#Shopify Robots.txt Example
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Shopify Robots.txt Example for Better SEO: What to Block and Why
Not all pages deserve Google’s attention. This comprehensive blog shows you how a tailored Shopify robots.txt strategy can boost your SEO by preventing the indexing of unimportant or duplicate content. From tag pages to parameter-based collection URLs, the default Shopify structure can create dozens of unnecessary indexed pages — and Google doesn't like clutter.
That’s why this blog offers a clear, copy-paste-ready Shopify robots.txt example, paired with step-by-step editing instructions. You’ll discover how to access your theme’s code editor, create a robots.txt.liquid template, and insert intelligent disallow rules.
By customizing your Shopify robots.txt file, you’re essentially guiding Google to your most valuable content. This reduces crawl waste, strengthens topical authority, and improves how your pages are ranked. It’s an essential move for every SEO-conscious Shopify user.
0 notes
Text
How to Hide Content from Bots in Shopify: A Simple Guide
As e-commerce evolves, Shopify remains one of the most popular platforms for online business owners. However, many merchants are becoming increasingly concerned about how to safeguard their content from bots—those annoying crawlers that can steal your hard work, scrape product information, and even impact your site's SEO. Fortunately, there are efficient ways you can employ to hide content from bots in Shopify while maintaining user experience. Let's dive in!
Understanding the Need for Content Protection
Bots are automated programs that scan websites for a variety of reasons. While some bots are harmless (such as search engine crawlers), others may try to scrape your content, steal your product photos, or even build competing listings. This can result in missed purchases and decreased visibility for your store. By protecting your content, you ensure that your brand's unique value propositions remain exclusive.
Use Robots.txt Effectively
The robots.txt file is one of the simplest ways to set up how bots interact with your website. This file informs crawlers about which pages they can and cannot visit.
How to edit robots.txt in Shopify:
• Access your Shopify Admin Panel. • Click "Online Store" > "Preferences." • Edit the "robots.txt" section accordingly.
For example, you can prevent bots from accessing certain portions of your site by adding lines like:
Utilize Noindex Tags
Another way to prevent bots is to use noindex tags on specified pages. This informs search engines not to index particular pages, making them less inviting for bots to scrape.
How to Add Noindex Tags?
To edit the theme code, go to "Online Store" > "Themes."
Select "Actions" > "Edit code."
Open the template file for the page you want to hide and add:
Implement Captchas
Implementing captchas on forms and checkout pages can effectively prevent bots. Captchas affect users to complete a difficult test that bots cannot bypass, guaranteeing that only legitimate consumers may progress.
How to Add Captchas to Shopify:
• Use Shopify App Store apps, such as "Shopify Captcha" or "Google reCAPTCHA." • Follow the app's installation instructions to incorporate it into your business.
Watermark Your Images
Watermarking product photos can stop bots from using them without your consent if that's a big worry. By overlaying a unique design or your company's emblem over the photos, watermarks can discourage image scrapers.
How Watermarks Are Added: • Before publishing your photos to your store, add watermarks to them using Photoshop or other image editing software or internet resources like Canva.
Consistently check your website
You can identify and stop bots in their tracks by keeping a close eye on your website for any unusual activity. Utilize analytics software to monitor traffic trends and spot anomalous increases that might be signs of scraping activities. In this context, tools such as Google Analytics can be quite helpful.
In summary It's simple to keep the content of your Shopify store safe from bots. You may securely protect your sensitive data without sacrificing usability by putting these tactics into practice. Never forget that the objective is to build an online store that is safe from unsanctioned bot intervention and friendly to customers. You'll be well on your way to protecting your content and building a successful online business with these pointers.
0 notes
Text
Types of Website migration
Types of Website Migrations
Protocol change
Migrating a website from HTTP to HTTPS is an example of a protocol change.
Subdomain or subfolder change
When a company chooses to move from one ccTLDs into subdomains or subfolders. Eg. www.example.com.au to www.au.example.com or www.example.com/au
Domain name change
This usually happens when a business is rebranding and has to switch from one domain to another. Eg. www.example.com to www.sample.com
Top-level domain change
This happens when a company decides to either launch the business abroad or limit it to a certain country. Eg. www.example.com to www.example.com.au or vice versa.
Site structure changes
These are improvements to the layout of the site, which usually affect the internal reference and URL structure of the page.
Replatforming
This is when a website is switched from one platform to another. Eg. switching from WordPress to Shopify.
Mobile setup changes
Things such as shifting to a mobile setup, indexing applications or creating a PWA website are often called partial website migrations.
Content Migration
Rewriting, consolidation or pruning of content can have a major impact on the visibility of organic search.
Redesigns
This can be anything from minor design changes to a complete website revision with major changes in code and copy.
The things to keep in mind while you are looking to migrate your website from one domain to another:
Calculate the risks and brace for the consequences.
Create backups and download them.
Pay attention to the URL structure.
Consider redirecting the URL as a major factor for SEO.
Use the change of address tool in the search console to communicate the site migration at the domain level.
Maintain the same directory and folder structure.
Remove broken links and 404 pages.
Set up a new directory for robots.txt.
Prioritize websites with a higher authority.
Plan your rebranding strategies.
Replatforming
This type of site migration involves shifting to a new platform or a CMS. For instance, if your website previously used WordPress as its CMS and you shift to Magento, that would require a website migration. This type of website migration can also involve redesigning websites and even URL changes.
Mobile setup changes
Many technical procedures for a site’s mobile setup can also involve partial or full website migration. These procedures can include building an AMP site, enabling app indexing, coding a PWA website, and more. When an existing website for mobile devices is replaced by an app, PWA, or an AMP, that also requires site migration.
Content Migration
This type of site migration involves a major update in the content of a website. This can include major content rewrites, content pruning, and consolidation. These activities cause a huge impact on a website’s SEO and its search visibility, and can affect your website’s taxonomy, internal linking, and more.
Structural changes
This type of site migration is caused by making significant changes in your website’s taxonomy, navigation, and changes or updates in website architecture. This can affect the internal linking in your website, its navigation as a whole, and user journeys.
Hybrid migrations
As the name suggests, this type of site migration combines various different types and reasons for updating a website. For instance, the types mentioned above can be combined in any way, and it would be a hybrid migration. This type of migration often ends up increasing the complexity of the process, and risks in the results.
0 notes
Text
How and Why Usability Will Define SEO's Future

What if Google understood everything perfectly?
While the response to such a situation ranges from extremely improbable.
To impossible, there is substance to the proposition's underlying attitude.
This is definitely due to Google's progress in comprehending the text on a webpage.
Furthermore, with products like MUM, this appears to be a trend that will only grow exponentially.
It's a trend that, in my opinion, will significantly change SEO.
Here's why and how it works.
As technology advances, I believe “usability” will come to dominate SEO.
Why SEO Will Get Redefined
As a result, the concept of Google completely comprehending material is rather ridiculous
(at least in this author's perspective).
However, when viewed as a trend or a direction in which things are heading, it is a very practical question.
So much so that John Mueller brought it up at a July 2021 Google Hangout discussion.
Indeed, if you go through John's remarks, you'll see that they revolve around.
Both Google's content decoding advances and the progress of the CMS in terms of managing things like H1s, etc.
The advances of numerous CMSes, as well as Google itself,
Combine to produce an atmosphere favorable to genuine change.
These adjustments will undoubtedly have an impact on SEO.
I believe that these developments will be so substantial that.
They will reshape SEO in a variety of ways (though not totally, of course).
Before we go into the evolution of SEO, let's take a closer look at the confluence of CMS innovations and Google's upgrades.
Redefining SEO: The Role of Google’s Comprehension Advancement
Along with Google's improved ability to analyze text and understand its meaning, there is an equalization.
The ranking potential of a material that was not developed or optimized.
By a marketing expert grows in proportion to Google's capacity to better understand the content.
This does not imply that Google will or will not rank such material.
But rather that it may now rank such stuff if it so desires.
This tendency is exemplified by what Google has said about Passage Ranking.
(Again, for the record, I am not claiming that Google has arrived.)
Major strides have been achieved, although there may still be substantial gaps).
Simply said, Google's capacity to better comprehend material in.
The future means that less effort is required to guarantee Google knows your content.
It's a rather straightforward equation.
Things on your website that exist just to help Google better comprehend your content becomes less important.
Following its logical conclusion, this dynamic would, in principle, affect what SEOs should focus on.
Redefining SEO: The Role of the CMS
Whether you like it or not, the CMS will play a significant role in "all of this."
CMSes are becoming increasingly advanced in terms of SEO.
Shopify, for example, is now providing access to the robots.txt file, among other things.
While Wix provides a high level of URL modification.
The true advances, though, are the ones that go unnoticed.
CMSes frequently include automated page caching, lazy loading image.
Image conversion to WebP, and other features.
This is especially true when it comes to the foundations of a website.
That allow it to be crawled and indexed.
CMSes perform a "very excellent job" for the average SMB or SME's site, to to John Mueller.
As a consequence, the business owner can generate content.
That is not blocked from showing on the SERP for technical reasons.
It's easy to see why some SEOs would be concerned about the importance of their job here.
In other words, no matter how you slice it and no matter.
Whatever corner of SEO you stand in (content, technical, etc.).
The present paradigm appears to be on the verge of significant upheaval.
Google is better equipped to comprehend content, and site owners.
May focus on their content by letting CMSes handle many of the technical parts of SEO.
Simply said, Google is becoming better at understanding content and will grow.
Much better when the barriers to generating material.
That ranks are eliminated for a large number of people at the same time.
A point of confluence.
So, what is the future of SEO?
What happens as a result of this?
What does SEO become?
Why Usability Will Come into Increased Focus
I used to be a great admirer of Mr. Rogers when I was a youngster.
So, for the sake of nostalgia, let us travel to the "Land of Make-Believe."
Assume Google understands all text completely.
What would occur?
For starters, Google would not require you (or anybody else) to assist.
It in comprehending the information on the website.
It wouldn't require H1s, title tags, schema, or anything else to comprehend what's on the page.
Not that it couldn't utilize it, but just as a reader wouldn't require.
Those components in a "perfect world," so would Google.
So, what happens to SEO?
In such a case, SEO from a content standpoint is no longer about “optimizing”.
The website for search engines, but rather about concentrating the page on.
The appropriate users at the right time.
In other words, all of the efforts we do to guarantee Google understands our content.
All of the best practices for keywords here and page structure there — will be rendered ineffective.
If Google understands material properly, it won't need any crutches to go where it wants to go.
Google would comprehend the page if it effectively addressed a topic.
Let us ask the question differently.
What would distinguish one piece of content from another.
Assuming both sites are topically relevant to equal extents if.
Google were omniscient and could comprehend content perfectly?
The solution is the content's effectiveness.
The more successful and efficient a page is at disseminating material.
The better it is for users and, by extension, search engines.
Usability becomes the differentiating factor in a world where.
The components on the website don't matter about Google's comprehension of the page.
Returning to reality, as Google improves at comprehending material more.
"intrinsically," relying less on various crutches for comprehension, usability becomes more important.
Google may increasingly focus on how efficient and effective.
The page is in transmitting its message as it has less to worry about ensuring.
It properly understands the material on the page.
This is precisely what Google has done with every core upgrade since 2018.
By not having to invest X amount of work attempting to guarantee.
It understands the page, Google can focus massively on ensuring the page is effective in terms of usability.
What Might SEO Focused on Usability Look Like?
I'm going to summon my inner Barry Schwartz and declare.
That Google's shift toward usability is "not new."
As I have stated, this is a pattern that has been evident since at least 2018.
You may call it E-A-T or anything you like, but the goal is to ensure.
That the user's experience is significantly more aligned with expectations and content consumption efficiency.
Google has always attempted to shift the attention away from bots and onto users.
What I'm suggesting here is that, at some point, a quantity of modifications transforms into a qualitative shift.
The more water you add, the more a ripple becomes a tidal wave.
Google has prioritized the page's/usability sites and experience.
The Page Experience Update is the finest example.
Google is taking a firm position on the entire user experience.
What I'm suggesting is that this attention will get considerably more intense as time passes.
The issue is, what will this look like in the future?
Usability & the User Experience: Content & SEO
“SEO content” focused on usability brings to the forefront many of the principles that are becoming prominent in SEO.
Most significantly, the concept of "speaking to the user" would become much more important than it is now.
Fundamentally, the usability of a site or a page is proportional to its capacity to communicate to a certain sort of user.
What is "useful" for one user group is utterly useless for another.
Take, for example, a medical magazine.
It may include the most detailed, correct, and authoritative material on a certain.
Health subject, yet it is utterly useless to someone who does not have a medical background.
Speaking to certain user profiles, on the other hand, determines how usable a website will be.
When the question of what is on the page and how trustworthy.
It is becomes less important, the deciding factor between two related pages.
Becomes how successful the material is in reaching an audience.
The audience's nature must be determined in accordance with the nature of the inquiry.
Is the search query indicating a more advanced user vs a layman, and so on?
Usability is subjective.
The capacity of a page to effectively transmit information is dependent on the target audience.
That is, the nature of the audience and the content's capacity to target.
That demographic will become a significantly bigger "factor" by definition.
This can take a variety of shapes and have various degrees of intricacy.
That is, a page's capacity to be "useful" to a very specialized audience.
May be determined by complicated or simple page components (or any other number of variables).
To illustrate this further, consider headers.
Two pages from separate websites may have the same content.
Both may be correct, authoritative, and so forth.
Assume, for example, that one page used its headers to produce an easy-to-follow.
Flow of information whereas the other did not.
While both sites are equally comprehended by Google in this situation.
They differ considerably in terms of how successful.
They are at conveying information efficiently and effectively to the intended audience.
(For the record, an overreliance on-page structure may detract from the abstract character of the material and may not fit with a more sophisticated audience.)
Headers and other “good” page structure components are fantastic examples.
We frequently consider headers, tables, and even schema markup
(particularly schema markup)
To be essential components in assisting Google in understanding the content on the page.
What I'm suggesting is that these components will play less of a role in assisting.
Google and more of a role in distinguishing one page from another in terms of usability.
The practical difference will be, at least in part, the lack of consistency.
With which these components will play (and already play) in the “SEO” picture.
While page structural components may be regarded as objectively assisting.
Google in understanding page content, they are, to a large part, subjective in terms of usability.
Certain page structure components will be more or less significant depending on the audience to whom the material is relevant.
Usability & the User Experience: Technical SEO
On the technological side, I believe we have already seen what the future will look like.
The Page Experience Update was not dubbed "The 2021 Speed Update," but rather
"The Page EXPERIENCE Update," and with good cause.
One of the good things about the change is that it combined technical SEO with user experience.
It wasn't about increasing speed to please Google.
It was all about making sure your site is useable in the best possible way.
This results in a more fluid atmosphere.
What is a fundamental vital in 2021 may not be in 2025, or more vitals may be introduced as time passes.
(I am aware that Google had discussed including FCP as one of the essentials at one point.)
Technical optimization in the context of user experience, in either event, is not a passing trend.
It will only evolve and continue.
Furthermore, as the web and users change, user-focused technological optimization will become a much more fluid affair.
Conclusion
What I'm suggesting here is that we must understand.
where Google is headed and strategically align with its objectives.
Does this imply that some SEO structures that work today but may not in the future be abandoned?
No.
What it does imply is being aware of these places inside.
The realm of optimization and being cautious not to become overly reliant on them.
Rather, a far more significant strategy would be to coordinate with
Google in all directions to the greatest extent feasible.
You may contact Nummero since we are the best digital marketing agency in Bangalore.
#How and Why Usability Will Define SEO's Future#digital marketing#digital marketing companies in bangalore
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Buyer Calls for By Your Faceted Navigation
New Post has been published on https://tiptopreview.com/fulfill-untapped-customer-demands-through-your-faceted-navigation/
Fulfill Untapped Buyer Calls for By Your Faceted Navigation

The writer’s views are fully his or her personal (excluding the unlikely occasion of hypnosis) and should not at all times mirror the views of Moz.
Faceted navigation permits clients to slender down search outcomes primarily based on particular product attributes. They usually exist on Product Itemizing Pages (PLPs) and are a good way to assist customers intuitively uncover merchandise however managing this filtering system is a typical web optimization problem. Crawling and indexation have to be managed.
Nevertheless, if we glance past their inherent performance, sides can supply us appreciable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail key phrase alternatives, you’ll be capable to strategically make the most of shopper intent, safe further net conversions, and enhance income ranges.
Match shopper intent with long-tail search queries
Having a longtime model and a strong area backlink profile gained’t assure success. That is nice information for smaller manufacturers, as trade giants aren’t essentially going to win at this recreation.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we will see how David’s Bridal’s optimized aspect web page (Area Authority: 67/100, Web page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the highest rating place, whereas Nordstrom’s end result (Area Authority: 87/100, Web page Authority: 39/100) seems within the third place for this explicit question. We’ll check out what makes this web page so efficient later.
When how we will optimize faceted navigations, it’s necessary to acknowledge that product attributes convey shopper wants and aspirations. If, for instance, I’m searching for a marriage gown, then I could tailor my search by the colour, cloth, neckline form, and the sleeve size.
In line with the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for as much as 70% of all natural searches. They’re extremely focused queries that provide massive traffic-driving alternatives.
In the previous few years, we’ve seen a giant shift within the trade in the direction of capitalizing this intent with long-form content material. Weblog articles and magnificence guides have change into the go-to strategies for a lot of to seize these guests, as we will see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ “Inspire Me” part:
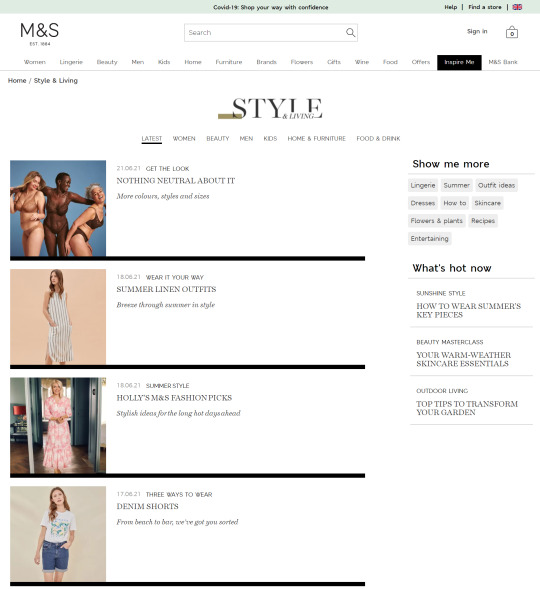
Individuals usually search for inspiration once they’re procuring, and these pages present an efficient means so as to add extra inside hyperlinks to class and product pages. However counting on this strategy is one-dimensional, on condition that these deeper content material pages are likely to have decrease PageRank. An intensive quantity of effort and time will, subsequently, be required to realize the specified end result.
As compared, Product Itemizing Pages often goal broader search phrases, and faceted navigations usually exist as passive features. It is because they’re usually blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any web optimization worth. Waterstones (a well known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for his or her on-page filters:
On this explicit instance, I’ve utilized a filter to solely present me books for five – eight yr olds, however the appended URL (https://www.waterstones.com/class/childrens-teenage/aspect/498) is blocked within the robots.txt file. That is going to stop such pages from being served within the SERPs regardless of them having the potential to satisfy particular buyer wants. This reveals that there could be a elementary disconnect in matching buyer intent to the pages we’re offering them within the natural outcomes.
From the diagram beneath, we will see how editorial content material usually focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” levels, while Product Itemizing Pages are typically extra according to the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the proper content material to customers all through their shopping for journey is pivotal to success. For a lot of retailers, opponents are persevering with to prioritize broader, high-volume key phrases in saturated markets. They’re concentrating on the identical phrases to safe a proportion of the identical search site visitors. It is a very difficult prospect to face, and with out carving out a niche within the market, they gained’t essentially ship the outcomes they search to safe. Likewise, counting on informational guides to focus on long-tail key phrases implies that you’re lacking a big proportion of customers who’ve very particular shopping for necessities. Sure, they’re able to make a purchase order!
By shifting your focus to handle your buyer’s actual wants and expectations, you’ll be capable to ship a satisfying, frictionless expertise at each interplay and all through to that ultimate buy.
The answer
Step 1: Conduct long-tail key phrase analysis
Construct a extremely complete view of your potential clients by harnessing knowledge from quite a lot of sources, together with:
a) Key phrase analysis instruments like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest outcomes, Individuals Additionally Ask, and the associated search hyperlinks on the backside of the web page.
c) Competitor exercise — except for utilizing web optimization monitoring software program, you need to use a knowledge mining extension software like Scraper, which is able to extract faceted choices immediately from competitor Product Itemizing Pages. These instruments are sometimes free to obtain and will let you shortly switch product classes.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to find out which key phrases and URLs are securing the very best variety of visits and net conversions. Inside search knowledge may offer you nice shopper insights.
e) Converse to your merchandising crew to grasp product calls for and achievement capabilities.
Step 2: Group into significant sub-topics
When you’ve collated all this info right into a spreadsheet, you’ll be capable to uncover long-tail, consideration-orientated key phrases. Whereas individually they might not boast enormous month-to-month search estimates, they’ll collectively spotlight the place buy intentions may be higher fulfilled.
To assist illustrate this level, we will take a look at a small subset of lingerie key phrases and the sides the searches signify:
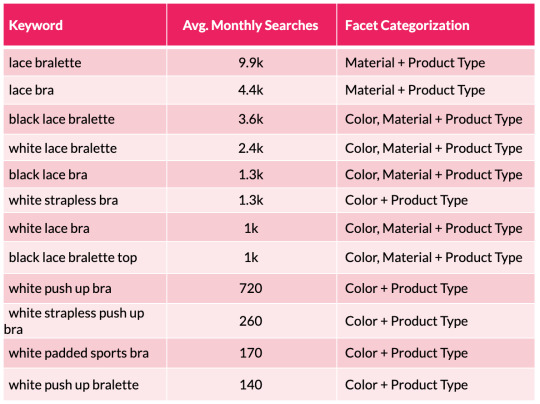
From the desk above we will shortly see a sample rising with coloration and materials variations showing throughout the search phrases. We are able to then substantiate this info with session and income estimates with using a acknowledged CTR mannequin. This permits us to assist forecast the potential natural uplift and quantify the dimensions of the prize for quite a few completely different situations which are on supply from every new aspect mixture. This may occasionally embody estimations for securing place 10, 7, 5, three and 1 in Google.
One factor to notice right here is that it’s value excluding synonyms, as they may falsely inflate your calculations. An instance right here can be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k month-to-month searchers) when reviewing the efficiency for “chest of drawers” (201ok m/s). Together with each variants will trigger a false optimistic end result and can lead you to attract incorrect conclusions.
Step three: Dig deeper into broader phrases round affords, scores, and worth
These product filters are discovered within the “Sort” dropdown field and, from my expertise, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they merely enable customers to re-order web page outcomes. Actually, content material administration techniques like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
This is smart since their goal is to permit guests to easily kind or slender web page content material somewhat than providing different outcomes and extra worth (which is obtainable by faceted navigation). As such, filter usually produce duplicate outcomes which shouldn’t be discoverable past the speedy second. However this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t at all times apply completely in the actual world. For this reason we have to take a look at our particular person industries and perceive what’s necessary to our distinctive set of shoppers.
If we take a look at the world of gifting, we regularly see individuals procuring with a specific funds in thoughts. Subsequently, phrases like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are moderately widespread, and opening up related itemizing pages could possibly be helpful for buyers.
Step four: The technical steps
Side taxonomies are vastly complicated and the variety of attributes that may be strung collectively will increase with the dimensions of the area. We, subsequently, must rigorously handle the flood gates and mitigate towards any potential dangers together with crawl inefficiencies and hyperlink fairness dilution.
We are able to do that by:
1. Avoiding skinny/doorway pages by frequently re-assessing your product providing. For example, you might contemplate there to be little worth in creating a brand new listings web page should you’re promoting a really small vary of low worth level merchandise. On this case, you might resolve towards opening up a further Product Itemizing Web page whenever you promote as few as 10 eligible merchandise. Nevertheless, this isn’t a hard and fast rule, so it’s fairly doable that your standards could also be decrease for explicit product traces. Both means, these numbers will change over time. Take into account seasonal developments, when new collections are launched, and once they change into discontinued. Establishing a product retirement strategy to handle expired merchandise and classes at scale in parallel with this step can also be extremely beneficial.
2. Stop content material cannibalization by arranging chosen sides based on their worth and significance. “Size” is essential for some electrical items like TVs, laptops, and cameras, however is much less so for magnificence equipment or vacuum cleaners. It’s essential to additionally be sure web page content material is distinctive and displays the main target of your chosen aspect(s). Seek advice from step 5 for extra particulars.
three. Comply with the sequence through which adjectives and sides are usually chosen by your clients. This will differ relying on the place your viewers lives. So, while merchandise typically have 5 or extra distinguishable options, English vernacular determines that we use greater than 4 adjectives (e.g. measurement + coloration + materials + form) to explain one thing.
four. Management the controllables by coping with overlapping variations. This usually happens when multiples co-exist and every displays good search metrics. For example, it’s cheap for somebody to concurrently search for a number of coloration and/or cloth combos within the alternative ways beneath.
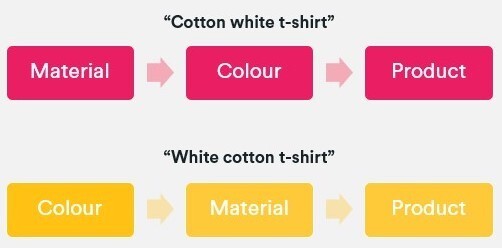
When this case happens, we should always comply with the identical linguistic guidelines as above and select a most popular sequence. On this case, it might be coloration + materials + product kind.
Compared to the noindex tag prompt for on-page filters you must canonicalize pointless sides to their dad or mum web page (remembering that that is merely a touch and never a directive). It will allow you to regulate how crawlers cope with extremely comparable end result pages and can, subsequently, assist to stop your web site from being demoted within the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters ought to proceed to be outlined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed within the robots.txt file, and configured by Google’s URL parameter software (inside your Search Console account) to inform crawlers the aim of your parameters and the way you want to them to be handled. It is a useful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, however keep in mind that this final tip gained’t affect how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your sides in phases and domesticate it right into a test-and-learn course of. It will allow you to establish points rather a lot sooner and implement facet-wide options in a well timed method. With out having to unravel these further layers of complexity, issues reminiscent of crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or extreme indexation may be swiftly resolved.
To point out you what this might appear like, I’ve supplied a phasing plan that was created for one in all our e-commerce purchasers. Our analysis confirmed a big web optimization alternative for opening up a number of the sides and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” aspect (UK):
What’s extra, after we prolonged our forecast to incorporate different aspect combos, we calculated a further income alternative of as much as +£207Ok/pcm (earlier than filtering out combos with no merchandise providing).
Step 5: Optimize your aspect URLs
Optimize your new aspect class URLs to determine relevancy on your chosen search phrases. The important thing on-page components to give attention to embody:
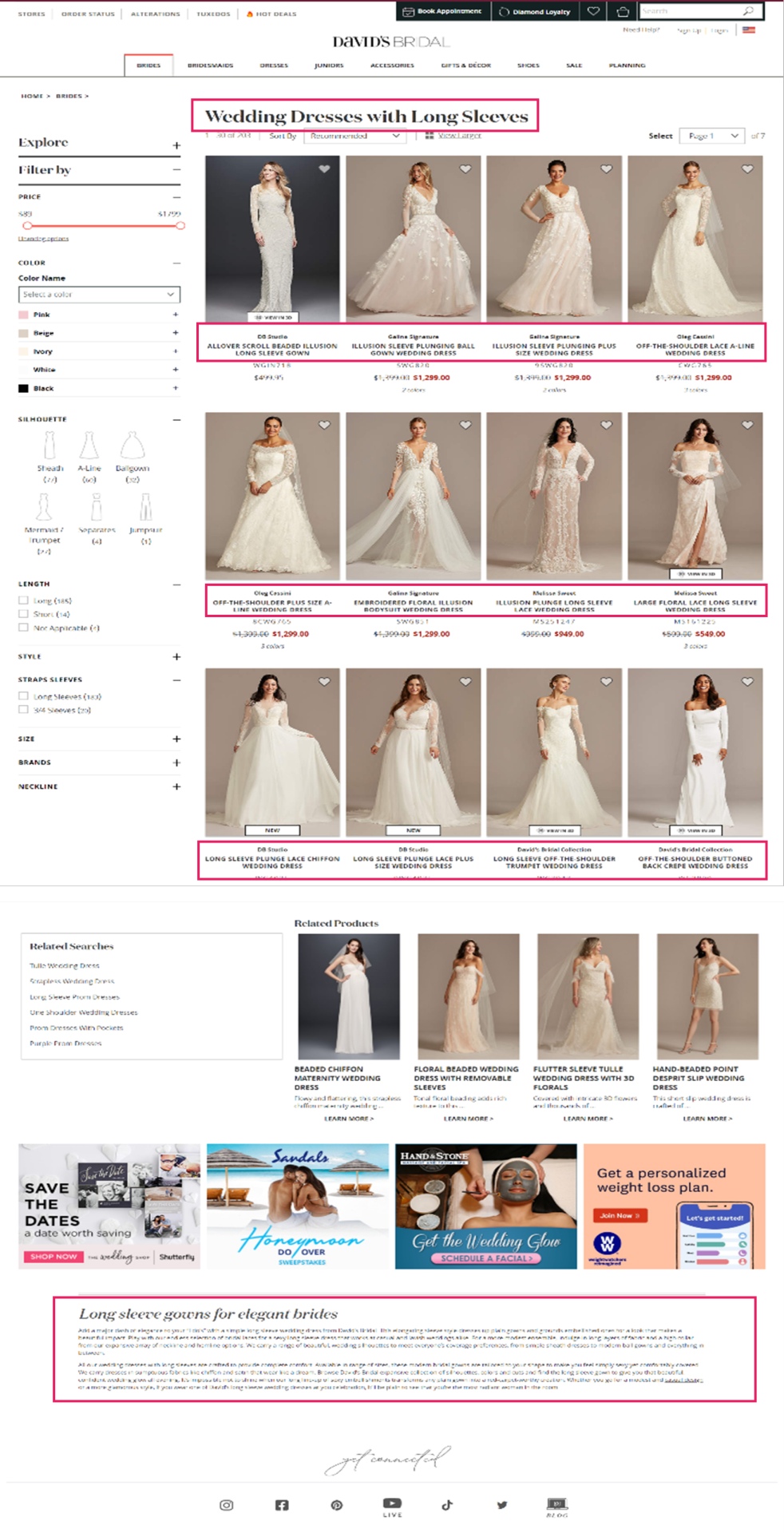
David’s Bridal is an effective instance of a retailer that has accomplished this nicely. Trying again on the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Itemizing Web page, we will see that they’ve curated distinctive content material and adopted elementary optimization ways on the touchdown web page in a means that feels useful to the person.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Web page Title: Lengthy Sleeve Wedding ceremony Clothes & Robes | David’s Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of carrying a lengthy sleeve wedding ceremony gown in your massive day? Store David’s Bridal vast number of wedding ceremony robes with sleeves in lace & different designs!
6. Present accessibility and construct web page authority
When you’ve opened up your new aspect Product Itemizing Pages, you have to start cultivating hyperlink fairness in the direction of them. It will be certain that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Guarantee they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
You probably have one function per aspect URL, then add them to your faceted navigation throughout CLP and Product Itemizing Web page pages.
You probably have two or extra options per aspect URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” possibility inside your CLPs.
Make the most of your mega menu to showcase your new class touchdown pages. This won’t solely will let you direct a big proportion of hyperlink fairness, however it’ll additionally safe the very best click-through charge amongst your guests.
Combine your editorial technique by creating partaking content material with in-copy hyperlinks. Take into consideration how you need to use descriptive long-tail anchor textual content in regards to the Product Itemizing Web page you wish to hyperlink to somewhat than counting on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect with them through href hyperlinks so that you’re not solely counting on hyperlinks from the principle navigation or content material hyperlinks. As that is tough to do at scale, it may be accomplished by modules reminiscent of “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, and many others.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that may safe high quality, exterior backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and sturdy technique will assist you to to safe exponential progress out of your new business touchdown pages.
Conclusion
There may be an excessive amount of natural alternative that exists inside your faceted navigation should you start to leverage mid- and long-tail search phrases.
Search out the chance from prolonged key phrase analysis and competitor evaluation earlier than deciding which variants fulfill shopper calls for and ship optimum natural classes and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for every alternative and open them up for crawl and indexation. Guarantee PageRank is distributed to them (each internally and externally) and develop your touchdown web page content material according to high quality optimization practices. This strategy will assist you to to keep away from having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having skinny doorway pages. In flip, your web site might be higher suited to draw highly-targeted customers and information them down the acquisition funnel.
Maximizing UX and decreasing reliance on different marketing channels implies that your faceted navigation can actually ship natural ROI. We’ve got seen this work for our purchasers.
Source link
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
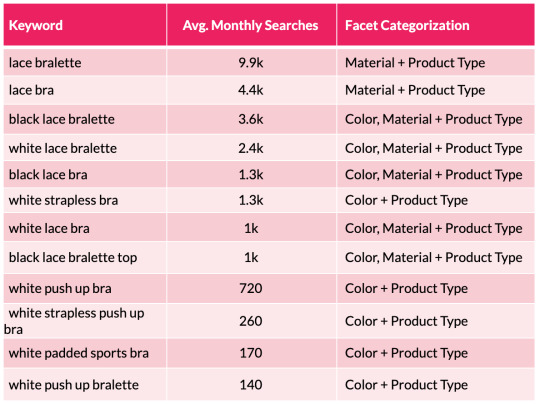
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
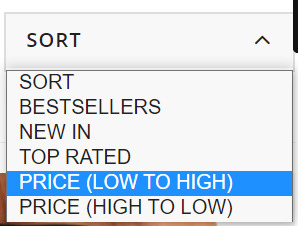
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
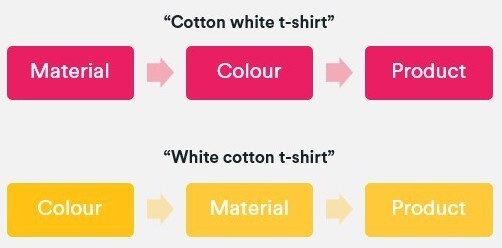
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
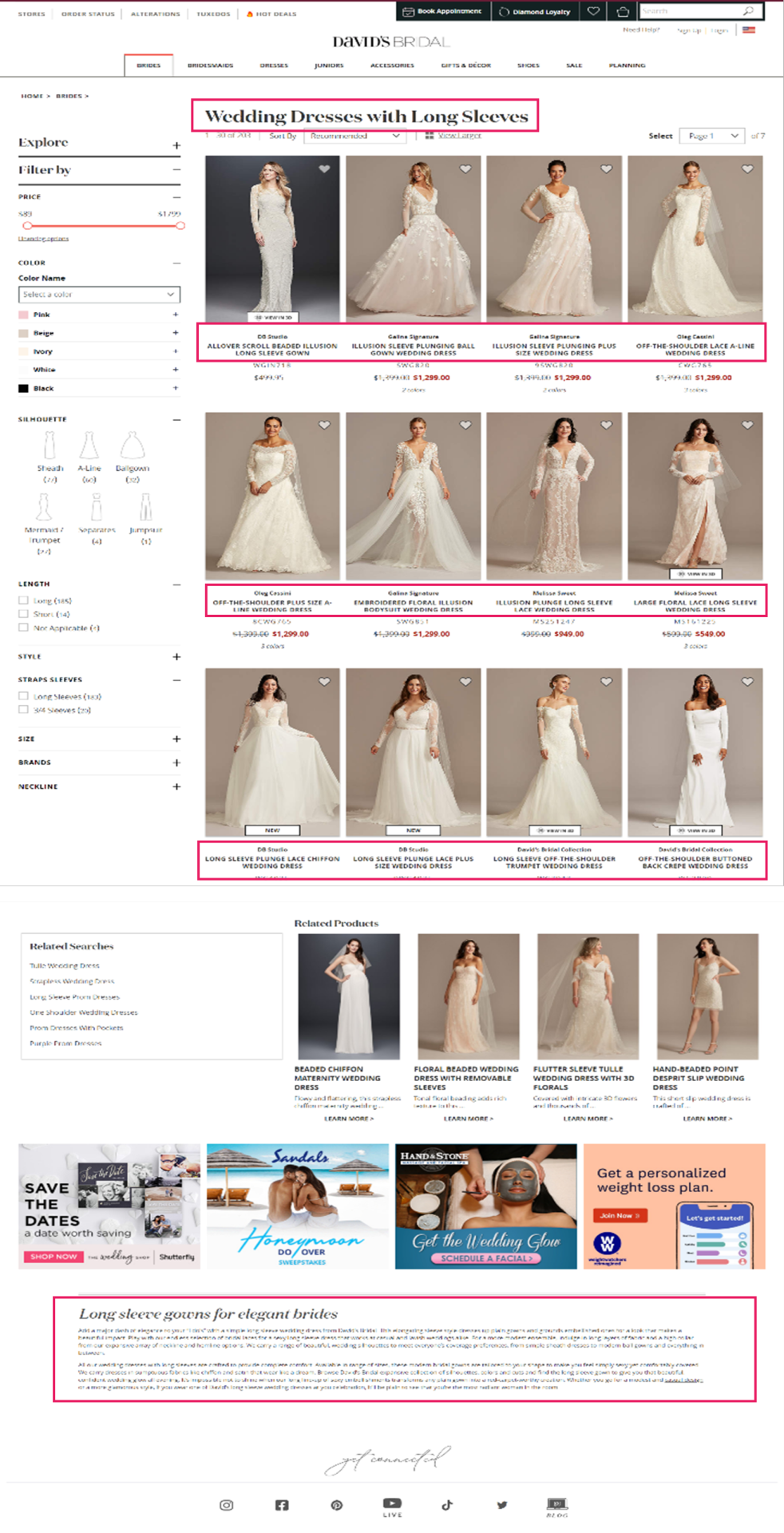
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
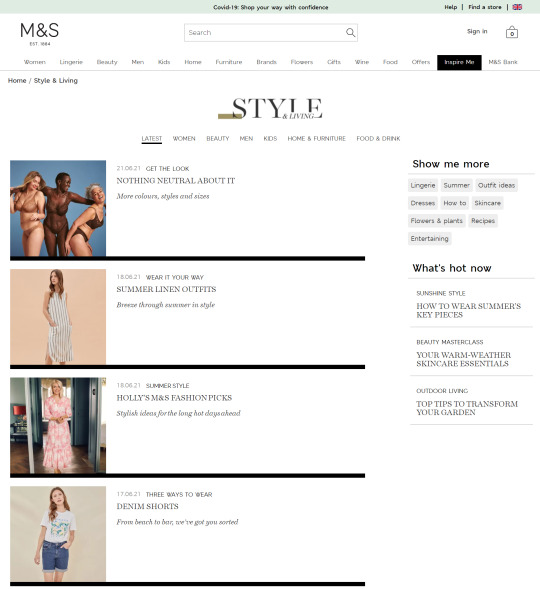
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
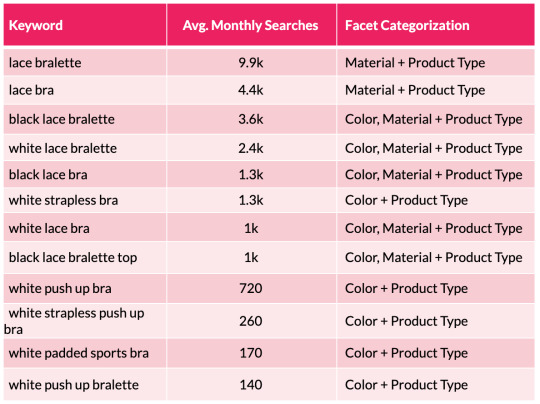
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
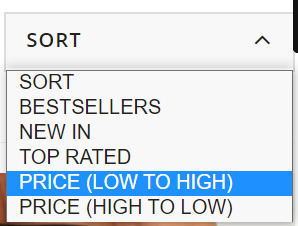
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
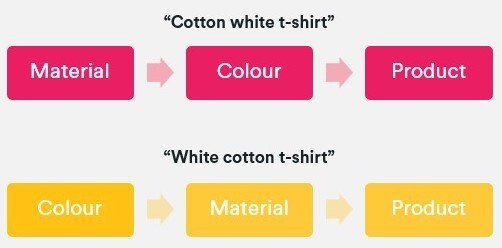
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
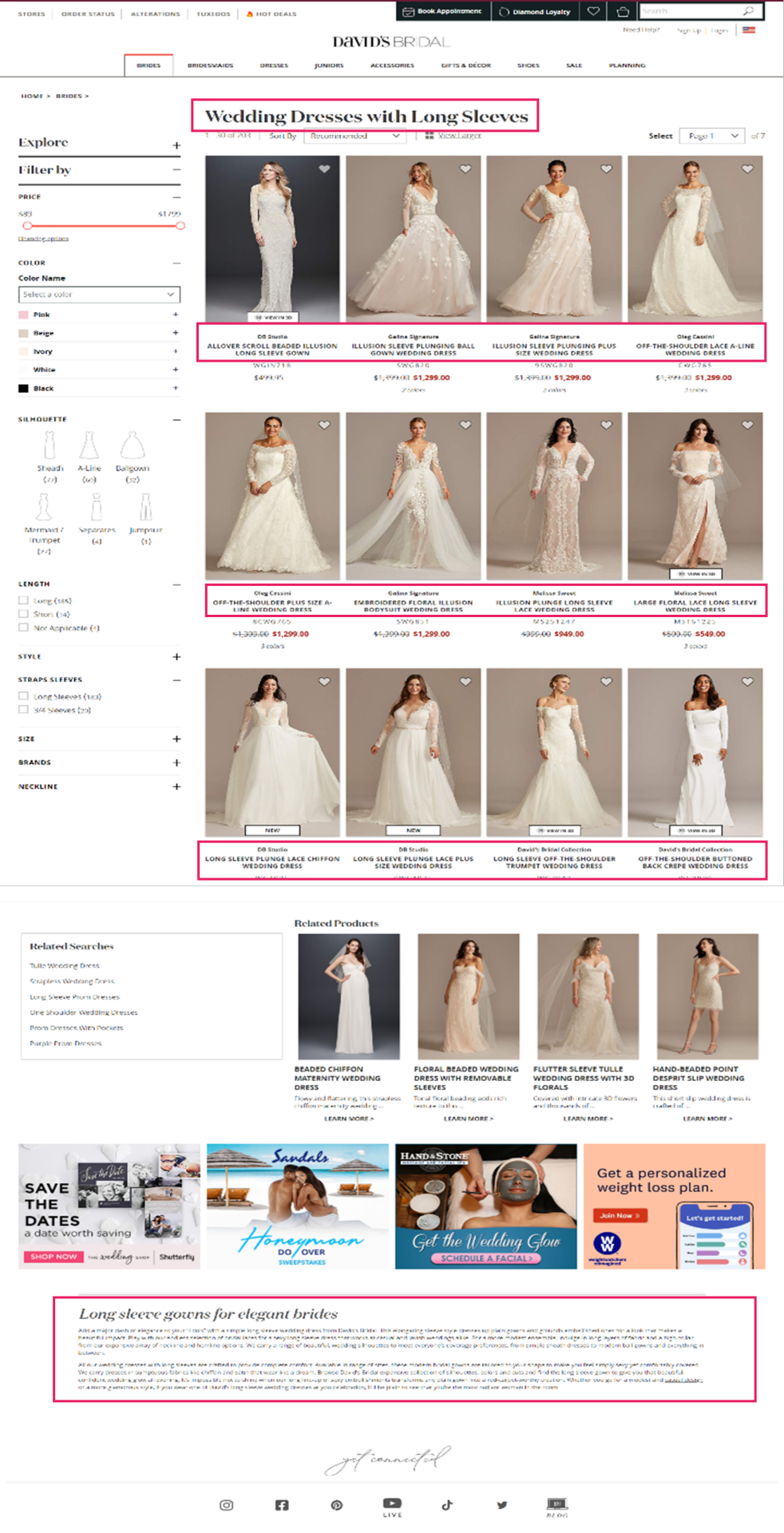
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
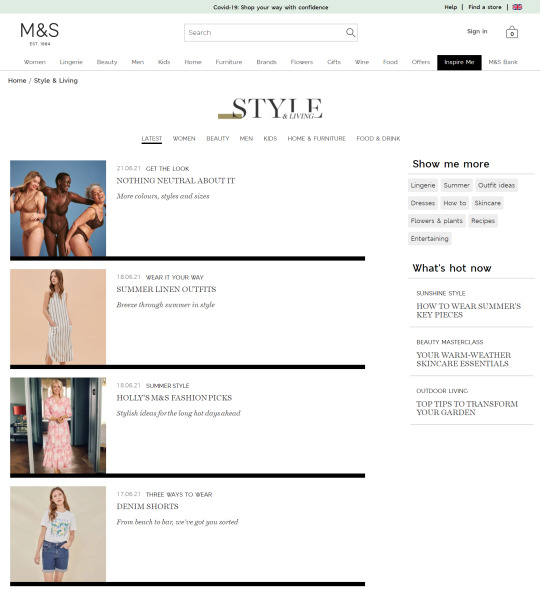
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
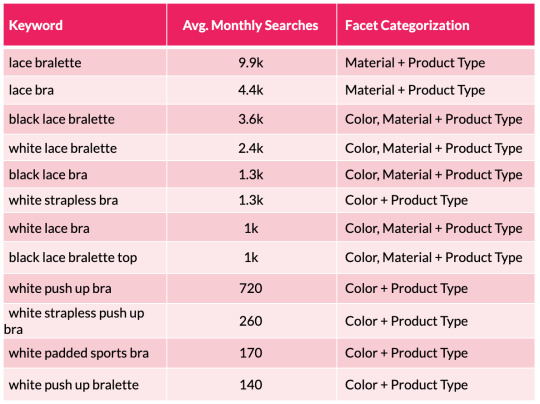
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
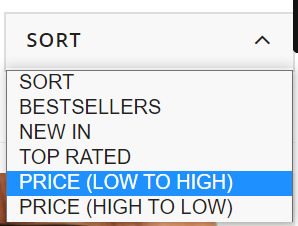
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.

When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
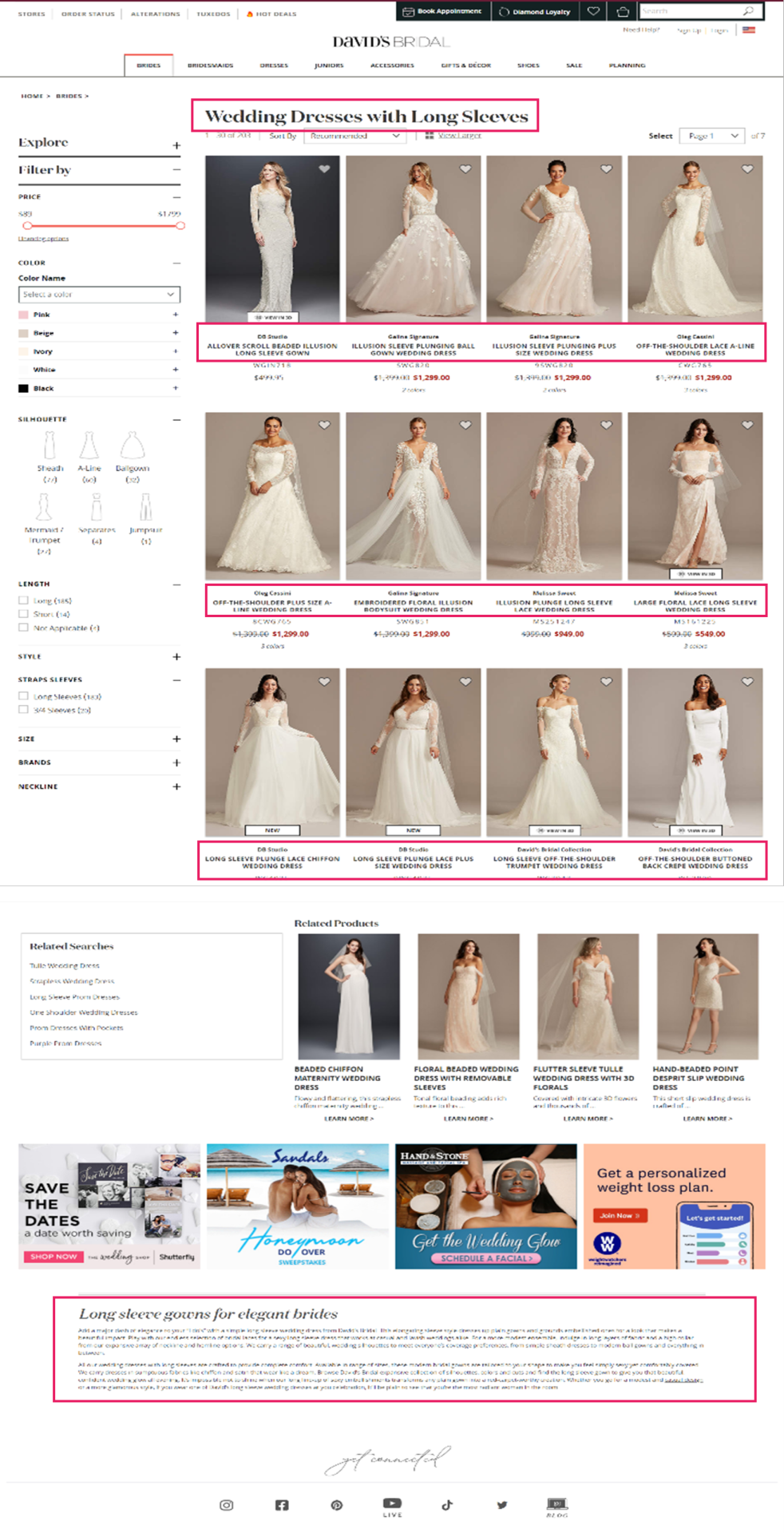
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
#túi_giấy_epacking_việt_nam #túi_giấy_epacking #in_túi_giấy_giá_rẻ #in_túi_giấy #epackingvietnam #tuigiayepacking
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
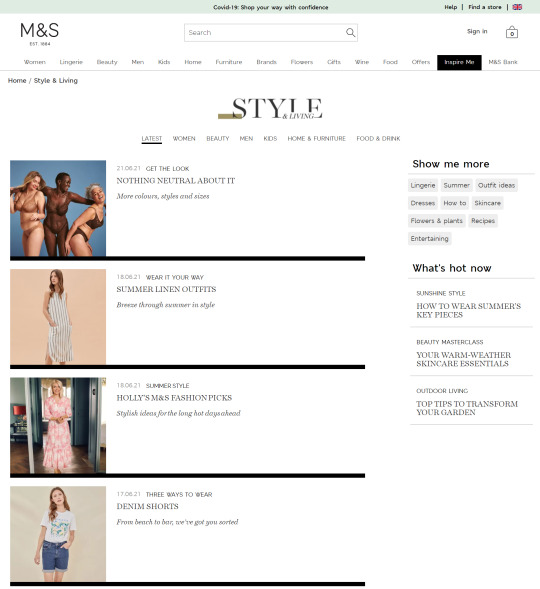
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://www.waterstones.com/category/childrens-teenage/facet/498) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
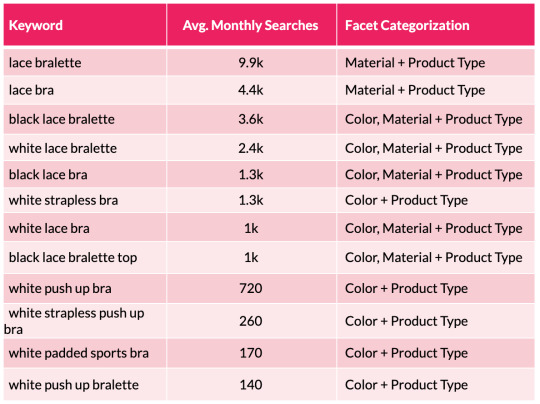
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
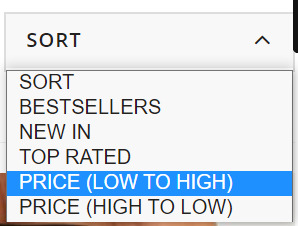
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
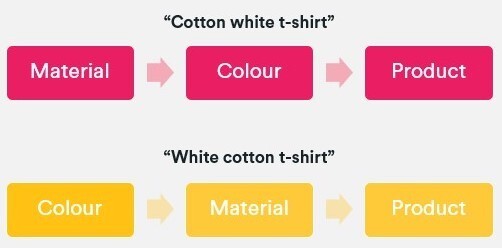
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
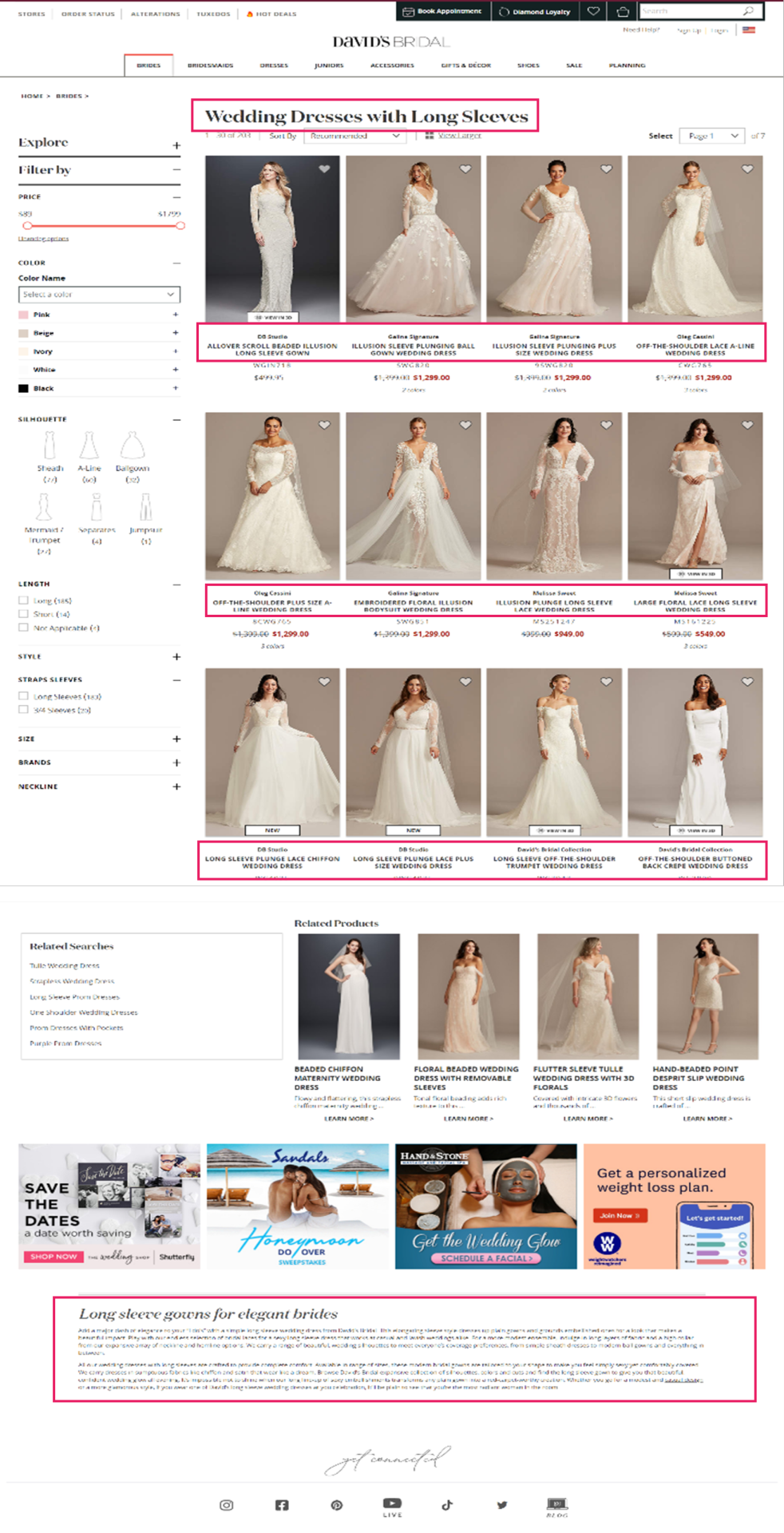
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
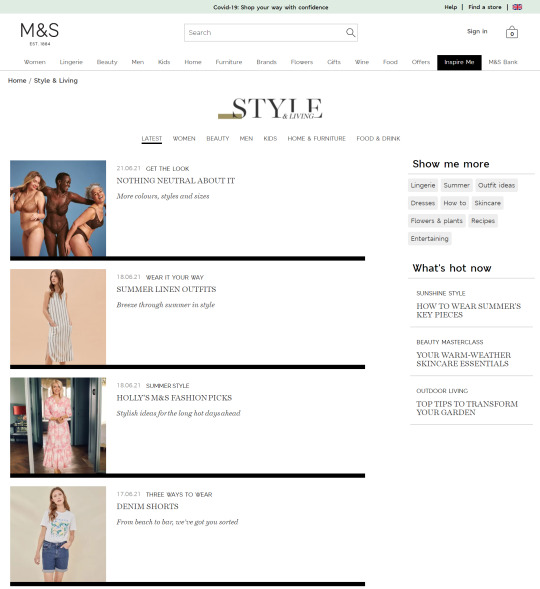
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://bit.ly/2VccAT1) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
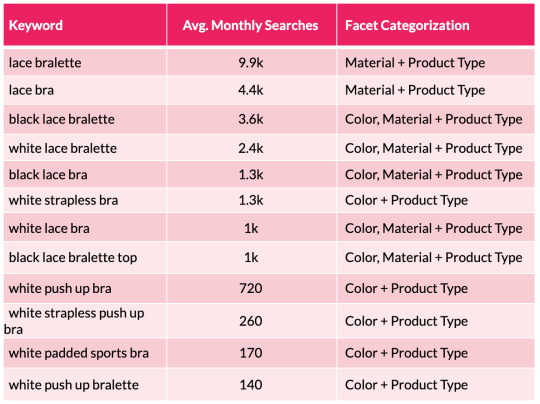
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
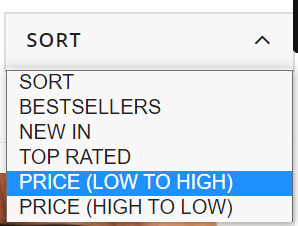
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.

When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
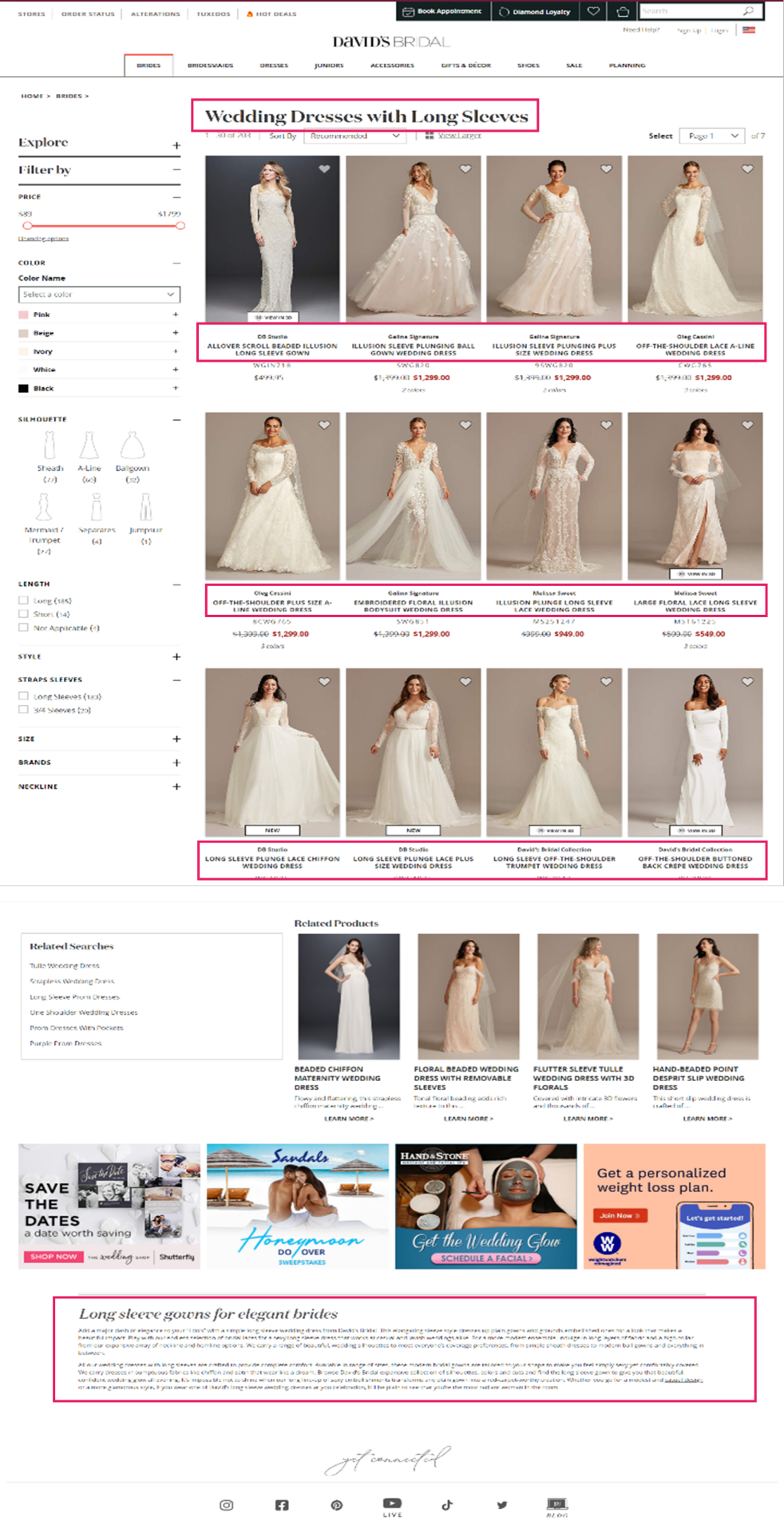
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
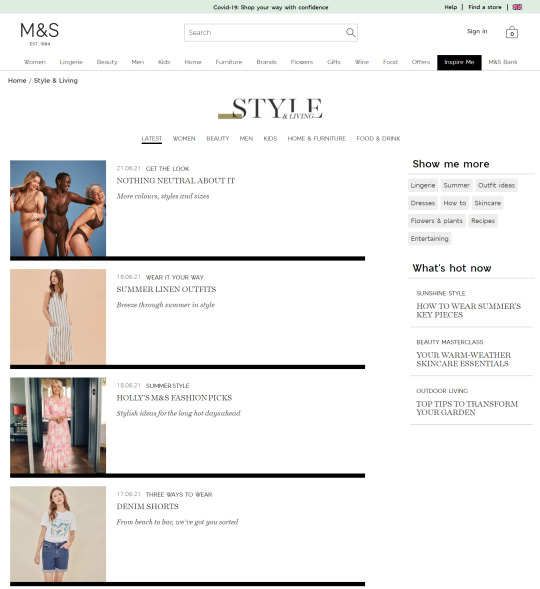
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
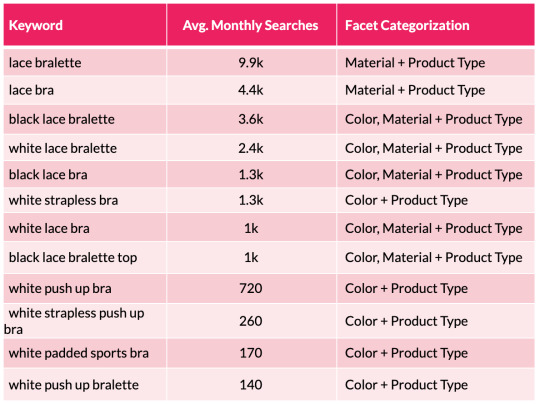
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
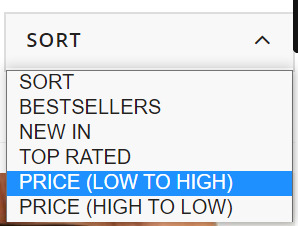
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
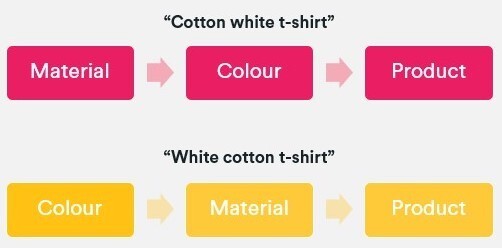
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
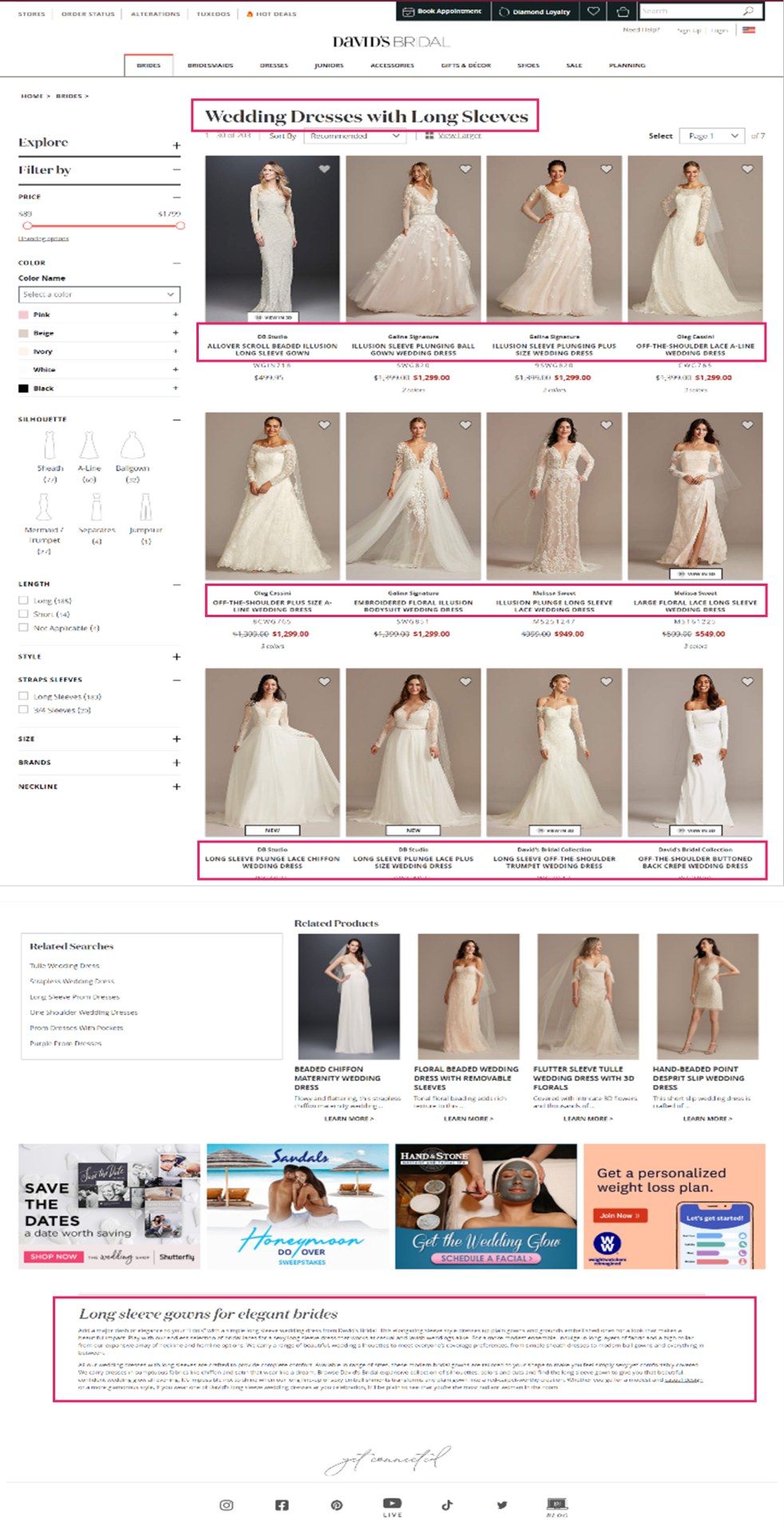
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
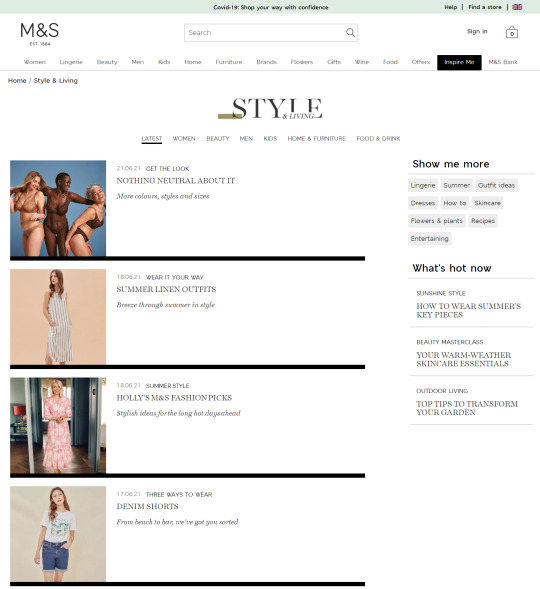
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
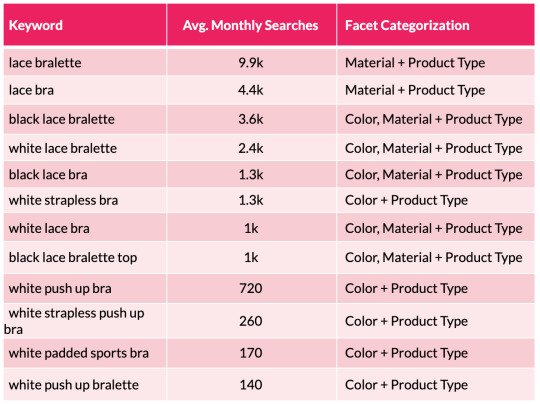
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
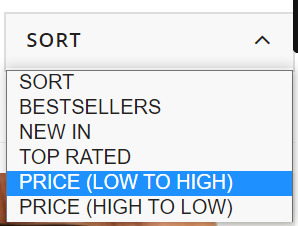
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
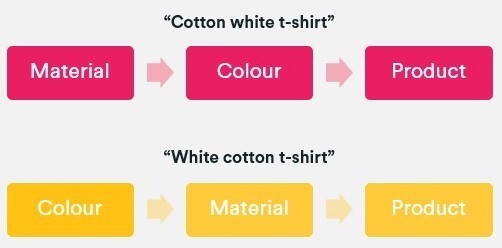
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
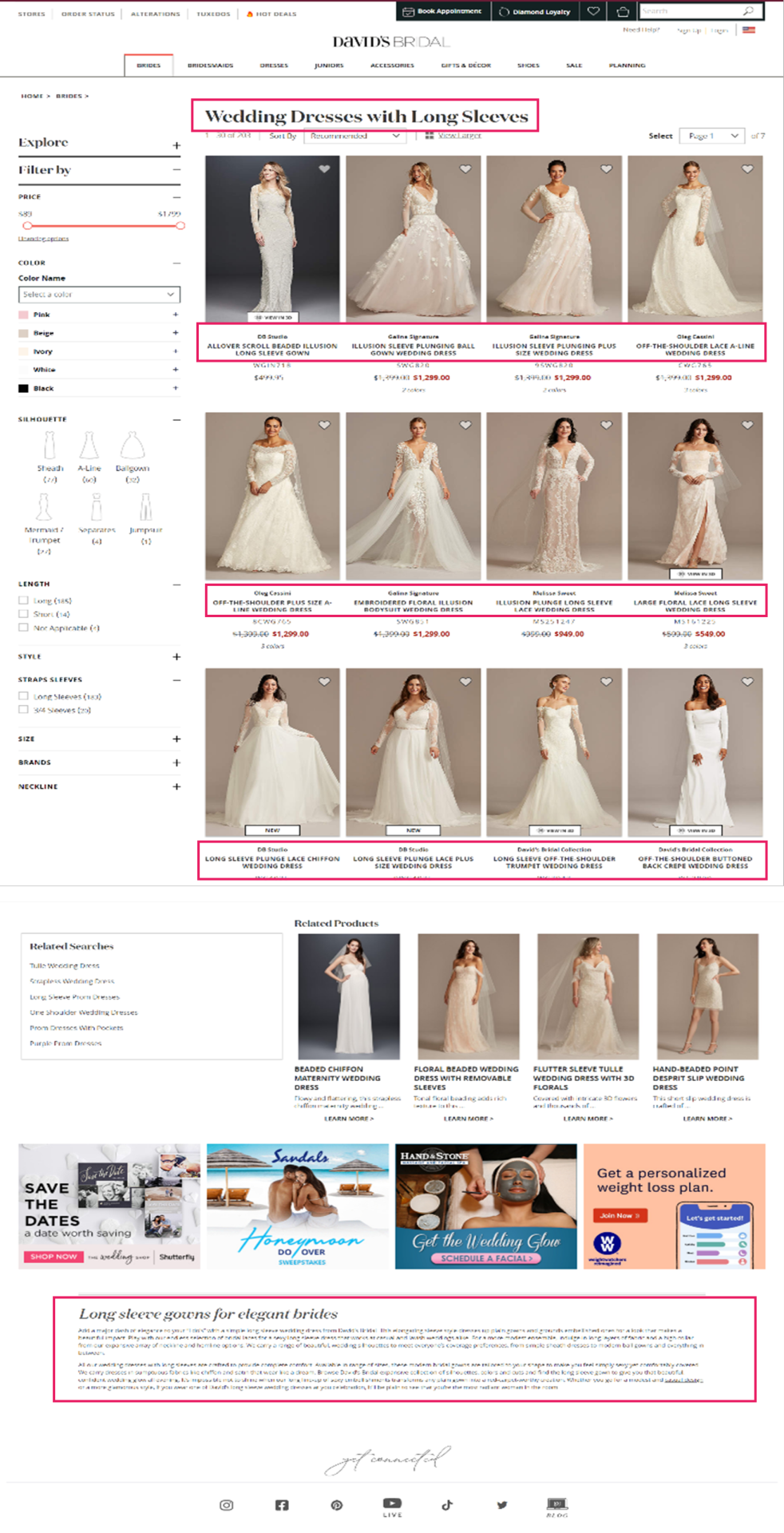
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
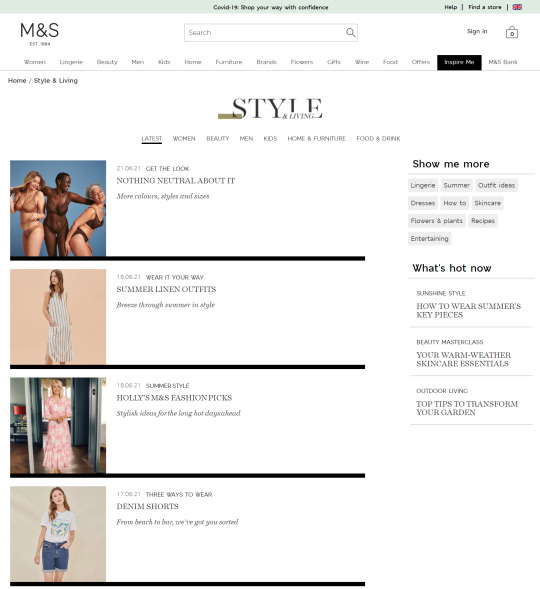
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
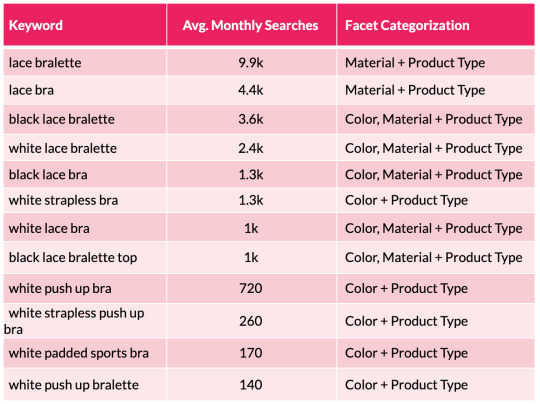
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
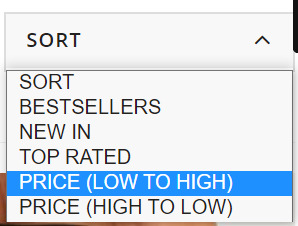
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
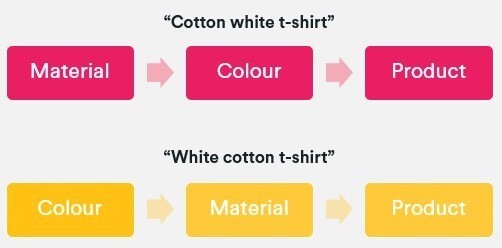
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
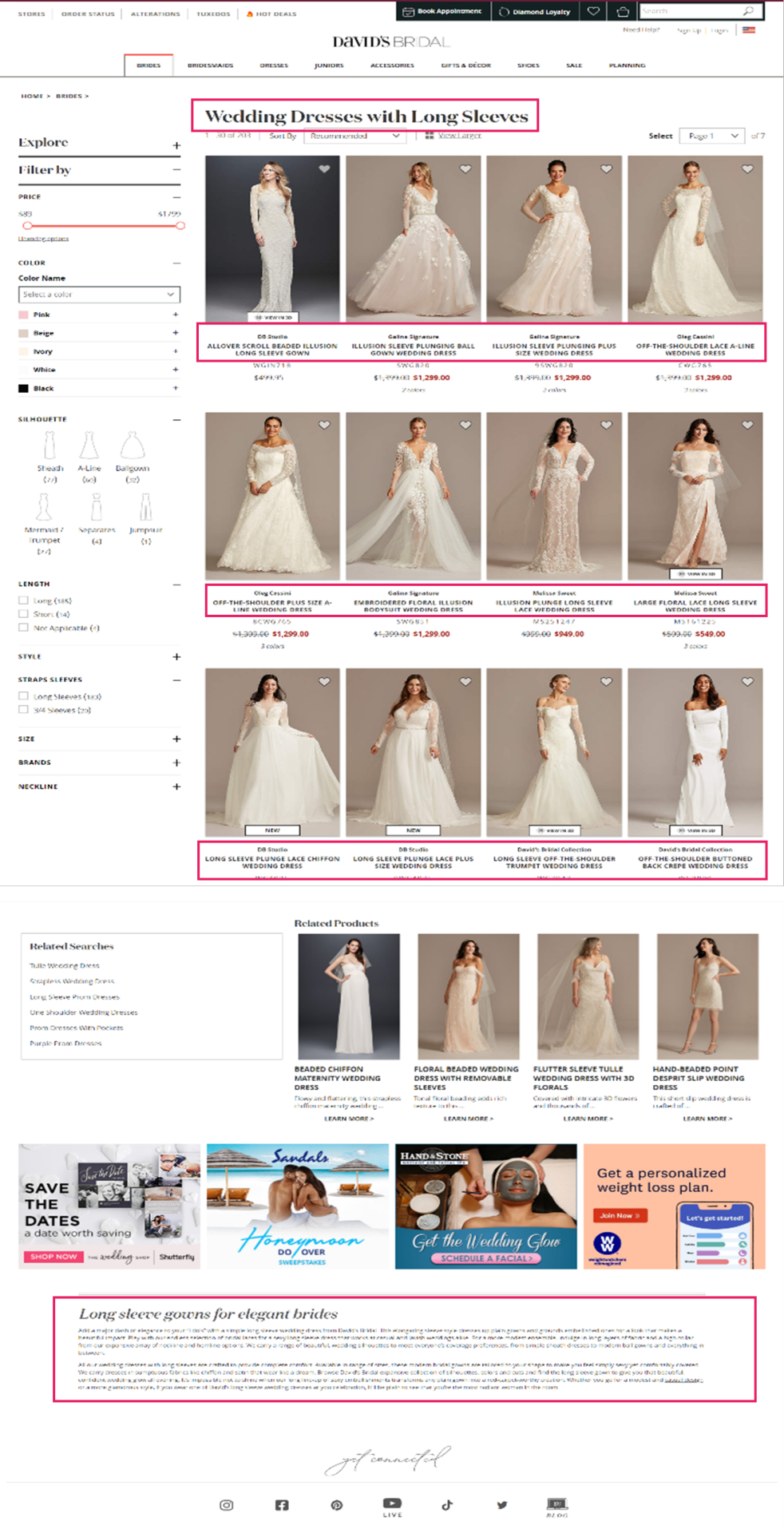
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
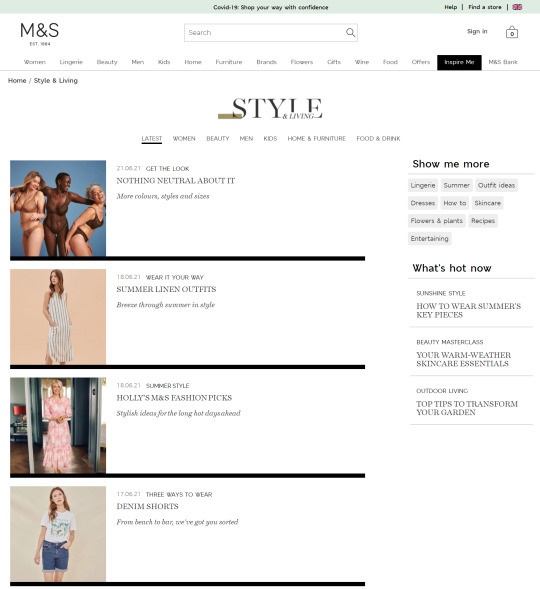
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://ift.tt/3xrpOJS) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:

From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
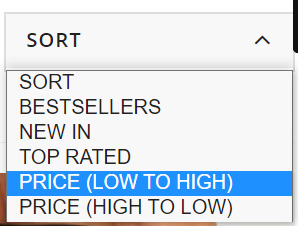
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
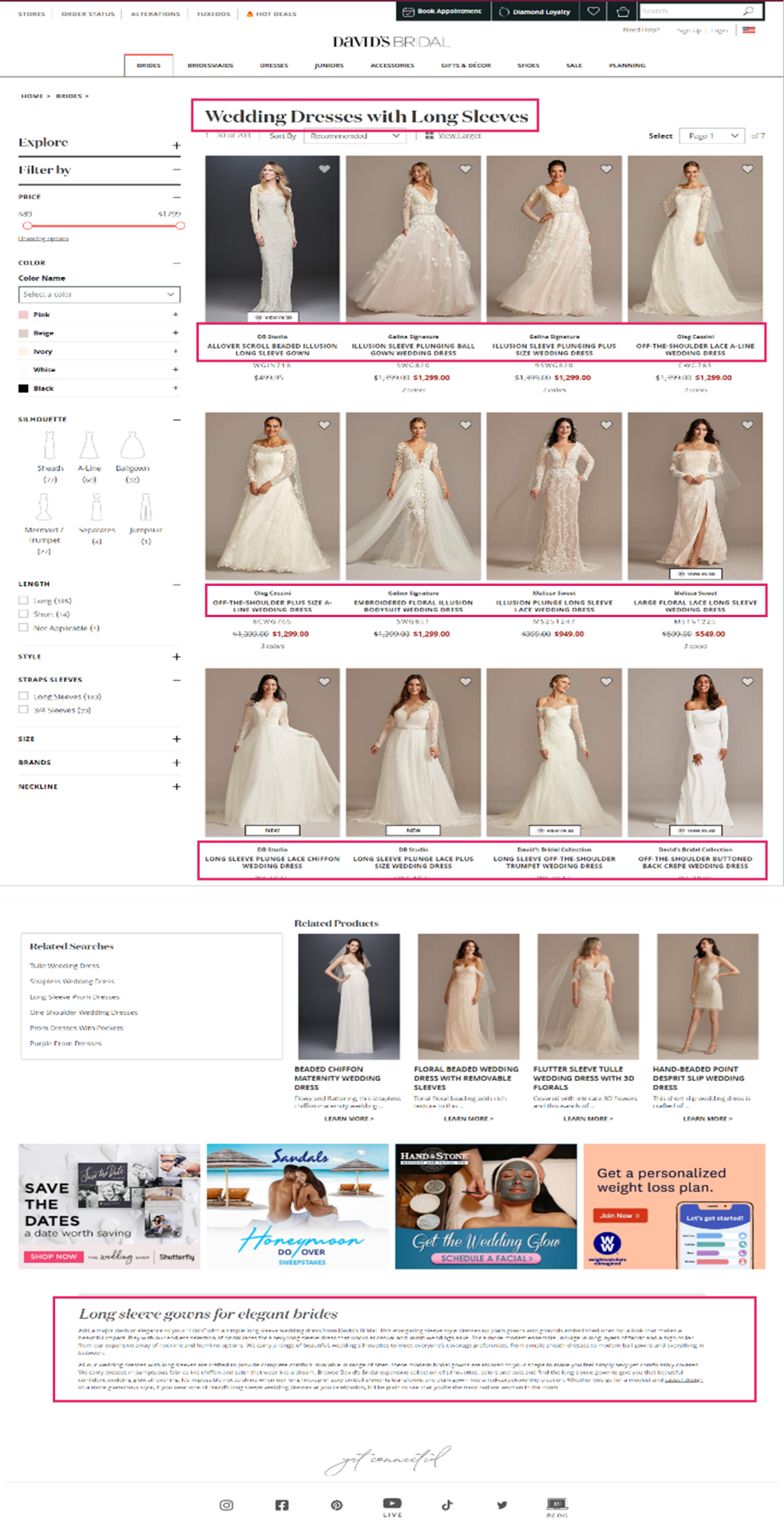
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
https://ift.tt/3qUUr85
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
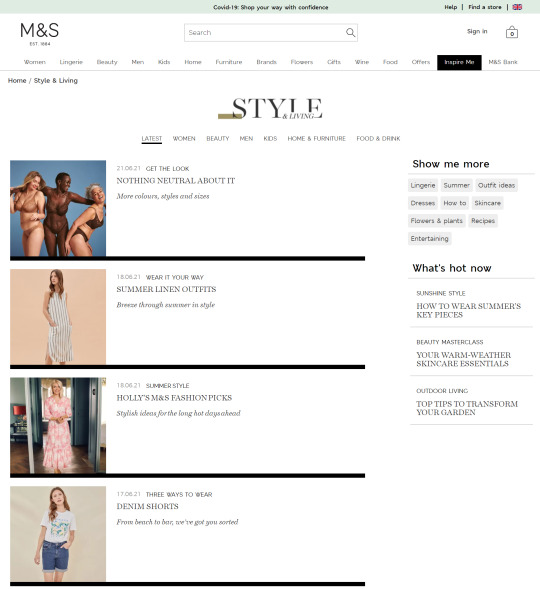
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://www.waterstones.com/category/childrens-teenage/facet/498) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:

From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
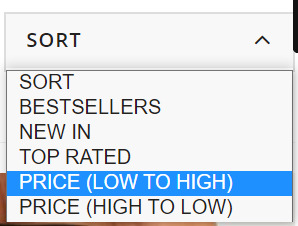
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.
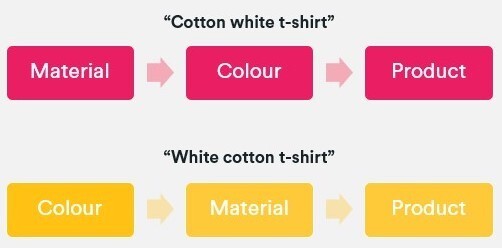
When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
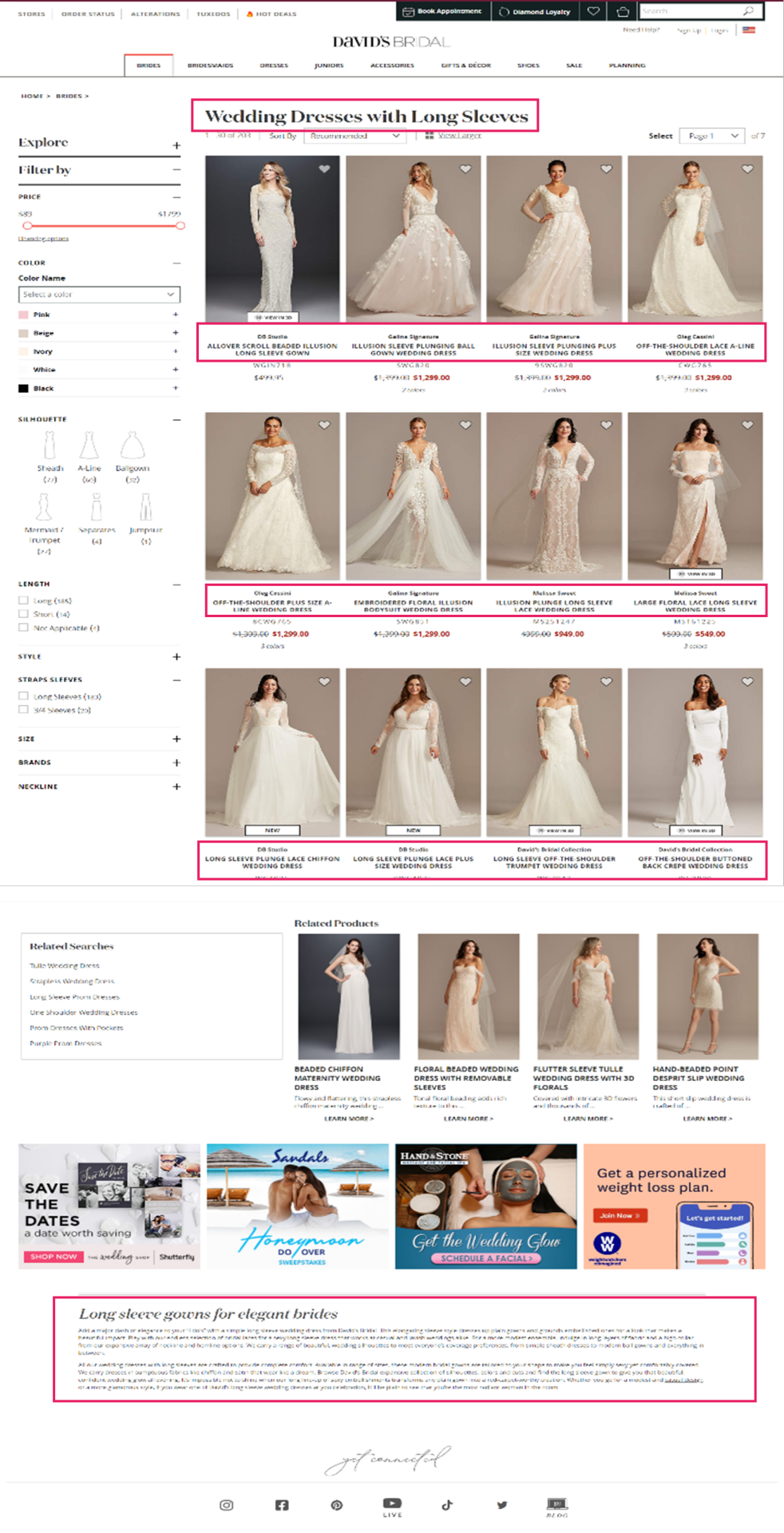
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes
Text
Fulfill Untapped Customer Demands Through Your Faceted Navigation
Faceted navigation allows customers to narrow down search results based on specific product attributes. They typically exist on Product Listing Pages (PLPs) and are a great way to help users intuitively discover products but managing this filtering system is a common SEO challenge. Crawling and indexation need to be controlled.
However, if we look beyond their inherent functionality, facets can offer us considerable potential. By centering your secondary navigation on long-tail keyword opportunities, you’ll be able to strategically utilize consumer intent, secure additional web conversions, and boost revenue levels.
Match consumer intent with long-tail search queries
Having an established brand and a solid domain backlink profile won’t guarantee success. This is great news for smaller brands, as industry giants aren’t necessarily going to win at this game.
If we search for “long sleeve wedding dresses”, we can see how David’s Bridal’s optimized facet page (Domain Authority: 67/100, Page Authority: 47 / 100) has obtained the top ranking position, while Nordstrom’s result (Domain Authority: 87/100, Page Authority: 39/100) appears in the third position for this particular query. We’ll take a look at what makes this page so effective later.
When looking at how we can optimize faceted navigations, it’s important to recognize that product attributes convey consumer needs and aspirations. If, for example, I’m looking for a wedding dress, then I may tailor my search by the color, fabric, neckline shape, and the sleeve length.
According to the search demand curve, long-tail queries account for up to 70% of all organic searches. They are highly targeted queries that offer big traffic-driving opportunities.
In the last few years, we’ve seen a big shift in the industry towards capitalizing this intent with long-form content. Blog articles and style guides have become the go-to methods for many to capture these visitors, as we can see from the examples taken from Marks & Spencers’ "Inspire Me" section:
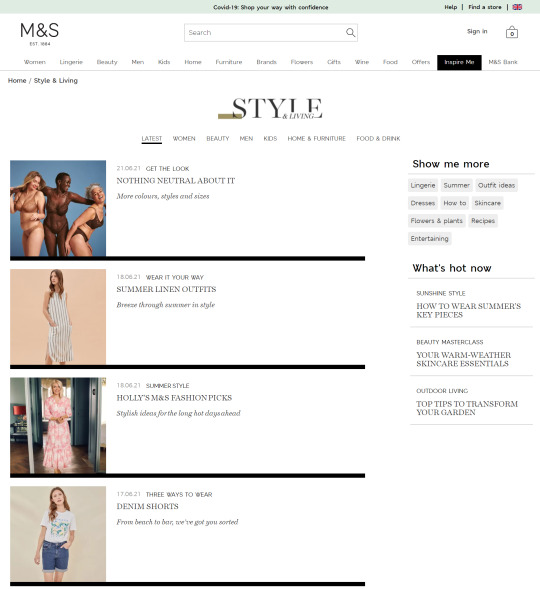
People often look for inspiration when they’re shopping, and these pages provide an effective way to add more internal links to category and product pages. But relying on this approach is one-dimensional, given that these deeper content pages tend to have lower PageRank. An extensive amount of time and effort will, therefore, be required to achieve the desired result.
In comparison, Product Listing Pages usually target broader search terms, and faceted navigations typically exist as passive functions. This is because they’re often blocked from crawlers, making them devoid of any SEO value. Waterstones (a well-known British bookstore) is one retailer that applies this rule for their on-page filters:
In this particular example, I’ve applied a filter to only show me books for 5 – 8 year olds, but the appended URL (https://www.waterstones.com/category/childrens-teenage/facet/498) is blocked in the robots.txt file. This is going to prevent such pages from being served in the SERPs despite them having the potential to meet specific customer needs. This shows that there can be a fundamental disconnect in matching customer intent to the pages we’re providing them in the organic results.
From the diagram below, we can see how editorial content typically focuses on the “awareness” and “interest” stages, whilst Product Listing Pages tend to be more in line with the “consideration” and “purchase” phases:
Serving the right content to users throughout their buying journey is pivotal to success. For many retailers, competitors are continuing to prioritize broader, high-volume keywords in saturated markets. They’re targeting the same terms to secure a proportion of the same search traffic. This is a very challenging prospect to face, and without carving out a gap in the marketplace, they won’t necessarily deliver the results they seek to secure. Likewise, relying on informational guides to target long-tail keywords means that you’re missing a large percentage of users who have very specific buying requirements. Yes, they’re ready to make a purchase!
By shifting your focus to address your customer’s real needs and expectations, you’ll be able to deliver a satisfying, frictionless experience at every interaction and all the way through to that final purchase.
The solution
Step 1: Conduct long-tail keyword research
Build a really comprehensive view of your potential customers by harnessing data from a variety of sources, including:
a) Keyword research tools like Moz, Google Keyword Planner, and Answer The Public.
b) The SERPs — get inspiration from the auto-suggest results, People Also Ask, and the related search links at the bottom of the page.
c) Competitor activity — aside from using SEO monitoring software, you can use a data mining extension tool like Scraper, which will extract faceted options directly from competitor Product Listing Pages. These tools are often free to download and allow you to quickly transfer product categories.
d) Your Google Search Console, Analytics, and PPC accounts to determine which keywords and URLs are securing the highest number of visits and web conversions. Internal search data can also give you great consumer insights.
e) Speak to your merchandising team to understand product demands and fulfillment capabilities.
Step 2: Group into meaningful sub-topics
Once you’ve collated all this information into a spreadsheet, you’ll be able to discover long-tail, consideration-orientated keywords. While individually they may not boast huge monthly search estimates, they can collectively highlight where purchase intentions can be better fulfilled.
To help illustrate this point, we can look at a small subset of lingerie keywords and the facets the searches represent:
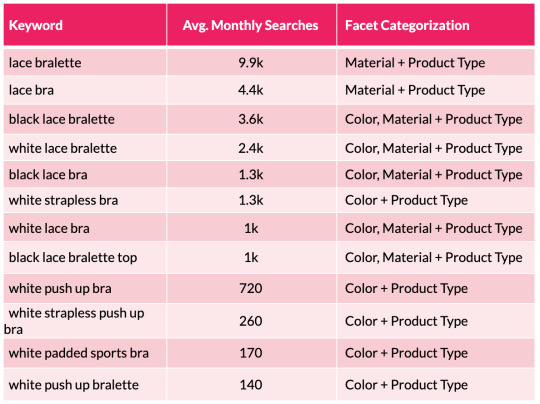
From the table above we can quickly see a pattern emerging with color and material variations appearing across the search terms. We can then substantiate this information with session and revenue estimates with the use of a recognized CTR model. This enables us to help forecast the potential organic uplift and quantify the size of the prize for a number of different scenarios that are on offer from each new facet combination. This may include estimations for securing position 10, 7, 5, 3 and 1 in Google.
One thing to note here is that it’s worth excluding synonyms, as they will falsely inflate your calculations. An example here would be to exclude “storage drawers” (22.2k monthly searchers) when reviewing the performance for “chest of drawers” (201k m/s). Including both variants will cause a false positive result and will lead you to draw incorrect conclusions.
Step 3: Dig deeper into broader terms around offers, ratings, and price
These product filters are found in the “Sort” dropdown box and, from my experience, these are set to “noindex” from the outset as they simply allow users to re-order page results. Certainly, content management systems like Shopify and Shopware have this as a default.
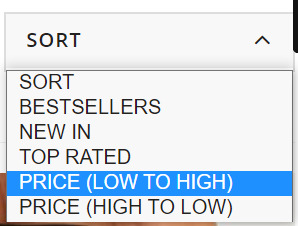
This makes sense since their purpose is to allow visitors to simply sort or narrow page content rather than offering alternative results and additional value (which is offered through faceted navigation). As such, filter typically produce duplicate results which should not be discoverable beyond the immediate moment. But this hard-and-fast rule doesn’t always apply perfectly in the real world. This is why we need to look at our individual industries and understand what’s important to our unique set of customers.
If we look at the world of gifting, we often see people shopping with a particular budget in mind. Therefore, terms like “birthday gift under £20” (40 m/s) or “Secret Santa gift under £10” (2.9k m/s) are reasonably common, and opening up relevant listing pages could be useful for shoppers.
Step 4: The technical steps
Facet taxonomies are hugely complex and the number of attributes that can be strung together increases with the size of the domain. We, therefore, need to carefully manage the flood gates and mitigate against any potential risks including crawl inefficiencies and link equity dilution.
We can do this by:
1. Avoiding thin/doorway pages by regularly re-assessing your product offering. For instance, you may consider there to be little value in creating a new listings page if you’re selling a very small range of low price point products. In this case, you may decide against opening up an additional Product Listing Page when you sell as few as 10 eligible products. However, this is not a fixed rule, so it’s quite possible that your criteria may be lower for particular product lines. Either way, these numbers will change over time. Consider seasonal trends, when new collections are launched, and when they become discontinued. Setting up a product retirement strategy to manage expired products and categories at scale in parallel with this step is also highly recommended.
2. Prevent content cannibalization by arranging selected facets according to their value and significance. “Size” is very important for some electrical goods like TVs, laptops, and cameras, but is less so for beauty accessories or vacuum cleaners. You must also make sure page content is distinctive and reflects the focus of your chosen facet(s). Refer to step 5 for more details.
3. Follow the sequence in which adjectives and facets are typically selected by your customers. This can vary depending on where your audience lives. So, whilst products generally have five or more distinguishable features, English vernacular determines that we use more than four adjectives (e.g. size + color + material + shape) to describe something.
4. Control the controllables by dealing with overlapping variations. This typically occurs when multiples co-exist and each exhibits good search metrics. For instance, it’s reasonable for someone to simultaneously look for several color and/or fabric combinations in the different ways below.

When this situation occurs, we should follow the same linguistic rules as above and choose a preferred sequence. In this case, it would be color + material + product type.
In comparison to the noindex tag suggested for on-page filters you should canonicalize unnecessary facets to their parent page (remembering that this is merely a hint and not a directive). This will enable you to control how crawlers deal with highly comparable result pages and will, therefore, help to prevent your site from being demoted in the SERPs. Dynamic search parameters should continue to be defined with a “noindex, nofollow” meta robots tag, disallowed in the robots.txt file, and configured through Google’s URL parameter tool (within your Search Console account) to tell crawlers the purpose of your parameters and how you would like them to be treated. This is a helpful guide on parameter handling for Googlebots, but bear in mind that this last tip won’t influence how Bing or Yahoo user-agents interpret these pages.
5. Open your facets in phases and cultivate it into a test-and-learn process. This will enable you to identify issues a lot sooner and implement facet-wide solutions in a timely manner. Without having to unravel these additional layers of complexity, problems such as crawl inefficiencies, PageRank dilution, or excessive indexation can be swiftly resolved.
To show you what this could look like, I’ve provided a phasing plan that was created for one of our e-commerce clients. Our research showed a significant SEO opportunity for opening up some of the facets and filters: potential +£263Kpcm for the “colour + type” facet (UK):
What’s more, when we extended our forecast to include other facet combinations, we calculated an additional revenue opportunity of up to +£207K/pcm (before filtering out combinations with no products offering).
Step 5: Optimize your facet URLs
Optimize your new facet category URLs to establish relevancy for your selected search terms. The key on-page elements to focus on include:
URL
Page title
Breadcrumb anchor texts
H tags
Content snippets (e.g. introductory text and FAQ copy)
Image ALT texts
Product names
Link out to similar facet category pages (i.e. via a “You May Also Like” feature box)
David’s Bridal is a good example of a retailer that has done this well. Looking back at the ‘Long Sleeve Wedding Dress’ Product Listing Page, we can see that they’ve curated unique content and followed fundamental optimization tactics on the landing page in a way that feels helpful to the user.
URL: davidsbridal.com/long-sleeve-wedding-dresses
Page Title: Long Sleeve Wedding Dresses & Gowns | David's Bridal
Meta Description: Do you dream of wearing a long sleeve wedding dress on your big day? Shop David's Bridal wide variety of wedding gowns with sleeves in lace & other designs!
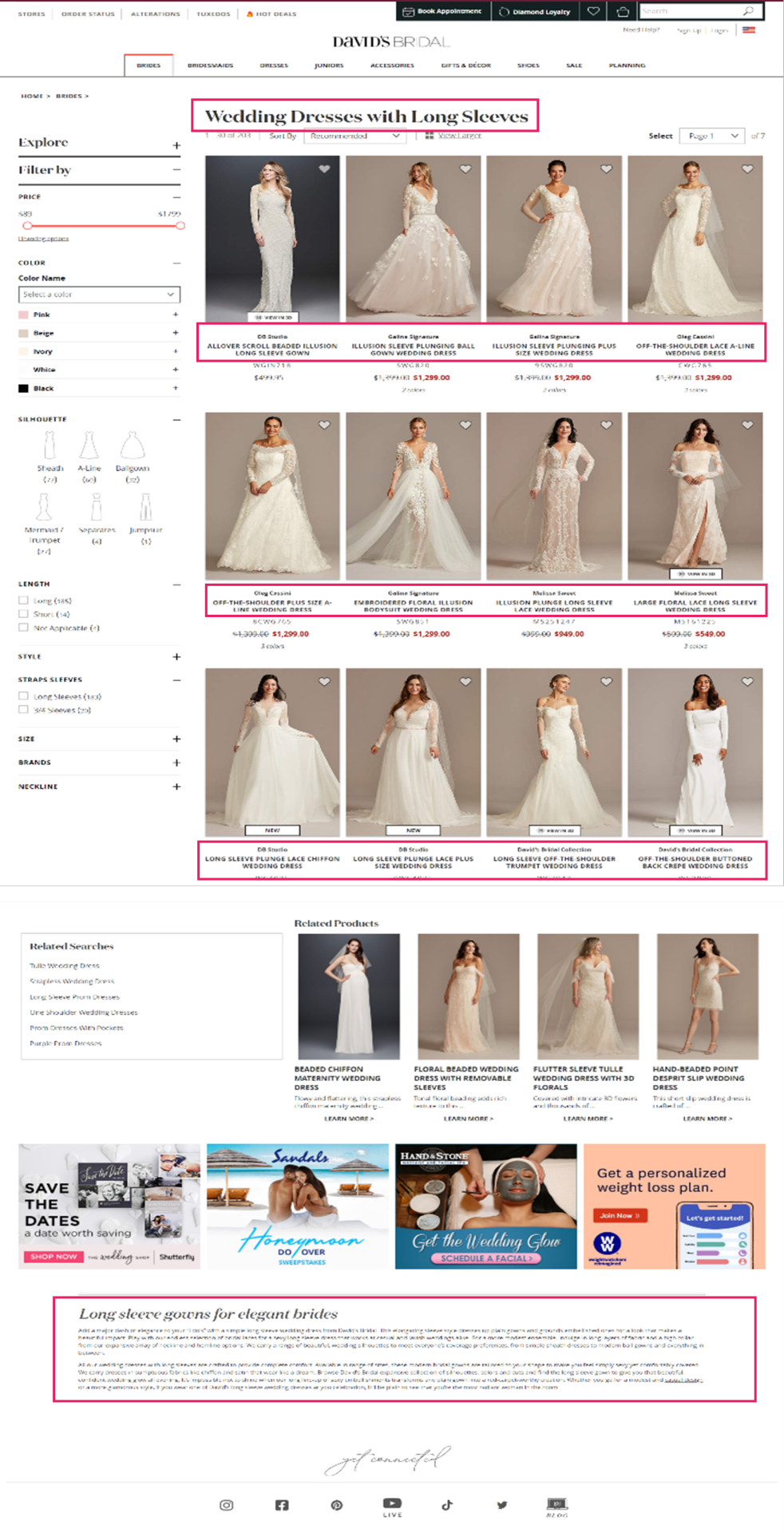
6. Provide accessibility and build page authority
Once you’ve opened up your new facet Product Listing Pages, you need to begin cultivating link equity towards them. This will ensure that they don’t exist as orphan URLs with no PageRank:
Ensure they’re referenced in your product XML sitemap.
If you have one feature per facet URL, then add them to your faceted navigation across CLP and Product Listing Page pages.
If you have two or more features per facet URL, then create a “Popular Searches” or “Related Searches” option within your CLPs.
Utilize your mega menu to showcase your new category landing pages. This will not only allow you to direct a large proportion of link equity, but it will also secure the highest click-through rate amongst your visitors.
Integrate your editorial strategy by creating engaging content with in-copy links. Think about how you can use descriptive long-tail anchor text about the Product Listing Page you want to link to rather than relying on “click here” or “see more”.
Connect to them via href links so you’re not solely relying on links from the main navigation or content hyperlinks. As this is difficult to do at scale, it can be done through modules such as “related categories”, “other subcategories”, “related products”, etc.
Devise strategic outreach campaigns that will secure quality, external backlinks to them.
Implementing this holistic and robust strategy will help you to secure exponential growth from your new commercial landing pages.
Conclusion
There is a great deal of organic opportunity that exists within your faceted navigation if you begin to leverage mid- and long-tail search terms.
Seek out the opportunity from extended keyword research and competitor analysis before deciding which variants fulfill consumer demands and deliver optimal organic sessions and onsite conversions. Configure a single faceted URL for each opportunity and open them up for crawl and indexation. Ensure PageRank is distributed to them (both internally and externally) and develop your landing page content in line with quality optimization practices. This approach will help you to avoid having crawl inefficiencies, over indexation, cannibalization, or having thin doorway pages. In turn, your website will be better suited to attract highly-targeted users and guide them down the purchase funnel.
Maximizing UX and reducing reliance on other marketing channels means that your faceted navigation can truly deliver organic ROI. We have seen this work for our clients.
0 notes