#International Disability and Development Consortium
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
As a person born with intersex traits, I had the honor of speaking on the importance of celebrating Women’s Month in South Africa and the need to realign societal values to protect the rights of all women and promote inclusion and diversity.
The Wits University Gender Equity Office provides a platform for men, women, and people of all identities to explore their differences and collaborate on the change we envision for our communities, enhancing human rights and inclusion.
The panel discussion I participated in was themed “Strategies and Stories of Women Shaping Political Landscapes in South Africa and Beyond.” Panelists included Honorable Naledi Chirwa of the EEF, Zulaika Patel, and myself. We examined gaps in promoting gender equity and the economic inclusion of women, youth, and persons with disabilities. Honorable Chirwa provided a historical perspective, explaining how apartheid’s segregationist policies shaped South Africa’s spatial, political, and economic landscape. She emphasized the need for redress, healing, and radical transformation to empower marginalized communities and foster economic freedom.
Zulaika Patel focused on the diverse identities of women, advocating for freedom in expressing femininity without stereotypes. She highlighted the importance of recognizing women’s unpaid work and the role of local and international organizations in guiding sustainable development and supporting lawful protest.
I discussed the work of state departments, executive government, private sector, and nonprofit organizations in advancing sustainable development and improving quality of life across South Africa, the region, and the continent. I also shared the mission of my organization, the Global Development Consortium, in 2024, including our engagement in UN reporting for several countries and partnerships with international bodies to implement initiatives empowering marginalized groups and promoting human rights.
My contribution urged students, staff, and the Johannesburg community to intentionally contribute to solutions, co-create initiatives, and establish partnerships with both local and global institutions to achieve sustainable development and economic freedom.
#Wits #SRC2024 #SouthAfrica #Mzansi #Leadership #PersonalDevelopment

0 notes
Text
Fwd: Postdoc: WashingtonU.GenomicsBiodiversity
Begin forwarded message: > From: [email protected] > Subject: Postdoc: WashingtonU.GenomicsBiodiversity > Date: 20 September 2024 at 05:59:03 BST > To: [email protected] > > > The Living Earth Collaborative > (https://ift.tt/7yuZJIb), a consortium comprised > of Washington University, the Missouri Botanical Garden and the Saint > Louis Zoo, and the Washington University McDonnell Genome Institute > (https://ift.tt/7QpYg9t) are partnering to advance the use of genomics > for biodiversity research and conservation. As part of this collaboration, > we seek to hire a postdoctoral fellow with a proven track record utilizing > genomic and computational tools in biodiversity research and conservation. > > The Postdoctoral fellow will play an important role in developing > a portfolio of genomic projects from principal investigators at the > LEC partner institutions on diverse topics, which may include ecology, > conservation, conservation veterinary medicine, environmental justice, > behavior, evolution and One Health. The fellow is expected to be > an integral part of the Living Earth Collaborative participating in > and organizing events and interacting with the diverse LEC and MGI > communities. The fellowship will be up to three years. Salary will be > $61,428 plus benefits. > > Location > St. Louis, MO > > Application Instructions > Applicants should submit, as a single file, a cover letter, a CV, > and a description of previous research, conservation, and professional > accomplishments (ca. 2-3 pages). Postdocs are expected to be based in > Saint Louis and must have been awarded a PhD, DVM or comparable degree > by the beginning of their appointment. International applicants are > encouraged. > > Documents should be uploaded to https://jobs.wustl.edu/ specifying > Job Requisition JR69499. Applicants should also have three letters of > recommendation sent to [email protected]. Review of applications > will begin on November 1st and continue until the position is filled. > > Washington University is an Equal Opportunity Employer. All qualified > applicants will receive consideration for employment without regard to > race, color, religion, age, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity > or expression, national origin, genetic information, disability, or > protected veteran status. > > Questions should be directed to: [email protected] > > Living Earth Collaborative > E: [email protected] > W: https://ift.tt/7yuZJIb > > > > Living Earth Collaborative
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Your Converted PSD Website Meets Accessibility Standards
Many websites begin their life as a PSD (Photoshop Document) file, a visual blueprint for the final design. But the conversion from PSD to a functional website can sometimes overlook accessibility best practices. Here's how to bridge the gap and ensure your website is inclusive from the start.
Planning for Accessibility During Conversion
Semantic Structure: A well-structured website uses semantic HTML tags to define the meaning of content. This goes beyond just bolding text for emphasis; it means using heading tags (H1-H6) to define the hierarchy of information, and using list tags for actual lists. This clear structure is crucial for screen readers to navigate the page and convey the content effectively.
Alternative Text (Alt Text): Images are important for visual appeal, but they can be a barrier for users who can't see them. Adding alt text descriptions to images provides context for screen readers. Don't just stuff keywords here; write concise descriptions that accurately reflect the image content.
Color Contrast: Visual impairments can make it difficult to distinguish between colors with low contrast. Use a color contrast checker to ensure there's enough contrast between text and background colors. This improves readability for everyone, not just those with visual limitations.
Keyboard Navigation: Not everyone uses a mouse. Ensure your website can be fully navigated using just the keyboard. This means menus, buttons, and links should be accessible through the Tab key and have clear keyboard shortcuts.
Testing and Validation
Once your website is converted, it's vital to test its accessibility. Here are some resources:
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): Developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), WCAG is the international standard for web accessibility. It has three levels of conformance (A, AA, and AAA), with A being the minimum and AAA the most comprehensive. Use WCAG guidelines to check your website's accessibility.
Automated Testing Tools: Several online tools can scan your website for accessibility issues. These tools are a great starting point, but they don't replace manual testing with assistive technologies.
Beyond the Basics
Accessibility is an ongoing process. As your website evolves, consider these additional points:
User Testing: Involve users with disabilities in your testing process. Their feedback is invaluable in identifying and addressing accessibility barriers.
Content Management Systems (CMS): If you're using a CMS, ensure the chosen platform offers built-in accessibility features.
Building an Inclusive Web
By following these steps, you can ensure your website is accessible to a wider audience. This not only benefits users with disabilities, but also improves search engine optimization (SEO) and overall user experience. Remember, a website that's usable by everyone is a website that thrives. Incorporating PSD to WordPress into your development process can further enhance your site's functionality and accessibility.
0 notes
Text
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines

WCAG 2.2: Decoding The Latest Web Accessibility Guidelines
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, accessibility has become a non-negotiable imperative for all users. The updated and latest Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.2, released in October 2023, stands as a beacon of inclusivity, providing comprehensive guidelines for making web content accessible to people with disabilities. Moreover, lawsuits against businesses with non-compliant websites have proliferated. According to ADA attorney Nolan Klein, thousands of ADA lawsuits have been filed in federal court alleging non-compliance with WCAG standards. Implementation of WCAG 2.2 standards is therefore critical not only for inclusivity but also for proper litigation risk management. As we explore WCAG 2.2 and its anticipated updates in 2023, this article aims to simplify its complexities, shedding light on the importance of web accessibility for the general public.
What is Web Accessibility?
In today’s interconnected world, the Internet has become indispensable for communication, education, employment, and social engagement. Practically everyone turns to the internet for a solution to all their queries, be they booking tickets, job opportunities, or making purchases. However, for individuals with disabilities, the web can present a daunting landscape of barriers, hindering their ability to participate in the digital sphere fully. This is where web accessibility comes into play. It is the practice of designing and developing websites and web applications so that even people with disabilities can easily and comfortably access and use them. By removing accessibility barriers and ensuring that web content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust, web accessibility promotes inclusivity and empowers individuals with disabilities to navigate the digital world quickly.
The Significance of Web Accessibility
The importance of a strong web accessibility initiative cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental human right enshrined in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD). Moreover, web accessibility makes good business sense. By catering to a broader audience, businesses can expand their customer base, enhance their brand reputation, and gain a competitive edge.
Impact on Diverse User Experiences
Web accessibility considerations extend far beyond the realm of disabilities. They encompass a broad spectrum of user experiences, including those related to age, language barriers, and situational impairments. Examples of situational impairments include watching videos with only audio in libraries or those with stubby fingers preferring larger call-to-action buttons. By designing websites that are inclusive and accessible to all, we can create a more equitable and user-friendly digital landscape.
W3C Releases: Shaping the Evolution of Accessibility
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) plays a pivotal role in developing and maintaining WCAG, ensuring that the guidelines remain relevant and effective in the face of evolving technologies and user needs. The WCAG 2.2 was developed through the W3C process with other individuals and worldwide organizations to provide web content accessibility guidelines that meet international governments’, organizations’, and individuals’ accessibility needs. The W3C recommends using the WCAG 2.2 as a standard for the web.And thus provides the necessary resources and training as guidance and clarity on implementing WCAG.
WCAG 2.2: A New Standard for Web Accessibility
In October 2023, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) released WCAG 2.2, the latest iteration of the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. The WCAG 2.2 is built on WCAG 2.0 and 2.1, the previous versions were built on WCAG 1.0, designed to apply different present and future technologies and tested through manual and automated testing. The update incorporates new WCAG success criteria and techniques, addressing the evolving needs of users with cognitive, language, and learning disabilities and reflecting advancements in web technologies.
WCAG 2.2 and Its Relevance
The release of WCAG 2.2 marks a significant step forward in pursuing web accessibility. By adopting these guidelines, web developers, content creators, and organizations ensure their digital products and services are accessible to a wider audience, fostering a more inclusive and equitable online experience.
Multiple Layers of Guidance
The various individuals and organizations using WCAG include policymakers, web designers, teachers, and students. Thus, multiple layers of guidance meet this varied audience’s comprehensive needs. These layers include:
Overall Principles
The foundation of WCAG 2.2 rests upon four fundamental principles: perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. These principles, each encompassing specific guidelines and measurable success criteria, form the cornerstone of accessible web content.
Perceivable: Content must be presented so that users with visual, auditory, or other sensory impairments can perceive it.
Operable: Users with diverse abilities, including motor and speech impairments, must be able to operate a user interface component and navigate content effectively.
Understandable: Content must be presented clearly and unambiguously so that users with cognitive, learning, or language disabilities can comprehend it easily.
Robust: Content must remain accessible across all various assistive technology and user environments.
General Guidelines
These come next and are the 13 guidelines providing the goals authors adhere to for making content more accessible to users with different disabilities. While they aren’t testable, they provide the basic framework for authors to understand success criteria and, thus, better implement techniques.
Testable Success Criteria
Each guideline has testable success criteria to ensure WCAG 2.2 is used wherever requirements and performance testing are required. This includes design specifications, contractual agreements, and purchasing. WCAG 2.2 defines three levels of conformance level: A, AA, and AAA, each representing a progressive level of accessibility in different groups and situations.
Level A: The minimum level of accessibility, ensuring basic functionality for all users.
Level AA: A higher level of conformance, addressing the needs of many disabled users. It is considered the recommended level for most websites.
Level AAA: The most stringent level, catering to a wider range of disabilities and user preferences. It is often considered an aspirational goal for websites.
Sufficient and Advisory Techniques
Various techniques are used for each guideline and success criterion in WCAG 2.2, divided into two categories. Sufficient techniques for meeting success criteria and advisory techniques that let authors go beyond the individual success criteria to address guidelines better. They may address accessibility problems or barriers the testable success criteria do not cover. These layers of guidance together guide web developers to make content more accessible by applying as many layers as possible. This includes including advisory techniques so that the content addresses the needs of most users.
WCAG 2.2: A Watershed Moment in Digital Accessibility
WCAG 2.2 addresses the ever-changing technological landscape and evolving user needs, thus emerging as a pivotal step forward from its predecessor, WCAG 2.1. This enhanced iteration introduces nine tool accessibility guidelines and new success criteria meticulously crafted to enhance accessibility for users with visual, physical, and cognitive disabilities. These additional success criteria encourage:
1. Improved Focus Management
WCAG 2.2 introduces three enhanced focus management success criteria catering to users with motor impairments. These success criteria enable users to navigate web content smoothly and efficiently. These success criteria are:
2.4.11 Focus Not Obscured (Minimum) (AA): According to this success criterion, there might be some degree of hiding or obscuring keyboard-focused user interface components like buttons or links in a website or app design.
2.4.12 Focus Not Obscured (Enhanced) (AAA): According to this success criterion, content web developers create, like website and app design, cannot hide any part of keyword-focused user interface components.
2.4.13 Focus Appearance (AAA): According to this success criterion, visible keyboard focus indicator parts must be a minimum of a 2 CSS pixel thick perimeter of unfocused components or sub-components. They should also have a minimal 3:1 ratio between pixels in focused and unfocused states.
2. Enhanced Touch Input Support
Recognizing the growing prevalence of touch-enabled devices, WCAG 2.2 introduces refined guidelines for touch input and page break navigation. This ensures seamless interaction for users with limited or no mouse interaction. These success criteria are:
2.5.7 Dragging Movements (AA)
According to this success criterion, a single pointer can perform dragging movements without dragging. Exceptions are when dragging is crucial to the functionality or the user agent dictates the functionality and remains unaltered by the author.
2.5.8 Target Size (Minimum) (AA)
According to this success criterion, the minimum size for pointer input targets is 24 by 24 CSS pixels, with exceptions in:
Spacing: Targets smaller than 24 by 24 CSS pixels can be positioned so that, if a 24 CSS pixel diameter circle is centered on each target’s bounding box, the circles do not intersect with other targets.
Equivalent: The same function can be accomplished through a different control on the same page, meeting the 24 by 24 CSS pixel criterion.
Inline: The target is within a sentence, or its size is constrained by the line height of non-target text.
User-agent control: The user agent determines the target size and remains unaltered by the author.
Essential: A specific presentation of the target is deemed essential or is legally required for conveying the information.
3. Clearer Color Contrast Guidance
WCAG 2.2 provides clearer and more stringent guidelines for color contrast to address the needs of low-vision users. It thus ensures text is easily distinguishable from its background. These success criteria are:
3.2.6 Consistent Help (A)
According to this success criterion, if web pages include certain help mechanisms like human contact details, human contact mechanisms, self-help options, and fully automated contact mechanisms, they should maintain a consistent order across multiple pages unless a user-initiated change occurs.
3.3.7 Redundant Entry (A)
According to this success criterion, user-provided information that must be repeatedly entered in the same process is auto-populated or made available for the user to select. Exceptions are when:
Re-entering the information is deemed essential
The information is necessary for ensuring content security
The previously entered information is no longer valid
3.3.8 Accessible Authentication (Minimum) (AA)
According to this success criterion, an authentication process does not mandate cognitive function tests like remembering a password or solving a puzzle. Exceptions are when the step offers at least one of the following:
Alternative: Another authentication method that doesn’t involve a cognitive function test.
Mechanism: A mechanism aids the user in completing the cognitive function test.
Object Recognition: The cognitive function test involves recognizing objects.
Personal Content: The cognitive function test identifies non-text content the user provides to the website.
3.3.9 Accessible Authentication (Enhanced) (AAA)
According to this success criterion, cognitive function tests, like recalling a password or solving a puzzle, are not obligatory at any stage in an authentication process unless the step offers either:
Alternative: An alternative authentication method not dependent on a cognitive function test.
Mechanism: A mechanism is accessible to aid the user in completing the cognitive function test.
The new success criteria may reference new terms that have also been added to the glossary and form part of the normative requirements of the success criteria. WCAG 2.2 also introduces new sections detailing aspects of specifications impacting privacy and security.
Was Any Success Criterion Removed from WCAG 2.2?
Yes, the success criterion 4.1.1 Parsing was removed from WCAG 2.2. It was removed as it was considered obsolete due to the advancements in web technology. Besides, new success criteria in WCAG 2.2 provide a more robust and up-to-date approach to ensuring accessible web content to disabled users. Here is why 4.1.1 Parsing was removed from WCAG 2.2:
It was primarily focused on older technologies, such as HTML 4.0 and earlier versions of XHTML, which are no longer widely used.
It was not well-defined and could be interpreted differently, leading to inconsistencies in implementation.
It was not as effective as other success criteria in ensuring that web content is parsable by user agents.
Removing 4.1.1 Parsing from WCAG 2.2 does not mean the parsing issue is no longer important. However, the new success criteria in WCAG 2.2 provide a more comprehensive and effective way to address this issue.
WCAG 2.1 vs. WCAG 2.2- The Differences
The latest Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, WCAG 2,2, builds upon its predecessor, WCAG 2.1, to further enhance web accessibility for people with disabilities. While WCAG 2.1 laid a solid foundation for accessible web development, WCAG 2.2 introduces new success criteria, refines existing guidelines, and provides clearer instructions to make accessibility more achievable and maintainable. There are thus these five major differences between the two:
1. New Success Criteria in WCAG 2.2
WCAG 2.2 introduces nine additional success criteria, addressing areas such as:
Focus appearance: Ensuring that focus indicators are sufficiently visible and distinguishable to aid navigation for users with low vision or cognitive disabilities.
Page break navigation: Providing clear and consistent mechanisms for navigating between page breaks, particularly for users who rely on screen readers or keyboard navigation.
Dragging movements: Making drag-and-drop interactions accessible to users with motor disabilities by providing adequate target sizes and clear visual feedback.
Consistent help: Providing consistent and easily accessible help or support mechanisms throughout the website or application.
Visible controls: Ensuring that all controls, including form fields and buttons, are clearly visible and distinguishable even to low-vision users.
These new success criteria reflect the evolving technological landscape and a deeper understanding of user needs, particularly those with cognitive disabilities.
2. Enhanced Mobile Accessibility
WCAG 2.2 continues to refine mobile accessibility guidelines, recognizing the growing prevalence of mobile devices and the need for websites and applications to be accessible across all platforms. This includes improvements in:
Touch target sizes: Ensuring touch targets are large enough and spaced appropriately to accommodate ease of use to users with motor disabilities or limited dexterity.
Input modalities: Providing alternative input modalities, such as voice control or keyboard navigation, to cater to users with different physical abilities.
Context-aware activation: Preventing unintentional activation of elements, such as pop-ups or overlays, that could hinder navigation for users with cognitive disabilities.
3. Improved Usability and Clarity
WCAG 2.2 aims to make the guidelines more user-friendly and actionable for developers and content creators through:
More explicit guidelines: Provide clearer and more explicit instructions for each success criterion to reduce the need for interpretation and ensure consistent implementation.
Additional examples: Offer more comprehensive and illustrative examples to demonstrate how to meet each success criterion in real-world scenarios.
Improved organization: Structuring the guidelines more logically and intuitively makes it easier for developers to find the information they need.
4. Backward Compatibility and Continuous Evolution
WCAG 2.2 maintains backward compatibility with WCAG 2.1, meaning that websites and applications conforming to WCAG 2.2 also adhere to WCAG 2.1 accessibility standards. This ensures that accessibility efforts are not lost with each new guidelines version. As technology and user needs evolve, WCAG will adapt and refine its guidelines to ensure that the web remains an inclusive and accessible space for all.
5. Removal of One Success Criterion
The success criterion 4.1.1 Parsing was removed from WCAG 2.2 as it was considered obsolete compared to web technology advancements. Besides, new additional success criteria in WCAG 2.2 ensure web content is accessible to users with disabilities.
Impact on User Experience
As always, the WCAG 2.2 offers an improved user experience, rendering digital content more user-friendly and inclusive for everyone, including users with disabilities. By adhering to the latest WCAG 2.2 guidelines, websites, and digital platforms become more accessible to all their users and visitors, regardless of their abilities. It doesn’t matter what disability the user may have or where they are, they can easily navigate, comprehend, and interact with the digital content. This is thus a win-win situation for both users and web developers. For example, visually impaired users easily navigate websites with images with alt text. In addition to improved accessibility, the alt text helps with SEO, thus improving the digital platform’s SEO rankings. Similarly, users with physical impairments and, in general, all users can easily navigate websites that are keyboard-navigable.
WCAG and Its Benefits for Businesses:
Embracing web accessibility guidelines should never be considered a waste of time or investment. It’s because web accessibility perfectly aligns with any and every business’s interests. It offers benefits like:
Broader Customer Base
Not only does WCAG 2.2 ensure everyone has equal access to the web, but the additional success criteria in WCAG 2.2 address additional disabilities to foster a broader customer base. People with disabilities form a major part of any website visitors. They will not be able to use or visit inaccessible websites. This, in turn, prevents them from accessing important information or performing important tasks like applying for jobs, booking tickets, or making purchases.
Increased Compliance
Adhering to WCAG 2.2 guidelines helps businesses and organizations comply with legal standards like accessibility laws and regulations protecting the rights of users with disabilities. Examples include the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, and the European Web Directive. With businesses adhering to the latest WCAG 2.2, there are reduced chances of users filing cases for inaccessibility. Businesses thus save money by avoiding lawsuits. Besides, by ensuring equal access to users with disabilities, organizations and businesses contribute to creating a more inclusive and equitable digital environment for all.
Common Challenges in WCAG 2.2 Implementation and Useful Solutions:
Implementing WCAG 2.2 can be complex and challenging for businesses and organizations, as incorporating them into web development and maintenance processes can pose significant hurdles.
5 Common Challenges Businesses Face
The five common challenges faced by most businesses and web developers while implementing WCAG 2.2 include:
Lack of Awareness and Understanding: Many businesses and organizations lack a comprehensive understanding of WCAG 2.2 and its implications for their websites and applications. This lack of knowledge can lead to unintentional non-compliance and potential legal issues.
Resource Constraints: Implementing WCAG 2.2 often requires significant financial and human resources. Businesses may need to allocate additional funds for accessibility testing, training, and software tools while dedicating staff time to address accessibility issues.
Legacy Technology and Codebases: Websites and applications built on older technologies or with complex codebases may be more challenging to adapt to WCAG 2.2 standards. This can require extensive, time-consuming, and costly refactoring and code remediation.
Content Management Systems (CMS) and Third-party Tools: Integrating WCAG 2.2 compliance into CMS and third-party tools can be tricky, especially in tools lacking built-in accessibility features.
Ongoing Maintenance and Testing: WCAG 2.2 compliance is not a one-time project. It requires ongoing maintenance and testing to ensure new content and updates adhere to the guidelines. This can add to the ongoing costs and resource demands for maintaining an accessible website.
Practical Solutions to Overcome Challenges
The good news is that there are practical solutions that web developers can easily use to overcome these challenges. They include:
Educating and Training Staff: Regular training sessions for web developers, designers, and content creators raise awareness of WCAG 2.2 guidelines and best practices.
This helps ensure that accessibility considerations are integrated into all web development and maintenance aspects.
Prioritize Accessibility from the Start: Incorporating accessibility considerations into web development projects’ planning and design phases helps.
This proactive approach can help identify and address potential accessibility issues early on, thus preventing costly retrofits later.
Utilize Accessibility Testing Tools: Employing automated accessibility testing tools to identify and troubleshoot accessibility issues throughout the development process also helps.
These tools can provide valuable insights and help streamline the remediation process.
Choose Accessible CMS and Third-party Tools: When selecting CMS and third-party tools, prioritize those that offer built-in accessibility features and support WCAG 2.2 compliance.
This can save time and effort in the long run. Businesses may need to customize these tools or find alternative solutions that meet accessibility requirements.
Establish an Accessibility Workflow: Implementing a clear accessibility workflow that outlines roles, responsibilities, and procedures for ensuring and maintaining WCAG 2.2 compliance helps.
This will help keep accessibility at the forefront of web development and maintenance.
Clearing Common WCAG 2.2 Implementation Misconceptions
A few common misconceptions about implementing WCAG 2.2 discourage web developers from implementing them. Here are 5 common misconceptions dispelled:
Accessibility is Expensive: True
Yes, implementing WCAG 2.2 can involve upfront costs. However, the long-term benefits of an accessible website outweigh these expenses. An accessible website can increase user engagement, improve brand reputation, and reduce the risk of legal issues.
Accessibility is Only for People with Disabilities: False
Accessibility benefits everyone, not just those with disabilities. An accessible website is more user-friendly and usable for all, regardless of their abilities or limitations.
Accessibility is Too Technical: True
While some technical expertise is required to implement WCAG 2.2, accessibility is not solely a technical issue. It requires collaboration between designers, developers, content creators, and stakeholders to ensure a truly accessible user experience.
Accessibility Can Wait: False
Accessibility should not be an afterthought for website owners. It is essential to integrate accessibility considerations into all web development and maintenance phases. Addressing accessibility early on can save time and resources in the long run.
Accessibility is Binary: False
Accessibility is not a pass-fail situation but a spectrum of conformance levels. Businesses should strive to achieve the highest level of accessibility possible, as even incremental improvements can make a significant difference for users with disabilities.
Conclusion
WCAG 2.2 marks a significant milestone in pursuing digital accessibility by addressing more accessibility needs. It builds on WCAG 2.1 by adding new guidelines and success criteria and clarifying and updating existing ones. It makes the web more accessible and offers a roadmap for creating inclusive and user-friendly websites for individuals with diverse abilities. By adhering to these guidelines, web developers, content creators, and organizations play a pivotal role in bridging the digital divide, thus ensuring everyone has equal access to digital content across the internet.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines Experts – ADA Site Compliance
Contact ADA Site Compliance today for all your ADA website compliance and website accessibility needs! Get your FREE SITE SCAN now. We are leaders in assistive technologies and making all your websites accessible.
#https://adasitecompliance.com/wcag-2-2-decoding-latest-web-accessibility-guidelines/#wcag 2.2#web accessibility guidelines#ada compliance#web content accessibility guidelines#accessibility standards#decoding wcag 2.2#latest web accessibility guidelines#digital accessibility#inclusive design#ada website compliance#wcag compliance#accessibility best practices#web accessibility updates#accessibility testing#a11y (short for accessibility)#usability for all#assistive technology#accessibility features#ada website requirements#web accessibility checklist
0 notes
Text
Accessibility standards in practice
The World Wide Web consortium or better known as “W3” is an international standards organization that governments, businesses and consumers look towards for guidelines regarding accessibility focused website development (Caldwell, Cooper, Guarino Reid, & Vanderheiden, 2008). These standards were named “WCAG2” standards and they were created for the consumers and yet according to the WebAIM’s “million” webpage study regarding accessibility, over “98.1% of home pages had detectable WCAG2 failures!” (AIM, 2020). What are some of the top factors that contribute to this high percentage of failure and why? Are government websites more compliant with WCAG2 than non-government websites? Will a browser accommodate for these lapses in accessible design by overriding some of the features? These are important questions that arise when discussing website design with an emphasis on accessibility and what we can do to ensure accessibility.
“85.4% of pages had low contrast text, 61.9% had missing alternative text, 63.4% had empty links, 56.1% had missing form input labels.” (AIM, 2020), what does it mean when text has low contrast? According to WebAIM, It’s when “contrast is a measure of the difference in perceived ‘luminance’ or brightness between two colors” (AIM, 2018). This perceived brightness is often harsh on the visually impaired as they cannot properly understand information on a webpage, which greatly lowers the quality of the visit. Such violations are overlooked simply because it doesn’t make for a beautiful, cathartic experience which website designers aim for as businesses cater to the majority, for their revenues are dependent on a delectable experience for the majority. According to the World health organization, over 4% of the World population has some sort of visual impairment which clearly puts the minority at a disadvantage (WHO, 2019). To mitigate such a blatant disregard for accessibility, browsers have started to add support for websites that lack high contrast text which makes a seamless transition between low contrast text to high contrast text (Lyles, 2020). This isn’t a permanent fix, it’s a workaround. But how can we ensure there’s no workaround required? That’s something you’ll have to get to the end for.
The rest of the top factors that websites don’t comply with, usually showcase a lack of good development as these issues only occur when designing lacks basic fundamentals. We’ll talk about the alternative text soon, but let’s focus on the very notion of bad development that comes from bad designing. Broken functionality is a major accessibility issue, as major components that are used in websites are dispersed across the internet and it’s very difficult and tedious to ensure that all components of a website work as intended; when they should be. When any one of those components fail to load when a visitor receives a landing page, their lovely favorite browser will trudge on and still display the page but with very little noticeable difference. This trudging on is the reason why such accessibility errors arise, as the browsers are meant to continue until their last breath. Fixing such an issue is futile, unless the web designers put a little more effort into ensuring that all functionality passes the tests and browsers must ensure they don’t showcase the website at all if it’s broken.
Now, let’s talk designers who often overlook the power of text as it has the power to draw a viewer in, if correctly and responsibly chosen for the context the text is written in. The lack of alternative text is astonishing as the most basic task of a designer is to “avoid decorative or overly stylized fonts, which are often difficult to read even for users without visual impairments or reading disabilities” (BOIA, 2017). Some of the best fonts that ensure clean readability are of sans serif aesthetic such as, Arial, Helvetica, Lucida Sans, Tahoma, and Verdana (BOIA, 2017). If that isn’t accessible enough, there are fonts such as, Read Regular, Lexie Readable, and Tiresias which provides aid to individuals with dyslexia or visual impairments. To make matters even worse, these fonts are completely free to use. Of-course, this too can be handled by the browser which is in full support of the minority. But, why does the browser keep picking up the slack of the websites that should be doing it first on their end and then have the browsers as a fail safe?
We know that the government entities are forced to provide an accessible environment of their webpages, how do they rank up in this mess?
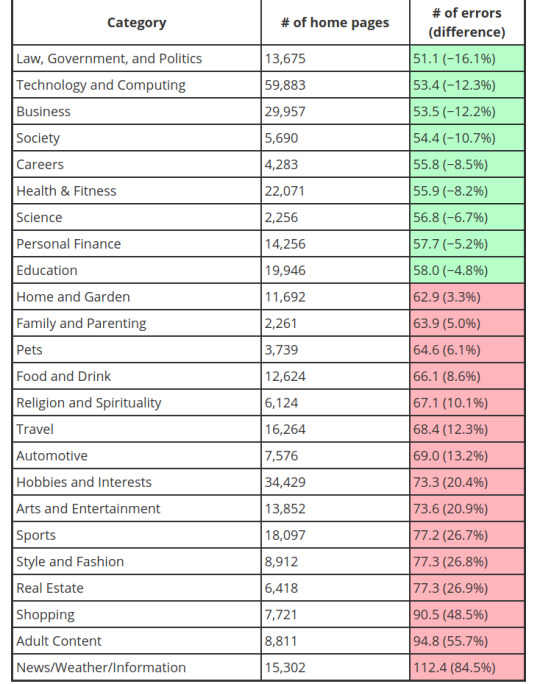
(AIM, 2020)
As seen from the graph, government entities are least worst culprits and every year they do better by reducing the accessibility gap that progressively gets worse for non-government entities. You might ask, why is the government the least worst culprit? Let’s take Canada for example, the Federal Government was sued by Jodhan in a disability discrimination lawsuit in 2012 and won (CCD, 2012). That lawsuit brought forth strong changes in the federal government with how website accessibility is dealt with in Canada, firstly by forcing a default open source framework that the federal government provided for its provincial counterparts and secondly by having this requirement added into the Charter of Rights. This framework that was constructed complies with WCAG2 guidelines right out of the sandbox, which is why if you visit any Canadian government website, the layout, text and color is relatively in the same ballpark. Precisely this type of lawsuit and the need for prevention, caused governments all around the world to be morally held liable for providing the most accessible experience to any and all of its citizens possible. Funny enough, the very needs (services) of our daily lives are improving but the luxury of having the wants (services), is what keeps getting worse.
Since we know that the internet is composed of non-government entities, having this framework be mandatory for all of these outstanding entities would greatly reduce the WCAG2 violations made. How can we make this framework mandatory?
Push for WCAG2 guidelines to be made law for all business and government entities operating in the residing country so they are legally liable into providing an accessible experience, so that these entities don’t earn wholesome, public loving points for choosing to offer a service that should be the norm. As demonstrated, conforming to the guidelines is not hard at all. There are even tools, all over the internet, that will alert you of any guidelines you don’t conform to. If that isn’t enough, pressure the website developers/owners into providing the necessary accessible features.
Change is very much possible if the floor can be turned into money burning lava.
References
Caldwell, B., Cooper, M., Guarino Reid, L., & Vanderheiden, G. (2008). Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0. Retrieved July 28, 2020, from https://www.w3.org/TR/WCAG20/
AIM, W. (2020). The WebAIM MillionAn annual accessibility analysis of the top 1,000,000 home pages. Retrieved July 28, 2020, from https://webaim.org/projects/million/
AIM, W. (2018). Contrast and Color AccessibilityUnderstanding WCAG 2 Contrast and Color Requirements. Retrieved July 28, 2020, from https://webaim.org/articles/contrast/
WHO, W. (2019). Vision impairment and blindness. Retrieved July 28, 2020, from https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blindness-and-visual-impairment
BOIA, B. (2017). Best Fonts To Use for Website Accessibility. Retrieved July 28, 2020, from https://www.boia.org/blog/best-fonts-to-use-for-website-accessibility
Lyles, T. (2020, March 11). Chrome tool helps developers make websites more color blind friendly. Retrieved July 28, 2020, from https://www.theverge.com/2020/3/11/21174735/google-chrome-dev-tools-new-color-blind-friendly
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is W3C Validation? & Its Best Practices
W3C validation refers to the process of checking whether a website or web document complies with the standards and guidelines set forth by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The W3C is an international community that develops and maintains web standards, including HTML, CSS, and other web technologies.
W3C validation is important because it helps ensure that your web pages are built using correct and consistent code, which promotes better cross-browser compatibility, accessibility, and overall quality. By validating your code, you can identify and fix errors, making your website more reliable and robust.
Here are some best practices for W3C validation:
Use a Markup Validation Service: The W3C provides an online Markup Validation Service (validator.w3.org) that allows you to validate your HTML and XHTML documents. Submit your web pages through this service to check for errors and warnings.
Validate CSS: In addition to HTML, it's important to validate your Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) code. The W3C CSS Validation Service (jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator) can be used to validate your CSS files and ensure they conform to the recommended standards.
Validate on Multiple Browsers: Different web browsers may interpret HTML and CSS code differently. Therefore, it is beneficial to validate your website on multiple browsers, such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer, to ensure consistent rendering.
Fix Validation Errors: Once you've validated your code, review the error and warning messages provided by the validator. Address these issues by modifying your code accordingly. Fixing validation errors will improve the correctness and reliability of your website.
Use a Doctype Declaration: Always include a proper doctype declaration at the beginning of your HTML documents. This declaration tells the browser which version of HTML or XHTML you are using and helps ensure proper rendering.
Use Semantic Markup: Utilize HTML elements in a way that reflects their intended purpose. For example, use heading tags (h1-h6) for headings, paragraph tags (p) for paragraphs, and lists for listing content. This practice enhances accessibility and aids search engine optimization.
Separate Structure and Presentation: Use CSS to control the visual presentation of your web pages, rather than relying on deprecated or inline styling attributes. Separating structure and presentation improves code maintainability and facilitates consistent design updates.
Provide Alternative Text for Images: When including images on your website, use the alt attribute to provide descriptive alternative text. This improves accessibility for visually impaired users and helps search engines understand the image content.
Test for Accessibility: Conduct accessibility testing to ensure your website is usable by individuals with disabilities. Consider using tools like the WAVE Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool (wave.webaim.org) to identify and resolve accessibility issues.
By following these best practices, you can improve the quality, compatibility, and accessibility of your website while adhering to the W3C standards.
0 notes
Text
Building Beautiful Websites with Accessibility in Mind Having a website is essential for businesses and organizations who want to effectively reach their target audience. The quality of a website is just as important as its function. Your website needs to visually appealing while still being easy to navigate and use. Accessibility should never be an afterthought when it comes to building beautiful websites. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) is an international organization that has established the standards for web accessibility. The organization provides tips and guidelines for building websites that are accessible to all. As such, it is important that designers and developers understand these requirements before they begin to create websites. Making a website accessible goes beyond just making sure that it looks good. When building a website, accessibility should be an integral part of the process. Here are some tips you can implement when creating a website: 1. Make Your Website Responsive Responsive website design ensures that the website will look great and function properly on any device. It is important to consider the different devices and screen sizes that people will use to access the website. Responsive design makes sure that the website layout and content are optimized for different devices. Furthermore, website designs should also consider how people with disabilities access websites. For instance, users that are visually impaired use screen readers to access websites. If a website is not designed properly, they may encounter difficulties while navigating the website. Responsive design will ensure that all users have a smooth and frictionless experience on the website, regardless of their abilities. 2. Utilize Contrast and Colour Using proper contrast and colour is important when it comes to making a website accessible. All website content should have enough contrast to make sure that it is legible. This includes text, images, buttons, and forms. Using proper contrast is especially important for people with visual impairments, as they rely on high contrast to be able to read the website content. In addition, designers should also consider how the colour choices affects people with colour blindness. Different colour combinations may not be visible to them. Make sure to select colours that are visible to all users and avoid using colour to convey information. 3. Optimize for Keyboard and Touch User input is one of the most important aspects of a website. Making sure that the website can be easily navigated with both a keyboard and a mouse is essential. People with physical impairments often rely on keyboard navigation instead of a mouse. This is why it is important to make sure that all website elements are easily accessible with a keyboard. Designers should also make sure that their website is optimized for touchscreen devices, like smartphones and tablets. These devices have become the most popular way in which people access websites. Designers should ensure that all elements are large enough to be tapped with a fingertip. 4. Provide Text Alternatives It is important to provide text alternatives for images and other visual elements on the website. People with visual impairments rely on these alternatives to understand the website content. Text alternatives can also help website visitors who have slow internet connections or do not have the ability to view the images. When creating text alternatives, make sure that the descriptions are accurate and succinct. Providing detailed descriptions for images will help people with visual impairments better understand the content. 5. Utilize Accessible Forms Having an accessible form is essential in order to ensure that all users can submit their data. When designing forms, make sure that they are labelled correctly and easy to fill out. It is important to provide input fields which are large enough for people to fill out with ease. It is also recommended
to remove any unnecessary scripts or on-page validation as these could cause difficulties for people using assistive technologies. 6. Test for Accessibility The best way to make sure that a website is accessible is to actually test it. There are a number of tools and services out there which can help designers and developers test their websites for accessibility. These tools are usually easy to use and can provide accurate feedback that can be used to improve the website’s accessibility. Conclusion Building a website that is accessible to all is not just important for legal reasons, it also makes sure that everyone can use the website regardless of their abilities. Ensuring that your website is accessible will help you reach more people, as well as improving your website’s usability. At Clean Visuals, we offer web design services that are tailored to meet your specific needs. Our experienced team of designers will create a unique website that is optimized for performance and user experience. With Clean Visuals, you can rest assured that we will deliver high-quality results. Check out our web design pricing for more information about our services. What are the benefits of building accessible websites? 1. Reach a Wider Audience: By making websites more accessible, they will be available to people with disabilities as well as people who do not have any disability. This will enable businesses to reach more potential customers and increase their audience base. 2. Increase Engagement: Accessible websites are more user-friendly, so people with disabilities are able to more easily navigate, which increases website engagement and usability. 3. Improved brand perception: Accessible websites make your business seem more understanding and considerate of its customers’ needs, which can lead to a more positive perception of your brand. 4. Increase conversions: By providing an easily navigable website, visitors are more likely to stay longer and ultimately convert into customers. 5. Compliance with web accessibility standards: Businesses are required to adhere to web accessibility standards. Building accessible websites assists in ensuring compliance with these standards.
0 notes
Text
IGNOU University - Courses, MBA Fees Structure, Placements, Admission, Syllabus.

Since its establishment by an Act of Parliament in 1985, the Indira Gandhi National Open University IGNOU University has worked tirelessly to create an inclusive knowledge society through inclusive education. By providing top-notch instruction via the Open and Distance Learning (ODL) mode, it has attempted to raise the Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER).
With 4,528 students, the University started out by providing two academic programmes in 1987: a diploma in management and a diploma in distance learning.
Today, it supports the educational aspirations of over 3 million students in India and other countries through a network of 67 Regional Centers, 2,000+ Learner Support Centers, and 20 international institutions, as well as 21 Schools of Studies. Over 35,000 academic counsellors from traditional institutions of higher learning, professional organisations, and industry, among others, make up the University’s staff of nearly 250 faculty members and 230 academic staff at the headquarters and regional centres, which offers about 200 certificates, diploma, degree, and doctoral programmes.
The University’s mission is to:
provide all societal segments with access to higher education;
Offer all those in need of them high-quality, cutting-edge, and need-based programmes at various levels;
Reach out to the underprivileged by providing affordable programmes across the nation, and the educational standards of the nation’s open and distance learning programmes are promoted, coordinated, and controlled.
The University uses a range of media and the most recent technology to deliver education in order to accomplish the twin goals of increasing access for all societal groups and offering ongoing professional development and training to all economic sectors. This is reflected in the IGNOU’s developed vision, which states the following while keeping its goals in mind:
By utilising cutting-edge technologies and methodologies and ensuring the convergence of existing systems for large-scale human resource development, the Indira Gandhi National Open University, the National Resource Center for Open All people will have easy access to quality education, skill development, and training that is sustainable and learner-centric thanks to distance learning, which has gained international recognition and presence.
The University has had a big impact on community education, higher education, and ongoing professional development. For the purpose of enhancing the educational opportunities it provides, the University has formed partnerships with reputable public institutions and private businesses. It has received awards for excellence from the Commonwealth of Learning (COL), Canada, a global leader in distance education.
The university is dedicated to providing high-quality instruction, research, training, and extension services, and it serves as a national hub for ODL system infrastructure and expertise. To concentrate on particular learner groups and improve the distance learning system, the university established the National Centre for Disability Studies and the National Centre for Innovation in Distance Education.
The University has ushered in a new era of technology-enabled education in the nation with the launch of EduSat (a satellite exclusively for education) on September 20, 2004, and the creation of the Inter-University Consortium. Active two-way video conferencing network connectivity has been made available to all regional centres and high enrollment Learners Support, enabling the exchange of interactive digital content.
Within the framework of integrated distance and online learning, emphasis is now placed on developing interactive multimedia and online learning and enhancing the traditional distance education delivery mode with contemporary technology-enabled education.
IGNOU Admissions
IGNOU also provides a graduate-level online Master of Business Administration (Online MBA) program. Both recent graduates and working professionals who want to continue their education online can use the program.
After successfully completing a three-year UG degree with a minimum score of 50%, applicants can apply for admission to the IGNOU Online MBA two-year management degree program. No entrance exam will be required for admission to the online program.
The application process for the MBA program is organized through the IGNOU Online official website. The first and second semesters of the IGNOU MBA online program cost INR 14,000 each. The cost for the third and fourth semesters is INR 16,000, however.
A bachelor’s degree is the bare minimum requirement for enrollment in an online MBA program. A minimum grade of 50% was required to receive the UG degree. There are numerous specializations available, including
Human Resource Administration
Financial Administration
marketing administration
Operations Administration
Services Administration
The students will be able to learn and obtain the degree of such a highly required program without attending an offline class by choosing the online MBA course in the July 2022 session. Aspirants who had given up on pursuing this professional degree were given the chance to do so thanks to the online degree MBA program.
Every eligible person now has the opportunity to continue their education without changing their current financial situation thanks to the addition of an MBA as an online course. Multiple digital self-learning options, including self-study materials, e-lectures, and IGNOU E-Content, will be made available to students. The deadline for IGNOU Online MBA Admission 2022–23 is August 12, 2022.
Eligibility for IGNOU University
Below are the requirements for admission to the online, two-year MBA graduate program:
BBA degree with a minimum grade point average of 50% (or 45% for sc/st students) from an accredited institution
A 50 percent score on other UGs or equivalent degrees will be accepted.
The passing degree cannot be obtained in less than three years.
IGNOU Online MBA Fees
Fees for the Ignou MBA program are as follows for both domestic and foreign applicants:
The student who is an Indian national must pay 14,000 INR per semester (1st, 2nd, & 4th)
The third semester’s tuition is 16,000 rupees.
There will be no additional fees for SAARC students compared to Indian citizens.
Non-SAARC candidates will need to pay 81,306 INR as a deposit for each semester (1st, 2nd, and 4th)
Entry into the third semester will be contingent on a deposit of 10,7176 rupees.
Learn More…
0 notes
Text
After-Effects Of Covid-19 On The Global Stock Clamshell Market Outlook: Ken Research
Buy Now
Expansion of Manufacturing Plants:
Companies are setting up manufacturing plants in India. International semiconductor consortium (ISMC), a joint venture between Abu Dhabi-based Next Orbit Ventures and Israel’s Tower Semiconductor, plans to invest Rs 22,900 crore ($3 billion) in a chip fab. In May 2022, it signed an agreement with the Karnataka government to set up an Electronics Manufacturing Cluster over 150 acres of land in Kochanahalli Industrial Area.
The Indian Government has been promoting SPECS to help offset the disability for domestic manufacturing of electronic components and semiconductors in order to strengthen the electronics manufacturing ecosystem in the country.
Ease of Market Entry:
There is a lot of scope for new players to enter. This is because of untapped potential, favourable government incentive plans and schemes. It is expected that competition in the market will continue to increase as existing competitors improve or expand their product offerings and as new companies enter the market.
Adoption of 5G network and AI
With increasing internet penetration from 35% in 2016 to ~50% in 2021 and adoption of smart devices are contributing to the semiconductor market growth. The electronics system design manufacturing market is the fastest growing industry in India. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the development of intelligent hardware or software that can copy human activities like learning and problem-solving. Semiconductors are expected to play an important role in the AI opportunity's acceleration.
Demand from end-user Industries:
The huge demand for semiconductors from end-user industries like industrial machinery, automobiles, telecommunication equipment, office automation, among others for computing purposes is expected to accelerate the growth of the semiconductor market in the coming years.
The publication titled “India Semiconductor Market Outlook to 2027- Driven by increasing demand by end user industries and increasing adoption for smart devices” provides a comprehensive analysis of the semiconductor industry by analyzing historical statistics and corresponding developments in the semiconductor market. The market growth declined during COVID as it impacted the workforce and operations, the operations of the customers, and those of the respective vendors and suppliers. Given the consolidated competition structure in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, analysts have elaborated on competitive landscape of major manufacturing players on the basis of business model and operational parameters. The report also covers a snapshot on the players business model, value chain analysis, growth drivers, Porters 5 forces analysis, impact of COVID-19 and factors governing the future outlook of industry. The report also provides comprehensive insight on the market size and segmentation of the industry. The report highlights the pain points of the semiconductor manufacturing industry along with detailed company profiles of major players in India. The report concludes with projections for future industry market size, market segmentations and analyst take on future market scenario.
Request For Sample Report-https://kenresearch.com/sample-report.php?Frmdetails=MzQxMjEx
Key Segments Covered in Indian Semiconductor Market
By Type of Semiconductors
Intrinsic
Extrinsic
By Type of Design
VLSI
Embedded Software
Electronic Design Automation
By Region
North
South
East
West
By Type of Application
Mobile
IT
Automotive
Consumer Electronics
Others
By Type of Distribution Channels
Online
Offline
By Type of Distributors
International
Local
Time Period Captured in the Report:
Historical Period: FY 2017-2022
Forecast Period: FY 2023F-2027F
Semiconductor Manufacturing Industry Players
NXP
Broadcom
Samsung
Moschip
Texas Instruments
Saankhya Labs
Key Topics Covered in the Report
Ecosystem of Semiconductor Industry
Business Lifecycle and Value Chain Analysis Semiconductor Industry
Market Overview of Semiconductor Industry
Market Size of Semiconductor Industry
Market Segmentation of Semiconductor Industry by type of semiconductors, type of design, type of application, type of region, type of distributors, type of distribution channel
Competitive Scenario of the Semiconductor Industry
Issues and Challenges in Semiconductor Market
Trends and Developments in the Semiconductor Industry
Porter’s Five Forces analysis of the Semiconductor Industry
Growth Drivers of Semiconductor Industry
Challenges and Restraints in the Semiconductor Industry
Government Rules and Regulations in the Semiconductor Industry
Impact of Covid-19 on Semiconductor Industry
Future Market Size of Semiconductor Industry
Future Market Segmentation of Semiconductor Industry by type of semiconductors, type of design, type of application, type of region, type of distributors, type of distribution channel
Analyst Recommendations
Research Methodology
For more information on the research report, refer to the below link:
India Semiconductor Market Major Players
Related Reports
UAE Data Center and Cloud Services Market Outlook to 2026F – Driven by Rapid Digital Penetration along with Increasing Investments to meet the Rising Demand for Data Storage and Cloud Services
India Social E-Commerce Market Outlook to 2027 (Second Edition): Driven by growing internet penetration rate and consumers shifting preference towards availing digital medium for purchases
Follow Us
LinkedIn | Facebook | Twitter| YouTube
Contact Us:
Ken Research
Ankur Gupta, Head Marketing & Communications
+91-9015378249
0 notes
Text
Fwd: Graduate position: UCologne_Germany.BiologyGeologyEvolution
Begin forwarded message: > From: [email protected] > Subject: Graduate position: UCologne_Germany.BiologyGeologyEvolution > Date: 22 August 2024 at 06:58:15 BST > To: [email protected] > > > > CRC 1211 Earth - Evolution at the Dry Limit Faculty of Mathematics > and Natural Sciences, University of Cologne, Germany > > PhD position (f/m/x) on riverine species and landscape evolution in > hyperarid regions > > Application deadline 15.9.2024 > > > PhD position (f/m/x) on riverine species and landscape evolution in > hyperarid regions > > The speciation of aquatic insects is likely to be closely linked to the > development of the rivers they inhabit, so the genetic record of riverine > species can help us understand fluvial histories and impactful tectonic > and environmental changes. This PhD project aims to better understand > and develop this concept in arid regions, focusing on the Atacama Desert > in South America and the Namib Desert in Southern Africa. The topic > is part of a larger research consortium Earth - Evolution at the Dry > Limit (CRC 1211 - https://ift.tt/0VoFqYX), which includes several > interconnected projects hosted across several German universities, which > focus on the links between biological and geoscientific disciplines > in arid environments. The successful applicant will be hosted at the > University of Cologne and supervised by Kathrin Lampert and Steven Binnie > in either the Institutes of Biology or Geology. They will also work > closely with researchers in the group of Jean Braun at the GFZ German > Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam to integrate findings from > field studies into a modelling framework. > > YOUR TASKS > Combine geomorphological and biological research > Analyse the connection of river drainage reorganization and biodiversity > Modelling using AdaScape/FastScape > Molecular (DNA) laboratory work > Data analyses and integration > Fieldwork in Namibia > Present and disseminate research results in scientific conferences > and publications > > YOUR PROFILE > Excellent academic record > MSc Geology/Geomorphology or MSc Biology > Background in landscape evolution studies and/or phylogenetic analyses > and willingness to conduct interdisciplinary research > Comfortable doing field work in remote areas > Experience with basic programming is an asset > Fluent in English (spoken, reading and writing) > High motivation, commitment, good communication skills, ability to work > in a team and independently > Drivers license > > WE OFFER > An exciting research project at the cutting edge of interdisciplinary > research in an international working group > A diverse working environment with equal opportunities > Support in balancing work and family life > Extensive advanced training opportunities > Occupational health management offers > Flexible working time models > > The University of Cologne promotes equal opportunities and > diversity. Women will be considered preferentially in accordance > with the Equal Opportunities Act of North Rhine-Westphalia > (Landesgleichstellungsgesetz LGG NRW). We also expressly welcome > applications from all suitable candidates regardless of their gender, > nationality, ethnic and social origin, religion, disability, age, sexual > orientation and identity. > > The position is available from 1 November 2024 on a part-time basis > (29,87 hours per week). The position is to be filled for a fixed term > until 30 June 2028. If the applicant meets the relevant wage requirements > and personal qualifications, the salary is based on remuneration group > 13 TV-L of the pay scale for the German public sector. > > Please apply online with proof of the required qualifications without > a photo under: https://ift.tt/VDZHxBo. The reference number is > Wiss2408-13. The application deadline is 15 September 2024. For further > inquiries, please contact Kathrin Lampert ([email protected]) or > Steve Binnie ([email protected]). > > Kathrin Lampert
0 notes
Text
ADA Site Compliance

Boosting User Experience: 10 Simple Tips For Making Your Website More Accessible
Your website is not just an attractive piece of real estate you have online. It is a powerful marketing tool that works 24/7 at explaining to the world what you have to offer and give them. But it’s effective only if the website’s accessibility is accessibility is optimal for everyone to access. Otherwise, you may lose top clients because they cannot find the site or interact because of the site design!
And this is the segment of the market suffering from disabilities like motor, visual and cognitive disabilities. They, however, are your target audience, so just by tweaking your website for website compliance, you can tap into and monetize the segment. By boosting your website or mobile app accessibility, it gets more accessible and useful to generate more income. This is where ADA Site Compliance can help, as we are the #1 resource for ensuring ADA website compliance!
What is web accessibility?
Web accessibility ensures all web pages of a website are developed so that everyone, including people with disabilities, can access it. The goal is to provide an equal website experience for those with and without limitations. Website accessibility addresses these primary disabilities:
Visual disabilities include but are not limited to blindness, color blindness, and poor eyesight. It can also have difficulties reading text because of the sunlight and other similar situations.
Auditory impairments include but are not limited to deafness and users who are hard of hearing.
Motor impairments that include but are not limited to muscle slowness, loss of muscle control, and the inability to use hands.
Neurological disabilities that include and are not limited to seizures, cerebral palsy, and epilepsy.
Intellectual and cognitive disabilities that include but are not limited to developmental and learning disabilities like dyslexia and non-verbal learning.
Why make a website accessible?
Not only will you reach a larger audience with an accessible website, but accessibility is also required by law in some industries and countries for the following reasons. A website should be designed to be accessible to:
Provide equal access to everyone
Improve website navigation
Provide multiple and equal avenues of interaction to communicate
Prove your brand commitment to serving your target audience
Protect your website from lawsuits and fines for inaccessibility
How to make your website accessible
If you want to learn how to make your website accessible, then you can get started with the help of these ten tips:
10 Simple Tips For Making Your Website More Accessible
The World Wide Web Consortium developed the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 & 2.1 to create an international standard of web content accessibility. They remove and restrict digital access barriers for people, governments, and organizations through detailed requirements, success criteria, and techniques to follow for website accessibility!
1. Use more helpful alt text or text alternatives for images
Use descriptive alt text for images to support accessibility. Include text alternatives for videos, graphics, and audio content to help convey your message and allow screen reader users to read your content. The alt text should describe the image and its relationship with the content. This improves your online visibility and web compliance!
2. Include captions and text transcripts
Including captions and transcripts for videos makes them accessible to users who can't hear the audio. Avoid using flash, time-based or autoplay content as they can harm those with photosensitive disorders and induce seizures. Display warnings if you must use them on your web page!
3. Have a logical page layout
A logical page layout with proper heading hierarchy, interactive elements placement, and relevant categories makes it easier for users to navigate and access the website's content. Using appropriate headings like H1, H2, and H3 indicate different sections and aid screen reader users in accessing the content!
4. Accessible navigation
Accessible navigation means creating websites that are easy to navigate, with consistent fonts, colors, and designs. Descriptive text for links is important for accessibility, as it helps screen reader users and people using other assistive technologies understand the purpose of the link. Writing helpful and informative error messages is also essential to avoid confusion and frustration for users. Error messages should be specific and use plain language, without overusing them!
5. Keep it simple
To keep your website user-friendly, eliminate unnecessary elements and opt for a clean layout with plenty of white space, a two or three-color scheme, and two fonts. Purposeful graphics that are clickable and insightful are also beneficial. Ensure adequate color contrast, so visitors with visual impairments can read content. To aid users with poor sight, consider alternative means of determining text beyond just color. For example, use colored buttons with appropriate alt tags for screen readers!
6. Mobile-friendly and responsive website
Make a mobile-friendly and responsive website to improve web compliance and digital marketing. Over 50% of web traffic comes from mobile devices, so a mobile-optimized website is essential to avoid visitors abandoning your site. Additionally, Google crawls desktop and mobile websites, so a mobile-friendly site can improve your online visibility. Optimize all desktop information for mobile devices and place buttons in the center of the screen for quick access using thumbs. The layout should be designed for single-touch interaction using one or two hands!
7. Make use of accessible website forms
Website forms are essential for conversions and lead generation, so it's crucial to ensure a user-friendly experience for everyone. Marking all form fields, using larger label sizes, contrasting colors, and simple controls like text boxes and checkboxes can help increase form accessibility. Avoid using placeholder text as labels and provide helper text above the form field for users to understand what to write!
8. Readable site text
The right website text enhances the website user’s experience. This is why font choice plays an integral part in ensuring the readability of the text. Some users may find reading text with curved lines challenging, as the font may be too wide or narrow because of the lines. Always let users enlarge or zoom too small text to read it comfortably if they find it difficult!
9. Do not use color for displaying critical information
There is always the chance of people suffering from color blindness visiting your site. So having important data like graph data in forms and error fields in different colors only make it difficult for users with low vision or impairments to read the data. Instead, it is better to describe the data in a graph using components like colored labels and patterns to make them easily distinguishable to the visitor!
10. Ensure there is an option for keyboard website navigation
This tip suggests adding an option for keyboard navigation on your website to ensure accessibility for users with physical disabilities. Users should be able to navigate interactive elements using the tab key and activate functionality elements like forms, links, and dropdown menus using the enter or space buttons. A logical tab order and visual focus indicators can make the process even smoother. Testing the keyboard navigation is important to ensure it works properly and indicates where the user is on the page!
In conclusion, improving website accessibility is essential for creating an inclusive and user-friendly experience for all visitors, including those with disabilities. By following the ten tips outlined in this guide, you can make your website more accessible and compliant with WCAG guidelines. However, it's also important to periodically check your website's accessibility using tools and professional web developers. At ADA Site Compliance, we can help ensure your website is accessible and provide support to maintain compliance!
#https://adasitecompliance.com/boosting-user-experience-10-simple-tips-making-website-more-accessible/#web accessibility#assistive technologies#website accessibility#accessibility solutions#website & digital accessibility solutions#ADA web accessibility solution#accessibility resources#Americans with disabilities Act#digital accessibility#legal compliance experts#ADA site compliance#ADASiteCompliance#adasitecompliance.com
0 notes
Text
Professional’s Assistance for Law Firm Website WCAG - ADA for Web

Are you a lawyer by profession? Or do you own a law firm? Well, if you are, or you do, have you prioritized digital accessibility? Well, the topic of the discussion here is the law firm website WCAG. Let us discuss more on this.
You must pay attention to the fact that more potential clients continue to search for attorneys online, and that is why your law firm must prioritize digital accessibility. Digital accessibility simply refers to making sure the technology is available to a wide range of users, including people with disabilities. Here, the focus is on people with disabilities because they may have trouble learning and utilizing new technologies.
Keeping Your Law Firm Up to Date with Accessibility
If you want to keep your firm up to date with accessibility, you should pay attention to bookmarking and periodically audit the Web Accessibility Initiative website posting news on digital accessibility updates and amendments. So, now, it is essential to know and learn about the law firm website WCAG. As far as the WCAG is concerned, it was published in January 1995 and revamped in December 2008. The complete form is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. These are the definitive guidelines law firms can use to ensure their website is digitally accessible. The World Wide Web Consortium published it for the international standards body for the internet.
Matters related to law firm website ADA compliance can be complex and typical. So, if you are looking forward to knowing more, implementing the right solutions to bring this into practice, then you should seek a professional’s assistance. We, ADA for Web, are a leading and trusted agency. We offer service to clients having businesses and seeking Accessible Web Design, keeping WCAG and Compliance in consideration. We partner with clients and focus on identifying their needs and fulfill them at best. Feel free to contact us.
Read Related Blogs
How to Choose Consulting Firm Looking After ADA for Web?
Considerations While Choosing ADA Compliant Website Design and Development Services
Originally published on - https://sites.google.com/view/ada-for-web/professionals-assistance-for-law-firm-website-wcag
0 notes
Text
Space Force backs development of commercial orbital debris removal systems
https://sciencespies.com/space/space-force-backs-development-of-commercial-orbital-debris-removal-systems/
Space Force backs development of commercial orbital debris removal systems

WAILEA, Hawaii — A Space Force general endorsed the development of commercial systems for removing space debris, saying they can address congestion in Earth orbit without the policy concerns a government-run alternative might have.
Maj. Gen. DeAnna Burt, vice commander of the Space Force’s Space Operations Command, told an audience of space traffic management experts that active debris removal is essential to address the growing population of objects in low Earth orbit that pose a threat to government and commercial satellites.
“We need to pick up debris. We need trash trucks. We need things to go make debris go away,” she said in a keynote at the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies, or AMOS, Conference here Sept. 15. “I think there is a use case for industry to go after that as a service-based opportunity.”
Burt, who is also commander of the Combined Force Space Component Command of U.S. Space Command, said that concern was driven by the inability to do anything if there is a threat of a collision between two non-maneuverable objects, like debris. “Those are bad days,” she said, within nothing to do other than hope that the predicted conjunction passes without any new debris objects tracked.
Later in her presentation, she emphasized that orbital debris removal was not only important, but also should be done by the private sector. “Absolutely there’s a business case for debris removal for industry,” she said.
Orbital debris is a job for companies, she said, because a government-led effort would cause some to believe the technology would also used as a weapon to disable active satellites. “When you say the military is going to develop a capability to pick up trash or pick up debris, it’s automatically seen as dual use,” she said.
A company, or consortium of companies, that attempted orbital debris removal would be “very valuable,” she concluded. “It is a growing discussion on the international stage as well. I think it will get solved in the next few years, but we definitely want to see more of that technology.”
Several companies have expressed an interest in orbital debris removal, including projects to demonstrate technologies needed to capture and deorbit objects. However, they face other stumbling blocks, from uncertain regulatory regimes for removing debris to identifying who will pay for debris removal, and how much.
Debris removal fits into a broader picture of space traffic management or, as she described it, space traffic awareness. The difference is that, unlike air traffic management, where there are clear authorities and regulations for directing aircraft, the Space Force has little ability to direct operational, or live, satellites to maneuver if it identifies a potential collision.
“If that live object is a DOD capability, then absolutely I have the authority to tell them, ‘you need to move and here’s direction you’re moving,’” she said. “If that object is anything other than a U.S.-flagged Department of Defense asset, I am making them aware there is a collision, but it’s their choice what they do.”
She supported efforts to transfer civil space traffic management to the Commerce Department. “We, as the Department of Defense, look forward to the Department of Commerce taking on this mission and standing up,” she said. “We stand shoulder to shoulder to help them to do that and to be successful.”
Handing those responsibilities to Commerce Department, she argued, would better separate civil and military roles, allowing Space Command to focus on “battlespace awareness” including fighting a war that extended to space.
“We will continue to do the space traffic awareness mission until we are told not to and the Department of Commerce is fully up and capable,” she said. “But we want them to be successful because we need to get out of that business because the threat is growing. It is critical that, to normalize this domain, we continue to work in that direction.”
#Space
0 notes
Text
After-Effects Of Covid-19 On The Global Stock Clamshell Market Outlook: Ken Research
Buy Now
Expansion of Manufacturing Plants:
Companies are setting up manufacturing plants in India. International semiconductor consortium (ISMC), a joint venture between Abu Dhabi-based Next Orbit Ventures and Israel’s Tower Semiconductor, plans to invest Rs 22,900 crore ($3 billion) in a chip fab. In May 2022, it signed an agreement with the Karnataka government to set up an Electronics Manufacturing Cluster over 150 acres of land in Kochanahalli Industrial Area.
The Indian Government has been promoting SPECS to help offset the disability for domestic manufacturing of electronic components and semiconductors in order to strengthen the electronics manufacturing ecosystem in the country.
Ease of Market Entry:
There is a lot of scope for new players to enter. This is because of untapped potential, favourable government incentive plans and schemes. It is expected that competition in the market will continue to increase as existing competitors improve or expand their product offerings and as new companies enter the market.
Adoption of 5G network and AI
With increasing internet penetration from 35% in 2016 to ~50% in 2021 and adoption of smart devices are contributing to the semiconductor market growth. The electronics system design manufacturing market is the fastest growing industry in India. Artificial intelligence (AI) is the development of intelligent hardware or software that can copy human activities like learning and problem-solving. Semiconductors are expected to play an important role in the AI opportunity's acceleration.
Demand from end-user Industries:
The huge demand for semiconductors from end-user industries like industrial machinery, automobiles, telecommunication equipment, office automation, among others for computing purposes is expected to accelerate the growth of the semiconductor market in the coming years.
The publication titled “India Semiconductor Market Outlook to 2027- Driven by increasing demand by end user industries and increasing adoption for smart devices” provides a comprehensive analysis of the semiconductor industry by analyzing historical statistics and corresponding developments in the semiconductor market. The market growth declined during COVID as it impacted the workforce and operations, the operations of the customers, and those of the respective vendors and suppliers. Given the consolidated competition structure in the semiconductor manufacturing industry, analysts have elaborated on competitive landscape of major manufacturing players on the basis of business model and operational parameters. The report also covers a snapshot on the players business model, value chain analysis, growth drivers, Porters 5 forces analysis, impact of COVID-19 and factors governing the future outlook of industry. The report also provides comprehensive insight on the market size and segmentation of the industry. The report highlights the pain points of the semiconductor manufacturing industry along with detailed company profiles of major players in India. The report concludes with projections for future industry market size, market segmentations and analyst take on future market scenario.
Request For Sample Report-https://kenresearch.com/sample-report.php?Frmdetails=MzQxMjEx
Key Segments Covered in Indian Semiconductor Market
By Type of Semiconductors
Intrinsic
Extrinsic
By Type of Design
VLSI
Embedded Software
Electronic Design Automation
By Region
North
South
East
West
By Type of Application
Mobile
IT
Automotive
Consumer Electronics
Others
By Type of Distribution Channels
Online
Offline
By Type of Distributors
International
Local
Time Period Captured in the Report:
Historical Period: FY 2017-2022
Forecast Period: FY 2023F-2027F
Semiconductor Manufacturing Industry Players
NXP
Broadcom
Samsung
Moschip
Texas Instruments
Saankhya Labs
Key Topics Covered in the Report
Ecosystem of Semiconductor Industry
Business Lifecycle and Value Chain Analysis Semiconductor Industry
Market Overview of Semiconductor Industry
Market Size of Semiconductor Industry
Market Segmentation of Semiconductor Industry by type of semiconductors, type of design, type of application, type of region, type of distributors, type of distribution channel
Competitive Scenario of the Semiconductor Industry
Issues and Challenges in Semiconductor Market
Trends and Developments in the Semiconductor Industry
Porter’s Five Forces analysis of the Semiconductor Industry
Growth Drivers of Semiconductor Industry
Challenges and Restraints in the Semiconductor Industry
Government Rules and Regulations in the Semiconductor Industry
Impact of Covid-19 on Semiconductor Industry
Future Market Size of Semiconductor Industry
Future Market Segmentation of Semiconductor Industry by type of semiconductors, type of design, type of application, type of region, type of distributors, type of distribution channel
Analyst Recommendations
Research Methodology
For more information on the research report, refer to the below link:
India Semiconductor Market Major Players
Related Reports
UAE Data Center and Cloud Services Market Outlook to 2026F – Driven by Rapid Digital Penetration along with Increasing Investments to meet the Rising Demand for Data Storage and Cloud Services
India Social E-Commerce Market Outlook to 2027 (Second Edition): Driven by growing internet penetration rate and consumers shifting preference towards availing digital medium for purchases
Follow Us
LinkedIn | Facebook | Twitter| YouTube
Contact Us:
Ken Research
Ankur Gupta, Head Marketing & Communications
+91-9015378249
0 notes
Text
Fwd: Postdoc: UAuckland_NZ.WildPop_imputation
Begin forwarded message: > From: [email protected] > Subject: Postdoc: UAuckland_NZ.WildPop_imputation > Date: 4 December 2023 at 05:43:07 GMT > To: [email protected] > > > Filling the gaps to better predict adaptive potential in wild populations – > imputation from low coverage sequencing > > We are pleased to offer a 2-year postdoctoral fellowship based with Dr Anna > Santure (https://ift.tt/of9qNZH) in the School of > Biological Sciences, Waipapa Taumata Rau – The University of Auckland, > Aotearoa New Zealand. This project is an exciting opportunity to assess > strategies for genotype imputation to ‘fill the gaps’ from low coverage > sequencing in wild populations. The project will include (i) > individual-based modelling to create populations with different levels of > structure and genetic variation to test when best to leverage family and/or > population variation for imputation, and (ii) the application of optimal > imputation methods to our existing low coverage datasets to accurately > characterise genetic variation and structure. > > Improving and validating our use of low coverage data has direct outcomes > for how we handle the generation and analysis of whole genome resequencing > data in conservation and evolutionary biology. The candidate will be > working alongside a vibrant research group with aligned research interests, > including the use of whole genome resequencing data to infer, for example, > the ability of taonga (precious) species such as hihi (stitchbird) to adapt > and persist, and of invasive species such as common myna to further expand > their invasive range. The project will be conducted in collaboration with Dr > Audald Lloret-Villas ( > https://ift.tt/gFbhf0p) in the > Population Genetics Consortium, Arizona State University. > > The ideal candidate will have experience in imputation and/or the analysis > of whole genome resequencing data and/or individual based modelling, as > well as a passion for evolution and conservation biology and a track record > of publishing in leading journals. In addition, experience in reproducible > pipeline development (Snakemake or Nextflow), Python and/or R, > bioinformatics tools and Bash scripting are highly desirable. Candidates > who do not fully meet the previous criteria but have experience in > genomics, bioinformatics, computational biology, evolutionary biology, > statistics, quantitative genetics or population genetics are also > encouraged to apply. > > The postdoctoral fellowship is available with a salary range of > approximately NZD $88,194 - $98,533 p.a. (depending on experience as > assessed by an independent committee). The start date is negotiable but > must begin before 1 May 2024. We welcome informal enquiries, please contact > Anna Santure at [email protected]. > > Applications must be emailed to [email protected] by 11:59pm Monday > 15 January 2024 (New Zealand time) to be considered. Please include a cover > letter and your CV highlighting how you can meet the skills and experiences > detailed above. > > Applicants must have completed or submitted their PhD at time of > application. We welcome applications from all qualified persons. > International applicants are welcome to apply. Our group ( > https://ift.tt/b1Nsg6x) aims to be inclusive, > representative, collaborative and fun. > > The University is committed to meeting its obligations under Te Tiriti o > Waitangi and achieving equity outcomes for staff and students in a safe, > inclusive, and equitable environment. For further information on services > for Māori, Pasifika, women, LGBTQIATakatāpuiMVPFAFF+, people with > disabilities, parenting support, flexible work and other personal > circumstances go to https://ift.tt/5UkhtoI. > > Anna Santure
0 notes
Text
First Psychiatry Consortium funded project announced for schizophrenia

A partnership between University of Oxford, the Earlham Institute, and the global pharmaceutical companies Biogen Inc and Boehringer Ingelheim is announced today to investigate a new drug target for the treatment of schizophrenia.
This is the first project to be funded by the international Psychiatry Consortium, a £4 million collaboration between seven global pharmaceutical companies, and two leading research charities, convened and managed by the Medicines Discovery Catapult, that supports high-value drug discovery projects in this area of unmet patient need.
The world-leading team of academic researchers will use their newly designed technical approach to assess which proteins are selectively produced by the kalirin gene in the human brain, and how this differs from other human tissues.
Once this is understood it may be possible to identify the proteins that represent the most promising drug targets for the potential treatment of schizophrenia, how they affect the function of cells, and begin to develop drugs to alter their function.
Liz Tunbridge, Associate Professor at the University of Oxford, and lead investigator for the study, commented:
“We desperately need new treatments for schizophrenia because current drugs can cause side effects, do not work for everyone and do not improve all the symptoms. However, it has been difficult to improve this situation because of our limited understanding of the changes in the brain that underlie schizophrenia. This exciting collaboration will enable us to start the long journey from genetic research to the development of new drugs. Ultimately, we hope that our research will one day lead to new medicines that improve the lives of people with schizophrenia.”
Dr. Hugh Marston, Head of Department CNS Diseases Research at Boehringer Ingelheim said:
“Schizophrenia is a serious mental health condition that alters a person’s perception of reality, impacts how they think, feel, and behave. Current treatment options leave significant room for improvement through the development of new therapeutics. We recognize the importance of finding new solutions for people living with neuropsychiatric disorders with our innovative CNS research program as a key focus area at Boehringer Ingelheim. As this program focuses on improving our understanding of the mechanisms that underly these complex disorders, we are pleased to be part of this first research project of the Psychiatry Consortium. We hope a successful completion will make a real impact on the development of innovative treatment options.”
Diana Gallagher, Head of External Innovation, Biogen said:
“At Biogen we recognise the enormous impact psychiatric disorders have on mental health. The significant gap in treatment options leaves many with poor long-term quality of life and disability. Being part of the Medicines Discovery Catapult (MDC) Psychiatry Consortium, builds on Biogen’s recent licensing and partnership of later-stage drug candidates for psychiatry, and participation in this project, and its successful outcome, could inform our thinking on neuropsychiatric disorders where Biogen will aim to develop new treatments for patients.”
Professor Chris Molloy, Chief Executive Officer at Medicines Discovery Catapult (MDC) said:
“At a time when mental health research is gravely underfunded, this group of academic and industrial scientists, brought together in the Psychiatry Consortium by Medicines Discovery Catapult, is delivering improved understanding of schizophrenia in ways that can be directly applied to new drug discovery.
“This is a landmark for the Psychiatry Consortium – one of many to follow – intended to yield tangible improvements for those living with schizophrenia.”
The post First Psychiatry Consortium funded project announced for schizophrenia appeared first on .
from https://pharmaphorum.com/partner-content/first-psychiatry-consortium-funded-project-announced-for-schizophrenia/
0 notes