#SystemStability
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#AutomotiveElectronics#ECU#IsolationAmplifiers#EVTech#SystemStability#AutoEVTimes#SmartVehicles#VehicleSafety#TechInAutomotive#electricvehiclesnews#evtimes#evbusines
0 notes
Text

The Arteche CD-2R High-Speed Contactor Relay plays a crucial role in ensuring fast and secure operations within power systems. Designed for high-speed switching, the CD-2R relay is ideal for applications where rapid response times are essential, such as in circuit breaker control and fault isolation. Its robust design and reliability make it indispensable in maintaining system stability and minimizing downtime during critical operations. By utilizing the Arteche CD-2R relay, industries can significantly enhance the efficiency and safety of their power systems, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted performance.
#ArtecheRelays#HighSpeedRelays#PowerSystemProtection#ContactorRelay#electricalsafety#FaultIsolation#SystemStability#CircuitBreakerControl#industrialautomation#PowerSystemReliability#RelayTechnology#energyefficiency#substationautomation#electricalengineering#SwitchgearProtection
0 notes
Text

Resistoflex Spring Isolators are perfect for reducing vibration and shock in HVAC systems, heavy machinery, and industrial equipment.
.
.
.
Get in Touch:
📧 Email: [email protected]
🌐Website: https://www.resistoflex.in/
#VibrationControl#ShockAbsorption#HVACSolutions#IndustrialEquipment#HeavyMachinery#SpringIsolators#SmoothOperation#DurablePerformance#EngineeringExcellence#MechanicalInnovation#NoiseReduction#SystemStability#ReliablePerformance#EngineeringSolutions#Resistoflex
0 notes
Text
.
#sorry ik i need to stop taking posts on twt seriously#but i just think some tennis fans want their faves to be oppressed so bad#which is very unserious when said fave is a… White European Man#who is playing a sport that has been largely dominated by… White European Men????#like i admit as a SEA person i am not privy to the geopolitics of european regions n they play a part im sure#but LMAO maybe read the room !!!#i promise u ur multimillionaire white european man who travels around the world to hit a ball is not systemstically discriminated against
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
man how does anyone function with remembering things. I pulled out of a derealization/depersonalization episode, so now I'm remembering everything all at once rn and it sucks.
#and like i Could theoretically talk about it#but it's like just a continuation of the same plot n themes I've shared before#not much new in the realm of 'i was systemstically and psychologically destroyed n neglected by my caregivers' I'm afraid
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
votescolding for the UK elections is funny, because Labour is already poised to win like it was a puppet election in a dictatorship, but are also very systemstically removing leftists and pro-Palestine candidates, while giving some of the safest seats for Tory MP��s who have jumped ship because the party is in freefall, and some of them are also very virulent Islamophobes. And Keir Starmer has basically just said Labour will do everything the Tories have done but ”smarter and more responsibly”.
10 notes
·
View notes
Note
[WELCOME TO YOUSYSTEM!]
[SYSTEMSTATE: AWAKE]
...
...
Ow... Trying to turn off HURT...
( @totally-roku-tv)
Roku are you awake now?
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trans folk no matter what race get harassed. But, black trans folk almost certainly end up being harassed more because they dont benefit from the structural whiteness of america. Theyre getting fucked over twice as badly as white trans folk.
Ideally, this needs to be acknowledged. Infighting only starts when people feel like their suffering is being downplayed and they feel like they're being betrayed. Everyones issues are real issues, but sadly not everyones issues are equal in number nor severity. I do think that infighting is a real issue but its put forward more out of feeling ignored or disregarded, and the best way to solve it is to look at everything objectively.
Trans women generally seem to have it worse than trans men because male societal expectations dont have flexibility for feminine behavior, while trans men generally are given some societal flexibility through masculine women being generally acknowledged as existing. In both scenarios, neither trans men nor women are being treated by society as a man or a woman but as their assigned birth gender with behavior or traits of their new gender.
Neither transmasc nor transfem people get treated fully as their new gender due to bigotry and societal norms. It just so happens that if you were born a man, family values in this shit country value a Strong Male to carry on the family than a daughter to carry on another family's line, thus transitioning makes a lot of hateful parents.
This isnt even mentioning the horrible steriotype the right pushes that all transfems are pedophiles.
Regardless, I guess this is a very long way of saying everyone is dealing with awful shit but theres some things that need to be acknowledged as fact, not opinion.
- Minorities have it harder than white people as a baseline due to structural racism in this shithole country
- Black americans in particular have been systemstically fucked with by the government for over a hundred fucking years
- Transfems have extra difficulty when it comes to societal acceptance of who they are after transitioning and are profiled as pedophiles more often than transmascs due to sexist sentiments pushed by the government
All this adds up to generally, a White Transfem will have it easier than a Black Transfem. Yes, everyone is being fucked over, but the black community is being especially fucked over.
~ A White Genderfluid who was assigned male at birth
given all the rising transphobia and shit, we should remember that white trannies are still relatively safe and will be able to endure more escalation more easily, we're not at the top of any shit list even if we near if, trans women of color however are very vulnerable, and we need to remember they're our sisters, not our shields
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 10 Essential Car Parts Every Driver Should Know About | Complete Guide
https://autorepairlebanontn.com/?p=4097 Top 10 Essential Car Parts Every Driver Should Know About | Complete Guide When it comes to understanding your vehicle, knowing the most important parts of a car isn’t just helpful—it’s essential. We’ve all experienced that moment of panic when something goes wrong with our cars and we’re left wondering what exactly needs fixing. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the critical components that keep your vehicle running smoothly. From the engine that powers your journey to the brakes that ensure your safety, we’ll explore the parts that demand your attention and maintenance. Whether you’re a new car owner or looking to deepen your automotive knowledge, understanding these key elements will help you make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and even purchasing your next vehicle. Table of Contents Toggle What Are the Most Important Parts of a CarEngineTransmissionBraking SystemSuspension SystemSteering SystemElectrical SystemFuel SystemThe Engine: The Heart of Your VehicleHow the Engine FunctionsCommon Engine TypesTransmission System: Converting Power to MotionManual vs. Automatic TransmissionsMaintaining Your TransmissionBraking System: Essential for SafetyComponents of the Braking SystemTypes of BrakesWarning Signs of Brake ProblemsSuspension and Steering: Control and ComfortComponents of SuspensionSteering MechanismsElectrical System: Powering EverythingBattery and AlternatorEssential Electrical ComponentsSafety Features: Protecting PassengersPassive Safety SystemsActive Safety TechnologiesConclusionFrequently Asked QuestionsWhat are the most important parts of a car to understand?How does a car engine work?What’s the difference between manual and automatic transmissions?How do I know when my brakes need service?What does the suspension system do?How important is the electrical system in modern cars?What are the most important car safety features?How often should I check my car’s fluids?What’s the difference between disc and drum brakes?How can I extend my car’s lifespan? What Are the Most Important Parts of a Car A car contains many components working together to keep you moving safely on the road. Understanding these critical parts helps with maintenance decisions and troubleshooting potential issues. Here’s a breakdown of the most crucial car components: Engine The engine serves as the heart of any vehicle, converting fuel into mechanical energy that powers the car’s movement. Most modern cars use internal combustion engines with several key components: Cylinder block: Houses the pistons and serves as the main structure Pistons: Move up and down to create power from combustion Crankshaft: Converts the pistons’ linear motion into rotational force Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of intake and exhaust valves Fuel injection system: Delivers precise amounts of fuel to each cylinder Regular oil changes and maintenance keep this complex system running smoothly and extend its lifespan considerably. Transmission The transmission transfers power from the engine to the wheels while allowing for different speed ratios. Cars typically feature either manual or automatic transmissions: Manual transmissions: Require driver operation of the clutch and gear selector Automatic transmissions: Change gears without driver input using hydraulic systems CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission): Provides seamless acceleration without distinct gear shifts Dual-clutch transmissions: Combine manual transmission efficiency with automatic convenience Transmission fluid checks and periodic services prevent costly repairs and maintain smooth operation. Braking System The braking system provides crucial stopping power and requires immediate attention if any issues arise. Modern vehicles use hydraulic brake systems with these components: Brake pads: Create friction against the rotors to slow the wheels Rotors/discs: Spin with the wheels and provide a surface for brake pads Calipers: House the brake pads and apply pressure to them Master cylinder: Converts pedal pressure into hydraulic pressure Brake lines: Carry brake fluid throughout the system Regular brake inspections ensure your vehicle can stop effectively in emergency situations. Suspension System The suspension system supports the vehicle’s weight, absorbs road shocks, and maintains wheel alignment. Key suspension components include: Shock absorbers: Dampen bounce and vibration Springs: Support vehicle weight and absorb impacts Control arms: Connect the suspension to the frame Sway bars: Reduce body roll during cornering Ball joints: Allow steering movement while supporting weight A properly functioning suspension delivers comfort, handling precision, and extended tire life. Steering System The steering system translates driver input into directional changes. Modern vehicles typically use: Steering wheel: The driver interface Steering column: Connects the wheel to the steering mechanism Rack and pinion: Converts rotational motion to linear movement Power steering pump: Provides hydraulic assistance (in hydraulic systems) Electric motor: Provides assistance in electric power steering systems Proper steering maintenance ensures responsive handling and driving safety. Electrical System The electrical system powers everything from starting the engine to operating entertainment features. Critical electrical components include: Battery: Stores electrical energy and provides power for starting Alternator: Generates electricity while the engine runs Starter motor: Initiates engine operation Fuses and relays: Protect circuits from damage Sensors: Monitor various systems and provide feedback Regular battery checks and prompt attention to warning lights prevent unexpected breakdowns. Fuel System The fuel system stores and delivers fuel to the engine at the proper pressure and quantity. Main components include: Fuel tank: Stores gasoline or diesel Fuel pump: Pressurizes and delivers fuel to the engine Fuel injectors: Spray precise amounts of fuel into the combustion chamber Fuel filter: Removes contaminants from the fuel Fuel pressure regulator: Maintains optimal fuel pressure Clean filters and quality fuel help maintain engine performance and efficiency. The Engine: The Heart of Your Vehicle The engine serves as the powerhouse of your car, converting fuel into energy that propels the vehicle forward. Modern vehicles typically use either internal combustion engines or electric motors as their primary power source. How the Engine Functions Internal combustion engines operate through a complex mechanical process involving several key components. Cylinders form the core chambers where fuel-air mixtures ignite, with their number and arrangement directly influencing performance and operational smoothness. Pistons move vertically inside these cylinders, transforming combustion pressure into mechanical energy. Connected to these pistons, the crankshaft converts this up-and-down motion into rotational force that eventually drives the wheels. In gasoline engines, spark plugs create the electrical spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture within each cylinder. The camshaft controls the precise timing of intake and exhaust valves, ensuring the engine “breathes” correctly during each phase of the combustion cycle. Electric vehicles function differently, relying on a rechargeable battery that stores electricity to power the electric motor. This motor transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy, delivering instant torque and exceptionally smooth acceleration without the multiple moving parts found in traditional engines. Common Engine Types Internal combustion engines generate power by igniting an air-fuel mixture and come in two primary varieties. Gasoline engines use spark plugs to ignite this mixture, offering higher RPM capabilities and smoother operation. Diesel engines, by contrast, compress air to extremely high pressures until the fuel spontaneously ignites when injected, providing greater torque and fuel efficiency at lower RPMs. Electric engines use motors powered by rechargeable battery packs. These engines provide many advantages over their fuel-powered counterparts, including faster acceleration, quieter operation, and zero direct emissions. Electric motors deliver peak torque instantly, eliminating the need for complex transmission systems while offering a simpler mechanical design with fewer moving parts to maintain. Transmission System: Converting Power to Motion The transmission system transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing drivers to control speed and torque. It’s a complex mechanical assembly that serves as the critical link between the engine’s power generation and the vehicle’s actual movement on the road. Manual vs. Automatic Transmissions Manual transmissions require active driver participation through a clutch pedal and gear shifter. Drivers select the appropriate gear ratio based on speed and road conditions, physically captivating and disengaging the clutch to change gears. This transmission type offers greater control over the vehicle’s performance and typically delivers better fuel economy than its automatic counterparts. Automatic transmissions shift gears without driver intervention, using a torque converter instead of a clutch. These systems monitor vehicle speed and engine load to select the optimal gear, creating a smoother driving experience especially in stop-and-go traffic. Modern automatic transmissions have evolved significantly, with some high-end models featuring 8-10 gears for improved efficiency. Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) represent an advanced automatic option that uses belts and pulleys rather than fixed gears. CVTs provide seamless acceleration by continuously adjusting the gear ratio, eliminating the distinctive shifting feeling found in traditional transmissions. This design optimizes engine performance at various speeds, contributing to improved fuel efficiency in many vehicle models. Maintaining Your Transmission Transmission maintenance directly impacts vehicle longevity and performance. Regular fluid checks form the foundation of proper transmission care, as low or contaminated fluid causes increased friction, overheating, and potential system failure. Transmission fluid should maintain a bright red color – if it appears brown or smells burnt, immediate replacement becomes necessary. Filter replacement represents another essential maintenance task for transmissions with serviceable filters. These filters trap contaminants and prevent debris from circulating through the system, protecting sensitive components from premature wear. Many manufacturers recommend filter changes every 30,000-60,000 miles depending on driving conditions. Temperature management plays a crucial role in transmission health. Extreme heat accelerates fluid breakdown and component wear, while cold temperatures can cause delayed engagement and sluggish performance. The cooling system must function properly to maintain optimal transmission operating temperature, especially during high-stress activities like towing or mountain driving. Vehicle loading directly affects transmission performance and lifespan. Exceeding manufacturer-recommended weight limits places excessive strain on transmission components, particularly the clutches, bands, and planetary gear sets. Following towing guidelines and avoiding overloading helps prevent premature transmission wear and costly repairs. Braking System: Essential for Safety The braking system represents one of the most critical safety components in any vehicle. It’s responsible for slowing and stopping your car, making it fundamental for preventing accidents and ensuring passenger safety. Components of the Braking System Brake pads create the friction needed to stop your vehicle by pressing against the rotors when you apply the brake pedal. These pads wear down over time and typically require replacement every 30,000 to 70,000 miles depending on driving habits and conditions. Brake rotors (or discs) are the metal components that rotate with the wheel until the brake pads clamp onto them to slow the vehicle. They’re commonly found on front wheels and increasingly on all four wheels in modern vehicles. Brake drums function similarly to rotors but use a different mechanism where brake shoes press against the inside of the drum rather than clamping from outside. Many vehicles still use drum brakes on rear wheels due to their cost-effectiveness. The master cylinder converts pressure from your foot on the brake pedal into hydraulic force that activates the entire braking system. This crucial component ensures consistent braking performance throughout the vehicle. Brake fluid transfers the hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder to the individual wheel brakes. This specialized fluid doesn’t compress under pressure, allowing for immediate and reliable brake response. Types of Brakes Disc brakes offer superior stopping power and heat dissipation compared to other braking systems. They’re standard on front wheels of most vehicles and increasingly common on all four wheels, particularly in performance or luxury models. Drum brakes use curved brake shoes that press outward against a rotating drum when activated. Though less efficient at heat dissipation than disc brakes, they’re often installed on rear wheels of economy vehicles due to their lower manufacturing cost and adequate performance for less demanding braking scenarios. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) prevent wheel lockup during emergency stops, maintaining steering control and reducing stopping distances on slippery surfaces. ABS accomplishes this by automatically pulsing the brakes when sensors detect impending wheel lockup. Warning Signs of Brake Problems Squealing or grinding noises indicate worn brake pads or rotors that need immediate attention. The squealing typically comes from wear indicators on brake pads, while grinding suggests metal-on-metal contact that can damage rotors. A spongy brake pedal feels soft and requires more pressure than normal to engage the brakes fully. This symptom usually points to air in the brake lines or low brake fluid levels, both requiring prompt professional attention. Vibrations during braking, especially felt through the steering wheel, signal warped brake rotors or uneven pad wear. These vibrations typically worsen as vehicle speed increases and can lead to longer stopping distances if not addressed. Dashboard warning lights specifically for brakes should never be ignored as they indicate system malfunctions detected by onboard diagnostics. Modern vehicles monitor brake fluid levels, pad wear, and system pressure to alert drivers before catastrophic failures occur. Pulling to one side when braking reveals uneven braking force between the right and left sides of the vehicle. This dangerous condition can result from stuck brake calipers, contaminated brake fluid, or uneven pad wear that compromises directional control during stops. Suspension and Steering: Control and Comfort The suspension and steering systems work together to provide control, comfort, and safety while driving. These critical components ensure your vehicle stays stable on the road and responds accurately to your directional inputs, making them among the most important parts of any car. Components of Suspension The suspension system absorbs road irregularities and maintains vehicle stability through several key components. Sway bars (also called stabilizer bars) connect the left and right sides of the suspension, reducing body roll during cornering and keeping the vehicle level during turns. Ball joints function as crucial pivot points between the suspension and steering knuckle, enabling smooth movement when steering or driving over uneven terrain. Springs and shock absorbers form the core of the suspension system. Springs—whether coil or leaf type—support the vehicle’s weight and absorb initial impacts, while shock absorbers dampen spring oscillations to prevent continuous bouncing after hitting bumps. Control arms connect the suspension to the vehicle’s frame, maintaining proper wheel alignment and allowing vertical wheel movement while keeping the wheels properly positioned. Steering Mechanisms Steering systems translate driver input into directional changes through precisely engineered components. The steering rack and pinion is the central mechanism that converts the turning motion of your steering wheel into the side-to-side movement that turns the front wheels. This system offers responsive and precise control, particularly at higher speeds where accuracy becomes more critical. Tie rods connect the steering rack to the wheels via the steering knuckle, transmitting the force needed to turn the wheels in either direction. These components play a vital role in maintaining proper wheel alignment and predictable steering response. Worn tie rods often lead to uneven tire wear, poor alignment, and unpredictable handling characteristics that compromise safety. Both suspension and steering systems require regular inspection and maintenance to perform optimally. Their combined function affects everything from ride comfort and handling precision to overall vehicle safety and tire longevity. Deterioration in either system can lead to compromised control, especially during emergency maneuvers or adverse weather conditions. Electrical System: Powering Everything The electrical system serves as the nervous system of your vehicle, connecting and powering various components that make modern driving possible. From starting the engine to powering your headlights and entertainment system, these electrical components work together to keep your car functioning properly. Battery and Alternator The battery functions as the primary power source in both conventional and electric vehicles. In traditional cars, it provides the initial surge of electricity needed to start the engine, while in electric vehicles, it stores the energy that drives the motor. Car batteries supply power to essential systems including the ignition, lighting, and all electronic accessories when the engine isn’t running. Without a functioning battery, your vehicle simply won’t start. The alternator works alongside the battery, recharging it and powering electrical systems while the engine runs. This component converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. The alternator ensures your battery maintains its charge during operation and supplies consistent power to all electrical components. Regular testing of both the battery and alternator helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and electrical system failures. Essential Electrical Components Spark plugs play a critical role in gasoline engines by igniting the fuel-air mixture inside the cylinders. These small but mighty components create the spark necessary for combustion, directly affecting engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Most vehicles require spark plug replacement every 30,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the type. The starter motor transforms electrical energy from the battery into mechanical force that turns over the engine during ignition. This component engages with the engine’s flywheel when you turn the key or press the start button. Proper functioning of the starter motor is essential for reliable vehicle starting in all conditions. Electrical wiring connects all components in a complex network throughout your vehicle. These wires distribute power from the battery and alternator to various systems and are protected by fuses that prevent dangerous electrical overloads. The ignition coil generates the high voltage needed for spark plugs to create their spark, while many sensors and control modules—like the engine control module (ECM)—manage your car’s complex systems for optimal performance and efficiency. Safety Features: Protecting Passengers Car safety features are engineered to safeguard occupants and prevent accidents on the road. These systems fall into two main categories: passive safety systems that protect during a crash and active technologies that help prevent collisions from occurring in the first place. Passive Safety Systems Passive safety systems activate during a collision to minimize injuries and protect passengers. Airbags serve as mandatory safety equipment that deploys upon impact, cushioning occupants from severe trauma during accidents. Seat belts, required by law since 1968, significantly reduce fatality risks by restraining passengers during collisions and preventing them from becoming dangerous projectiles within the vehicle. Tire pressure monitoring systems alert drivers to underinflated tires that compromise vehicle stability and increase crash risks. Backup cameras, mandatory since 2018, enhance visibility by reducing blind spots, particularly when reversing out of parking spaces or driveways. Active Safety Technologies Active safety technologies work proactively to prevent accidents before they happen. Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS), required in all new vehicles since 2012, prevent tire lockup during hard braking situations, maintaining steering control when drivers need it most. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), mandatory as of 2022, detects potential collisions with stalled vehicles, pedestrians, and road debris, automatically applying brakes if drivers don’t respond in time. Electronic Stability Control (ESC) monitors multiple vehicle parameters like steering input and wheel speed, selectively braking individual wheels to keep the car on its intended path. Forward Collision Warning (FCW) employs sensors and cameras to track distances between vehicles, providing audio and visual alerts when collision risks increase. Adaptive Cruise Control paired with Lane Centering reduces driver workload by maintaining safe following distances and helping vehicles stay centered in their lanes. Blind Spot Warning and Rear Cross Traffic Warning systems alert drivers to vehicles in hard-to-see areas, significantly reducing side-impact and backing collision risks. Conclusion Understanding your car’s vital components is a powerful step toward becoming a more informed vehicle owner. From the engine that powers your journey to the brakes that keep you safe the knowledge we’ve shared empowers you to make better maintenance decisions and communicate effectively with mechanics. Regular attention to these critical systems extends your vehicle’s lifespan while improving your driving experience and safety. Whether you’re maintaining your current vehicle or shopping for a new one this foundation of automotive knowledge serves as your roadmap. Remember that modern vehicles are sophisticated machines requiring specialized care. By prioritizing maintenance for these essential components we’re not just preserving our cars but also protecting our investment and ensuring peace of mind on every drive. Frequently Asked Questions What are the most important parts of a car to understand? The most crucial components to understand include the engine (the vehicle’s powerhouse), transmission (transfers power to wheels), braking system (provides stopping power), suspension system (ensures comfort and handling), steering system (controls direction), electrical system (powers components), and fuel system (delivers fuel to engine). Understanding these systems helps with maintenance decisions and troubleshooting problems. How does a car engine work? A car engine converts fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. In internal combustion engines, fuel mixes with air in cylinders where pistons compress it, and spark plugs ignite the mixture, creating explosions that move the pistons. This motion transfers to the crankshaft, generating rotational power that eventually reaches the wheels. Electric motors, by contrast, use electrical energy from batteries to create rotation without combustion. What’s the difference between manual and automatic transmissions? Manual transmissions require drivers to physically shift gears using a clutch pedal and gear stick. Automatic transmissions shift gears without driver input, using hydraulic systems to select appropriate gear ratios based on speed and throttle position. Automatic transmissions offer easier driving, especially in traffic, while manuals typically provide better fuel economy and more direct control over the vehicle’s performance. How do I know when my brakes need service? Warning signs include squealing or grinding noises when braking, a soft or spongy brake pedal, vibration during braking, pulling to one side when stopping, or an illuminated brake warning light on your dashboard. You should also have brakes inspected if stopping distances increase or if you notice brake fluid leaks. Regular brake inspections (approximately every 10,000-15,000 miles) help prevent costly repairs. What does the suspension system do? The suspension system connects your vehicle to its wheels, absorbing road irregularities for a smoother ride while maintaining optimal tire contact with the road. Components include springs, shock absorbers, struts, control arms, and sway bars. The system balances comfort and handling by controlling body roll during turns and reducing bounce after bumps, while also supporting vehicle weight and maintaining proper wheel alignment. How important is the electrical system in modern cars? The electrical system is critically important in modern vehicles, functioning as the car’s nervous system. It powers everything from engine ignition and starting to lights, infotainment, climate control, and safety features. The system consists of a battery (stores power), alternator (generates electricity while driving), starter motor, and complex wiring networks. As vehicles become more technologically advanced, the electrical system grows increasingly sophisticated and essential. What are the most important car safety features? Key safety features include passive systems like airbags, seat belts, and crumple zones that protect during accidents, and active technologies that help prevent collisions. Essential active safety features include Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), Electronic Stability Control (ESC), traction control, backup cameras, and blind-spot monitoring. Newer vehicles may also include automated emergency braking, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control for enhanced protection. How often should I check my car’s fluids? You should check engine oil monthly or before long trips. Coolant levels should be checked quarterly, especially before extreme weather seasons. Transmission fluid requires checking every 30,000-60,000 miles for automatic transmissions. Power steering, brake fluid, and windshield washer fluid should be checked quarterly. Always consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations, as intervals vary by vehicle make and model. What’s the difference between disc and drum brakes? Disc brakes use calipers to squeeze pads against a rotor attached to the wheel, creating friction to stop the vehicle. Drum brakes have components housed inside a drum that rotates with the wheel, using internal shoes that press outward against the drum. Disc brakes dissipate heat better, provide stronger stopping power, and are easier to service, which is why they’re typically used on front wheels where braking forces are greatest. How can I extend my car’s lifespan? Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule for oil changes, fluid checks, and part replacements. Don’t ignore warning lights or unusual noises. Practice gentle driving habits by avoiding rapid acceleration and hard braking. Keep your car clean to prevent rust and corrosion. Store your vehicle properly when not in use, preferably in a garage. Address small issues before they become major problems, and use quality parts and fluids for all maintenance. https://autorepairlebanontn.com/?p=4097 Absolute Auto Repair
0 notes
Text

[ #SuccessStory 🖨️ ] | https://lnkd.in/dn_B5DTf | Read how Emergys played a crucial role in supporting a printing and packaging solutions enterprise in stabilizing their system operations using SAP. #systemstability #sapsolutions #Emergys
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Harness the Power of the Multi-Dimensional Coupling Model as a Tool for Architecting Modular, Evolvable Software SystemsIn this definitive guide, Vlad Khononov introduces a novel approach to designing modular software systems that turns coupling into a powerful design tool.Software, like all systems, is composed of components that interact to form the system itself. Coupling is the metric used to represent the interdependence between connected components, and the magnitude of coupling ultimately affects the adaptability and success of the software system. Balancing Coupling in Software Design surveys existing methods of evaluating coupling and combines them into a comprehensive model for making design decisions that manage complexity while increasing the modularity of your software system.Coupling is everywhere in software development. Whatever your job level or title, whether you are writing a function, designing an object model, or architecting distributed systems, this book is for you.Understand coupling and the ways it manifests itself in software designEvaluate the multi-dimensional forces of couplingUnderstand how the dimensions of coupling interact to impact your systemSteer your systems away from complexity and toward modularityThe principles discussed inBalancing Coupling in Software Design are ubiquitously relevant in software engineering and will transform the way you think about software design. [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
🔌⚡ Understanding Fault Currents in High Voltage Power Systems: Key Insights and Considerations 💡🔍
Fault currents play a vital role in the safe and reliable operation of high voltage power systems. Let's dive into some essential aspects and considerations!
1️⃣ Magnitude: Fault currents in high voltage power systems can reach exceptionally high levels, impacting equipment and system stability. #FaultCurrentMagnitude #PowerSystemSafety
2️⃣ Transient Nature: Fault currents are transient and short-lived, quickly rising to peak values and decaying as protective devices activate. #TransientFaultCurrents #SystemStability
3️⃣ Equipment Impact: Fault currents pose significant stress on power system equipment such as transformers, circuit breakers, cables, and conductors. #EquipmentProtection #SystemReliability
4️⃣ Protection Coordination: Coordinating protective devices is crucial to isolate faulty sections while maintaining operational continuity in the rest of the system. #SelectiveTripping #ProtectionCoordination
5️⃣ Fault Analysis: Conducting fault analysis studies helps identify worst-case scenarios, calculate fault current magnitudes, and assess potential risks to power system components. #FaultAnalysis #RiskAssessment
Understanding and analyzing fault currents are essential for designing effective protection schemes, selecting suitable protective devices, setting appropriate relay settings, and ensuring the reliable and safe operation of high voltage power systems.
0 notes
Text
having a real what's the fucking point day tbh
#we're in the middle of a pandemic with other disease that should probably be declared a pandemic if anyone knows what's good for anything#the world's literally on fire#no one cares about doing anything about it#no one even fucking cares enough to wear a fucking mask in the grocery store to protect vulnerable people#from a potentially debilitating virus#we're going to have MORE pandemics because no one cares to do anything about anything and we're gutting public health#growing more and more disgusted with people as a whole by the day#and i'm just fucking tired#literally bc i have chronic fatigue (from a virus FIVE YEARS AGO)#(like sidenote it you FUCKS knew what it's like to live with a chronic condition maybe you wouldn't be so fucking cavalier#about a potentially fucking debilitating virus)#and also existentially. i'm just tired. i'm going to bed.#personal#to be deleted#god for a second i almost forgot about the systemstic degredation of my/our basic human rights lmfao like#there's just so much!
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
I personally have a variety of issues towards religion, particularly christianity (not related to any trauma). While I'm not a fan of it, I know from personal experience that religion can in fact be helpful to people, especially in their youth. I have a friend who's been depressed practically his whole life (many deaths in his family when he was young), and he's said in the past that his religion is in part what kept him going. So, yes, highly anecdotal, but I'm sure there's many similar views and experiences on the matter. I suppose all this to say that even my cynical atheist ass can see some benefits in religion in youth, and obviously as everyone above said, this would be no beuno for minorities
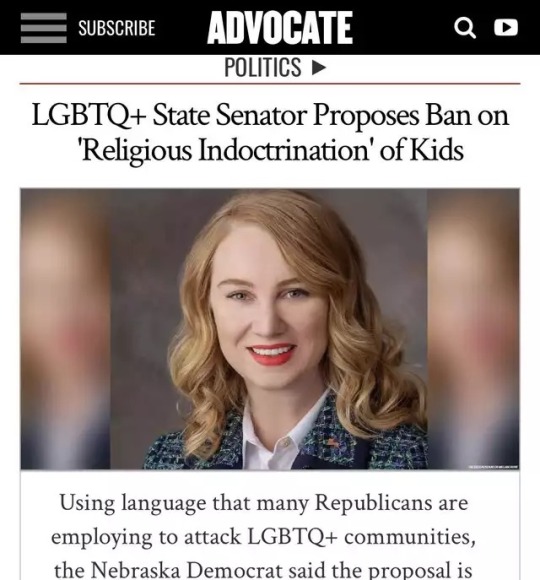
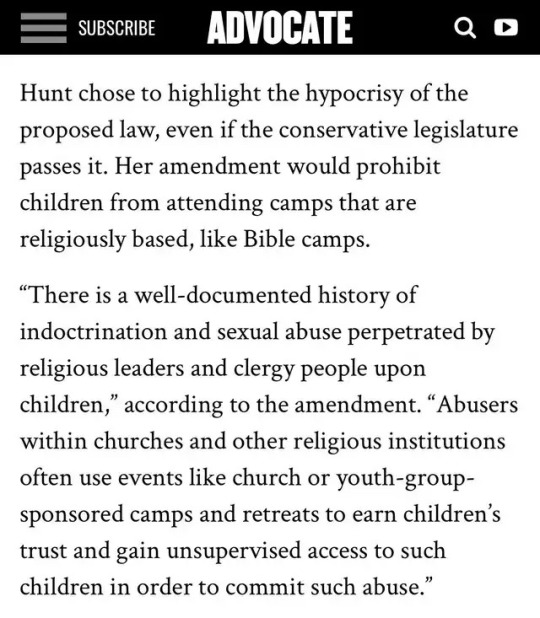
#but also#i know it's a big systemstic issue#but something should be done about the abuse of children in there#it's so damn widespread
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cats, new doggo: if you don’t like it why are you doing it?
Me: …good question. :((
#let’s be icarus#life with pets#what’s gonna be more satisfying: a bonfire or using the printed chapters as poop liner for merlin#short term satisfaction & fire for a boring and psychologically distressing class (for me)#or long term pettiness of seeing it systemstically covered in parrot shit#…eh. prolly enough paper for both#tho liner is more ‘practical’#…buuut I’m bored enough that seeing these pages go up in flames would be satisfying#albeit less methodical
0 notes
Text
If only it was only the oldest vampires that were bloodthirsty monsters that inevitably cause death and suffering no matter what they do. Hm.
It's systemstic.
4 notes
·
View notes