#Journal of Biosensors and Renewable Sources
Text
Biomethane: Opportunities and Challenges on the Transitional Pathway to a Zero Carbon Future

Jeffrey M Seisler
Abstract
Fossil fuels are being targeted for extinction due to their impacts on global warming. But the multiple transitional pathways to completely replace fossil fuels with renewable energy sources is a long journey that is not likely to be fully realized until at least the end of the 21st century. Adapting the existing fossil energy businesses and infrastructures while developing the renewable, alternative energy infrastructures (and adapting existing ones) will be key to the timing and success of the transition. Despite the aspirations and visions of many technologists and policy makers who see the‘long-term’ future at 2050, the trajectory of the transition will be lengthy, disruptive and uncertain. There are, however, some fuels and technologies contributing to the so-called circular economy that should not be sidelined or overlooked completely.
Keywords: Global warming; greenhouse gas; biomethane; bio waste
Introduction
Natural gas, comprised mostly of methane (CH4), recognized as the cleanest of fossil fuels, is under duress as a greenhouse gas (GHG) for its Global Warming Potential [1]. Fortunately, methane also has a renewable pathway – ‘the new molecule’ – as biomethane [2] created through anaerobic digestion (AD) [3] of agricultural waste (plant and animal), wastewater (solids, human organic materials, etc.), urban waste (organic landfill garbage), and a variety of other organic waste such as fats, oils and grease. Biomethane has been under-appreciated and sometimes ignored by many policymakers internationally in favor of liquid biofuels that have been seen as more compatible with traditional liquid fuels in internal combustion engines. Like every other fuel and technology, biomethane has both opportunities and challenges but, it can make a major contribution to reducing the human carbon footprint on a global scale as both an energy strategy as well as a waste management strategy.
Read more about this article:
https://lupinepublishers.com/biosensors-renewable-sources/fulltext/biomethane-opportunities-and-challenges-on-the-transitional-pathway-to-a-zero-carbon-future.ID.000138.php
Read More About Lupine Google Scholar:
https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=T4c9RDkAAAAJ&citation_for_view=T4c9RDkAAAAJ:JV2RwH3_ST0C
#biosensors#journalofbiosensorsandrenewablesources#journal of biosensors and renewable sources#geology
0 notes
Text
lupine publishers|Nanotechnology in Wireless Communication
Nanotechnology in Wireless Communication

Abstract
Nanotechnology is the projected ability to construct items at nanoscale from the bottom up, using techniques and tools being
developed today to make complete, high-performance products. Nanotechnology for wireless communication will add on high
quality, low cost, high sensitivity, reliability, robustness, high accuracy and computer function- ability. Though it has initial high
research, development and manufacturing costs yet that can be compensated by low bulk manufacturing costs. Portable energy
storage using super capacitor-battery hybrids based on new materials including carbon nano-horns and porous electrodes, fuel
cell technologies, energy harvesting, and more efficient solar cells will help increase life of energy sources and transportability
and reduce size and equipment weight Electronics and computing advances reaching beyond IC scaling limits, new computing
approaches and architectures, embedded intelligence and future memory technologies, nano-scale transducers for mechanical,
optical and chemical sensing, bio-mimetics in sensor signal processing and nano-scale actuation will increase network intelligence
and efficiency.
The concept of ambient intelligence could result in our living environment in the home, car and office becoming sensitive and
responsive to our presence. For continuous and much simpler interaction with information to enhance quality of life, improve
working conditions and increase productivity appliances such as computers, multimedia equipment and communications devices
would be integrated into that environment. Flexible mobile phones able to act at the same time as personal digital assistants (PDA),
electronic purses and interactive media providers will be available at an affordable cost. Combined mobile communications and
global location units will enable the dispatch of assistance quickly to elderly or handicapped people in trouble.
Such recent advances in nano-scale technologies can be exploited not only to lead to new mass markets for electronic
communication but also to provide the high-technology experience and low-cost manufacturing expertise required to develop other
nanotechnology industries
Keywords: Nanotechnology; Nanomaterials; Wireless Communication; Ambient Intelligence
Introduction
These days we describe the advancements in wireless
technologies in the form of generations. Presently we are going
through the second generation (2G) and are about to enter third
generation (3G) and have started planning for fourth generation
(4G) and dreaming of fifth generation (5G). Nanotechnology is
going to be the key technology to help this great change. The
purpose of this paper is to outline what we are going to enter
soon and then develop on this the 4G and 5G and how this
nanotechnology is going to change things, so that we may know as
to what is in store for us when we are too old to enjoy the benefits
while the new generations live the different form of technical life.
Our first- and second-generation mobile telephony was intended
for voice transmission. The third generation of mobile telephony
will serve both voice and data applications. What will be in store of
4G is not yet fully clear, though it is going to be something different,
something more advanced in nature from 3G, e.g., an entirely
packet switched network with all digital network elements and
extremely high available bandwidth. True multimedia capabilities
such as high-speed data access and video conferencing to the
handset will be provided by 5G system. 4g also holds the promise
of worldwide roaming using a single handheld device followed by
communication without even moving your lips, transmission of
thoughts directly from one mind to another. This may take us to
5G. One of the latest development in the communication is the
“nanotechnology”. (nano=10-9) which will help attain this. It is a
great wonder that such a seemingly simple communication and
information transportation system is going to use “nanotechnology”
at a large scale.
Purpose
Purpose of this paper is to discuss the impact of Nanotechnology
on wireless communication.
Technology Development in Wireless Communica-
tions
Wireless communication: The term “wireless” [1] has
become a generic and all-encompassing word used to describe
communications in which electromagnetic waves or RF carries
a signal over part or the entire communication path. Wireless
industry aims at ambient intelligence. For this the computation and
communication should be always available and ready to serve the
user in an intelligent way This requires mobile devices embedded in
human environment. A new platform with autonomous and robust
devices has to be created to enables ubiquitous sensing, computing,
and communication (Figure 1). They can be deployed easily, and
they survive without explicit management or care. Mobility also
implies limited size and restrictions on the power consumption.
Seamless connectivity with other devices and fixed networks is
a crucial enabler for this. The demands data rates of the wireless
links. Intelligence, sensing, context awareness is increased for which
more memory and computing power is needed. Severe challenges
in thermal management however arise with size limitations.
for more information about Journal of Biosensors & Renewable sources archive page click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/biosensors-renewable-sources/archive.php
for more information about lupine publishers page click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/index.php
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
MFC-Based Biosensors Known as an Integrated and Self-Powered System - BJSTR Journal
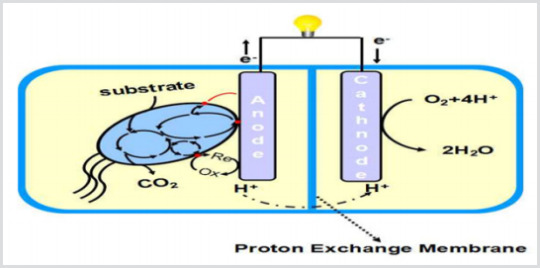
MFC-Based Biosensors Known as an Integrated and Self-Powered System by Mostafa Rahimnejada* in Biomedical Journal of Scientific & Technical Research
https://biomedres.us/fulltexts/BJSTR.MS.ID.002538.php
Main sources of energy are classified into three significant batches such as fossil fuels, nuclear sources and renewable ones [1], in which fossil fuels and nuclear ones known as non-renewable sources of energy involve a massive quota energy uses all around the world [2]. Carbon dioxide emission, global warming and atmospheric contamination are the main drastic disadvantages of non-renewable energy consumption by the people, which negatively influence whole the environment [3]. As a piece persuasive solution to the energy crisis, tremendous efforts have been done by huge number of scientists by turning the eyes into consumption of renewable sources of energy rather than non-renewable ones [4]. Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) as the main type of Fuel Cells (FCs) can apply active microorganisms as biocatalysts instead of those metal ones in an anaerobic anode part for bioelectricity production [5,6]. By an overall view, MFCs consist of a cathode and an anode compartments separated by a Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Figure 1, in which electrons as protons in anode compartment are produced by oxidizing of organic matters with the help of biocatalysts [7]. Generated protons directed to the cathode part through PEM and the electrons conduct through the external circuit. Along with Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) in cathode part, protons and electrons reacted there which resulted in water molecule production. Electricity generation, biohydrogen production and as an energy production technology in wastewater treatments, are the most significant applications of MFCs nowadays [8].
For more articles on Journal on Medical Science please click here
bjstr
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/Biomedres01
Follow on Blogger : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/
Like Our Pins On : https://www.pinterest.com/biomedres/
#Journals on Psychology#Neurological Disorders#Immunological Diseases#Biopsychological Medicine#Journals on Vaccination
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cotton Cloth: Diversified Applications beyond Fashion and Wearable Cloth - Juniper Publishers
To know more about Journal of Fashion Technology-https://juniperpublishers.com/ctftte/index.phpTo know more about open access journals Publishers click on Juniper PublishersTo know more about Journal of Fashion Technology-https://juniperpublishers.com/ctftte/index.phpTo know more about open access journals Publishers click on Juniper Publishers

Abstract
Recent developments in the field of textile industry highlighting cotton cloth/fabric to a new interest in another application. The cotton cloth that is well known as one of the most comfortable wearable fabric has positioning itself to various new significant functions and application especially in the area of wastewater treatment technology, medical and surgery devices, electronic applications, enzyme and lipase production, crop and harvesting procedure, energy storage devices and etc. This article emphasizing few studies from various researches regarding the use of cotton cloth either as a substrate, template material, function modification or even as storage or covering materials. This proved the versatility of cotton cloth to be used in vast areas of technology.Keywords: Cotton cloth; Cotton fabric; Cotton cloth substrate; Wearable cloth; Cotton cloth applicationAbbreviations: GOS: Galacto-Oligo Saccharides; RGO: Reduced Graphene Oxide; ISTA: International Seed Testing AssociationGo to
Introduction
Daily clothes such as blouses, T-shirts, sweater, robes, under garments and even sheets or blanket mainly originated from natural cotton fibers. Weaving activity of cotton fiber has produced a flexible and porous cotton fabric with soft yet strong, durable and comfort properties [
1
]. Cotton is suitable and matched with weather in Asia and perfect for wearing in the summer. Cotton cloth is one of the most popular fabrics to wear because of it many advantages. It definitely have a comfortable, wearable and breathable cloth, since it able to draw heat away from skin, easily absorb body moisture and evaporate in the air, keeping cool and comfortable in hot weather [
2
,
3
]. Cotton fabric irregularly causes allergic responses and wearing cotton cloth is often suggested for those with skin allergic [
3
]. The medical product such as bandages and gauze also produced from cotton. In addition to that, cotton cloth is the best choice of fabric when it comes to baby/children clothing [
2
]. Cotton is allowing air circulation that discourages fungi from growing in dark and moist atmosphere [
2
,
3
]. The affordable cost of cotton cloth make more appealing and high in demand. Thus, cotton cloth with various advantages has make it a perfect choice for people nowadays to wear with coziness in daily life.The rapid growth and exploration of emerging technology nowadays allows cotton cloth to be further explored, designed and manufactured for a broader spectrum of applications. A significant progress has been achieved through modified and improved it surface function, structure and morphology. For instances, it is applicable in wastewater treatment technology [
4
-
6
], medical and surgery devices [
1
], electronic applications [
79
], enzyme and lipase production [
10
,
11
], in crop and harvesting procedure [
12
], energy storage devices [
9
] and the number keep increasing from one technology to another.
Diversified cotton cloth application
The specialty of cotton cloth includes less in weight, very flexible to be folded or recovered, thin in diameter sizes, good mechanical strength, and lower cost, have good breathability, abundance in nature, renewability, versatility and easily to get from any cloth shops around the world. The following describe the use of cotton cloth in another technology application.The cotton cloth has been effectively used as a filter to remove radioactive ions such as uranium which mainly comes from nuclear industry. The synthesis of cotton cloth filter was grafted by acrylonitrile and methacrylic acid onto cotton cloth using mutual irradiation technique and the subsequent amidoximation of the reactive intermediate nitrile groups. The grafting on cotton/cellulose materials have several advantages due to high hydrophilicity, high adsorption capacity and fibrous structure of cellulosite material. Plus, this filter can be biodegraded after used and possesses good morphology and chemical stability which is SEM image of cotton cloth filter fabricated to remove uranium suitable for practical application [
13
].
Figure 1
illustrates the ion from radioactive waste treatment.
The enormous use of fossil fuels can cause severe consequences toward environment such as air pollution and global warming. In order to reduce the high reliance of fossil fuels, the expansion of high-performance electrochemical energy storage devices is required for renewable energy and electric vehicles. Energy storage devices will be highly in demand upon meeting criteria of flexible, lightweight, efficient, wearable or portable e.g.to be used in artificial biosensor or implantable medical devices. The cotton textile used as starting substance for constructing wearable super capacitors because of its low cost, high flexibility, great strength, good breathability, abundance, renewability and versatility [
8
].
Figure 2
shows the fabrication process of wearable super capacitor using cotton textile as substrate.
Galacto-OligoSaccharides (GOS) production from lactose by β-galactosidase is introduced in food product and dairy industry due to many health benefits. Previous practice basically used free enzyme in solution for its production. However, compared with enzyme immobilizing on a solid support using reactor, it provides many advantages including enzyme reusability, operated continuously, controllable, simpler and efficient in processing. Besides, immobilized enzyme reactor generally more economic compare to free enzyme reactor due to higher productivity and able to minimize the downtime, enzyme costs and reactor size. With the used of cotton cloth packed in loose spiral form in the reactor, it has produce lower pressure drop, good flow rate and minimized the diffusion limitation [
10
]. In order to get clear understanding of enzyme cotton-cloth reactor, the schematic diagram is shown in
Figure 3.
The lipase from thermo myceslanuginosus is a single chain protein with amino acid that produced enzyme. The enzyme is biotechnology relevant and is widely used in many industries such as food, fine chemicals, detergents, waste water treatment, cosmetics, paper and pulp, pharmaceuticals and leather industry Cotton cloth as immobilization matrix has many advantages e.g. high porosity, large surface area, good mechanical strength and relatively inexpensive. It serves as an excellent choice as support matrix for immobilization [
11
].
Nanomaterial offer comprehensive potential applications when assimilated with fabric substrates such as to be used for heat generation application [
14
]. A study conducted using Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) nanosheets coated on cotton cloth based films as heating element for wearable body warmer. The fabric cloth coated nanomaterials being an interactive material for heating elements due to their special and exceptional properties such as large surface to volume ratio, less in weight, dimensionality, and corrosion free. Directly it minimizing the common problem faced by the device like heavyweight, inflexibility, and low heating proficiency. Hence, by considering all the advantages, the textile electronic devices can be employed in automobile, biomedical and electronic wearable technology For example, the heating element application in biomedical field can be vast, for instances as medical blankets for patients, jacket for soldiers and electrotherapy treatment [
1
].
Figure 4
exhibits the fabricated RGO coated cotton cloth for heating element devices.
Practically, microalgae cultures are sustained using a variety of techniques which include serial subculture, lyophilisation and cryopreservation. The maintenance and conservation of microalgae are tedious and require specific conditions. Due to several limitations, researchers have developed an easy and convenient method for long-term preservation and conservation of microalgae which is by using cotton fabric for the immobilization of microalgae [
15
].
Figure 5
presents the culture of microalgae immobilized on cotton cloth and SEM image of algal cell.
Sorghum
(Sorghum bicolor L
.) is in forth ranking of cereal crop in the world after wheat, rice and maize. It is a tropical crop which belong to a grass family. In Tanzania, Sorghum is one of the most important source of subsistence in their country. For common practice, sorghum seed germination test has to be conducted using International Seed Testing Association (ISTA) paper substrate. The ISTA paper has to be imported since it was not manufactured in their country. As an alternative solution, cotton cloth is used as a substrate since the seed germination performance can be maintained similar to the use of ISTA paper. The cotton cloth has minimized the cost of importing ISTA paper due to local availability and lower in price [
16
].
Figure 6
shows the Sorghum seedlings laboratory germination tests using cotton cloth and ISTA paper.
The use of cotton cloth is also diversified and tested for wastewater treatment technology. Focusing on effluent from textile and other dyeing industries such as paper, printing, leather, food and plastic industries, the presence of dyes create an environmental problem due to their high visibility, resistance and toxic impact [
17
]. Dyes can be eliminated by various methods, and most common method used is adsorption. Researchers coated the adsorbent on the cotton cloth as a substrate. The aim is to simplify the maintenance activity after the adsorption process as well as improving the surface area to weight ratio of the adsorbent and minimizing the quantity of solid adsorbent required. The cotton cloth was chosen as substrate due to its large surface area, thin, light weight, easy to handle and reasonable in price [
18
].
Figure 7
illustrates the cotton cloth adsorbent coating strip.
A brief summary on the usage, function and advantages of cotton cloth in various field of applications is tabulated in
Conclusion
The current study contributes to our knowledge by addressing several issues.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge the Research University Grant (1001/PJKIMIA/814269) and Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi for providing My PHD as financial support throughout the study.
To know more about Journal of Fashion Technology-https://juniperpublishers.com/ctftte/index.php
To know more about open access journals Publishers click on Juniper Publishers
#Juniper Publishers#Juniper Publishers Group#Fashion Technology#Textile Engineering#Juniper Open access Journals
0 notes
Text
Biosensor for stem cells could lead to Alzheimer’s therapies
New biosensor technology monitors the fate of stem cells by detecting genetic material involved in turning such cells into brain cells, according to a study.
The technology, which features a unique graphene and gold-based platform and high-tech imaging, may lead to safe stem cell therapies for treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and other neurological disorders, researchers report.
Stem cells can become many different types of cells. As a result, stem cell therapy shows promise for regenerative treatment of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke, and spinal cord injury, with diseased cells needing replacement or repair. But researchers must solve the problem of characterizing the cells and controlling their fate before they can use them in treatments. The formation of tumors and uncontrolled transformation of stem cells remain key barriers.
“A critical challenge is ensuring high sensitivity and accuracy in detecting biomarkers—indicators such as modified genes or proteins—within the complex stem cell microenvironment,” says senior author KiBum Lee, a professor in the chemistry and chemical biology department at Rutgers University–New Brunswick. “Our technology, which took four years to develop, has demonstrated great potential for analyzing a variety of interactions in stem cells.”
The team’s unique biosensing platform consists of an array of ultrathin graphene layers and gold nanostructures. The platform, combined with high-tech imaging (Raman spectroscopy), detects genes and characterizes different kinds of stem cells with greater reliability, selectivity, and sensitivity than today’s biosensors.
The team believes the technology can benefit a range of applications. By developing simple, rapid, and accurate sensing platforms, Lee’s group aims to facilitate treatment of neurological disorders through stem cell therapy.
Stem cells may become a renewable source of replacement cells and tissues to treat diseases including macular degeneration, spinal cord injury, stroke, burns, heart disease, diabetes, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, according to the National Institutes of Health.
The research appears in the journal Nano Letters.
Additional researchers from Rutgers and Sogang University in South Korea contributed to the study.
Source: Rutgers University
The post Biosensor for stem cells could lead to Alzheimer’s therapies appeared first on Futurity.
Biosensor for stem cells could lead to Alzheimer’s therapies published first on https://triviaqaweb.weebly.com/
0 notes
Text
Eco-Friendly Substitutes for Plastics

Introduction
Plastic is a semi-synthetic or synthetic organic polymer. It can be made from different organic feed stocks, but the majority of industrial plastic is manufactured from petrochemicals. There are two types of plastic, thermosets which harden into an enduring shape, whereas thermoplastics they can be heated and remolded many, many times. Lot of additives like colorants, plasticizers, fillers, stabilizers, and reinforcements are used while making these plastics. The specific properties of any plastic depend on these additives. Examples of plastic, PET - polyethylene terephthalate, HDPE - high-density polyethylene, PVC - polyvinyl chloride and PS - polystyrene, these are among the different plastics that are used. Leo Baekeland was the first person who made plastic, and it is named as Bakelite in the year 1907.
Read more about this article: https://lupinepublishers.com/biosensors-renewable-sources/fulltext/eco-friendly-substitutes-for-plastics.ID.000107.php
Read more
LupinePublishersGoogleScholarArticles:https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=5ql0QHJV55QC&citation_for_view=5ql0QHJV55QC:L8Ckcad2t8MC
#lupine#lupine publishers#journal of biosensors and renewable sources#biosensors#astronomy#climate change#waste energy
0 notes
Text
Soil-Sensors for Real Time Irrigation to Match Crop Water Requirement in Subsurface Drip System

Introduction
Globally, water availability is becoming progressively scarce and by 2025 more than one-third of the world population would face severe water shortage [1,2]. The arid and semi-arid regions of Asia, the Middle-East, and sub-Saharan Africa, which are having a high concentration of the world’s population with a large section living below the poverty line, will be the worst affected areas. While demand for food and other agricultural commodities in these areas is increasing due to fast-growing population, freshwater availability is continuously declining.
Read more about this article: https://lupinepublishers.com/biosensors-renewable-sources/fulltext/artificial-neural-networks-based-modeling-in-sustainable-energy-domain.ID.000105.php
ReadmoreLupinePublishersGoogleScholarArticles:
https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=5ql0QHJV55QC&citation_for_view=5ql0QHJV55QC:mVmsd5A6BfQC
#lupine publishers#open access journals#Journal of Biosensors and Renewable Sources#Soil Solar energy#Nuclear thermal
0 notes
Text
Happy Thanksgiving!!!
Greetings from Journal of Biosensors and Renewable Sources (JBRS)

We are deeply thankful for your confidence and loyalty towards our Journal of Biosensors and Renewable Sources (JBRS), and we extend to you our best wishes for a happy and healthy Thanksgiving Day!!
0 notes
Text
lupine publishers|The Electrochemical Sensing of Nalbuphine Opioid Analgesic Drug by the Cyclic Voltammetric and
Conductometric Titration Techniques
The Electrochemical Sensing of Nalbuphine Opioid Analgesic Drug by the Cyclic Voltammetric and Conductometric Titration Techniques

Abstract
A novel reliable electrochemical sensing method was suggested for direct and sensitive determination of Nalbuphine (NB)
analgesic drug. The effect of copper ions (Cu +2) as sensor towards NB determination was evaluated using cyclic voltammetry
method and conductometry. They have been utilized to predict the possible electrochemical sensitivity and complexation reaction
between Nalbuphine Hydrochloride (NB) and divalent copper (II) metal ions. Cyclic voltammetry study of CuSO 4.5H2O in absence
and presence of (NB) was performed using different concentration from Cus and NP·HCl at different scan rates. Redox mechanism
of the system was determined from the resulted data. Moreover, thermodynamic parameters show valuable information about
chelate metal ions. The resulted data obtained from cyclic voltammetry measurements was supported by conductometric titration
measurements, since complexation of Cu (II) with (NB) has been investigated conductometric ally. The formation constants of the
prepared complexes were obtained from the relation between the molar conductance and the ratio of metal to ligand concentrations
indicating the formation of 1:2 and 1:1 (M: L) stoichiometric complexes. As the temperature increases, the formation constants of
the complexes increase indicating that the reaction is endothermic. The negative results of ∆G indicated that the reactions between
NB·HCl and Cu (II) tend to proceed spontaneously.
Keywords: Electrochemical Sensing; Nalbuphine Hydrochloride; Glassy Carbon Electrode; Cyclic Voltammetry; Stability Constant
and Conductivity
Introduction
Nalbuphine, is a semisynthetic narcotic selective receptor
modulators or known as mixed agonist/antagonist analgesic of the
phenanthrene series [1]. Nalbuphine, structurally belongs to the
strong potent opiate agonists oxymorphone and to most used opioid
antagonists, naloxone and naltrexone [2]. Analytical methods such as
HPLC, spectroscopy, and electrochemical techniques are influential
tools for determining drug concentrations of NB in biological and
pharmaceutical samples [3-5]. Detection of the complex formation
reaction by cyclic voltammetry and condctometry methods
confirm the potential for electrochemical sensing of Nalbuphine
hydrochloride by copper ions as an electrochemical sensor.
Electrochemical sensing do not face the obstacle of high cost and
complexity of setup. Cyclic voltammetry is one of the most powerful
electrochemical techniques [6]. It can quickly give qualitative data
about electrochemical reactions [7]. The data obtained from cyclic
voltammetry investigate the behavior of electrochemical reaction.
The potential and the current at which the analyte is reduced and
oxidized can be obtained [8]. Stability constant and thermodynamic
properties such as Gibbs free energy ΔG [9], enthalpy ΔH, and
entropy ΔS [10] can be calculated where they indicate the nature of
the complexation reaction [9,10].
Results and Discussion
Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements
Effect of different concentrations of Cu+2 and NB with different
scan rates were studied as such as Effect of different scan rates.
The Ip is directly proportional to ν1/2 which support a diffusion
controlled reaction. The different solvation parameters ( Гc, Q c, Гa
& Qa) decreased by the increase of the scan rate also supporting
the diffusion process of solvation. The increase of scan rate was
followed by the increase of the potential difference ( ΔE) but E ̊value is nearly constant. Also, the redox peaks currents decreased
by decreasing the scan rates. The linear relation between -I pa and
Ipc with the square root of scan rate demonstrated that the reaction
was governed by the surface diffusion processes [11].
The addition of NB to the solution and step wisely increasing
its concentration, the redox peaks current decreased than observed
with Cu+2 alone indicating the complex reaction between metal
and ligand, hence the method is sensitive to detect NB. Also, The
heterogeneous rate constant (k s) and the kinetic parameters
decreased due to the lowering of charge transfer velocity indicating
more interaction between copper ions and Nalbuphine.
Effect of different scan rates in presence of Nalbuphine
HCl
The influence of different scan rates for 1:1 ratio between
copper and nalbuphine had been studied. The decrease of the scan
rate was followed by the decrease of the redox peaks currents and
the heterogeneous rate constant (ks), but the solvation parameters
like ((Гc, Q c, Гa & (-) Qa) increased. The linear relation between
the peak current and square root of scan rate confirmed that the
reaction was governed by diffusion processes.
The stability constant for (Cu-Nalbuphine) complex
The values of stability constant (Log βj) and Gibbs free energy
(∆G) increased by increasing the j (L/M) ratio, indicating the
tendency towards the formation of the complex
Conductometry measurements
The specific conductance values (Ks) of the solutions of different
concentrations of CuSO 4.5H2O were measured experimentally in
absence and in presence of ligand at different temperatures. The
molar conductance (Λm) values were calculated. The experimental
data of ( Λm) were analyzed for the determination of formation
constants for each type of the stoichiometric complexes. The
formation constants (Kf) for CuSO 4.5H2O complex were calculated
for each type of complexes (1:2) and (1:1) (M: L) [12]. The obtained
values of log (Kf) for the metal-ligand stoichiometric complexes
are presented in for CuSO 4.5H2O in (MeOH-H 2O) mixture. The
relation between Ʌm and the [M]/[L] molar ratio for CuSO 4.5H2O in
presence of Nalbuphine HCl showed the inflections which indicate
the
formation of different complexes. Increasing temperature is
followed by decrease in log Kf favouring less solvation for interaction
of CuSO 4.5H2O with Nalbuphine HCl indicating migration of ions
away from the collecting area. The Gibbs free energies of formation
for 1:1 and 1:2 (M:L) stoichiometry complexes ( ΔGf°) were
calculated [13].
The enthalpy (ΔHf) for the metal salt complexes were calculated
for each type of complexes, (1:2) and (1:1) (M: L) by using van’t
Hoff equation: On plotting of log Kf versus 1/T different lines are
obtained for the formation of 1:2 and 1:1 (M: L) stoichiometric
complexes for CuSO 4.5H2O with Nalbuphine HCl. Formation
thermodynamic parameters ( ΔGf, ΔHf, T ΔSf, ΔSf) were calculated
Decreasing in ΔGf
° by increasing in temperatures indicating more
spontaneous process.
Conclusion
In the present work, an effective glassy carbon electrode has
been designed to sensing electrochemical behavior of Nalbuphine
opioid analgesic drug by the cyclic voltammetry technique as well
conductometric titration technique. Under optimized conditions
the cyclic voltammetry results such as the electro-active surface
coverage (Г), the transfer coefficient (α), standard rate constant (Ks)
and diffusion coefficient (D) were calculated. The obtained data give
good analytical performance including suitable precision, excellent
linear dynamic range and good detection and reproducibility. The
results were obtained for different concentration of NB in mixed
solvent (Methanol/ Water) with (30: 70 % V/V). We suggest that the
cyclic voltammetry technique can be used as a beneficial method to
be applicable in the pharmaceutical quality control laboratory and
other medical applications
for more information about Journal of Biosensors & Renewable sources archive page click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/biosensors-renewable-sources/archive.php
for more information about lupine publishers page click on below link
https://lupinepublishers.com/index.php
1 note
·
View note