#PFPE
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Perfluoropolyether (PFPE)
Perfluoropolyether (PFPE) is a highly specialized lubricant that offers exceptional performance in various industrial applications. PFPE grease, oil, and lubricants are widely used in demanding environments where extreme temperatures, chemical resistance, and low friction are crucial.
PFPE grease is a type of lubricating grease made from perfluoropolyether oil as its base. With its excellent thermal stability, PFPE grease can withstand high temperatures without compromising its lubricating properties. This makes it ideal for use in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor manufacturing, where equipment operates under extreme conditions.
PFPE oil, also derived from perfluoropolyether, is known for its superior chemical resistance and non-flammability. It provides long-lasting lubrication and protection for various mechanical components, even in harsh chemical environments. PFPE oil finds applications in chemical processing plants, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and vacuum systems where the integrity of the lubricant is critical.
As a perfluoropolyether-based lubricant, PFPE offers unique advantages over traditional oils and greases. Its low surface tension and high thermal stability contribute to reduced friction and wear, enhancing the overall durability and efficiency of machinery. Moreover, PFPE's inert nature prevents it from reacting with most materials, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of metals, elastomers, and plastics.
When it comes to choosing the right lubricant, PFPE lube stands out as an excellent choice. Its high viscosity index and exceptional load-carrying capacity make it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Whether it's providing lubrication in gears, bearings, or seals, PFPE lube ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of critical equipment.
In summary, perfluoropolyether (PFPE) lubricants, including PFPE grease, oil, and lubricants, offer unparalleled performance in extreme conditions. Their thermal stability, chemical resistance, and low friction properties make them indispensable in various industries. With their exceptional reliability and versatility, PFPE-based lubricants play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and longevity of industrial machinery.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
High and low temperature planetary gearboxes will be delivered to Slovenia
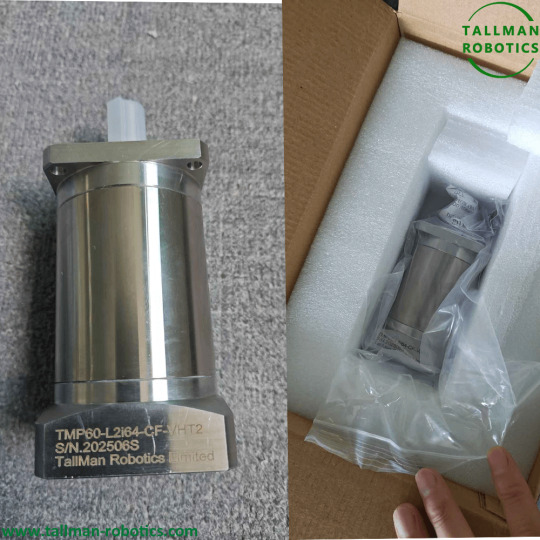

A high and low temperature planetary gearbox is a specialized type of planetary gearbox designed to operate reliably under extreme temperature conditions, ranging from very low (e.g., -60°C or below) to very high (e.g., 200°C or above) temperatures. These gearboxes are used in industries where standard gearboxes would fail due to thermal expansion, material degradation, or lubrication issues. High and low temperature planetary gearboxes provide the reliability needed in such challenging environments. Key Features of High and Low Temperature Planetary Gearboxes 1. Specialized Materials Gear Components: Made from high-performance alloys (e.g., stainless steel, titanium, or heat-treated steels) to resist thermal deformation. Housing: Often aluminum alloy or stainless steel with thermal-resistant coatings. These materials are essential for planetary gearboxes operating at high and low temperatures. Bearings: Ceramic or high-temperature steel bearings to prevent failure under thermal stress. 2. High-Temperature Lubrication Synthetic lubricants (e.g., perfluoropolyether (PFPE) or silicone-based greases) that remain stable across a wide temperature range, crucial for high-low temperature planetary operations. Solid lubricants (e.g., graphite or molybdenum disulfide) for vacuum or ultra-high-temperature applications. 3. Thermal Management Heat-resistant seals to prevent lubricant leakage are important in maintaining planetary gearboxes under high and low temperature conditions. Thermal insulation or cooling systems (e.g., heat sinks or forced air cooling) for extreme environments. 4. Precision Engineering Tight tolerances to account for thermal expansion/contraction. Precision is key when engineering planetary gearboxes that withstand high and low temperatures. Optimized gear meshing to prevent binding or excessive wear. Applications Aerospace & Defense: Satellite mechanisms, drone actuators, missile systems. Oil & Gas: Downhole drilling equipment, high-temperature pumps. Industrial Automation: Furnace conveyors, steel mill machinery. Automotive: Electric vehicle (EV) drivetrains in extreme climates. These high and low temperature planetary gear reducers ensure effective operation across varied conditions. Scientific & Research: Cryogenic systems, space exploration rovers. Would you like recommendations for a specific application? You are welcome to watch more projects or visit our website to check other series or load down e-catalogues for further technical data. Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/@tallmanrobotics Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/tallmanrobotics Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/tallman-robotics Read the full article
#Backlash-FreePrecisionPlanetaryGearboxes#IndustrialPlanetaryGearboxes#PlanetaryGearBox#Planetarygeartransmissions#PlanetaryGearboxes#Planetarygearheadsformaximumtorque#PrecisionPlanetaryGearboxes
0 notes
Text
https://github.com/shilpaarya222/Zenith-Shift-Holdings/blob/main/PFPE Market.mdt
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Beginner Guide to Roof Safety Systems:

There is a wealth of information on roof safety systems, varying in quality, from articles produced by AI to beautifully written articles from experts in the field. Ensuring your safety and the safety of your employees is of the utmost importance. So, from the myriad of articles, how do you know how to trust? While we provide some critical points on roof safety, it's crucial to remember that your safety is best ensured by reaching out to professionals in the field of roof safety systems. Most will provide free consultations and are available to answer any questions you may have, guiding you towards the best safety solutions for your specific needs.
So, without further ado, let's dive in!
Introduction to Height Safety Systems
Height safety systems are essential for workers' safety. These mechanisms and procedures are designed to prevent falls and ensure the safety of workers operating at elevated heights. Height safety systems are crucial across various industries, including construction, maintenance, roofing, and any sector where tasks are performed above ground level.
Importance in Various Settings:
Construction: Construction workers frequently operate at significant heights, making them vulnerable to falls. Height safety systems like roof anchor points, ladder brackets, guardrails, safety nets, and personal fall protection equipment (PFPE) are critical to prevent accidents and fatalities.
Maintenance and Roofing: Regular maintenance and roofing tasks often require workers to access high areas. Roof anchor points, lifelines, and ladder brackets help ensure these workers are secure and can perform their duties safely.
Industrial and Warehousing: In industrial settings, platforms, elevated walkways, and storage areas pose fall risks. Implementing height safety systems, such as guardrails and harnesses, helps protect workers in these environments.
Types of Height Safety Systems:
Personal Fall Protection Equipment (PFPE): This includes a wide range of gear, such as harnesses, lanyards, and lifelines, that workers wear to prevent falls, catering to different work environments and tasks.
Collective Protection: Systems like guardrails and safety nets that protect multiple workers simultaneously without requiring personal gear.
Access Equipment: Ladders, scaffolding, and roof access hatches provide a safe way to reach elevated work areas.
To understand how they work, let's examine each main component of height safety systems more closely.
Personal Fall Protection Equipment (PFPE)
Personal Fall Protection Equipment (PFPE) includes essential gear such as harnesses, lanyards, and lifelines that workers wear to prevent falls. These items are designed to secure an individual directly, providing critical support and minimising the risk of injury during a fall. Remember, properly using PFPE is not just a requirement; it's a responsibility. Maintaining safety standards and ensuring workers can securely perform their duties at elevated heights is vital.
Guardrails
Guardrails are collective protection systems designed to prevent falls by creating physical barriers at the edges of roofs, platforms, and walkways. They are crucial for protecting multiple workers simultaneously without needing individual gear. By installing guardrails, employers can significantly reduce the risk of falls and enhance overall safety in areas where workers are frequently exposed to height-related hazards.
Safety Nets
Safety nets are another form of collective protection designed to catch workers in the event of a fall. These nets are typically installed below the working area and provide a crucial safety measure, especially in construction and maintenance scenarios where the risk of falling is high. Safety nets help to prevent severe injuries by absorbing the impact of a fall, ensuring that workers have an additional layer of protection while performing their tasks at height.

Ladder Brackets
Working with ladders is a dangerous task. In Australia, on average, 30 people lose their lives each year from falling from a ladder. Falls from ladders account for the highest number of fatalities in height safety-related incidents, with half of the falls from less than 3 meters, resulting in death. This stark reality should be a powerful reminder of the potential risks involved when working at heights, the underscoring urgency and importance of professional consultation and proper safety systems.
Ladder brackets reduce the risk of working with ladders by preventing slippage and movement, thus eliminating the need for a second person to stabilise the ladder's base. They also allow workers to access a roof safely.

Roof Access Hatches
Roof access hatches provide a secure and easy access point to the roof from inside the building, especially for tall buildings where ladder access is difficult or impossible. They are generally the safest way to access a roof, significantly reducing the risk of falling by removing the need to climb ladders, as they can usually be accessed via a staircase. This reassurance of safety should alleviate any concerns about roof access.
These hatches are typically found in non-residential buildings such as hospitals, office buildings, warehouses, commercial centres, and larger apartment buildings.
For optimal safety, a roof anchor point should be placed within one meter of the access hatch so workers can securely connect their harnesses before stepping onto the roof.

Roof Anchor Point
A roof anchor point is precisely what the name suggests: a point on a roof to which you can attach yourself with a lifeline or lanyard. There are multiple types, but generally, they fall into two types:
Fall restraints: Prevent the user from getting close enough to the edge to fall, removing the possibility of falling.
Fall arrest: Minimise injury during a fall, stopping the user from hitting the ground.
A wide range of roof anchor points are available to suit every type of roof, whether it's tiles, terracotta, concrete, slate, iron, Colorbond® steel, or metal sheeting. This variety lets you choose the most suitable anchor point for your specific roof type, ensuring the user's safety.
Roof anchor points are divided into two main groups: temporary and permanent. Of course, both have their specific uses. Each group includes various types of anchor points, such as concrete-mounted, rafter-mounted, steel-fit, eye bolts, rail systems, I-beam, metal decking, parapet, and speciality anchors. Understanding these categories and types helps you decide on the most suitable anchor point for your needs.
However, temporary roof anchor points should be used in particular circumstances, such as a building site where walls are being placed, and they will no longer be needed in the short term.
A key feature of modern anchor points is energy absorption. These are designed to cushion a fall, reducing the risk of injury and preventing roof damage from the kinetic force of a fall. An example of this would be the Froglink roof anchor from SafetyLink, whose unique design slows you down before coming to a complete stop.

Froglink by SafetyLink
How many anchor points should I have on my roof?
Finding the correct installation points on a roof is vital to creating a height safety system that complies with all necessary legislation and offers an easy-to-use system.
Roof anchor points guidelines provide an idea of how many anchor points you will need:
Distance from Roof Edge: Never place an anchor over 10 meters from the roof edge. Otherwise, the user will require a rope line longer than the standard 15 meters, which will be overly cumbersome.
Spacing Between Anchors: Never leave more than 6 meters between anchor points. Greater distances create dead zones at the roof edge, increasing the fall risk.
Main Anchor Point Placement: The main anchor point should always be placed at the midpoint between the gutter edge and the gable end of the roof.
Every roof is different and requires a unique safety system to ensure all workers are safe and legally compliant. While it's good to know about roof anchor points, under Australian legislation, roof anchor points must be certified and recertified by professionals yearly. To avoid issues in the future, it is best to consult a professional installer. A good installer will also know how and where to install anchor points, achieving full coverage with minimal anchors.
When Must Height Safety Systems Be Used?
The Work Health & Safety (WHS) legislation (act 2011, compilation 15) requires employers to provide a safe working environment. Therefore, as far as is practical, they must implement a safety system for everyone on the worksite.
Who Can Install Height Safety Systems?
The Australian Standards AS/NZS 1891.4 states that anchor points, horizontal and vertical static lines, lifelines, and rails used for fall protection or when working at heights must be inspected and certified every 12 months. This requirement ensures the equipment remains in good working order and compliant with safety regulations. Regular inspections help prevent equipment failure and ensure the safety of workers using these systems.
Only qualified installers can install, inspect, and certify height safety systems. But if you are working on a high roof, wouldn't you be more comfortable knowing that a professional rather than a DIYer has installed the safety system?
Training & Competency
Proper training is also essential for workers who use height safety systems; if the tools are there but no one knows how to use them, they are worthless. Training programs should cover the correct use of personal fall protection equipment (PFPE), emergency procedures, and the specific safety protocols relevant to the work environment. Accredited training providers offer courses tailored to various industries and work scenarios. This is not a one-time thing; training should be refreshed regularly, typically every 12 months, to ensure that workers remain competent and up-to-date with the latest safety practices and regulations. It also helps workers not to be complacent; when people work at heights for a long time, they tend not to see the dangers anymore. Continuous training helps to reinforce safety awareness and skills, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
Summary & Key Takeaways
Height safety systems protect workers from falls in various industries. Key components include personal fall protection equipment (PFPE), guardrails, safety nets, ladder brackets, roof anchor points and roof access hatches. It is essential to understand the importance of regular maintenance and inspections, which should be conducted annually to ensure compliance and safety. Proper training and competency are crucial, with training programs needing regular refreshments to maintain high safety standards. Adhering to these practices ensures a safe working environment and aligns with legal requirements and best practices in height safety management. Always consult professional installers and safety experts to achieve optimal coverage and compliance with all necessary legislation.
#health and safety#working at heights#sydney#anchor points#roof anchor points#ladder safety#safety tips#informative
0 notes
Text
Understanding Reflow Ovens in Surface Mount Technology
Understanding Reflow Ovens in Surface Mount Technology
Reflow ovens play a crucial role in the assembly of printed circuit boards (PCBs) with surface mount electronic components. These ovens facilitate reflow soldering, ensuring reliable connections between components and PCBs. Let’s delve into the details of reflow ovens and their various types.Get more news about Reflow Oven,you can vist our website!
Types of Reflow Ovens: Infrared and Convection Ovens: Infrared reflow ovens use ceramic infrared heaters positioned above and below the conveyor belt. These heaters emit radiation, transferring heat to the PCBs. Convection ovens, on the other hand, heat air within chambers and use it to transfer heat via convection and conduction. Convection ovens provide more accurate temperature control than infrared ovens because they indirectly heat the PCBs using air. This is essential because PCBs and components have varying infrared absorptance. Some ovens combine infrared radiative heating with convection, known as “infrared convection” ovens. Additionally, certain ovens create an oxygen-free atmosphere by using nitrogen gas during reflow to minimize oxidation of soldered surfaces. Vapour Phase Ovens: Vapour phase soldering relies on the phase transition of a heat transfer liquid (e.g., PFPE) condensing on the PCBs. The chosen liquid has a specific boiling point to suit the solder alloy. Advantages of vapour phase soldering include high energy efficiency, oxygen-free soldering, and prevention of overheating. Maximum assembly temperatures are limited by the boiling point of the medium, making this process safe and controlled. Thermal Profiling: Thermal profiling involves measuring temperature points on a circuit board during the soldering process. Statistical process control (SPC) helps determine if the reflow process adheres to defined parameters based on soldering technologies and component requirements. Applications: Reflow ovens find applications in both high-volume commercial production lines (using conveyorized ovens) and prototyping/hobbyist scenarios (using smaller ovens). In commercial settings, PCBs travel through multiple individually heated zones, each with adjustable temperature settings. For hobbyists, small ovens with doors accommodate PCBs for reflow soldering. In summary, reflow ovens are essential tools for achieving reliable solder joints in surface mount technology. Whether you’re assembling complex electronic devices or experimenting with your DIY projects, understanding reflow ovens ensures successful PCB assembly.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
0 notes





