#SQL Server Error Log
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Auditing SQL Server Restarts: Strategies for Multi-DBA Environments
In the complex tapestry of modern IT environments, particularly those with multiple Database Administrators (DBAs) possessing sysadmin permissions, tracking the genesis of critical actions such as SQL Server restarts becomes paramount. While SQL Server’s Audit feature adeptly records the when of stop and start events, it falls short in capturing the who, specifically the hostname or IP address of…
View On WordPress
#Extended Events SQL Server#SQL Server auditing#SQL Server error logs#third-party SQL monitoring tools#Windows Event Log analysis
0 notes
Text
The Story of KLogs: What happens when an Mechanical Engineer codes
Since i no longer work at Wearhouse Automation Startup (WAS for short) and havnt for many years i feel as though i should recount the tale of the most bonkers program i ever wrote, but we need to establish some background
WAS has its HQ very far away from the big customer site and i worked as a Field Service Engineer (FSE) on site. so i learned early on that if a problem needed to be solved fast, WE had to do it. we never got many updates on what was coming down the pipeline for us or what issues were being worked on. this made us very independent
As such, we got good at reading the robot logs ourselves. it took too much time to send the logs off to HQ for analysis and get back what the problem was. we can read. now GETTING the logs is another thing.
the early robots we cut our teeth on used 2.4 gHz wifi to communicate with FSE's so dumping the logs was as simple as pushing a button in a little application and it would spit out a txt file
later on our robots were upgraded to use a 2.4 mHz xbee radio to communicate with us. which was FUCKING SLOW. and log dumping became a much more tedious process. you had to connect, go to logging mode, and then the robot would vomit all the logs in the past 2 min OR the entirety of its memory bank (only 2 options) into a terminal window. you would then save the terminal window and open it in a text editor to read them. it could take up to 5 min to dump the entire log file and if you didnt dump fast enough, the ACK messages from the control server would fill up the logs and erase the error as the memory overwrote itself.
this missing logs problem was a Big Deal for software who now weren't getting every log from every error so a NEW method of saving logs was devised: the robot would just vomit the log data in real time over a DIFFERENT radio and we would save it to a KQL server. Thanks Daddy Microsoft.
now whats KQL you may be asking. why, its Microsofts very own SQL clone! its Kusto Query Language. never mind that the system uses a SQL database for daily operations. lets use this proprietary Microsoft thing because they are paying us
so yay, problem solved. we now never miss the logs. so how do we read them if they are split up line by line in a database? why with a query of course!
select * from tbLogs where RobotUID = [64CharLongString] and timestamp > [UnixTimeCode]
if this makes no sense to you, CONGRATULATIONS! you found the problem with this setup. Most FSE's were BAD at SQL which meant they didnt read logs anymore. If you do understand what the query is, CONGRATULATIONS! you see why this is Very Stupid.
You could not search by robot name. each robot had some arbitrarily assigned 64 character long string as an identifier and the timestamps were not set to local time. so you had run a lookup query to find the right name and do some time zone math to figure out what part of the logs to read. oh yeah and you had to download KQL to view them. so now we had both SQL and KQL on our computers
NOBODY in the field like this.
But Daddy Microsoft comes to the rescue
see we didnt JUST get KQL with part of that deal. we got the entire Microsoft cloud suite. and some people (like me) had been automating emails and stuff with Power Automate

This is Microsoft Power Automate. its Microsoft's version of Scratch but it has hooks into everything Microsoft. SharePoint, Teams, Outlook, Excel, it can integrate with all of it. i had been using it to send an email once a day with a list of all the robots in maintenance.
this gave me an idea
and i checked
and Power Automate had hooks for KQL
KLogs is actually short for Kusto Logs
I did not know how to program in Power Automate but damn it anything is better then writing KQL queries. so i got to work. and about 2 months later i had a BEHEMOTH of a Power Automate program. it lagged the webpage and many times when i tried to edit something my changes wouldn't take and i would have to click in very specific ways to ensure none of my variables were getting nuked. i dont think this was the intended purpose of Power Automate but this is what it did
the KLogger would watch a list of Teams chats and when someone typed "klogs" or pasted a copy of an ERROR mesage, it would spring into action.
it extracted the robot name from the message and timestamp from teams
it would lookup the name in the database to find the 64 long string UID and the location that robot was assigned too
it would reply to the message in teams saying it found a robot name and was getting logs
it would run a KQL query for the database and get the control system logs then export then into a CSV
it would save the CSV with the a .xls extension into a folder in ShairPoint (it would make a new folder for each day and location if it didnt have one already)
it would send ANOTHER message in teams with a LINK to the file in SharePoint
it would then enter a loop and scour the robot logs looking for the keyword ESTOP to find the error. (it did this because Kusto was SLOWER then the xbee radio and had up to a 10 min delay on syncing)
if it found the error, it would adjust its start and end timestamps to capture it and export the robot logs book-ended from the event by ~ 1 min. if it didnt, it would use the timestamp from when it was triggered +/- 5 min
it saved THOSE logs to SharePoint the same way as before
it would send ANOTHER message in teams with a link to the files
it would then check if the error was 1 of 3 very specific type of error with the camera. if it was it extracted the base64 jpg image saved in KQL as a byte array, do the math to convert it, and save that as a jpg in SharePoint (and link it of course)
and then it would terminate. and if it encountered an error anywhere in all of this, i had logic where it would spit back an error message in Teams as plaintext explaining what step failed and the program would close gracefully
I deployed it without asking anyone at one of the sites that was struggling. i just pointed it at their chat and turned it on. it had a bit of a rocky start (spammed chat) but man did the FSE's LOVE IT.
about 6 months later software deployed their answer to reading the logs: a webpage that acted as a nice GUI to the KQL database. much better then an CSV file
it still needed you to scroll though a big drop-down of robot names and enter a timestamp, but i noticed something. all that did was just change part of the URL and refresh the webpage
SO I MADE KLOGS 2 AND HAD IT GENERATE THE URL FOR YOU AND REPLY TO YOUR MESSAGE WITH IT. (it also still did the control server and jpg stuff). Theres a non-zero chance that klogs was still in use long after i left that job
now i dont recommend anyone use power automate like this. its clunky and weird. i had to make a variable called "Carrage Return" which was a blank text box that i pressed enter one time in because it was incapable of understanding /n or generating a new line in any capacity OTHER then this (thanks support forum).
im also sure this probably is giving the actual programmer people anxiety. imagine working at a company and then some rando you've never seen but only heard about as "the FSE whos really good at root causing stuff", in a department that does not do any coding, managed to, in their spare time, build and release and entire workflow piggybacking on your work without any oversight, code review, or permission.....and everyone liked it
#comet tales#lazee works#power automate#coding#software engineering#it was so funny whenever i visited HQ because i would go “hi my name is LazeeComet” and they would go “OH i've heard SO much about you”
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
SQLi Potential Mitigation Measures
Phase: Architecture and Design
Strategy: Libraries or Frameworks
Use a vetted library or framework that prevents this weakness or makes it easier to avoid. For example, persistence layers like Hibernate or Enterprise Java Beans can offer protection against SQL injection when used correctly.
Phase: Architecture and Design
Strategy: Parameterization
Use structured mechanisms that enforce separation between data and code, such as prepared statements, parameterized queries, or stored procedures. Avoid constructing and executing query strings with "exec" to prevent SQL injection [REF-867].
Phases: Architecture and Design; Operation
Strategy: Environment Hardening
Run your code with the minimum privileges necessary for the task [REF-76]. Limit user privileges to prevent unauthorized access if an attack occurs, such as by ensuring database applications don’t run as an administrator.
Phase: Architecture and Design
Duplicate client-side security checks on the server to avoid CWE-602. Attackers can bypass client checks by altering values or removing checks entirely, making server-side validation essential.
Phase: Implementation
Strategy: Output Encoding
Avoid dynamically generating query strings, code, or commands that mix control and data. If unavoidable, use strict allowlists, escape/filter characters, and quote arguments to mitigate risks like SQL injection (CWE-88).
Phase: Implementation
Strategy: Input Validation
Assume all input is malicious. Use strict input validation with allowlists for specifications and reject non-conforming inputs. For SQL queries, limit characters based on parameter expectations for attack prevention.
Phase: Architecture and Design
Strategy: Enforcement by Conversion
For limited sets of acceptable inputs, map fixed values like numeric IDs to filenames or URLs, rejecting anything outside the known set.
Phase: Implementation
Ensure error messages reveal only necessary details, avoiding cryptic language or excessive information. Store sensitive error details in logs but be cautious with content visible to users to prevent revealing internal states.
Phase: Operation
Strategy: Firewall
Use an application firewall to detect attacks against weaknesses in cases where the code can’t be fixed. Firewalls offer defense in depth, though they may require customization and won’t cover all input vectors.
Phases: Operation; Implementation
Strategy: Environment Hardening
In PHP, avoid using register_globals to prevent weaknesses like CWE-95 and CWE-621. Avoid emulating this feature to reduce risks. source
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Defines a Truly Secure Website?

In today's digital landscape, a website is often the front door to a business, a personal brand, or vital information. With cyber threats constantly evolving, the question isn't just "Is my website online?" but "Is my website truly secure?" Many users look for the padlock icon and "HTTPS" in the address bar and breathe a sigh of relief. While essential, that green lock is merely the beginning of true website security.
HTTPS signifies that the connection between your browser and the website's server is encrypted, protecting data in transit. But a truly secure website goes far beyond encrypting data between two points. It's built on a multi-layered defense strategy, addressing vulnerabilities at every level of the application and infrastructure.
So, what are the characteristics of a website you can genuinely trust?
1. Always Uses HTTPS with Strong TLS Protocols
This is the foundational layer, but its proper implementation is crucial.
What it is: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the communication between the user's browser and the website's server using TLS (Transport Layer Security, the modern successor to SSL) certificates.
Why it's essential: It prevents eavesdropping, tampering, and message forgery, ensuring that the data you send (like login credentials or credit card numbers) and receive remains private and integral. Modern browsers flag sites without HTTPS as "Not Secure." Crucially, truly secure websites use strong, up-to-date TLS versions (like TLS 1.2 or 1.3), not older, vulnerable ones.
2. Robust Input Validation and Output Encoding
These are fundamental defenses against some of the most common web attacks.
Input Validation: Every piece of data a user submits (forms, search queries, URLs) must be strictly validated before the server processes it. This prevents attackers from injecting malicious code (e.g., SQL Injection, Command Injection) that could manipulate the database or execute commands on the server.
Output Encoding: Any data retrieved from a database or user input that is displayed back on the website must be properly encoded. This prevents Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, where malicious scripts could be executed in a user's browser, stealing cookies or defacing the site.
3. Strong Authentication & Authorization Mechanisms
Security starts with knowing who is accessing your site and what they are allowed to do.
Authentication:
Strong Password Policies: Enforce minimum length, complexity (mix of characters), and disallow common or previously breached passwords.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Offer and ideally mandate MFA for all user accounts, especially administrative ones. This adds a critical layer of security beyond just a password.
Secure Session Management: Use secure, short-lived session tokens, implement proper session timeouts, and regenerate session IDs upon privilege escalation to prevent session hijacking.
Authorization: Implement the principle of least privilege. Users should only have access to the data and functionalities strictly necessary for their role. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is key here, ensuring a customer can't access admin features, for instance.
4. Regular Security Updates & Patch Management
Software is complex, and vulnerabilities are constantly discovered.
Continuous Patching: The website's underlying operating system, web server software (e.g., Apache, Nginx), Content Management System (CMS) like WordPress or Drupal, plugins, themes, and all third-party libraries must be kept up-to-date with the latest security patches.
Why it's essential: Unpatched vulnerabilities are a common entry point for attackers. A truly secure website has a rigorous system for identifying and applying updates swiftly.
5. Comprehensive Error Handling & Logging
What happens when things go wrong, or suspicious activity occurs?
Generic Error Messages: Error messages should be generic and not reveal sensitive system information (e.g., database connection strings, file paths, or specific error codes) that attackers could use to map your system.
Robust Logging: All security-relevant events – failed login attempts, successful logins, administrative actions, suspicious requests, and critical system events – should be logged. These logs should be stored securely, centrally, and monitored in real-time by a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for anomalies and potential attacks.
6. Secure Development Practices (SDL)
Security isn't an afterthought; it's built in from the ground up.
Security by Design: A truly secure website is born from a development process where security considerations are embedded at every stage – from initial design and architecture to coding, testing, and deployment. This is known as a Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL).
Code Reviews & Testing: Regular security code reviews, static application security testing (SAST), and dynamic application security testing (DAST) are performed to identify and fix vulnerabilities before the code ever goes live.
7. Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF acts as a protective shield for your website.
What it does: It monitors and filters HTTP traffic between the web application and the internet. It can detect and block common web-based attacks (like SQL injection, XSS, DDoS, brute-force attempts) before they reach the application.
Why it helps: It provides an additional layer of defense, especially useful for mitigating new threats before a patch is available or for protecting against known vulnerabilities.
8. Data Encryption at Rest
While HTTPS encrypts data in transit, data stored on servers needs protection too.
Sensitive Data Encryption: Databases, file systems, and backups containing sensitive user information (passwords, PII, financial data) should be encrypted.
Why it's important: Even if an attacker manages to breach your server and access the underlying storage, the data remains unreadable without the encryption key, significantly mitigating the impact of a breach.
9. Regular Security Audits & Penetration Testing
Proactive testing is key to finding weaknesses before malicious actors do.
Vulnerability Scanning: Automated tools scan your website for known vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing (Pen-Testing): Ethical hackers simulate real-world attacks to exploit vulnerabilities, test your defenses, and assess your overall security posture. These should be conducted regularly and after significant changes to the website.
10. Clear Privacy Policy & Data Handling Transparency
While not a strictly technical security feature, transparency builds user trust and demonstrates responsible data stewardship.
What it includes: A clear, easily accessible privacy policy explaining what data is collected, why it's collected, how it's used, how it's protected, and who it's shared with.
Why it matters: It shows commitment to data security and respects user privacy, a fundamental aspect of a truly trustworthy online presence.
A truly secure website is not a static state achieved by checking a few boxes. It's a continuous commitment to vigilance, proactive measures, and a deep understanding that security is an ongoing process involving people, technology, and robust policies. In a world where digital trust is paramount, building and maintaining a genuinely secure website is an investment that pays dividends in reputation, customer loyalty, and business continuity.
0 notes
Text
PHP with MySQL: Best Practices for Database Integration
PHP and MySQL have long formed the backbone of dynamic web development. Even with modern frameworks and languages emerging, this combination remains widely used for building secure, scalable, and performance-driven websites and web applications. As of 2025, PHP with MySQL continues to power millions of websites globally, making it essential for developers and businesses to follow best practices to ensure optimized performance and security.
This article explores best practices for integrating PHP with MySQL and explains how working with expert php development companies in usa can help elevate your web projects to the next level.
Understanding PHP and MySQL Integration
PHP is a server-side scripting language used to develop dynamic content and web applications, while MySQL is an open-source relational database management system that stores and manages data efficiently. Together, they allow developers to create interactive web applications that handle tasks like user authentication, data storage, and content management.
The seamless integration of PHP with MySQL enables developers to write scripts that query, retrieve, insert, and update data. However, without proper practices in place, this integration can become vulnerable to performance issues and security threats.
1. Use Modern Extensions for Database Connections
One of the foundational best practices when working with PHP and MySQL is using modern database extensions. Outdated methods have been deprecated and removed from the latest versions of PHP. Developers are encouraged to use modern extensions that support advanced features, better error handling, and more secure connections.
Modern tools provide better performance, are easier to maintain, and allow for compatibility with evolving PHP standards.
2. Prevent SQL Injection Through Prepared Statements
Security should always be a top priority when integrating PHP with MySQL. SQL injection remains one of the most common vulnerabilities. To combat this, developers must use prepared statements, which ensure that user input is not interpreted as SQL commands.
This approach significantly reduces the risk of malicious input compromising your database. Implementing this best practice creates a more secure environment and protects sensitive user data.
3. Validate and Sanitize User Inputs
Beyond protecting your database from injection attacks, all user inputs should be validated and sanitized. Validation ensures the data meets expected formats, while sanitization cleans the data to prevent malicious content.
This practice not only improves security but also enhances the accuracy of the stored data, reducing errors and improving the overall reliability of your application.
4. Design a Thoughtful Database Schema
A well-structured database is critical for long-term scalability and maintainability. When designing your MySQL database, consider the relationships between tables, the types of data being stored, and how frequently data is accessed or updated.
Use appropriate data types, define primary and foreign keys clearly, and ensure normalization where necessary to reduce data redundancy. A good schema minimizes complexity and boosts performance.
5. Optimize Queries for Speed and Efficiency
As your application grows, the volume of data can quickly increase. Optimizing SQL queries is essential for maintaining performance. Poorly written queries can lead to slow loading times and unnecessary server load.
Developers should avoid requesting more data than necessary and ensure queries are specific and well-indexed. Indexing key columns, especially those involved in searches or joins, helps the database retrieve data more quickly.
6. Handle Errors Gracefully
Handling database errors in a user-friendly and secure way is important. Error messages should never reveal database structures or sensitive server information to end-users. Instead, errors should be logged internally, and users should receive generic messages that don’t compromise security.
Implementing error handling protocols ensures smoother user experiences and provides developers with insights to debug issues effectively without exposing vulnerabilities.
7. Implement Transactions for Multi-Step Processes
When your application needs to execute multiple related database operations, using transactions ensures that all steps complete successfully or none are applied. This is particularly important for tasks like order processing or financial transfers where data integrity is essential.
Transactions help maintain consistency in your database and protect against incomplete data operations due to system crashes or unexpected failures.
8. Secure Your Database Credentials
Sensitive information such as database usernames and passwords should never be exposed within the application’s core files. Use environment variables or external configuration files stored securely outside the public directory.
This keeps credentials safe from attackers and reduces the risk of accidental leaks through version control or server misconfigurations.
9. Backup and Monitor Your Database
No matter how robust your integration is, regular backups are critical. A backup strategy ensures you can recover quickly in the event of data loss, corruption, or server failure. Automate backups and store them securely, ideally in multiple locations.
Monitoring tools can also help track database performance, detect anomalies, and alert administrators about unusual activity or degradation in performance.
10. Consider Using an ORM for Cleaner Code
Object-relational mapping (ORM) tools can simplify how developers interact with databases. Rather than writing raw SQL queries, developers can use ORM libraries to manage data through intuitive, object-oriented syntax.
This practice improves productivity, promotes code readability, and makes maintaining the application easier in the long run. While it’s not always necessary, using an ORM can be especially helpful for teams working on large or complex applications.
Why Choose Professional Help?
While these best practices can be implemented by experienced developers, working with specialized php development companies in usa ensures your web application follows industry standards from the start. These companies bring:
Deep expertise in integrating PHP and MySQL
Experience with optimizing database performance
Knowledge of the latest security practices
Proven workflows for development and deployment
Professional PHP development agencies also provide ongoing maintenance and support, helping businesses stay ahead of bugs, vulnerabilities, and performance issues.
Conclusion
PHP and MySQL remain a powerful and reliable pairing for web development in 2025. When integrated using modern techniques and best practices, they offer unmatched flexibility, speed, and scalability.
Whether you’re building a small website or a large-scale enterprise application, following these best practices ensures your PHP and MySQL stack is robust, secure, and future-ready. And if you're seeking expert assistance, consider partnering with one of the top php development companies in usa to streamline your development journey and maximize the value of your project.
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Tools for Salesforce Data Migration in 2025

Data migration is a critical aspect of any Salesforce implementation or upgrade. Whether you’re transitioning from legacy systems, merging Salesforce orgs, or simply updating your current Salesforce instance, choosing the right tool can make or break the success of your migration. In 2025, the landscape of Salesforce data migration tools has evolved significantly, offering more automation, better user interfaces, and improved compatibility with complex datasets.
If you're a business looking to ensure a smooth migration process, working with an experienced Salesforce consultant in New York can help you identify the best tools and practices. Here's a detailed look at the top five Salesforce data migration tools in 2025 and how they can help your organization move data efficiently and accurately.
1. Salesforce Data Loader (Enhanced 2025 Edition)
Overview: The Salesforce Data Loader remains one of the most popular tools, especially for companies looking for a free, secure, and reliable way to manage data migration. The 2025 edition comes with a modernized UI, faster processing speeds, and enhanced error logging.
Why It’s Top in 2025:
Improved speed and performance
Enhanced error tracking and data validation
Seamless integration with external databases like Oracle, SQL Server, and PostgreSQL
Support for larger datasets (up to 10 million records)
Best For: Organizations with experienced admins or developers who are comfortable working with CSV files and need a high level of control over their data migration process.
Pro Tip: Engage a Salesforce developer in New York to write custom scripts for automating the loading and extraction processes. This will save significant time during large migrations.
2. Skyvia
Overview: Skyvia has emerged as a go-to cloud-based data integration tool that simplifies Salesforce data migration, especially for non-technical users. With drag-and-drop functionality and pre-built templates, it supports integration between Salesforce and over 100 other platforms.
Why It’s Top in 2025:
No coding required
Advanced transformation capabilities
Real-time sync between Salesforce and other cloud applications
Enhanced data governance features
Best For: Mid-sized businesses and enterprises that need a user-friendly platform with robust functionality and real-time synchronization.
Use Case: A retail company integrating Shopify, Salesforce, and NetSuite found Skyvia especially helpful in maintaining consistent product and customer data across platforms.
Expert Advice: Work with a Salesforce consulting partner in New York to set up your data models and design a migration path that aligns with your business processes.
3. Jitterbit Harmony
Overview: Jitterbit Harmony is a powerful data integration platform that enables users to design, run, and manage integration workflows. In 2025, it remains a favorite for enterprises due to its AI-powered suggestions and robust performance in complex scenarios.
Why It’s Top in 2025:
AI-enhanced mapping and transformation logic
Native Salesforce connector with bulk API support
Real-time data flow monitoring and alerts
Cross-platform compatibility (on-premise to cloud, cloud to cloud)
Best For: Large enterprises and organizations with complex IT ecosystems requiring high-throughput data migration and real-time integrations.
Tip from the Field: A Salesforce consulting firm in New York can help fine-tune your Jitterbit setup to ensure compliance with your industry regulations and data handling policies.
4. Informatica Cloud Data Wizard
Overview: Informatica is well-known in the enterprise data integration space. The Cloud Data Wizard is a lightweight, Salesforce-focused tool designed for business users. In 2025, its intuitive interface and automated field mapping make it a favorite for quick and simple migrations.
Why It’s Top in 2025:
Automatic schema detection and mapping
Pre-built Salesforce templates
Role-based access control for secure collaboration
Integration with Salesforce Flow for process automation
Best For: Companies needing quick, on-the-fly migrations with minimal IT involvement.
Case in Point: A nonprofit organization used Informatica Cloud Data Wizard for migrating donor information from spreadsheets into Salesforce Nonprofit Success Pack (NPSP) with minimal technical assistance.
Pro Insight: Partner with a Salesforce consultant in New York to evaluate whether the Cloud Data Wizard meets your scalability and security needs before committing.
5. Talend Data Fabric
Overview: Talend Data Fabric combines data integration, quality, and governance in one unified platform. In 2025, it leads the way in enterprise-grade data migration for Salesforce users who require deep customization, high security, and data lineage tracking.
Why It’s Top in 2025:
Full data quality and compliance toolset
AI-driven suggestions for data cleaning and transformation
End-to-end data lineage tracking
Integration with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Best For: Industries with strict compliance needs like finance, healthcare, or government, where data accuracy and traceability are paramount.
Strategic Advantage: A Salesforce consulting partner in New York can help configure Talend’s governance tools to align with HIPAA, GDPR, or other regulatory requirements.
Why Choosing the Right Tool Matters
Data migration is more than just moving records from one system to another—it’s about preserving the integrity, security, and usability of your data. Choosing the right tool ensures:
Fewer errors and data loss
Faster deployment timelines
Higher end-user adoption
Better alignment with business goals
Partnering with Salesforce Experts in New York
Working with an experienced Salesforce consultant in New York can help you navigate the complexities of data migration. Local consultants understand both the technical and business landscapes and can offer personalized support throughout the migration journey.
Whether you're a startup looking for lean, cost-effective solutions or a large enterprise needing advanced governance, engaging with Salesforce consultants in New York ensures you make the most informed decisions.
These professionals can:
Conduct data audits and mapping
Recommend the best tool for your specific use case
Build custom scripts or integrations as needed
Ensure a smooth transition with minimal business disruption
Final Thoughts
In 2025, Salesforce data migration is no longer a cumbersome, manual task. With tools like Salesforce Data Loader, Skyvia, Jitterbit, Informatica, and Talend, businesses of all sizes can achieve fast, secure, and seamless migrations. The key lies in selecting the right tool based on your business size, technical capacity, and compliance needs.
Moreover, partnering with a knowledgeable Salesforce consulting partner in New York gives you access to tailored solutions and hands-on support, making your data migration journey smooth and successful.
Ready to migrate your data the right way? Consult with a trusted Salesforce consulting in New York expert and empower your business to scale with confidence.
#salesforce consultant in new york#salesforce consulting in new york#salesforce consulting partner in new york#salesforce consultants in new york#salesforce developer in new york#Top 5 Tools for Salesforce Data Migration in 2025
0 notes
Text
nMon Nulled Script 1.12

Discover the Power of nMon Nulled Script for Website Monitoring If you’re looking for a reliable and cost-effective solution to keep your website and server performance under control, the nMon Nulled Script is your perfect choice. This advanced monitoring tool empowers webmasters and developers to track their websites seamlessly, ensuring uptime and speed are optimized without any hassle. Available for free download from our website, the nMon Nulled Script offers an all-in-one service monitoring solution that caters to every website owner’s needs. What Is nMon Nulled Script? – A Detailed Product Description The nMon is a professional-grade website and server monitoring script originally developed to provide comprehensive real-time analytics. It offers features such as uptime monitoring, speed analysis, and detailed reports that help you understand how your site is performing at any moment. With the nulled version available for free download on our platform, you get access to all premium functionalities without paying a penny. Whether you manage a personal blog, an e-commerce platform, or a corporate site, the nMon ensures you never miss a critical alert that could impact your online presence. The script integrates easily with various hosting environments and requires minimal configuration, making it user-friendly for beginners and professionals alike. Technical Specifications of nMon Nulled Script Compatible with most web servers including Apache and Nginx Supports PHP 7.2 and above for smooth operation Database integration with MySQL or MariaDB Responsive interface optimized for desktop and mobile devices Real-time data visualization using interactive charts and tables Customizable alert system with email and SMS notifications Lightweight code ensuring minimal server resource consumption Features and Benefits of Using nMon Nulled Script The nMon Nulled Script offers a rich set of features designed to make website monitoring effortless and efficient: Real-Time Monitoring: Get instant updates on website uptime and server performance to tackle issues proactively. Comprehensive Reports: Analyze traffic, response times, and error logs to enhance your site’s reliability. Easy Integration: Seamlessly incorporate the script into your existing infrastructure with straightforward setup guides. Free Access: Download the nMon Nulled Script for free from our website, enabling budget-friendly website management. Boost SEO Performance: Maintain optimal website speed and availability, key factors in search engine rankings. Use Cases for nMon Nulled Script This script is highly versatile and suitable for various scenarios: Website Owners: Keep your site up and running smoothly to deliver the best user experience. Developers: Monitor client websites and servers effectively with a tool that supports multiple environments. Digital Agencies: Offer premium monitoring services to your customers without extra licensing costs. E-commerce Platforms: Ensure uninterrupted service during peak sales periods to maximize conversions. Installation and Usage Guide for nMon Script Getting started with the Nulled Script is straightforward: Download the Script: Access the nulled version directly from our website without any fees. Upload to Server: Transfer the files to your web server via FTP or your hosting control panel. Configure Database: Create a MySQL database and import the provided SQL file to set up necessary tables. Adjust Settings: Modify configuration files with your database credentials and preferred monitoring parameters. Access the Dashboard: Log in to the admin panel to start monitoring your website and server statistics. For enhanced website design, consider pairing this tool with wpbakery nulled, which is available for free download on our site. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Is the nMon Nulled Script safe to use? Yes, our version is thoroughly tested to ensure it functions correctly without security risks. Always download nulled scripts from trusted sources like our website.
Can I customize the monitoring alerts? Absolutely! The script allows you to set up email and SMS notifications tailored to your monitoring preferences. Does it support mobile devices? Yes, the interface is fully responsive and accessible on smartphones and tablets. Where can I get professional design plugins to complement nMon? We recommend trying elementor nulled pro for advanced page building features.
0 notes
Text
Migrate or move WordPress website to a new host in 2025
Why You Might Need to Move Your WordPress Site
Your website is important. But sometimes, your web host may be slow, expensive, or not helpful. When that happens, it’s smart to move your website to a better hosting company. A better host can help your site load faster, stay online, and keep visitors happy.
You can move your website in two ways:
Manually (you do everything step by step)
Automatically (you use a plugin to help)
This full guide will show you both ways. It will also teach you what to do after you move your site to make sure everything works.
If this sounds hard, don’t worry. You can also get help from Creation Wave LLC. We help people move WordPress websites safely and quickly.
Table of Contents
Manual vs Automatic Migration
Manual Migration – Step by Step
How to Move WordPress Without cPanel
How to Use a Plugin to Migrate Your Site
What to Check After Migration
Final Thoughts and Expert Help
Should You Move Your Site Manually or Use a Plugin?
There are two ways to move your WordPress site:
Manual Migration
This is where you download your files and database and upload them to the new host yourself. It gives you more control, but you need to be careful. One small mistake can break your site. This is better for large websites or people with some technical skills.
Automatic Migration
This uses a WordPress plugin to move your site. It is easier and faster. It is perfect for small websites or beginners. You don’t have to touch any code.
If you're not sure which to pick, try a plugin first. If it doesn't work or gives errors, you can move it manually or get expert help.
Need help? Creation Wave LLC offers both manual and automatic WordPress migration services.
Manual WordPress Migration (Step-by-Step Guide)
This part will show you how to manually move your WordPress website to a new host.
Step 1: Choose a New Hosting Company
Make sure your new host is fast, secure, and helpful. Look for companies that offer good customer support and daily backups.
Types of hosting:
Shared hosting (basic and cheap)
VPS hosting (faster and more private)
Managed WordPress hosting (easy and fully managed)
Dedicated server (for very large sites)
If you need help picking the right host, Creation Wave LLC can help you choose the best one.
Step 2: Backup Your WordPress Files
Your website files are very important. They include your theme, plugins, images, and settings.
To back them up:
Use an FTP client like FileZilla.
Connect to your old host using FTP login details.
Find the folder named “public_html” or your WordPress folder.
Download all the files to your computer.
Wait until the download finishes before going to the next step.
Step 3: Export Your Database
Your website database has all your posts, pages, user accounts, and comments.
To export it:
Log in to cPanel on your old host.
Open phpMyAdmin.
Click your WordPress database name on the left.
Click the “Export” tab at the top.
Choose “Quick” and “SQL” format.
Click “Go” to download the file.
Save this file in a safe place.
Step 4: Create a New Database on Your New Host
Now go to your new hosting account. Do this:
Log into cPanel.
Click “MySQL Databases.”
Create a new database.
Create a new user and give it a strong password.
Add the user to the database and give it all permissions.
Write down the database name, user name, and password. You will need them soon.
Step 5: Upload WordPress Files to New Host
Now it’s time to put your website files on the new server.
To upload:
Open FileZilla again.
Connect to your new host with your new FTP details.
Go to the folder named “public_html” or root folder.
Upload all your website files from your computer.
Wait for the upload to finish before moving on.
Step 6: Import Your Database
Now you need to import your old database to the new host.
Log in to cPanel on the new host.
Open phpMyAdmin.
Click your new database name.
Click the “Import” tab.
Choose the .sql file you downloaded earlier.
Click “Go.”
This will add your old content to your new hosting account.
Step 7: Update the wp-config.php File
WordPress needs to know how to connect to the database.
In FileZilla, find and open the file “wp-config.php.”
Right-click and choose Edit.
Update the database name, user, and password:
define('DB_NAME', 'your_new_db_name'); define('DB_USER', 'your_new_db_user'); define('DB_PASSWORD', 'your_new_password');
Save and close the file.
Now WordPress can talk to the new database.
Step 8: Point Your Domain to the New Host
This is the final step.
Log into the account where you bought your domain (like GoDaddy or Namecheap).
Find DNS or Nameserver Settings.
Change the nameservers to the new hosting company’s nameservers.
Save and wait.
It can take 1–24 hours for the DNS to update fully. After that, your site will be live on the new host.
How to Migrate Without cPanel
Some hosting providers don’t use cPanel. That’s okay. You can still migrate your website.
Here’s what to do:
Ask your host for FTP access and MySQL access.
Use FileZilla to upload files.
Use another tool like Adminer or CLI (command-line) to import your database.
Update your wp-config.php file as shown earlier.
If this sounds too technical, Creation Wave LLC can do it for you.
How to Use a Plugin to Migrate Your WordPress Site
If you want an easier way, use a migration plugin. Here are three good ones:
All-in-One WP Migration
Simple drag-and-drop tool.
Great for beginners.
Duplicator
Makes a full copy of your website.
Offers more options for developers.
UpdraftPlus (Paid)
Does backups and migrations.
Good support.
To use a plugin:
Install the plugin on your old website.
Use the plugin to export the full site.
Set up a clean WordPress install on your new host.
Install the same plugin there.
Import the file you exported earlier.
After a few minutes, your site should be live.
What to Check After Migration
After moving your website, test everything. Check the following:
Is your homepage loading fast?
Are all your pages and posts showing?
Are your images loading?
Can you log into the WordPress dashboard?
Are all your plugins working?
Is the site mobile-friendly?
Also test your contact forms, menus, and links. You can use free tools like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed to check speed.
If anything looks broken, go back and check your steps.
Need help? Creation Wave LLC offers a full post-migration checkup.
Final Thoughts
Moving your WordPress website can feel scary. But with the right steps, it’s not so hard. This guide helps you move your site by yourself or with a plugin. You also learned how to test your site after moving.
A better host can give you faster speed, better uptime, and better support. If you don’t want to take risks or waste time, you can let experts do it for you.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Reading and Importing Data in SAS: CSV, Excel, and More
In the world of data analytics, efficient data importation is a fundamental skill. SAS (Statistical Analysis System), a powerful platform for data analysis and statistical computing, offers robust tools to read and import data from various formats, including CSV, Excel, and more. Regardless of whether you are a beginner or overseeing analytics at an enterprise level, understanding how to import data into SAS is the initial step towards obtaining valuable insights.
This article breaks down the most common methods of importing data in SAS, along with best practices and real-world applications—offering value to everyone from learners in a Data Analyst Course to experienced professionals refining their workflows.
Why Importing Data Matters in SAS
Before any analysis begins, the data must be accessible. Importing data correctly ensures integrity, compatibility, and efficiency in processing. SAS supports a range of formats, allowing analysts to work with data from different sources seamlessly. The most common among these are CSV and Excel files due to their ubiquity in business and research environments.
Understanding how SAS handles these files can drastically improve productivity, particularly when working with large datasets or performing repetitive tasks in reporting and modelling.
Importing CSV Files into SAS
Comma-Separated Values (CSV) files are lightweight, easy to generate, and commonly used to exchange data. In SAS, importing CSVs is straightforward.
When importing a CSV file, SAS treats each line as an observation and each comma as a delimiter between variables. This format is ideal for users who deal with exported data from databases or web applications.
Best Practices:
Clean your CSV files before importing—ensure no missing headers, extra commas, or encoding issues.
Use descriptive variable names in the first row of the CSV to streamline your SAS workflow.
Always review the imported data to verify that variable types and formats are interpreted correctly.
Professionals undertaking a Data Analyst Course often begin with CSV files due to their simplicity, making this an essential foundational skill.
Importing Excel Files into SAS
Excel files are the go-to format for business users and analysts. They often contain multiple sheets, merged cells, and various data types, which adds complexity to the import process.
SAS provides built-in tools for reading Excel files, including engines like XLSX and the Import Wizard, which are available in SAS Studio or Enterprise Guide. These tools allow users to preview sheets, specify ranges, and even convert date formats during import.
Key Considerations:
Ensure the Excel file is not open during import to avoid access errors.
Use consistent formatting in Excel—SAS may misinterpret mixed data types within a single column.
If your Excel workbook contains multiple sheets, decide whether you need to import one or all of them.
Advanced users and those enrolled in a Data Analytics Course in Mumbai often work with Excel as part of larger data integration pipelines, making mastery of these techniques critical.
Importing Data from Other Sources
Beyond CSV and Excel, SAS supports numerous other data formats, including:
Text files (.txt): Often used for raw data exports or logs.
Database connections: Through SAS/ACCESS, users can connect to databases like Oracle, SQL Server, or MySQL.
JSON and XML: Increasingly used in web-based and API data integrations.
SAS Datasets (.sas7bdat): Native format with optimised performance for large datasets.
Each format comes with its own import nuances, such as specifying delimiters, encoding schemes, or schema mappings. Familiarity with these enhances flexibility in working with diverse data environments.
Tips for Efficient Data Importing
Here are a few practical tips to improve your SAS data importing skills:
Automate repetitive imports using macros or scheduled jobs.
Validate imported data against source files to catch discrepancies early.
Log and document your import steps—especially when working in team environments or preparing data for audits.
Stay updated: SAS frequently updates its procedures and import capabilities to accommodate new formats and security standards.
Learning and Upskilling with SAS
Importing data is just one piece of the SAS puzzle. For aspiring data professionals, structured training offers the advantage of guided learning, hands-on practice, and industry context. A Data Analyst training will typically begin with data handling techniques, setting the stage for more advanced topics like modelling, visualisation, and predictive analytics.
For learners in metro regions, a Data Analytics Course in Mumbai can provide local networking opportunities, expert mentorship, and exposure to real-world projects involving SAS. These programs often include training in data import techniques as part of their curriculum, preparing students for the demands of modern data-driven roles.
Final Thoughts
Reading and importing data into SAS is a vital skill that underpins all subsequent analysis. Whether you're working with CSV files exported from a CRM, Excel spreadsheets from finance teams, or direct connections to enterprise databases, mastering these tasks can significantly enhance your efficiency and accuracy.
By understanding the nuances of each data format and leveraging SAS's powerful import tools, you’ll be better equipped to manage data workflows, ensure data quality, and drive valuable insights. And for those committed to building a career in analytics, a course could be the stepping stone to mastering not just SAS but the entire data science pipeline.
Business name: ExcelR- Data Science, Data Analytics, Business Analytics Course Training Mumbai
Address: 304, 3rd Floor, Pratibha Building. Three Petrol pump, Lal Bahadur Shastri Rd, opposite Manas Tower, Pakhdi, Thane West, Thane, Maharashtra 400602
Phone: 09108238354,
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
A Day in the Life of a Fullstack Web Developer: Balancing Frontend and Backend Mastery
Ever wonder what it's like to walk in the shoes of a full stack web developer? From designing sleek user interfaces to diving deep into server logic, databases, and APIs — their day is anything but monotonous. These digital multitaskers blend creativity with logic, structure with style, and vision with execution.
Whether you're considering becoming one or hiring one, let’s take a walk through a typical day in the life of a full stack developer — where frontend flair meets backend brainpower.
Morning: Sync, Strategy, and Setting Up
Most full stack developers start their day with a team stand-up meeting — a quick daily sync often used in agile development. Here, they update the team on what they worked on yesterday, what they plan to do today, and any blockers they’re facing.
Key morning tasks:
Reviewing tickets from tools like Jira or Trello
Prioritizing bug fixes or new features
Collaborating with designers, PMs, or stakeholders
Checking version control platforms (like GitHub or GitLab)
Then, it’s time to open the editor. Depending on the day, they might start on the frontend — building a responsive page in React — or dive straight into the backend to improve database queries or tweak an API endpoint.
Midday: Coding, Collaborating, and Coffee
Here’s where the magic happens. This is the most productive block for many full stack developers.
If they’re working on the frontend, they might:
Build UI components with frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular
Style pages with CSS, Sass, or Tailwind
Implement animations, interactions, and responsive design
Optimize page load speed and performance
On the backend side, their work could involve:
Writing RESTful APIs or GraphQL endpoints
Integrating third-party services (payment gateways, login systems, etc.)
Handling server-side logic with Node.js, Python, or Ruby
Managing data with SQL or NoSQL databases (like PostgreSQL or MongoDB)
And because they span both worlds, they constantly switch contexts, debugging frontend issues while simultaneously optimizing backend logic.
Collaboration never stops:
Code reviews and pull requests
Testing features across devices
Pair programming with team members
Syncing with DevOps for deployment or CI/CD pipeline updates
Afternoon: Testing, Tweaking, and Troubleshooting
The post-lunch hours are often spent on refinements and fixes. For full stack developers, this could mean:
Writing unit and integration tests
Debugging bugs across the stack (yes, even those weird CSS layout issues)
Monitoring logs and server errors
Fixing cross-origin or authentication issues
Because they own both sides of the development process, full stack web developers play a key role in ensuring that everything works together — seamlessly.
Common tools used during this time:
Browser DevTools
Postman or Swagger for API testing
Docker and containerization tools
Git for version control and rollbacks
Evening Wrap-Up: Documentation and Deployment
As the day winds down, most developers document their work — for the team, future developers, and sometimes even for users.
Tasks may include:
Writing README files or internal documentation
Updating wikis or knowledge bases
Merging final pull requests
Deploying code to staging or production environments
Running a last set of tests before end-of-day commits
In agile teams, this could also include a quick retrospective or check-in with a product manager or tech lead.
Why It’s So Rewarding
Ask any experienced full stack developer and they’ll tell you — the balance of frontend and backend makes the job both challenging and fulfilling.
Here’s what makes it worth it:
Creativity: Building interfaces users interact with every day.
Impact: Touching every layer of the application — from UX to performance.
Growth: Constant learning, as technologies evolve across the stack.
Problem-solving: Debugging complex issues that span the full architecture.
Ownership: Seeing a feature through from concept to production.
Final Thoughts
The life of a full stack web developer isn’t just about writing code — it’s about building complete digital experiences. Balancing frontend beauty with backend logic requires focus, flexibility, and constant communication. It’s no surprise that businesses value developers who can wear multiple hats and adapt to the full life cycle of modern web development.
In a world where the boundaries between roles are blurring, full stack web development is not just a skill — it’s a mindset.
0 notes
Text
Checking SQL Server Error Logs
Error logs contain critical information for troubleshooting issues Followings are the commands: EXEC sp_readerrorlog; EXEC xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N''; Checking the log files directly: By default, SQL Server error logs are located in the LOG folder within the SQL Server installation directory (e.g., C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.n\ MSSQL\LOG\ERRORLOG).
0 notes
Text
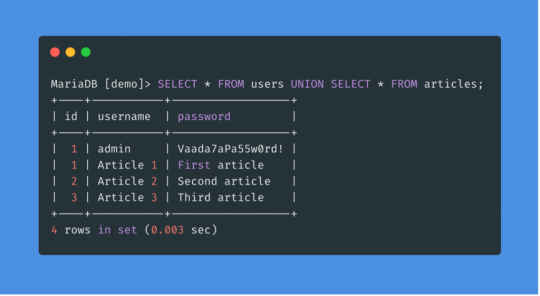
Explanation of the Injection technological principles
Overview and explanation of several injection attack types will be performed now: XSS, Shell and SQL. Let’s start with Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
XSS attacks can generally be categorized into two categories: reflected and stored. There is a third, much less well-known type of XSS attack called DOM Based XSS.
Reflected XSS Attacks (Non-Persistent or Type-I XSS)
The injected script is reflected off the web server, such as in an error message, search result, or any other response that includes some or all the input sent to the server as part of the request.
Delivered to victims via another route, such as in an e-mail message, or on some other website. When a user is tricked into clicking on a malicious link, submitting a specially crafted form, or even just browsing to a malicious site, the injected code travels to the vulnerable web site, which reflects the attack back to the user’s browser.
The browser then executes the code because it came from a “trusted” server. The attack is carried out through a single request / response cycle.
Stored XSS Attacks (Persistent or Type-II XSS)
The injected script is permanently stored on the target servers, such as in a database, in a message forum, visitor log, comment field, etc.
The victim then retrieves the malicious script from the server when it requests the stored information.
Blind Cross-site Scripting is a form of persistent XSS which generally occurs when the attacker’s payload is saved on the server and reflected to the victim from the backend application.
For example, in feedback forms, an attacker can submit the malicious payload using the form, and once the backend user/admin of the application will open the attacker’s submitted form via the backend application, the attacker’s payload will get executed.
Blind Cross-site Scripting is hard to confirm in the real-world scenario but one of the best tools for this is XSS Hunter.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Data Movement in Azure Data Factory: Key Concepts and Best Practices
Introduction
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is a fully managed, cloud-based data integration service that enables organizations to move and transform data efficiently. Understanding how data movement works in ADF is crucial for building optimized, secure, and cost-effective data pipelines.
In this blog, we will explore: ✔ Core concepts of data movement in ADF ✔ Data flow types (ETL vs. ELT, batch vs. real-time) ✔ Best practices for performance, security, and cost efficiency ✔ Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
1. Key Concepts of Data Movement in Azure Data Factory
1.1 Data Movement Overview
ADF moves data between various sources and destinations, such as on-premises databases, cloud storage, SaaS applications, and big data platforms. The service relies on integration runtimes (IRs) to facilitate this movement.
1.2 Integration Runtimes (IRs) in Data Movement
ADF supports three types of integration runtimes:
Azure Integration Runtime (for cloud-based data movement)
Self-hosted Integration Runtime (for on-premises and hybrid data movement)
SSIS Integration Runtime (for lifting and shifting SSIS packages to Azure)
Choosing the right IR is critical for performance, security, and connectivity.
1.3 Data Transfer Mechanisms
ADF primarily uses Copy Activity for data movement, leveraging different connectors and optimizations:
Binary Copy (for direct file transfers)
Delimited Text & JSON (for structured data)
Table-based Movement (for databases like SQL Server, Snowflake, etc.)
2. Data Flow Types in ADF
2.1 ETL vs. ELT Approach
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Data is extracted, transformed in a staging area, then loaded into the target system.
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): Data is extracted, loaded into the target system first, then transformed in-place.
ADF supports both ETL and ELT, but ELT is more scalable for large datasets when combined with services like Azure Synapse Analytics.
2.2 Batch vs. Real-Time Data Movement
Batch Processing: Scheduled or triggered executions of data movement (e.g., nightly ETL jobs).
Real-Time Streaming: Continuous data movement (e.g., IoT, event-driven architectures).
ADF primarily supports batch processing, but for real-time processing, it integrates with Azure Stream Analytics or Event Hub.
3. Best Practices for Data Movement in ADF
3.1 Performance Optimization
✅ Optimize Data Partitioning — Use parallelism and partitioning in Copy Activity to speed up large transfers. ✅ Choose the Right Integration Runtime — Use self-hosted IR for on-prem data and Azure IR for cloud-native sources. ✅ Enable Compression — Compress data during transfer to reduce latency and costs. ✅ Use Staging for Large Data — Store intermediate results in Azure Blob or ADLS Gen2 for faster processing.
3.2 Security Best Practices
🔒 Use Managed Identities & Service Principals — Avoid using credentials in linked services. 🔒 Encrypt Data in Transit & at Rest — Use TLS for transfers and Azure Key Vault for secrets. 🔒 Restrict Network Access — Use Private Endpoints and VNet Integration to prevent data exposure.
3.3 Cost Optimization
💰 Monitor & Optimize Data Transfers — Use Azure Monitor to track pipeline costs and adjust accordingly. 💰 Leverage Data Flow Debugging — Reduce unnecessary runs by debugging pipelines before full execution. 💰 Use Incremental Data Loads — Avoid full data reloads by moving only changed records.
4. Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid��Them
❌ Overusing Copy Activity without Parallelism — Always enable parallel copy for large datasets. ❌ Ignoring Data Skew in Partitioning — Ensure even data distribution when using partitioned copy. ❌ Not Handling Failures with Retry Logic — Use error handling mechanisms in ADF for automatic retries. ❌ Lack of Logging & Monitoring — Enable Activity Runs, Alerts, and Diagnostics Logs to track performance.
Conclusion
Data movement in Azure Data Factory is a key component of modern data engineering, enabling seamless integration between cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments. By understanding the core concepts, data flow types, and best practices, you can design efficient, secure, and cost-effective pipelines.
Want to dive deeper into advanced ADF techniques? Stay tuned for upcoming blogs on metadata-driven pipelines, ADF REST APIs, and integrating ADF with Azure Synapse Analytics!
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/azure-data-factory-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
In an already volatile IT world, it could all change in a moment, particularly when it comes to cybersecurity. And since PHP is the most powerful server-side language and the backbone for almost every website, it demands the adoption of best security practices. Therefore, PHP security shouldn’t be neglected at any cost. To prevent your PHP website from such attacks and vulnerabilities, we’ve compiled the top seven tips to help keep your website safe and secure online. Let’s have a look! 1. Keep Your Software Updated Keeping your software updated is a foundational practice of keeping your site safe and secure. It applies to both the server operating system and any software that you may be running on websites such as CMS or forums. Unfortunately, hackers can quickly attempt to abuse any vulnerabilities found in website security. If you are using third-party software on your websites, such as a CMS or forum, you should quickly apply any security patches. Most vendors have a mailing list or RSS feed detailing website security issues. In addition, there are many other CMSes such as WordPress and Umbraco that notify you of available system updates when you log in. Many developers use Composer, npm, and RubyGems to evaluate their software dependencies and security vulnerabilities. Unfortunately, if you do not pay enough attention to this area, your PHP website can be easily caught out by hackers. Ensure to keep your dependencies up to date and use tools like Gemnasium to get automatic notifications when there is a vulnerability in one of your components. 2. Beware of Error Messages Most importantly, you must know how much information you should give regarding error messages. You only need to provide only minimal errors to your users. This way, you can ensure that they don’t leak any sensitive information on your server, such as database passwords, API keys, etc. Also, pay attention not to provide full exception details so as not to invite complex attacks like SQL injection. You should keep all the detailed errors in your server logs and show your users only the information they need. 3. Check Your Passwords Many web admins often fail to use strong passwords despite this practice being considered an essential security requirement. Here, we’ve compiled a list of some effective password practices to prevent security breaches: The passwords can be more protected by storing the same encrypted values. The quality hashing algorithms can be used for this. The standard practice is to use at least eight-character passwords, including a number and a blend of uppercase and lowercase letters. If the password is still being accessed or guessed, you can use hashed passwords as they can’t be decrypted. 4. Protect Against XSS Attacks Do you know that XSS (Cross-site scripting) is one of the most common methods of hacking a website? It is done by injecting malicious JavaScript code into the web pages, which can permanently harm the website. In general, programs can run on the browsers used by the users and interfere with the user experience. XSS mainly happens through malicious program links posted through comments and other kinds of user-generated content. Using frameworks like AngularJS and EmberJS equipped with protection from cross-site scripting is a great way to prevent such attacks. In addition, it would help prevent the mixing of client-side and server-side rendering, reducing malicious JavaScript injections. There is another effective way to prevent XSS attacks; CSP (Content Security Policy) works like a server-side header to direct the browser about the JavaScript execution on any given page. In addition, it can be a potent tool to prevent cross-site scripting attacks. 5. Get Website Security Tools It’s time to test your website security when you think you have done all you can. The most effective way of doing this is using some website security tools, often referred to as penetration tests or pen-testing. There are several commercial and free products to assist you with this.
They work on a similar basis to script hackers. In this, they test all known exploits and attempts to compromise your site using SQL Injection. Check Out Some Free Tools Which are Worth Looking Into Xenotix XSS Exploit Framework: It is a tool based on OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project), which includes many XSS attack examples. This can be run to quickly confirm whether the site’s inputs are vulnerable in Chrome, Firefox, and IE. SecurityHeaders.io: This free online check tool allows free security and configuration checks for your website. OpenVas: It’s a free and open-source security testing tool with many advanced features. This tool is claimed to be the most advanced open source security scanner. It is suitable for testing known vulnerabilities and recently scanned over 25,000. Netsparker: This tool is available in both free and trial versions. It is ideal for testing XSS attacks as well as SQL injection. 6. Use HTTPS This is a protocol that is used to provide security over the Internet. HTTPS ensures what users expect in terms of security and that nobody else can change the content they see in transit. If users want anything private, it’s highly advisable to use only HTTPS to deliver it. For example, the credit card and other login pages have login forms. A login form often sets a cookie, which is sent with every other request to the website that a logged-in user makes. And it is used to authenticate those requests. An attacker might steal this sensitive information and take over the user’s login session. You only need to use HTTPS for your entire site to prevent attacks. It is now no longer as expensive as it was earlier. Let’s Encrypt offers free and automated certificates, which you’ll need to enable HTTPS. Also, there are existing community tools available for a wide range of common platforms and frameworks, which are automatically set up. Moreover, according to the report, Google will enhance those websites in search engine rankings that are equipped with HTTPS. This way, SEO benefits will also be provided to them. If you are already using HTTPS, then go further and set up HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS), an easy header that you can add to your server responses to disable insecure HTTP for your entire domain. 7. Input Validation Gazillions of PHP websites still depend on client-side programs for validating inputs. The client-side programs mean JavaScript-based input validation programs, which can easily be bypassed. You can also use rather server-side input validation programs. Final Thoughts When security threats have become more sophisticated than ever before, it’s not a good idea to depend on outdated security practices. Now you have excellent and comprehensive security strategies to prevent your PHP website from hacking. Furthermore, hiring mobile app developers for professional and advanced support is highly advisable.
0 notes
Text
A new SAP BASIS consultant faces several challenges when starting in the role. Here are the most common ones:
1. Complex Learning Curve
SAP BASIS covers a broad range of topics, including system administration, database management, performance tuning, and security.
Understanding how different SAP components (ERP, S/4HANA, BW, Solution Manager) interact can be overwhelming.
2. System Installations & Migrations
Setting up and configuring an SAP landscape requires deep knowledge of operating systems (Windows, Linux) and databases (HANA, Oracle, SQL Server).
Migration projects, such as moving from on-premise to SAP BTP or HANA, involve risks like downtime and data loss.
3. Performance Tuning & Troubleshooting
Identifying bottlenecks in SAP system performance can be challenging due to the complexity of memory management, work processes, and database indexing.
Log analysis and troubleshooting unexpected errors demand experience and knowledge of SAP Notes.
4. Security & User Management
Setting up user roles and authorizations correctly in SAP is critical to avoid security breaches.
Managing Single Sign-On (SSO) and integration with external authentication tools can be tricky.
5. Handling System Upgrades & Patching
Applying support packs, kernel upgrades, and enhancement packages requires careful planning to avoid system downtime or conflicts.
Ensuring compatibility with custom developments (Z programs) and third-party integrations is essential.
6. High Availability & Disaster Recovery
Understanding failover mechanisms, system clustering, and backup/restore procedures is crucial for minimizing downtime.
Ensuring business continuity in case of server crashes or database failures requires strong disaster recovery planning.
7. Communication & Coordination
Working with functional consultants, developers, and business users to resolve issues can be challenging if there’s a lack of clear communication.
Managing stakeholder expectations during system outages or performance issues is critical.
8. Monitoring & Proactive Maintenance
New BASIS consultants may struggle with configuring SAP Solution Manager for system monitoring and proactive alerts.
Setting up background jobs, spool management, and RFC connections efficiently takes practice.
9. Managing Transport Requests
Transporting changes across SAP environments (DEV → QA → PROD) without errors requires an understanding of transport logs and dependencies.
Incorrect transport sequences can cause system inconsistencies.
10. Staying Updated with SAP Evolution
SAP is rapidly evolving, especially with the shift to SAP S/4HANA and cloud solutions.
Continuous learning is required to stay up-to-date with new technologies like SAP BTP, Cloud ALM, and AI-driven automation.
Mail us on [email protected]
Website: Anubhav Online Trainings | UI5, Fiori, S/4HANA Trainings

0 notes
Text
How to Improve Node.js Performance for High-Traffic Apps

The high-traffic applications today hinge on flawless performance with rapid responsiveness in the domain of digital technology. Node.js boasts a non-blocking event-based architecture, which is, therefore, preferred for scalable applications. For a lack of optimization, the apps might slow down, increase the latency, or even crash during heavy-load operations.
The blog presents development techniques that can enhance the performance of Node.js applications, keeping them fast, responsive, and dependable when under high users. If one wishes to master these techniques, consider Node.js Training in Chennai to pursue these on an advanced level.
Optimize Asynchronous Operations The single-threaded event loop is somewhat the heart of Node.js, therefore, it becomes important to optimize how it handles different tasks. Synchronous badly written code can block the execution and therefore cause inefficiency.
Best Practices: ✅ Always use non-blocking operations to enhance the requested processing. ✅ Handle queries to databases, file operations, and API calls asynchronously. ✅ Avoid callback hell by embracing any of the new ways - Promises or async/await.
Optimize Database Performance A major reason for slow applications is slow database queries. Accelerating this is mandatory to achieve a rapid application response.
Best Practices: ✅ Use indexing to quickly execute the query after searching. ✅ Optimize data retrieval methods to prevent redundant queries. ✅ Use connection pools to handle multiple databases efficiently.
Carry Out Caching for Fast Data Retrieval Caching implies storing data in the memory for fast access and reuse so that the repetitive process is avoided and thereby, improves load time.
Best Practices: ✅ Cache frequently-requested data using Redis or Memcached. ✅ Cache static files using Content Delivery Networks (CDN). ✅ Set HTTP caching headers to help optimize browser-side performance.
Load Balancing Toward Scalability The increase in traffic may not allow a single Node.js server to handle all requests without load balancing to share incoming traffic across multiple servers.
Best Practices: ✅ Setting load-balance requests using NGINX or HA Proxy. ✅ Implement horizontal scaling: spin up multiple Node.js instances across several servers. ✅ Use cloud solutions like AWS Elastic Load Balancer for auto-scaling.
Optimize Middleware and Request Handling Every middleware function in a Node.js app adds extra processing. Minimal use of unnecessary middleware means better performance.
Best Practices: ✅ Get rid of the middleware that has no use in your app for faster execution. ✅ Use faster alternatives. ✅ Optimize the request payload to transmit less data unnecessarily.
Minimize Unrequired Dependencies Many npm packages will end up bogging down the performance of your app. Lesser dependencies are better for performance and security.
Best Practices: Regularly audit and purge unused dependencies from the project in order to keep it lightweight. Opt for a more performance-friendly library instead of using a bulky library that consumes too much memory. The new Node.js version will help improve the efficiency as well as security patches.
Performance Monitoring and Debugging Issues However, continuous monitoring helps in identifying those points that have bottlenecks as well as weak areas that can be improved much further.
Best Practices: Performance monitoring tools like New Relic, Datadog, or Prometheus should be used for performance monitoring. Track memory usage along with response time to assess and identify performance dips. Keep errors and warnings in a log for quick retrieval regarding troubleshooting.
Securing Performance Issues Security loopholes often lead to data loss and application slowdowns.
Best Practices: ✅ Use security headers to prevent from other common attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS). ✅ Validate user inputs to prevent SQL shots and other malevolent exploitable actions. ✅ Monitored and updated dependencies for any potential vulnerabilities.
Conclusion Optimizing the performance of Node.js is crucial to constructing a high-traffic application that is also scalable and efficient. Through asynchronous processing, caching, load balancing, middleware optimization, and security improvements, one can ensure that the application performs efficiently, even under severe user load.
For hands-on experience and deeper understanding, Node.js Training in Chennai offers practical guidelines on high-performance application development.
All this will keep your Node.js app running fast and scalable, ready to handle even the largest loads without a catch. 🚀
0 notes