#IZiel Healthcare
Text
What is an MDR Gap Analysis?
Until today, medical devices were complying with the Medical Device Directive to sell their products in Europe. However major amendments are made in the current MDD to keep up with the growing technological advances in healthcare and medical devices. The new regulations passed by the Council of the European Union is Medical Device Regulations (MDR) 2017/745 that came into force in May 2017 & manufacturers have a transition time of three years until May 2021 to comply with the new regulations.
An MDR Gap Analysis is the process of systematically examining a medical device’s clinical evidence portfolio to determine whether it demonstrates conformity with all relevant MDR requirements. It is a crucial first step in developing and maintaining an MDR compliance strategy.
Typically, all MDD-MDR transition projects initiate with Gap Assessment. Gap Assessment is a crucial activity during MDR transition & our team with engineering & regulatory expertise are well equipped to conduct this activity with an analytical mindset, resolve any regulatory concern and develop robust regulatory strategy for medical device manufacturers.
IZiel’s “ONE-STOP COMPLETE SOLUTION” include –
· Gap Assessment
· Technical File Preparation
· QMS Documentation
· Expert Review & Recommendations
· European Authorized Representative (EC REP)
· EUDAMED
· Mock Audits & Trainings
· PRRC Services
· Clinical Evaluation Plan & Report
· Software Validation
IZiel team of specialists and quality professionals look forward to support more medical device companies to file their devices under the MDR 2017/745.
0 notes
Text
IZiel Group partners with the Best-in-Class Companies to provide comprehensive services to various Multinational Clients in the Engineering and Healthcare Sectors.
0 notes
Link
Iziel Healthcare is offering complete solution in Process Validation for Medical Devices. Our team is Design for Six Sigma (DFSS - Black Belt Level) trained and is fully competent to conduct requirements management, process validations, that are ISO13485, US FDA & CE approval compliant
0 notes
Text
Common Issues in Healthcare Mergers and Acquisitions
Mergers & Acquisition in the healthcare industry has been strong in recent years and is expected to grow. Acquiring a new company or product line can have a positive business impact, but it also comes with implementation, process, quality & regulatory challenges. Especially, in the medical device industry, failure to comply with regulations can result in the loss of authority to deliver products and services.

While the impact of COVID-19 on these deals is yet to be felt, it remains an advantageous avenue for organizations to pursue. But what are the common issues in healthcare mergers and acquisitions?
· Failed Cultural Integrations
This type of issue has the potential of increasing operational costs. Staff are unsure about the correct working procedures or administrative processes, agreed upon by the integrated management but not accurately communicated business wide. This could result in mismanaged patients, poor results, and even costly mistakes.
· Standardizing Operational Procedures
Structural change like this isn’t easy — it requires dedication, communication, and a lot of training. But it’s not impossible. Overall, it can influence improved behavioral changes. However, remember that all changes need to reflect the needs of the staff. Something implemented universally that only benefits or works for 50% of healthcare providers isn’t something worth pursuing.
Clinical practice unification is the best way of ensuring that what were two or more separate healthcare providers now view themselves as a collective.
· Supply Chain Risks
In most cases, the costs of supplies will increase post-merger, almost immediately. This is to be expected, as two separate market shares become one, which can drive up prices, especially if that market share is a large one.
· Reduction in Care Quality
It comes down to an issue we’ve already mentioned — clinical variation. Merged systems have different ways of doing things, meaning that Care Variation Reduction (CVR) is a common problem within healthcare M&As.
The two parties need to approach the process with foresight and caution. There needs to be an early focus on capturing similarity within your care offerings, alongside a singular approach to IT and administrative tasks. In the best-case scenarios, this is implemented before the actual merger is completed.
Strong Project Management, Medical device Expertise, Quick Scalability of Skilled Resources are the key enablers of our success for Acquisition Integration Projects. As depicted above, IZiel’s approach has been very comprehensive and methodical. IZiel team can support your team in various ways.
Why to Choose IZiel?
At IZiel, our team has upgraded thousands of documents for various acquisition integration projects of Class I, II & III medical device companies. Our Outcome Based & Onshore-Offshore Delivery Model has worked effectively to complete the Post-Merger Integration with significant reduction in timelines and budgets.
#acquisition integration#mergers & acquisition#Post Acquisition Integration for medical device#IZiel Healthcare
0 notes
Text
Configuration Management in the Medical Device Industry
Configuration management is “a process for establishing and maintaining the consistency of a product’s performance, functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design and operational information throughout its life.”
It is imperative to develop product configurations and manage effectively. A structured configuration management program ensures accurate and consistent product documentation (e.g., requirements, design, test, and acceptance documentation) along with the actual physical design of the product. Configuration Management plays an important role to ensure thorough product variations to enhance customer satisfaction, competitiveness, profitability & continuous changes / requirements. Therefore, it’s critical that the product and process configuration is unified across the organization, which minimizes handoffs of specialized information.
Configuration Management must include –
1. Enterprise or Unified Supply Chain Configuration Solution
2. Error-Proofing
3. Intuitive and Flexible
IZiel has highly trained configuration managers who will be able to create, coordinate and implement the Configuration Management Plan (CMP – includes responsibilities and resources, (including personnel), training requirements, administrative meeting guidelines (including a definition of procedures and tools), baselining processes, configuration control and configuration-status accounting, naming conventions, audits and reviews, subcontractor / vendor configuration management requirements, regulatory requirements) for Product Creation Process (PCP) projects in co-operation with the Project Managers and Operations Department.
0 notes
Text
What is Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up?
PMCF study is carried out for CE certified medical devices that are placed in the market. It’s a method of proactive collection of clinical data to analyze the emergent risks/side-effects of the medical device to demonstrate the safety and performance as per the intended purpose, throughout the expected lifetime of the device.
Performance and safety parameters are predefined with acceptance criteria based on the benchmark devices data, and milestones are designed for several PMCF studies and activities. The literature screening and registries study also supports PMCF findings. The sample size is predefined as per the sales of the device to study the emergent risks. Benefit-risk ratio analysis is performed as per the PMCF findings, for the acceptability of the device in the market. The PMCF findings are also documented in Technical Documentation, Risk File, SSCP, CER and PSUR
PMCF Includes
PMCF Procedure
PMCF Plan
PMCF Report
PMCF Plan
PMCF Protocol
Sample Size
Design of Milestones with follow-up period
Design of measurable endpoints for performance and safety
Ethical Committee approval
Questionnaire/Survey form
Patient/subjects consent form
Clinical Investigation/Trial procedure (if any)
Real World Evidence
Statistical Significance
PMCF Report
Milestones completion
Real World Evidence analysis
Literature Screening
Registries
Questionnaires and Surveys results
Feedback from users/end user
Clinical Investigations/Trials results (if planned any)
Outcome of performance and safety endpoints
Risk benefit analysis
Residual Risks (if any)
Statistical Analysis
CER citation
Frequency of PMCF update
IZiel Healthcare offers PMS services to our clients where we perform end to end Post Market Surveillance activities. These services can be PMS Plan, PMS/PSUR Reports, PMCF Plan and Reports, Trend Reporting, Complaint Handling, Clinical Evaluation, Risk Benefit Management and many more.
We have expertise in designing PMCF Plan and drafting reports for our clients for all the Classes of Medical devices – Class IIa, Class IIb and Class III.
You may contact us at Contact Us – Iziel.
0 notes
Text
Demystifying Medical Device Software Validation: Ensuring Safety and Compliance
Briefly introduce the importance of medical device software validation.
Explain that the blog post will provide an overview of the key concepts, processes, and regulations related to medical device software validation.
I. Understanding Medical Device Software
Define what medical device software is and its significance in healthcare.
Discuss the different types of medical device software (e.g., embedded, standalone, mobile apps).
Emphasize the increasing reliance on software in modern medical devices.
II. Why Software Validation Matters
Explain the critical role of software validation in ensuring patient safety.
Discuss the potential risks and consequences of inadequate software validation.
Highlight real-world examples of medical device software failures and their implications.
III. Regulatory Framework
Introduce the regulatory bodies and standards governing medical device software validation (e.g., FDA, ISO 13485, IEC 62304).
Explain the classification of medical devices and how it affects validation requirements.
Provide an overview of the FDA's Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) guidance.
IV. The Software Validation Process
Outline the key steps in the software validation process:
Requirements analysis and specification
Risk assessment and management
Design and development
Testing and verification
Validation and documentation
Emphasize the importance of traceability and documentation.
V. Common Challenges and Solutions
Discuss common challenges in medical device software validation (e.g., changing requirements, evolving technology).
Provide practical solutions and best practices for overcoming these challenges.
VI. Case Studies
Present real-world case studies of successful medical device software validation projects.
Highlight the benefits of proper validation, including improved patient outcomes and reduced liability.
VII. Future Trends in Medical Device Software Validation
Explore emerging trends and technologies in medical device software validation (e.g., artificial intelligence, machine learning).
IZiel has highly trained software engineers with multiple years of experience in software coding, software verification and software validation. The team consists of senior engineers who have worked in design and development of highly sophisticated implantable devices at industry leading companies, with direct expertise in software V&V. This team, with the support of IZiel’s regulatory and clinical experts, are decidedly equipped to handle complex software validation activities for medical device manufacturers. Integrating risk assessments into the validation lifecycle and documenting the basis for what was done also provides a level of assurance to management and regulatory authorities that the system was properly defined, designed, built, tested, operated, and maintained.
0 notes
Text
Risk Management for Medical Devices
Risk management for medical devices is a critical process that involves identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential risks associated with the design, manufacturing, and use of medical devices. The goal is to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and quality of these devices throughout their lifecycle. The risk management process is typically guided by international standards, with ISO 14971 being one of the most widely recognized standards for medical device risk management. Here's an overview of the key steps and concepts involved:
1. Risk Management Process:
- Risk Identification: Identify potential hazards and potential sources of harm associated with the device and its use.
- Risk Evaluation: Assess the severity of potential harm and the likelihood of its occurrence.
- Risk Control: Develop and implement strategies to mitigate or reduce identified risks.
- Risk Residual Evaluation: Reassess the residual risks after applying control measures.
- Risk Review: Periodically review and update the risk management process throughout the device's lifecycle.
2. Risk Analysis:
- Severity: Evaluate the potential consequences of a hazard in terms of patient harm.
- Probability: Assess the likelihood of a hazard leading to harm.
- Detectability: Consider the likelihood of detecting a potential hazard before it causes harm.
3. Risk Control Measures:
- Elimination: Remove the hazard or unsafe condition from the device design.
- Substitution: Replace a hazardous component with a safer alternative.
- Engineering Controls: Design features that minimize the risk of harm.
- Warnings and Labels: Provide clear instructions and warnings to users about potential risks and proper use.
- User Training: Ensure users are trained to properly operate the device and manage risks.
- Protective Measures: Implement features that protect users from harm (e.g., safety guards).
- Information for Safety: Provide relevant safety information in user manuals.
4. Risk Documentation:
- Maintain comprehensive records of the risk management process, including risk assessments, control measures, and decisions made.
5. Post-Market Surveillance:
- Continuously monitor the device's performance and user feedback to identify any new risks or issues that might arise during real-world use.
6. Risk Management Report:
- Compile a risk management report that outlines the identified hazards, risk assessment results, risk control measures, and justification for the risk acceptability.
7. Risk Management File:
- Create a risk management file that documents the risk management process and is available for regulatory authorities to review.
8. Risk Management as Part of Product Lifecycle:
- Integrate risk management activities into the overall product development lifecycle, from initial design to manufacturing, distribution, and post-market surveillance.
Remember, regulatory requirements can vary based on the country or region in which the medical device will be marketed. Proper risk management not only ensures regulatory compliance but also contributes to patient safety and the reputation of the manufacturer.
IZiel Healthcare team uses the structural approach defined by ISO 14971 to construct the risk management file. The risk management file starts with drafting the risk management plan; it consists of the methodology of a risk management process and risk policy. Afterwards, hazards, hazardous situations and harm are determined using tools like FMEA (pFMEA and dFMEA) and hazard analysis. The identified risks are then controlled or mitigated by applying risk control and the evaluation of residual risk then follows it. If the residual risk is not acceptable, then a risk versus benefit analysis is carried out.
0 notes
Text
Complaint Handling Procedure for Medical Devices
Complaint handling procedures for medical devices are crucial to ensure the safety, quality, and effectiveness of the devices, as well as maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. Here is a general outline of a complaint-handling procedure for medical devices:
1. Definition of Complaint: Clearly define what constitutes a complaint. A complaint can be any written, electronic, or oral communication from a customer, user, patient, healthcare professional, distributor, or any other stakeholder expressing dissatisfaction, concern, or potential adverse event related to a medical device.
2. Complaint Receipt and Documentation:
- Designate a responsible person or team to receive and document complaints.
- Establish a system for capturing complaint details, including the complainant's contact information, device information, date of occurrence, description of the issue, and any relevant attachments.
3. Initial Assessment:
- Evaluate the complaint to determine its severity and potential risk to patients, users, or the quality of the device.
- Classify the complaint as major, minor, or non-conformance based on the impact and risk level.
4. Investigation:
- Initiate an investigation into the complaint. Gather relevant information, records, and data.
- Assign responsibilities for investigating the complaint, which may involve quality control, regulatory affairs, engineering, clinical, and other relevant departments.
- Identify the root cause of the complaint and its contributing factors.
5. Risk Assessment:
- Assess the potential risk and impact associated with the complaint. Use risk management techniques to determine the severity and likelihood of recurrence.
- If the complaint relates to a serious adverse event or potential patient harm, consider reporting it to the relevant regulatory authorities in accordance with regulatory requirements.
6. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA):
- Develop and implement appropriate corrective and preventive actions based on the investigation findings.
- Ensure that CAPAs are designed to address the root cause and prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.
- Assign responsibilities for implementing CAPAs and set deadlines for completion.
7. Communication and Feedback:
- Communicate with the complainant regarding the resolution of the complaint, actions taken, and any necessary follow-up.
- Provide feedback to relevant departments regarding the complaint's outcome and the effectiveness of implemented actions.
8. Documentation and Record Keeping:
- Maintain detailed records of the complaint, investigation, risk assessment, and actions taken.
- Ensure all documentation is organized, stored securely, and easily retrievable for future reference or regulatory audits.
9. Trending and Analysis:
- Regularly review and analyse complaint data to identify trends, recurring issues, and opportunities for continuous improvement.
- Use the information gained to enhance the device design, manufacturing processes, and overall quality.
10. Training and Review:
- Train employees involved in complaint handling on the procedure, regulatory requirements, and best practices.
- Periodically review and update the complaint handling procedure to ensure it remains current and effective.
Remember that complaint-handling procedures can vary depending on the specific regulatory environment and the type of medical devices your organization deals with. Always ensure compliance with relevant regulations and standards, such as ISO 13485 and applicable regional regulations (e.g., FDA in the United States, EU MDR in the European Union).
IZiel works with medical device companies to effectively manage Complaints Handling, thereby, helping you provide better, safer, more effective & quality product.
0 notes
Text
Risk Management for medical devices
Risk management for medical devices is a crucial process aimed at identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential hazards and risks associated with the use of these devices throughout their lifecycle. Proper risk management helps ensure the safety, effectiveness, and quality of medical devices, and it is a fundamental requirement for regulatory compliance in many countries, including the United States (FDA) and the European Union (CE marking).
Here are the key steps and concepts involved in risk management for medical devices:
Risk Management Process: The risk management process typically follows the principles outlined in international standards, such as ISO 14971: Medical devices - Application of risk management to medical devices. The process includes the following steps:
Risk Identification: Identify potential hazards and potential harms that could result from using the medical device. This includes considering both intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse scenarios.
Risk Analysis: Assess the identified hazards and estimate the severity of harm and the probability of occurrence.
Risk Evaluation: Evaluate the level of risk based on the analysis results to determine if any risks are unacceptable.
Risk Control: Implement risk control measures to reduce or eliminate identified risks. These measures can include design modifications, protective mechanisms, safety features, labelling, and instructions for use.
Residual Risk Evaluation: After applying risk controls, reevaluate the risk to determine if it is at an acceptable level.
Risk Management Report: Document all the steps taken in the risk management process in a comprehensive report.
Risk Management File: Maintain a risk management file that includes all the documentation related to the risk management activities for the medical device.
Post-Market Surveillance: Continue monitoring the device's performance and safety in real-world use through post-market surveillance and feedback mechanisms. Any emerging risks or issues should be addressed promptly.
Benefit-Risk Analysis: Conduct a benefit-risk analysis to ensure that the benefits of the medical device outweigh its potential risks.
Human Factors Engineering: Consider human factors in the design and use of the medical device to minimize the risk of human error.
Usability Engineering: Assess the device's usability and user interface design to ensure safe and effective use.
Regulatory Compliance: Comply with relevant regulatory requirements for risk management and submit the necessary documentation to regulatory authorities.
Risk Management Plan: Develop a risk management plan early in the device development process to guide risk management activities throughout the product lifecycle.
Risk Management Team: Establish a multidisciplinary team responsible for risk management activities, including representatives from engineering, clinical, regulatory, quality, and other relevant disciplines.
Continuous Improvement: Maintain a process for continuous improvement of risk management based on feedback, post-market data, and emerging information.
It's essential for medical device manufacturers to integrate risk management into their development and manufacturing processes from the very beginning to ensure the safety and effectiveness of their products. Regulatory bodies worldwide emphasize the importance of risk management to protect patient safety and promote public health.
IZiel Healthcare team uses the structural approach defined by ISO 14971 to construct the risk management file. The risk management file starts with drafting the risk management plan; it consists of the methodology of a risk management process and risk policy. Afterward, hazards, hazardous situations and harm are determined using tools like FMEA (pFMEA and dFMEA) and hazard analysis. The identified risks are then controlled or mitigated by applying risk control and the evaluation of residual risk then follows it. If the residual risk is not acceptable, then a risk versus benefit analysis is carried out.
0 notes
Text
Best Medical Device Risk Management Consultant for 2023
Medical devices have caused so many patient deaths and over a million injuries in the past decade. A qualified medical device risk management consultant can help you resolve safety issues and, ideally, remove your anxiety that your products could harm the end user.
Risk management is an important part of the medical device product development lifecycle. It helps medical device manufacturers to ensure that the final product is reliable, works as expected and causes no harm. The main purpose of the risk management process is to reduce or mitigate the chances of failure in the product.
IZiel’s Expertise
IZiel Healthcare has the expertise to write risk management procedures as per ISO 14971 and then create or restructure the risk management file as per the established procedures. IZiel Healthcare has broad experience creating risk management files from simple (Class I) to complex (Class III) medical devices. Our team uses the following tools to identify the risk associated with the medical device:
· Preliminary Hazard Analysis
· Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (Design and Process)
· Hazard Analysis
· Fault Tree Analysis
With the use of the above-defined tools, IZiel identifies, evaluates and controls the risk associated with a medical device to the patient, user and environment.
#Risk Analysis#Risk Management for Medical Devices#ISO 14971 Risk Management#Risk Analysis for Class I Medical Devices#Risk Analysis for Class II Medical Devices#Risk Analysis for Class III Medical Devices
0 notes
Text
What is the importance of clinical Evaluation Report?
A clinical evaluation report is important to healthcare because it confirms that a medical device has achieved its intended purpose. It also indicates that the medical device does not expose patients and other users to further risk.
Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) makes a strong case for your device and its intended use backed by impactful scientific evidence. A CER aims to reduce the risk that the users and patients are exposed to when using a medical device.

IZiel completes the Clinical Evaluation Report (CER) as per the following changes in revision Med-Dev Rev. 4 with focus on detailing and clarity on every step of the clinical evaluation process that has been conducted by the manufacturers and evaluators.
Working in-tandem with our clients, we endeavor to provide every detail asked for and more, keeping a keen eye on objectivity, completeness and evidence-backed content, throughout the process.
0 notes
Text
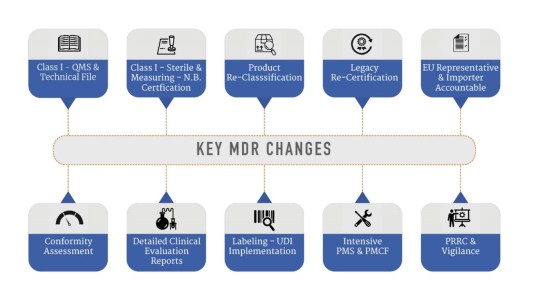
What are the key MDR changes?
Until today, medical devices were complying with the Medical Device Directive to sell their products in Europe. However major amendments are made in the current MDD to keep up with the growing technological advances in healthcare and medical devices.

Typically, all MDD-MDR transition projects initiate with Gap Assessment. Gap Assessment is a crucial activity during MDR transition & our team with engineering & regulatory expertise are well equipped to conduct this activity with an analytical mindset, resolve any regulatory concern and develop robust regulatory strategy for medical device manufacturers.
IZiel team of specialists and quality professionals look forward to support more medical device companies to file their devices under the MDR 2017/745.
0 notes
Text
MDD to MDR Transition
Why is the modification in the regulation (MDD to MDR Transition) adapted?
History: You may be aware of the breast implant scandal in France wherein instead of medical grade Silicon, a low-quality Silicon was used as a raw material for breast implants which got ruptured and there were several complaints filed which led to the recall of the device by the manufacturer.
Because of these kinds of incidents, the MODIFICATION to MDD came into the picture and it’s called MDR, which is more comprehensive and detailed than MDD.

How do we adapt to MDR?
· Gap analysis while considering additional requirements of MDR.
· Refer Annexure XVII of MDR
MDR focuses on the safety and performance assurance of the devices placed on the market. MDR assures that the product causes no harm to the customers. Clinical and Non-Clinical testing methods include Clinical Investigation, PMCF studies, Literature Searches Screening and Appraisal, bench tests, in-vitro tests, biocompatibility testing, and product-specific performance Tests (if any) are utilized to establish clinical evidence for demonstrating the safety and performance of the device. The Manufacturing facility audits are conducted as per ISO 13485 to comply with Cleanroom requirements and applicable standards. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA) needed to be taken depending upon the severity of complaints generated through Field Safety Notices/Field Safety Corrective Actions. The IFUs and electronic IFUs are to be supplied by the manufacturer. Product retractability with UDI implementation has become a must for troubleshooting and the appropriate diagnosis of the complaint or defect related to the product.
Let us identify the requirements in MDD to MDR transition.
· The major changes to be adapted in MDR.
· MD Classification
· Clinical Data Sources
· Risk Management
· Process Validation
· Software Validation
· GSPR checklist
· Product Retraceability
Major Inclusions in MDR
· PRRC
· SRN for Economic Operators
· Annexure XVI includes products without an intended medical purpose like contact lenses, brain stimulators, cosmetic products, etc.
· Active Implantable Medical Devices
· Sterilization
· EN ISO 13485 and MDSAP Requirements
· Conformity Assessment Routes
· EUDAMED, UDI and Labelling
· Technical Documentation
· Clinical Evaluation
· Clinical Investigation and PMCF
· Reporting of serious incidents or failures to member states and trend reporting
· IFU and eIFU Requirements
· Cybersecurity
· SSCP linked to EUDAMED open to all end-users (including a layman)
· GSPR
We at IZiel Healthcare have a long-standing collaboration with Obelis, a Belgium-based (European Authorized Representatives) to provide a “One-Stop Solution” to fully support Class I, IIa, IIb & III medical device manufacturers across USA, Europe & Asia. This collaboration would ensure to obtain conformity with the MDR (2017/745) requirements and maintain the CE Marking of global medical devices through technical support, consultancy, representation, and device registration services.
0 notes
Text
Post-Merger Integration Challenges for Medical Devices & How to Overcome Them
Mergers & Acquisition in the healthcare industry has been strong in recent years and is expected to grow. Acquiring a new company or product line can have a positive business impact, but it also comes with implementation, process, quality & regulatory challenges. Especially, in the medical device industry, failure to comply with regulations can result in the loss of authority to deliver products and services.

Post-Merger Integration Issues
· Maintaining Momentum
· Employee Engagement
· Senior Management Issues
· The Culture Shift
· Technology Integration
· Synergy Implementation
· Customer Engagement
· Communication Challenges
How to Avoid Them
· Start integration as soon as the deal is announced
· Select integration team members
· Plan the integration structure
· Create an internal communication plan
· Keep the overall message consistent
· Establish clear exit criteria
Why Choose IZiel?
At IZiel, our team has upgraded thousands of documents for various acquisition integration projects of Class I, II & III medical device companies. Our Outcome Based & Onshore-Offshore Delivery Model has worked effectively to complete the Post-Merger Integration with a significant reduction in timelines and budgets.
0 notes
Text
ISO 14971 Risk Management Consulting for Medical Device Companies
Risk management is an important part of the medical device product development lifecycle. It helps medical device manufacturers to ensure that the final product is reliable, works as expected, and causes no harm. The main purpose of the risk management process is to reduce or mitigate the chances of failure in the product.
What ISO 14971 is important?
ISO 14971 helps your company establish, document, and maintain a systematic process to manage the risks associated with the use of a medical device. This includes ongoing monitoring of field experience, thereby embracing the concepts of continuous improvement and state-of-the-art device performance. To maximize the effectiveness of your risk management system, ISO 14971 can and should be an integral part of your quality management system (QMS) as required by ISO 13485.
Steps Involved in Risk Management for Medical Devices
· Risk Management Framework & Planning
· Risk Analysis
· Risk Evaluation
· Risk Control
· Reports and Documents
· Production & Post-Production Information
Why should we perform Risk Management?
· To identify hazards
· To estimate & evaluate the risk
· Risk analysis is required by law
· Identification of device design problems prior to distribution eliminates extra costing associated with the medical device
· To ensure the safety of the medical device
IZiel Healthcare team uses the structural approach defined by ISO 14971 to construct the risk management file. The risk management file starts with drafting the risk management plan; it consists of the methodology of a risk management process and risk policy. Afterwards, hazards, hazardous situations, and harm are determined using tools like FMEA (pFMEA and dFMEA) and hazard analysis. The identified risks are then controlled or mitigated by applying risk control and the evaluation of residual risk then follows it. If the residual risk is not acceptable, then a risk versus benefit analysis is carried out.
#Risk Analysis for Medical Device#Risk Management for Medical Devices#ISO 14971 Risk Management Process#Risk Analysis
0 notes