#QR code RFID reader
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
QR code RFID reader: The Future of Data Capture

Technology continues to advance rapidly, making it increasingly common to combine different technologies. A powerful tool for capturing and tracking data is created when QR code and RFID technology are integrated. We will explore the innovative world of QR code RFID readers in this article, exploring their capabilities, applications, and potential impact on a wide range of industries.
RFID and QR Codes: An Introduction:
The two technologies underpinning QR code RFID readers must be understood first before we dig into the nitty gritty of these innovative devices.
The Quick Response (QR) code is a two-dimensional barcode that can store a variety of information, including URLs, text, and other data. Easily scanned by smartphones and tablets, they are a popular choice for product tracking, marketing campaigns, and authentication.
By contrast, radio frequency identification (RFID) technology uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track objects that are attached to tags automatically. In addition to storing unique identifiers that can be read remotely, RFID tags can also be used to track and monitor assets, inventories, and individuals seamlessly.
QR Codes and RFID Technology:
Incorporating QR code technology with RFID technology creates a powerful data collection solution that combines the strengths of both technologies. Using a QR code RFID reader, one can capture and track data with both QR codes and RFID tags, providing a comprehensive and versatile solution.
It is possible for organizations to streamline data capture processes and improve efficiency by using a single device that can read both QR codes and RFID tags. As an example, a QR code RFID reader can track inventory by using RFID tags and provide customers with detailed product information via QR codes in a retail setting.
QR Code RFID Reader Applications:
There are a wide range of uses for QR code RFID readers, spanning industries and use cases across the globe. Here are just a few examples:
RFID readers can be used to track inventory levels in real time, reducing shelf discrepancies and ensuring accurate inventory counts.
A QR code RFID reader can be used to tag and track valuable assets, equipment, and tools, which enhances visibility and prevents loss or theft.
Using RFID tags or QR codes, authorized personnel can enter restricted areas using QR code RFID readers for secure access control.
A QR code RFID reader can be used by retailers to provide product information, promotions, and discounts to shoppers.

A QR code RFID reader can be used within healthcare settings to enhance patient identification, medication management, and inventory tracking, ensuring both patient safety and operational efficiency. Get more info about RFID reader factory.
In conclusion:
Data tracking and data capture capabilities have been significantly improved with the integration of QR code and RFID technology in QR code RFID readers. Organizations across various industries can improve efficiency, improve visibility, and streamline operations by combining QR codes and RFID technology.
As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of innovative solutions like QR code RFID readers will undoubtedly reshape the way data is captured, managed, and utilized in the digital age. QR code RFID readers hold a bright future, offering endless possibilities for improving data capture and improving business processes, thanks to their broad applications and potential impact.
0 notes
Text
NFC vs. QR Code Business Cards: Which One is Right for You?

In a world where networking is vital, digital business cards have become a game-changer. NFC (Near Field Communication) business Cards and QR Code business cards are two popular options for quickly sharing contact information and other digital content. Each has its strengths, but how do you choose the one that best suits your needs? Here’s a straightforward comparison of NFC vs. QR Code business cards, highlighting their key differences, ease of use, and features to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding NFC Business Cards
NFC (Near Field Communication) is a wireless technology that enables devices to communicate when they are nearby, usually within a few centimeters. NFC business cards have embedded chips that store data, which can be read by tapping a smartphone against the card.
Key Features of NFC Business Cards:
Ease of Use: NFC cards are incredibly easy to use. With a simple tap, users can instantly share contact information, social media profiles, websites, or other digital content without the need to open any apps.
Technology Integration: NFC business cards leverage advanced technology, offering a seamless experience for users with modern smartphones.
Customization: Data on NFC chips can be updated or customized to meet various needs, such as sharing a portfolio or sending users to a specific website.
Speed: NFC technology allows for almost instantaneous data transfer, making it faster than scanning a QR code.
Professional Appeal: NFC cards feel modern and tech-savvy, making them ideal for industries where innovation is key.
However, NFC business cards do have some limitations. Not all smartphones are equipped with NFC readers, especially older models. Additionally, these cards can be more expensive to produce compared to traditional QR code cards.
Understanding QR Code Business Cards
QR (Quick Response) codes are 2D barcodes scannable by smartphones. When scanned, the code directs users to a website, social media page, or other digital content.
Key Features of QR Code Business Cards:
Wide Compatibility: Almost all smartphones come with built-in QR code scanners, either within the camera or through a downloadable app, making it highly accessible.
Cost-Effective: QR code business cards are generally cheaper to produce than NFC cards. You only need to print the QR code on the card, and it can be scanned multiple times.
No Additional Tech Required: Since scanning QR codes requires no special hardware, it can be used by a broader audience, including those without NFC-enabled phones.
Customizable: Just like NFC cards, QR codes can be linked to various forms of content, such as websites, portfolios, or social media profiles.
Printable: QR codes can be added to any material, whether it’s a business card, a flyer, or even a product package.
However, QR codes have some downsides. They require users to open their phone’s camera or an app, which might take slightly longer than NFC’s tap-and-go functionality. Additionally, scanning QR codes in low light or from a damaged surface can be tricky.
A Side-by-Side Comparison
Feature NFC Business Cards QR Code Business Cards
Ease of Use - Tap to transfer information instantly - Requires opening camera to scan code
Cost - Higher due to NFC chip production - Lower, simply print the QR code
Speed - Instantaneous data transfer - Slight delay due to the scanning process
Customization - Easily programmable and updatable - Customizable but fixed once printed
Compatibility - Limited to NFC-enabled devices - Works with nearly all smartphones
Durability - Chip could wear over time - QR codes can be damaged or faded
Which is Best for Your Business?
Choosing between NFC and QR code business cards depends on your business needs, audience, and budget.
NFC Cards: These are ideal if you want to present yourself as cutting-edge and tech-savvy. If your audience is likely to have modern smartphones and you’re looking for an easy, fast, and seamless way to share data, NFC cards are a great option. Industries like tech, marketing, and startups may benefit from the professional appeal of NFC business cards.
QR Code Cards: If you’re looking for a cost-effective solution that can reach a broader audience, QR code business cards are a solid choice. They work with nearly any smartphone and don’t require special hardware, making them more accessible to people who may not have the latest technology. They are also perfect for mass distribution, especially in industries like retail, events, or hospitality.
Final Thoughts
Both NFC and QR code business cards have their unique benefits and challenges. NFC cards provide a sleek, modern approach to networking but come with higher costs and limited compatibility. QR code cards are highly accessible and affordable but may not offer the same speed or ease of use as NFC cards. By considering your target audience, business goals, and budget, you can decide which type of digital business card will best suit your needs.
#NFC Cards#Business Cards#QR Code Business Cards#NFC Business Cards#NFC Technology#RFID Technology#Near Field Communication#NFC Reader
0 notes
Text
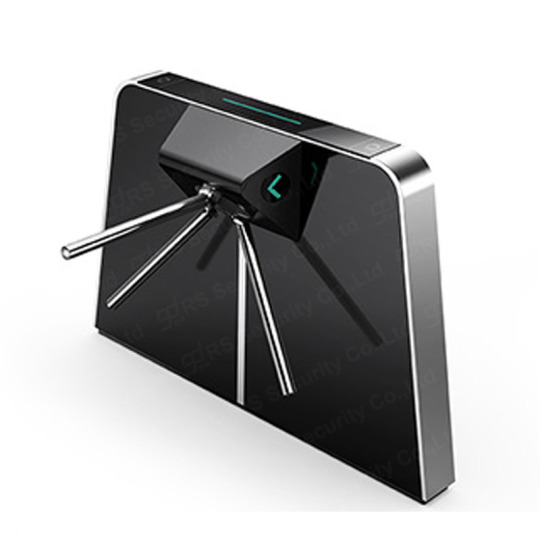

Tripod Turnstile Overview Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and also Flap Turnstile( RS Security Co., Ltd: www.szrssecurity.com) are modern control devices for pedestrian passages. They are used in position where the entrance and departure of individuals need to be managed, such as clever neighborhoods, canteens, hotels, galleries, gyms, clubs, subways, terminals, docks, and so on area. Using Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and Flap Turnstile can make the flow of individuals organized. Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, Flap Turnstile are used in mix with smart cards, fingerprints, barcodes as well as other recognition system tools to form an intelligent access control network control system; they are used in mix with computers, accessibility control, presence, billing monitoring, ticket systems and other software application to create a The intelligent Turnstile Gate extensive management system can understand functions such as accessibility control, attendance, usage, ticketing, and current limiting. This Turnstile Gate management system belongs to the "all-in-one card" and also is mounted at flows such as areas, factories, smart buildings, canteens, etc. It can finish numerous monitoring functions such as worker card traveling control, presence at get off job and also meals, and eating. Tripod Turnstile system features Fast and practical: check out the card in and out with one swipe. Utilize the licensed IC card and also wave it before the clever Tripod Turnstile viewers to finish the Tripod Turnstile gate opening and also cost recording work. The card analysis is non-directional and also the reading and also composing time is 0.1 secs, which is practical and also rapid. Safety and security and also discretion: Use background or local verification, authorized issuance, and special identification, that is, the card can just be made use of in this system, and it is private as well as secure. Dependability: Card superhigh frequency induction, dependable and also stable, with the ability to judge and think. Flexibility: The system can flexibly establish entrance and also leave control employees consents, period control, cardholder credibility as well as blacklist loss coverage, including cards and also other features. Flexibility: Through authorization, the customer card can be utilized for "one-card" administration such as car park, presence, accessibility control, patrol, intake, and so on, making it very easy to recognize several uses one card. Simpleness: Easy to install, straightforward to attach, the software has a Chinese interface and also is easy to operate. Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and also Flap Turnstile( RS Security Co., Ltd: www.szrssecurity.com) are modern control devices for pedestrian flows. The use of Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, as well as Flap Turnstile can make the flow of people organized. Utilize the authorized IC card as well as wave it in front of the wise Tripod Turnstile reader to complete the Tripod Turnstile gate opening and cost recording work.
#Tripod Barrier Turnstile#Systeme Anpr#Qr Code Scanner#Manual Turnstile#Barrier Gate 4 6m#Electric Bolt Lock#Qr Code Scanner Box#Uhf Rfid Reader Chip#Manual Lifting Column#Turnstile Barrier Gate
0 notes
Text
Scan the online brochures of companies who sell workplace monitoring tech and you’d think the average American worker was a renegade poised to take their employer down at the next opportunity. “Nearly half of US employees admit to time theft!” “Biometric readers for enhanced accuracy!” “Offer staff benefits in a controlled way with Vending Machine Access!”
A new wave of return-to-office mandates has arrived since the New Year, including at JP Morgan Chase, leading advertising agency WPP, and Amazon—not to mention President Trump’s late January directive to the heads of federal agencies to “terminate remote work arrangements and require employees to return to work in-person … on a full-time basis.” Five years on from the pandemic, when the world showed how effectively many roles could be performed remotely or flexibly, what’s caused the sudden change of heart?
“There’s two things happening,” says global industry analyst Josh Bersin, who is based in California. “The economy is actually slowing down, so companies are hiring less. So there is a trend toward productivity in general, and then AI has forced virtually every company to reallocate resources toward AI projects.
“The expectation amongst CEOs is that’s going to eliminate a lot of jobs. A lot of these back-to-work mandates are due to frustration that both of those initiatives are hard to measure or hard to do when we don’t know what people are doing at home.”
The question is, what exactly are we returning to?
Take any consumer tech buzzword of the 21st century and chances are it’s already being widely used across the US to monitor time, attendance and, in some cases, the productivity of workers, in sectors such as manufacturing, retail, and fast food chains: RFID badges, GPS time clock apps, NFC apps, QR code clocking-in, Apple Watch badges, and palm, face, eye, voice, and finger scanners. Biometric scanners have long been sold to companies as a way to avoid hourly workers “buddy punching” for each other at the start and end of shifts—so-called “time theft.” A return-to-office mandate and its enforcement opens the door for similar scenarios for salaried staff.
Track and Trace
The latest, deluxe end point of these time and attendance tchotchkes and apps is something like Austin-headquartered HID’s OmniKey platform. Designed for factories, hospitals, universities and offices, this is essentially an all-encompassing RFID log-in and security system for employees, via smart cards, smartphone wallets, and wearables. These will not only monitor turnstile entrances, exits, and floor access by way of elevators but also parking, the use of meeting rooms, the cafeteria, printers, lockers, and yes, vending machine access.
These technologies, and more sophisticated worker location- and behavior-tracking systems, are expanding from blue-collar jobs to pink-collar industries and even white-collar office settings. Depending on the survey, approximately 70 to 80 percent of large US employers now use some form of employee monitoring, and the likes of PwC have explicitly told workers that managers will be tracking their location to enforce a three-day office week policy.
“Several of these earlier technologies, like RFID sensors and low-tech barcode scanners, have been used in manufacturing, in warehouses, or in other settings for some time,” says Wolfie Christl, a researcher of workplace surveillance for Cracked Labs, a nonprofit based in Vienna, Austria. “We’re moving toward the use of all kinds of sensor data, and this kind of technology is certainly now moving into the offices. However, I think for many of these, it’s questionable whether they really make sense there.”
What’s new, at least to the recent pandemic age of hybrid working, is the extent to which workers can now be tracked inside office buildings. Cracked Labs published a frankly terrifying 25-page case study report in November 2024 showing how systems of wireless networking, motion sensors, and Bluetooth beacons, whether intentionally or as a byproduct of their capabilities, can provide “behavioral monitoring and profiling” in office settings.
The project breaks the tech down into two categories: The first is technology that tracks desk presence and room occupancy, and the second monitors the indoor location, movement, and behavior of the people working inside the building.
To start with desk and room occupancy, Spacewell offers a mix of motion sensors installed under desks, in ceilings, and at doorways in “office spaces” and heat sensors and low-resolution visual sensors to show which desks and rooms are being used. Both real-time and trend data are available to managers via its “live data floorplan,” and the sensors also capture temperature, environmental, light intensity, and humidity data.
The Swiss-headquartered Locatee, meanwhile, uses existing badge and device data via Wi-Fi and LAN to continuously monitor clocking in and clocking out, time spent by workers at desks and on specific floors, and the number of hours and days spent by employees at the office per week. While the software displays aggregate rather than individual personal employee data to company executives, the Cracked Labs report points out that Locatee offers a segmented team analytics report which “reveals data on small groups.”
As more companies return to the office, the interest in this idea of “optimized” working spaces is growing fast. According to S&S Insider’s early 2025 analysis, the connected office was worth $43 billion in 2023 and will grow to $122.5 billion by 2032. Alongside this, IndustryARC predicts there will be a $4.5 billion employee-monitoring-technology market, mostly in North America, by 2026—the only issue being that the crossover between the two is blurry at best.
At the end of January, Logitech showed off its millimeter-wave radar Spot sensors, which are designed to allow employers to monitor whether rooms are being used and which rooms in the building are used the most. A Logitech rep told The Verge that the peel-and-stick devices, which also monitor VOCs, temperature, and humidity, could theoretically estimate the general placement of people in a meeting room.
As Christl explains, because of the functionality that these types of sensor-based systems offer, there is the very real possibility of a creep from legitimate applications, such as managing energy use, worker health and safety, and ensuring sufficient office resources into more intrusive purposes.
“For me, the main issue is that if companies use highly sensitive data like tracking the location of employees’ devices and smartphones indoors or even use motion detectors indoors,” he says, “then there must be totally reliable safeguards that this data is not being used for any other purposes.”
Big Brother Is Watching
This warning becomes even more pressing where workers’ indoor location, movement, and behavior are concerned. Cisco’s Spaces cloud platform has digitized 11 billion square feet of enterprise locations, producing 24.7 trillion location data points. The Spaces system is used by more than 8,800 businesses worldwide and is deployed by the likes of InterContinental Hotels Group, WeWork, the NHS Foundation, and San Jose State University, according to Cisco’s website.
While it has applications for retailers, restaurants, hotels, and event venues, many of its features are designed to function in office environments, including meeting room management and occupancy monitoring. Spaces is designed as a comprehensive, all-seeing eye into how employees (and customers and visitors, depending on the setting) and their connected devices, equipment, or “assets” move through physical spaces.
Cisco has achieved this by using its existing wireless infrastructure and combining data from Wi-Fi access points with Bluetooth tracking. Spaces offers employers both real-time views and historical data dashboards. The use cases? Everything from meeting-room scheduling and optimizing cleaning schedules to more invasive dashboards on employees’ entry and exit times, the duration of staff workdays, visit durations by floor, and other “behavior metrics.” This includes those related to performance, a feature pitched at manufacturing sites.
Some of these analytics use aggregate data, but Cracked Labs details how Spaces goes beyond this into personal data, with device usernames and identifiers that make it possible to single out individuals. While the ability to protect privacy by using MAC randomization is there, Cisco emphasizes that this makes indoor movement analytics “unreliable” and other applications impossible—leaving companies to make that decision themselves.
Management even has the ability to send employees nudge-style alerts based on their location in the building. An IBM application, based on Cisco’s underlying technology, offers to spot anomalies in occupancy patterns and send notifications to workers or their managers based on what it finds. Cisco’s Spaces can also incorporate video footage from Cisco security cameras and WebEx video conferencing hardware into the overall system of indoor movement monitoring; another example of function creep from security to employee tracking in the workplace.
“Cisco is simply everywhere. As soon as employers start to repurpose data that is being collected from networking or IT infrastructure, this quickly becomes very dangerous, from my perspective.” says Christl. “With this kind of indoor location tracking technology based on its Wi-Fi networks, I think that a vendor as major as Cisco has a responsibility to ensure it doesn’t suggest or market solutions that are really irresponsible to employers.
“I would consider any productivity and performance tracking very problematic when based on this kind of intrusive behavioral data.” WIRED approached Cisco for comment but didn’t receive a response before publication.
Cisco isn't alone in this, though. Similar to Spaces, Juniper’s Mist offers an indoor tracking system that uses both Wi-Fi networks and Bluetooth beacons to locate people, connected devices, and Bluetooth tagged badges on a real-time map, with the option of up to 13 months of historical data on worker behavior.
Juniper’s offering, for workplaces including offices, hospitals, manufacturing sites, and retailers, is so precise that it is able to provide records of employees’ device names, together with the exact enter and exit times and duration of visits between “zones” in offices—including one labeled “break area/kitchen” in a demo. Yikes.
For each of these systems, a range of different applications is functionally possible, and some which raise labor-law concerns. “A worst-case scenario would be that management wants to fire someone and then starts looking into historical records trying to find some misconduct,” says Christl. "If it’s necessary to investigate employees, then there should be a procedure where, for example, a worker representative is looking into the fine-grained behavioral data together with management. This would be another safeguard to prevent misuse.”
Above and Beyond?
If warehouse-style tracking has the potential for management overkill in office settings, it makes even less sense in service and health care jobs, and American unions are now pushing for more access to data and quotas used in disciplinary action. Elizabeth Anderson, professor of public philosophy at the University of Michigan and the author of Private Government: How Employers Rule Our Lives, describes how black-box algorithm-driven management and monitoring affects not just the day-to-day of nursing staff but also their sense of work and value.
“Surveillance and this idea of time theft, it’s all connected to this idea of wasting time,” she explains. “Essentially all relational work is considered inefficient. In a memory care unit, for example, the system will say how long to give a patient breakfast, how many minutes to get them dressed, and so forth.
“Maybe an Alzheimer’s patient is frightened, so a nurse has to spend some time calming them down, or perhaps they have lost some ability overnight. That’s not one of the discrete physical tasks that can be measured. Most of the job is helping that person cope with declining faculties; it takes time for that, for people to read your emotions and respond appropriately. What you get is massive moral injury with this notion of efficiency.”
This kind of monitoring extends to service workers, including servers in restaurants and cleaning staff, according to a 2023 Cracked Labs’ report into retail and hospitality. Software developed by Oracle is used to, among other applications, rate and rank servers based on speed, sales, timekeeping around breaks, and how many tips they receive. Similar Oracle software that monitors mobile workers such as housekeepers and cleaners in hotels uses a timer for app-based micromanagement—for instance, “you have two minutes for this room, and there are four tasks.”
As Christl explains, this simply doesn’t work in practice. “People have to struggle to combine what they really do with this kind of rigid, digital system. And it’s not easy to standardize work like talking to patients and other kinds of affective work, like how friendly you are as a waiter. This is a major problem. These systems cannot represent the work that is being done accurately.”
But can knowledge work done in offices ever be effectively measured and assessed either? In an episode of his podcast in January, host Ezra Klein battled his own feelings about having many of his best creative ideas at a café down the street from where he lives rather than in The New York Times’ Manhattan offices. Anderson agrees that creativity often has to find its own path.
“Say there’s a webcam tracking your eyes to make sure you’re looking at the screen,” she says. “We know that daydreaming a little can actually help people come up with creative ideas. Just letting your mind wander is incredibly useful for productivity overall, but that requires some time looking around or out the window. The software connected to your camera is saying you’re off-duty—that you’re wasting time. Nobody’s mind can keep concentrated for the whole work day, but you don’t even want that from a productivity point of view.”
Even for roles where it might make more methodological sense to track discrete physical tasks, there can be negative consequences of nonstop monitoring. Anderson points to a scene in Erik Gandini’s 2023 documentary After Work that shows an Amazon delivery driver who is monitored, via camera, for their driving, delivery quotas, and even getting dinged for using Spotify in the van.
“It’s very tightly regulated and super, super intrusive, and it’s all based on distrust as the starting point,” she says. “What these tech bros don’t understand is that if you install surveillance technology, which is all about distrusting the workers, there is a deep feature of human psychology that is reciprocity. If you don’t trust me, I’m not going to trust you. You think an employee who doesn’t trust the boss is going to be working with the same enthusiasm? I don’t think so.”
Trust Issues
The fixes, then, might be in the leadership itself, not more data dashboards. “Our research shows that excessive monitoring in the workplace can damage trust, have a negative impact on morale, and cause stress and anxiety,” says Hayfa Mohdzaini, senior policy and practice adviser for technology at the CIPD, the UK’s professional body for HR, learning, and development. “Employers might achieve better productivity by investing in line manager training and ensuring employees feel supported with reasonable expectations around office attendance and manageable workloads.”
A 2023 Pew Research study found that 56 percent of US workers were opposed to the use of AI to keep track of when employees were at their desks, and 61 percent were against tracking employees’ movements while they work.
This dropped to just 51 percent of workers who were opposed to recording work done on company computers, through the use of a kind of corporate “spyware” often accepted by staff in the private sector. As Josh Bersin puts it, “Yes, the company can read your emails” with platforms such as Teramind, even including “sentiment analysis” of employee messages.
Snooping on files, emails, and digital chats takes on new significance when it comes to government workers, though. New reporting from WIRED, based on conversations with employees at 13 federal agencies, reveals the extent to Elon Musk’s DOGE team’s surveillance: software including Google’s Gemini AI chatbot, a Dynatrace extension, and security tool Splunk have been added to government computers in recent weeks, and some people have felt they can’t speak freely on recorded and transcribed Microsoft Teams calls. Various agencies already use Everfox software and Dtex’s Intercept system, which generates individual risk scores for workers based on websites and files accessed.
Alongside mass layoffs and furloughs over the past four weeks, the so-called Department of Government Efficiency has also, according to CBS News and NPR reports, gone into multiple agencies in February with the theater and bombast of full X-ray security screenings replacing entry badges at Washington, DC, headquarters. That’s alongside managers telling staff that their logging in and out of devices, swiping in and out of workspaces, and all of their digital work chats will be “closely monitored” going forward.
“Maybe they’re trying to make a big deal out of it to scare people right now,” says Bersin. “The federal government is using back-to-work as an excuse to lay off a bunch of people.”
DOGE staff have reportedly even added keylogger software to government computers to track everything employees type, with staff concerned that anyone using keywords related to progressive thinking or "disloyalty” to Trump could be targeted—not to mention the security risks it introduces for those working on sensitive projects. As one worker told NPR, it feels “Soviet-style” and “Orwellian” with “nonstop monitoring.” Anderson describes the overall DOGE playbook as a series of “deeply intrusive invasions of privacy.”
Alternate Realities
But what protections are out there for employees? Certain states, such as New York and Illinois, do offer strong privacy protections against, for example, unnecessary biometric tracking in the private sector, and California’s Consumer Privacy Act covers workers as well as consumers. Overall, though, the lack of federal-level labor law in this area makes the US something of an alternate reality to what is legal in the UK and Europe.
The Electronic Communications Privacy Act in the US allows employee monitoring for legitimate business reasons and with the worker’s consent. In Europe, Algorithm Watch has made country analyses for workplace surveillance in the UK, Italy, Sweden, and Poland. To take one high-profile example of the stark difference: In early 2024, Serco was ordered by the UK's privacy watchdog, the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO), to stop using face recognition and fingerprint scanning systems, designed by Shopworks, to track the time and attendance of 2,000 staff across 38 leisure centers around the country. This new guidance led to more companies reviewing or cutting the technology altogether, including Virgin Active, which pulled similar biometric employee monitoring systems from 30-plus sites.
Despite a lack of comprehensive privacy rights in the US, though, worker protest, union organizing, and media coverage can provide a firewall against some office surveillance schemes. Unions such as the Service Employees International Union are pushing for laws to protect workers from black-box algorithms dictating the pace of output.
In December, Boeing scrapped a pilot of employee monitoring at offices in Missouri and Washington, which was based on a system of infrared motion sensors and VuSensor cameras installed in ceilings, made by Ohio-based Avuity. The U-turn came after a Boeing employee leaked an internal PowerPoint presentation on the occupancy- and headcount-tracking technology to The Seattle Times. In a matter of weeks, Boeing confirmed that managers would remove all the sensors that had been installed to date.
Under-desk sensors, in particular, have received high-profile backlash, perhaps because they are such an obvious piece of surveillance hardware rather than simply software designed to record work done on company machines. In the fall of 2022, students at Northeastern University hacked and removed under-desk sensors produced by EnOcean, offering “presence detection” and “people counting,” that had been installed in the school’s Interdisciplinary Science & Engineering Complex. The university provost eventually informed students that the department had planned to use the sensors with the Spaceti platform to optimize desk usage.
OccupEye (now owned by FM: Systems), another type of under-desk heat and motion sensor, received a similar reaction from staff at Barclays Bank and The Telegraph newspaper in London, with employees protesting and, in some cases, physically removing the devices that tracked the time they spent away from their desks.
Despite the fallout, Barclays later faced a $1.1 billion fine from the ICO when it was found to have deployed Sapience’s employee monitoring software in its offices, with the ability to single out and track individual employees. Perhaps unsurprisingly in the current climate, that same software company now offers “lightweight device-level technology” to monitor return-to-office policy compliance, with a dashboard breaking employee location down by office versus remote for specific departments and teams.
According to Elizabeth Anderson’s latest book Hijacked, while workplace surveillance culture and the obsession with measuring employee efficiency might feel relatively new, it can actually be traced back to the invention of the “work ethic” by the Puritans in the 16th and 17th centuries.
“They thought you should be working super hard; you shouldn’t be idling around when you should be in work,” she says. “You can see some elements there that can be developed into a pretty hostile stance toward workers. The Puritans were obsessed with not wasting time. It was about gaining assurance of salvation through your behavior. With the Industrial Revolution, the ‘no wasting time’ became a profit-maximizing strategy. Now you’re at work 24/7 because they can get you on email.”
Some key components of the original work ethic, though, have been skewed or lost over time. The Puritans also had strict constraints on what duties employers had toward their workers: paying a living wage and providing safe and healthy working conditions.
“You couldn’t just rule them tyrannically, or so they said. You had to treat them as your fellow Christians, with dignity and respect. In many ways the original work ethic was an ethic which uplifted workers.”
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Education: The Power of a Classroom Attendance System
In the fast-evolving world of education, technology continues to redefine how teachers manage classrooms, students engage with learning, and administrators track performance. One such innovation making waves in schools, colleges, and universities is the Classroom Attendance System. Gone are the days of roll calls and paper registers — digital attendance systems offer accuracy, efficiency, and deeper insights into student behavior and performance.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what a classroom attendance system is, how it works, its key benefits, and why your institution should consider implementing one today.
What is a Classroom Attendance System?
A Classroom Attendance System is a digital tool designed to automate and streamline the process of tracking student attendance. It replaces traditional methods with smart solutions such as biometric scanners, QR code readers, RFID systems, mobile apps, or facial recognition technology.
These systems can be standalone or integrated into broader Learning Management Systems (LMS) or School Management Systems (SMS), providing real-time data and analytics to teachers, administrators, and even parents.
How Does a Classroom Attendance System Work?
While various systems offer different features, the core functionality of a classroom attendance system typically includes:
Student Identification: Through ID cards, biometric inputs, QR codes, or facial recognition.
Automated Tracking: The system automatically logs the presence or absence of students as they enter the classroom.
Real-Time Updates: Attendance data is instantly updated in the system, accessible to authorized users.
Reports and Analytics: Detailed attendance records, patterns, and statistics are generated for performance reviews.
Cloud-based systems also offer mobile and web applications that allow remote access and real-time tracking.
Benefits of a Classroom Attendance System
Implementing an automated classroom attendance system offers numerous advantages for students, teachers, and school administrators:
1. Increased Accuracy and Accountability
Manual attendance is prone to errors, manipulation, and time delays. An automated system ensures that data is recorded accurately and can’t be falsified, promoting greater accountability among students.
2. Time Efficiency
Teachers save significant class time by avoiding manual roll calls. This time can be redirected towards more meaningful teaching activities, increasing overall classroom productivity.
3. Real-Time Insights
Administrators gain real-time access to attendance records, enabling quick identification of trends such as frequent absences or late arrivals. Early intervention can be made to support at-risk students.
4. Parental Engagement
Some systems allow parents to receive instant notifications when their child is marked absent or late. This helps keep them informed and involved in their child’s academic life.
5. Data-Driven Decisions
With detailed attendance analytics, institutions can correlate student attendance with academic performance and engagement. This data helps in making strategic decisions around curriculum design, counseling, and disciplinary actions.
6. Enhanced Security
Systems that use biometrics or facial recognition prevent proxy attendance and impersonation, enhancing the overall integrity of attendance records.
Types of Classroom Attendance Systems
There are several types of attendance systems suited for different institutional needs:
Biometric Attendance Systems: Use fingerprint or facial recognition to verify student presence.
RFID-Based Systems: Students carry RFID cards that are scanned upon entry.
QR Code Systems: QR codes are scanned using a mobile device or scanner.
Mobile App-Based Systems: Students or teachers mark attendance using a mobile application.
Web-Based Systems: Cloud-based solutions accessible from any device with an internet connection.
Each type has its pros and cons, and institutions should choose based on budget, infrastructure, and scalability.
Why Schools and Colleges Should Adopt Digital Attendance Systems
In today’s data-driven educational landscape, manual processes are quickly becoming outdated. A digital classroom attendance system not only improves accuracy and saves time but also contributes to a more organized, transparent, and student-focused learning environment.
Moreover, these systems support hybrid and online learning environments, where tracking attendance becomes more challenging without digital tools.
Final Thoughts
The Classroom Attendance System is no longer a futuristic concept — it’s a present-day necessity for modern educational institutions. With benefits ranging from operational efficiency to improved student engagement, implementing a robust digital attendance system is an investment in both academic success and institutional growth.
0 notes
Text
Barcode Definitions 101 | Uses & Guide | AIDC INDIA – 2025
Barcodes play a vital role in today’s business environment. From retail checkout systems to inventory tracking, they have transformed the way data is collected and managed. As we step into 2025, it becomes more important to understand barcode definitions and their role in modern operations. This guide from AIDC Technologies India is designed to simplify everything you need to know about barcodes and their practical uses.
2. What Is a Barcode? A Simple Definition Explained
A barcode is a machine-readable code represented as numbers and parallel lines or squares. Barcode definitions explain how this code is structured and what type of data it holds. Barcodes typically encode product information like SKU, batch number, or manufacturing details. They are scanned using barcode readers, which instantly convert visual patterns into digital data.
3. Types of Barcodes Used in 2025
There are various types of barcodes in use, each with its own format and function. Barcode definitions help identify which format suits a particular industry or task:
1D Barcodes: These are linear barcodes like UPC, EAN, and Code 128, often used in retail and inventory.
2D Barcodes: These include QR codes and Data Matrix codes, used for storing more complex data.
PDF417: A stacked linear barcode used on IDs and transport documents.
Each format has a specific barcode definition and is designed to meet unique requirements based on space, readability, and data needs.
4. How Barcodes Work: From Scanning to Data Collection
The basic process begins with printing a barcode on a label or product. A barcode scanner reads the lines or squares, and decoding software extracts the stored information. Barcode definitions help determine what type of scanner and software are needed to read the code accurately. This simple process eliminates manual entry and ensures fast, reliable data capture across operations.
5. Key Uses of Barcodes in Modern Industries
Barcode definitions are foundational in a wide range of sectors. In retail, barcodes are used for pricing and checkout. In warehouses, they track stock movement and inventory levels. Healthcare uses barcodes for labeling medicine and managing patient records. Logistics companies depend on barcodes for real-time tracking of shipments. The correct use of barcode definitions ensures that the data captured is accurate and usable.
6. AIDC India’s Role in Barcode Solutions
AIDC Technologies India provides complete barcode systems—from labels and scanners to printers and integration software. Our deep understanding of barcode definitions allows us to recommend the right type of barcode solution for your specific industry. We support clients in retail, manufacturing, healthcare, education, and logistics with customized systems that improve data tracking and minimize errors.
7. Benefits of Using Barcodes in Business
Barcodes offer several benefits that go beyond just automation. Proper use of barcode definitions brings improvements in many business areas:
Speed: Barcodes speed up scanning and reduce checkout time.
Accuracy: Minimizes manual errors in data entry.
Inventory Control: Keeps track of stock movement in real time.
Cost Savings: Reduces labor and improves efficiency.
By applying the right barcode definitions, businesses can unlock these advantages more effectively.
8. Barcode Definitions vs QR Codes vs RFID
Understanding how barcode definitions compare to other technologies helps in selecting the best system. Barcodes are simpler and more cost-effective for small to medium-sized operations. QR codes, which are 2D barcodes, can store more data and are often used in mobile marketing or payment systems. RFID, which uses radio waves, allows item tracking without line-of-sight scanning. However, barcode systems remain more accessible and easier to implement.
9. Smart Barcode Scanning Solutions by AIDC India
AIDC India offers barcode scanning devices that are optimized to read all standard barcode definitions. Whether it’s a handheld scanner for retail or an industrial-grade scanner for warehouses, our devices ensure fast, accurate, and error-free data collection. We also provide software tools that integrate these scanners with your inventory or billing systems for seamless workflows.
10. Choosing the Right Barcode System for Your Business
Barcode definitions help businesses choose the right format, printing method, and scanning tools. AIDC India helps you evaluate your operational needs, the volume of data you need to encode, and the environment where scanning takes place. Based on these factors, we recommend and implement barcode systems that align with your goals.
11. Future of Barcodes: Trends to Watch in 2025
As we look ahead, barcode definitions are evolving with technology. Mobile barcode scanning is becoming more popular, especially in e-commerce and delivery services. Smart inventory systems are using AI to analyze barcode data for forecasting and planning. Environment-friendly printing solutions are also emerging. AIDC India stays updated with these trends to provide future-ready barcode solutions for businesses of all sizes.
12. Get Started with Barcode Solutions from AIDC India
Barcodes are a small but powerful part of your business infrastructure. With the right barcode definitions and tools, you can automate operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. AIDC Technologies India offers everything you need—from barcode labels and printers to scanners and integration support.
Call to Action: Ready to streamline your operations with smart barcode solutions? Contact AIDC Technologies India today for a free consultation, customized recommendations, and reliable tools that match your business goals.
#BarcodeDefinitions2025#BarcodeGuide#BarcodeUses#AIDCIndiaBarcode#BarcodeTechnology#SmartTrackingSolutions#BarcodeBasics#InventoryManagement#BarcodeScanning#RetailTech2025
0 notes
Text
ZKTeco Integration with Access Control and Door Locks: Revolutionizing Security
In an era where security and convenience are paramount, ZKTeco has emerged as a global leader in biometric identification, access control, and smart lock solutions. By seamlessly integrating its advanced technologies with access control systems and door locks, ZKTeco offers businesses, residences, and institutions a robust, scalable, and user-friendly approach to safeguarding assets and people.
ZKTeco’s Access Control Solutions: The Foundation
ZKTeco’s access control portfolio is diverse, offering standalone devices, networked panels, readers, and accessories tailored to small businesses, enterprises, and everything in between. Key components include:
Standalone Biometric Terminals: Devices like the Horus E2 combine facial, fingerprint, multi-tech card, and QR code authentication for single-door control. Running on Android 10, they support Wi-Fi and 4G LTE for seamless connectivity and third-party app integration.
IP-Based Control Panels: The C3 Plus series (C3-100 Plus, C3-200 Plus, C3-400 Plus) manages up to 100,000 users and QR code transactions, supporting Wiegand and OSDP protocols for reader compatibility. AES 256-bit and 128-bit encryption ensure secure data storage and communication.
Readers: The ProID Multi-tech readers handle 125KHz and 13.56MHz RFID cards (ID, IC, NFC, DESFire EV1 & EV2), integrating via RS485 or Wiegand with ZKTeco’s InBioPro series or third-party controllers.
Software: ZKBio CVSecurity and other platforms provide web and mobile interfaces for real-time monitoring, configuration, and reporting.
These solutions form the backbone of ZKTeco’s integration with door locks, enabling precise control over who enters, when, and where.
Smart Door Locks: ZKTeco’s Innovative Edge
ZKTeco’s smart door locks blend security, convenience, and modern technology, offering multiple authentication methods and remote capabilities. Notable models include:
SL01-T430H: A mortise-style lock with a lever handle, featuring fingerprint recognition, a touch keypad, and remote unlocking via the ZSmart app over Wi-Fi. It includes a doorbell button, a “Do Not Disturb” schedule, and voice command compatibility with Amazon Echo or Google Home. It’s ideal for luxury homes and apartments.
TL800: A fully automatic lock with a built-in LCD screen for indoor monitoring. It supports remote unlocking via ZSmart over Wi-Fi, allowing users to view outdoor activity and enhance home security.
TL300Z: An advanced fingerprint keypad lock with Zigbee communication and a robust zinc alloy casing. Paired with a Zigbee Gateway, it offers remote unlocking, log history, and temporary passcode sharing via the ZSmart app, perfect for private houses and short-term rentals.
ML300: An entry-level fingerprint and keypad lock with Bluetooth, easy to install on single-hole doors. It supports remote unlocking and voice commands via Bluetooth Gateway and ZSmart, suited for homes and junior apartments.
ML200: A digital keypad lock with Bluetooth for semi-outdoor use, offering simple setup and smart functionality.
These locks integrate biometric, RFID, passcode, and mobile app controls, making them versatile for residential, commercial, and hospitality settings.
How ZKTeco Integrates Access Control and Door Locks
ZKTeco’s integration of access control and door locks creates a cohesive security ecosystem. Here’s how it works:
1. Seamless Hardware Connectivity
ZKTeco’s access control panels, like the InBioPC Main Controller, connect to door units (e.g., DE-10) and locks via TCP/IP, RS485, or Wiegand protocols. The InBioPC supports 4/8 access points, powering door units via PoE (IEEE802.3, PSE@30W) for efficient data transfer and control. For example, the ProMA series—outdoor multi-biometric terminals (ProMA-QR, ProMA-RF, ProMA)—combines facial, fingerprint, and RFID authentication, linking to locks with IP66 water/dust resistance and IK07 vandal protection.
2. Biometric and Multi-Tech Authentication
ZKTeco integrates advanced biometrics into both access control and locks. The KF1100 Pro and KF1200 Pro facial readers capture and convert face images into 512-byte templates, transmitting them to InBio Pro Plus controllers via RS485 for authentication. These readers also function standalone with a DM10 door lock extension panel. Locks like the TL300Z and ML300 use fingerprint, RFID, and passcode options, ensuring secure, flexible entry.
3. Software Integration: ZKBio CVSecurity and ZSmart
The ZKBio CVSecurity platform unifies access control and lock management, offering real-time tracking, interlock logic, and anti-passback enforcement. It integrates with hotel modules for a “One-Card-Solution,” allowing a single RFID card to unlock rooms, elevators, and facilities. The ZSmart mobile app enhances this, enabling remote unlocking, log history checks, and temporary passcode sharing for locks like the SL01-T430H and TL800. Users can monitor entry, manage users, and trigger alarms (e.g., low battery, tampering) from anywhere.
4. Compatibility and Scalability
ZKTeco’s systems support third-party integration via Wiegand (W26/W34/W66) and OSDP (Ver 2.1.7) protocols, connecting to readers like QR50, QR500, and QR600. The Atlas series (e.g., Atlas160, Atlas260, Atlas460) offers pre-configured kits for 1, 2, or 4 doors, with built-in web applications—no software installation needed. This scalability suits small offices, multi-site enterprises, and temporary setups.
5. Specialized Features
Dynamic QR Codes: The C3 Plus series and ZKBio CVSecurity generate QR codes for visitor access, integrating with locks for temporary entry.
Touch and Remote Options: The TLEB301 touch exit button, with a 2.5D tempered glass panel and IK04 vandal resistance, pairs with locks for easy exit, while remote unlocking via ZSmart or Bluetooth/Zigbee enhances convenience.
Glass Door Compatibility: Accessories like LBB-1, LBB-2, and UBB-1 enable electric mortise locks (LB12, LB22, LB35) to secure glass doors, bridging access control and lock functionality.
Benefits of ZKTeco’s Integration
Enhanced Security
By combining biometrics, RFID, and encryption (AES 256-bit for storage, AES 128-bit for communication), ZKTeco ensures only authorized users gain entry. Features like anti-passback, duress password entry, and tamper alarms (e.g., SL01-T430H) fortify protection against unauthorized access or breaches.
Convenience and Flexibility
Remote unlocking via the ZSmart app, voice commands with Amazon Echo/Google Nest, and multi-method authentication (fingerprint, face, card, passcode) make access effortless. Users can manage locks and control systems from a smartphone or web interface, ideal for remote sites or rentals.
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
From standalone devices like the Horus E2 to networked panels like the Atlas460, ZKTeco scales to any need. In-house manufacturing keeps costs low, while robust designs (e.g., IP68-rated ProFace X(DS)) ensure long-term value.
Versatility Across Industries
ZKTeco’s integration shines in:
Corporate Offices: Atlas kits and ProMA terminals secure doors and track entry.
Hotels: The hotel module and locks like SL01-T430H offer one-card access and remote tenant management for Airbnb or hotels.
Residences: TL300Z and ML300 provide smart, secure home solutions.
Institutions: Multi-door controllers and biometric readers suit schools and government facilities.
Real-World Applications
Imagine a small business using the Atlas160 bundle—a single-door access control panel with a biometric reader and ML300 lock. Employees clock in via fingerprint, unlock the door via Bluetooth, and managers monitor entry remotely. In a hotel, the ZKBio CVSecurity hotel module integrates with TL800 locks, allowing guests to use RFID cards for rooms and elevators, while staff manage access via ZSmart. For a multi-site enterprise, the C3-400 Plus controls four doors, syncing with ProMA-QR terminals and electric mortise locks, ensuring secure, trackable access across locations.
Conclusion: ZKTeco’s Integrated Future
ZKTeco’s integration of access control and door locks redefines security by blending cutting-edge biometrics, smart locks, and intuitive software. Products like the InBioPC, ProMA series, and SL01-T430H, paired with ZKBio CVSecurity and ZSmart, deliver a seamless, secure, and scalable solution. Whether protecting a home, office, or hotel, ZKTeco offers unmatched precision, convenience, and adaptability. Ready to revolutionize your security? Explore ZKTeco’s offerings at website or contact [email protected] to discover the perfect integrated solution for you.
0 notes
Text
Flexographic Electronics: The Fastest Growing Segment in Printed Tech

Flexographic printing technology employs flexible relief plates to directly print functional inks such as PEDOT/PSS, silver-based, and dielectric formulations onto substrates ranging from plastics and metals to paper and fabrics. While historically focused on packaging labels, bags, and flexible pouches, recent innovations have extended its scope into electronics. Applications now include organic thin-film transistors (OTFTs), photovoltaic cells, electrochromic displays, wearable sensors, and more. In 2023, the global Flexography Printed Electronics market was valued at US$ 1.9 Bn, and is projected to reach US$ 5.9 Bn by 2034, growing at a robust 10.9% CAGR over the forecast period.
“Expansion of the consumer electronics industry and the surge in demand for environmentally friendly printing solutions are expected to propel the Flexography Printed Electronics Market to new heights,” says lead analyst at Global Industry Research. “With a forecasted CAGR of 10.9% from 2024 through 2034, the market presents a lucrative opportunity for new entrants to establish manufacturing facilities and drive technological advancement. Flexography’s adaptability and cost efficiency have made it the preferred choice across diverse applications beyond traditional packaging, reinforcing its critical role in the broader printed electronics ecosystem. Asia Pacific, buoyed by rapid adoption in consumer electronics, is poised to lead global growth.”
Market Drivers & Trends
Surge in Adoption of Conductive Inks: Manufacturers are increasingly embracing silver-based and other conductive inks to replace traditional PCB techniques, reducing production costs and simplifying supply chains. Conductive inks facilitate rapid prototyping and mass manufacturing of printed circuitry for sensors, RFID tags, and flexible interconnects.
Smart Packaging Integration: The demand for smart packaging featuring printed sensors for temperature, humidity, and freshness monitoring, as well as printed RFID/QR codes for authentication and inventory tracking is accelerating. Flexography’s high-throughput capabilities and low per-unit cost make it ideal for embedding electronics into mainstream packaging.
Environmental and Cost Efficiency: Silver conductive inks have eclipsed gold and platinum alternatives by offering a more affordable, scalable solution. Flexography’s relatively low solvent usage and compatibility with eco-friendly substrates further enhance its environmental credentials.
Latest Market Trends
Flexible, Rollable Displays: Flexography-printed displays for e-readers, tablets, wearables, and automotive heads-up displays are garnering strong interest. Manufacturers can now produce bendable, durable screens that maintain clarity and performance under repeated flexing.
In-Mold Electronics (IME): Integration of printed electronics into molded plastic parts such as smart device housings and automotive interiors is on the rise. IME enables seamless, lightweight integration of sensors and antennas.
Organic Electronic Materials: Advances in organic semiconductive and dielectric inks are unlocking novel applications in OLED lighting, organic photovoltaic films, and bio-sensors, offering low-temperature processing and roll-to-roll manufacturing compatibility.
Key Players and Industry Leaders
The Flexography Printed Electronics market remains fragmented, characterized by numerous specialized providers investing heavily in R&D and strategic partnerships. Notable players profiled in the latest report include:
Alstom SA
Brückner Maschinenbau GmbH & Co. KG
DuraTech Industries
Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
InkTec Co., Ltd
Jabil Inc.
KOMURA-TECH CO., LTD.
Molex, LLC.
Nissha Co., Ltd
TRITEK CO.,LTD
Witte Technology GmbH
Other Key Players
New/ Emerging Players
Recent Developments
Henkel’s Bridgewater Adhesive Technologies Center (May 2023): Opened in the U.S., this hub focuses on printed electronics innovations for applications spanning hygiene products to engineered wood, fostering collaboration across more than 800 industry segments.
XSYS nyoflex FTV Plate Launch (March 2023): The company introduced a digital photopolymer plate designed for high-efficiency plate production and superior print quality with solvent-based inks, targeting flexible packaging and printed electronics sectors.
Examine key highlights and takeaways from our Report in this sample - https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=S&rep_id=86362
Market Opportunities
Entry of New Manufacturers: The market’s high growth trajectory and relatively low capital barriers present an ideal window for startups and regional players to invest in flexographic printing capacities and carve out niche segments.
Technological Innovation: Breakthroughs in ink formulation particularly in eco-friendly, water-based conductive inks offer differentiation opportunities. Co-development partnerships between ink formulators and press manufacturers can yield turnkey solutions tailored for electronics applications.
Adjacent Industry Adoption: Increased integration of printed electronics in medical wearables, industrial sensors, and aerospace components opens new verticals beyond packaging and consumer electronics.
Future Outlook
Over the next decade, the Flexography Printed Electronics market is expected to benefit from:
Advancements in Roll-to-Roll Manufacturing: Higher line speeds and improved process controls will reduce unit costs and enhance print resolution, enabling complex circuitry fabrication.
Smart Textiles and Wearables: Printed flexible batteries, textile-integrated sensors, and conductive threads will drive demand in health monitoring and fitness markets.
Automotive Electronics: As vehicles incorporate more distributed sensors for safety and connectivity, flexo-printed antennas, heaters, and interface films will gain prominence.
Market Segmentation
Material:
Substrates: Polymers, Papers, Fabrics, Silicon, Glass, Metals
Inks: Conductive, Dielectric, Semiconductive
Application:
Sensors & Switches, Displays, Medical Wearables, Photovoltaic Cells, Antennas, Heaters, In-Mold Electronics, Lighting, Others
Industry Vertical:
Automotive & Transportation, Consumer Electronics, Healthcare, Aerospace & Defense, Industrial, Others
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific (41.1% share, 2023): Dominant region driven by large-scale consumer electronics manufacturing in China, South Korea, and Japan. Government initiatives in smart cities and electric vehicles further bolster demand.
North America: Growth fueled by smart packaging uptake in food and pharmaceuticals, and strong R&D ecosystem for printed electronics in the U.S. and Canada.
Europe: Adoption across automotive, healthcare, and packaging sectors, with Germany and the U.K. leading in process innovation and regulatory support for sustainable manufacturing.
Middle East & Africa / Latin America: Emerging markets exhibit steady growth as packaging converters upgrade facilities and multinationals extend regional footprints.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the projected market size of Flexography Printed Electronics by 2034? The market is forecast to grow from US$ 1.9 Bn in 2023 to US$ 5.9 Bn by the end of 2034, representing a CAGR of 10.9%.
2. Which region leads the market? Asia Pacific dominated the market in 2023 with a 41.1% share, driven by massive consumer electronics manufacturing in China, South Korea, and Japan.
3. What are the key drivers of growth? Primary drivers include the adoption of cost-effective conductive inks, demand for smart packaging solutions, growth in flexible displays, and the push for sustainable manufacturing practices.
4. Who are the leading players in this industry? Key players include Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG, Molex, LLC, Nissha Co., Ltd, InkTec Co., Ltd, among others that hold significant market share and lead in innovation.
5. What future trends will impact the market? Trends such as roll-to-roll high-speed manufacturing, smart textiles, automotive printed sensors, and advanced organic inks will shape market growth through 2034. About Transparency Market Research Transparency Market Research, a global market research company registered at Wilmington, Delaware, United States, provides custom research and consulting services. Our exclusive blend of quantitative forecasting and trends analysis provides forward-looking insights for thousands of decision makers. Our experienced team of Analysts, Researchers, and Consultants use proprietary data sources and various tools & techniques to gather and analyses information. Our data repository is continuously updated and revised by a team of research experts, so that it always reflects the latest trends and information. With a broad research and analysis capability, Transparency Market Research employs rigorous primary and secondary research techniques in developing distinctive data sets and research material for business reports. Contact: Transparency Market Research Inc. CORPORATE HEADQUARTER DOWNTOWN, 1000 N. West Street, Suite 1200, Wilmington, Delaware 19801 USA Tel: +1-518-618-1030 USA - Canada Toll Free: 866-552-3453 Website: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text

Great question—it’s always fascinating (and a little bittersweet) to think about what tech might fade into the past. While it’s impossible to predict the future with total accuracy, there are definitely some technologies that are likely on their way out in the next 10 years due to evolving trends, innovation, and changing user habits.
Here are a few that are likely to disappear—or at least become niche:
⸻
1. Physical Passwords & Traditional Passwords
• Why: Biometric authentication (like Face ID, fingerprints) and passwordless systems (like passkeys) are becoming the norm.
• Replacement: Biometrics, 2FA, hardware security keys, and decentralized identity systems.
2. Magnetic Stripe Credit Cards
• Why: They’re less secure and being replaced by chip (EMV) cards and contactless payments.
• Replacement: NFC (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay), QR code payments, digital wallets.
3. Gas-Powered Cars (in many regions)
• Why: Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining momentum, and several countries have plans to ban new gas car sales by the 2030s.
• Replacement: EVs, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (maybe).
4. Cable TV
• Why: Streaming is more convenient, customizable, and cheaper.
• Replacement: On-demand services (Netflix, YouTube TV, etc.), IPTV, and even AI-curated media.
5. DVDs, Blu-rays, and Optical Drives
• Why: Everything is going digital or cloud-based. Laptops are even shipping without disc drives now.
• Replacement: Streaming, cloud storage, digital downloads.
6. Landline Phones
• Why: Mobile phones offer better flexibility and VoIP is cheaper for businesses.
• Replacement: Smartphones, internet calling (Zoom, WhatsApp, etc.)
7. Standalone GPS Devices
• Why: Smartphones have integrated GPS and real-time traffic data.
• Replacement: Smartphone apps (Google Maps, Waze, Apple Maps).
8. Fax Machines
• Why: They’re outdated, inefficient, and mostly kept around for legacy compliance.
• Replacement: Email, secure document sharing platforms (like DocuSign).
9. Public Phone Booths
• Why: Almost everyone carries a mobile phone now.
• Replacement: They may remain as novelty items or be repurposed (e.g., mini libraries, WiFi hubs).
10. Physical Car Keys
• Why: Keyless entry, phone-based controls, and biometrics are gaining popularity.
• Replacement: Smartphone apps, biometrics, RFID.
⸻
Would you like a futuristic blog post or article draft based on this theme? I could help you write one that explores what’s disappearing and what’s replacing it—readers usually love that kind of thing.
Ah, the classic floppy disk! 💾 It’s practically the emoji for “save,” but in real life? Yeah, floppy disks are definitely already a relic—and they’ll be even more extinct in the next decade.
Here’s where they stand today:
Current Use (Surprisingly… still around?)
• Legacy systems: Some very old government, aviation, and industrial systems still use them (yes, really).
• Airplane tech: Older aircraft like the Boeing 747 reportedly used floppy disks for software updates—though that’s being phased out.
• Archival storage: A few niche collectors or retro tech hobbyists still mess around with them.
Why Floppy Disks Are Fading Fast:
• Minuscule Storage: 1.44 MB is less than most modern text files.
• Fragility: They’re easily damaged by dust, magnets, and time.
• Obsolete Hardware: New computers haven’t had floppy drives for over a decade.
• Better Alternatives: Flash drives, SD cards, cloud storage—literally everything is better.
What’s Replacing Them:
• Cloud Storage: Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive.
• USB Flash Drives: Still useful for offline quick transfers.
• Solid State Drives (SSDs): For long-term, fast storage.
• Secure Servers: For enterprise-level data handling.
⸻
Want a fun blog post idea? How about:
“From Floppy to Cloud: The Wild Evolution of Data Storage”
I can help you write it if you want! Could be a mix of nostalgia, tech history, and a peek into what’s next.
0 notes
Text
Access Control Devices Explained: Types, Features, and Benefits
In a world where digital transformation is rapidly reshaping business operations, physical security is evolving too. Gone are the days when traditional lock-and-key systems were sufficient to secure offices, commercial buildings, or sensitive areas. The modern workplace demands smarter, more efficient ways to control who can access specific spaces. That’s where access control devices come into play.
These devices are essential tools that help businesses manage entry, enhance security, and improve convenience for employees, visitors, and facility managers alike. Let’s explore the different types of access control devices available today, their key features, and how they benefit organizations across industries.

What Are Access Control Devices?
Access control devices are hardware components used in a broader access control system to grant or restrict entry to secure areas. These devices verify a user’s identity through credentials like keycards, PIN codes, biometric data, or mobile authentication before allowing access.
Modern access control systems often integrate these devices with cloud-based platforms, enabling remote management, real-time monitoring, and seamless integration with attendance tracking or visitor management solutions.
Types of Access Control Devices
The choice of access control device depends on the level of security required, the number of users, and the type of facility. Here’s a look at the most common types:
1. Keypad-Based Access Devices
These are basic access control devices where users input a numerical PIN code to gain entry. While affordable and easy to install, they may pose security risks if codes are shared or compromised.
2. RFID Card Readers
RFID and smart card readers are widely used in offices and commercial spaces. They require users to carry a card or fob to unlock doors. These systems are convenient but can be vulnerable to loss or duplication if not encrypted properly.
3. Biometric Devices
For higher security needs, biometric access devices offer advanced identity verification through fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. They are accurate and eliminate the need for physical credentials, making them ideal for data centers, labs, and corporate offices.
4. Bluetooth & Mobile Access Devices
As mobile technology advances, smartphones are increasingly used as credentials. Bluetooth-enabled access control devices allow users to unlock doors via mobile apps, offering a contactless, secure, and user-friendly experience — especially valuable in today’s hybrid work environment.
5. Cloud-Connected Controllers
These devices connect to cloud-based platforms that manage access across multiple locations. With centralized control and real-time insights, businesses can monitor activity, update access rights, and view logs remotely.
Key Features of Modern Access Control Devices
Today’s access control devices are more than just door locks. They are part of intelligent ecosystems offering a range of features that enhance functionality and security:
✅ Real-Time Monitoring
Track who accessed what area and when, allowing for quick action in case of suspicious activity.
✅ Mobile Integration
Users can gain access using their smartphones via Bluetooth or QR codes, improving convenience and hygiene in the workplace.
✅ Cloud-Based Management
Manage all devices, users, and locations through a unified, cloud-based dashboard. This makes it easy to scale and manage access remotely.
✅ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Combine two or more forms of authentication, like a fingerprint and a mobile credential, for added security.
✅ Integration with Other Systems
Modern devices seamlessly integrate with visitor management, time and attendance systems, and surveillance setups — streamlining overall operations.
Benefits of Using Access Control Devices
Implementing the right access control devices can deliver significant advantages to your organization:
🔐 Enhanced Security
Limit unauthorized access and improve control over sensitive or restricted areas. Whether you manage a co-working space, corporate office, or healthcare facility, having the right devices in place significantly reduces physical security risks.
👨💻 Improved Operational Efficiency
Automating entry points reduces reliance on physical keys and manual processes. With cloud-enabled systems, administrators can grant or revoke access in seconds — saving time and reducing errors.
🧾 Audit Trails & Compliance
Access control devices keep detailed logs of all entry events. This is especially important for industries with regulatory requirements, such as healthcare or finance, where compliance and accountability matter.
📱 Contactless Convenience
Bluetooth and mobile-enabled devices allow users to unlock doors without touching shared surfaces — ideal for hygiene-sensitive environments like hospitals or modern office buildings.
🌐 Scalable for Future Growth
Whether you’re adding new doors, onboarding more employees, or expanding into new locations, cloud-integrated devices make scaling easy and cost-effective.
Choosing the Right Access Control Devices for Your Business
Selecting the best access control solution isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. It’s important to assess:
Your organization’s size and structure
The types of users (staff, visitors, contractors)
Required security levels for different zones
Integration with your existing systems
Need for remote access and cloud-based control
Many forward-thinking businesses are moving toward wireless, mobile-first, and biometric access control systems to match their evolving workspace needs. Solutions that combine flexibility, real-time control, and easy scalability offer the best return on investment.
For businesses seeking a smart, seamless approach to physical access management, it helps to explore platforms that offer modern features like smartphone-based credentials, biometric authentication, and cloud-based dashboards. One such solution used by progressive companies is a platform that removes the need for keycards, wiring, and complex installations — leveraging mobile technology to simplify security.
Conclusion
Access control devices have come a long way from basic locks and keypads. Today, they are a cornerstone of intelligent building security — offering real-time control, enhanced convenience, and seamless integration with workplace technologies. As organizations continue to embrace hybrid work models, cloud-based and mobile-enabled solutions are quickly becoming the standard.
Investing in the right access control technology like Spintly not only strengthens security but also improves user experience and operational agility. If your business is ready to upgrade from traditional systems to smarter, more scalable solutions, the time to act is now.
#access control system#access control solutions#mobile access#visitor management system#accesscontrol#spintly#smartacess#biometrics#smartbuilding#biometric attendance
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
AI will take over all code writing
I was suspicious of this comment, and I don't think it's completely true. I develop software for the health club industry. There's quite a lot involved. It's a check-in system that tracks visits, and it interfaces with a QR reader or a barcode reader or an RFID reader. The QR scanner sends data to a server which in turns sends an Allowed or Denied response back to a door access system to tell it to open the front door or not. To have AI build that module alone is a huge task, inclusive of building the correct database and fields in the proper tables. The next module is membership module that stores membership information and billing information and account information. Another massive undertaking for a coder or AI. We must have 100 processes going on in that module. Then you have a scheduling module to book appointments, the ability to cancel or rebook appointments, the ability to email club members that a class is full or to later send an email that a different member canceled and a new slot has opened up. Then you have the monthly billing process. Then you have the Point of Sale system. There's thousands of things going on in each module. Employee time clock module. Reporting module. Custom reporting module. I have to guess that yes AI can build the entire application, but only if it receives the correct instructions from a user. That user has to know all of the tables, and fields and be able to specify to AI what each button will do. Button Add Member will display a new member screen with 42 fields for the user to populate, then on Save it will send all of the form data to four different tables correctly so that that data can be used in all of the other modules that are interfacing with the same data. Yeah it can be done, but definitely still a large task even for AI to get it right. It will involve a lot of tweaking, and as we coders know, when you touch one thing in this module it might break a process in another module. Then you need AI to have robust troubleshooting skills. I used AI to write a game where balloons were floating from the bottom of the screen and you pop them as they rise up, and you get points. That took over an hour for AI to get right. That was as simple a game as you can create. The future of coding is allowing AI to build small modules or screens in an application, one at a time, and the coder will review and update/cleanup the code to make things work right. Will AI get it all right in the end? Yes but the end we're talking about is after we're all dead and gone, in 100 years. For the next 50-100 years we'll be tweaking and fixing and updating AI to get it to Level 9000 for those to use in 50 to 100 years from now. We ARE the Testers, and there's lots of testing to do....a hundred years worth
Edit: More like 5 to 10 years...and we're about to be the Test Group of the AI revolution. Chaos for at least a decade or more.
0 notes
Text
The Role of Automation: How Barcode & QR Codes Boost WMS Efficiency
Introduction
With the rapidly evolving logistics and supply chain sector today, automation is an essential contributor to efficiency and productivity. Perhaps the most efficient way to automate warehouse functions is to incorporate barcode and QR code technology in a warehouse management system (WMS) .These technologies make it easier to monitor inventory, manage orders, and warehouse operations in general by reducing errors and increasing speeds. In this, we examine how WMS efficiency increases with automation using barcode and QR code technology, and how they transform the warehouse business.
Warehouse Management System (WMS)
A warehouse management system (WMS) is software that is used to automate different warehouse activities like inventory management, stock replenishment, picking, packing, and shipping. It helps the warehouse manager maintain accurate levels of inventory, automates processes, and improves productivity. With the integration of barcode and QR code technology, a WMS receives even more power, enabling it to monitor warehouse activities in real-time and automate warehouse activities.
How Barcode & QR Code Technology is Applied in WMS
Barcode Technology
Barcodes are 1D bar codes that are applied to encode product data in the form of parallel lines. Scanned and read by a barcode reader, the data is fetched directly and saved in the WMS. This facilitates quick processing of inventories and removes the need for manual entry.
QR Code Technology
QR codes are 2D codes with the ability to hold more intricate data, including product descriptions, batch numbers, expiration dates, and even URLs. QR codes are unique from barcodes as they can be read through mobile phones and are more flexible when it comes to managing data.
The Role of Automation in WMS Efficiency
Barcoding and QR code technology used in WMS automates most warehouse activities, resulting in enhanced efficiency. Some of the key ways in which automation enhances WMS functionality are explained below:
1. Improved and Streamlined Inventory Management
Existing manual tracking techniques of inventories make use of hand-held scanning as well as hand data entry and thus are easily liable to faults. Real-time updated inventory may be kept with the help of speedy barcodes as well as QR code scans by warehouse staff. This clears stock discrepancies and maintains accurate inventory up-to-date.
2. Improved Order Fulfillment Process
Order fulfillment is often the most critical warehouse management function. Barcode and QR code automation support quicker picking and packing by enabling staff to validate product details in real-time. This negates order processing errors and ensures punctual deliveries.
3. Reduction of Human Errors
Manual data entry increases the likelihood of errors in stock records, order details, and monitoring shipments. Scanners of barcodes and QR codes allow automatic data collection, minimizing manual error and increasing overall accuracy.
4. Enhanced Warehouse Productivity
Automation speeds up warehouse operations by removing redundant handoffs. Employees have less time handling paperwork and more on activities of value, such as rationalizing storage space and improving order handling.
5. Real-Time Data and Analytics
WMS integration with barcode and QR code provides warehouse managers with real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, and warehouse operations. Information that helps to decide, forecast demand, and optimize warehouse planning.
6. Integration with Other Technologies
Barcodes and QR codes can further be integrated with other automated technology such as RFID, IoT sensors, and robots. It forms a networked warehouse system in which different systems are networked and they are in communication so that they enable greater efficiency.
7. Cost Savings and ROI Improvement
By automating warehouse operations, businesses are able to save labor, prevent losses due to inefficiently managed inventory, and improve overall warehouse efficiency. The initial cost of barcode and QR code technology is quickly offset by long-term cost savings and improved warehouse performance.
Implementing Barcode and QR Code Automation in WMS
Step 1: Select a Barcode/QR Code-Supported WMS
Choose a WMS that can perform barcode and QR code scanning to enable easy integration with existing warehouse operations.
Step 2: Implement Proper Labeling
Tag all inventory items, storage bins, and shelves with barcodes or QR codes so they can be scanned and monitored easily.
Step 3: Invest in Scanning Devices
Equip warehouse personnel with barcode and QR code scanners or mobile devices that can accurately capture and process data
Step 4: Train Warehouse Staff
Train personnel in the use of barcode and QR scanners for maximum return from automation.
Step 5: Monitor and Optimize Performance
Review WMS data regularly to identify where improvements can be made and optimize warehouse operations accordingly.
The Future of Automation in Warehouse
As technology advances, barcode and QR code automation will be even more sophisticated. Future trends are:
AI-Driven WMS Solutions: Artificial intelligence (AI) will augment barcode and QR code functionality by allowing predictive analytics and automated decision-making.
Cloud-Based WMS: Cloud integration will enable warehouses to operate remotely with real-time data access.
Robotic and IoT Integration: Autonomous robots and IoT-enabled devices will be used in conjunction with barcode and QR code systems to build highly efficient and automated warehouses.
Conclusion
The use of barcode and QR code technology in Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) is transforming warehouse operations. Through automated tracking of inventory, order picking, and warehouse operations, companies can greatly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and cost reduction. With further advancements in automation, barcode and QR code technology will be an integral part of contemporary warehouse management, increasing productivity and overall supply chain operations.
For businesses looking to optimize their warehouse operations, adopting barcode and QR code automation in WMS is no longer optional—it’s a necessity for staying competitive in the evolving logistics landscape. https://www.instagram.com/quickmovetechnologies/ https://youtu.be/PjDQMaFRazk?si=hGbrQasKB31iojDg
https://www.linkedin.com/company/6638777/admin/dashboard/
0 notes
Text
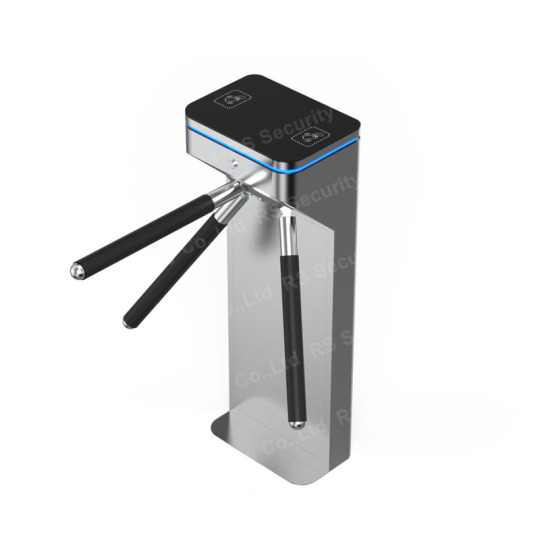

Tripod Turnstile Overview Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, as well as Flap Turnstile( RS Security Co., Ltd: www.szrssecurity.com) are modern control devices for pedestrian flows. They are used in position where the entrance as well as departure of individuals require to be regulated, such as clever communities, canteens, hotels, galleries, gyms, clubs, metros, stations, anchors, and so on location. Making use of Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, as well as Flap Turnstile can make the circulation of individuals organized. Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, Flap Turnstile are made use of in mix with smart cards, finger prints, barcodes and also various other recognition system tools to create an intelligent accessibility control network control system; they are used in mix with computers, access control, attendance, billing administration, ticket systems and also other software application to create a The intelligent Turnstile Gate thorough management system can understand features such as gain access to control, participation, consumption, ticketing, as well as current restricting. This Turnstile Gate monitoring system belongs to the "all-in-one card" and is mounted at flows such as neighborhoods, manufacturing facilities, smart structures, canteens, and so on. It can finish different monitoring features such as employee card traveling control, attendance at leave work and dishes, as well as dining. Tripod Turnstile system attributes Convenient and also rapid: review the card in and out with one swipe. Utilize the accredited IC card and wave it before the smart Tripod Turnstile reader to finish the Tripod Turnstile gate opening as well as fee recording work. The card reading is non-directional as well as the reading and also writing time is 0.1 secs, which is rapid and also hassle-free. Security and confidentiality: Use background or local verification, licensed issuance, as well as distinct identity, that is, the card can just be made use of in this system, and it is safe and also confidential. Reliability: Card superhigh frequency induction, reputable and stable, with the ability to judge as well as assume. Flexibility: The system can flexibly set entry and also departure control employees permissions, period control, cardholder legitimacy and also blacklist loss coverage, including cards and other features. Adaptability: Through permission, the customer card can be utilized for "one-card" management such as parking, presence, accessibility control, patrol, consumption, and so on, making it very easy to recognize several uses of one card. Simplicity: Easy to set up, easy to connect, the software program has a Chinese user interface and also is simple to run. Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and Flap Turnstile( RS Security Co., Ltd: www.szrssecurity.com) are contemporary control gadgets for pedestrian flows. The use of Tripod Turnstile, Swing Turnstile, and also Flap Turnstile can make the circulation of people orderly. Utilize the licensed IC card and also wave it in front of the wise Tripod Turnstile reader to complete the Tripod Turnstile gate opening and also charge recording work.
#Tripod Turnstile Doors#Gate Opener#Lock Cylinders#Subway Turnstile#Removable Bollard#Car Parking System#Rfid Qr Code Reader#Turnstile Gate Price#Subway Turnstile Gate#Mini Access Controller
0 notes
Text
How Do RFID Key Cards Unlock Hotel Doors?

In today's hotel industry, RFID key cards have become the go-to access control solution. They’re safer and more convenient than traditional mechanical keys, plus they can be integrated into hotel management systems for more efficient room management.
Lately, with advancements in smart technology, more hotels are rolling out RFID access control systems to enhance guest experiences, streamline management processes, and boost security. Still, a lot of users aren’t quite clear on how RFID key cards actually work and what the benefits are. So, how do RFID key cards operate? And how do they communicate with hotel door locks?
How RFID Key Cards Work
What is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses radio waves for identity recognition and data transfer. It’s all about reading and storing information wirelessly, allowing for data exchange without any physical contact.
An RFID system is made up of three main parts:
RFID Tag: This is the data holder that stores ID info, containing a chip and an antenna that communicates wirelessly with a reader. There are different types of tags, including read-only, writable, and active tags. Hotels typically use high-frequency (HF) rewritable tags, allowing them to update room info during guest check-in and check-out.
RFID Reader: This device reads and writes data from the tags and is usually built right into the hotel door lock. It sends out a wireless signal to activate the tag and gets the data back while decoding and verifying it. Modern readers often include encryption features to keep unauthorized access at bay.
Data Processing System: The information read by the reader gets processed by the hotel’s management system to determine if the key card has the right permissions to unlock the door. This system connects to the front desk, security systems, and other management modules to keep everything updated in real-time and avoid any security gaps.
RFID technology finds applications in access control, logistics, asset tracking, and other fields. In the hotel sector, RFID key cards offer a more efficient and secure way to manage guest stays.
Structure of RFID Key Cards
Hotel RFID key cards usually have these components:
Embedded Chip: This chip holds a unique identification code (UID) and encrypted data to make sure the key card is one-of-a-kind and to prevent unauthorized duplication.
Antenna: It receives and sends radio frequency signals, enabling the key card to communicate wirelessly with the door lock. The antenna design influences the transmission range and signal stability. Hotels typically use coil antennas for stable signals that work well for short-distance interactions.
Shell: This protective case keeps the internal electronic parts safe and is built to be durable, often printed with the hotel’s brand logo and room info. The design has to balance looks and durability, and some hotels even throw in a magnetic stripe or QR code for extra functionality.
How RFID Key Cards Communicate with Hotel Door Locks
When a guest brings their RFID key card close to the hotel room door, here’s what happens:
The RFID reader in the door lock sends out a radio signal that activates the chip in the key card. This signal usually runs at a frequency of 13.56 MHz for precise short-range recognition.
The key card’s antenna picks up the signal and shoots back its stored ID info to the reader, which includes room number, expiration date, and user permissions.
The door lock’s control system checks this info against the authorized data stored in the database to see if it matches. If there’s no match, the door stays locked.
If it matches, the door lock executes the unlock command, letting the guest in. This whole process happens in mere milliseconds, ensuring guests can get into their rooms quickly.
The entire procedure doesn’t require any physical contact, minimizing the risk of damaging keys or wear and tear from inserting and removing them.
Advantages of RFID Access Control Systems
Boosting Security
Copy Resistance: RFID key cards are way harder to duplicate or forge than traditional mechanical keys. If they get lost, you can deactivate them right away.
Dynamic Encryption: A lot of hotels use AES encryption or rolling code tech to make sure the data on these key cards isn’t easily cracked.
Permission Control: Hotels can set different access levels through their backend system, like allowing guests into their rooms while staff can get into cleaning and maintenance areas.
Usage Tracking: The system keeps a log of when and where key cards are used, which really ramps up security management.
Enhancing the Guest Experience
Contactless Unlocking: Guests just need to be close to the door lock to unlock it—no more fumbling with keys, making things a whole lot easier.
Multi-Functional Use: The same RFID card can work for room access, gym entry, elevator rides, and paying at restaurants, making the stay more convenient.
Integration with Mobile Devices: NFC-enabled phones or smartwatches can act like key cards, cutting down on the need for physical cards.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Lower Key Management Costs: If a traditional key goes missing, you have to change the entire lock. With RFID key cards, you can just deactivate and reissue them.
Remote Control: Hotels can easily update or revoke key card permissions from anywhere, making management smoother.
Eco-Friendly: Reusable RFID key cards help cut down on plastic waste, fitting into the push for more sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Why RFID Key Cards Are the Top Choice for Hotel Access Control?
RFID key cards have become the gold standard for modern hotel access control systems, thanks to their efficiency, security, and easy management. Sure, as technology keeps moving forward, smart access systems are gonna get fancier, but RFID key cards are still going to be the go-to for a long time.
If you’re curious to learn more about hotel key cards, check out RFIDCard.com. They’ve been in the game for over ten years, cranking out 100 million cards a year and supplying key card products and services to more than 2,000 hotels around the world.
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Education with School Attendance Systems: A Complete Guide
In today’s digital age, educational institutions are rapidly adopting technology to improve efficiency and student performance. One such essential innovation is the School Attendance System. Traditionally, attendance was recorded manually, consuming valuable class time and often resulting in inaccuracies. However, modern attendance systems are transforming this routine into a seamless, automated process.

In this blog post, we’ll explore what a school attendance system is, its key benefits, types, and how it is reshaping the education sector.
What is a School Attendance System?
A school attendance system is a digital solution designed to track, record, and manage student attendance. These systems automate the process of marking presence or absence, generate detailed reports, and often integrate with other educational management tools. They can be software-based, app-based, or integrated with biometric or RFID technologies.
Whether used in a primary school, high school, or college, these systems ensure accurate tracking of student participation while reducing administrative workload.
Why is School Attendance Important?
Attendance is a strong indicator of academic performance. Students who regularly attend school tend to have better grades, higher engagement, and more positive social interactions. For administrators and educators, maintaining accurate attendance records is crucial for:
Monitoring student behavior and performance
Identifying truancy patterns
Communicating with parents or guardians
Meeting government or institutional compliance
With an efficient attendance system, schools can take proactive steps to support student success.
Key Features of a Modern School Attendance System
Here are some core features that make modern attendance systems highly effective:
1. Automated Attendance Recording
Students can check in using biometric scanners, RFID cards, QR codes, or mobile apps. This eliminates the need for roll-calling and prevents time loss at the start of each class.
2. Real-Time Data Access
Teachers, parents, and administrators can view attendance records in real-time. If a student is absent, parents can be instantly notified via SMS or app notification.
3. Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive dashboards provide attendance trends, identify chronic absentees, and help in decision-making for student interventions.
4. Integration with School Management Systems
Most attendance systems integrate with broader School Management Software (SMS), allowing seamless syncing of student profiles, class schedules, and academic performance.
5. Mobile App Support
Many platforms offer mobile applications that enable teachers to mark attendance on-the-go, while parents can track their child’s daily presence from their smartphones.
Types of School Attendance Systems
There are several types of systems used by schools, depending on their size, budget, and tech infrastructure:
• Biometric Attendance Systems
These use fingerprint or facial recognition to mark attendance. They are highly accurate and prevent proxy attendance.
• RFID-Based Systems
Students carry ID cards embedded with RFID chips. When they pass through an RFID reader, their attendance is automatically logged.
• Web and App-Based Systems
These systems are cloud-based and allow attendance marking via desktops, tablets, or smartphones. They are ideal for remote or hybrid learning environments.
• QR Code Systems
Teachers display a QR code in class, and students scan it with their phones to register their presence. It's a quick and contactless method.
Benefits of a School Attendance System
Implementing an attendance system offers a wide range of advantages:
Accuracy: Eliminates human error and prevents fraudulent attendance.
Time-Saving: Reduces the time spent on manual roll calls.
Parental Involvement: Keeps parents informed, improving accountability.
Data Security: Stores data securely and ensures privacy.
Improved Compliance: Helps schools adhere to regulatory requirements and audit readiness.
Choosing the Right Attendance System for Your School
When selecting a system, schools should consider:
Ease of Use: Choose user-friendly software with intuitive interfaces.
Scalability: Make sure the system can grow with the institution’s needs.
Customization: Look for flexible settings to match your school’s policies.
Customer Support: Ensure the vendor offers strong after-sales support.
Budget: Consider both upfront and recurring costs.
Some of the most popular school attendance software in 2025 includes MyClassAttendance, SchoolTime, and EduTrek, each offering unique features tailored to different types of institutions.
The Future of Attendance in Schools
As Artificial Intelligence and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies continue to evolve, attendance systems are likely to become even more intelligent and autonomous. For example, facial recognition cameras could automatically log attendance as students enter a classroom, while predictive analytics could identify patterns of absenteeism and suggest interventions before problems escalate.
Final Thoughts
A reliable school attendance system is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern educational institutions. It enhances operational efficiency, promotes student responsibility, and ensures a transparent communication channel between schools and families. As education continues to go digital, investing in an attendance management solution is a smart move toward a more organized, accountable, and future-ready learning environment.
0 notes