations to monitor inventory levels, track orders, and streamline logistics. By optimizing procurement, production, and distribution processes, businesses can reduce lead times, enhance supplier collaboration, and achieve cost savings.
5. Customer-Centric Approach:
In today’s customer-centric era, delivering exceptional experiences is crucial for business success. SAP System solutions enable organizations to understand customer behavior, preferences, and trends through robust customer relationship management (CRM) functionality. This empowers businesses to personalize marketing efforts, improve customer service, and build lasting relationships. By gaining a 360-degree view of customers, organizations can offer tailored products and services that meet their unique needs.
6. Enhanced Analytics and Reporting:
Data-driven decision-making is the cornerstone of modern businesses. SAP System solutions offer powerful analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights from their data. With intuitive dashboards and visualizations, businesses can monitor KPIs, identify trends, and uncover growth opportunities. Advanced analytics tools facilitate predictive modeling and forecasting, empowering businesses to make proactive decisions and stay ahead of the competition.
Conclusion:
SAP System Solutions provide a comprehensive suite of integrated software solutions that empower organizations to transform their operations, drive efficiency, and achieve sustainable growth.
By leveraging SAP’s robust capabilities in financial management, supply chain optimization, customer relationship management, and data analytics, businesses can gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace. Whether it’s a small startup or a global enterprise, SAP System solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and innovation to meet the evolving needs of organizations across industries.
Embrace SAP System solutions to unlock your business’s true potential and embark on a journey toward success.
1 note
·
View note