#Prognostics and Health Management
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Diabetes
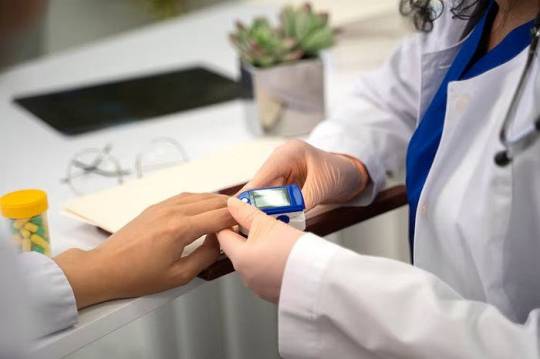
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, arises from abnormalities in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The condition’s prevalence has reached epidemic proportions globally, with significant health, economic, and social implications.
Types of Diabetes
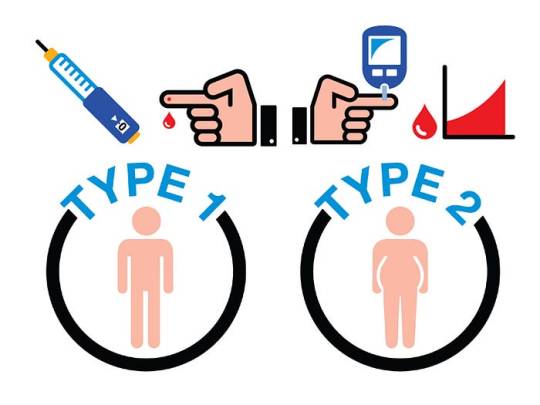
Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune disease results from the destruction of pancreatic beta cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Genetics and environmental triggers play pivotal roles in its pathogenesis. Despite being less common than Type 2 diabetes, its onset during childhood or adolescence significantly impacts individuals’ lives.
Type 2 Diabetes: Predominantly a disorder of insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes accounts for the majority of diabetes cases worldwide. Lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and obesity contribute to its development. Its insidious onset often leads to delayed diagnosis and increased risk of complications.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurring during pregnancy, gestational diabetes poses risks to both maternal and fetal health. Hormonal changes and insulin resistance characterize its pathophysiology. Effective screening and management are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes.
Other Types of Diabetes: Variants like MODY, LADA, and secondary diabetes present unique challenges in diagnosis and management, requiring tailored approaches to care.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Diabetes prevalence varies across demographics, with disparities observed in age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. The escalating burden of diabetes underscores the urgent need for targeted prevention and management strategies.
Symptoms and Causes
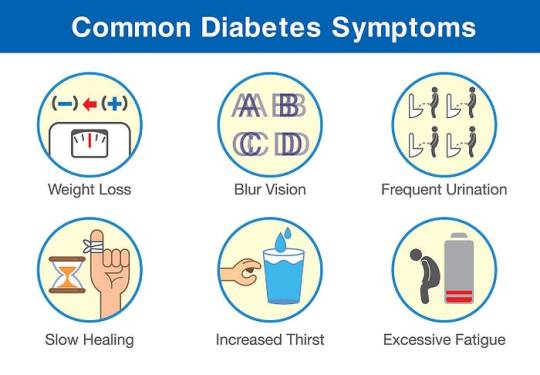
Hyperglycemia-induced symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, and unexplained weight loss serve as clinical indicators for diabetes diagnosis. Understanding the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors elucidates the condition’s etiology.
Complications
Diabetes complications encompass a spectrum of microvascular and macrovascular disorders, significantly impacting quality of life and life expectancy. From diabetic retinopathy to cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and diabetic foot complications, the ripple effects of uncontrolled diabetes are profound.
Diagnosis and Tests
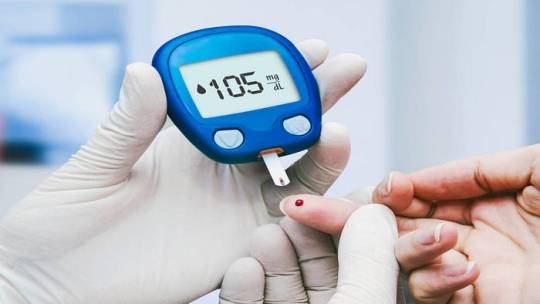
Accurate diagnosis relies on comprehensive evaluation, including fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance tests, and hemoglobin A1c measurements. Screening recommendations aim to identify at-risk individuals early, facilitating timely intervention and risk reduction.
Management and Treatment
Diabetes management strategies encompass pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, patient education, and multidisciplinary care. Individualized treatment plans address glycemic control, blood pressure management, lipid optimization, and prevention of complications.
Prevention
Prevention initiatives target modifiable risk factors through health promotion, public health interventions, and community engagement. Emphasizing the role of nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral changes empowers individuals to mitigate their diabetes risk.
Outlook and Prognosis
Prognostic factors such as glycemic control, adherence to therapy, comorbidity burden, and psychosocial support influence long-term outcomes. Enhanced collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential to improve diabetes prognosis globally.
Living With Diabetes

Coping with diabetes requires resilience, self-management skills, and social support networks. Empowering individuals through education, self-monitoring tools, and peer support enhances their capacity to navigate the challenges of daily diabetes management.
Impact on Individuals and Society
Diabetes exerts a profound socioeconomic burden, encompassing healthcare costs, productivity losses, and reduced quality of life. Addressing the psychosocial dimensions of diabetes care is integral to fostering holistic well-being and societal resilience.
Future Directions and Research

Advancements in diabetes research, including precision medicine, digital health technologies, and novel therapeutics, offer promising avenues for disease management and prevention. Collaborative research endeavors aim to translate scientific discoveries into tangible clinical benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes represents public health challenge necessitating a comprehensive, patient-centered approach. By fostering awareness, promoting early detection, and advancing evidence-based interventions, we can mitigate the impact of diabetes on individuals, families, and communities worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at [email protected]��for assistance.
#assignment help#healthcare#medical students#nursing student#nursing school#medical school#medical student#medicine#health tips#health and wellness#health#health & fitness#diabetes#diabetic#medical help#medical assistance#pharmacy student#pharmacy technician#homework help#academic assignments#expert assignment writers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Quantum Computing in Kidney Disease Research: Revolutionizing Medical Data Analysis and Predictive Health Modeling
Quantum computing represents a groundbreaking advancement in computational power, poised to transform kidney disease research by enabling the analysis of complex medical data and enhancing predictive health modeling. Exploring Quantum Computing in Kidney Disease Researchreveals how these advanced computational techniques can accelerate breakthroughs in nephrology.
Advanced Computational Techniques in Kidney Research
Unlike traditional computers, quantum computers leverage quantum bits (qubits) to process vast amounts of data simultaneously. This capability offers:
Efficient Handling of Big Data: Analyzing large-scale genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic datasets related to kidney disease with unprecedented speed.
Complex Pattern Recognition: Identifying subtle correlations and biomarkers that elude classical computing methods.
Optimization Problems Solving: Enhancing algorithms for drug discovery, treatment planning, and resource allocation.
Simulation of Biological Systems: Modeling kidney molecular interactions and disease pathways at the quantum level.
These techniques enable deeper insights into kidney disease mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Complex Medical Data Analysis Empowered by Quantum Computing
Kidney disease research involves multifactorial data from diverse sources. Quantum computing facilitates:
Integration of Heterogeneous Data: Combining clinical, genetic, environmental, and imaging data for comprehensive analysis.
Real-Time Data Processing: Accelerating data throughput to support timely clinical decision-making.
Error Reduction: Quantum algorithms improve accuracy in predictive models by minimizing computational noise.
Personalized Medicine Insights: Tailoring prevention and treatment strategies based on highly detailed patient data.
This advanced analysis drives precision nephrology forward.
Predictive Health Modeling for Kidney Disease Outcomes
Quantum computing enhances predictive models by:
Machine Learning Enhancement: Powering quantum machine learning to classify disease stages and forecast progression.
Risk Stratification: Early identification of high-risk patients through sophisticated pattern analysis.
Treatment Response Prediction: Anticipating individual patient responses to therapies for optimized care.
Resource Optimization: Guiding healthcare system planning through predictive analytics.
Such modeling improves prognosis and patient management.
Benefits of Quantum Computing in Kidney Disease Research
Embracing Quantum Computing in Kidney Disease Research offers:
Accelerated discovery of novel biomarkers and drug targets.
Enhanced accuracy of diagnostic and prognostic tools.
Personalized treatment regimens informed by comprehensive data.
Facilitated collaboration across interdisciplinary research teams.
Final Thoughts
Quantum computing stands to revolutionize kidney disease research by unlocking the potential of advanced computational techniques, complex medical data analysis, and predictive health modeling. As this technology matures, partnering with specialized kidney research institutes can ensure integration of quantum-powered innovations into nephrology, enhancing patient outcomes and fostering cutting-edge scientific progress.
#KidneyHealth#KidneyCare#KidneyDisease#KidneyDiseaseTreatment#KidneyTransplant#Nephrology#NephrologyCare#ChronicKidneyDisease#KidneyWellness#KidneyAwareness#KidneySupport#KidneyHealthTips#KidneyDiseaseAwareness#KidneyHealthMatters#KidneyCareCenter#KidneyTreatment#KidneySpecialists#KidneyDiagnosis#KidneyPatientCare#HealthyKidneys
0 notes
Text
How Does Pancreatic Cancer Start? Understanding Its Origins
Pancreatic cancer begins when abnormal cells in the pancreas start to grow uncontrollably. These cells may originate in the ducts or the hormone-producing parts of the pancreas. How does pancreatic cancer start? The process usually involves genetic mutations that cause cells to divide more rapidly and avoid the body’s natural cell death mechanisms. Over time, these cells form tumors that can disrupt the pancreas’s normal functions, leading to disease progression.
Advances in Pancreatic Cancer Reasearch
Cutting-edge pancreatic cancer reasearch is crucial for improving early diagnosis and developing better treatments. Researchers focus on understanding the molecular and genetic basis of pancreatic cancer, aiming to identify biomarkers for early detection. Clinical trials are exploring new drugs, immunotherapies, and combination therapies to improve patient survival rates. These research efforts provide hope for future breakthroughs in managing this aggressive disease.
How Long Does Pancreatic Cancer Take to Develop
The timeline of tumor development varies among individuals. How long does pancreatic cancer take to develop? Typically, pancreatic cancer develops silently over several years, starting as small precancerous lesions that gradually progress to invasive cancer. Because early symptoms are often absent or nonspecific, many cases are diagnosed only after the cancer has advanced. This slow but hidden progression complicates efforts for early detection and timely intervention.
How Rare Is Pancreatic Cancer? Examining Its Incidence
Pancreatic cancer is relatively uncommon compared to other cancer types. Understanding how rare is pancreatic cancer helps contextualize its impact on public health. It accounts for about 3% of all cancers but is among the leading causes of cancer-related deaths. While less frequent, its aggressive nature and poor prognosis make it a significant concern, emphasizing the need for improved detection methods and treatments.
How Is Pancreatic Cancer Found? Diagnostic Approaches
Early detection of pancreatic cancer remains challenging due to subtle symptoms. How is pancreatic cancer found typically involves imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, and endoscopic ultrasounds to visualize tumors. Blood tests looking for specific markers like CA 19-9 can support diagnosis but are not definitive. Biopsy procedures confirm the presence of cancer cells. Detecting the disease before it spreads significantly improves treatment options and patient outcomes.
What Are the Different Pancreatic Cancer Types
Pancreatic cancer is not a single disease but includes several pancreatic cancer types. The most common form is pancreatic adenocarcinoma, which arises from the exocrine cells. Less common types include neuroendocrine tumors that originate from hormone-producing cells. Different types vary in their behavior, treatment responses, and prognosis. Proper classification is essential for tailoring therapy and providing accurate prognostic information.
Early Warning Signs of Pancreatic Cancer: What to Watch For
Recognizing the early warning signs of pancreatic cancer can be life-saving. Common early symptoms include unexplained weight loss, abdominal or back pain, jaundice, and digestive difficulties. New-onset diabetes or blood clots may also be indicators. Due to the vague nature of these signs, individuals at higher risk should consult healthcare professionals promptly when such symptoms occur, facilitating earlier diagnosis and improved management.
0 notes
Text
Global Biomarkers Market: Advancements in Biomarkers and Their Role in 11-14% CAGR Growth by 2029
The biomarkers market is expected to grow at 11-14% CAGR in the next 5 years. The increased demand for personalized medicine, the rising prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases, the growing demand for early and accurate diagnostics, advancement in biomarkers technologies, the growing importance of companion diagnostics, significant investment in R&D for developing advanced biomarkers, and growing applications of biomarkers in diagnostics are some of the key factors driving the biomarkers market.
Biomarkers are measurable indicators or characteristics that offer insights into different biological processes within the body. They are essential in disease research, as they include molecular changes that support disease diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and drug development. Key types include prognostic, predictive, pharmacodynamic, and exposure-related biomarkers, each playing a critical role in understanding and managing diverse diseases.
🔗 Want deeper insights? Download the sample report: https://meditechinsights.com/global-biomarkers-market/request-sample/
The rising impact of biomarkers in precision healthcare and research fuels its demand
Biomarkers have become indispensable in healthcare and medical research, serving as an early warning system that reveals critical insights into our health. They play a pivotal role across multiple areas of healthcare and research, including:
Early Disease Detection: Biomarkers serve as silent sentinels, enabling early diagnosis and monitoring of diseases before they become severe. This allows healthcare professionals to intervene proactively, potentially preventing the progression of conditions like cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Precision Medicine: Biomarkers are essential for identifying patient-specific disease mechanisms and predicting treatment responses. By analyzing an individual’s unique genetic and molecular profile, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans, resulting in more targeted, effective therapies with fewer side effects.
Monitoring Treatment Responses: Biomarkers provide real-time indicators of the body’s response to treatments. By tracking changes in gene expression, protein levels, or metabolic patterns, healthcare professionals can assess therapy effectiveness and make timely adjustments for optimal results.
Clinical Trials and Drug Development: With drug failure rates as high as 90%, especially for complex conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, reliable biomarkers are critical in drug discovery. In early drug development phases, biomarkers serve as measurable indicators of a treatment's impact, helping researchers identify promising candidates and streamline the often lengthy, resource-intensive clinical trial process.
Expanding applications of biomarkers in diagnostics drive market growth
The expanding applications of biomarkers in diagnostics are transforming healthcare, providing tools for early detection, personalized treatment, disease monitoring, and improved patient outcomes. As technology advances, new biomarkers are continuously being discovered, further expanding their role in diagnostics across a wide range of diseases and medical fields. While oncology (detecting early signs for better prognosis), has been a major driver of the biomarker market, the applications are expanding into other therapeutic areas, such as neurology (for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases), cardiology (for heart failure and cardiovascular risk), diabetes (for blood sugar management and offering insights into how well glucose is controlled over time), and immunology (for autoimmune disorders). Thus, this broadening scope and the increasing demand for precision medicine and early disease intervention are key factors driving the continuous growth of the biomarkers market.
Competitive Landscape Analysis
The global biomarkers market is marked by the presence of innovative and emerging market players such as Abbott Laboratories, Qiagen, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Illumina, BD Biosciences, Siemens Healthineers, Agilent Technologies, Myriad Genetics, Hologic, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Biodesix, Exact Science, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., and Roche Diagnostics, among others. Some of the key strategies adopted by market players include product innovations, investing in R&D, strategic partnerships, and collaborations.
Gain a competitive edge-request a sample report now! https://meditechinsights.com/global-biomarkers-market/request-sample/
Market Segmentation
This report by Medi-Tech Insights provides the size of the global biomarkers market at the regional- and country level from 2022 to 2029. The report further segments the market based on product and service, type, indication, application, and end user.
Market Size & Forecast (2022-2029), By Product & Service, USD Million
Consumables
Assay Kits
Reagents & Chemicals
Columns and Filters
Services
Software
Market Size & Forecast (2022-2029), By Type, USD Million
Safety Biomarkers
Efficacy Biomarkers
Predictive Biomarkers
Surrogate Biomarkers
Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers
Prognostics Biomarkers
Validation Biomarkers
Market Size & Forecast (2022-2029), By Indication, USD Million
Infectious Diseases
Cancer
Cardiovascular Disease
Neurological Disease
Immunological Disease
Other Indication
Market Size & Forecast (2022-2029), By Application, USD Million
Diagnostics
Drug Discovery & Development
Personalized Medicine
Clinical Research
Other Applications
Market Size & Forecast (2022-2029), By End User, USD Million
Hospitals & Diagnostics Laboratories
Clinical Laboratories
Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology Companies
Research & Academic Institutes
Other End Users
Market Size & Forecast (2022-2029), By Region, USD Million
North America
US
Canada
Europe
UK
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
Rest of Asia Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
About Medi-Tech Insights
Medi-Tech Insights is a healthcare-focused business research & insights firm. Our clients include Fortune 500 companies, blue-chip investors & hyper-growth start-ups. We have completed 100+ projects in Digital Health, Healthcare IT, Medical Technology, Medical Devices & Pharma Services in the areas of market assessments, due diligence, competitive intelligence, market sizing and forecasting, pricing analysis & go-to-market strategy. Our methodology includes rigorous secondary research combined with deep-dive interviews with industry-leading CXO, VPs, and key demand/supply side decision-makers.
Contact:
Ruta Halde Associate, Medi-Tech Insights +32 498 86 80 79 [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Role of a Surgical Intensivist

A surgical intensivist is a physician trained in surgery and critical care who specializes in managing critically ill surgical patients. Unlike general surgeons, they oversee life-threatening conditions before, during, and after surgery, ensuring comprehensive ICU care. Their expertise allows them to anticipate complications, manage physiological stressors, and provide advanced life support, including mechanical ventilation and precise fluid and medication management.
The responsibilities of a surgical intensivist extend beyond performing procedures. They stabilize patients with complex post-surgical needs, managing ventilation, hemodynamic monitoring, and multi-organ dysfunction. By integrating critical care principles with surgical expertise, they make time-sensitive decisions that can be life-saving. Their vigilance ensures continuous monitoring and timely treatment adjustments, reducing severe complications and improving survival rates in postoperative infections or acute organ failure.
The presence of surgical intensivists in the ICU significantly improves patient outcomes. Studies indicate that intensivist-led care models reduce mortality rates, shorten ICU stays, and optimize resource utilization. Their expertise ensures effective management of critical conditions such as sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and post-surgical infections. By quickly adapting treatment plans, they reduce hospital-acquired complications and enhance ICU efficiency while maintaining individualized care.
Collaboration is central to the work of a surgical intensivist. They function as part of a multidisciplinary team that includes anesthesiologists, internal medicine specialists, nurses, and respiratory therapists. This collective approach ensures that surgical patients receive holistic care that addresses their immediate and long-term medical needs. Their leadership in ICU rounds allows for real-time decision-making, optimizing surgical recovery and overall patient health.
Surgical intensivists also play a key role in ethical decision-making within the ICU. They help families choose life-sustaining therapies by balancing medical feasibility and patient requests. Their clarity and sensitivity in communicating complicated prognostic information ensure that patients and their families actively participate in long-term care and quality-of-life decisions.
In addition to direct patient care, surgical intensivists contribute significantly to medical education and research. They play an integral role in training surgical and critical care fellows, imparting knowledge that strengthens future physicians. Their experience managing high-acuity patients allows them to develop and refine treatment protocols, leading to advancements in the field. Integrating data-driven decision-making into their practice will enable them to continually assess and refine strategies for improving patient care, ensuring that evidence-based methods drive their interventions.
The evolution of surgical intensive care has underscored the importance of specialization in critical care medicine. With the increasing complexity of surgical procedures and a growing population of high-risk patients, the demand for surgical intensivists continues to rise. Their expertise is vital in trauma centers and academic hospitals, where patients often require advanced interventions beyond standard surgical care. The integration of intensivists into these settings has reshaped critical care, emphasizing the need for dedicated specialists who can navigate the intricate challenges of modern medicine.
Beyond immediate critical care, surgical intensivists contribute to post-ICU recovery strategies, recognizing that survival alone is not the ultimate goal. They work with rehabilitation professionals to reduce cognitive impairment, muscular atrophy, and functional deterioration. Addressing these issues early improves patient outcomes outside the ICU, easing the transition to regular life and boosting well-being.
The surgical intensivist's role remains indispensable as healthcare systems refine their critical care approaches. Their unique combination of surgical accuracy and critical care abilities enhances patient survival and rehabilitation. In addition to patient treatment, their research and teaching advance critical care medicine. Surgical intensivists in the ICU demonstrate the need for specialized, high-quality treatment for the most vulnerable patients in an era of increased scrutiny of patient outcomes.
1 note
·
View note
Text
[ad_1] To enable knowledge sharing for laboratory personnel on technological advancement and best practices made towards assessment of Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Acute Leukemia & Myeloma, BD Life Sciences-Biosciences, a segment of BD (Becton, Dickinson, and Company) organized a 2-day workshop at the Christian Medical College (CMC) Vellore. This knowledge-sharing workshop where eminent speakers from leading medical colleges and hospitals elaborated on the technical and analytical components of MRD assessment was attended by nearly 75 participants, from across the country, Philippines, and Australia. Clinicians and laboratory personnel at workshop on minimum residual disease (MRD) by BD India and CMC Vellore Commenting on the initiative, Atul Grover, Managing Director, BD India/South Asia said, “Flow cytometry has proven to be an invaluable asset in several clinical applications and can play a key role in the detection of Minimal Residual Disease. In view of this, this knowledge-sharing workshop was organized with the objective of providing a platform for laboratory personnel to access best practices and knowledge on technological advancements. At BD our aim is to bring clinical technologies to the market that help advance patient outcomes in alignment with our purpose of Advancing the World of Health.” A speaker at workshop on minimum residual disease (MRD) by BD India and CMC Vellore Minimal residual disease (MRD) is a term used to describe the small number of cancer cells in the body after cancer treatment. An MRD positive test result means that the disease was still detected after treatment. Doctors use MRD to measure the effectiveness of treatment and to predict which patients are at risk of relapse. It can also help doctors confirm and monitor remissions and possibly identify an early return of cancer. Monitoring the response to chemotherapy and the depth of remission plays a critical role in the management of patients with hematological malignancies. It is important for practicing hematopathologists to understand the prognostic and therapeutic significance of the MRD result and be aware of the advances made in this field. Flow Cytometry is a process used to sort, separate and examine microscopic particles, such as cells and chromosomes. It plays an important role in clinical diagnostics and research. BD offers a growing portfolio of flow cytometry instruments for Leukemia/Lymphoma phenotyping, stem cell research, immunology, and CD4 testing. About BD-India BD is one of the largest global medical technology companies in the world and is advancing the world of health by improving medical discovery, diagnostics, and the delivery of care. BD helps customers enhance outcomes, lower costs, increase efficiencies, improve safety, and expand access to health care. Disclaimer All content, including text, graphics, images and information etc., contained in or available through this literature is intended to be general, educational information in relation to raising awareness about minimal residual diseases and should not be construed as brand promotional in any shape, way or form. The information provided herein is not meant to be used to diagnose or treat any medical condition. For diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition, please consult your physician/doctor. Becton Dickinson India Private Limited or any of their subsidiaries, affiliates or employees are not liable for any damages/claims to any persons in any manner whatsoever. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414');
0 notes
Text
[ad_1] To enable knowledge sharing for laboratory personnel on technological advancement and best practices made towards assessment of Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Acute Leukemia & Myeloma, BD Life Sciences-Biosciences, a segment of BD (Becton, Dickinson, and Company) organized a 2-day workshop at the Christian Medical College (CMC) Vellore. This knowledge-sharing workshop where eminent speakers from leading medical colleges and hospitals elaborated on the technical and analytical components of MRD assessment was attended by nearly 75 participants, from across the country, Philippines, and Australia. Clinicians and laboratory personnel at workshop on minimum residual disease (MRD) by BD India and CMC Vellore Commenting on the initiative, Atul Grover, Managing Director, BD India/South Asia said, “Flow cytometry has proven to be an invaluable asset in several clinical applications and can play a key role in the detection of Minimal Residual Disease. In view of this, this knowledge-sharing workshop was organized with the objective of providing a platform for laboratory personnel to access best practices and knowledge on technological advancements. At BD our aim is to bring clinical technologies to the market that help advance patient outcomes in alignment with our purpose of Advancing the World of Health.” A speaker at workshop on minimum residual disease (MRD) by BD India and CMC Vellore Minimal residual disease (MRD) is a term used to describe the small number of cancer cells in the body after cancer treatment. An MRD positive test result means that the disease was still detected after treatment. Doctors use MRD to measure the effectiveness of treatment and to predict which patients are at risk of relapse. It can also help doctors confirm and monitor remissions and possibly identify an early return of cancer. Monitoring the response to chemotherapy and the depth of remission plays a critical role in the management of patients with hematological malignancies. It is important for practicing hematopathologists to understand the prognostic and therapeutic significance of the MRD result and be aware of the advances made in this field. Flow Cytometry is a process used to sort, separate and examine microscopic particles, such as cells and chromosomes. It plays an important role in clinical diagnostics and research. BD offers a growing portfolio of flow cytometry instruments for Leukemia/Lymphoma phenotyping, stem cell research, immunology, and CD4 testing. About BD-India BD is one of the largest global medical technology companies in the world and is advancing the world of health by improving medical discovery, diagnostics, and the delivery of care. BD helps customers enhance outcomes, lower costs, increase efficiencies, improve safety, and expand access to health care. Disclaimer All content, including text, graphics, images and information etc., contained in or available through this literature is intended to be general, educational information in relation to raising awareness about minimal residual diseases and should not be construed as brand promotional in any shape, way or form. The information provided herein is not meant to be used to diagnose or treat any medical condition. For diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition, please consult your physician/doctor. Becton Dickinson India Private Limited or any of their subsidiaries, affiliates or employees are not liable for any damages/claims to any persons in any manner whatsoever. !function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '311356416665414');
0 notes
Text
Essay Topic Examples - The Role of Gallstones in the Pathogenesis of Acute Pancreatitis: Explore how gallstones form and subsequently lead to acute pancreatitis. Discuss the pathophysiological mechanisms involved, the prevalence of gallstone-induced pancreatitis, diagnostic methods to detect the presence of gallstones, and treatment options available for managing this condition. - Alcohol Consumption and Its Impact on Acute Pancreatitis: Examine the association between alcohol abuse and the development of acute pancreatitis. Detail the epidemiology, the effects of alcohol on pancreatic tissue, risk factors, prevention strategies, and the socioeconomic implications of alcohol-induced pancreatitis. - Advancements in the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis: Investigate recent medical and technological advancements in the treatment of acute pancreatitis. Cover aspects such as improved diagnostic procedures, innovative therapeutic approaches, surgical interventions, and the potential benefits and drawbacks of emerging treatments. - Acute Pancreatitis: A Comprehensive Overview of Current Diagnostic Criteria: Analyze the criteria used to diagnose acute pancreatitis, including the role of clinical presentation, laboratory testing, and imaging studies. Discuss the challenges of early diagnosis and the importance of differentiating acute pancreatitis from other abdominal disorders for effective treatment. - Nutritional Management in the Care of Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: Delve into the role of nutrition in the management of acute pancreatitis. Discuss dietary considerations, the timing and mode of nutrition delivery (enteral vs. parenteral), the impact of nutrition on patient outcomes, and guidelines for reintroducing food after an acute episode. Essay Title Examples - The Pathophysiology of Acute Pancreatitis: Understanding the Inflammatory Cascade - Clinical Management Strategies for Acute Pancreatitis: An Evidence-Based Approach - Acute Pancreatitis: Risk Factors, Diagnostic Modalities, and Prognostic Indicators - Nutritional Interventions in the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis: From Theory to Practice - The Role of Endoscopic and Surgical Interventions in the Management of Acute Pancreatitis Thesis Statement Examples 1. The association between gallstones and alcohol consumption is the primary etiological factor in the onset of acute pancreatitis, suggesting a need for increased public health initiatives focused on dietary and lifestyle interventions. 2. Early aggressive fluid therapy in the management of acute pancreatitis significantly improves outcomes by reducing systemic complications and should be a cornerstone of initial treatment protocols. 3. The Ranson's Criteria remains a viable prognostic tool in the assessment of acute pancreatitis severity, aiding clinicians in identifying patients at higher risk for morbidity and mortality, and tailoring aggressive therapeutic interventions accordingly. 4. Minimally invasive surgical approaches in managing complications associated with acute pancreatitis, such as necrosectomy, offer reduced postoperative morbidity rates compared to open surgery and should be the preferred treatment modality when intervention is necessary. 5. The application of protease inhibitors in the management of acute pancreatitis has the potential to revolutionize treatment outcomes by directly targeting the pathological proteolytic activity, though further clinical trials are needed to confirm their efficacy and safety profiles. Essay Introduction Examples Introduction #1 Introduction to Acute Pancreatitis Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas, a large gland behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and insulin. This condition can be mild and self-limiting, or severe and life-threatening, depending on the extent of pancreatic damage. Acute pancreatitis is commonly caused by gallstones or excessive alcohol consumption, but other factors such as infections, trauma, certain medications, and high levels of calcium or fats in the blood can also contribute to its development. Understanding the Causes and Symptoms of Acute Pancreatitis Acute pancreatitis can be caused by various factors that lead to the activation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas, causing them to attack the tissue and trigger inflammation. The most common causes are gallstones, which can block the pancreatic duct and prevent the enzymes from flowing properly. Symptoms of acute pancreatitis include severe abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea, vomiting, fever, rapid pulse, and tenderness in the abdomen. In severe cases, complications such as pancreatic necrosis, infection, organ failure, and death can occur. Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Acute Pancreatitis Diagnosing acute pancreatitis involves a combination of physical exams, blood tests, imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs, and sometimes endoscopic procedures to examine the pancreatic duct. Treatment for acute pancreatitis focuses on relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and addressing the underlying cause. This may include hospitalization, intravenous fluids, pain medication, nutritional support, and in severe cases, surgery to remove obstructions or damaged tissue. It is crucial for individuals with acute pancreatitis to avoid alcohol, follow a low-fat diet, and take prescribed medications to manage symptoms and prevent future episodes. Introduction #2 Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Acute Pancreatitis In addition to gallstones and excessive alcohol consumption, certain lifestyle choices can also increase the risk of developing acute pancreatitis. Smoking, for example, has been identified as a risk factor for the development of this condition. Tobacco use can lead to constriction of blood vessels, reduced oxygen delivery to the pancreas, and increased inflammation, all of which can contribute to the onset of acute pancreatitis. In addition, maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the risk of this condition, as obesity is a known risk factor for pancreatitis. Complications and Prognosis for Patients with Acute Pancreatitis While most cases of acute pancreatitis resolve with proper treatment and management, some individuals may experience complications that can have long-term effects on their health. Complications of acute pancreatitis can include pancreatic pseudocysts, which are fluid-filled sacs that form on the pancreas, as well as the development of chronic pancreatitis, a condition characterized by persistent inflammation and scarring of the pancreas. Patients with severe acute pancreatitis may also be at risk of developing systemic complications such as sepsis or acute respiratory distress syndrome, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. Overall, the prognosis for patients with acute pancreatitis depends on the severity of the condition, the presence of complications, and the individual's response to treatment. Essay Body Examples Acute pancreatitis represents a swift and sudden inflammation of the pancreas, a gland situated behind the stomach that plays a pivotal role in the digestion of food and regulation of blood sugar. The condition manifests with a multitude of symptoms, with severe abdominal pain being the most prominent. It can develop from various etiologies, including gallstones, excessive alcohol consumption, or as a side-effect of certain medications. The clinical presentation of acute pancreatitis can range from a mild, self-limiting disorder to a severe, life-threatening illness that necessitates immediate medical attention. The complexity of its progression and the potential for significant morbidity and mortality make understanding its pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of utmost importance within the realms of gastroenterology and emergency medicine. Emerging trends within the study of acute pancreatitis have revealed varying patterns of its occurrence, with an incidence that appears to be increasing globally. The underlying pathogenic mechanisms are multifactorial and involve intricate interactions between the activation of digestive enzymes, inflammatory pathways, and cellular injury. The management of the disease requires a multidisciplinary approach, encompassing early recognition, supportive care, and in some cases, advanced interventional techniques. As the foundation for exploring the complexities of acute pancreatitis, this essay will delve into current understanding of its pathogenesis, the evolving paradigms in its treatment, and the ongoing efforts to improve patient outcomes through research and innovation. Essay Conclusion Examples In summary, acute pancreatitis represents a significant medical challenge characterized by the inflammation of the pancreas. The condition demands prompt recognition and intervention to mitigate the severe complications that may arise from delayed treatment. This essay has discussed the etiology of acute pancreatitis, including factors such as gallstones and alcohol abuse, underlining their contributions to the disease. Diagnostic approaches, such as imaging and serum enzyme analysis, have been explored, highlighting their role in the timely and accurate detection of the condition. Treatment strategies, encompassing both medical and surgical interventions, have been elaborated upon, with an emphasis on the importance of addressing the root causes and managing the complications. The multifaceted nature of acute pancreatitis underscores the necessity for an integrated healthcare response to ensure optimal outcomes for patients. As our understanding of acute pancreatitis continues to evolve, it is crucial that future research focuses on developing improved methods for early diagnosis and innovative treatments that can alleviate the burden of the disease. The collaboration between clinicians, researchers, and patients is pivotal in advancing our knowledge and therapeutics in the realm of acute pancreatitis. This essay urges the medical community and stakeholders to invest in education, prevention, and research initiatives aimed at curtailing the incidence and impact of this debilitating condition. Together, through concerted efforts and application of evidence-based practices, we can enhance patient care and outcomes for those afflicted with acute pancreatitis, offering a beacon of hope in the face of this painful and potentially life-threatening disease. In-Text Citation Examples In-Text Citation: Studies have recommended evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines e1-e15; Vege et al. 10991101). Sources Used: 1. Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology, vol. 13, no. 4 (Suppl 2), 2013, pp. e1e15. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063. 2. Vege, Santhi Swaroop, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology, vol. 150, no. 4, 2016, pp. 10991101. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.01.032. Primary Sources Vege, Santhi Swaroop, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology, vol. 150, no. 4, 2016, pp. 10991101. https://www.paperdue.com/customer/paper/acute-pancreatitis-2180532#:~:text=Logout-,AcutePancreatitis,-Length6pages Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology, vol. 13, no. 4 (Suppl 2), 2013, pp. e1e15. Wu, Bechien U., et al. The Early Prediction of Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis: A Large Population-Based Study. Gut, vol. 57, no. 12, 2008, pp. 16981703. Banks, Peter A., et al. Classification of Acute Pancreatitis2012: Revision of the Atlanta Classification and Definitions by International Consensus. Gut, vol. 62, no. 1, 2013, pp. 102111. Petrov, Maxim S., and Anna K. Kukosh, and Nicholas J. Emelyanov. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Enteral versus Parenteral Feeding in Patients with Predicted Severe Acute Pancreatitis Shows a Significant Reduction in Mortality and in Infected Pancreatic Complications with Total Entero Nutrition. Digestive Surgery, vol. 24, no. 5, 2007, pp. 387393, Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Market: Industry Overview and Forecast 2024-2032

According to SNS Insider, the Biomarkers Market was valued at USD XX billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD XX billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of XX% over the forecast period 2024-2031. The increasing emphasis on personalized medicine, advancements in proteomics and genomics technologies, and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders are the major factors driving market growth.
Market Description
Biomarkers are measurable indicators of a biological condition or disease, playing a pivotal role in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic evaluation. With their applications spanning drug discovery, diagnostics, and personalized treatment strategies, biomarkers have revolutionized healthcare by enabling earlier detection and targeted therapies. Technological developments in next-generation sequencing, bioinformatics, and molecular diagnostics have further accelerated biomarker discovery and validation processes.
Get Free Sample Report @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3260
Regional Analysis
North America dominates the biomarkers market due to high healthcare expenditure, a strong presence of key pharmaceutical and biotech companies, and early adoption of advanced healthcare technologies. The U.S. leads the region owing to increasing incidences of cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Europe holds the second-largest market share, supported by favorable government initiatives, robust R&D activities, and increasing focus on precision medicine.
Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. Factors such as rapidly improving healthcare infrastructure, growing patient population, and rising clinical research activities in countries like China, India, and Japan contribute to this surge.
Latin America, Middle East, and Africa show steady growth, with increasing healthcare investments and awareness programs supporting biomarker adoption.
Market Segmentation
By Type:
Safety Biomarkers
Efficacy Biomarkers
Validation Biomarkers
Predictive Biomarkers
Prognostic Biomarkers
Diagnostic Biomarkers
By Application:
Drug Discovery & Development
Disease Diagnostics
Personalized Medicine
Risk Assessment
Others
By Disease Indication:
Cancer
Cardiovascular Diseases
Neurological Disorders
Immunological Diseases
Others
By Region:
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
Key Players
Some major players in Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Market are Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Novartis AG, Bharat Biotech., GlaxoSmithKline plc., Merck & Co. Inc, Inovio Pharmaceuticals Inc, Xenetic Biosciences, Inc., Johnson & Johnson and other players.
Key Points
Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, particularly cancer and cardiovascular diseases, is driving market growth.
Rising demand for personalized medicine and targeted therapies.
Technological advancements in genomics, proteomics, and molecular diagnostics fueling biomarker research.
Growing pharmaceutical R&D investment and strategic collaborations between biotech firms and research organizations.
North America leads the global market, while Asia-Pacific presents lucrative opportunities due to rapid healthcare development.
Future Scope
The future of the biomarkers market appears promising, with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning expected to enhance biomarker discovery and data interpretation. Integration of multi-omics approaches (genomics, proteomics, metabolomics) is set to unlock novel biomarker candidates, leading to breakthroughs in precision medicine. Additionally, the shift toward non-invasive biomarkers, such as liquid biopsies, and advancements in digital health platforms will further transform disease management and patient outcomes globally.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the biomarkers market is poised for significant growth, fueled by technological innovations, increasing healthcare demands, and the critical role biomarkers play in early disease detection and personalized treatment strategies. As pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and research institutions continue to invest heavily in biomarker-driven solutions, the market is expected to witness sustained momentum over the coming years.
Contact Us: Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
Other Related Reports:
Smart Healthcare Market
Optometry Equipment Market
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment Market
#Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Market#Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Market Share#Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Market Trends#Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine Market Size
0 notes
Text
https://github.com/casijacasija/crystall/blob/main/Prognostics-Health-Management-System-Market-Size-by-Applications%2C-by-Type%2C-by-End-User%2C-by-Deployment-%26-by-Technology-2032.md
0 notes
Text
Trading by Link Earn Hub

Link Earn Hub is an innovative trading platform designed for both beginners and experienced traders. It provides an intuitive interface, advanced tools, and a wide range of educational resources to help users navigate the complexities of trading. Link Earn Hub Provide best trading course for beginners
Key Features of Link Earn Hub User-Friendly Platform: A clean and simple interface ideal for beginners. Educational Resources: Tutorials, webinars, and articles to guide you through trading strategies and market analysis. Diverse Markets: Access to stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Advanced Tools: Integrated charting tools, indicators, and risk management features. Community Support: Forums and chat groups for connecting with other traders.
How to Get Started on Link Earn Hub Sign Up:
Create an account on the platform by providing basic details and completing the verification process. Explore Educational Materials: Learn the basics of trading using the platform’s free resources. Start Trading: Use the platform’s tools and insights to execute trades confidently.
Why Choose Link Earn Hub?
Link Earn Hub stands out for its focus on education and community, making it an excellent choice for beginners. Its robust tools and diverse market offerings also cater to advanced traders, ensuring a comprehensive trading experience for all Trading by Link Earn Hub for newcomers Your companion to Getting Started Trading can be an instigative and potentially satisfying adventure, but it’s also a field that requires medication, education, and discipline. Whether you are drawn to the idea of fiscal independence or intrigued by the mechanics of the requests, it’s important to approach trading with the right mindset and knowledge. This companion will walk you through the fundamentals of trading as a freshman and help you take your first way with confidence. best trading course for beginners by Link Earn Hub.
What's Trading?
Trading involves buying and dealing fiscal instruments like stocks, currencies, goods, or cryptocurrencies with the thing of making a profit. Unlike investing, which frequently focuses on long- term growth, trading generally involves shorter timeframes and further frequent deals. Dealers aim to subsidize on price movements, whether the request is going up or down. Types of Trading There are several types of trading styles, each suited to different personalities and pretensions Day Trading Buying and dealing means within the same day, frequently counting on specialized analysis and quick decision- timber. Swing Trading Holding positions for several days or weeks to capture short- to medium- term trends. Scalping Making multitudinous small trades within twinkles or hours to benefit from small price changes. Position Trading Holding positions for weeks, months, or indeed times, analogous to investing but with active operation. Essential generalities for newcomers Before diving into the requests, familiarize yourself with these crucial trading generalities
1. request Basics Stocks Shares of power in a company. Forex Trading currencies against one another. Goods Trading physical goods like gold, oil painting, or agrarian products.
2. Risk Management Always use stop- loss orders to limit implicit losses. No way risk further than 1- 2 of your trading capital on a single trade. Diversify your portfolio to avoid overexposure to one asset or request.
3. Specialized and Abecedarian Analysis Specialized Analysis Using maps, patterns, and pointers to prognosticate price movements. Abecedarian Analysis assessing the fiscal health of an asset, company, or frugality.
4. Trading Psychology Stay disciplined and stick to your trading plan. Avoid emotional opinions, similar as vengeance trading after a loss. Exercise tolerance and thickness.
Steps to Start Trading
1. Educate Yourself Take online courses or watch tutorials on platforms like Udemy, Coursera, or YouTube. Read freshman-friendly books like Trading for a Living by Dr. Alexander Elder or The Little Book That Still Beats the request by Joel Greenblatt.
2. Choose a request elect a request that matches your interests and trading style. Research the volatility, liquidity, and trading hours of your chosen request.
3. Open a Trading Account elect a estimable broker that offers a stoner-friendly platform, educational coffers, and competitive freights. Start with a rally account to practice trading without risking real plutocrat.
4. Develop a Trading Plan Define your pretensions, threat forbearance, and favored trading style. Set clear entry and exit rules, and establish how you'll manage threat.
5. Start Small Begin with small quantities of capital to minimize threat while literacy. Gradationally increase your position size as you gain confidence and experience.
6. Review and Acclimate Keep a trading journal to track your trades, strategies, and performance. dissect your successes and failures to identify areas for enhancement. Tools and coffers for newcomers Trading Platforms Meta Trader, Think or Swim, or Robinhood. Charting Tools Trading View or Stock Charts. News and Analysis Bloomberg, CNBC, or Reuters. Simulators Paper trading accounts to exercise without real plutocrat. Common miscalculations to Avoid Skipping Education Jumping into trading without understanding the basics is a form for failure. Overtrading Making too numerous trades frequently leads to advanced costs and gratuitous pitfalls. Ignoring threat operation Always cover your capital with stop- loss orders and position sizing. Emotional Trading opinions grounded on fear, rapacity, or frustration frequently affect in losses.
Final studies
Trading is a skill that requires time, trouble, and tolerance to master. While the eventuality for profit can be charming, it’s pivotal to approach trading with a mindset of nonstop literacy and chastened practice. By starting small, managing pitfalls, and enriching your strategies, you can make a solid foundation for long- term success. Flash back, every successful dealer was formerly a freshman. Take your time, stay married, and enjoy the trip of literacy and growth. Happy trading! By Link Earn Hub best trading course for beginners. For more information visit our website https://linkearnhub.com/ & Contact us on +91 7011866994 Watch our webinar’s video on Instagram & YouTube https://linktr.ee/Link_Earn_Hub Location:- Wave City Center, Sector 32, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301, India
1 note
·
View note
Text
Colon Therapy in Chennai
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is one of the most prevalent cancers globally. Early detection, followed by timely treatment, greatly increases survival rates. This blog aims to provide in-depth insights into colon cancer, covering its diagnosis, stages, treatment options, risk factors, and prognostic indicators, with a special focus on colon therapy in Chennai. By the end of this guide, you will be better informed about colon cancer and the steps to take if you're concerned about your risk.
Exploring Colon Therapy in Chennai
What is Colon Cancer?
Colon therapy encompasses various procedures designed to cleanse, heal, and improve the colon’s health. These therapies include:
Colon Hydrotherapy: A non-invasive treatment for flushing toxins from the body.
Medical Interventions: Surgical or non-surgical treatments for colon-related issues.
Cancer-Focused Therapies: Advanced treatments, including chemotherapy and targeted therapies for colon cancer.
These therapies are vital in managing digestive health and treating conditions like irritable bowel syndrome, colitis, and colon cancer.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Early detection is crucial for improving outcomes in colon cancer. Many early signs, however, can be subtle or mistaken for other digestive issues. Common symptoms include:
Blood in the stool
Changes in bowel habits (e.g., diarrhea, constipation)
Unexplained weight loss
Persistent abdominal discomfort (e.g., cramps, bloating, pain)
A sensation of incomplete bowel emptying
If any of these symptoms persist, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider, particularly one specializing in colon therapy in Chennai.
What Happens When Colon Health Declines?
An unhealthy colon can lead to various physical and systemic problems, such as:
Digestive Disruptions: Persistent constipation, bloating, and irregular bowel movements affecting daily comfort.
Toxin Build-up: A sluggish colon leads to toxin accumulation, contributing to fatigue, headaches, and poor skin health.
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation may progress to conditions like IBS or ulcerative colitis if untreated.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor colon function hinders nutrient absorption, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and related issues.
Colon Cancer Risk: Long-term colon health problems can increase the risk of colon cancer, making timely treatment in Chennai essential.
If these symptoms persist, seeking professional colon therapy in Chennai can help prevent further complications and restore digestive health.
Natural Methods to Cleanse the Colon
Several natural ways can support colon health and detoxification, including:
Fiber-Rich Diet: Consuming whole grains, fresh fruits, and vegetables supports healthy digestion.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush waste and maintains hydration.
Probiotics: Incorporating yogurt and fermented foods like sauerkraut strengthens gut health.
Detox Drinks: Warm lemon water, green smoothies, or apple cider vinegar can aid digestion.
Exercise: Regular physical activities, such as yoga or walking, help stimulate digestion.
Limit Processed Foods: Avoiding excessive consumption of fried and sugary foods helps prevent toxin build-up.
Combining these methods with professional colon therapy in Chennai can keep your colon clean and healthy. For severe conditions, seeking colon cancer treatment in Chennai ensures optimal care.
Colon Cancer Diagnosis and Testing
Early detection of colon cancer is key to effective treatment. Diagnostic tools include:
Colonoscopy: A procedure involving a flexible tube with a camera to examine the colon.
CT Colonography (Virtual Colonoscopy): A non-invasive imaging method for colon examination using CT scans.
Stool Tests: DNA and occult blood tests to detect cancer-related markers in stool.
Biopsy: If a suspicious area is found, tissue is collected for analysis.
These tests help identify colon cancer and determine the best treatment approach, including colon cancer treatment in Chennai.
Stages of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is categorized into four stages based on its spread:
Stage 0: Early-stage cancer confined to the inner lining of the colon.
Stage I: Cancer has spread into the colon’s muscle layer.
Stage II: Cancer has spread beyond the colon to nearby tissues.
Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs like the liver or lungs.
The stage of cancer influences treatment decisions and potential outcomes, with advanced stages often leading to higher treatment costs.

Understanding Colon Cancer Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing colon cancer:
Health History: A family history of colon cancer, polyps, or conditions like IBD increases risk.
Lifestyle Choices: Diets high in red meat, smoking, and alcohol consumption are risk factors.
Age: Risk increases after the age of 50, making regular screenings important.
Being aware of these risk factors underscores the importance of early screening and colon therapy in Chennai.
Colon Cancer Treatment Options
Treatment options depend on the cancer stage. Key treatments include:
Surgery: The primary approach for early-stage colon cancer, often using minimally invasive techniques.
Chemotherapy: Used after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells or as a primary treatment for advanced stages.
Radiation Therapy: Utilized for advanced cases, often in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy.
Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific cancer-causing molecules, minimizing damage to healthy cells.
Each treatment type varies in cost, and advanced therapies may increase the overall colon cancer treatment cost in Chennai.
Surgical Interventions for Colon Cancer
Early-Stage Surgery: Local excision or polypectomy can remove small tumors, offering quick recovery.
Advanced Surgery: Partial or total colectomy is required for advanced cancer, sometimes involving lymph node removal.
Prognostic Factors and Recurrence
Several factors influence colon cancer prognosis, including:
Cancer Stage at Diagnosis: Early detection offers the best outcomes.
Tumor Grade: Indicates the cancer’s aggressiveness and potential for recurrence.
Genetic Factors: Mutations can influence treatment response.
Recurrence is a concern, especially within the first few years after treatment. Regular follow-up care, including colonoscopies and scans, is vital for early detection.
Conclusion
Colon cancer is a significant concern, but with early detection and advanced treatment options available in Chennai, including colon therapy, the prognosis can improve dramatically. Understanding your risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment options are essential for managing this condition. Whether through natural therapies or medical interventions, timely care in Chennai can offer the best chance for successful treatment and recovery. For more details,https://targetcancer.care/targeting-cancer/radiation-oncology/
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Kussmaul’s Sign- In a patient with Severe PAH by Javaid Ahmad Dar in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences
Case Report
The patient is a 33 years old male who had a history of acute pulmonary embolism three and a half years back. He had received thrombolysis with alteplase and was subsequently on oral anticoagulants. After one year of the index episode, the patient started to experience progressive worsening of breathlessness. Further evaluation led to the diagnosis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). Patient was offered pulmonary endarterectomy which he declined and preferred medical management. He did not show clinical improvement and eventually developed refractory heart failure. And patient presented to Emergency department (ED) with worsening of breathlessness. On presentation to the ED, patient was in distress with pulse of 110/min, BP of 100/60 with no evidence of pulsus paradoxus, Respiratory rate of 22/min and chest was revealing bilateral basal crepts and CVS examination revealed pansystolic mummer at left parasternal edge. JVP was elevated and showed only one prominent outward crest, which is a prominent CV wave and one dominant downward trough, a prominent Y descent, and there was a paradoxical rise in the JVP on inspiration (video 1) which is an important clinical sign in heart failure commonly known by the eponym Kussmaul’s sign. The prominent CV wave in this paitent reflected sever Tricuspid regurigitation (TR). On echo, patient had severe RV dysfunction with severe TR with Pulmonary hypertension. Patient was treated with intravenous diuretics, and pulmonary vasodilators and improved symptomatically and was referred for work up for heart-lung transplantation.
Discussion
Kussmaul’s sign is characterized by paradoxical increase in right atrial pressure on inspiration due to decrease in RV compliance as in pericardial diseases like chronic constrictive pericarditis, cardiac tamponade, advanced heart failure and pulmonary hypertension. In this patient’s JVP, only prominent upstroke and downstroke is against the constrictive pericarditis which is the most common condition in which Kussmaul’s sign is seen. Constrictive Pericarditis has prominent X and Y descends in contrast to only prominent Y descend here. In this patient with a history of previous history of CTEPH, Kussmaul’s sign reflects advance disease with severe RV dysfunction. In patients with pulmonary hypertension, Kussmaul’s sign is thought to result due to decreased RV compliance, however in a study in patients with severe PAH, Kussmaul’s sign was shown to reflect severe pulmonary vascular physiology and correlated independently as a poor prognostic factor.1 In a meta-analysis in patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction, Kussmaul’s sign has been found to be very specific for RV involvement and portends an increased preload requirement with intravenous fluids.2 Correctly identifying these clinical signs in a patient presenting to ED, adds in the appropriate management of the patient. This would be most appropriate in patients presenting with inferior wall MI’s where Kussmaul’s sign identifies a subset of patients with RV involvement who have a much sinister prognosis. And in heart failure population, Kussmaul’s sign is common in patients referred for heart transplantation and is associated with adverse cardiopulmonary hemodynamics.3
#Kussmaul’s Sign#Severe PAH#Javaid Ahmad Dar#pulmonary#hemodynamics#Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences.#jcrmhs
0 notes