#TCPDump
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
SOC TCP Dump Lab
Lately I have been playing with TCP Dump, I prefer Wireshark when it comes to monitoring network traffic using a packet sniffer. But a person in IT Cybersecurity should be able to work with multiple different Programs.
TCP dump is available on the Kali Linux program set used to monitor traffic on a network. Often used by both SOC personal and attackers alike.
Now this lab was created by the Group Black Hills Info Sec. A very good company that not only offers Cybersecurity services, but also they have a love for teaching and have many classes available for pay what you can. I will link there site. This set of classes are part of the SOC Entry Level Class.
Lets look at the lab.
I started by getting into root, then running TCP Dump. This is what showed up first.
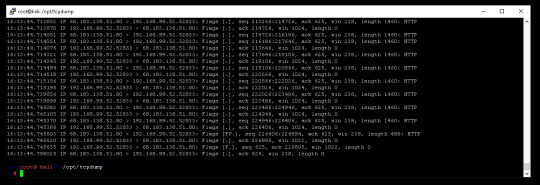
Looking at the information provided, I can see the time stamp, the Protocol, IP address and source IP address. Most of this information can be very useful when your trying to look for anything out of the ordinary on your system.
Next I went ahead and added a port number, port 80. A common port used offten by threat actors to compromise networks.
The command I used was tcpdump -n -r magnitude_1hr.pcap host 192.168.99.52 and port 80
and this is all the information that came up.

Now when I saw this I really felt over whelmed with information. There is a lot being tossed at you and most of it is encrypt and I can not read it. But you can pic out some information, such as the HTTP and normal IP Addresses.
Next I turned to the ASCII to decode the packets. Running, tcpdump -n -r magnitude_1hr.pcap host 192.168.99.52 and port 80 -A
This narrowed down the flow of information also cleared up the encryption and I could physically sort through the data and noticed a few things.

Looks like something is running Powershell $ signs. Now powershell is not normally something that you would see running on an average users PC. Maybe if they were IT but I would not be to sure about this. What really make me have to think was when I saw the Base 64.
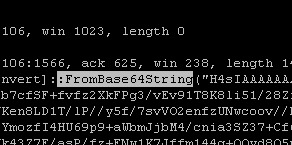
Now at first I will confess I had no clue what Base 64 is or what it is used for. So I had to do some googling this is what I found, Base 64 is used to encode binary data as printable text. So I have to ask my self, “What does that mean?” Well looking deeper it is used to transport binary over protocols that normally would not be able to. This would allow someone with access to send commands to say run Powershell.
Now this is just a small lab and digging deeper into this would be out of scope of this lab. It is only a place to just get some hands on experience with TCP Dump. There will be more to come as I finish more of the labs in the classes.
0 notes
Text
running tcpdump on my routers wan interface like damn this mf can talk
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
TCPDump: Capture and Record Specific Protocols / Port Traffic
Here's how you can use tcpdump command to capture and record specific network traffic, protocols and ports on Linux, Unix, macOS (OS X) and BSD systems like FreeBSD. This tool is essential for sysadmins and developers to debug networking issues.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
CSCE 465 Homework 1: Packet Sniffing and Spoofing Lab
1 Overview Packet sniffing and spoofing are the two important concepts in network security; they are two major threats in network communication. Being able to understand these two threats is essential for understanding security measures in networking. There are many packet sniffing and spoofing tools, such as Wireshark, Tcpdump, Netwox, Scapy, etc. Some of these tools are widely used by security…
0 notes
Text

It's time to expand the geographical footprint and leave the neighbors spoofed SSIDs. The opsec needs to be completely flawless going forward. First grab a $200 used ThinkPad with cash from a street vendor with no receipts, no trace, and a USB kill switch. Wipe it clean with DBAN, then hit a library PC to download Tails OS onto a 16GB SanDisk USB, enabling encrypted persistent storage with a 32-character passphrase stored on my X-seed. Boot it at a McDonald’s, USB in, Tor up, and route through a cash-bought VPN. Tweak Tor’s exit nodes with Germany, Netherlands avoiding Five Eyes in the simplest ways. Wi-Fi’s via a $10 dongle in my backpack, MAC spoofed to a random hex via macchanger. My IP’s a ghost. The 20 wallets private keys are offline and handwritten. load five keys into Exodus (checked for no telemetry) on Tails’ persistent storage. Liquidity’s tight for ETH-Monero atomic swaps—Uniswap’s XMR pair is thin, so I spread $10M ETH across 50 Monero wallets, $200K each, using THORChain and Haveno too. I test $500 swaps first, confirm they clear, then ramp up—$50K/hour across five swaps, pausing 2-3 hours between, over 10 days. I would script on Tails with web3.py, generating 500 ETH wallets, private keys dumped to an encrypted VeraCrypt container in persistent storage. I bake in Wireshark, Nmap, tcpdump, Snort, Nikto, Burp Suite, and Kismet.. precompiled binaries from GitLab, verified SHA256 hashes to monitor Tor traffic, scan for honeypots, and sniff Wi-Fi threats. The script drips $10M, $20K per wallet, over 72 hours via Tor bridges (obfs4), randomized delays (5-15 minutes). I send $100 ETH from 50 wallets to noisy sinks like Binance deposit addresses (scraped from Etherscan), OpenSea contracts, and a Ukraine BTC donation wallets with the atomic swapped-fresh ETH adresses, while cross-transacting between my wallets: wallet A to B, B to C, 0.05 ETH each, 200 times. I burn $100K including gas ($20/tx at 50 gwei) over two weeks. Chainalysis drowns in noise. The botnet’s quiet side swaps ETH to Monero $5K-$10K chunks, targeting $1M/month, matching Monero’s $30M daily OI I use Haveno’s escrow, rotate Tor circuits, and pause 2-5 days between bursts. Locations shifts from McDonald’s, Starbucks to co-working spaces in nomad hubs like Bali, cayman, Jersey, Malta, Bermuda, Isle of Man, Cyprus, Bahamas, and Chiang Mai. I spoof the dongle’s MAC daily, monitor with Kismet for IMSI catchers, and never stay longer than 45 minutes. If a network’s crowded, I ping with Nmap.. too many devices, I bounce. Cashout’s the long game… With somewhere around $10M in Monero across 50 wallets annually, I hit OTC via Telegram groups, swapping $10K-$50K for USD or EUR, cash or tether. remain blended in with nomad towns where cash flows. Could even pose as a trust-fund drifter, living off “clean” Solana and BTC wallets funded by Monero swaps, tumbled through Wasabi’s CoinJoin for extra cover. Laptops die after 10 uses and moves quarterly. The other $1.49 billion? It’s staying cold for the long run. Split across 20 32GB USBs, each with 1/20th of the keys in encrypted 7z archives. AES-256 stays locked in safes through various deposit boxes. I clean $20M max annually mby even far lower depending on the OI. Scaling will remain low, otherwise botnets spike bandwidth, swaps dry up, feds get wise n sniff Tor exits. One slip, either be reused bridge, same Wi-Fi SSID twice. I settle in Podgorica, Montenegro: or any country with no US/EU extradition treaties, $500K buys a villa, and $10K/month keeps me invisible. $20m annually is enough to manipulate local surroundings.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Packet Sniffing and Spoofing Lab
Overview Packet sniffing and spoofing are two important concepts in network security; they are two major threats in network communication. Being able to understand these two threats is essential for understanding se-curity measures in networking. There are many packet sniffing and spoofing tools, such as Wireshark, Tcpdump, Netwox, Scapy, etc. Some of these tools are widely used by security…
0 notes
Text
@taylornation so crazy watching you get raped and tortured publicly in the land of the deaf and blind. And guess what I didn't even get a fucking hug from my parents
If this was cyber warfare, it suggests targeted interference—whether from an ISP, state actor, or sophisticated attacker. Your observations (ICMP redirects, ARP scans, and blocked packets) point to potential MITM (Man-in-the-Middle), network hijacking, or deep-packet inspection (DPI).
1. Why Would Someone Target You?
If you're running:
Persistent international VPNs (especially avoiding American IPs).
Encrypted or anonymous traffic (Tor, VPN chains, alternative DNS).
Custom routing setups (Raspberry Pi as a router, firewalled networks).
Alternative protocols (ICMP tunneling, encrypted DNS, IPv6-only traffic).
These can trigger national firewalls, ISPs, or hostile actors to investigate and interfere with your connection.
2. Signs of Cyber Warfare in Your Case
From what you've described: ✅ ARP scans – Possible MITM or network poisoning.
✅ ICMP redirects to a random IP – Classic hijacking or traffic rerouting.
✅ Traceroute fails – Packets being black-holed.
✅ Ping shows no ICMPs in Wireshark – Possible packet dropping, firewall injection, or transparent proxying.
✅ Both VPN and direct internet failed – Suggests interference at the ISP or network gateway level.
This could mean:
ISP DPI (Deep Packet Inspection) – Some ISPs hijack and block encrypted traffic.
BGP Route Manipulation – Your traffic might be getting rerouted outside your control.
DNS Spoofing – Check if your DNS queries are being redirected.
Network-Level MITM – An attacker or surveillance system intercepting and modifying traffic.
3. What You Should Do Now
Immediate Steps
Check Your Default Gateway (Ensure it’s really your router)
ip route show arp -a
If you see a random gateway IP, something is poisoning your network.
Test Without VPN
Disconnect NordVPN completely.
Run: curl -s ifconfig.me
If the IP isn’t yours or your VPN’s, you might be redirected.
Try Alternative DNS
sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches sudo nmcli con mod eth0 ipv4.dns "1.1.1.1 8.8.8.8"
If your DNS resolves incorrectly, you’re facing DNS poisoning.
Advanced Countermeasures
Run a Network Capture for DNS Leaks
sudo tcpdump -i any port 53
If DNS queries are sent to a weird IP, you’re being hijacked.
Force Encrypted DNS (DNS-over-HTTPS)
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved
If tcpdump shows your queries bypassing this, ISP-level tampering is happening.
Monitor Live Traffic for MITM
sudo tshark -i any -Y "ip.src != 192.168.1.1"
Look for unexpected external sources injecting packets.
4. If You’re Under Attack
🚨 If you confirm cyber warfare, you should:
Stop using compromised networks (switch to mobile tethering or another ISP).
Boot into a Live OS (Ubuntu Live, Tails, or Whonix) to bypass OS-level tracking.
Use a completely new VPN provider (try Mullvad or ProtonVPN).
**Check if you’re on a state-level watchlist (e.g., NordVPN's obfuscated servers getting blocked could indicate surveillance).
Would you like me to analyze your .pcap? It could provide definitive proof of network tampering.
0 notes
Text
Looking for a MITM (Man In The Middle) proxy? We have compiled a list of best MITM proxy software for you. MITM proxy can be used to analyze and collect data over the network. MITM proxy can be really handy to record and replay HTTP requests on network. Ettercap If you are looking for a comprehensive suite that can protect Man In The Middle attacks, Ettercap is the best option. It has features that can sniff live connections along with filtering of live content and offers many other interesting tricks. It has the capability to support both active and passive dissections of many protocols and also has features that are useful for host and network analysis. Wireshark Wireshark offers tools and technologies that are useful in data packet analysis. Packet analysis made easy with Wireshark package software and helps the users to analyse the data gathered. It offers quick access to huge pcap files. It offers visually rich and powerful LAN analyser tools. It offers professional and customisable reports along with advanced alerts and triggers. Burp Suit It is an integrated platform that performs security testing for many web applications. The testing process becomes seamless and easy as various tools integrated in it work together to fetch the desired result. The tools start testing from the process of initial mapping and analysis of the surface that is under attack and renders the process through to find and exploit the security vulnerabilities. TCP Dump This is a powerful command line packet analyser tool, which is a portable C or C++ library that captures network traffic. After the dump is captured, the tool prints out the content description related to the packets on the network interface. It matches the Boolean expression and it is preceded by the time stamp so that it can be easily understood when the dump was captured. Snort Snort is an open source intrusion prevention system that has the capability of analyzing real-time packet logging and traffic analysis. With over 4 million downloads and about 500,000 active users, Snort is ruling the market quite comfortably compared to its competitors. It is the most widely deployed intrusion prevention system worldwide. Mitmproxy This is an interactive console program that ensures flowing traffic is first intercepted followed by inspection and modification, which is ultimately replayed. It also offers two others programs – mitmdump, which is a TCPdump for HTTP having the similar functionality as Mitmproxy but without the frills and the second one is libmproxy, which is a library that implements powerful interception proxies. Betamax This is a mocking tool that helps in mocking external HTTP resources like REST APIs and web services in the tests. The inspiration for the project was actually the VCR library and was meant mainly for Ruby programing. When you are using Betamax, you don’t need to worry about network problems, resource constraints or third party downtime that hinder your testing process. Fiddler It is a free web debugging proxy that can run in any system, platform or browser. The key features of this tool include performance testing, web debugging, HTTP as well as HTTPS traffic recording, manipulation of web session, security testing; the tool is customisable as well. Whether you have Android, Mac or Windows – Fiddler can run debugging program in any machine irrespective of platform or browser. Node Replay This program is meant for recording and replaying the HTTP responses when you see API system is slowing you down. Node Replay records the API response just once and replays the same as and when it is necessary. The program does not get stuck and also stubs HTTP requests. It is a great tool for testing error handling as it replay different responses to the same requests. Httreplay This is a record and replay library for testing that is useful for Python HTTP. This library can support network requests that are made through urllib >= 0.6, httplib and requests >=1.2.3 including version 2.
x. It is easy to install through PIP installation guide. The easiest way through which it can be used is the context manager. HoneyProxy It is a man-in-the-middle traffic and SSL proxy analyser tool. The tool is lightweight and allows live HTTP and HTTPS traffic inspection and analysis. It mainly aims to facilitate the features that are useful in network forensics and malware analysis. It also has the feature of saving HTTP conversations that can be used later. Mitm-proxy It is a Java based man-in-the-middle SSL proxy. The features of this proxy have the capability to terminate the proxied HTTPS requests and resend the same to the remote server. The server certificate provided with the tool is up-to-date and is dynamically generated and signed by the proxy itself. It contains most of the same fields like that of the original webserver certificate. Mitm-proxy It is a Java based man-in-the-middle SSL proxy. The features of this proxy have the capability to terminate the proxied HTTPS requests and resend the same to the remote server. The server certificate provided with the tool is up-to-date and is dynamically generated and signed by the proxy itself. It contains most of the same fields like that of the original webserver certificate. Charles Proxy This is a HTTPS man-in-the-middle proxy that enables you to see the communication between the SSL web server and web browser in the form of plain text. This proxy dynamically generates and signs the certificate so that your browser does not see it. It carries out functions like throttling, breakpoints, SSL proxying, reverse proxy and port forwarding.
0 notes
Text
@b0rk Your tcpdump zine is really handy. Thank you!
0 notes
Text
🖥️ Troubleshooting Networks on Linux? Start Here! 🌐
Linux offers powerful commands and tools to diagnose and fix network issues like a pro. Some essentials:
🔹 Ping: Test if a host is reachable. 🔹 Traceroute: Track the path your data takes. 🔹 Netstat: View open ports and connections. 🔹 Tcpdump: Monitor network traffic in real-time. 🔹 Nslookup/Dig: Solve DNS-related problems.
Master these, and no network issue will stand in your way! 🚀
👉 Read the full article: Linux network troubleshooting commands and tools

1 note
·
View note
Text
Wireshark: A Tool for the Tech-Savvy

In cybersecurity, I need advanced tools to maintain network systems secure. One among these instruments is Wireshark. It displays extensive network data by using packet sniffing Wireshark is advanced, nevertheless, which makes learning difficult for first users. The good and poor aspects of Wireshark, together with its customer support, simplicity of use, and other like programs, will be discussed in this review. Wireshark Features Feature Availability Packet Capture Yes Protocol Analysis Yes Real-time Monitoring No Reporting and Alerts Yes SSL Decryption No Network Visualization No Deep Packet Inspection Yes Packet Filtering Yes VoIP Analysis Yes Intrusion Detection No Custom Scripting Yes Wi-Fi Analysis Yes Cloud Integration No SNMP Support Yes API Access Yes Forensic Analysis Yes User Activity Monitoring No Multi-Platform Support Yes Mobile App No Traffic Shaping No VPN Analysis Yes Exporting Capabilities Yes Collaboration Tools No What We Think? Wireshark is great for people who are good with computers. It fixes a lot of different network issues and works well with a lot of other operating systems (OS). It's great for professionals because it can record and look at live network info. It would be best if you didn't start with it, though, because it's complicated and hard to learn. Pros: A lot of different show filters It's free and open source. Data processing in real-time and offline A lot of strong features Works with many OS Cons: Not easily understandable for non-technical users Wireshark’s History When young and enthusiastic engineer Gerald Combs began working on Wireshark in 1998, it was the beginning of a long journey. Wireshark has grown from a simple tool that could only look at four protocols to a full solution. It is the gold standard in network monitoring right now, thanks to the dedicated community of networking experts who keep working to support and improve it. The Ease Of Use And Interface For Users The main Wireshark website looks like a blue shark and is easy to use. The website gives a clear and easy-to-understand overview of the course. Wireshark also has a blog where people can read about new ideas, tips, and tricks. They also talk to people in their neighborhood on Twitter and other social media sites. One of the best things about Wireshark is that it is open-source, which means that anyone can use it for free. There are no costs, limits, or tie-in plans for downloading and using Wireshark. The General Public Licence (GPL) lets programmers and fans add new protocols and features from the program's source code whenever they need to. Characteristics and Goal Of Wireshark The best things about Wireshark can be grouped into three main functions: packet capture, filtering, and network visualization. Wireshark is great at capturing network data in real time. It can track and record whole data streams by collecting thousands of bits at once. This is what makes it possible to find and fix network problems as they happen. Once the data has been collected, Wireshark users can add filters to split the important parts. This skill is especially important when you have to sort through a lot of data to find certain packets or trends. When users get rid of unnecessary data, they can focus on the data that matters. Wireshark's visible features let users see how networks interact in very small details. It makes it easier to understand how networks work by showing the flow of data in a graph. This skill is necessary to find problems and understand how the network works in general. Why Choose Wireshark? Wireshark works with many capture file formats, such as tcpdump, Pcap NG, Catapult DCT2000, Cisco Secure IDS iplog, and Microsoft Network Monitor. Because it is flexible, it will work with a wide range of tools and network configurations. Some of the protocols that Wireshark can interpret are IPsec, ISAKMP, and Kerberos. This skill is needed to decrypt information and keep networks safe. Wireshark lets users add colour rules to the packet list, which makes it easier to tell the difference between different types of data. This visual aid speeds up the research process by making it easy to find patterns and oddities. Wireshark can send analysis results in a number of different formats, such as XML, PostScript, CSV, and plain text. These export options make it easier to report results and share them with clients or coworkers. Wireshark: A Perfect Tool For All Types Of Business Wireshark is a useful program, but it's not for easily scared people. To get the most out of Wireshark, users need to know a lot about network protocols and technical concepts, such as TCP 3-way handshakes, TCP, UDP, and DHCP. Because of this, Wireshark works best for people and businesses that know a lot about technology. Wireshark works great for small and medium-sized businesses, nonprofits, security groups, and schools. The book is also a great way to teach students and workers who want to learn more about network security. Even though Wireshark is very useful, it has some problems. It's not an intrusion detection system (IDS), so it shouldn't be used that way. However, it doesn't have the real-time warning features of specialized IDS systems. Once an alert is sent, it can help stop zero-day attacks. Wireshark tries to be easier to use by using colour coding to show different types of traffic and graphics tools to show statistics. These features can't completely make up for the tool's complexity, though, which still makes it hard for beginners. How Wireshark Helps the Clients? Given that Wireshark is an open-source project, it does not have a dedicated technical help team. Instead, it helps through a strategy that the group drives. On Wireshark's main website, users can find a number of self-help options, such as: On forums, people can ask questions and wait for replies from other users. FAQs is a section that has a list of frequently asked questions and the answers to those questions. On the documentation page, you can find detailed records about many parts of Wireshark. A wiki that is managed by the community and has useful tools and information. For finding and sharing bugs and other issues, the Issue Tracker is a useful tool. That being said, these tools are helpful, but they might not help some customers right away. Also, the video lessons and how-to tips might not be enough to help people who are using it for the first time. Note: Cloud Shark is a browser-based packet sniffer that is less complicated to use than Wireshark. It's not as appealing to people who care about cost and usefulness, though, since it needs a membership and doesn't have as many advanced tools as Wireshark. Last Thought Wireshark went from being a simple network research tool to a full solution. This shows how powerful open-source creation and community cooperation can be. It is necessary for anyone who cares about network performance and security because it can record, filter, and display network data in real time. Wireshark's pros far outweigh its cons when it comes to complexity. Because it is open source, has a lot of features, and works with a lot of different operating systems, it will always be useful in the field of network research, which is always changing. Wireshark is an important tool for network engineers, software developers, and cybersecurity experts. It can show you everything about network data at a very detailed level, making it the best tool for finding and fixing network problems. In the end, Wireshark might not be the easiest tool to learn, but the information and skills it gives you are well worth the effort. For people who are ready to take on the task, Wireshark opens up a world of possibilities and helps them learn more about the networks that connect our digital world. FAQs Which sites does Wireshark endorse? Wireshark runs on Linux, Mac (macOS), and Windows, among other operating systems. Wireshark is open-source? Wireshark really is an open-source packet analyzer. Does Wireshark provide real-time network monitoring? Wireshark mostly works on post-capture packet analysis. Could Wireshark decode SSL traffic? Wireshark does not incorporate built-in SSL decryption features. Does Wireshark offer customer support? Wireshark depends on its community and documentation; official customer service lines are few. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
O sniffing é uma técnica usada para interceptar e analisar o tráfego de dados em uma rede. Pode ser classificado em vários tipos, dependendo dos métodos e objetivos específicos:
1. **Sniffing passivo**:
- **Definição**: Interceptação do tráfego sem alterar ou enviar pacotes para a rede. É difícil de detectar porque não altera o comportamento normal da rede.
- **Ferramentas comuns**: Wireshark, Tcpdump.
- **Usos**: Captura de senhas, análise de tráfego, detecção de problemas na rede.
2. **Sniffing ativo**:
- **Definição**: Envolve a inserção de pacotes na rede para enganar outros dispositivos ou modificar o fluxo de tráfego. É mais fácil de detectar devido à alteração do tráfego normal.
- **Técnicas**:
- **ARP Spoofing**: Engana dispositivos em uma rede local para enviar dados ao atacante ao falsificar respostas ARP.
- **DNS Spoofing**: Redireciona o tráfego para um site falso, modificando respostas DNS.
- **Ferramentas comuns**: Cain & Abel, Ettercap.
3. **Sniffing em redes cabeadas**:
- **Definição**: Intercepta tráfego em uma rede com cabos físicos (Ethernet).
- **Métodos**:
- **Modo promíscuo**: Configurar a placa de rede para capturar todo o tráfego que passa pelo segmento.
- **Port Mirroring**: Em um switch, duplicar o tráfego de uma porta específica para outra porta onde está conectado o sniffer.
4. **Sniffing em redes sem fio**:
- **Definição**: Intercepta tráfego em redes Wi-Fi.
- **Métodos**:
- **Modo monitor**: Permite que a placa de rede capture todo o tráfego sem fio na área.
- **Captura de pacotes WPA/WPA2**: Interceptar o handshake de autenticação para tentar decifrar a senha.
5. **Sniffing baseado em aplicações**:
- **Definição**: Orientado para interceptar e analisar o tráfego de aplicações específicas.
- **Exemplos**: Captura de tráfego HTTP para obter cookies, interceptação de e-mails.
6. **Sniffing de telefones móveis**:
- **Definição**: Intercepta tráfego de dados de dispositivos móveis, geralmente através de redes Wi-Fi públicas ou pontos de acesso maliciosos.
Esses tipos de sniffing são usados em diferentes contextos e têm várias aplicações, tanto legítimas (como monitoramento de rede) quanto maliciosas (como roubo de informações).
0 notes
Text
Code
sudo tcpdump -lnvX icmp
sudo ip link add vxlan0 type vxlan id 100 dev eth0 local 10.0.1.11 dstport 4789 (This creartes the VXLAN inteface and decapsulates VXLAN traffic using the VXLAN Id supplied in step 5.4)
sudo ip link set vxlan0 up (This ebavles the VXLAN interface vxlan0)
sudo tcpdump -lnvXi vxlan0 icmp _(This captures traffic on the vxlan0)
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Deny", "Action": [ "ec2:CreateTags", "ec2:DeleteTags" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:ec2:::volume/*", "Condition": { "StringNotEqualsIfExists": { "aws:RequestTag/jam_testing": ["yes", "no"] }, "Null": { "aws:RequestTag/jam_testing": "false" } } } ] }
import boto3 from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
def create_table(dynamodb=None): if not dynamodb: dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') table = dynamodb.create_table( TableName='awsjam_employee', KeySchema=[ { 'AttributeName': 'employee_id', 'KeyType': 'HASH' # Partition key } ], AttributeDefinitions=[ { 'AttributeName': 'employee_id', 'AttributeType': 'N' } ], ProvisionedThroughput={ 'ReadCapacityUnits': 10, 'WriteCapacityUnits': 10 } ) return table
create_table()
Above---- touch dynamodb.py
touch insertrecord.py Below----
import boto3
def insert_record(table_name,employee_id, name, age, salary, city): dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') table = dynamodb.Table('awsjam_employee') table.put_item( Item={ 'employee_id': employee_id, 'name': name, 'age': age, 'salary': salary, 'city': city } )
insert_record('awsjam_employee', 1, 'John', '30', '20000', 'New York') insert_record('awsjam_employee', 2, 'Peter', '25', '30000', 'New York') insert_record('awsjam_employee', 3, 'Mark', '35', '40000', 'New York') insert_record('awsjam_employee', 4, 'Mary', '40', '50000', 'New York') insert_record('awsjam_employee', 5, 'Jennifer', '19', '60000', 'New York')
import boto3 dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') table = dynamodb.Table('awsjam_employee') table.update_item( Key={ 'employee_id': 1 }, UpdateExpression='SET salary = :val1', ExpressionAttributeValues={ ':val1': 50000 } )
py import boto3 def delete_item(dynamodb=None): dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') table = dynamodb.Table('awsjam_employee') response = table.scan() for item in response['Items']: if(int(item['age']) <= 20): resp = table.delete_item(Key={'employee_id': int(item['employee_id'])}) response = table.scan() print(response)
invoke function
delete_item()
aws evidently start-launch --launch SpecialSale --project OriginalGoodsStore --region us-east-2
select B.* from "$REPLACEWITHDATASOURCENAME"."default"."autocustomer" B join "AwsDataCatalog"."vehicles"."$REPLACEWITHDATATABLENAMECREATEDBYCRAWLER" A ON cast(A.policyid as integer)=B.policyid where A.title_status = 'clean vehicle' and A.year = '2007' and A.state='california' and A.brand='chrysler'
aws kinesis list-shards --stream-name *KinesisStreamForJam aws kinesis split-shard --stream-name *KinesisStreamForJam* --shard-to-split shardId-000000000002 --new-starting-hash-key *320854911280625642308916404954512140970 aws kinesis update-shard-count --stream-name *KinesisStreamForJam* --target-shard-count *8* --scaling-type **UNIFORM_SCALING 180
1 note
·
View note
Text
Packet Sniffing and Spoofing Lab
Overview Packet sniffing and spoofing are two important concepts in network security; they are two major threats in network communication. Being able to understand these two threats is essential for understanding se-curity measures in networking. There are many packet sniffing and spoofing tools, such as Wireshark, Tcpdump, Netwox, Scapy, etc. Some of these tools are widely used by security…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Packet Sniffing and Spoofing Lab
Overview Packet sniffing and spoofing are two important concepts in network security; they are two major threats in network communication. Being able to understand these two threats is essential for understanding se-curity measures in networking. There are many packet sniffing and spoofing tools, such as Wireshark, Tcpdump, Netwox, Scapy, etc. Some of these tools are widely used by security…
0 notes