#Print and Apply Labeling Systems
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top Print and Apply Labeling Systems Manufacturers in the UK: What You Need to Know
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment, print and apply labeling systems have become a critical component of efficient packaging and logistics operations. Whether you're in food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, e-commerce, or logistics, choosing the right manufacturer can significantly impact your productivity and compliance. Here’s a complete guide to the top print and apply labeling system manufacturers in the UK and what to consider before making a purchase.
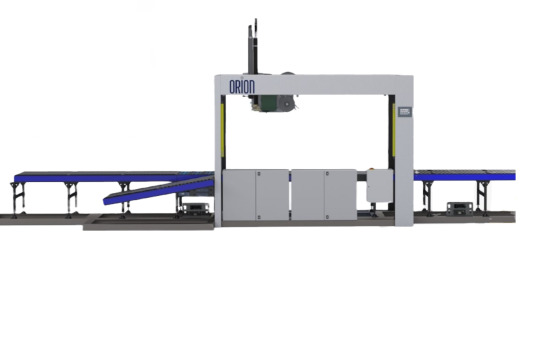
🔹 What Are Print and Apply Labeling Systems?
Print and apply labeling systems are automated machines designed to print labels (with barcodes, batch codes, expiry dates, etc.) and apply them directly onto products, cartons, or pallets. These systems ensure fast, accurate, and reliable labeling, which is essential for inventory tracking, traceability, and supply chain efficiency.
🔹 Benefits of Print & Apply Labeling Machines
Improved Efficiency: Automates the labeling process, reducing manual labor.
Accuracy: Reduces human error and mislabeling.
Scalability: Ideal for high-volume operations.
Compliance: Meets industry regulations (e.g., GS1 standards, FDA, EU directives).
Versatility: Works with different product types, sizes, and surfaces.
🔹 Top UK Print and Apply Labeling System Manufacturers
1. Domino Printing Sciences
One of the leading global players headquartered in the UK, Domino offers high-speed, integrated labeling systems with a focus on traceability, efficiency, and sustainability.
2. Label-Aire Europe
Label-Aire is known for robust and flexible labeling systems that integrate seamlessly into existing production lines. Their UK division offers strong technical support and custom solutions.
3. Logopak UK
Logopak specializes in high-performance print and apply systems for demanding industrial applications. They are a trusted name in food, beverage, and logistics sectors.
4. Advanced Labelling Systems (ALS)
Based in Oxfordshire, ALS provides reliable labeling automation with comprehensive support, including installation, servicing, and training.
5. Herma UK
Herma is known for German engineering with UK-based service. They deliver precision labeling machines with user-friendly interfaces and high output rates.
🔹 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Manufacturer
Speed and Output: Match the labeling speed to your production line requirements.
Print Quality: Look for machines that offer high-resolution printheads.
Maintenance & Support: Choose manufacturers that offer reliable after-sales service in the UK.
Integration Capabilities: Ensure the system integrates with your ERP, WMS, or existing production line.
Labeling Accuracy: Essential for compliance and barcode scanning efficiency.
🔹 Industries That Benefit Most
Food & Beverage: Date codes, nutrition labels, and allergen compliance.
Pharmaceuticals: Serialization and tamper-evident labeling.
Retail & E-Commerce: Inventory tracking and shipping labels.
Logistics: Pallet labeling and warehouse barcoding.
🔹 Final Thoughts
Investing in a print and apply labeling system from a reputable UK manufacturer ensures long-term efficiency, compliance, and productivity. With options ranging from standard to fully customized solutions, UK-based companies are leading the way in innovation and reliability. Take the time to assess your specific needs and choose a manufacturer that offers robust service and industry expertise.
0 notes
Text
Labelling Machines Market Global Market Size 2025–2035
Market Overview
The Labelling Machines Market accounted for USD 2.96 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 5.22 Billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of around 5.3% between 2025 and 2035. These machines are widely adopted across industries like food & beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemicals to automate labeling processes with efficiency and regulatory precision.
Growing consumer demand for packaged goods and automation in manufacturing are major contributors to the market growth. Furthermore, advancements in AI and IoT technologies are making labeling systems smarter and more efficient. The push for sustainable and modular packaging solutions also propels demand for innovative labeling equipment. Request Sample-https://www.metatechinsights.com/request-sample/1825
Segmental Analysis
By Product Type:
Front and Back Labelling Machines
Wrap Around Labelling Machines
Top and Bottom Labelling Machines
Side Labelling Machines
Tamper-Evident Labelling Machines
Print and Apply Labelling Machines
Full Report-https://www.metatechinsights.com/industry-insights/labelling-machines-market-1825
Wrap-around labelling machines hold the largest share due to their versatility in bottle labeling, widely used in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical sectors.
By Technology:
Pressure-Sensitive (Self-Adhesive) Labelling
Sleeve Labelling
Glue-Based Labelling
Roll-Fed Labelling
Heat Transfer Labelling
Digital Labelling Technology
Pressure-sensitive labeling dominates due to its cost-efficiency, surface compatibility, and widespread use across multiple industries.
By Application:
Food and Beverages
Pharmaceutical and Healthcare
Cosmetics and Personal Care
Chemical and Industrial
Electronics
Logistics and Transportation
Others
Buy Now-https://www.metatechinsights.com/checkout/1825
By Material Compatibility:
Plastic
Glass
Metal
Paper
Fabric
By Distribution Channel:
Direct Sales
Distributors and Dealers
E-commerce
Regional Overview
North America is experiencing significant growth due to technological advancements like machine vision, AI, and robotics. The U.S. leads in automated labeling systems, supported by environmental initiatives and increasing investments in smart factories.
Asia Pacific dominates in volume, driven by a booming middle class and expanding demand for packaged goods. Countries like India benefit from government initiatives like ‘Make in India’, pushing for local production and tech upgrades in labeling machinery.
Europe follows with high adoption rates in the food and beverage and cosmetics industries, fueled by stringent labeling regulations and sustainability mandates.
Competitive Landscape: Leading players include Krones AG, ProMach, and Sacmi Imola S.C. Krones offers modular machines with digital enhancements, while ProMach focuses on eco-friendly systems. Accutek Packaging Equipment and Fuji Seal International are integrating IoT in their labeling solutions to improve productivity and traceability.
Recent Developments:
August 2024: FOX IV Technologies launched the 6312 Label Printer-Applicator designed for SMEs, eliminating the need for external PCs.
January 2024: Domino introduced the MX-Series print-and-apply machines to improve traceability and pallet labeling under GS1 compliance.
#Labelling Machines Market#Automatic Labelling Solutions#Packaging Equipment#Food Labeling Machines#Pharmaceutical Labeling Systems#Self-Adhesive Labels#Print and Apply Technology#E-commerce Packaging#Global Labelling Industry Trends#Sustainable Labelling Equipment
0 notes
Text
Made in the USA: Wage Theft, Fraud and Hidden Sweatshops
Unrolled twitter thread by derek guy (@dieworkwear)
4 Oct 24 • Read on X
ALT enabled on all images. Video has closed captions but is not transcribed.
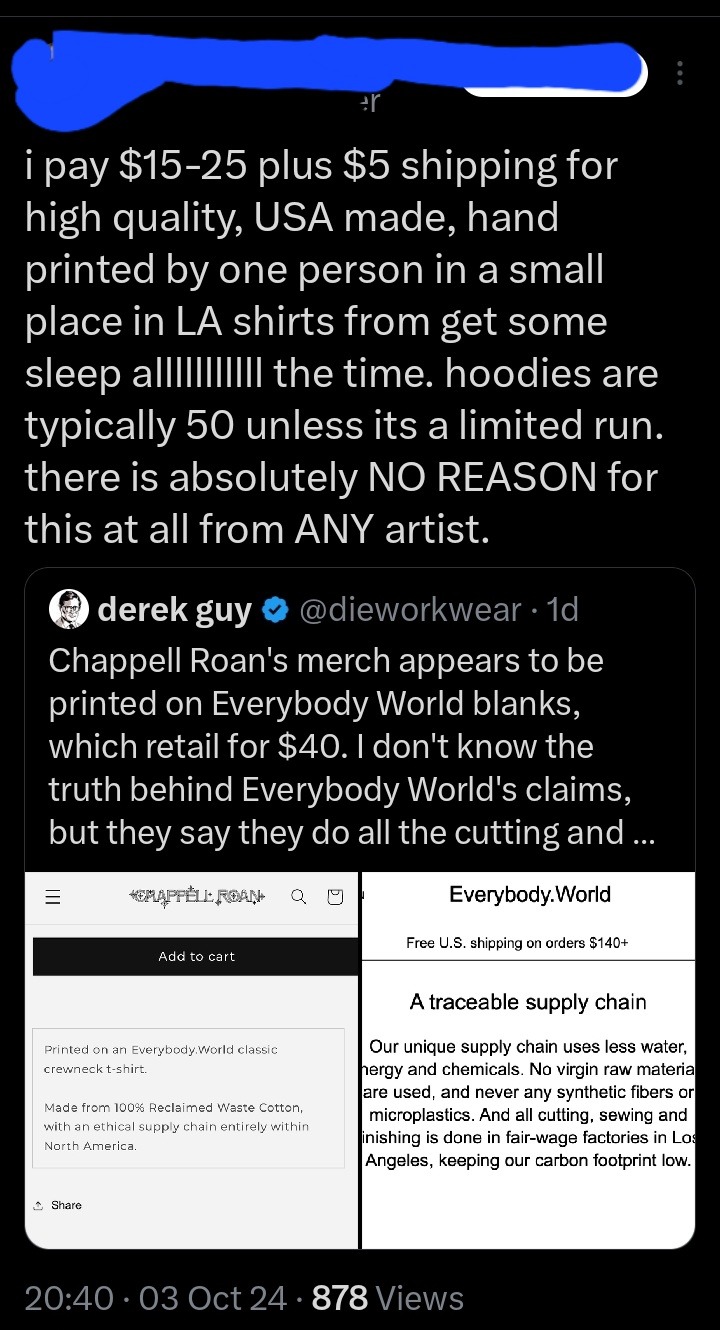
Not trying to create a pile-on here. But let's talk about why something might still be made in unethical conditions even though it bears a "made in USA" tag. 🧵
The first thing to understand is that not all workers are covered by US labor laws. You might assume that workers get paid a minimum wage (after all, it says "minimum"). In fact, many garment workers in the US toil under what's known as the piecework system.
Piecework means you get paid not by the amount of time you work but the number of operations you complete. This system should be familiar to many of you. As a writer, I get paid per word. The pay is the same whether it takes me 100 or 10 hours to write a 1,000 word article.
My situation is fine bc I get paid enough to eat. But for a garment worker, the pay structure can be peanuts: three cents to sew a zipper or sleeve, five cents for a collar, and seven cents to prepare the top part of a skirt. These are real numbers for LA-based garment workers.
Piecework is how companies skirt minimum wage laws. Among labor organizers, the term "wage theft" refers to the difference between what a worker should have earned under min wage laws and what they actually earned through the piece rate system.
This system is incredibly common. A 2016 UCLA Labor Center study showed the median piece-rate worker in Los Angeles scrapes together $5.15 per hour—less than half the state’s mandated minimum wage. Labor conditions are also very bad: poor ventilation, dusty air, rats and mice.

A Federal Department of Labor investigation the same year found that 85 percent of Los Angeles garment factories were breaking labor laws. In 2016, these violations amounted to $1.3 million in back wages owed to 865 workers in a sample of 77 factories. This is wage theft.
In 2021, labor organizers won a fight to get piecework banned in California. But two years later, it's still incredibly common. I interviewed an LA-based garment worker who toils 12 hrs a day for $50. She sleeps in the corner of a kitchen. From my article in The Nation:

Currently, there's a new fight get piecework banned nationwide through the FABRC Act. I would link, but Twitter throttles threads that have outbound links, so I would prefer if you Google how you can support this legislation. Or follow @GarmentWorkerLA for more info.
The other reason why a "made in USA" tag may not mean much has to do with how the label is applied.
When you see this label inside your garment, what do you assume? Think about this before moving on to the next tweet.

The Federal Trade Commission has pretty strict rules on who gets to apply that label. For clothes, the item has to be cut and sewn in the US using materials that were made in the US. The FTC tries to match its rules with the common understanding of what "made in US" means.
If you're a giant company like Levi's or LL Bean, you may have lawyers who are advising you on these rules. This is why you see labels like "imported," which means the item was made abroad. Or "made in the US from imported materials" when they can't meet the MiUSA standard.
But it's incredibly common for companies to violate FTC rules. In 2022, the FTC fined the pro-Trump brand Lions Not Sheep $211k for labeling their t-shirts "made in USA" when the shirts were actually imported from China and other countries.
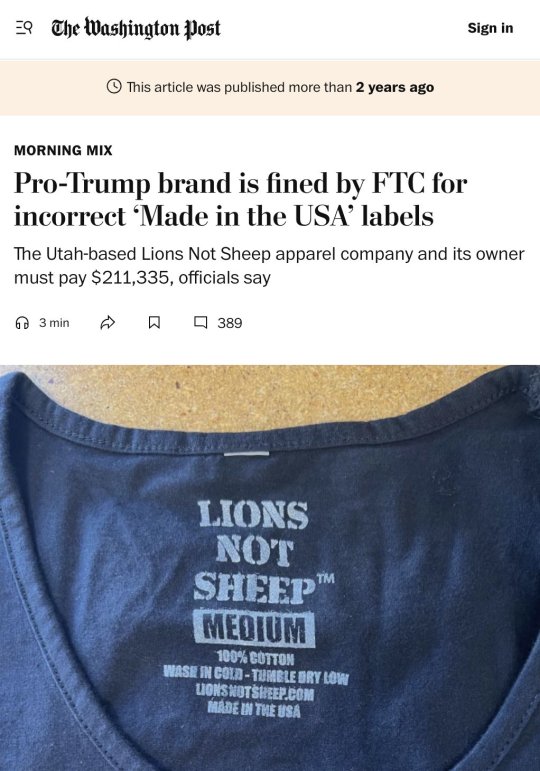
The company was basically importing blanks from China, ripping out the "made in China" label, screen printing the shirt in the US, and then applying a new screen-printed "made in US" label. CEO Sean Whalen claimed he was being persecuted for his pro-Trump views.
But the whole thing started bc Whalen made a video about how his customers are price sensitive, so he imports blanks from China. That's what kicked off the FTC investigation. So while this mislabeling is common, it's hard to get caught unless you make a video about your crimes.
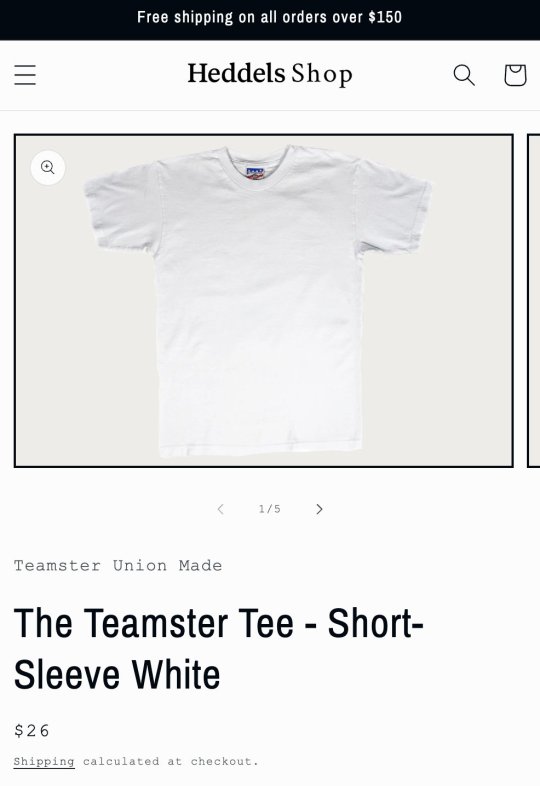
The truth is that making a t-shirt in the USA according to FTC standards will result in a relatively expensive garment. Heddels and Velva Sheen both produce shirts in the US from US grown cotton. The first is $26; second is $90 for a two-pack.

Once you add things such as screenprinting—or if you want a more unique cut and not just basic blanks—the costs go up. This is why Bikers for Trump sourced their merch from Haiti. They knew their customers would not pay an extra $8 for true made-in-USA production.
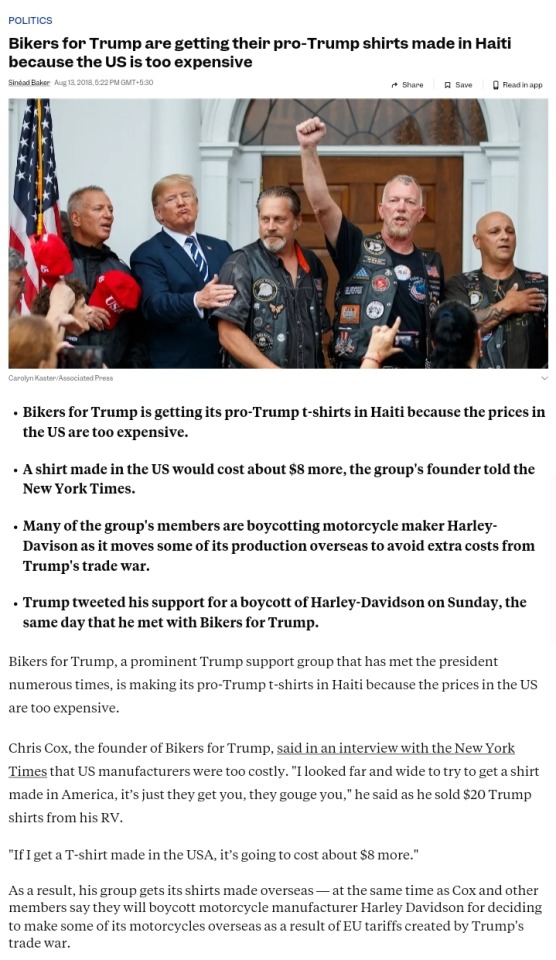
Today, there are countless companies that make merch for other organizations. They source their t-shirts from a variety of places—some made in the US, most not—and then screenprint a design and fulfill orders. This way, the other org doesn't have to do any work but marketing.
When you see a screenprinted t-shirt for $20, ask yourself: Where was the material grown? Where were the yarns spun? Where was the cutting, sewing, and finishing performed? Where was the screenprinted done? What were the wages and labor conditions along these steps?
I'm not a nationalist, so I don't prioritize American jobs over foreign ones. But I do care about fair wages and labor protections. Just because something was made abroad doesn't mean it was made in a sweatshop. Just because it was made in the US doesn't mean fair wages.

Paying more for a garment is also no guarantee of ethical manufacturing. But when the price of a garment is so low, you leave little on the table for workers. Just because you see a $20 t-shirt that says "made in USA" doesn't mean it was made fairly.
Please don't harass the person who posted that original tweet. My intention is not to cause harm or stress for anyone. Only to help shed light on what goes into garment manufacturing, fair labor, and labeling. Hopefully, you will consider these issues when shopping.
For the inevitable question: "How do I make sure my clothes were made ethically?" This is very difficult to answer in a thread. My simplest answer is that we should elect pro-worker politicians, fight for pro-labor laws, and empower unions so workers can advocate for themselves.

--------------------End----------------------
TL; DR: Doesn't matter if it's the US, if it's not union it's probably a sweatshop. And not all merch is priced high because of fair labour conditions (looking at Taylor Swift and Beyoncé). Look for supply chain transparency.
#sweatshops#fashion#american sweatshop#chappell roan merch#sweatshirt#chappell roan#merchandise#made in usa#garment industry#fast fashion#worker rights#labour rights#labour unions#capitalism#worker exploitation#us politics#us law#knee of huss
134 notes
·
View notes
Text
Matthew Barney’s Self-Lubricating Frames
A small, lingering question I’ve had for 20 years: what is a “self-lubricating frame”? At the Guggenheim "Cremaster" exhibit and later exhibits, I wondered about this phrase on the label cards of Barney’s film stills, with custom frames, they are described as “chromogenic print in self-lubricating frame.” Perhaps easily answered, but because I wasn’t holding a phone connected to the internet in the museum back then, never answered.

Recently I went to a screening of Matthew Barney’s “Cremaster 3” (2002), with a Q&A between Barney and Martine Syms. Nostalgia lured me to Santa Monica, as I haven’t seen the complete 3-hour film since seeing the entire cycle at San Francisco's Castro Theater in 2003.
While the earlier films retained a video look, "Cremaster 3" (the final film) must have been shot on one of the better HD DV formats of the era at 24P, because it looks very filmic, the degraded 35mm print we watched certainly contributed to that vibe.

If you are new to Barney’s work, his long-term projects like "Cremaster" have sculptural and architectural aspects. Some sculptures could be construed as props and parts of a set for performance. In a gallery setting they are firmly sculpture. A film of the performance becomes its own highly edited and crafted artifact, which is then used in the spaces that exhibit the objects.
How do framed photographs fit into this system? As with the films, they are artifacts of the performance, a Barney exhibit might have the sculpture (often quite large) in the center of a gallery space, with the framed photographs on the walls, in the same way a video monitor might be on a wall with the dangling headphones.
Barney cites "Cremaster" as beginning in 1994, but this framed football magazine is from 1991, with what became the Cremaster logo applied in the center. This example suggests these framed photographs exist as collectables with some connection to how a sports or music fan collects still images of action, or a cinema fan would collect a production still.

Along with vaseline or beeswax, self-lubricating plastic as used in sculpture or framed photographs can be considered one of Barney's core materials. Was it selected due to the fact it resembles beeswax? Here's another 1991 example, with a black and white silver print.

The "Cremaster"-era prints themselves are exquisitely lit and printed, mostly color, many seem to be photographed by Michael James O’Brien, though I don't recall ever seeing his name on a museum or gallery label. The photographer is like the fabricator of the frame, a craftsperson Barney hires to execute the object. My recollection is they are printed luxuriously matte, which works well with the creamy frames. The "Cremaster 3" prints are of larger dimensions that became popular at the fin de siècle with Gursky, or more relevant to Barney as his own lead actor, the portraits of Rineke Dijkstra. These are titled film stills, the convention of the Cremaster stills seems to be “movie : subject.” (e.g. Cremaster I: Orchidella).

My memory of the framed Cremaster photographs is that they were of somewhat uniform size and look: a creamy beeswax plastic, in line with the other sculpture you might see in his exhibits, no sharp edges, but not particularly different from other plastics you might encounter in our modern wonderland of PFAS. When I first read "self-lubricating frame," I assumed it was partially a joke, a reference to petroleum jelly/ vaseline, one of Barney’s other preferred materials. Or perhaps lubricated condoms.
Looking online at the auction houses, it appears my memory was way off, there were many variations in size, shape and even color. Ireland is a core part of the "Cremaster" mythology, and this "Cremaster 4" print is in delightful Shamrock Shake green.

After that screening of "Cremaster 3," I went on the typical bender of reading old blog posts and writings on the topic. There’s a 2004 doc streaming on Kanopy (the library video app, excellent for art documentaries), where the NYT art critic Michael Kimmelman walks through the Guggenheim Cremaster exhibit with Barney answering questions, explaining references, personal and mythical, cutting to scenes from the relevant films. About nine minutes into the doc, my question is answered. Barney explains about a sculpture they are looking at: “[it's] high density polyethylene, from the same family as Teflon is from, has a resistance to friction. And in that way it’s a self-lubricating plastic, in that it generates its own lubrication.”
OK! So "self-lubricating" is a description for a class of industrial plastic products, which Barney has fabricated his frames of and adopted the phrase. "Self-lubricating plastic frame" is more accurate if more mundane sounding. There's no liquid aspect to it, but if we were able to rub at it, in a repetitive fashion, could we perhaps notice it was different? It's a specific material - not a condom joke, or even like using the word "giclée" to gussy up "ink jet" print.
This material is described as:
solid lubricants are embedded as microscopic particles in millions of tiny chambers in the fiber-reinforced material. From these chambers, the plastic bushings release tiny amounts of solid lubricant during movement.
Another description of how it works once molded into an industrial form:
The bearing achieves this by transferring microscopic amounts of material to the mating surface, creating a film that lubricates and reduces friction over the entire length of the rail or shaft.

When you read this and see some of the examples of how it's used in actual products (Linear Bearing for 8mm rod pictured above), this wasn't selected by Barney just because it resembles beeswax, but because conceptually it's a classic Barney material. A plastic, honeycombed with microscopic bits of lubricant! There's an added tension looking at these objects, knowing the material is designed for friction, but will likely never experience it. After the organic forms are molded, the films are shot, the stills are taken, the photographs mounted in the frame, they will only ever be handled by people wearing white gloves.
(Previously on the topic of artist's frames: Robert Mapplethorpe’s “Kitchen Sink", 2016)
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
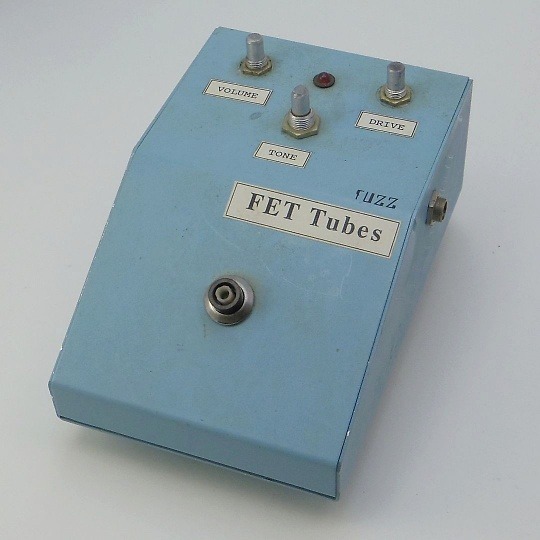


AMZFX - FET Tubes Fuzz
"Another ancient pedal from the boxes in my garage. This one has the same type LMB folded aluminum enclosure. It also uses the cmos switching system with a soft-touch footswitch that has been broken over the years and the top pad is missing. I am not sure what the circuit is in this pedal but I opened it up and took a quick peek inside. I could not get much of a view without removing the pots and jacks, but it looks to be using an opamp and a couple of jfet transistors. The clear finish is dirty just like the previous pedal, and not easily removed or cleaned. The labels appear to be dot-matrix printed on adhesive backed label stock, cut out and then stuck in place. The clearcoat was applied last over the labels and paint. At some point I stole the knobs to be used on some other project."
cred: muzique.com/news/fet-tubes, instagram.com/amzfx
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Everything You Need to Know About Thermal Paper: A Guide by Parthivi Labels and Paper"
Welcome to the ultimate guide to thermal paper, brought to you by Parthivi Labels and Paper! Whether you're a business owner, a printer, or someone interested in the world of labels and receipts, thermal paper plays an important role in many industries. Let’s dive into what thermal paper is, its uses, and why choosing the right type of thermal paper is essential for your business.
What is Thermal Paper?
Thermal paper is a special type of paper that is coated with a chemical layer that changes color when exposed to heat. Unlike regular paper, thermal paper doesn't require ink or toner for printing. Instead, a thermal printer applies heat to the surface of the paper, causing it to react and form the text or images.
Thermal paper is commonly used in receipt printers, barcode labels, and point of sale (POS) systems due to its convenience and cost-effectiveness.
Types of Thermal Paper
At Parthivi Labels and Paper, we offer a variety of thermal paper products to meet the diverse needs of our clients. Here's a breakdown of the different types of thermal paper:
Standard Thermal Paper
Used in most receipt printers and POS systems.
Ideal for short-term use as it tends to fade over time when exposed to light or heat.
Top coated Thermal Paper
Has an additional coating to protect the print from fading.
Ideal for applications that require longer-lasting prints like shipping labels and tickets.
Black Thermal Paper
Features a black color as opposed to the standard white or cream.
Often used in specialty printing like high-end tickets or custom receipts.
Eco-friendly Thermal Paper
Coated without harmful chemicals like BPA.
A great option for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
Why is Thermal Paper So Popular?
Thermal paper is widely used in various industries for several reasons:
Efficiency: Thermal printers are fast and require no ink, making them cheaper to maintain.
Cost-Effective: The simplicity of thermal printing cuts down on the costs of ink cartridges, toners, and ribbons.
Durability: Thermal paper prints are resistant to smudging, and the print quality remains clear under normal use (though it can fade if exposed to excessive light or heat).
Space-Saving: With no ink or toner cartridges, thermal printers are often more compact, making them ideal for smaller spaces.
How Does Thermal Paperwork?
Thermal paper has a special heat-sensitive coating that reacts when exposed to the heat generated by a thermal printer’s print head. As the print head heats up specific areas of the paper, the chemicals in the coating turn black, creating the printed image or text.
Tips for Choosing the Right Thermal Paper
When selecting thermal paper for your business, it's important to consider the following factors:
Printer Compatibility: Ensure that the thermal paper rolls fit your printer’s specifications (e.g., size, diameter).
Print Duration: If you need prints that last longer, opt for top-coated thermal paper or eco-friendly options.
Environmental Considerations: Look for BPA-free thermal paper if sustainability is important to your business.
At Parthivi Labels and Paper, we specialize in high-quality, BPA-free thermal paper options that are perfect for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental footprint without compromising quality.
How to Store Thermal Paper
Proper storage is essential to maintain the quality of your thermal paper. To keep your paper in the best condition:
Store rolls in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture.
Avoid exposure to chemicals like cleaning agents or oils.
Keep thermal paper rolls in their original packaging until you're ready to use them.
Conclusion: Why Choose Parthivi Labels and Paper?
At Parthivi Labels and Paper, we are committed to providing top-quality thermal paper solutions that meet the needs of various industries. From receipt paper to custom labels, we have the products that can help your business run smoothly. Plus, our eco-friendly and BPA-free thermal papers are a great choice for businesses looking to make sustainable choices.
Ready to get started? Visit our website today and discover our range of high-quality thermal paper products that can help streamline your business operations. https://www.parthivilabelsandpapers.in/
Explore our full range of thermal paper products at Parthivi Labels and Paper. Reach out today to learn more or get personalized recommendations for your business!
#ThermalPaper #Labels #Receipts #Printing #BusinessSupplies #BPAFree #Sustainability #ParthiviLabels
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
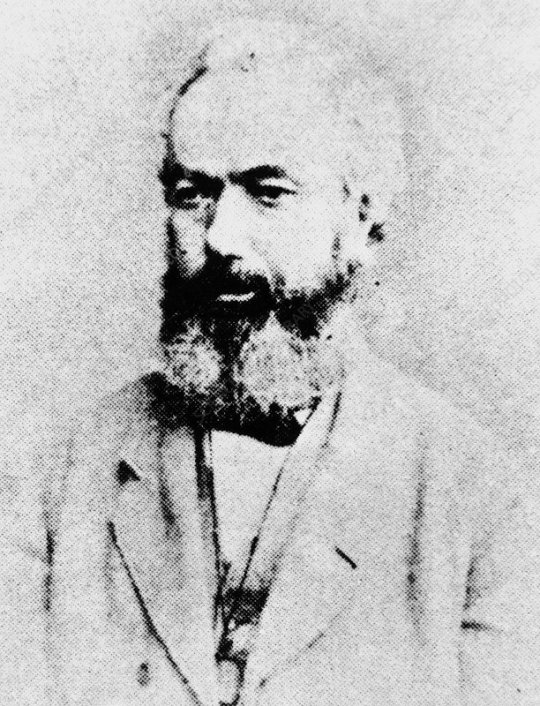





On January 2nd 1877 Alexander Bain, the Scottish inventor died at Kirkintilloch.
Bain was one of the most prolific inventors of the 19th century, and is one of the least remembered. His inventions are all the more remarkable given his background.
"When the lecture was over, and the audience were leaving, a few gentlemen accompanied the lecturer, and conversed with him on the subjects of the lecture. There was a humble lad walking behind them, and listening attentively to what was said … he never forgot the lecture, nor the subsequent conversation.”
After nearly seven years of clockmaking apprenticeship, he left the north of Scotland, briefly for Edinburgh, and then London.
Working in London, Bain went to evening lectures and saw some impractical clocks that used static electricity to maintain the swing of the pendulum. He thought he could do better. By the middle of 1840 he had made a clock powered by electric current, as well as a ‘printing telegraph’. He also thought “to make a common clock transmit its time to other distant clocks…” In Bain’s first electric clock, the pendulum bob was an electromagnet swinging between two permanent magnets. In his ‘printing telegraph’, the character for transmission was selected by stopping a moving pointer at the correct location on a labelled disc. In the receiver, the printing type-wheel was rotated into position by a clock escapement released by an electromagnet, one tooth at a time, by the appropriate number of received electrical pulses.
Bain displayed his electric clock at the Polytechnic Institution, and with John Barwise, a chronometer maker, and they applied for a patent in October 1840. The next month, Charles Wheatstone, professor of physics at King’s College London, demonstrated an electric clock to the Royal Society, claiming to have invented it. Bain’s patent, ‘Improvements in the Application of driving power to Clocks and Time Pieces’ was granted in January 1841, and a furious public dispute ensued.
Bain’s cause was supported by many, including John Finlaison (a Treasury civil servant, and Actuary of the National Debt.) By coincidence, Finlaison hailed from Thurso, and had been impressed by a demonstration of Bain’s printing telegraph:
It wasn't only the electric clock he is famous for, he then worked on an experimental facsimile machine in 1843 to 1846/ He used a clock to synchronise the movement of two pendulums for line-by-line scanning of a message. For transmission, Bain applied metal pins arranged on a cylinder made of insulating material. An electric probe that transmitted on-off pulses then scanned the pins. The message was reproduced at the receiving station on electrochemically sensitive paper impregnated with a chemical solution similar to that developed for his chemical telegraph. In his patent description dated 27 May 1843 for “improvements in producing and regulating electric currents and improvements in timepieces, and in electric printing, and signal telegraphs,” he claimed that “a copy of any other surface composed of conducting and non-conducting materials can be taken by these means”. This was way ahead of his time!
In 1844 Bain had married Matilda Bowie, the widowed sister-in-law of his greatest champion, John Finlaison, and moved his business to Edinburgh. He and his wife had five children to add to Matilda’s daughter from her first marriage.
Bain won a contract from the Glasgow and Edinburgh Railway to construct a telegraph line along their route, 46 miles long. The price quoted was £50 per mile; Cooke and Wheatstone were charging the Great Western Railway £250 per mile. Finlaison loaned £3,000 to the project and the finished system proved the capability of time distribution, with the master electric pendulum clock in Edinburgh transmitting to a "slave" clock in Glasgow.
It wasn't all plain sailing for the intrepid Scot, he traelled to America with his "electric telegraph" plans, but Samuel Morse had already built a telegraph between Baltimore and Washington D.C so was ahead in the game. After applying for a patent Morse challenged him in the courts, saying his patents already covered what Bain had laid out, it went all the way to the suoreme courts and Morse won, although the unimplemented patent claims of Morse were rejected, this was scant comfort to Bain, who left America and had to file for bankrupcy back home, the cost of his failed venture in the Americas cost him dearly.
Bain ended up pretty much back where he started, working for a watchmaker in Glasgow, repairing clocks for a living. One of his customers was the University’s William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) who recognised Bain’s genius and his plight. Thomson arranged a grant of £150 from the Royal Society, and successfully petitioned the Gladstone government to award Bain a Civil List pension of £80 per year.
Bain died on this day in 1877, cheated of fame and fortune by bad luck and poor choices. Aside from electric clocks and the chemical telegraph, he patented many other inventions, including a fire alarm; a marine depth sounder; a system for recording ships’ direction and speed at sea; a device for producing punched tape and a piano for playing the tape remotely; a current regulator for voltaic cells; a drinking fountain tap operated by pressing the receptacle on a lever, and perhaps too fondly, a device for drawing a measure of liquid from a container, similar to a bar optic for spirits.
Alexander Bain is buried in the Auld Aisle Cemetery, Kirkintilloch.
A Wetherspoons pub in Wick, close to where Alexander Bain served his apprenticeship, is now named after the inventor, it is also the most northerly Wetherspoons in the country. Also, as a tribute to his inventions, the main BT building in Glasgow is named Alexander Bain House.
There is also a commemorative plaque to Bain at his former workshop on Hanover Street in Edinburgh as seen in the pics.
As usual; I have slimmed this account of Bain's life down, if you want to read the full story check out this link https://www.slhf.org/sites/default/files/publications/slhf12_alexanderbain.pdf
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Barcode Definition: 5 Types & Common Applications You Should Know

In today’s digital-first business landscape, speed and accuracy are no longer optional—they're essential. Barcodes are one of the simplest yet most powerful technologies that help companies track, manage, and optimize inventory. Understanding the barcode definition in 2025 is vital for businesses aiming to boost productivity, streamline processes, and reduce errors. At AIDC Technologies India, we empower businesses with the right barcode solutions that fit industry-specific needs.
What is a Barcode? A Simple Barcode Definition
The barcode definition refers to a machine-readable visual representation of data that is typically used to identify and manage products, items, or assets. A barcode is made up of a series of black and white lines or patterns that store information such as product codes, serial numbers, or pricing.
When scanned using a barcode reader, the information is instantly retrieved and processed by a software system. This simple yet powerful technology is used in everything from grocery billing to industrial warehouse management. At AIDC Technologies India, we help businesses apply the barcode definition in real-world environments with customized solutions.
Components of a Barcode System: From Scanners to Software
To understand the practical application of the barcode definition, you need to know the main components of a barcode system:
Barcode Labels – Printed tags or stickers containing barcodes.
Barcode Scanners – Devices that read the barcode and capture the information.
Software – Systems that process and organize barcode data.
Printers – Tools used to generate barcode labels for different items.
AIDC Technologies India provides complete barcode systems—integrating hardware and software to create end-to-end tracking and identification solutions. Our offerings ensure seamless operation and high accuracy.
5 Types of Barcodes You Should Know
Understanding the barcode definition means recognizing the different types of barcodes and their specific uses. Here are five popular barcode types used widely in 2025:
UPC (Universal Product Code): One of the most recognized barcode types, used mainly in retail for identifying products at checkout.
QR Code (Quick Response Code): A 2D barcode that stores more data, including URLs, contact details, and payment info—commonly used in marketing and mobile apps.
Data Matrix: A compact 2D barcode used in healthcare, electronics, and manufacturing for marking small items and components.
PDF417: A stacked linear barcode that can store large amounts of data, often used in identification cards and travel documents.
Code 128: A high-density barcode ideal for logistics and shipping labels where space is limited but data needs to be precise.
AIDC Technologies India helps clients choose the most appropriate barcode type based on their industry, product, and operational needs.
Real-World Applications of Barcodes Across Industries
The barcode definition is best understood when you see how it works in real business environments. Here are key industry applications:
Retail: Barcodes enable fast checkout, accurate billing, and real-time inventory updates.
Healthcare: Used for patient ID, tracking medication, and managing medical supplies.
Logistics and Warehousing: Ensures precise inventory control, package tracking, and delivery verification.
Manufacturing: Tracks raw materials, components, and final products across the supply chain.
Education and Libraries: Helps track books, student materials, and assets in schools and universities.
At AIDC Technologies India, we design barcode systems to fit each industry’s specific requirements, ensuring compliance, accuracy, and operational ease.
Benefits of Barcode Technology for Businesses
Adopting the barcode definition into daily operations comes with multiple advantages:
Accuracy: Reduces manual errors during data entry.
Speed: Instant scanning improves customer service and operational efficiency.
Inventory Control: Provides real-time visibility into stock levels.
Cost Savings: Minimizes waste, reduces losses, and saves on labor.
Traceability: Enables complete tracking of products from source to delivery.
Our clients at AIDC India experience these benefits firsthand through custom-tailored barcode implementation strategies that enhance both scalability and efficiency.
How AIDC Technologies India Powers Barcode Solutions
AIDC Technologies India provides end-to-end support for barcode implementation, including system consultation, hardware deployment, software integration, training, and post-sale support.
We ensure that our clients not only understand the barcode definition but also experience its full power in their daily workflows. Whether you need barcode printers for product labels or scanners integrated with your ERP system, we make the process seamless. Our industry experience allows us to handle barcode projects for retail, warehousing, manufacturing, and more with high precision and scalability.
Barcode Technology Trends to Watch in 2025
The barcode definition continues to expand as technology evolves. In 2025, several key trends are influencing the future of barcode use:
Mobile Scanning: Smartphones are increasingly used for reading barcodes in retail and field operations.
Cloud Integration: Barcode systems are now cloud-enabled for real-time data access across locations.
Sustainable Labeling: Eco-friendly label materials are gaining popularity.
AI Integration: Barcode data is used to train AI for predictive analytics and smart inventory planning.
Hybrid Tracking: Combining barcodes with RFID for layered tracking and better asset management.
AIDC India stays updated with these trends to ensure our clients are equipped with future-ready barcode solutions.
Conclusion: Unlock Efficiency with AIDC's Barcode Solutions
The barcode definition may seem basic, but its impact is powerful and far-reaching. With the right barcode system in place, businesses can achieve better control, faster processes, and increased customer satisfaction. From small retail stores to massive industrial operations, barcodes play a key role in digital transformation.
AIDC Technologies India is here to support you in your barcode journey. We offer professional-grade hardware, custom software integration, and expert consulting to ensure your business gets the best results from barcode technology.
Call to Action
Looking to boost your business with barcode technology? Partner with AIDC Technologies India for reliable, scalable, and industry-specific barcode systems.
#BarcodeDefinition2025#TypesOfBarcodes#BarcodeApplications#BarcodeTechnology#BarcodeSolutions#SmartBarcodeUses#BarcodeInBusiness#AIDCBarcode
0 notes
Text
Bottle Labeling Machine: Complete Guide to Precision Product Labeling

What is a Bottle Labeling Machine?
A bottle labeling machine is an automated or semi-automated system used to apply labels onto bottles of various shapes and sizes—round, flat, oval, or square. These machines are engineered for high accuracy, speed, and uniformity, significantly reducing labor costs and errors associated with manual labeling.
Whether it's a wrap-around label on a soda bottle or a front-and-back label on a shampoo container, these machines handle it all with seamless efficiency.
Types of Bottle Labeling Machines
1. Manual Bottle Labeling Machines
Ideal for small-scale or home-based operations
Hand-cranked or foot-pedal operated
Low investment, minimal automation
2. Semi-Automatic Bottle Labeling Machines
Operator places the bottle, and the machine handles the labeling
Perfect for startups and small to mid-sized businesses
Compatible with wrap-around, single-side, and double-side labels
3. Fully Automatic Bottle Labeling Machines
Bottles are fed and labeled automatically on conveyors
Suitable for high-speed production lines
High output, precise alignment, reduced labor needs
4. Rotary Labeling Machines
Designed for ultra-high-speed lines
Uses a carousel system to label multiple bottles simultaneously
Often used in beverages, pharma, and cosmetics industries
5. Shrink Sleeve Labeling Machines
Applies shrink labels using heat tunnels for 360° branding
Common in juice, soft drinks, and energy drink packaging
Applications of Bottle Labeling Machines
Food & Beverage Industry
Juices, mineral water, milk, sauces, syrups, oils, alcohol
Date coding, branding, and compliance labels
Pharmaceuticals
Tablets, syrups, liquid drugs
Includes batch number, expiry date, and dosage information
Cosmetics & Personal Care
Shampoos, conditioners, lotions, perfumes
Requires visually appealing labels to reflect brand identity
Chemicals and Agro-Products
Fertilizers, pesticides, cleaning products
Requires resistant, long-lasting adhesive labels
Core Features of Advanced Bottle Labeling Machines
1. High Labeling Speed
Capable of labeling 20 to 300 bottles per minute, depending on model and label type.
2. Accuracy and Precision
Label placement tolerance as low as ±1 mm, ensuring professional appearance.
3. Label Sensor System
Automatically detects label gaps and bottle positions to prevent misalignment.
4. Adjustable Conveyor System
Compatible with a wide range of bottle sizes and shapes.
5. Integrated Coding Devices
Allows real-time printing of batch numbers, barcodes, and expiry dates.
6. PLC and Touchscreen Control
Easy programming, operation, and error diagnostics through HMI systems.
Benefits of Using a Bottle Labeling Machine
Enhanced Branding: Professionally applied labels elevate product appeal
Time-Saving: Speeds up production lines exponentially
Reduced Human Error: Increases labeling accuracy and consistency
Compliance Assurance: Meets global labeling standards (FDA, FSSAI, EU)
Versatility: One machine can handle different bottle types and label formats
Low Operational Costs: Cuts labor costs while boosting throughput
0 notes
Text
Find top Print Apply Labeling Systems manufacturers in the UK offering reliable, automated labeling solutions for various industries. Enhance packaging efficiency with precision-engineered machines designed for speed, accuracy, and durability. Suitable for warehouses, logistics, and production lines.
0 notes
Text
Water Based Inks for Flexographic Printing: Eco-Friendly and Efficient Solutions
In today’s rapidly evolving printing industry, sustainability and efficiency have become top priorities for manufacturers and brands alike. Among the many innovations transforming the sector, water-based inks for flexographic printing stand out as a leading eco-friendly and high-performance option that delivers exceptional print quality while reducing environmental impact.
This blog explores everything you need to know about water-based inks in flexographic printing — from their benefits and applications to why choosing a trusted supplier can make a crucial difference in your printing projects.
What Is Water Based Inks for Flexographic Printing?
Flexographic printing, commonly known as flexo printing, is widely used for packaging, labels, and other large-volume print jobs due to its speed and versatility. Traditionally, flexo printing relied heavily on solvent-based inks, which, despite their effectiveness, contribute significantly to VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions.
Water based inks, as the name suggests, use water as the primary solvent instead of harsh chemicals. These inks are specially formulated to provide vibrant colors, excellent adhesion, and fast drying times compatible with the flexo process — all while being much safer for workers and the environment.
Key Benefits of Water Based Inks for Flexographic Printing
Eco-Friendly and Low VOC Emissions
Water based inks drastically reduce VOC emissions, making them an environmentally responsible choice that aligns with stricter global regulations and corporate sustainability goals.
Superior Print Quality
Advances in ink chemistry ensure that water-based inks provide sharp images, consistent color reproduction, and strong adhesion across a wide variety of substrates.
Improved Workplace Safety
With reduced exposure to harmful solvents, workers enjoy a safer environment with fewer health risks.
Cost-Effective Production
Reduced need for complex ventilation and solvent recovery systems translates to lower operational costs.
Wide Application Range
Suitable for printing on paper, films, foils, and various packaging materials.
Common Applications of Water Based Flexographic Inks
Water based inks are widely used in:
Food and beverage flexible packaging
Labels and tags
Shopping bags and paper sacks
Wrappers and cartons
The versatility and safety profile make them especially popular in industries where direct food contact regulations apply.
Why Partner with a Professional Supplier?
Transitioning to water-based inks requires expert guidance to ensure seamless integration with existing flexographic printing equipment and processes. Selecting the wrong ink formulation can lead to issues such as poor adhesion, slow drying, or color inconsistency.
How We Support Your Sustainable Printing Goals
Our commitment extends beyond product supply. We help your business:
Meet environmental compliance and sustainability targets
Improve print quality and production efficiency
Minimize waste and reduce operational costs
Stay ahead of industry trends with cutting-edge ink technologies
By partnering with us, you gain a reliable supplier dedicated to helping your printing operations succeed both economically and environmentally.
Final Thoughts
Water based inks for flexographic printing represent a powerful combination of eco-consciousness and print excellence. By adopting these inks, you not only reduce your environmental footprint but also improve workplace safety and operational efficiency.
0 notes
Text
Everything You Need to Know About a UV DTF Printer: The Future of Custom Printing
In today’s fast-evolving printing industry, UV DTF printers are making a bold statement. With the ability to print directly on a wide variety of surfaces without the need for heat transfer or weeding, these innovative machines are revolutionizing how we think about custom design and branding. If you're a business owner, designer, or print enthusiast, learning about UV DTF printers could be your next big step forward.
What is a UV DTF Printer? A UV DTF (Direct to Film) printer is a cutting-edge printing device that uses ultraviolet (UV) light to instantly cure ink printed onto a special film. The printed film is then transferred directly to hard or irregular surfaces like glass, wood, metal, acrylic, ceramics, leather, and plastic. Unlike traditional DTF printing used mostly for fabric, UV DTF printers cater to more rigid and varied surfaces, making them ideal for personalized items and promotional products.
How Does a UV DTF Printer Work? The UV DTF printing process typically involves three layers:
Color Ink Layer – The design is first printed in CMYK colors.
White Ink Layer – A white ink layer follows to enhance vibrancy and allow printing on dark or transparent surfaces.
Gloss or Varnish Layer – This layer gives your design a polished and durable finish.
Once printed, the film is applied with transfer adhesive and peeled off, leaving the design cleanly adhered to the target surface.
Key Features of UV DTF Printers Instant UV curing: No drying time needed.
Versatile Surface Compatibility: From mugs and phone cases to glass and wood.
No Weeding: Unlike vinyl cutting, there's no need to weed excess material.
High Durability: Scratch-resistant, waterproof, and UV-resistant.
High-Resolution Output: Excellent print clarity and color saturation.
Benefits of Using a UV DTF Printer
Expand Your Product Line
With a UV DTF printer, businesses can offer personalized products that were previously hard to customize. This includes:
Customized tumblers and mugs
Acrylic keychains
Personalized phone cases
Wooden plaques and gifts
Branded glassware
Cost-Effective for Small Runs
Traditional screen printing or pad printing is expensive for small quantities. A UV DTF printer allows you to do one-off prints or small batch runs with minimal waste and setup.
No Heat Required
One of the standout features is the no-heat application. Unlike sublimation or standard DTF printing that requires heat presses, UV DTF relies on UV light and adhesive, making it safer and faster.
Environmentally Friendly
UV-curable inks are more eco-friendly than solvent-based inks, producing fewer VOCs and requiring no water for cleanup.
Who Can Benefit from a UV DTF Printer?
Small Businesses & Entrepreneurs Etsy sellers, custom gift shops, and local printing services can all benefit from the versatility and low-cost operation of a UV DTF printer.
Branding Agencies Create branded promotional items such as logo-printed merchandise without needing multiple machines.
Artists & Designers Print unique artwork on unconventional surfaces like wood blocks or acrylic sheets for home décor and art installations.
Industrial Applications Even industries like automotive, packaging, and signage find UV DTF useful for labeling and customization on curved or textured surfaces.
UV DTF Printer vs. Other Printing Technologies Technology Best For Requires Heat Weeding Surface Types UV DTF Printer Hard & irregular items No No Glass, wood, plastic Regular DTF T-shirts & fabrics Yes No Soft materials Sublimation Polyester fabrics Yes No Fabric, coated items Vinyl Cutting Stickers & labels Sometimes Yes Limited
Things to Consider Before Buying a UV DTF Printer
Print Size Capacity Choose a printer based on the size of items you plan to print. Some models support A4 or A3 sizes, while industrial-grade printers can handle much larger surfaces.
Ink System and Refills Make sure the printer uses reliable and readily available UV inks. Some printers come with bulk ink systems that are more economical over time.
Software Compatibility Check whether the printer is compatible with your design software like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW, and supports common file formats like PNG, SVG, or PDF.
Maintenance Requirements Like all printers, UV DTF machines need regular maintenance. Look for models that offer easy access to parts and have available technical support.
Top UV DTF Printer Brands in the Market Here are a few reliable brands known for UV DTF printing:
Lopo UV DTF Printers – Ideal for small businesses with beginner-friendly features.
A3 Pro UV DTF Printer – Offers high resolution and built-in laminating.
ComColor UV DTF Machines – Industrial grade, suitable for bulk production.
Final Thoughts The UV DTF printer is a game-changer for the world of customized printing. Whether you're starting a new business or expanding your current product offerings, this technology offers flexibility, affordability, and high-quality output that traditional methods simply can't match.
As demand for personalization grows across industries, investing in a UV DTF printer can help you stay ahead of the curve—and create products that wow your customers.
0 notes
Text
Save Time and Money With These Essential Moving Supplies
A successful move doesn’t start on moving day—it starts with the right supplies.
Without the proper tools, you could end up wasting hours, damaging your belongings, or overspending.
This complete guide to moving supplies will help you stay on track, protect your valuables, and stick to your budget.
Boxes Aren’t Just Boxes—Choose Wisely
Not all boxes are created equal. Standard moving boxes come in different sizes and strengths, and using the right one can save space and prevent damage.
Use small boxes for heavy items, such as books, and larger boxes for lighter goods, like bedding or clothes.
You can often find free boxes from local retailers or recycling groups, making this one of the most budget-friendly packing tools for any move.
Invest in a few specialty boxes, such as wardrobe boxes or dish packs, if you want to protect fragile or bulky items.
Label, Color-Code, and Stay Organized
One of the biggest time-savers is a proper labeling system. Write the room name and contents on every box, or better yet, color-code using tape or stickers.
This strategy helps movers (or friends) place boxes in the correct rooms, reducing confusion and speeding up the process.
It’s one of the most overlooked time-saving moving essentials, yet it makes a huge difference on moving day.
Consider printing out a checklist to stay organized and avoid missing any essential supplies. This is a simple but effective way to apply a complete guide to moving supplies in real time.
Protective Materials Make All the Difference
Wrap fragile items, such as dishes, glasses, and electronics, in bubble wrap or packing paper.
If you’re on a tight budget, towels, t-shirts, and newspapers work as good alternatives.
Furniture blankets, corner protectors, and stretch wrap are also smart supply choices to keep larger items safe from scratches and dents. A little protection goes a long way toward avoiding costly damage.
Tools and Dollies Keep It Efficient
You don’t need a full toolbox, but a few essentials—screwdrivers, Allen keys, scissors, and zip ties—will help you disassemble and reassemble furniture with ease.
Having these tools on hand means fewer delays and less frustration.
Rent or borrow a dolly to move heavy boxes and furniture. It protects your back and speeds up the process. These time-saving moving essentials are well worth the small investment.
Don’t Forget the Personal Touches
Think beyond the basics. Include sandwich bags for storing screws, a box cutter for quick unpacking, and clear bins for must-have items like chargers, snacks, and toiletries.
Creating a "moving day kit" with essentials can eliminate the stress of digging through boxes when you first arrive.
These smart supply choices not only keep you organized but also make settling in more enjoyable.
Final Thoughts
Every move is different, but having the right tools can make all the difference. From labeling systems to protective wraps, this complete guide to moving supplies will help you pack faster, stay organized, and save money in the process..
0 notes
Text
Who needs ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda?

What is ISO 22000?
ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda ISO 22000 is delineated as the most recognized Food Safety Management System (FSMS) standard, which is made utilizing the help of ISO. International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It applies to all the organizations that are part of that supply chain for food. It incorporates:
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) concepts
Think about it from a risk-based perspective
Process-based management
Continual improvement strategies
The objective is to limit the risk to food safety, ensure the security of food items and protect the health of those who consume them.
Why is ISO 22000 in Uganda Important?
The production of food and agricultural production powers Uganda’s economy, as well as the exports of agricultural products. However, problems like improper handling, contamination and the absence of a proper regulatory framework can hinder the growth of businesses and present serious health risks. ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda:
Assures food safety from the farm to fork
It is in line with Uganda National Bureau of Standards (UNBS) standards
Improves access to markets and export-ready
Improves customer confidence and boosts the brand’s reputation
Reduces the risk of food safety and disruptions to operations
Who Needs ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda?
1. Food and Beverage Producers: Companies that are involved in packaging drinks or the preparation of drinks and food products must adhere to ISO 22000 consultants in Uganda to ensure hygiene and control of foodborne contamination and to ensure compliance with rules. Examples:
Grain millers
Bottled water companies
Processors of juice and dairy
Processors of fish and meat
2. Food Exporters and Agro-Processors: Ugandan food exporters face a number of rigorous requirements from international buyers. ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda is usually an essential requirement for exporting their products to countries within the EU, Middle East, USA, and COMESA regions. Examples:
Exporters of tea and coffee
Processors of fruits and vegetables
Exporters of cereals and maize flour
3. Agricultural Cooperatives and Farms: Large cooperatives and farms that provide bulk food products profit from ISO 22000 by implementing traceability, handling protocols and hygiene checks. Examples:
Poultry farms
Dairy farms and livestock farms
Fisher farms, hatcheries and fish farms
Fruit plantation cooperatives
4. Food Packaging Manufacturers: The security of packaging material is essential. Companies that make food packaging designed for contact must comply with the requirements for hygiene and security guidelines for products that comply in accordance with ISO 22000. Examples:
Plastic bottles are manufactured by companies that manufacture plastic bottles.
Printing companies that print labels and cartons
Food wrapper and aluminium foil producers
5. Food Storage and Distribution Companies: ISO 22000 also applies to businesses that handle food transportation, warehouses as well, and logistical support for cold chains. Keeping the proper temperature and cleanliness, as well as controlling pests, are essential. Examples:
Cold storage warehouses
Food logistics and services for freight
Wholesale and distribution centres as well as wholesale suppliers
6. Catering Services and Restaurants: If catering to hospitals, schools, airlines, schools, or other public occasions, food catering companies and restaurants must ensure clean cooking and handling in order to prevent foodborne illness. Examples:
Hotel restaurants
Canteens at schools
Hospital catering and airline services
Fast food chains
7. Supermarkets and Retail Chains: Retailers who sell food products directly to customers must make sure that the food products they sell originate from accredited, reliable sources. ISO 22000 certification consultants in Uganda also increases the credibility of their brand. Examples:
Grocery stores and supermarkets
Online food retailers
Wholesale markets
8. Food Equipment and Chemical Suppliers: Suppliers of food-grade cleaning equipment, utensils, and production equipment should make sure that their products are compatible with the food safety requirements of their customers. Examples:
Chemical companies for sanitation
Manufacturers of food processing equipment
Water purification systems that provide purification
Benefits of ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda
Legal Compliance: Complies in accordance with local legislation as well as international guidelines on food safety.
Market expansion: Vital to gain access to the export market and in working supply chains across the globe.
Customer trust: It demonstrates an unwavering dedication to food safety and quality control.
Risk Reduction: a method of identifying and managing food safety hazards prior to their impact on consumers.
Operational Efficiency: Standardizes the procedures for handling food, reduces waste, and increases awareness among staff.
Eligibility to tender: Aids you to be eligible for hospital, government and contract for food supplies.
Process of Getting ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda
1. Gap Analysis: Review your current practices in relation to ISO 22000 standards.
2. System Development: Develop a food safety program, HACCP plan, risk assessments, and controls.
3. Employee Training: Make sure your team is trained in the hygiene of food, critical points of control, and documenting protocols.
4. System Implementation: Implement food safety protocols across all departments as well as Supply chain outlets.
5. Internal Audit: Examine your system to ensure the system is in place and to address any deficiencies.
6. Management Review: Review audit findings and verify that you are ready for certification.
7. Certification Audit: Employ a certified ISO certification organization for an audit of the end (Stage 1. and Stage 2.).
8. Certification Issued: Acquire the ISO 22000 certification (valid for up to three years, with annual audits of surveillance).
Why Factocert for ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda
We provide the best ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda who are knowledgeable and provide the best solutions. Kindly contact us at [email protected]. ISO 22000 Certification consultants in Uganda and ISO 22000 auditors in Uganda work according to ISO standards and help organizations implement ISO 22000 certification consultants in Uganda with proper documentation.
For more information, visit ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda.
Related Link:
ISO Certification in Uganda
ISO 9001 Certification in Uganda
ISO 14001 Certification in Uganda
ISO 45001 Certification in Uganda
ISO 13485 Certification in Uganda
ISO 27001 Certification in Uganda
ISO 22000 Certification in Uganda
CE Mark Certification in Uganda
0 notes
Text
Barcode Definitions: Clear Explanations and Uses | Info in 2025

Barcodes are no longer just lines on a label. In 2025, they represent a smarter way of tracking, managing, and organizing data across industries. Barcode Definitions have evolved with technology to include both traditional linear codes and modern 2D formats like QR codes and Data Matrix. Understanding these updated Barcode Definitions helps businesses adapt, innovate, and improve day-to-day operations with ease.
What Is a Barcode? Understanding the Basics
A barcode is a visual pattern that stores data in a machine-readable form. It allows information to be quickly scanned and processed using barcode readers or smartphones. At the core of Barcode Definitions lies this concept of simplifying data input and retrieval. Whether it’s a UPC code on a product or a QR code on a billboard, each barcode tells a story the system can understand instantly.
Types of Barcodes Used in 2025
Barcode Definitions now include a wide variety of code types. One-dimensional (1D) barcodes like Code 128, EAN, and UPC are common in retail and logistics. Two-dimensional (2D) codes like QR codes, PDF417, and Data Matrix can store more complex data such as URLs, documents, or user credentials. Each of these barcode types serves a specific purpose and offers unique advantages in readability, capacity, and space usage.
How Barcode Technology Works
When a barcode is scanned, the pattern of lines or squares is interpreted into data by a barcode reader. This process includes detecting the barcode, decoding it, and sending the information to a connected system. Barcode Definitions involve not just the printed symbol but the entire workflow — from printing to scanning to data integration. This seamless communication saves time, reduces errors, and improves productivity.
Key Applications of Barcodes Across Industries
From retail checkouts to hospital equipment tracking, Barcode Definitions apply to countless real-world uses. In warehouses, barcodes help manage inventory. In transport, they assist in package tracking. In healthcare, barcodes on patient wristbands ensure proper medication administration. Each industry relies on the clarity and precision of Barcode Definitions to operate safely and efficiently.
Benefits of Using Barcode Technology in Modern Businesses
Barcode systems offer more than just convenience. They bring structure, reduce manual effort, and support real-time monitoring. Barcode Definitions help businesses minimize errors, improve speed, and track assets or goods with greater accuracy. As a result, businesses save money, improve workflow efficiency, and gain visibility over their operations.
Barcode vs QR Code: What’s the Difference in 2025?
While both are part of Barcode Definitions, traditional barcodes and QR codes are used in different ways. A linear barcode stores less information but is great for product labels and shelf tags. A QR code holds much more data and is better suited for mobile apps, payments, and online interactions. The choice depends on what type of data you want to store and where it will be used.
Emerging Trends in Barcode Systems
Barcode Definitions are expanding to include newer technologies like mobile barcode scanning, digital barcodes, and AI-based analytics. Businesses are now using barcodes for contactless transactions, warehouse automation, and even customer engagement. Smart labels that update in real-time and IoT-integrated scanning systems are also on the rise, making barcodes more powerful and adaptable than ever before.
AIDC Technologies India’s Expertise in Barcode Solutions
AIDC Technologies India has been a trusted provider of barcode solutions across sectors like retail, logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare. With years of experience in customizing Barcode Definitions to client needs, AIDC offers hardware, software, and consulting services that are reliable and future-ready. Whether you need basic barcode printing or full system integration, AIDC ensures you have the right tools for success.
How to Choose the Right Barcode System for Your Needs
Not all barcodes are created equal. Your business needs determine which format, scanner, or software is ideal. Barcode Definitions help guide the selection process. For example, if you're in retail, you may need high-speed scanners and thermal printers. For warehouse environments, durability and scanning range become important. AIDC Technologies India offers expert consultation to help you make the best choice.
Barcode Integration with Business Software
A modern barcode system should not function in isolation. It must work smoothly with your inventory software, ERP, or point-of-sale system. Barcode Definitions today include how barcodes interact with these platforms. Integration allows for real-time inventory updates, automated billing, and enhanced reporting. AIDC India helps clients connect barcode hardware with the software they already use.
Inventory Management with Barcode Systems
Managing stock is simpler and more accurate with barcodes. Barcode Definitions in inventory involve assigning codes to every product or asset, making it easy to track movement, count stock, and prevent loss. Automated systems reduce human error and enable businesses to make data-driven decisions. AIDC Technologies India specializes in building smart inventory solutions powered by barcode technology.
Ensuring Barcode Standards and Compliance
Using barcodes means following global standards such as GS1 or ISO/IEC to ensure compatibility and readability. Barcode Definitions must comply with these rules, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and food where traceability is critical. AIDC India helps businesses create and maintain barcodes that meet regulatory and operational standards.
Custom Barcode Labeling Services by AIDC India
Every industry has unique labeling needs. That’s why AIDC India offers custom barcode label printing services. Whether it’s waterproof labels, tamper-evident tags, or labels for high-temperature environments, AIDC creates labels that align with the right Barcode Definitions and business requirements. These labels ensure accuracy and durability in even the toughest conditions.
Why AIDC India Leads in Barcode Innovation in 2025
AIDC Technologies India continues to lead in offering high-performance barcode solutions that grow with your business. With a strong focus on innovation, support, and integration, AIDC tailors each solution based on updated Barcode Definitions. Their barcode systems empower businesses to operate with speed, control, and confidence in 2025 and beyond.
Call to Action Looking to upgrade your barcode systems for 2025? Partner with AIDC Technologies India for reliable, scalable, and industry-specific barcode solutions.
#BarcodeDefinitions2025#BarcodeTechnology#SmartBarcodeUses#BarcodeInBusiness#AIDCBarcodeSolutions#BarcodeTracking#BarcodeScanning#InventoryManagement2025#RetailTechTrends#BarcodeAutomation
0 notes