#Modular Robotics previous data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Market Size of the Lab Automation Industry: A Comprehensive Overview

The Lab Automation Market size was estimated at USD 5.74 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 9.14 billion by 2031 with a growing CAGR of 6.19% during the forecast period of 2024-2031.The lab automation market is a dynamic ecosystem driven by technological advancements and increasing demands for efficiency in scientific research and diagnostics. As laboratories worldwide embrace automation, the landscape is evolving rapidly, integrating robotics, AI-driven analytics, and sophisticated software solutions. This convergence not only streamlines workflows but also enhances precision and reproducibility, crucial for modern scientific endeavors. From pharmaceuticals to biotechnology and clinical diagnostics, the adoption of automated systems promises to revolutionize how experiments are conducted and results interpreted. As the market expands, fueled by innovations in miniaturization and integration, the future holds exciting prospects for accelerating scientific discovery and improving healthcare outcomes through seamless automation solutions.
The Lab Automation Market research provides forecasts for the next several years as well as an assessment of the market's current revenue growth. These market forecasts were developed by examining the impact of a variety of social, political, and economic factors, as well as existing market dynamics, on market growth. The market study provides an overview of past year's revenue growth as well as forecasts for the following years.
Get Sample Of This Report @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3718
Segmentation View
By Process
Continuous Flow
By Workflow
Sequential Processing
Parallel Processing
By Components
Consumables
Equipment
Discrete Processing
By Method
Centrifugal Discrete Processing
Random Access Discrete Processing
By Components
Consumables
Equipment
By Workflow
Dependent Analysis
Independent Analysis
By Automation Type
Total Automation Systems
By Steps
Pre-analysis
Centrifugation
Sample Preparation
Sample Sorting
Transport Mechanisms
Liquid Handling
Sample Storage
Sample Analysis
Modular Automation Systems
By Steps
Specimen Acquisition & Identification & Labelling
Transport Mechanisms
Sample Preparation
Sample Loading & Aspiration
Reagent Handling & Storage
Sample Analysis & Measurements
By End User
Photometry & Fluorometry
Immunoassay Analysis
Electrolyte Analysis
Clinical Chemistry Analysis
Other end-user
Research Methodology
Primary research entails conducting telephonic interviews with various industry experts, questionnaires via email, and in some cases face-to-face interactions after accepting an appointment for conducting telephonic interviews, questionnaires via email, and in some cases face-to-face interactions for a more detailed and unbiased review of the global Lab Automation Market across various geographies. Primary interviews with industry professionals are frequently conducted to gain current market understandings and validate previous data analysis.
Primary interviews, among other things, give vital information about market trends, market size, competitive landscape, growth trends, and prognosis. These criteria aid in the validity and consistency of secondary research findings, as well as the development of market expertise among the analytic team.
Competitive Outlook
Over the preceding five years, the competitive landscape includes the market rankings of the top competitors, as well as new service/product launches, collaborations, corporate expansions, and acquisitions by companies featured in the Lab Automation Market study. The leading market players are profiled in detail, with an overview, insights, product benchmarking, and SWOT analysis. The industry's current and future market prospects, including development possibilities and drivers, as well as difficulties and restraints in both emerging and developed markets, are discussed in light of recent changes.
Reasons to Buy the Lab Automation Market Report
This study provides a precise forecast of each segment's contribution to the growth of the Lab Automation Market , as well as actionable market insights into COVID-19's impact on each segment. An examination of the factors that will drive market growth in the coming years. This provides the report with a unique perspective and overview of the research's global aspects, supporting with accurate and appropriate decision-making. Our strategic insights are developed to provide dependable and practical answers to the needs of market participants.
About Us
SNS Insider is a market research and insights firm that has won several awards and earned a solid reputation for service and strategy. We are a strategic partner who can assist you in reframing issues and generating answers to the trickiest business difficulties. For greater consumer insight and client experiences, we leverage the power of experience and people.
When you employ our services, you will collaborate with qualified and experienced staff. We believe it is crucial to collaborate with our clients to ensure that each project is customized to meet their demands. Nobody knows your customers or community better than you do. Therefore, our team needs to ask the correct questions that appeal to your audience in order to collect the best information.
Related Reports
Patient Portal Market Analysis
Plasma Therapy Market Analysis
Preeclampsia Diagnostics Market Analysis
Serum free Media Market Analysis
Glaucoma Therapeutics Market Analysis
0 notes
Text
Neuralink Rival Sets Brain-Chip Record With 4,096 Electrodes On Human Brain! Precision Expects Its Minimally Invasive Brain Implant To Hit The Market Next Year.
Brain-computer interface company Precision Neuroscience says that it has set a new world record for the number of neuron-tapping electrodes placed on a living human's brain—4,096, surpassing the previous record of 2,048 set last year, according to an announcement from the company on Tuesday.
— Beth Mole | May 28th, 2024
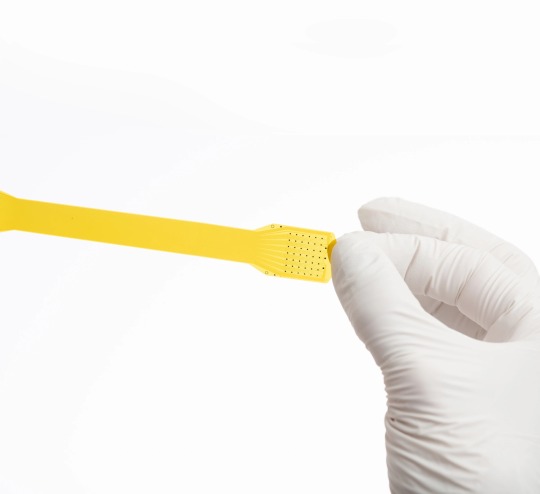
Each of Precision's microelectrode arrays comprises 1,024 electrodes ranging in diameter from 50 to 380 microns, connected to a customized hardware interface.
The high density of electrodes allows neuroscientists to map the activity of neurons at unprecedented resolution, which will ultimately help them to better decode thoughts into intended actions.
Precision, like many of its rivals, has the preliminary goal of using its brain-computer interface (BCI) to restore speech and movement in patients, particularly those who have suffered a stroke or spinal cord injury. But Precision stands out from its competitors due to a notable split from one of the most high-profile BCI companies, Neuralink, owned by controversial billionaire Elon Musk.
Precision was co-founded by neurosurgeon and engineer Ben Rapoport, who was also a co-founder of Neuralink back in 2016. Rapoport later left the company and, in 2021, started rival Precision with three colleagues, two of whom had also been involved with Neuralink.
In a May 3 episode of The Wall Street Journal podcast "The Future of Everything," Rapoport suggested he left Neuralink over safety concerns for the company's more invasive BCI implants.
To move neural interfaces from the world of science to the world of medicine, "safety is paramount," Rapoport said. "For a medical device, safety often implies minimal invasiveness," he added. Rapoport noted that in the early days of BCI development—including the use of the Utah Array—"there was this notion that in order to extract information-rich data from the brain, one needed to penetrate the brain with tiny little needlelike electrodes," he said. "And those have the drawback of doing some amount of brain damage when they're inserted into the brain. I felt that it was possible to extract information-rich data from the brain without damaging the brain." Precision was formed with that philosophy in mind—minimal invasiveness, scalability, and safety, he said.
Neuralink's current BCI device contains 1,024 electrodes across 64 thinner-than-hair wires that are implanted into the brain by a surgical robot. In the first patient to receive an implant, the wires were inserted 3 millimeters to 5 mm into the brain tissue. But, 85 percent of those wires retracted from the patient's brain in the weeks after the surgery, and some of the electrodes were shut off due to the displacement. Neuralink is reportedly planning to implant the wires deeper—8 mm—in its second patient. The Food and Drug Administration has reportedly given the green light for that surgery. The Utah Array, meanwhile, can penetrate up to 1.5 mm into the brain.
Precision's device does not penetrate the brain at all, but sits on top of the brain. The device contains at least one yellow film, said to be a fifth the thickness of a human hair, that contains 1,024 electrodes embedded in a lattice pattern. The device is modular, allowing for multiple films to be added to each device. The films can be slipped onto the brain in a minimally invasive surgery that requires cutting only a thin slit in the skull, which the yellow ribbon-like device can slide through, according to Precision. The film then conforms to the surface of the brain. The processing unit that collects data from the electrodes is designed to sit between the skull and the scalp. If the implant needs to be removed, the film is designed to slide off the brain without causing damage.
In April, a neurosurgery team from the Mount Sinai Health System placed one of Precision's devices containing four electrode-containing films—totaling 4,096 electrodes—onto the brain of a patient who was having surgery to remove a benign brain tumor. While the patient was asleep with their skull opened, Precision researchers used their four electrode arrays to successfully record detailed neuronal activity from an area of approximately 8 square centimeters of the brain.
"This record is a significant step towards a new era," Rapoport said in a press release Tuesday. "The ability to capture cortical information of this magnitude and scale could allow us to understand the brain in a much deeper way."
The test of the implant marks the 14th time Precision has placed its device on a human brain, according to CNBC, which was present for the surgery in New York. Precision says that it expects to have its first device on the commercial market in 2025.
#ARS Technica#Step Forward#Neuralink#Brain 🧠-Chip#Electrodes | Human Brain 🧠#Minimally Invasive#Brain 🧠 | Implant#Brain-Computer | Interface Company | Precision Neuroscience
0 notes
Text

Lockheed invests $100 million in its loyal wingman Speed Racer project
Fernando Valduga By Fernando Valduga 09/18/2022 - 11:00 in Military
Lockheed Martin revealed more details about the Speed Racer: a project to create a multifunction drone tailored to accompany the F-35 Lightning II fighter. The investment, within the Carrera project of US$ 100 million in distributed teams, is evolving in manned and unmanned operations
From autonomous cars to useful robotic assistants, the man-machine team is a powerful duo that can help make life safer and more productive. Now expand this dynamic to a team of several autonomous systems distributed in partnership with piloted aircraft. Pilots need an improved survival capacity and an information advantage to make more effective decisions that ensure that our forces stay ahead of emerging threats in today's highly contested and non-licensive airspace.
youtube
With this thought, Lockheed is investing $100 million in distributed clustering technologies to not only provide these resources today, but also to update them with short, medium and long-term improvements.
Collaboration between man and machine is not a new concept; however, Lockheed is aligning this concept with today's complex battle space, turning it into something comprehensive: distributed team building. With distributed grouping, pilots can extend the range of networked sensors, increase the survival capacity of piloted platforms and allow the collection, fusion and distribution of data that inform their decisions and achieve tactical execution. According to the manufacturer, this is what is needed now, and this is what the company is doing with the Carrera Project.

Project Carrera is Lockheed Martin's $100 million investment in clustering technologies to enable a future view of distributed clustering in support of USAF's All Domain Joint Operations vision. Project Carrera brings almost a decade of Lockheed Martin's experience in distributed architecture efforts and will leverage investments and advanced technologies from across the company and customer communities to fully explore what the ideal 5th generation distributed teams can be like.

Lockheed's $100 million investment in the Carrera Project is divided into three areas:
$20 million for F-35 upgrades and for the development of unmanned assets
$42 million for "team enablers" that include AI development, network-enabled poles, advanced waveforms such as 5G and open architecture technology
$38 million for "Battle Space Multipliers", an interesting pot of money that includes low-Earth orbit satellites that will provide communications beyond the line of sight between the fighter and drones, as well as "advanced survival platforms" that may include a sensor"
The core of the approach is the partnership of manned survival platforms, such as the F-35, with modular and affordable unmanned assets, such as the SPEED RACER. The Carrera Project will incorporate demonstrations in phases of capacity updates in operational scenarios, incrementally introducing the stack and experimentation of JADO technology, digital engineering, man-machine interfaces capable of autonomy and artificial intelligence (AI) and much more.
youtube
As the Carrera Project proves the optimal air combat collaboration, its demonstrations will incorporate 21st century security solutions. In today's networked battle space, connected systems need to share data between platforms with different data links and security environments.
That's why Lockheed is using open architectures to allow the fast and affordable integration of new features for the combatant on the tactical edge. As a result, current and future systems in operation will be able to share information for a comprehensive view of battle space, allowing pilots to make better decisions and faster.
Tags: Military AviationDronesF-35 Lightning IILockheed MartinLoyal WingmanCarrera Project
Previous news
Walt Disney's Grumman Gulfstream I aircraft goes to a museum in California
Next news
VIDEO: RAAF discloses 360o view of the F/A-18F jet flying in the middle of buildings during the Riverfire test
Fernando Valduga
Fernando Valduga
Aviation photographer and pilot since 1992, he has participated in several events and air operations, such as Cruzex, AirVenture, Dayton Airshow and FIDAE. It has works published in specialized aviation magazines in Brazil and abroad. He uses Canon equipment during his photographic work in the world of aviation.
Related news
MILITARY
Russian invasion of Ukraine shows 'airpower value', says head of USAF
09/18/2022 - 16:00
AIR SHOWS
VIDEO: RAAF discloses 360o view of the F/A-18F jet flying in the middle of buildings during the Riverfire test
09/18/2022 - 14:52
MILITARY
Chinese high-altitude surveillance drone WZ-7 is seen near Taiwan for the first time
09/17/2022 - 18:04
Khibiny-U EW Complex installed on the Su-30SM jet (Photo: topcor.ru)
MILITARY
Ukrainians seize ultra-secret Russian electronic warfare system mounted on Su-30SM aircraft
09/17/2022 - 16:00
U.S. Marines with the Marine Heavy Helicopter Squadron (HMH) 461 carry a cargo container with a CH-53K King Stallion at Mountain Home Air Base, Idaho, August 11, 2022. (Photo: U.S. Marine Corps / Cpl. Adam Henke)
HELICOPTERS
USMC deploys the CH-53K King Stallion in an exercise for the first time
09/17/2022 - 14:00
U.S. Air Force Lieutenant Colonel Daniel Griffin, A-10C Thunderbolt II pilot assigned to the 104th Fighter Squadron, Maryland National Air Guard, with a Brazilian Air Force pilot during Exercise Tapio in Campo Grande, Brazil, August 24, 2022.
BRAZILIAN AIR FORCE
USAF A-10 pilots train FAB pilots in the Tápio Exercise
09/17/2022 - 12:00
homeMain PageEditorialsINFORMATIONeventsCooperateSpecialitiesadvertiseabout
Cavok Brazil - Digital Tchê Web Creation
Commercial
Executive
Helicopters
HISTORY
Military
Brazilian Air Force
Space
Specialities
Cavok Brazil - Digital Tchê Web Creation
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gaps & Difficulties faced by Investment Banks today
As discussed in one of my previous blogs, Investment Banking could be a really lucrative career option if one’s willing to put in the time and effort required. It would be beneficial to know the major challenges faced by the industry today, so let’s begin by understanding the challenges faced by the Investment Banking industry in the post-pandemic world.
Like all other financial sectors, IB is currently going through some threatening and transformative changes. Companies operating in IB secrets are facing difficulties regaining their pre-pandemic levels. The coronavirus pandemic has compelled these companies to restructure their strategies. Increased uncertainty regarding public health, economic, and societal impacts of the pandemic has intensified the forces that create challenges and accelerates disruption in the industry.
Some of the most challenging issues include- volatile equity prices, liquidity stress, evolving financial regulations, market democratization, pricing pressure, increased client sophistication, shifts to remote working arrangements, and rapid technology advances. In order to overcome these hurdles, IBs are required to be more diverse, all-inclusive, dynamic, creative, globally networked, and client-focused with well-defined regulators. Let’s discuss, in detail, three major hurdles faced by IBs today:
1. Cybersecurity- I cannot stress this enough, the ever changing threat landscape has made it very difficult for the financial sector to determine the levels of cybersecurity. Protecting the valuable and sensitive financial data of their clients (Corporations, MNCs, etc) is always a top priority for the IB industry. Cyber threats are at their peak and traditional technologies have become a risk factor. Introducing more modular solutions can contribute to coping with security threats as compared to the rigid traditional methods. If the hackers are evolving, then why shouldn't we?
2. Containing Costs- The prices of goods are services are getting lower, leading to lower margins. The only way to cope up is to reduce costs, including but not limited to transaction costs, regulatory costs, and legal fees. The cost income ratios are out of control and some major restructuring has to be done. One way to do is to keep a balance between optimizing the current core activities via ensuring robotic processes & digitization while investing in new services.
3. FinTech- This topic is so vast that it would require it’s own series of blogs to be understood properly. Basically, as the name suggests, FinTech stands for Financial Technologies. This sector is growing rapidly, providing the same banking services at a much cheaper scale. But how does it affect Investment Banking, an industry associated with helping corporations grow? Modern FinTech companies are more efficient at raising capital than IBs, making investment banking & the rest of other sectors considering innovative technology and flexibility to boost their reliability among clients. Of course we don't want to lose clients to these new FinTech oriented companies.
As a result of these and many more hurdles, Investment Banks are moving away from their traditional underwriting services and focusing on diversifying their set of services provided, including Mergers & Acquisitions, selling securitized products, hedging, and advisory to MNCs.
~Lakshya Kapoor
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Makers: ARCTIC LiDAR Video Installation

The Makers is a series that highlights students and faculty from ACSA member schools to show the unique work coming out of architecture schools across the globe. Check out more on the blog by searching “The Makers.” Project: ARCTIC LiDAR Lead Architects: Daniele Profeta with Maya Alam Office: A/P Practice Client: Syracuse University Design Team: Zexi Tang and Erick Sanchez Collaborator: Liam Young with the New Normal program of STRELKA Institute for Media, Architecture, and Design Graphic Design: Common Name ARCTIC LiDAR is an immersive 360° Video Installation exploring the quickly expanding logistic landscape of the Arctic coast. ARCTIC LiDAR_ACC Festival from A/P Practice on Vimeo. Logistics can be defined as the detailed coordination of the complex space constituted by infrastructures, information, goods, and people that make the production and circulation of stuff possible. Stretching across nation-state borders, redefining territoriality through the cartographic space of global supply chains and constructing an operational state of unencumbered continuous movement of goods, the space of logistics is dramatically transforming the world we inhabit. Part documentary, part projective narrative, the video presented in this installation articulates projective scenarios for the expanding logistics space of global commerce along the coast of the Arctic. Using 3-D LiDAR scanning, this project captures the primary nodes of this far-reaching infrastructure, ranging from Dry Ports to Ice Breakers and Rail Terminals, and re-assembles them in a composite, speculative landscape. LiDAR, an acronym for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses light pulses to measure and three-dimensionally map vast territories with ever-increasing precision. A sensor emitting pulses of infrared light, millions of times per second, constructs point-clouds as a representation of the environment being surveyed: a spatial database so detailed that can be used to detect and interact with surrounding objects: across the territory of the Arctic, it is used to establish politics, protocols, and economies of autonomous distribution. It is through the lens of the apparatus of machinic vision and its network of activations that we can begin to see the traces of this emerging urbanism of logistics across the territory.

Photograph of the installation exhibited at the Smithsonian Institution Museum of American History during the 2019 ACCelerate Festival showing the relationship between VR headset experience and the physical installation.

Photograph of the installation exhibited at the Smithsonian Institution Museum of American History during the 2019 ACCelerate Festival showing the relationship between VR headset experience and the physical installation. Using a Virtual Reality headset, the viewers are transported in the automated landscape of logistics, where driverless trucks, robotic cranes and remote-sensing drones operate through the dense point cloud. Immersed in a 360° video moving across this speculative landscape, this operative mode of vision is slowly contaminated by atmospheric elements foreign to the machinic eye, prompting the viewer to develop an intimate engagement with the material. The viewers are caught in an ambiguous territory where a bodily experience of this harsh landscape and its extreme climate re-asserts its presence in an otherwise human-less environment. And yet, their point of view is constrained to the rigid linear movement of what appears to be indifferent machines, reinforcing the agency of the automated infrastructure upon the construction of this territory.

A drawing showing the overall setup of the installation. The (x5) panels, milled out of high-density foam, are held up by a metal frame, displaying additional information on its back. PreviousNext





Overall photographs of the back-side of the freestanding panels showing the graphics utilized as a communication device to the general public.

Serial image of the different nodes of the logistics infrastructure highlighted in this project. From top left to bottom right, the LiDAR scans depict Dry Port Container Harbor, Ice Breaker Dock, Custom Clearance, Railway Terminal, Unloading Dock, Residential units for locals and the overall speculative landscape reconstructed.

Aerial view of the composite landscape constructed from the different LiDAR Scans. The modularity of these nodes reinforces the continuity of this infrastructure across a planetary scale.

Still from the 360o video displayed in the installation: here the scene shows the Dry Port Container Harbor area. The initial Scan data is infiltrated by atmospheric elements (in this case snow and lighting fog) to further reinforce a bodily experience of these sites.





Similarly, the physical space of the installation engages with the three-dimensional database of LiDAR vision by sampling a series of spatial elements surveyed on these sites to construct a space of engagement across multiple mediated realities. The digital trace of the surfaces of cargo containers, one of the artifacts that most dramatically transformed this network of logistics, gantry cranes, ice-breaker navigation control panels and train wagons are translated into relief panels to extend and confront the content presented through the VR headset. Rather than focusing on the re-production of accurate digital copies, these artifacts attempt to highlight the tension between their material surfaces and the machinic vision that surveyed them by juxtaposing their true ‘RGB’, Red, Green and Blue color information, with the ‘XYZ’ data, a so-called ‘normal map’ visualizing the directionality of each of the points surveyed. Each panel is CNC milled out of high-density foam and is then printed with this edited texture layer. Ultimately the installation urges the viewers to understand the architecture of logistics beyond a ‘technicality’, a politically neutral act of management, but rather predicates itself around ideas of anticipation and prediction, acting as a transforming agent of the built environment, of territories as well as of bodies.

Still from the constructed digital scene showing the Control Room area of the Ice Breaker. The dense point cloud here reads as a continuous image representing the interior of this space. Videos ARCTIC LiDAR _ ExhibitionVideo from A/P Practice on Vimeo. Arctic LiDAR_Embedded View from A/P Practice on Vimeo. Learn more about Syracuse University’s Architecture Program. The post The Makers: ARCTIC LiDAR Video Installation appeared first on Study Architecture | Architecture Schools and Student Information. Source link Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
#Modular Robotics previous data#Modular Robotics forecast#Modular Robotics vendors#Modular Robotics analysis#Modular Robotics market trends#Modular Robotics market size#Modular Robotics market share#Modular Robotics market#Global Modular Robotics market#Modular Robotics
0 notes
Text
Industry 4.0 Trends and Smart Factories

Industry 4.0 Trends and Smart Factories
Modern industrial developments have continued for several hundred years, and three major industrial revolutions have emerged until today. Currently, we are in the fourth industrial revolution as Industry 4.0 trends and smart factories. In the first industrial revolution (1.0), industry was turning water to steam power. The second industrial revolution (2.0) occurred 30 years later when the first mass-production assembly line working by electricity was functional. In the late 1960s, the first programmable logistic controller (PLC) allowed factory automation via the use of electrical and IT systems, marking the beginning of the third industrial revolution (3.0). Industry 4.0 refers to the simultaneous maturation of many important technological advancements that may drastically alter the manufacturing industry's environment. As these technologies — advanced robots, artificial intelligence, sophisticated sensors, cloud computing, and big data analytics – connect with one another, the real and virtual worlds will merge and revolutionize the industrial business. It takes over production with robots that communicate with each other, detect the environment with sensors, and realize the needs by analyzing data and aims to produce better quality, cheaper, faster, and less wasteful production. In addition, it monitors physical processes with cyber-physical systems in modular smart factories, allowing objects to communicate with each other and people, and as a result, decentralized collaborative decisions are made.

From the first industrial revolution to the fourth industrial revolution: The world continues to develop with four revolutions in industry.And we know that in the transitions between these revolutions, innovations have taken their place along with previous technologies. The important milestones that emerged in the four industrial revolutions of the world, namely Industry 1.0 to 4.0, are explained below. - Application of Mechanical Production Facilities - Transition to Mass Production Based on Electricity and Division of Labor - Automation of Production Processes - Autonomous Machines and Virtual Environments The elements that started in 2000 are the triggers and infrastructure of Industry 4.0. In other words, they are the components of today's smart factories. Thus, companies now needed interdisciplinary work and the fourth industrial revolution. So that all objects communicate and interact over the internet, has emerged. Smart factories are the non-digital component of Industry 4.0 and are concretely visible and observable parts of society. Potentials of Industry 4.0 : Objectives of Industry 4.0 are to provide mass customization of products produced by information technologies, to ensure automatic and flexible adaptation of the production chain, to monitor parts and products, to facilitate communication between parts, products, and machines, to implement human-machine interaction (HMI) paradigms, to optimize production with the internet of things in smart factories, and in terms of value, it can be listed as offering new types of services and business models. Despite the growing complexity of the Industry 4.0 system, it also has the potential outlined below. - Increasing competition and flexibility arising from the dynamic nature of business processes (quality, time, risk, robustness, price, and environmental friendliness), - Eliminating malfunctions in the demand chain, - Optimizing decision making with real-time end-to-end visibility - Provide increased resource productivity(it produces the highest output from a given volume of resources). And efficiency (uses the lowest possible amount of resources to achieve a given output), - Creating value opportunities (innovative services, new forms of employment, development opportunities for SMEs and start-ups), - Reducing energy and personal costs. Industry 4.0 Trends : Industry 4.0 encompasses numerous technologies and associated paradigms. Some of these emerging paradigms are Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Enterprise Resource Planning, Internet of Things ( IoT ), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), 3D printing, Cyber-Physical Systems, cloud-based manufacturing, smart factory, smart product, big data, etc. These features are not only highly correlated with internet technologies and advanced algorithms. But also indicate that it is a value-added information processing and industrial value-added process. In Industry 4.0, one of the important places where objects communicate with each other is the smart factories. They are equipped with intelligent technologies and are also called dark factories because there are no people to work with. The number of workers in China's first dark factory. And it produces mobile phone modules, decreased by 90%, while the rate of defective product formation dropped from 25% to 5%.

The impact of smart factories on this revolution: Among the factors that triggered this revolution, and at the very center of the revolution that created the transformation in the manufacturing industry, are smart technologies and smart factories. This revolution, of course, affects and changes all service sectors and infrastructures, along with manufacturing. Smart Factories of Industry 4.0 include smart machines and systems that detect business needs with sensors, communicate with other remote production tools via the internet. Then extract the production information they need from Big Data in cloud systems. The communication and interaction of the means of production with each other are provided via the internet. All production resources (sensors, actuators, machines, robots, conveyors, etc.) do not only automatically exchange information, but also be conscious and smart enough to predict and maintain machines to control the production process and manage the factory system. In addition, many production processes such as product design, production planning, production engineering, production, and services can work modularly. Summary Industry 4.0 currently has a significant impact on the manufacturing industry and this impact will continue exponentially in the future. And many smart factories working with minimal people have already started production. It will enable us to achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency. And also allow us to accelerate our productivity by introducing new types of advanced manufacturing and industrial processes toward machine-human collaboration and symbiotic product realization in the future. In other words, the new level with digital transformation and Industry 4.0 will ensure that people, objects, and systems come with interconnection. Therefore, companies that want to increase their competitiveness in the future should apply this revolution to their production organizations. So that they should apply technologies such as smart robots, cyber-physical systems, and cloud-based manufacturing in their factories. Read the full article
0 notes
Photo

Illustration Photo: Measured carbon dioxide concentrations in Vancouver, Canada (credits: UBC Micrometeorology / Background Data: Google / Flickr Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0))
AI, Data and Robotics for the Green Deal
For European Union, Albania, Armenia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Faroe Islands, Georgia, Iceland, Israel, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia, Switzerland, Tunisia, Turkey, Ukraine
Proposals are expected to integrate and optimise AI, data and robotics solutions in order to demonstrate, by addressing use-cases scenarios in actual or highly realistic operating environments, how they can directly contribute to the Green Deal. The proposed methodology should be supported by industry or service relevant KPIs, making the case for the added value of such technologies, and demonstrating scalability, and deployment potential. Technology performance as well as added value to the application field should be demonstrated by qualitative and quantitative KPIs, demonstrators, benchmarking and progress monitoring. The environmental impacts of the proposed solutions should also be taken into account when making the case for the added value of the technology for the environment.
While the proposals must be application driven, involving problem owners to define needs and validate the proposed solutions, the focus is on optimising enabling AI, data and robotics technologies to maximise the benefit they bring in such applications. Proposals should adopt a concrete problem solving approach, exploiting and optimising the most suitable technologies and solutions at hand. The focus should be on real-world scenarios, which can benefit in short to mid-term from the technology and solutions and demonstrate substantial impact on the Green Deal, while taking into account the maturity of the technologies to solve the problems at hand.
Deep involvement of all relevant stakeholders (including SMEs), from technology providers to user industry, social partners, and relevant experts in operational and environmental impact assessment, will be essential. Special attention will be given to including users of diverse age, gender and background.
All proposals should incorporate training programs for non-expert users of AI, data and robotics systems, who are domain experts and need to know basic AI, data, robotics concepts, including the basics concepts of Trustworthy and ethical AI.
To reach their objectives, all proposals are expected to exploit synergies between at least two of the three components: AI, Data and Robotics and forge strong cooperation between to corresponding practitioners.
Proposals can involve either robotics-only solutions (for instance demonstrating robotics solutions in harsh environments), or a mix of robotics and non-robotics components (for instance in applications such as waste management, where a combination of robotics for waste segregation and data and sensor driven AI for process optimisation) or only include non-robotics AI and Data (for instance in energy optimisation, from production sites, through the network, and then end-user sites, with IoT components). All selected proposals are expected to include demonstrators at TRL 6 or above. At least half of the selected proposals will have to have a major robotics demonstrator; therefore, proposals should clearly specify their robotics demonstrator, if they chose to have one.
Proposals should clearly identify the expected outcome it will focus on.
Two types of proposals are expected:
Focused projects (EU contribution around EUR 3.00 million), involving the user industry and technology provider(s), Larger projects (EU contribution around EUR 5.00 million), where a number of companies in a given application sector will identify in the proposal common challenges and use-cases, and organise competitive calls for AI, data and robotics solution providers to address such challenges. Competitive calls will be open to all types of companies, but only SMEs and Start-ups[1] will receive financial support to third parties, with a maximum of EUR 200 000 per third party[2] and 70% funding (100% for start-ups). At least 40% of the requested amount should be dedicated to financial support to third parties. The consortium will provide technical support with expertise in engineering integration, testing and validation to support the selected SMEs and start-ups acting as technology providers to demonstrate the added value of their solutions to address the challenges of the use-cases. Maximum one type of third party project will be funded per expected outcome[3].
In all proposals, user industries are expected to play a major role in the requirement and validation phases.
Besides financial support, these SMEs and start-ups successfully demonstrating the potential of their solutions, must receive support from business experts, provided by the action, to further develop their business and develop their market reach, and maximise their business opportunities.
When possible, proposals should build on and reuse public results from relevant previous funded actions. Proposals should make use of connections to the Digital Innovation Hub networks, particularly those in Robotics, Data and AI. Full use should be made of the common resources available in the AI-on-Demand platform[4], Digital Industrial Platform for Robotics[5], data platforms[6] and, if necessary other relevant digital resource platforms. Communicable results from selected proposals should be delivered to the most relevant of these platforms in order to enhance the European AI, Data and Robotics ecosystem through the sharing of results and best practice.
If proposals use satellite-based earth observation, positioning, navigation and/or related timing services and data, they have to prioritise Copernicus and/or Galileo/EGNOS over equivalent competing solutions offering the same services/data.
All proposals are expected to allocate tasks to cohesion activities with the co-programmed partnership on AI, Data and Robotics and funded actions related to this partnership, including the CSA HORIZON-CL4-2021-HUMAN-01-02. Where relevant, synergies with other European partnerships and Horizon Europe Clusters (Cluster 4 and Cluster 6 in particular) are encouraged.
This topic implements the co-programmed European Partnership on Artificial Intelligence, Data and Robotics.
Specific Topic Conditions: Activities are expected to start at TRL 3-5 and achieve TRL 6-7 by the end of the project – see General Annex B.
Expected Outcome: Proposal results are expected to contribute to at least one of the following expected outcomes:
Innovative AI, data and robotics solutions for resource optimisation and minimisation of waste in any type of sector (from agri-food, to energy, utilities, transport, production, etc.), reduction of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions including exploitation of all data and information sources contributing to optimising applications for a greener planet. This includes among others contribution to enterprises’ sustainability programs in the context of their CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) strategies to reduce their ecological footprint, cutting costs and contributing to social welfare at the same time Optimised AI, data and robotics (including modular and adaptive solutions) to maximise contribution to the Green Deal in various applications such as environmental and waste management, including for instance waste clean-up (e.g. plastic collection, sorting), or in the circular economy value chain. Advanced physical intelligence and physical performance of robotics solutions in diverse harsh environments serving the Green Deal.
[1]In this context a start-up is a tech-oriented company. It should employ less than 10 people (but more than 2 full time equivalent staff) that has operated for less than three years and has attracted more than EUR €50 000 early stage private sector investment or has demonstrable sales growth over 50% pa – they will receive 100% financial support to third parties while other SMEs would receive 70% financial support. Startups would be expected to highlight the impact that the project will have on their overall Company strategy and growth prospects in the Impact section of their proposals (as well as the impact on society and European competitiveness.
[2]Maximum amount per third party, received from a given action, over its entire duration
[3]The 3 expected outcomes are : 1. Resource optimisation and minimisation of waste, energy or greenhouse gas emissions, 2. Environmental and waste management in the circular economy, 3. Robotics solutions in harsh environments serving the Green Deal
[4]Initiated under the AI4EU project https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/825619 and further developed in projects resulting from H2020-ICT-49-2020 call
[5]https://robmosys.eu/newsrobmosys-rosin-towards-an-eu-digital-industrial-platform-for-robotics/
[6]E.g.: https://www.big-data-europe.eu/
Application Deadline: 21 October 2021 17:00:00 Brussels time
Check more https://adalidda.com/posts/oBj2CrCEGXjytTanr/ai-data-and-robotics-for-the-green-deal
0 notes
Text
How to find the right warehouse? An in-depth guide
An In-Depth Guide On Choosing A Warehouse In India. An Industry Perspective.
Picking an optimal stockroom is a vital advance in the development and extension plans for some organizations. Motivation behind why it's anything but a top to bottom examination and an itemized comprehension of the industry just as the choices accessible. However, before we dive into the subtleties of how to pick the right stockroom, let us comprehend the difficulties confronted and openings offered by the Indian warehousing Industry to the two tenants and financial backers. You will likewise accumulate bits of knowledge identified with top areas for putting resources into this space and the ones which are projected to fill later on.
This piece will investigate how geographic perspectives profit or be adverse to organizations, how various areas deliberately focus on the spot, and what are a portion of the area based difficulties which India faces. We will likewise address the distinction in rentals between Grade-An and Grade-B stockrooms.
To guarantee that we bring you concrete, believable and significant data, this article has been prepared with information which has been extricated from trustworthy assets. Towards the end, you will likewise realize what IndoSpace as one of the innovators in the industry brings to the table, and how we supplement the change of the warehousing industry in India with future-driven contributions and approach.
Warehousing and Logistics – A Wider Perspective
The assembling and web based business enterprises have filled dramatically in the previous 5 years and the coordinations and warehousing area has kept up to turn into a fundamental connection in associating these organizations to their buyers.
Not just has the idea of the business advanced, the application and incorporation of innovation in the warehousing and coordinations area is likewise effectively changing; and there is tremendous potential for development in the years to come.
While the coordinations area in India has consistently stayed promising, measures like GST and the Logistics Parks Policy achieved by the Central Government has genuinely changed the game lately, causing it to seem like the ideal time for the industry to thrive. The warehousing area in India is drawing extraordinary premium from financial backers who will put long haul capital in this resource class.
Likewise? There is more prominent force in the improvement of Grade-A mechanical and coordinations stops because of interest from distribution center occupiers who are progressively picking elite consistent offices which are better overseen and work with functional efficiencies.
The warehousing area in India has likewise seen a huge interest from huge internet business and FMCG organizations, and the transitory merchandise area during and after the COVID-19 lockdown period, as these organizations need to keep their stock in closeness to significant utilization communities.
IndoSpace, as India's head engineer of mechanical and coordinations land, is outfitted to fulfill the rising need of the industry with a tremendous organization of 36 Grade-A parks present the nation over.
India is Betting Big on Warehousing
As indicated by a Knight Frank 2020 report, warehousing exchanges saw a three-crease expansion over the most recent a long time from 14 mn. square feet in 2017 to 46 million square feet starting at 2019. A Research and Markets report from September 2020, likewise expresses that the Indian Warehousing Market is required to develop from USD 12.2 billion of every 2020 to an expected USD 19.5 billion by 2025. Till 10 years back, without an incorporated expense framework and restricted spotlight on robotization, there was minimal motivating force for organizations to accomplice enormous, coordinated coordinations land designers. Be that as it may, with the presentation of strategy changes and more prominent push on usefulness, supportability and consistence, coordinated warehousing has acquired foothold in India.
The development drivers of this industry are:
Huge and Growing Economy
India has supported its position as one of the quickest developing huge economies on the planet. It is required to break into the world's three biggest economies by the following decade.
Draft National Logistics Policy 2018
India as of now faces a major test on the grounds that the coordinations cost in India is a huge 13%-14% of GDP contrasted with a lot more modest figure of 8%-10% in its worldwide partners. As per Knight Frank's India Warehousing Market Report 2019, the Draft National Logistics Policy 2018 has been drafted with an engaged point of giving a lift to coordinated advancement of the coordinations area in the country. The industry is exceptionally disorderly in nature and has an extremely slanted multi-modular blend under which street adds up to practically 60% of the cargo development that happens. It is such various failures that this noteworthy strategy is embarked to handle. What's more, that as well, as fast as could be expected. The division of coordinations framed under the Ministry of Commerce will likewise fill in as a solitary organization for the incorporation of different groups of the coordinations esteem chain and make efficiencies.
Institutional Investments
What contributes enormously to new venture possibilities of the nation's distribution center property area is the execution of GST and the 'Make in India' push on assembling. The proceeded with government center around building modern passageways and the guarantee offered by the Indian utilization market further add esteem and contribute towards the development of this industry.
Institutional financial backers and designers have together put over USD 6.8 billion in the warehousing area since 2014, with a normal speculation for each arrangement of USD 282 million.
Post-COVID-19 Considerations
There's no uncertainty that the pandemic has changed buyers' buying designs. As individuals make a social shift from purchasing disconnected to shopping on the web, numerous web based business classifications are required to blast.
While different designers are attempting to corner the market, IndoSpace is India's biggest engineer of modern and warehousing parks offering 37.3 mn. sq. ft (3.47 mn. sq. m) dish India, of which 17.3 million square feet) has effectively been conveyed.
.
An In-Depth Guide On Choosing A Warehouse In India. An Industry Perspective.
Picking an optimal stockroom is a vital advance in the development and extension plans for some organizations. Motivation behind why it's anything but a top to bottom examination and an itemized comprehension of the industry just as the choices accessible. However, before we dive into the subtleties of how to pick the right stockroom, let us comprehend the difficulties confronted and openings offered by the Indian warehousing Industry to the two tenants and financial backers. You will likewise accumulate bits of knowledge identified with top areas for putting resources into this space and the ones which are projected to fill later on.
This piece will investigate how geographic perspectives profit or be adverse to organizations, how various areas deliberately focus on the spot, and what are a portion of the area based difficulties which India faces. We will likewise address the distinction in rentals between Grade-An and Grade-B stockrooms.
To guarantee that we bring you concrete, believable and significant data, this article has been prepared with information which has been extricated from trustworthy assets. Towards the end, you will likewise realize what IndoSpace as one of the innovators in the industry brings to the table, and how we supplement the change of the warehousing industry in India with future-driven contributions and approach.
Warehousing and Logistics – A Wider Perspective
The assembling and web based business enterprises have filled dramatically in the previous 5 years and the coordinations and warehousing area has kept up to turn into a fundamental connection in associating these organizations to their buyers.
Not just has the idea of the business advanced, the application and incorporation of innovation in the warehousing and coordinations area is likewise effectively changing; and there is tremendous potential for development in the years to come.
While the coordinations area in India has consistently stayed promising, measures like GST and the Logistics Parks Policy achieved by the Central Government has genuinely changed the game lately, causing it to seem like the ideal time for the industry to thrive. The warehousing area in India is drawing extraordinary premium from financial backers who will put long haul capital in this resource class.
Likewise? There is more prominent force in the improvement of Grade-A mechanical and coordinations stops because of interest from distribution center occupiers who are progressively picking elite consistent offices which are better overseen and work with functional efficiencies.
The warehousing area in India has likewise seen a huge interest from huge internet business and FMCG organizations, and the transitory merchandise area during and after the COVID-19 lockdown period, as these organizations need to keep their stock in closeness to significant utilization communities.
India is Betting Big on Warehousing
As indicated by a Knight Frank 2020 report, warehousing exchanges saw a three-crease expansion over the most recent a long time from 14 mn. square feet in 2017 to 46 million square feet starting at 2019. A Research and Markets report from September 2020, likewise expresses that the Indian Warehousing Market is required to develop from USD 12.2 billion of every 2020 to an expected USD 19.5 billion by 2025. Till 10 years back, without an incorporated expense framework and restricted spotlight on robotization, there was minimal motivating force for organizations to accomplice enormous, coordinated coordinations land designers. Be that as it may, with the presentation of strategy changes and more prominent push on usefulness, supportability and consistence, coordinated warehousing has acquired foothold in India.
The development drivers of this industry are:
Huge and Growing Economy
India has supported its position as one of the quickest developing huge economies on the planet. It is required to break into the world's three biggest economies by the following decade.
Draft National Logistics Policy 2018
India as of now faces a major test on the grounds that the coordinations cost in India is a huge 13%-14% of GDP contrasted with a lot more modest figure of 8%-10% in its worldwide partners. As per Knight Frank's India Warehousing Market Report 2019, the Draft National Logistics Policy 2018 has been drafted with an engaged point of giving a lift to coordinated advancement of the coordinations area in the country. The industry is exceptionally disorderly in nature and has an extremely slanted multi-modular blend under which street adds up to practically 60% of the cargo development that happens. It is such various failures that this noteworthy strategy is embarked to handle. What's more, that as well, as fast as could be expected. The division of coordinations framed under the Ministry of Commerce will likewise fill in as a solitary organization for the incorporation of different groups of the coordinations esteem chain and make efficiencies.
Institutional Investments
What contributes enormously to new venture possibilities of the nation's distribution center property area is the execution of GST and the 'Make in India' push on assembling. The proceeded with government center around building modern passageways and the guarantee offered by the Indian utilization market further add esteem and contribute towards the development of this industry.
Institutional financial backers and designers have together put over USD 6.8 billion in the warehousing area since 2014, with a normal speculation for each arrangement of USD 282 million.
Post-COVID-19 Considerations
There's no uncertainty that the pandemic has changed buyers' buying designs. As individuals make a social shift from purchasing disconnected to shopping on the web, numerous web based business classifications are required to blast.
.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the modular system

(The diagram above displays the drone patch)
Drone Patch
To receive an audio signal from both VCO's, it was essential to route the outputs to the mixer. Connecting the output of the mixer to the A input of the Rosie enabled me to route the audio signal to the mixing console. Using the send and return of the Rosie, enabled me to send the main output of the mixer to the reverb and blend it into the mix.
Connecting the Batumi low-frequency oscillator sine outputs to the FM and Timbre CV inputs of the Plaits VCO’s made it possible to modulate their pitch. Feeding the CV sine output of the Batumi to the Model gate input of a chosen VCO can modulate its time by cycling through two sound banks of eight models. (Mutable Instruments , User manual:1).
Modular live jam
In contrast to the previous session, where the Varigate 8+ was used to trigger a drum module by sending out gate information, the CV outputs were routed to the CV input of the 0-Coast to control the pitch.
The CV edit mode(indicated when the CV page button is red) of the ELOQUENCER offers an easy and quick way to change the notes by selecting individual steps for half a second and subsequently turning the DATA knob (Winter Modular, 2019:6).
Find the videos of the session in the link below:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=11cV1dk00vX2mED_IETOzEVc5u9F2Ki20
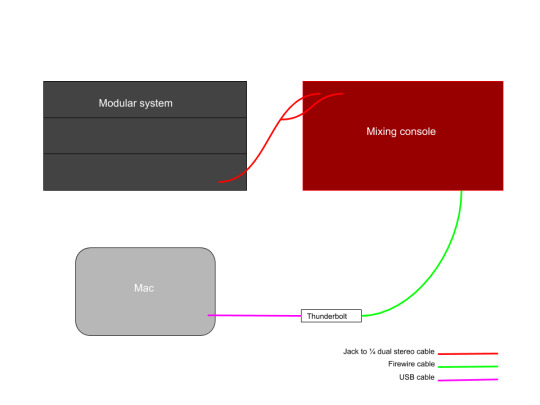
(Diagram of the audio routing setup)
Using the modular system inspired me to think about how music production could be approached differently in the future. Having knobs and buttons in front of me felt much more like playing a musical instrument. Physically shaping the music felt very tangible, which was much more exciting than working on a computer as some decisions resulted in happy accidents.
In an interview on YouTube, Techno Producer Headcell talks about his experience with modular hardware to produce his music (YouTube, 2017:1). It appears to be that other famous Techno producers, Like Benjamin Damage, also use indistinguishable production styles. This can be distinguished when listening to Len Faki - Robot Evolution (Benjamin Damage Live Remix) (YouTube , 2019:1).

(Picture of a more complex modular patch, demonstrating the progress from my previous setup)
Follow the link to hear a demo of me using the system in the picture above: https://drive.google.com/open?id=19n_Mw8pO21RnkjfHaX6t0nAvFySeXkj2
0 notes
Text
Han® 1A: Versatile lightweight
New range of rectangular plastic connectors – ideal for motors and smaller loads in machine engineering and automation.

The modular design of the Han® 1A offers maximum flexibility for the respective application.
India, November 27, 2019 --- The industrial sector is using ever smaller machines at the same time as the modularisation of plants and systems continues to progress. What is needed are compact, modular and robust connections for connecting small loads. HARTING is responding to this trend with the Han® 1A. The rectangular connector has a whole host of advantages: the connector is suitable for the transmission of data, signals and power, and provides an ideal solution for e.g. control systems, smaller drives and switch cabinet installations.
The housings, inserts and cable glands of the new series are made of high-performance plastic, which makes the connector a lightweight. The Han® 1A is smaller than all previous Han® solutions. In comparison to the Han® 3A – the smallest rectangular connector portfolio yet – the space requirement is reduced by about one third.
The modular design of the Han® 1A offers maximum flexibility for the respective application. Solutions for a wide variety of tasks can be developed from just a small number of elements. Power ratings up to 16 A / 400 V, signals with up to 12 contacts per insert, and data at a rate of 10 Gbps (Cat. 6A) can all be transmitted.
Depending on the customer's requirements, the new connector series offers the right solution. Users can thus decide between a classic metal clamp lock and a latched lock already integrated into the housing. There are also two options with regard to the connection technology: screw and crimp connection.
In addition, flexibility is enhanced by a wide range of useful accessories. Using e.g. cable glands or single-wire seals, within seconds the Han® 1A system can be transformed from an IP20 solution into an IP65 connector for harsh industrial environments.
Overview of the Han® 1A:
- Low overall weight: Thanks to plastic elements, the Han® 1A has a low overall weight, especially compared to metallic connectors.
- Versatility: "Custom" solutions for a variety of applications due to the modular concept. Han® 1A offers inserts for the transmission of data, signal and power, as well as a wide range of accessories.
- Time savings: The simple "Mate & Click" design of all individual components allows the connector to be assembled in just a few seconds.
- Space-saving: Han® 1A components conform to the trend towards miniaturisation. At the same time, they enable the construction of robust Han® connectors – even for harsh industrial environments.
- Cost savings: The modular system consists of a small number of individual components. Virtually an unlimited number of solutions can be created from just a few different parts, which leads to a reduction of storage costs.
- Data transmission up to Cat. 6A: The Han® 1A is extremely versatile. In addition to power and signal transmission, it also enables high-speed data transmission.
- IP-protected, if necessary: An IP65 solution can be easily achieved by using housing elements or single-wire seals.
About HARTING:
The HARTING Technology Group is one of the world's leading providers of industrial connection technology for the three lifelines of Data, Signal and Power and has 14 production plants and 44 sales companies. Moreover, the company also produces retail checkout systems, electromagnetic actuators for automotive and industrial series use, charging equipment for electric vehicles, as well as hardware and software for customers and applications in automation technology, mechanical and plant engineering, robotics and transportation engineering. In the 2017/18 business year, some 5,000 employees generated sales of EUR 762 million.
0 notes
Text
Robotics startup Picnic, known for its automated pizza assembly system, raises $5 million
Picnic, a robotics startup that focuses on food production, announced today that it has raised $5 million in additional seed funding. The new round was led by Creative Ventures, with participation from Flying Fish Partners and Vulcan Capital.
The company also said it has hired Kennard Nielsen, a product engineer who worked on the first four Kindle Fire tablets, Nike Fuelband, Microsoft Xbox and Doppler Labs’ HereOne from Doppler Labs at previous positions, as its new vice president of engineering.
The new funding will be used for product development, hiring and marketing.
Picnic is known for an automated pizza assembly system that launched in October. The configurable, modular platform currently focuses on high-volume pizza production and can reach rates of up to 180 18-inch pizzas or 300 12-inch pizzas an hour. The system fits into existing kitchen layouts, including food trucks and kiosks, and integrates with Picnic’s software to provide backend data and cloud analytics that help with consistency, speed and reducing food waste.
Picnic operates on a “robotics-as-a-service” model, with users paying for the system on a subscription basis. The pizza assembly system’s first customers were Centerplate, a food and hospitality provider for large event venues, and Washington-based restaurant chain Zaucer Pizza.
In June, Picnic also hired Mike McLaughlin, a food and beverage industry veteran who previously held roles at BUNN, Concordia Coffee Systems and Starbucks, as its vice president of product.
0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://magzoso.com/tech/robotics-startup-picnic-known-for-its-automated-pizza-assembly-system-raises-5-million/
Robotics startup Picnic, known for its automated pizza assembly system, raises $5 million


Picnic, a robotics startup that focuses on food production, announced today that it has raised $5 million in additional seed funding. The new round was led by Creative Ventures, with participation from Flying Fish Partners and Vulcan Capital.
The company also said it has hired Kennard Nielsen, a product engineer who worked on the first four Kindle Fire tablets, Nike Fuelband, Microsoft Xbox and Doppler Labs’ HereOne from Doppler Labs at previous positions, as its new vice president of engineering.
The new funding will be used for product development, hiring and marketing.
Picnic is known for an automated pizza assembly system that launched in October. The configurable, modular platform currently focuses on high-volume pizza production and can reach rates of up to 180 18-inch pizzas or 300 12-inch pizzas an hour. The system fits into existing kitchen layouts, including food trucks and kiosks, and integrates with Picnic’s software to provide backend data and cloud analytics that help with consistency, speed and reducing food waste.
Picnic operates on a “robotics-as-a-service” model, with users paying for the system on a subscription basis. The pizza assembly system’s first customers were Centerplate, a food and hospitality provider for large event venues, and Washington-based restaurant chain Zaucer Pizza.
In June, Picnic also hired Mike McLaughlin, a food and beverage industry veteran who previously held roles at BUNN, Concordia Coffee Systems and Starbucks, as its vice president of product.
0 notes
Photo

Objects
The second project of Major Studio 2 focused on objects and the psychological relationships that people have with objects. Leading question were:
// How does an interface create meaning?
// How does it structure & facilitate relationships?
// What is an affordance and how does it affect usage & meaning?
Continuing to work in groups, we were assigned to iteratively produce an object that addresses one of the scenarios developed during Project 1. First we had to propose three objects that could address one of our previous scenarios. Later on, we were to rapidly produce and iterate on a prototype of one of your proposed objects.
Proposal 1 _ Social Reputation Indicator
Context_
The near future is dominated by an ubiquitous AI that has sustainably changed the conditions of life on planet earth. People don't pursue ordinary professions anymore, but contribute their human brain power and analysis capabilities to constantly improving the AI. The AI outsources small virtual microtask to its army of online workers, who then perform them for a monetary remuneration. These tasks vary widely in scope and substance, but what links them all is that they’re essentially too difficult or too dependent on human analysis for a computer to do.
Examples: Data Verification, Information Gathering, Data Processing, Image Processing
Proposal_
We are proposing a physical interface that manages the transaction of labour, making microtasks accessible to the workers and providing them the infrastructure to share their labour with the AI in order to speculate on the future of labour and the influence of AI on our daily lives, our skill stack and creativity.
Reference_

Sketch_

Proposal 2 _ Social Reputation Indicator
Context_
In the near future, governments have incorporated social ranking systems to enable people to track, control and maintain their social reputation. These systems have become a sinister tool of social surveillance and pressure, turning people into virtuous robots seeking for “likes” and stigmatizing people with low social scores.
Proposal_
We are proposing a physical, social reputation indicator in order to investigate the cult of likability and its effect on people’s lives, exaggerate reputation culture and criticize on social rating systems.
Reference_

Sketch_

Proposal 3 _ Customizable and Modular Interfaces
Context_
In the near future programming has become basic knowledge and and is cultivated in people’s early lives. This lead to a change of people’s mindset to seek for highly customized and modualized digital products that would cater their individual needs. Technology companies have shifted their ventures towards selling decentralized modules rather than categories of centralized products, enabling people to assemble their own highly individualized interfaces.
Proposal_
We are proposing a novel modular system of digital components to speculate on the future of decentralized interfaces and devices as well as collective and additive manufacturing.
Reference_

0 notes
Photo

Illustration Photo: LG indoor/outdoor delivery robot (credits: LG전자 / Flickr Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0))
New generation of AI-Powered Robotics
Proposals are expected to develop technologies and systems that significantly enhance the cognitive ability of robots from the current state of the art to achieve greater levels of interaction and autonomy. Proposals will address as appropriate the following:
Develop enabling technologies, both new and existing, that extend the current state of the art in robotics perception, cognition, interaction and action as well as develop novel or advanced tools for the design and configuration of robots and robot systems that speed up the process of integration thereby reducing the time taken to deploy robot solutions. To do so by addressing the modularity and composability of solutions both in the operational context of a wide range of action and interaction use cases. There is also a need to address concepts such as trustworthiness, privacy, security and ethics already at the technology design phase. Develop lifelong autonomous robotics able to tackle unknown situations and adapt in the long term in pushing the state of the art of AI-based robots that combine monitoring, learning, planning and acting in order to evolve in difficult environments over long period of time. Support from simulation tools could be considered, as appropriate. Increase robot acceptance by handling adequately both human and robotic actions, with human-centric, advanced behavioural and elaborated planning models, and adopting multidisciplinary approaches including SSH[1], as well as end-user involvement in the design of solutions addressing human factors and interaction. Gender and intersectionality dimension[2] analysis should be a part of the proposals, where relevant. Push the limits of robotics interaction, adopting an interdisciplinary approach to integrate methods and techniques that allow the machines to engage in physical interactions with people or the environment, safely and intelligently, through specific enabling technologies: intuitiveness and responsive human-robot interfaces; integration of robot perception with natural and artificial intelligence; ability to physically, stably, dependably and safely interact with the environment, including users and surrounding people; development of advanced control tools fully integrating the human in the loop when performing a task; development of advanced control tools for dexterous and safe manipulation, assistance, and locomotion in diverse environments (ground, air, water, space, in-vivo and including safety critical and hazardous environments that are corrosive, explosive, nuclear or at extremes of pressure or temperature) and in general for improved performance of robots; energy autonomy and resilience to highly limited and imperfect communication networks in on-field applications.
Two types of proposals are expected, either focusing on higher level of autonomy, expecting less reliance on human supervision, or focusing on human-machine collaboration.
In each case, improvement in the level of robotics cognition should be demonstrated through at least three real-world scenarios (including measurements of functional performance), showing also the potential added value of such improvement in such use-cases scenarios. Scientific and technological progress should be demonstrated by qualitative and quantitative KPIs, demonstrators, benchmarking and progress monitoring. Activities are expected to achieve TRL 4-5 by the end of the project
The first type of proposals will further develop the level of autonomy in building on the latest developments in areas such as advanced perception, smart sensors, intelligent action and interaction, reasoning and learning, increased interpretation and understanding of the complex real-world environments (possibly involving human actions), anticipation of the effect of actions, adaptation and re-planning, graceful degradation, safety and security, etc. They will, as appropriate, further develop such components, and integrate them in an advanced robotics system, consider the balance of on-board vs off-board processes and the access and utilisation of external data and cloud resources to guide tasks and missions by adding external knowledge to internal reasoning and decision-making processes. The second type of proposals will further develop and integrate physical human-robot interaction, verbal/non-verbal communication as well as robot-environment/object interaction, embedding, as appropiate, safety, mutual understanding perception and interpretation of human actions, interaction situated in complex real-world environments and related motivations and social structures, joint goals, shared and sliding autonomy, ethical human-centric behaviour by understanding of physiological responses and emotions, etc. to reach truly smooth human-robot collaboration. This should as well integrate advanced control developments, and further develop them as necessary to guarantee the necessary speed for the required reactivity, ensuring natural, safe and smooth interactions with humans. Appropriate use should be made of data and knowledge accumulation from internal and external sources in order to guide reasoning and decision-making and the inclusion of explainability/transparency mechanisms[3] appropriate to the use case. Such proposals should adopt a multidisciplinary approach and involve the necessary expertise in SSH[1], in particular in ethics and human-centric design to enhance trust and acceptability. When possible proposals should build on and reuse public results from relevant previous funded actions. Proposals should make use of connections to the Digital Innovation Hub networks, particularly those in Robotics, Data and AI. Full use should be made of the common resources available in the AI-on-Demand platform[5], Digital Industrial Platform for Robotics[6], data platforms[7] and, if necessary other relevant digital resource platforms. Communicable results from projects should be delivered to the most relevant of these platforms so as to enhance the European AI, Data and Robotics ecosystem through the sharing of results and best practice.
All proposals should also take into consideration trustworthy AI principles[8] including respect of human dignity and agency, as appropriate, given the technology focus.
This topic implements the co-programmed European Partnership on AI, Data and Robotics.
All proposals are expected to allocate tasks to cohesion activities with the PPP on AI, Data and Robotics and funded actions related to this partnership, including the CSA HORIZON-CL4-2021-HUMAN-01-02. Where relevant, synergies with other PPPs are encouraged.
Expected Outcome: Proposal results are expected to contribute to the following expected outcome:
New generation of AI-Powered Robotics: Enabling robots to have more profound impacts than they currently have, in powering them with a deeper kind of AI, endowing them with a better perception and understanding of the world (up to semantic and explainable representations), This would allow the next generation of autonomous robots, with increased capabilities to work without/with limited supervision, as well as the next generation of interactive robots, with greatly improved intuitive, safe and efficient cognitive, social and physical capabilities, to assist humans. In addition, depending on the focus of the proposal, the results are expected to contribute to at least one of the following expected outcomes
Smarter robots with improved capabilities, functionalities (including complex functionalities such as manipulation of delicate, irregular, dynamic or deformable objects, navigation in un-controlled and variable or challenging and harsh environments, and continuous human-physical interactions) and an increased level of autonomy over the current state of the art, necessary to address real-world problems, while ensuring safety and reliability. Smooth and trustworthy (including safety and reliability) human-robot collaboration through advanced reactivity and mutual understanding, and human-centric automated adaptation of robots in human-robot interactions.
Application Deadline: 21 October 2021 17:00:00 Brussels time
Check more https://adalidda.com/posts/3sYopN8rs2WymnwDb/new-generation-of-ai-powered-robotics
0 notes