#aircraft maintenance mechanic
Text

Just flew in a heli to 5000 ft over the Alaskan tundra I'd just had taken apart over the last week. What an awesome feeling/experience this was!!! :DD
We did some auto rotating maneuver tests and on the heli and some touch n goes around the tundra too, it was soooo cool!!! AAAAA!! x3
#planeposting#come fly with me#mechanicposting#mechanic#aircraft maintenance#Alaska wrenching adventures
17 notes
·
View notes
Video
5th Air Force P-47 engine maintenance by TK622
Via Flickr:
A series of photos taken by a 5th Air Force aircraft mechanic showing engine work being performed on various 5th Air Force P-47 planes. The photos from this grouping (100+ images) were developed early post-war from damaged negatives and further suffered from poor storage. Exact date and location unknown, possibly Okinawa 1945, since some photos from the grouping can be placed there.
#P-47#thunderbolt#5th#air#force#us#army#ww2#world#war#two#airplane#aircraft#plane#mechanic#engine#repain#maintenance#pacific#theater#okinawa#flickr
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#militarytraining#Day in the Life#Crew#Military#Airbase#Aviation#Aviation Maintenance.#Mechanics#RAF#Air Force#Bomber#Aircraft#USAF#RAF Fairford#Maintenance#Bomber Maintenance#B-52 Stratofortress#Warplane#United States Air Force#B-52 Bomber#Fairford
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, about the black box in The Bifrost Incident
I keep reading fic that includes the black box and describes it as like. a literal black box. which. is fine, and honestly I can't say much, since until a couple weeks ago I also pictured it like that, but now I know, so: fun fact! there's an actual thing in planes called a black box that records flight data.
there are usually two in a plane, one in the front that records cockpit audio and radio signals and one in the back that records things about the actual flight (airspeed, altitude, heading, etc). they're used to investigate plane crashes and other incidents
now do I think all descriptions/renditions of the blackbox should make it look like this?

yes, actually. get to it /j
#I just want people to acknowledge that this isn't some random sci-fi thing#this was prompted by an A/N on a fic that was like#'I say the black box is just some weird cube that got exposed to the bifrost because it was on the train'#and like#no!#why would Lyf be so chill about the existence of the black box as part of the investigation if that were the case?#also#fully aware that this is just about planes#but like#I feel like a train designed to go through a wormhole would definitely have something similar#and also trains do also have black boxes#discovered this info when I was rambling about the mechs to my family and described the black box#as a collection of the train's camera data and stuff#and my father and brother#(a previous aircraft maintenance worker and a vehicle enthusiast respectively)#they both went#oh a black box?#so yeah#also no hard feelings with this#I am simply cursed with this knowledge and now this bothers me so I figured I'd share#the mechanisms#the bifrost incident#lyfrassir edda#inspector lyf#the mechs#the black box#trains#the bifrost
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
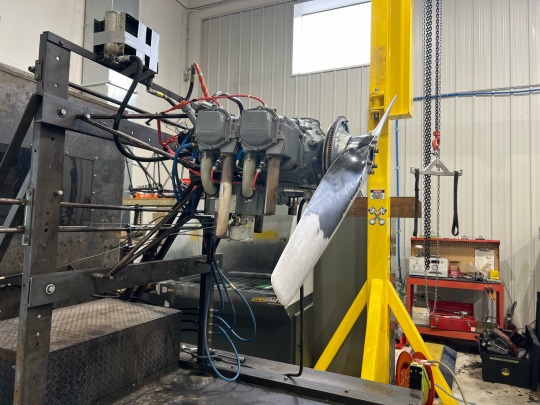

I finally got the good weather window to run the O-320, and it did not disappoint. Little thing ran beautifully, broke in nicely, and no indications of metal particles or anything amiss during post run checks. I’m excited to deliver her back to her owners after such positive results so they can put her back to work in their Piper Cherokee.
#lycoming engine#aviation maintenance#engine rebuild#engine overhaul#piston engines#aircraft engines#mechanic#women in aviation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Become a Certified Aircraft Mechanic with Online Training
Elevate your career prospects by becoming a certified aircraft mechanic online training. We make sure you get real-world experience by offering connecting modules with realistic settings and direct experiences. Become a part of our program now to begin your path to a fulfilling career in aircraft repair.

#aircraft mechanic online training#aircraft maintenance software#myfaa#Veryon Aircraft Maintenance Tracking#Aircraft maintenance software#Repair Station Training#FAA Accepted Courses
0 notes
Text
In this blog containes a detailed view about the future of the AME students and benefits of choosing aircraft maintenance engineering. Study from the best aircraft maintenance engineering colleges in India for the succesful career.
#college#airport#airplane#aircraft#aircraft carrier#aircraft maintenance engineering#aircraft parts#aircraft mechanic#aviation#airplanes#plane#aircraft manufacturing market#aircraft maintenance engineering
1 note
·
View note
Text
Choosing A Headlamp For Aircraft Mechanics
When choosing a headlamp as an aircraft mechanic, there are several factors to consider. Here’s a guide to help you select the right headlamp for your needs. Learn more at https://greasepilot.com/best-headlamp-for-aircraft-mechanics:
Brightness: Look for a headlamp with sufficient brightness for your work environment. Consider the lumens rating, which indicates the light output. Higher lumens generally result in brighter illumination.
Beam Distance and Focus: Assess the beam distance of the headlamp, as it determines how far the light can reach. Some headlamps offer adjustable focus to switch between a wide flood beam and a focused spot beam, providing versatility for different tasks.
Lighting Modes: Check if the headlamp offers different lighting modes such as high, low, strobe, red light, or night vision mode. These modes allow you to adjust the brightness and choose the most suitable lighting for various situations.
Battery Life and Power Source: Consider the battery life of the headlamp, especially if you require extended usage. Look for headlamps with longer runtimes or those that are rechargeable. Evaluate the power source (batteries or built-in rechargeable battery) and ensure it is convenient for your needs.
Durability: Aircraft maintenance often involves demanding environments, so opt for a headlamp that is rugged and durable. Look for headlamps with impact resistance, water resistance, and dust resistance to withstand the conditions you may encounter.
Comfort and Fit: Consider the headlamp’s weight, size, and comfort features such as adjustable straps or padding. Ensure it fits securely on your head without causing discomfort during extended use.
Hands-Free Operation: As an aircraft mechanic, you need both hands free for work. Choose a headlamp that provides easy and reliable hands-free operation, allowing you to focus on your tasks without worrying about holding a flashlight.
Additional Features: Some headlamps may offer features like a tilt or swivel mechanism to adjust the beam angle, a lockout feature to prevent accidental activation, or compatibility with accessories like helmet mounts.
Reviews and Recommendations: Read customer reviews and seek recommendations from other professionals in the aviation industry to gather insights on headlamp performance, reliability, and suitability for aircraft maintenance work.
By considering these factors and your specific work requirements, you can select a headlamp that provides the necessary brightness, durability, and functionality to assist you in your aircraft mechanic duties.
0 notes
Photo








(via Eat Sleep Fix Airplanes Repeat Gift Cap by desiredhope)
#findyourthing#redbubble#eat sleep fix repeat airplanes aircraft mechanic and sleep fix airplanes repeat maintenance fix airplanes and sleep airplane engineer planes
0 notes
Link
#jobs at Qatar#qatar 2022#work in Qatar#life in qatar#qatar airways#worldswin#cabin crew#sales#marketing#Food careers#maintenance#customer services#manager#adminstration#finance#Aircraft Engineer#aircraft mechanic#Airport Operations Management#Business Support & Administration#Chef#Cargo & Airport Operations#Engineering#Hotel Reception#Maintenance Planning & Scheduling
0 notes
Text
(( VOLUME /HIGH PITCH NOISE WARNING))
Paul the 727 lives!! And he is LOUD!! 😁🥰💕💕💕
Well we at least got his APU to fire up and power the electrical switches to the hydraulics. He's had a hydraulic leak from around the horizontal stabilizer :o
So shutting off fluid to that area fixed that. Here's what some of the plumbing looks like in the left rear portion of the fuselage. This is between the aft stairway of the 727. C:

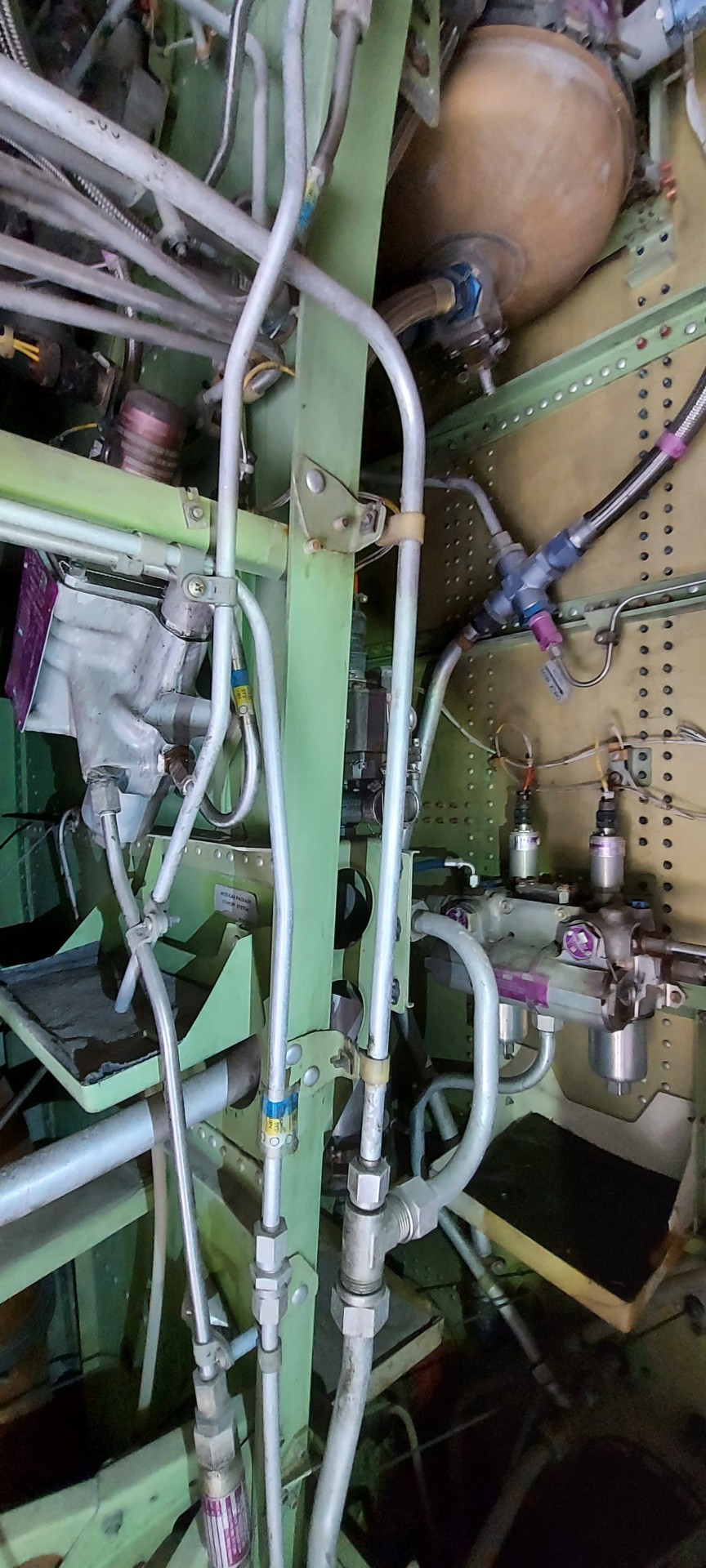
#planeposting#planes#airliner#aviation#avgeek#aircraft#boeing#boeing 727#mechanic#ash fixes stuff#aviation maintenance#paul the 727
104 notes
·
View notes
Text

What is the reason for modern aircraft not using swept back wings like the F-14 Tomcat?
The main reason modern aircraft do not use swept-back wings like the F-14 is due to the advancements in aerodynamics and materials science. Swept-back wings were initially developed to delay the onset of shock waves and reduce drag at transonic and supersonic speeds.
While this design was effective for the F-14, it came with trade-offs, particularly in terms of complexity and weight. The variable-sweep mechanism added significant weight and maintenance requirements, which are less desirable in today's cost-conscious and efficiency-driven aviation industry.
Also, modern aircraft benefit from advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and wind tunnel testing, allowing engineers to optimize wing shapes for specific performance criteria without relying on variable-sweep designs. This has led to the development of more efficient fixed-wing designs that can achieve similar or even superior performance across a broader range of speeds. For example, the F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II utilize fixed-wing designs with advanced aerodynamics and stealth capabilities, making them highly effective in modern combat scenarios.
Modern fighter jets are designed to be multi-role platforms, capable of performing a wide range of missions from air superiority to ground attack. This versatility demands a design that can perform well in various flight regimes, from low-speed, high-angle-of-attack maneuvers to high-speed intercepts. Fixed-wing designs, coupled with advanced flight control systems, provide the necessary performance and flexibility without the added complexity of variable-sweep wings.
The emphasis on stealth technology in modern military aviation has influenced wing design. Swept-back wings, while beneficial for high-speed flight, can create larger radar cross-sections, making the aircraft more detectable. Modern stealth aircraft are designed with smooth, continuous surfaces and internal weapon bays to minimize raddar signatures, which is more easily achieved with fixed-wing designs.
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
hi everyone!! as some of you may know ive been working towards being accepted into an aircraft maintenance mechanic course, and it's finally happened! i've been offered conditional acceptance IF i can pay the $400 deposit, due june 14th. i had begun saving for the fee, but i honestly thought i would have more time than this. i've come up with almost half already, and i've already borrowed some from my girlfriend, but i need help with the rest.
if you can assist, anything helps, please boost if you can't! happy pride!

$0 / $250
paypal
472 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vertibirds. 🚁⚙️🗡️🪽
So every wastelander and his dog know that the fallout 4 vertibirds crash more than settlements need help. But why is that? Here's my 2 caps on the matter. (Or: Bethesda doesn't understand aviation very well I think)
( So uh this is way longer than I expected, I was possessed🚁☢️:] )
TLDR: Horrific conditions for aviation, the difficulties of wasteland heavy maintenance, inexperienced pilots AND mechanics, and the WORST damn instrument layout I’ve ever seen
The Vertibird is designed as a fictional tilt rotor VTOL/STOL(Vertical/Short Take Off and Landing) aircraft which makes a ton of sense in the wasteland where suitable runways are rarer than hens teeth. One of Bethesda's primary visual design influences for the vertibird I suspect is the bell boeing v-22 Osprey.
This funky creature \/

This photo is from the Wikipedia page >Here<
[ID: a photo of a v22 osprey aircraft in flight as seen from below and to the right, the aircraft is a medium tilt rotor aircraft with very large propellers, the aircraft is current in vertical take off or landing with the engines pointed straight up. The landing gear is extended, the aircraft is painted in air-force grey with the faint decal “marines” and the American army star on horizontal stripes and the squadron and registration barley visible on the empennage. The cargo and forward doors are open and a soldier is hanging out the front. End ID]
Now the Osprey has a bit of a reputation among people I’ve met who’ve flown in them, I've personally been told things like "if it's not leaking hydraulic fluid, that means you're out of fluid" and "its terrifying to fly in".

My screenshot. [ID: A screenshot of a fallout 4 vertibird, seen from front left in flight over bushland. the Player is manning the minigun and Paladin Danse is a Passenger. End ID]
Looking at the Vertibirds themselves we can make a few assumptions here.
The shape of the cowling and the noise they make indicates that the engines are some form of turboprop engine, likely requiring liquid fuel akin to Avtur(Aviation turbine fuel). Confirmed by the Instruments visible in the cockpit.
The most weight efficient way to move big parts is hydraulics so, they likely have complex hydraulic systems for wing positioning / AOA(Angle Of Attack) / engine angle. Likely also for landing gear since they have retractable gear in fallout 4.
That the BoS has modified them from the original design at least partially, allowing attachment to the Prydwen, likely other modifications too.
I strongly suspect that they have an APU(Auxiliary Power Unit) in the aft fuselage / empennage somewhere, since they have a massive air intake scoop on the top fuselage, they can self start their primary engines which either requires a ridiculous amount of electricity / amps or a source of bleed air. Bleed air is the most likely candidate for self start and is reasonably common on real turbine aircraft, APUs also allows for ground power without having primary engines running. Also confirmed by the instruments in the cockpit.
All of these points are well and good and common in aviation, even modifications (ie. STOL kits, survey aircraft, agricultural mods, skiis, ect). But modern aviation has some advantages that the BoS doesn't have: access to new off the shelf parts, proper verified documentation, proper test processes & facilities, and experienced personnel.
Don't get me wrong, I think Proctor Ingram is awesome, very knowledgeable and practically a miracle worker (especially with that one terminal entry about an engine failure field recovery she pulls off!!), but one chief engineer cannot maintain an entire fleet AND the Prydwen, she comments on how things are breaking often on the ship that she is very busy! Training of new engineers takes *years* to even get to basic level! Ingram can’t train anyone she is too busy keeping everyone in the air 24/7! So who is training all of these scribes? There must be a huge amount of time teaching and supervising even simple tasks! Even at their best the BoS wouldn’t be able to hope to be near the prewar standards of training! Even Ingram or other senior scribes would not be thaaaaat experienced, 10 years is not a long time to completely learn a new aircraft and implement systems & processes of maintenance. The point here is that there are inexperienced scribes maintaining these aircraft.
WOLRDS BEST CHEIF ENGINEER ❤️ \/
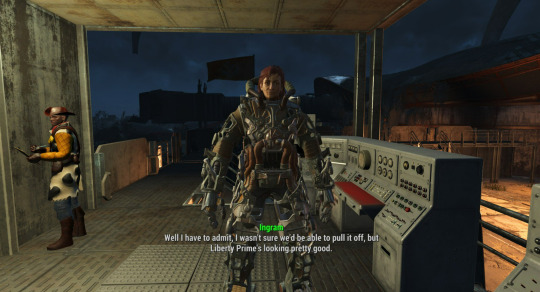
My Screenshot. [ID: A screenshot of proctor Ingram from fallout 4, she is standing in the Liberty prime control area. She is smiling. She is wearing her usual modified power armour frame. Preston is visible in the background with a clipboard and pen, he is wearing woody’s outfit from toy story. End ID]
Heavy maintenance in the wasteland, especially in an active combat zone would be an absolute nightmare, are the poor scribes doing overhauls on the flight deck?? Not really possible, so the BoS must have a ground facility at the airport somewhere. Also side note where is the rest of Boston airport? There is more to an airport than a terminal and 1 runway, where are all the hangars?? Likely underwater but still, no ruins??
Back to maintenance, aircraft need a huge amount of care, way way way more than cars do. light civilian aircraft IRL need a full inspection every 100 hours of flight time, which adds up incredibly quickly! For example if you have a one hour commute twice a day that’s MR(Maintenance Release) hours reached in 50 days! You legally cannot fly out of hours. And a service for small aircraft takes about 3 personnel / 2 days and that’s without any major repairs or ADs (Airworthiness Directives) to address! $$$$! Aircraft operating in adverse conditions also need additional maintenance, and coastal areas like Boston, are considered adverse conditions since the salt air corrodes aluminum and steel like nothing else! Corrosion untreated will damage your aircraft and if left too long can destroy the structural integrity of aluminum parts. The spars of aircraft are aluminum often!

My photo. [ID: The inside of a Cessna 172 wing trailing edge is shown looking inboard at the aft root rib, which is primer green, it is backlit by torchlight, the fuselage and a orange scat hose are visible behind it, it has 3 irregular shaped holes in it, 2 are by design but the third medium sized hole in the center of the image is eaten away by corrosion. End ID]
Vertibirds, between being shot at constantly and having a complex deign with a lot of precision moving parts will need a lot of repairs; moving parts means lots of upkeep, grease and inspections! The BoS by 2287 must have some sort of manufacturing back in capital, they cannot still be using old parts from the enclave after 10 years of maintenance, that’s a lot of grease, paint and hydraulic fluid!!!
The BoS must also have a refinery of some kind because Avtur is a refined fuel with some important additives like biocide. Manufacture and storage of fuel is very important since fuel contamination will bring down an aircraft! (and has multiple times IRL! :[ ). Water, microbes, and algae are real dangers to engines, with free water being the most common. Poorly sealed tanks or improper fuel storage combined with a incomplete or missed pre-flight inspection can lead to fuel starvation, since water is heavier than fuel and tank outlets are at the bottom of the tank. If you loose an engine on a twin, may God help you.

This image is from Concordia Bioscience >Here<
[ID: A photo of a sample of pale yellow Jet fuel in a clear container, the sample is contaminated with water and microbes and has separated into layers with water at the bottom, then microorganisms, and then Fuel at the top, the image is labeled as such. End ID]
Getting to the most likely crash reasons now (finally), In my opinion that is inexperienced pilots and; a horrific instrument layout.
While there must be some lancers in the BoS that have been flying for the whole 10 years that they’ve had Vertibirds, I think that is likely the exception not the rule, even if they crashed a fraction of the time that do in game that’s still A LOT of downed aircraft!
Experience is only gained in practice, and unfortunately for the BoS they are (self-declared) at war so resources are thin and safe zones are thinner. I suspect that there are a lot of very inexperienced pilots without the time for the experienced pilots to really teach.
Linking to my final point, experience on an airframe itself is also important, you want to be familiar with your aircraft, even among a group of the same model aircraft they will each have quirks, like slightly different instrument layouts, slightly different handling/feel i.e. "this one flies heavier / slower" (at least that's my experience with smaller civilian aircraft) I imagine that the apocalypse did nothing for improving manufacturing tolerances!
FINAL AND MOST DAMNING POINT:
Experience can only help lancers so much when veritibirds have such a strange instrument panel layout:

My screenshot. [ID: a screenshot of a instrument panel from a Fallout 4 vertibird. it is slanted on a approximately 30 degree angle. End ID]
A bit weird looking yeah? For reference Pilot is left seat and copilot is always right seat, this applies globally even in right hand drive countries.
lets take a closer look:
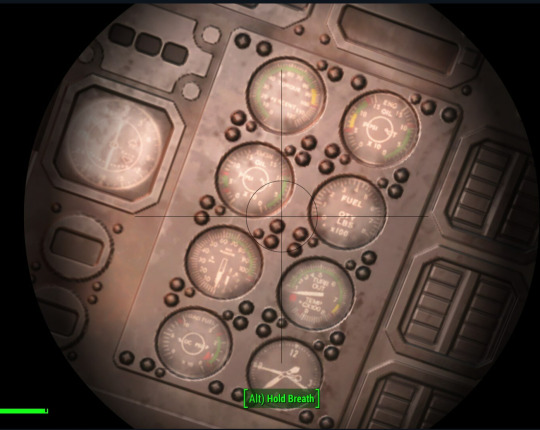



My Screenshots. [IDs: Three screenshots of the same Instrument panel as above, but zoomed in using a sniper rifle scope to get a better look. The first screen shot is the pilots side, the second the center, and the third the copilots side. End ID]
All righty! So reading from top to bottom, then left to right we have:
On the pilots side: A Rotor%RPM gauge, a VOR(Very high frequency Omni-directional Range) indicator, a DG(Directional Gyro), a HSI(Horizontal Situation Indicator), and then a huge AI(Attitude Indicator),
In the center section we have: presumably light clusters (likely master warnings & cautions, gear indicators, and other status lights), a second VOR gauge, likely magnetic compass as they are usually top centre (though I can’t see it being at all accurate with all of the steel around!), the engine instruments cluster, and the APU status / control panel at the bottom. unsure of what the 3 clusters of horizontal buttons are suppose to be other than input of some kind?
In the Engine cluster: Torque%, XMSN(transmission) oil temp / pressure dual gauge, a gas producer % RPM gauge with small integrated single percent dial (like having a seconds dial on your watch for accuracy) meaning the engines have free turbines (compressor not attached to the power turbine), a dual load / fuel psi gauge, a dual engine oil pressure and temperature gauge, fuel quantity in pounds, a turbine output temperature gauge (the hottest part of your engine), and a clock.
On the copilots side: a second Rotor%RPM dual gauge, a third VOR indicator, Airspeed in Knots and MPH, a RMI(Radio Magnetic Indicator) which uses VOR and ADF(Automatic Direction Finder) on compass, a second DG, a second HSI, and a teeny tiny altimeter right in the outboard corner.
the 4 instruments on the lower copilots panel are completely unlabeled
some things of note that are from game limitations:
most of the engine instruments don't have needles at all
the DGs and the RMI use the same background asset, resulting in the DG wrongly having 'VOR' and 'ASI' on its face, DGs are self contained air driven instruments that work on gyroscopic precession, not any outside data input.
all of the instruments with a compass face all say north despite this vertibird not quite facing north.
the AI is showing wings level despite this vertibird being crashed and on a ~30 degree angle
there are not engine controls at all not even flat assets, only flight controls.
There are a lot of instruments here and most of them are reasonably OK read individually, BUT there at least 1 key instrument missing and the layout outs emphasis on completely the wrong things:
WHERE IS THE VERTICAL SPEED INDICATOR(VSI)????? That's a pretty important gauge in a VERTICAL take off / landing aircraft!!!!!!!!!! It's one of the basic six pack!!! how was it omitted??? Speaking of the six pack why is there only one ASI and Altimeter?? and why are they tiny and ON THE COPILOTS SIDE ONLY???? the altimeter is LITERALLY the furthest instrument from the pilot in a vertibird, it should be right in front of the pilot!!! the easy to miss altimeter would make IFR(Instrument Flight Rules) flying incredibly dangerous! Also why are there four VOR based navigational instruments? VOR IS GROUND BASED NAVIGATION!!! unless the BoS has rebooted the multiple ground beacons for them to navigate from that's THREE dead instruments taking up space on the panel! the RMI is slightly more useful as ADF can tune to commercial radio frequencies, though these would need to be strong!
These poor inexperienced lancers are having to look all over the whole unnecessarily crowded cockpit for basic information that should be right in front of them, causing reaction delays and possible confusion. That delay could be the difference between whether or not they are flying home today.
-> Bethesda doesn't understand what half the instruments do and while they did a good job with most of the assets, in their quest to make it retro-future / visibly different from actual aircraft, they have completely destroyed any use of logic in the layout.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Thanks for reading! Here’s a video of me yeeting Danse with the ‘Get out of my face mod’ as compensation haha
My Video. [ID: a video capture from fallout 4 in first person. It is night and is at oberland station facing the water treatment plant. The player is wearing power armour and the HUD is visible. The player is very close to Paladin Danse, he turns away from them and they shove him with the voice line “stay out of my way”. Danse flys a long way away while rag-dolling. The Gamer’s laughter can be heard while Danse is flying. The player follows Danse’s fall with the crosshairs. The player then walks backwards. End ID]
#they look cool and faster than a chopper that’s for sure#big disclaimer: I am not American or military I haven't seen a Osprey up close. and all of my experience is light fixedwings#If you know more about Ospreys or I've made other mistakes please correct me !!#oh yeah real brain rot days#been thinking about this for a long while#this catastrophe of a train of though was kicked off a when I decided to zoom in on the dash a vertibird out of curiosity and discover that#they have actual gauges that corresponding to real ones. just in the worst layout I’ve ever seen it’s so counterintuitive#Typos’ tea time#fallout 4#fo4#bos#brotherhood of steel#vertibird#fictional aviation
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
F-14 TOMCAT ISSUES AND ACCIDENTS
The following is a compilation of issues with the F-14 Tomcat that have been encountered by pilots throughout its lifespan due to both mechanical and other reasons. Some are based on individual accidents and some cover epidemics in which many aircraft were lost to the issue *cough* compressor stalls *cough* basically it’s a bunch of ways you can hurt your fav characters in your fics so if you write something pls let me know cause I want to read it!!!
The issues range from minor hydraulic leaks to an explosion where pilots survive but the aircraft is literally in a million pieces.
LAST UPDATED 10/25/2023
Added some links to relavant FFFOTDs
Side note, the F-14 was a frickin massive tank of a fighter jet. She has taken damage to major components and still been able to land safely, so every situation is pretty unique.
Water Damage- Any type of water intrusion would cause issues with the electrical systems. It was a very common thing, so much so that they would have to duct tape anywhere water might be able to enter as a precaution when they knew it would rain.
Hydraulic Fluid Leaks - The F-14 did leak hydraulic fuel fairly often. There was a joke going around that if there isn't a bucket leaking hydraulic fluid underneath the plane then you are out of hydraulic fluid.
The Staple - On F-14 As and Bs, they would limit the jet to 4Gs maximum for three months and then they would install a metal staple to the bottom of the aircraft just forward of the tail hook. The point of the staple was to prevent severe bulkhead cracks and fuselage delamination by reducing the torquing moments caused by material fatigue. The staple is described as being a 1 foot-long and 1 inch wide solid steel part that looks exactly like a staple. As a part of their pre-flight checks, pilots would have to hang on it to ensure it wouldn’t fall out.
Airbags - Now and then, the airbags would rip and they would have to fix them.
Hydraulic Failures - Hydraulic failures happened somewhat often, but not often enough to be a prevalent issue. Generally speaking, it was common knowledge that if an F-14 wasn't leaking hydraulic fluid then it was out of hydraulic fluid. They would place buckets underneath to catch the liquid when the aircraft was not flying.
An incident from 1988 resulted from a complete hydraulic failure of both the main and the backup systems. They ruled the accident to be caused by the combination of failure of a relief valve and material failure. The Commander of the Pacific Fleet at the time believed that it could have possibly been the result of entrapped air that had been introduced into the hydraulic system through minor system maintenance.
AICS Programmers - They would have to start the airplane and then run the intake ramps aka would have to cycle the intake ramps otherwise they wouldn't be able to get off the ground.
Flap-Slat Lockout - If the flaps on either side of the jet didn't program at the same rate, it would cut it out and lock them up. They were then unable to move them as the lockout was a precaution to prevent asymmetry. This forced pilots to land without flaps, requiring an extra 22 knots during landing. It was difficult to land when they were locked out, and in many situations the end result would be pulling up next to the carrier and ejecting. Flap-Slat Lockout was a consistent issue throughout the Tomcat's life.
Unreliable Fire Warning Light - Sometimes the fire warning light would just barely start to flicker on and steadily become more prominent. Overall "just a bad system." You never actually know if there's a fire or not.
Wings Won’t Come Out - This happened at NAS Oceana. The airplane landed at a speed of 230 mph, so very close to the F-14’s stall speed. When the wings are stuck back, you can't hit the brakes during landing because there is no anti-skid and you would overheat them, if you pulled the stick back you would rotate, and with the wings back you have no spoilers so there is nothing to slow you down. In this particular incident, the pilot was able to take the long landing, but if this issue was encountered at sea it would require an ejection or divert to an airfield nearby if possible. No big explosions or fires though, it’d be a fairly calm procedure and the plane could fly into range of the ship for easy retrieval after ejection.
Low Fuel (Barricade Landing) - Bad weather at night combined with air traffic personnel being too occupied with diverting tons of airplanes, launching tankers, etc. can cause an aircraft to get low on fuel. There was a situation covered in the F-14 Tomcast episode called "F-14 Barricade" where they were unable to refuel using a tanker and were forced to do a barricade landing for their safety. They were almost forced to pull up alongside the carrier and eject. After the landing, one of the crew calculated based on the amount of fuel left that they only had about 90 seconds of flying left. This is literally the only night F-14 barricade landing ever I am pretty sure (in real life Maverick's doesn't count lol). I like it because the pilot and RIO had to tell the aircrew straight up "You have to take us now" because the pilot could no longer see the tape on the fuel gage. The crew tells their story really well and it’s really funny to listen to, especially considering the fact that they had to keep sending them around because they fucked up setting up the barrier.
Hitting the Canopy (During Ejection) - Goose's story is based on a real story in which a RIO hit the canopy during ejection and broke his spine. The reason the pilot does not also hit the canopy is because the ejection sends the RIO out first. The canopy is ejected after a couple of seconds after the handle is pulled, then the RIO is ejected after a second or two, and then the pilot another second later. The ejection seats also launch them in different trajectories so the pilot and the RIO do not collide in the air, meaning they may or may not end up in the same area. The solution would be to wait for the canopy to clear before ejecting but sometimes your don’t have that luxury.
Front Landing Gear Failure During Takeoff- While launching off of the catapult of the aircraft carrier, the nose gear attached to the shuttle broke. The landing gear and shuttle proceeded to the end of the runway without the jet, hitting the end of the ship at 305 knots and damaging the front of the carrier. The jet went off the ship with far less speed than necessary (at barely 60-70 knots) and began falling into the water as it was not enough to get the Tomcat in the air. They ejected to barely 50 feet high and were in serious danger of getting run over by the aircraft carrier. In the accident covered on the Fighter Pilot Podcast FPP004 - Ejection Seats, the RIO tells the story of his survival and the tragic loss of the pilot.
Radome (Nose Cone) Detachment - An F-14 Tomcat lost its radome during a flight due to the failure of the latching mechanism. The radome crashed into the canopy, shattering te glass of the windscreen. The pilot could only see out of a 3 inch hole in the windscreen due to the cracked windshield. He couldn't hear anything due to the noise of the wind in the cockpit, so he was unsure of the state of his RIO but assumed he was unconscious because he hadn't ejected them. The pilot flew over the carrier three times before successfully landing the plane, despite having glass in both eyes and a broken collarbone. It turns out that the RIO had been completely unharmed but with comms down he was unable to tell the pilot such. Upon landing the plane, the pilot was medevaced for eye surgery and then returned to the US.
Midair Collision - F-14A BUNo 159832 was a midair collision between two F-14 Tomcat. In this particular situation, one of the airplanes was able to divert to a nearby airport due to losing part of the right wing whereas the other crew was forced to eject. Obviously you could probably picture a situation where both jets went down.
Landng with Damage - Tomcats are a very sturdy aircraft, often described as being a tank both due to how much fuel they were able to carry and the sheer size of the aircraft. There has been an incident where an F-14 landed without one of its vertical stabilizers. In the Radome Deatchment section, the pilot was able to land the plane. The following video shows an aircraft, although not an F-14, landing aboard an aircraft carrier with significant damage on its right right side.
youtube
Single Engine Cat Shot- There was an incident where an aircraft had engine issues the moment it left the carrier. Immediately after the launch, they lost the left engine, and the first thing the pilot did was go through engine failure procedures, wingman at their side. They set up for an engine start using normal air before they attempted a cross-bleed air start using bleed air from the right engine to rotate the starter in the left engine, but neither worked. The pilot addressed the fuel distribution situation by feeding the right engine with fuel from the left to even them out and then they began dumping fuel to get to the "max trap" weight. Upon successfully landing, the Commanding Officer initially believed that the pilot had allowed the left engine throttle to roll back to idle during the acceleration of the catapult stroke, however, after maintenance personnel spun up the engine to troubleshoot, the engine spun well past its normal rpm immediately without the mechanical load it usually carried by the tower shaft meaning that something was very, very wrong. An image of the aircraft after launch can be seen below. Note the singular engine lit up.

F110 Afterburner Failure - The new engines installed were great, but they initially had a problem with the afterburner. In one recorded accident, the pilot lit the afterburner, damaging the afterburner can's lining and leading to an explosion. The Navy prohibited use of the afterburner below 10,000 ft on the F-14+/B/D until the problem could get solved but it took nearly a year to remedy.
"Thump Bang" - The easiest way to incorporate any sort of accident is to call it what the Naval Aviators call a "thump bang". A "thump bang" refers to a series of events that occur when an aircraft experiences some sort of issue they described as a "thump" and then an explosion. It's kind of hard to describe what is like in the cockpit during this sort of accident as it could have happened quickly or could have been a delayed explosion, and it could have been caused by any number of reasons. If they don't know what actually happened, they'll call it a "thump bang" and can only hypothesize what occurred. The likely scenario would have been an issue with the TF30 engines.
TF30 - The "Turd in the punch bowl, " the TF30s had two specific issues that were kind of intertwined.
Throwing Fan Blades - One of the largest issues with the TF30s was that they were with the fan blades. When the fan blades become eroded or damaged over time, they no longer compress the airflow efficiently, potentially leading to an engine stall (see Compressor Stall below). Additionally, the TF30 was known for "throwing" fan blades. This is when the fan blade becomes detached and is shot out to the side into the interior of the aircraft. Not good. Pretty bad actually. They didn't initially know they were throwing fan blades until after a couple of accidents. when they started to be more common they would retrieve the aircraft from the water (if in large enough pieces and then investigate the cause.
Compressor Stall - The actual biggest issue with the F-14 Tomcat and its TF30 engines is the compressor stalling. They literally happened all the time from a variety of different causes. Generally speaking, the compressor stalls were the result of disruption to the airflow into the compressor of the engine. The compressor has fan blades that require the airflow to be undisturbed for maximum efficiency. It was theorized to be the result of foreign object debris (FOD) ingestion into the engines. They check religiously for loose objects on the airplanes as a result, oftentimes having a crew member dive into the intake ducts to check for loose bolts. Additionally, compressor stalls could be caused by operating the aircraft outside of its limits, improper handling, etc.
The F-14 had a gated afterburner, meaning it had 5 “gates” inside of the afterburner and each one lit up a flame rack. There was no variable thrust, so it had to be either on or off. Each of the five racks was labeled as a zone. Zone 3 is what they were allowed to take off with. Coming in or out of afterburner with any angle or attack would cause the compressor to immediately stall. This was mostly due to poor design of the intake.
In general, approximately 30% of F-14A losses were attributed to high-altitude compressor stalls. When one engine stalls, more often than not it will induce the other engine to stall as well. There is a procedure to counteract the compressor stall, the specific protocol was to ease the amount of Gs, slow down, the T.I.T. would go crazy and you shut it down. Or in fighter pilot slang, “ease, slow cook it, shut it down.”
One incident in particular that was assumed to be caused by engine failure resulted in an explosion that looked so bad it was a miracle the pilot and RIO survived (see image below). The pilot escaped with minor burns to his hands, face, and neck and was able to fly within a couple of weeks. The RIO sustained more serious burns on his hands but was flying again after several weeks.
youtube
youtube
Not Touching Them For Two Days - True story; they flew best when they were used a lot.
#I’ll be your wingman anytime#fanfic writing wingman that is#it’s my birthday and all I want is for people to tag me when my posts help you because I want to read them!!!!!#I’m obsessed#I like angst#and airplanes#angst and airplanes#I like research#and f-14 tomcats#top gun#tom kazansky#top gun: maverick#iceman#top gun maverick#top gun iceman#pete mitchell#icemav#my boys#ron kerner#tgm#research#Youtube#mine#I like planes#tom iceman kazansky#just a little thing I wrote#EDIT 10/6: Expanded Hydraulic Failure section and added the single engine cat shot section#reference#f 14 tomcat has ✨issues✨#information
206 notes
·
View notes
