#but on the other hand that also means that they don't find the pre diagnosis of ms that unlikely
Text
After 2 days of sitting around the hospital for 8 hours and sporadically doing a few tests they finally did the one test I went there for (a spinal tap). Tbh it wasn’t as bad as I was afraid of but damn I am really starting to feel my lower back. I am definitely not dealing with homework today. Hopefully it’ll be better tomorrow cause I still need to buy a christmas gift and I want to go to the christmas market and drink some punch.👀 Maybe get a new fancy hat. We’ll see, but I think I deserve to spoil myself a little.
#personal#i don't a diagnosis yet and they said the results will still take a few weeks#so I'll hopefully be left alone for a little bit#and thankfully i didn't have to another mr which absolutely sucked#but on the other hand that also means that they don't find the pre diagnosis of ms that unlikely#but hey we'll see not like I can change it#i am in a strangely calm emotional state at the prospect#i'm not sure if I'm legit relaxed about it or if it just hasn't sunk in yet#so i have decided to just ignore it and enjoy my vacation#this post is mostly to spell it out for me and also be my own poor little meow meow about my ouchie back#but either way I'll get cheddar fries today and I am hyped let me tell you that shit is delicious
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Madame Web (2024) mild spoilers
So I saw Madame Web and I think I liked it. If you enjoyed the Venom movies for their awkward fun, then you might have a good time. Script is definitely messy and there's notable moments of awkward dubbing (especially for the bad guy's lines).
I do have mixed feelings about its handling of disability. In the comics, Cassandra Webb is an older woman who uses a wheelchair and is blind; these are caused by myasthenia gravis (MG), a neuromuscular junction disease, a major symptom being skeletal muscle weakness. Movie Cassandra is a young healthy paramedic; it's revealed in a flashback that she was diagnosed with MG in utero (not possible in real life but anyway), her mother died of a gun shot wound while giving birth to her, and a special spider bite cured her as a newborn (also gave her pre-cog abilities but those didn't activate until an adult near-death experience). Cassandra does end the movie using a wheelchair and blind, but both are due to in-battle injuries.
On the one hand, I kinda get it. The writers wanted an active character running around and protecting these three scared teenagers. It's the lazier option but I wasn't exactly expecting high-quality disability rep from the same writers of Morbius.
But it does feel like a missed opportunity, because they could have chosen an interesting middle ground: have Cassandra start getting the early symptoms, getting a diagnosis, and struggling to come to terms with that. It could tie into her character in an interesting way. She's awkward around people but also pushes people away in fear they'll see her as a burden in a few years, which could also tie into her existing abandonment issues from being in foster care after her mother's death. As a paramedic, she's trying to do as much good as possible before her disability means adjusting to a new way of doing things. And since this disease causes muscle weakness especially after exertion, that could be shown after an action scene where she has to debate how much to trust these girls with her illness while she's trying to protect them, eventually finding a balance where they support each other. That way the movie would be doing something interesting with a disabled character instead of having it tagged onto the end scene.
These changes wouldn't fix the script (and I don't really trust Sony to do it well) but it would make for an interesting layer to Cassie's character. Maybe a fic writer will do something interesting with it.
6 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi vik!
i just wanted to scoot in here and ask smth rq!! this is not an admonishment i’m just curious /gen
is there a reason skinny people have to be put down to lift fat people? like! idk personally i think body positivity should include All bodies big middle and small. if we’re skinny shaming people for their bodies we’re still commenting on how they look which can. really. have negative effects (as a person w eating issues)
plus like!! skinny is not always a choice just as fat is not always a choice. pre-diagnosis type 1 diabetics or people with overactive metabolisms or people who were in bad environments and developed an eating disorder just. idk it feels a little weird that body positivity (esp on tumblr) is Only about fat people it feels counterintuitive
this is all /nm /gen i am just!!! curious okay have a good day :D
Hi anon! I'm not quite sure what post you might be talking about, so I've scrolled through all my reblogs from the pst 24 hours to find all the posts about fat/skinny people to try and find the problem. If its not one of these post you were talking about feel free to send me the link of the one you were talking about, or that made you want to ask me this.
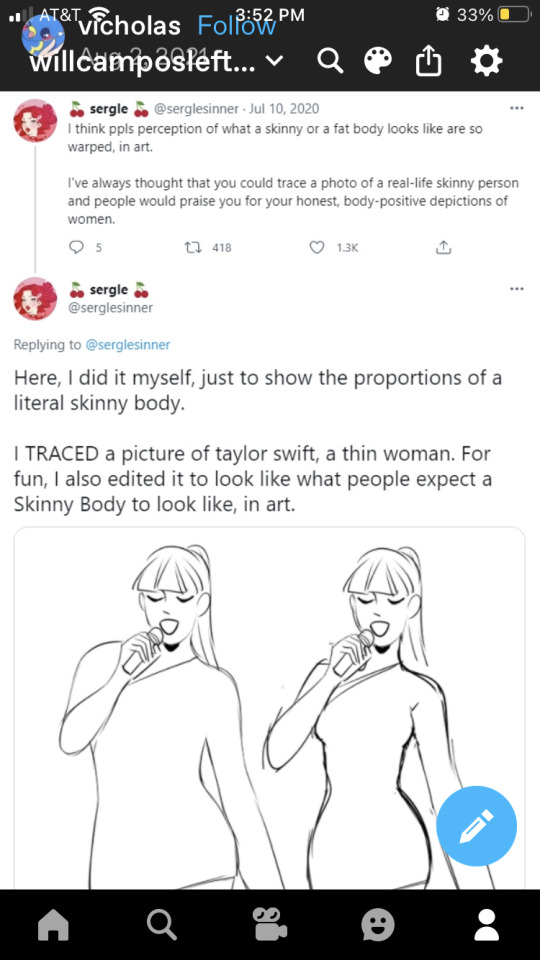

I don't think this is making fun of skinny people, just pointing out art often over exaggerates skinniness to an extreme, making people think any drawing where a woman isn't incredibly tiny is a "plus sized" drawing even though irl they would be considered skinny.
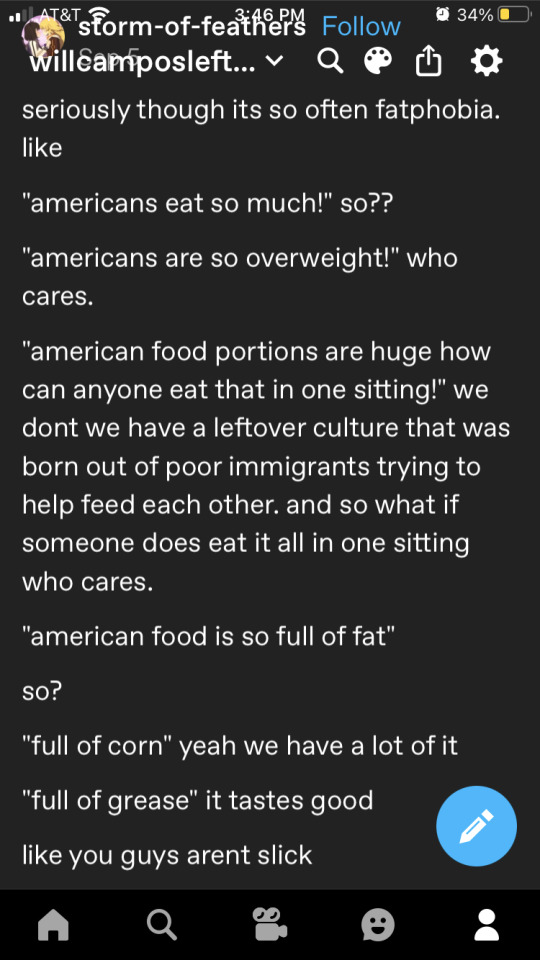
This one doesn't mention skinny people at all, just saying how some people from cultures out side of the us often like to dog pile on the idea "all Americans are fat and that makes them gross haha" which is a complete dog shit take for many reasons. I also say in the tags that we should not make fun of anyone for what they eat or how much they eat, that includes skinny people and people who only eat "healthy" foods, and people who don't eat a lot.

I mean both fat bitches and skinny bitches alike can not cast fireball. Sadly. There should be more fat bitches casting fireball in video games tho
I'm pretty sure this might be the one that made you upset, it has a much meaner tone then the rest. But it's also not making fun of skinny people. It's saying "if you reblog fat positive posts, just to say something along the lines of "i agree but im sooo small and skinny and tiny! But i agree!" You are scared of being seen as fat. And yes, I do understand that ED's play a real role in this, I have two teen sisters who both have ED's and last summer I only let myself eat anything other them sugar  free mints and black coffee once every three days I have both expected and seen first hand what ED's do. But that doesn't excuse the fact going on a fat positive post and showing everyone you are scared of being confused for a fat person can make fat people also scared about being seen as fat. It can also make anyone thats still pretty skinny or small thats even a bit bigger then you scared that maybe they are "too big"
I am really genuinely sorry if any I have personally said or reblogged has made you mad or hurt you anon. I don't think anything I've recently said was anti skinny or trying to make skinny people feel bad for there weight. Again if it wasn't one of these posts you were concerned about please send it to me so I can try and understand more of where you are coming from
/gen hope you have a good day too anon!!:3
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
well I've had an interesting first week of the year back at work. I managed to get through to my usual doctor this week, which is a bit of a miracle, considering she's always back late jan/early feb each year. she's recommended 3 places for me to ring to follow up on a probable ADHD diagnosis. the best one is one in Sydney, in Bondi.
but to do all of their tests would mean I'd try to jam them into a week, if I could (probs not let's be real), or each time I do one I spend on a hotel room to stay up there, since I just wouldn't feel bothered to the 2 hour drive home after 8 hours of tests. but the Sydney one gives you a brain scan which would be super cool. but also if you managed to get bulk billed, it's $1,200. also they don't focus on meds, they focus on "brain based" and behaviour change stuff.
the other 2 places are local to my area, but you have to ring to find out their prices. but on the other hand, my doc said to leave all this stiff until after I have my colonoscopy that's booked for a couple weeks from now, on the 16th.
work is better since I'm not at a tired low point like I was at the end of last year. my boss is a bit happier that I'm turning up at the office at around 8:50 roughly and set up by 9. but yeah I hate having to cut my pre work bed relax after my bath each morning to 7:15 to get out the door by 8;20. but rn 8:20 is only working bc it's the school holidays so I'm not locked into the mronjng school run traffic and school zones right next to my house (basically). so it means I will have to bother to leave at 8:15 or whatever when school starts back up again on jan 31st.
but yeah. I still haven't handed in any of my unfinished (or unstarted) cadestship assessments; bc I forgot right before we left of chrissy/NY break to ask our outsourced IT guys to set up our VPN access app (it just gives you a code to type in) on my phone to access the work hard drive at home lmao. so I've meant to start this week, but I just haven't.
aside from work, the other interesting thing is that someone from the catholic school I went to for years 7-10 from 2008 til 2011, decided to invite me to a 10 year reunion that someone else from our year group from that school set up on Tuesday on fb for October this year. and I was just so surprised that someone bothered to remember me and invite me.... and I feel kinda touched tbh lol. bc i didn't even graduate with them properly, in a way, in 2013, bc I obvs graduated at the public school that I transferred to. it's so random that someone thought to invite me all these years later.
and I'm also stressing over the event a little. mostly on the level of what to wear to it, obvs lmao. but also, most of these people are successful working in good jobs. or they run their own successful local businesses/take over their parentd businesses.
while, on the other hand. I finish my cadetship in march, and I have no idea whether i'll be kept on where I am or whether I'll be somewhere else or jobless lmao. but anyway. it's going to be so weird seeing anyone from that school again, when half of them have kids and are married now or some have even divorced or split from their partners that they married in our early 20s (or at least that's what I've deduced from their name changes on fb back to their original last name I knew them by in school).
also im bitterly jealous of a few of them because they've bought their first house or have a second house and are using their first as an investment property. like bruh. am I the only one who still hasn't moved out of home yet??? and obvs there are obvs other people renting but still. am i the only one still at home??? I don't want questions about that tbh.
like is it even worth catching up with these people, when I still remember the derision I got from one of the girls from my group from that school, when I ran into her at uni back in 2016??? how she told me that everyone was actually SO GLAD that I'd left bc apparently they were all secretly harbouring embarrassment for my behaviour and my "attention seeking" or whatever the fuck she said to me???? but also part of me hopes that rich boy goes and is happy to see me and I'll get to congratulate him in person on his engagement or perhaps being married by the time this event happens (if it even does lmao). and that's my other thing. could just be an elaborate joke where they do this, and I turn up, but NO ONE is there???? like hello trust issues, aren't you looking very sexy this week.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
High-Risk Pregnancy Symptoms: Don't Ignore These Warning Signs
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey, filled with excitement and anticipation. However, for some women, it can also be a time of worry, especially if they are classified as having a high-risk pregnancy. While most pregnancies progress smoothly, being aware of potential complications and their warning signs is crucial for both the mother and baby's health.

What is a High-Risk Pregnancy?
A high-risk pregnancy simply means there's an increased chance of complications for the mother, baby, or both. This can be due to various factors, including:
Pre-existing medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can influence pregnancy.
Age: Women under 18 or over 35 are considered to have a higher risk.
Pregnancy complications in the past: Previous miscarriages, preterm labor, or Cesarean sections can increase the risk.
Multiple pregnancy: Carrying twins, triplets, or more babies presents unique challenges.
Lifestyle factors: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain medications can pose risks.
High-Risk Pregnancy Symptoms You Shouldn't Ignore
High-Risk Pregnancy Symptoms you shouldn't ignore, while some common pregnancy discomforts are normal, certain symptoms can signal a potential complication. Here are some red flags to watch out for:
Vaginal bleeding or spotting: Any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is a cause for concern and requires immediate medical attention.
Severe abdominal pain: Persistent pain in your lower abdomen or pelvis can indicate various issues, including ectopic pregnancy or placental abruption.
Decreased or absent fetal movement: Once you reach a certain stage of pregnancy, you should feel your baby moving regularly. A significant decrease in movement or no movement at all could be a sign of distress.
Changes in vision: Blurred vision, flashing lights, or severe headaches can sometimes be linked to preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure.
Persistent nausea and vomiting: While morning sickness is common, excessive nausea and vomiting that don't improve or worsen can be a sign of dehydration or a hyperemesis gravidarum (severe morning sickness).
Fever or chills: A fever during pregnancy can indicate an infection, which needs prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
Severe swelling in hands, face, or legs: Sudden or excessive swelling can be a sign of preeclampsia and requires immediate medical evaluation.
Difficulty breathing: Shortness of breath or trouble catching your breath, especially when at rest, can be a symptom of preeclampsia or other complications.
Fainting or dizziness: Feeling faint or dizzy can be a sign of anemia or dehydration. However, it's crucial to get checked as it can also indicate other problems.
Pain or burning when urinating: This can be a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI), which requires treatment to prevent further complications.
Mental health concerns: Pregnancy can be emotionally challenging, but if you experience severe anxiety, depression, or suicidal thoughts, seeking professional help is crucial.
Early Detection is Key
If you experience any of the above symptoms during pregnancy, don't hesitate to contact your doctor or go to the nearest emergency department. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the chances of a healthy outcome for both mother and baby.
Importance of Regular Prenatal Care
Prenatal care is vital for all pregnancies, but it becomes even more crucial for high-risk pregnancies. Regular check-ups with your High-risk pregnancy doctor or a specialist allow for close monitoring of your health and your baby's development. This includes prenatal screenings, ultrasounds, and blood tests to identify potential problems early on.
Finding the Right Specialist in Lucknow
If you're experiencing a high-risk pregnancy in Lucknow, seeking guidance from an experienced and qualified obstetrician-gynecologist is essential. Here's where exploring treatment options with a specialist like Dr. Mansi Dhingra can be highly beneficial.
Dr Mansi Dhingra: Your Trusted Partner in Lucknow
Dr Mansi Dhingra is an accomplished Obstetrician and Gynecologist in Lucknow with over a decade of experience in the field. Her distinguished membership with the Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in London, UK, further bolsters her expertise. With a patient-centric approach and in-depth knowledge of high-risk pregnancies, Dr. Dhingra can provide comprehensive care and guidance throughout your pregnancy journey, ensuring the well-being of both you and your baby.
Remember: Early detection and proper management are key to navigating a high-risk pregnancy. Don't ignore any warning signs, and prioritize regular prenatal care with a qualified specialist. By taking charge of your health and seeking the right support, you can increase your chances of a healthy and positive pregnancy experience.
0 notes
Text
This Is What Obamacare's Critics Won't Admit Or Simply Don't Understand
THOUSAND OAKS, California ― Maryann Hammers is likely to die from ovarian cancer someday. But she hopes someday won’t come anytime soon.
Hammers, 61, received the diagnosis in late 2013, and doctors told her that it was stage 3-C, which meant that she could live for many years with the right treatment and a little luck. So far, she’s had both. She’s in remission for the second time, and her last course of chemotherapy ended a year and a half ago. But recent blood tests detected elevated levels of a protein associated with tumors, she explained when we met a few weeks ago. “Maybe it’s a fluke,” she said. “I hope so. I kinda feel like the clock is ticking.”
If the cancer is back, Hammers said, she may need surgery similar to her two previous operations — “gigantic surgeries, gutted like a fish and hospitalized for many days.” Chemotherapy would likely come next, plus medication, hospitalization, and home care. But Hammers considers herself lucky because she’s been able to get treatment at City of Hope, a highly respected Southern California cancer research and treatment center, and luckier still that she’s been able to pay for the treatment with insurance — an Anthem Blue Cross policy she bought through Covered California, the exchange her state created under the Affordable Care Act.
To hear President Donald Trump, House Speaker Paul Ryan and other Republicans tell it, Obamacare has been a disaster, even for those who obtained coverage through the law. Hammers has a very different perspective. She’s a freelance writer and editor, which means she has no employer-provided insurance. In the old days, if she’d gone shopping for a policy with her cancer diagnosis, she would have struggled to find a carrier willing to sell her one.
I'm terrified. ... Do you know how easy it is to use a million dollars when you're getting cancer treatment?
Maryann Hammers, Thousand Oaks, California
And it’s not just the pre-existing condition guarantee, which even critics like Trump say they support, that Hammers has found so valuable. The Affordable Care Act requires insurers to cover a wide range of services and treatments — which, in her case, has included multiple shots of Neulasta, a medication that boosts white blood cell counts and typically costs several thousand dollars per injection. The law also prohibits annual or lifetime limits on benefits, which, as a long-term cancer patient, she would be a prime candidate to exceed.
Policies with such robust coverage inevitably cost thousands of dollars a year, more than Hammers could afford on her own — particularly since battling the disease has cut into her work hours. But the law’s generous tax credits discount the premiums and help with the out-of-pocket costs, too. “Without the Affordable Care Act, I honestly do not know what I would have done,” she said.
The coverage Hammers has today still isn’t as good as what she had years ago, when she worked for a company that provided benefits. But it’s better than what she had in the years right before the cancer diagnosis, when she was buying insurance on her own. The latter plan covered fewer services and came with out-of-pocket costs high enough to discourage her from getting checkups. Obamacare’s introduction of free preventive screenings led her to schedule a long-overdue colonoscopy. During routine preparation for that procedure, a physician first felt a lump in her abdomen.
Sometimes Hammers wonders whether, with less sporadic doctor visits, the cancer might have been caught a little sooner. “But I couldn’t afford a fat doctor’s bill. And I thought I was super healthy.”
These days, something else looms even larger in her mind — the possibility that Trump and the Republican Congress will repeal the health care law without an adequate replacement, or maybe with no replacement at all.
“I’m terrified — isn’t that crazy?” Hammers said. “My biggest source of stress right now isn’t the fact that I have incurable cancer. It’s the prospect of losing my insurance.”
What American Health Care Used To Look Like
To appreciate the significance of stories like Hammers’ and what they say about the Affordable Care Act, it helps to remember what used to happen to people like her before the law took effect. By 2009, when President Barack Obama took office, roughly 1 in 6 Americans had no health care insurance, and even the insured could still face crippling medical bills. As a reporter covering health care during those years, I met these people. Some of their stories stand out, even now, because they capture the old system at its callous, capricious worst.
Gary Rotzler, a quality engineer at a defense contractor in upstate New York, lost his family coverage in the early 1990s when he lost his job. He ended up uninsured for two years, while he juggled stints as an independent contractor. His wife, Betsy, made do without doctor visits even after she started feeling some strange pains. By the time she got a checkup, she had advanced breast cancer. Desperate efforts at treatment failed. After she died, Gary, a father of three, had to declare bankruptcy because of all the unpaid medical bills.
Jacqueline Ruess, a widow in south Florida, thought she was insured. But then she needed expensive tests when her physicians suspected she had cancer. Although the tests were negative, the insurer refused to pay the bills because, it said, a brief episode of a routine gynecological problem in her past qualified as a pre-existing condition.
Tony Montenegro, an immigrant from El Salvador living in Los Angeles, was uninsured and working as a security guard, until untreated diabetes left him legally blind.
Marijon Binder, an impoverished former nun in Chicago, was sued by a Catholic hospital over medical expenses she couldn’t pay.
And Russ Doren, a schoolteacher in a Denver suburb, believed he had good insurance until the bills for his wife’s inpatient treatment at a psychiatric hospital hit the limit for mental health coverage. The hospital released her, despite worries that she was not ready. A few days later, she took her own life.
The Affordable Care Act of 2010 was an effort to address these kinds of problems — to carry on the crusade for universal coverage that Harry Truman had launched some 60 years before. But precisely because Obama and his allies were determined to succeed where predecessors had failed, they made a series of concessions that necessarily limited the law’s ambition.
They expanded Medicaid and regulated private insurance rather than start a whole new government-run program. They dialed back demands for lower prices from drugmakers, hospitals and other health care industries. And they agreed to tight budget constraints for the program as a whole, rather than risk a revolt among more conservative Democrats. These decisions meant that health insurance would ultimately be more expensive and the new system’s financial assistance would be less generous.
Still, projections showed that the law would bring coverage to millions while giving policymakers tools they could use to reduce medical costs over time. When the Senate passed its version of the legislation in December 2009, then-Sen. Tom Harkin (D-Iowa) described the program as a “starter home” with a solid foundation and room for expansion.
Where Obamacare Failed And Where It Succeeded
Seven years later, Trump and the Affordable Care Act’s other critics insist that the program has been a boondoggle — that the Obamacare starter home needs demolition. Some of their objections are philosophical, and some, like the persistent belief that the law set up “death panels,” are fantastical. But others focus on the law’s actual consequences.
High on that list of consequences are the higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs that some people face. The new rules, like coverage of pre-existing conditions, have made policies more expensive, and Obamacare’s financial aid frequently doesn’t offset the increases. A “rate shock” wave hit suddenly in the fall of 2013, when insurers unveiled their newly upgraded plans and in many cases canceled old ones — infuriating customers who remembered Obama’s promise that “if you like your plan, you can keep it,” while alienating even some of those sympathetic to what Obama and the Democrats were trying to do.
I’ve interviewed plenty of these people, too. A few weeks ago, I spoke with Faisuly Scheurer, a real estate agent from Blowing Rock, North Carolina. She and her husband, who works in the restaurant business, were excited about the health care law because they’d struggled to find decent, affordable insurance. They make about $60,000 a year, before taxes, with two kids and college tuition looming in the not-distant future, she said.
In late 2013, they checked out their options and learned that, after tax credits, coverage would cost $360 a month. Scheurer said she remembers thinking, “OK, that is really tight. But if the benefits are good, we are going to have to skimp on other things to make it work.” Then she learned about the deductible, which was nearly $13,000 per year. “My disappointment was indescribable.”
The Scheurer family ultimately decided to remain uninsured. They’re not the only ones, and that has weakened the system as a whole. The people eschewing coverage tend to be relatively healthy, since they’re most willing to take the risk of no coverage. That’s created big problems for insurers, which need the premiums from healthy folks to offset the high medical bills of people with serious conditions.
Many insurers have reacted by raising premiums or pulling out of some places entirely, leaving dysfunctional markets in North Carolina and a handful of other states. Just this week, Humana, which had already scaled back its offerings, announced that it was pulling out of the Affordable Care Act exchanges altogether. At least for the moment, 16 counties in Tennessee don’t have a single insurer committed to offering coverage in 2018.
Trump, Ryan and other Republicans pounced on the Humana news, citing it as more proof of a “failed system” and the need for repeal. That’s pretty typical of how the political conversation about the Affordable Care Act has proceeded for the last seven years. The focus is on everything that’s gone wrong with Obamacare, with scant attention to what’s gone right.
And yet the list of what’s gone right is long.
In states like California and Michigan, the newly regulated markets appear to be working as the law’s architects intended, except for some rural areas that insurers have never served that well. Middle-class people in those states have better, more affordable options.
It looks like more insurers are figuring out how to make their products work and how to successfully compete for business. Customers have turned out to be more price-sensitive than insurers originally anticipated. In general, the carriers that struggle are large national companies without much experience selling directly to consumers, rather than through employers.
Last year’s big premium increases followed two years in which average premiums were far below projections, a sign that carriers simply started their pricing too low. Even now, on average, the premiums people pay for exchange insurance are on a par with, or even a bit cheaper than, equivalent employer policies — and that’s before the tax credits.
The majority of people who are buying insurance on their own or get their coverage through Medicaid are satisfied with it, according to separate surveys by the Commonwealth Fund and the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. The level of satisfaction with the new coverage still trails that involving employer-provided insurance, and it has declined over time. But it’s clearly in positive territory
And then there’s the fact that the number of people without health insurance is the lowest that government or private surveys have ever recorded. When confronted with questions about the people who gained coverage because of the law, Republicans often say something about sparing those people from disruption ― and then argue that even those who obtained insurance through the law are suffering and no better off. This claim is wildly inconsistent with the experience of people like Maryann Hammers ― and, more important, it’s wildly inconsistent with the best available research.
People are struggling less with medical bills, have easier access to primary care and medication, and report that they’re in better health, according to a study that appeared in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2015. The number of people forgoing care because of costs or being “very worried” about paying for a catastrophic medical bill dropped substantially among the newly insured, Kaiser Foundation researchers found last year when they focused on people in California.
A bunch of other studies have turned up similar evidence, All of them gibe with a landmark report on the effects of Massachusetts’ 2006 insurance expansion, which was a prototype for the national legislation. Residents of that state experienced better health outcomes and less financial stress, according to the study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Though it’s had no shortage of controversies and stumbles, there’s really no denying that the ACA has created historic gains in insurance coverage,” said Larry Levitt, a senior vice president at the Kaiser Foundation. “With better coverage that has fewer holes, access to health care has improved and many have better protection from crushing medical bills.”
What Repeal Would Really Mean
Reasonable people can disagree about whether these achievements justify Obamacare’s costs, which include not only higher premiums for the young and healthy but also hefty new taxes on the wealthiest Americans. That’s a debate about values and priorities as much as facts.
What’s not in dispute, or shouldn’t be, is the stark choice on the political agenda right now.
Democratic lawmakers still argue for the principle that Truman laid out in 1948: “health security for all, regardless of residence, station, or race.” They think the Affordable Care Act means the U.S. is closer to that goal and that the next step should be to bolster the law ― by using government power to force down the price of drugs, hospital services and other forms of medical care, while providing more generous government assistance to people who still find premiums and out-of-pocket costs too onerous. Basically, they want people like Faisuly Scheurer to end up with the same security that people like Maryann Hammers already have.
Some Republicans talk as if they share these goals. Trump has probably been the most outspoken on this point, promising to deliver “great health care at lower cost” and vowing that “everybody would be covered.” But other Republicans reject the whole concept of health care as a right. Although it’s theoretically possible to draw up a conservative health plan that would improve access and affordability, these aren’t the kinds of plans that Republicans have in mind.
There’s a face to this law, there’s a face to people that are going to be affected by it.
Angela Eilers, Yorba Linda, California
Their schemes envision substantially less government spending on health care, which would mean lower taxes for the wealthy but also less financial assistance for everybody else. Republicans would make insurance cheaper, but only by allowing it to cover fewer services and saddling beneficiaries with even higher out-of-pocket costs. The result would be some mix of more exposure to medical bills and more people without coverage. If Republicans repeal the Affordable Care Act without replacing it ― a real possibility, given profound divisions within the GOP over how to craft a plan ― 32 million more people could go uninsured, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
That would mean real suffering, primarily among those Americans who benefit most from the law now ― the ones with serious medical problems, or too little income to pay for insurance on their own, or both.
Jay Stout, a 20-year-old in Wilmington, North Carolina, is one of those people. He was in good health until a head-on car collision nearly severed his arm and landed him in the hospital for more than a month. Surgeries and rehabilitation would have cost him hundreds of thousands of dollars that, as a community college student working part-time as a busboy, he could never have paid — if not for the Blue Cross plan that his mother had bought through the Affordable Care Act. When we spoke a few weeks ago, he told me the insurance has been “irreplaceable” and that losing it “would be totally devastating.”
Meenakshi Bewtra had never had a serious health problem until her first year at the University of Pennsylvania medical school, when she developed severe gastrointestinal problems — the kind that forced her into the hospital for two months and drove her to drop out of school. Her insurance lapsed, which meant that her GI issues became a pre-existing condition. She eventually found coverage and today she’s a professor of medicine at Penn, where she moonlights as an advocate for universal health insurance.
“For the first time, I truly understood what comprehensive health insurance meant,” Bewtra said, remembering what it was like to become fully covered. “I did not have to worry about how many times I saw a doctor, or how many lab tests I had to get, or having to ration out medications.”
Angela Eilers, who lives in Yorba Linda, California, isn’t worrying about her own health. It’s her daughter Myka who has a congenital heart condition called pulmonary stenosis, which makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood to the lungs. The little girl has required multiple surgeries and will need intensive medical treatment throughout her childhood.
In 2012, Angela’s husband, Todd, was laid off from his job at an investment firm. Since going without insurance was not an option, they took advantage of COBRA to stay on his old company’s health plan. It was expensive, and Eilers recalled panicking over the possibility they might not be able to pay the premiums. “I remember sitting at the table, thinking of plans. What would be our plan? One of them was … giving up our parents rights to my mom, because she has really good health insurance.”
Eventually her husband started his own consulting business, and that gave them the income to keep up with premiums until 2014 — when they were able to obtain coverage through the Affordable Care Act. Today they have a gold plan, one of the most generous available, for which they pay around $20,000 a year. Even though they make too much to qualify for financial assistance, they’re grateful for the coverage. Seven-year-old Myka has already run up more than a half-million dollars in medical bills. In the old days, before Obamacare, they would have worried about hitting their plan’s lifetime limit on benefits.
The family’s coverage has become more expensive over the years. They wish the price were lower, but they’re also not complaining about that. “I’m thankful that the letter was a premium hike, rather than ‘Sorry, we are not going to cover your daughter anymore,’” Angela Eilers said.
When she thinks about the possibility of Obamacare repeal, she wonders if Trump and the Republicans understand what that would really mean. “There’s a face to this law, there’s a face to people that are going to be affected by it,” Eilers said. “It’s not me, it’s not him, it’s her. She’s only 7. And through no fault of her own, why should she suffer? And she’s not the only one.”
Sign up for the HuffPost Must Reads newsletter. Each Sunday, we will bring you the best original reporting, long form writing and breaking news from The Huffington Post and around the web, plus behind-the-scenes looks at how it’s all made. Click here to sign up!
-- This feed and its contents are the property of The Huffington Post, and use is subject to our terms. It may be used for personal consumption, but may not be distributed on a website.
This Is What Obamacare's Critics Won't Admit Or Simply Don't Understand published first on http://ift.tt/2lnpciY
0 notes
Text
This Is What Obamacare's Critics Won't Admit Or Simply Don't Understand
THOUSAND OAKS, California ― Maryann Hammers is likely to die from ovarian cancer someday. But she hopes someday won’t come anytime soon.
Hammers, 61, received the diagnosis in late 2013, and doctors told her that it was stage 3-C, which meant that she could live for many years with the right treatment and a little luck. So far, she’s had both. She’s in remission for the second time, and her last course of chemotherapy ended a year and a half ago. But recent blood tests detected elevated levels of a protein associated with tumors, she explained when we met a few weeks ago. “Maybe it’s a fluke,” she said. “I hope so. I kinda feel like the clock is ticking.”
If the cancer is back, Hammers said, she may need surgery similar to her two previous operations — “gigantic surgeries, gutted like a fish and hospitalized for many days.” Chemotherapy would likely come next, plus medication, hospitalization, and home care. But Hammers considers herself lucky because she’s been able to get treatment at City of Hope, a highly respected Southern California cancer research and treatment center, and luckier still that she’s been able to pay for the treatment with insurance — an Anthem Blue Cross policy she bought through Covered California, the exchange her state created under the Affordable Care Act.
To hear President Donald Trump, House Speaker Paul Ryan and other Republicans tell it, Obamacare has been a disaster, even for those who obtained coverage through the law. Hammers has a very different perspective. She’s a freelance writer and editor, which means she has no employer-provided insurance. In the old days, if she’d gone shopping for a policy with her cancer diagnosis, she would have struggled to find a carrier willing to sell her one.
I'm terrified. ... Do you know how easy it is to use a million dollars when you're getting cancer treatment?
Maryann Hammers, Thousand Oaks, California
And it’s not just the pre-existing condition guarantee, which even critics like Trump say they support, that Hammers has found so valuable. The Affordable Care Act requires insurers to cover a wide range of services and treatments — which, in her case, has included multiple shots of Neulasta, a medication that boosts white blood cell counts and typically costs several thousand dollars per injection. The law also prohibits annual or lifetime limits on benefits, which, as a long-term cancer patient, she would be a prime candidate to exceed.
Policies with such robust coverage inevitably cost thousands of dollars a year, more than Hammers could afford on her own — particularly since battling the disease has cut into her work hours. But the law’s generous tax credits discount the premiums and help with the out-of-pocket costs, too. “Without the Affordable Care Act, I honestly do not know what I would have done,” she said.
The coverage Hammers has today still isn’t as good as what she had years ago, when she worked for a company that provided benefits. But it’s better than what she had in the years right before the cancer diagnosis, when she was buying insurance on her own. The latter plan covered fewer services and came with out-of-pocket costs high enough to discourage her from getting checkups. Obamacare’s introduction of free preventive screenings led her to schedule a long-overdue colonoscopy. During routine preparation for that procedure, a physician first felt a lump in her abdomen.
Sometimes Hammers wonders whether, with less sporadic doctor visits, the cancer might have been caught a little sooner. “But I couldn’t afford a fat doctor’s bill. And I thought I was super healthy.”
These days, something else looms even larger in her mind — the possibility that Trump and the Republican Congress will repeal the health care law without an adequate replacement, or maybe with no replacement at all.
“I’m terrified — isn’t that crazy?” Hammers said. “My biggest source of stress right now isn’t the fact that I have incurable cancer. It’s the prospect of losing my insurance.”
What American Health Care Used To Look Like
To appreciate the significance of stories like Hammers’ and what they say about the Affordable Care Act, it helps to remember what used to happen to people like her before the law took effect. By 2009, when President Barack Obama took office, roughly 1 in 6 Americans had no health care insurance, and even the insured could still face crippling medical bills. As a reporter covering health care during those years, I met these people. Some of their stories stand out, even now, because they capture the old system at its callous, capricious worst.
Gary Rotzler, a quality engineer at a defense contractor in upstate New York, lost his family coverage in the early 1990s when he lost his job. He ended up uninsured for two years, while he juggled stints as an independent contractor. His wife, Betsy, made do without doctor visits even after she started feeling some strange pains. By the time she got a checkup, she had advanced breast cancer. Desperate efforts at treatment failed. After she died, Gary, a father of three, had to declare bankruptcy because of all the unpaid medical bills.
Jacqueline Ruess, a widow in south Florida, thought she was insured. But then she needed expensive tests when her physicians suspected she had cancer. Although the tests were negative, the insurer refused to pay the bills because, it said, a brief episode of a routine gynecological problem in her past qualified as a pre-existing condition.
Tony Montenegro, an immigrant from El Salvador living in Los Angeles, was uninsured and working as a security guard, until untreated diabetes left him legally blind.
Marijon Binder, an impoverished former nun in Chicago, was sued by a Catholic hospital over medical expenses she couldn’t pay.
And Russ Doren, a schoolteacher in a Denver suburb, believed he had good insurance until the bills for his wife’s inpatient treatment at a psychiatric hospital hit the limit for mental health coverage. The hospital released her, despite worries that she was not ready. A few days later, she took her own life.
The Affordable Care Act of 2010 was an effort to address these kinds of problems — to carry on the crusade for universal coverage that Harry Truman had launched some 60 years before. But precisely because Obama and his allies were determined to succeed where predecessors had failed, they made a series of concessions that necessarily limited the law’s ambition.
They expanded Medicaid and regulated private insurance rather than start a whole new government-run program. They dialed back demands for lower prices from drugmakers, hospitals and other health care industries. And they agreed to tight budget constraints for the program as a whole, rather than risk a revolt among more conservative Democrats. These decisions meant that health insurance would ultimately be more expensive and the new system’s financial assistance would be less generous.
Still, projections showed that the law would bring coverage to millions while giving policymakers tools they could use to reduce medical costs over time. When the Senate passed its version of the legislation in December 2009, then-Sen. Tom Harkin (D-Iowa) described the program as a “starter home” with a solid foundation and room for expansion.
Where Obamacare Failed And Where It Succeeded
Seven years later, Trump and the Affordable Care Act’s other critics insist that the program has been a boondoggle — that the Obamacare starter home needs demolition. Some of their objections are philosophical, and some, like the persistent belief that the law set up “death panels,” are fantastical. But others focus on the law’s actual consequences.
High on that list of consequences are the higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs that some people face. The new rules, like coverage of pre-existing conditions, have made policies more expensive, and Obamacare’s financial aid frequently doesn’t offset the increases. A “rate shock” wave hit suddenly in the fall of 2013, when insurers unveiled their newly upgraded plans and in many cases canceled old ones — infuriating customers who remembered Obama’s promise that “if you like your plan, you can keep it,” while alienating even some of those sympathetic to what Obama and the Democrats were trying to do.
I’ve interviewed plenty of these people, too. A few weeks ago, I spoke with Faisuly Scheurer, a real estate agent from Blowing Rock, North Carolina. She and her husband, who works in the restaurant business, were excited about the health care law because they’d struggled to find decent, affordable insurance. They make about $60,000 a year, before taxes, with two kids and college tuition looming in the not-distant future, she said.
In late 2013, they checked out their options and learned that, after tax credits, coverage would cost $360 a month. Scheurer said she remembers thinking, “OK, that is really tight. But if the benefits are good, we are going to have to skimp on other things to make it work.” Then she learned about the deductible, which was nearly $13,000 per year. “My disappointment was indescribable.”
The Scheurer family ultimately decided to remain uninsured. They’re not the only ones, and that has weakened the system as a whole. The people eschewing coverage tend to be relatively healthy, since they’re most willing to take the risk of no coverage. That’s created big problems for insurers, which need the premiums from healthy folks to offset the high medical bills of people with serious conditions.
Many insurers have reacted by raising premiums or pulling out of some places entirely, leaving dysfunctional markets in North Carolina and a handful of other states. Just this week, Humana, which had already scaled back its offerings, announced that it was pulling out of the Affordable Care Act exchanges altogether. At least for the moment, 16 counties in Tennessee don’t have a single insurer committed to offering coverage in 2018.
Trump, Ryan and other Republicans pounced on the Humana news, citing it as more proof of a “failed system” and the need for repeal. That’s pretty typical of how the political conversation about the Affordable Care Act has proceeded for the last seven years. The focus is on everything that’s gone wrong with Obamacare, with scant attention to what’s gone right.
And yet the list of what’s gone right is long.
In states like California and Michigan, the newly regulated markets appear to be working as the law’s architects intended, except for some rural areas that insurers have never served that well. Middle-class people in those states have better, more affordable options.
It looks like more insurers are figuring out how to make their products work and how to successfully compete for business. Customers have turned out to be more price-sensitive than insurers originally anticipated. In general, the carriers that struggle are large national companies without much experience selling directly to consumers, rather than through employers.
Last year’s big premium increases followed two years in which average premiums were far below projections, a sign that carriers simply started their pricing too low. Even now, on average, the premiums people pay for exchange insurance are on a par with, or even a bit cheaper than, equivalent employer policies — and that’s before the tax credits.
The majority of people who are buying insurance on their own or get their coverage through Medicaid are satisfied with it, according to separate surveys by the Commonwealth Fund and the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. The level of satisfaction with the new coverage still trails that involving employer-provided insurance, and it has declined over time. But it’s clearly in positive territory
And then there’s the fact that the number of people without health insurance is the lowest that government or private surveys have ever recorded. When confronted with questions about the people who gained coverage because of the law, Republicans often say something about sparing those people from disruption ― and then argue that even those who obtained insurance through the law are suffering and no better off. This claim is wildly inconsistent with the experience of people like Maryann Hammers ― and, more important, it’s wildly inconsistent with the best available research.
People are struggling less with medical bills, have easier access to primary care and medication, and report that they’re in better health, according to a study that appeared in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2015. The number of people forgoing care because of costs or being “very worried” about paying for a catastrophic medical bill dropped substantially among the newly insured, Kaiser Foundation researchers found last year when they focused on people in California.
A bunch of other studies have turned up similar evidence, All of them gibe with a landmark report on the effects of Massachusetts’ 2006 insurance expansion, which was a prototype for the national legislation. Residents of that state experienced better health outcomes and less financial stress, according to the study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Though it’s had no shortage of controversies and stumbles, there’s really no denying that the ACA has created historic gains in insurance coverage,” said Larry Levitt, a senior vice president at the Kaiser Foundation. “With better coverage that has fewer holes, access to health care has improved and many have better protection from crushing medical bills.”
What Repeal Would Really Mean
Reasonable people can disagree about whether these achievements justify Obamacare’s costs, which include not only higher premiums for the young and healthy but also hefty new taxes on the wealthiest Americans. That’s a debate about values and priorities as much as facts.
What’s not in dispute, or shouldn’t be, is the stark choice on the political agenda right now.
Democratic lawmakers still argue for the principle that Truman laid out in 1948: “health security for all, regardless of residence, station, or race.” They think the Affordable Care Act means the U.S. is closer to that goal and that the next step should be to bolster the law ― by using government power to force down the price of drugs, hospital services and other forms of medical care, while providing more generous government assistance to people who still find premiums and out-of-pocket costs too onerous. Basically, they want people like Faisuly Scheurer to end up with the same security that people like Maryann Hammers already have.
Some Republicans talk as if they share these goals. Trump has probably been the most outspoken on this point, promising to deliver “great health care at lower cost” and vowing that “everybody would be covered.” But other Republicans reject the whole concept of health care as a right. Although it’s theoretically possible to draw up a conservative health plan that would improve access and affordability, these aren’t the kinds of plans that Republicans have in mind.
There’s a face to this law, there’s a face to people that are going to be affected by it.
Angela Eilers, Yorba Linda, California
Their schemes envision substantially less government spending on health care, which would mean lower taxes for the wealthy but also less financial assistance for everybody else. Republicans would make insurance cheaper, but only by allowing it to cover fewer services and saddling beneficiaries with even higher out-of-pocket costs. The result would be some mix of more exposure to medical bills and more people without coverage. If Republicans repeal the Affordable Care Act without replacing it ― a real possibility, given profound divisions within the GOP over how to craft a plan ― 32 million more people could go uninsured, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
That would mean real suffering, primarily among those Americans who benefit most from the law now ― the ones with serious medical problems, or too little income to pay for insurance on their own, or both.
Jay Stout, a 20-year-old in Wilmington, North Carolina, is one of those people. He was in good health until a head-on car collision nearly severed his arm and landed him in the hospital for more than a month. Surgeries and rehabilitation would have cost him hundreds of thousands of dollars that, as a community college student working part-time as a busboy, he could never have paid — if not for the Blue Cross plan that his mother had bought through the Affordable Care Act. When we spoke a few weeks ago, he told me the insurance has been “irreplaceable” and that losing it “would be totally devastating.”
Meenakshi Bewtra had never had a serious health problem until her first year at the University of Pennsylvania medical school, when she developed severe gastrointestinal problems — the kind that forced her into the hospital for two months and drove her to drop out of school. Her insurance lapsed, which meant that her GI issues became a pre-existing condition. She eventually found coverage and today she’s a professor of medicine at Penn, where she moonlights as an advocate for universal health insurance.
“For the first time, I truly understood what comprehensive health insurance meant,” Bewtra said, remembering what it was like to become fully covered. “I did not have to worry about how many times I saw a doctor, or how many lab tests I had to get, or having to ration out medications.”
Angela Eilers, who lives in Yorba Linda, California, isn’t worrying about her own health. It’s her daughter Myka who has a congenital heart condition called pulmonary stenosis, which makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood to the lungs. The little girl has required multiple surgeries and will need intensive medical treatment throughout her childhood.
In 2012, Angela’s husband, Todd, was laid off from his job at an investment firm. Since going without insurance was not an option, they took advantage of COBRA to stay on his old company’s health plan. It was expensive, and Eilers recalled panicking over the possibility they might not be able to pay the premiums. “I remember sitting at the table, thinking of plans. What would be our plan? One of them was … giving up our parents rights to my mom, because she has really good health insurance.”
Eventually her husband started his own consulting business, and that gave them the income to keep up with premiums until 2014 — when they were able to obtain coverage through the Affordable Care Act. Today they have a gold plan, one of the most generous available, for which they pay around $20,000 a year. Even though they make too much to qualify for financial assistance, they’re grateful for the coverage. Seven-year-old Myka has already run up more than a half-million dollars in medical bills. In the old days, before Obamacare, they would have worried about hitting their plan’s lifetime limit on benefits.
The family’s coverage has become..
from DIYS http://ift.tt/2lVz2x4
0 notes
Text
This Is What Obamacare's Critics Won't Admit Or Simply Don't Understand
THOUSAND OAKS, California ― Maryann Hammers is likely to die from ovarian cancer someday. But she hopes someday won’t come anytime soon.
Hammers, 61, received the diagnosis in late 2013, and doctors told her that it was stage 3-C, which meant that she could live for many years with the right treatment and a little luck. So far, she’s had both. She’s in remission for the second time, and her last course of chemotherapy ended a year and a half ago. But recent blood tests detected elevated levels of a protein associated with tumors, she explained when we met a few weeks ago. “Maybe it’s a fluke,” she said. “I hope so. I kinda feel like the clock is ticking.”
If the cancer is back, Hammers said, she may need surgery similar to her two previous operations — “gigantic surgeries, gutted like a fish and hospitalized for many days.” Chemotherapy would likely come next, plus medication, hospitalization, and home care. But Hammers considers herself lucky because she’s been able to get treatment at City of Hope, a highly respected Southern California cancer research and treatment center, and luckier still that she’s been able to pay for the treatment with insurance — an Anthem Blue Cross policy she bought through Covered California, the exchange her state created under the Affordable Care Act.
To hear President Donald Trump, House Speaker Paul Ryan and other Republicans tell it, Obamacare has been a disaster, even for those who obtained coverage through the law. Hammers has a very different perspective. She’s a freelance writer and editor, which means she has no employer-provided insurance. In the old days, if she’d gone shopping for a policy with her cancer diagnosis, she would have struggled to find a carrier willing to sell her one.
I'm terrified. ... Do you know how easy it is to use a million dollars when you're getting cancer treatment?
Maryann Hammers, Thousand Oaks, California
And it’s not just the pre-existing condition guarantee, which even critics like Trump say they support, that Hammers has found so valuable. The Affordable Care Act requires insurers to cover a wide range of services and treatments — which, in her case, has included multiple shots of Neulasta, a medication that boosts white blood cell counts and typically costs several thousand dollars per injection. The law also prohibits annual or lifetime limits on benefits, which, as a long-term cancer patient, she would be a prime candidate to exceed.
Policies with such robust coverage inevitably cost thousands of dollars a year, more than Hammers could afford on her own — particularly since battling the disease has cut into her work hours. But the law’s generous tax credits discount the premiums and help with the out-of-pocket costs, too. “Without the Affordable Care Act, I honestly do not know what I would have done,” she said.
The coverage Hammers has today still isn’t as good as what she had years ago, when she worked for a company that provided benefits. But it’s better than what she had in the years right before the cancer diagnosis, when she was buying insurance on her own. The latter plan covered fewer services and came with out-of-pocket costs high enough to discourage her from getting checkups. Obamacare’s introduction of free preventive screenings led her to schedule a long-overdue colonoscopy. During routine preparation for that procedure, a physician first felt a lump in her abdomen.
Sometimes Hammers wonders whether, with less sporadic doctor visits, the cancer might have been caught a little sooner. “But I couldn’t afford a fat doctor’s bill. And I thought I was super healthy.”
These days, something else looms even larger in her mind — the possibility that Trump and the Republican Congress will repeal the health care law without an adequate replacement, or maybe with no replacement at all.
“I’m terrified — isn’t that crazy?” Hammers said. “My biggest source of stress right now isn’t the fact that I have incurable cancer. It’s the prospect of losing my insurance.”
What American Health Care Used To Look Like
To appreciate the significance of stories like Hammers’ and what they say about the Affordable Care Act, it helps to remember what used to happen to people like her before the law took effect. By 2009, when President Barack Obama took office, roughly 1 in 6 Americans had no health care insurance, and even the insured could still face crippling medical bills. As a reporter covering health care during those years, I met these people. Some of their stories stand out, even now, because they capture the old system at its callous, capricious worst.
Gary Rotzler, a quality engineer at a defense contractor in upstate New York, lost his family coverage in the early 1990s when he lost his job. He ended up uninsured for two years, while he juggled stints as an independent contractor. His wife, Betsy, made do without doctor visits even after she started feeling some strange pains. By the time she got a checkup, she had advanced breast cancer. Desperate efforts at treatment failed. After she died, Gary, a father of three, had to declare bankruptcy because of all the unpaid medical bills.
Jacqueline Ruess, a widow in south Florida, thought she was insured. But then she needed expensive tests when her physicians suspected she had cancer. Although the tests were negative, the insurer refused to pay the bills because, it said, a brief episode of a routine gynecological problem in her past qualified as a pre-existing condition.
Tony Montenegro, an immigrant from El Salvador living in Los Angeles, was uninsured and working as a security guard, until untreated diabetes left him legally blind.
Marijon Binder, an impoverished former nun in Chicago, was sued by a Catholic hospital over medical expenses she couldn’t pay.
And Russ Doren, a schoolteacher in a Denver suburb, believed he had good insurance until the bills for his wife’s inpatient treatment at a psychiatric hospital hit the limit for mental health coverage. The hospital released her, despite worries that she was not ready. A few days later, she took her own life.
The Affordable Care Act of 2010 was an effort to address these kinds of problems — to carry on the crusade for universal coverage that Harry Truman had launched some 60 years before. But precisely because Obama and his allies were determined to succeed where predecessors had failed, they made a series of concessions that necessarily limited the law’s ambition.
They expanded Medicaid and regulated private insurance rather than start a whole new government-run program. They dialed back demands for lower prices from drugmakers, hospitals and other health care industries. And they agreed to tight budget constraints for the program as a whole, rather than risk a revolt among more conservative Democrats. These decisions meant that health insurance would ultimately be more expensive and the new system’s financial assistance would be less generous.
Still, projections showed that the law would bring coverage to millions while giving policymakers tools they could use to reduce medical costs over time. When the Senate passed its version of the legislation in December 2009, then-Sen. Tom Harkin (D-Iowa) described the program as a “starter home” with a solid foundation and room for expansion.
Where Obamacare Failed And Where It Succeeded
Seven years later, Trump and the Affordable Care Act’s other critics insist that the program has been a boondoggle — that the Obamacare starter home needs demolition. Some of their objections are philosophical, and some, like the persistent belief that the law set up “death panels,” are fantastical. But others focus on the law’s actual consequences.
High on that list of consequences are the higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs that some people face. The new rules, like coverage of pre-existing conditions, have made policies more expensive, and Obamacare’s financial aid frequently doesn’t offset the increases. A “rate shock” wave hit suddenly in the fall of 2013, when insurers unveiled their newly upgraded plans and in many cases canceled old ones — infuriating customers who remembered Obama’s promise that “if you like your plan, you can keep it,” while alienating even some of those sympathetic to what Obama and the Democrats were trying to do.
I’ve interviewed plenty of these people, too. A few weeks ago, I spoke with Faisuly Scheurer, a real estate agent from Blowing Rock, North Carolina. She and her husband, who works in the restaurant business, were excited about the health care law because they’d struggled to find decent, affordable insurance. They make about $60,000 a year, before taxes, with two kids and college tuition looming in the not-distant future, she said.
In late 2013, they checked out their options and learned that, after tax credits, coverage would cost $360 a month. Scheurer said she remembers thinking, “OK, that is really tight. But if the benefits are good, we are going to have to skimp on other things to make it work.” Then she learned about the deductible, which was nearly $13,000 per year. “My disappointment was indescribable.”
The Scheurer family ultimately decided to remain uninsured. They’re not the only ones, and that has weakened the system as a whole. The people eschewing coverage tend to be relatively healthy, since they’re most willing to take the risk of no coverage. That’s created big problems for insurers, which need the premiums from healthy folks to offset the high medical bills of people with serious conditions.
Many insurers have reacted by raising premiums or pulling out of some places entirely, leaving dysfunctional markets in North Carolina and a handful of other states. Just this week, Humana, which had already scaled back its offerings, announced that it was pulling out of the Affordable Care Act exchanges altogether. At least for the moment, 16 counties in Tennessee don’t have a single insurer committed to offering coverage in 2018.
Trump, Ryan and other Republicans pounced on the Humana news, citing it as more proof of a “failed system” and the need for repeal. That’s pretty typical of how the political conversation about the Affordable Care Act has proceeded for the last seven years. The focus is on everything that’s gone wrong with Obamacare, with scant attention to what’s gone right.
And yet the list of what’s gone right is long.
In states like California and Michigan, the newly regulated markets appear to be working as the law’s architects intended, except for some rural areas that insurers have never served that well. Middle-class people in those states have better, more affordable options.
It looks like more insurers are figuring out how to make their products work and how to successfully compete for business. Customers have turned out to be more price-sensitive than insurers originally anticipated. In general, the carriers that struggle are large national companies without much experience selling directly to consumers, rather than through employers.
Last year’s big premium increases followed two years in which average premiums were far below projections, a sign that carriers simply started their pricing too low. Even now, on average, the premiums people pay for exchange insurance are on a par with, or even a bit cheaper than, equivalent employer policies — and that’s before the tax credits.
The majority of people who are buying insurance on their own or get their coverage through Medicaid are satisfied with it, according to separate surveys by the Commonwealth Fund and the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. The level of satisfaction with the new coverage still trails that involving employer-provided insurance, and it has declined over time. But it’s clearly in positive territory
And then there’s the fact that the number of people without health insurance is the lowest that government or private surveys have ever recorded. When confronted with questions about the people who gained coverage because of the law, Republicans often say something about sparing those people from disruption ― and then argue that even those who obtained insurance through the law are suffering and no better off. This claim is wildly inconsistent with the experience of people like Maryann Hammers ― and, more important, it’s wildly inconsistent with the best available research.
People are struggling less with medical bills, have easier access to primary care and medication, and report that they’re in better health, according to a study that appeared in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2015. The number of people forgoing care because of costs or being “very worried” about paying for a catastrophic medical bill dropped substantially among the newly insured, Kaiser Foundation researchers found last year when they focused on people in California.
A bunch of other studies have turned up similar evidence, All of them gibe with a landmark report on the effects of Massachusetts’ 2006 insurance expansion, which was a prototype for the national legislation. Residents of that state experienced better health outcomes and less financial stress, according to the study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
“Though it’s had no shortage of controversies and stumbles, there’s really no denying that the ACA has created historic gains in insurance coverage,” said Larry Levitt, a senior vice president at the Kaiser Foundation. “With better coverage that has fewer holes, access to health care has improved and many have better protection from crushing medical bills.”
What Repeal Would Really Mean
Reasonable people can disagree about whether these achievements justify Obamacare’s costs, which include not only higher premiums for the young and healthy but also hefty new taxes on the wealthiest Americans. That’s a debate about values and priorities as much as facts.
What’s not in dispute, or shouldn’t be, is the stark choice on the political agenda right now.
Democratic lawmakers still argue for the principle that Truman laid out in 1948: “health security for all, regardless of residence, station, or race.” They think the Affordable Care Act means the U.S. is closer to that goal and that the next step should be to bolster the law ― by using government power to force down the price of drugs, hospital services and other forms of medical care, while providing more generous government assistance to people who still find premiums and out-of-pocket costs too onerous. Basically, they want people like Faisuly Scheurer to end up with the same security that people like Maryann Hammers already have.
Some Republicans talk as if they share these goals. Trump has probably been the most outspoken on this point, promising to deliver “great health care at lower cost” and vowing that “everybody would be covered.” But other Republicans reject the whole concept of health care as a right. Although it’s theoretically possible to draw up a conservative health plan that would improve access and affordability, these aren’t the kinds of plans that Republicans have in mind.
There’s a face to this law, there’s a face to people that are going to be affected by it.
Angela Eilers, Yorba Linda, California
Their schemes envision substantially less government spending on health care, which would mean lower taxes for the wealthy but also less financial assistance for everybody else. Republicans would make insurance cheaper, but only by allowing it to cover fewer services and saddling beneficiaries with even higher out-of-pocket costs. The result would be some mix of more exposure to medical bills and more people without coverage. If Republicans repeal the Affordable Care Act without replacing it ― a real possibility, given profound divisions within the GOP over how to craft a plan ― 32 million more people could go uninsured, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
That would mean real suffering, primarily among those Americans who benefit most from the law now ― the ones with serious medical problems, or too little income to pay for insurance on their own, or both.
Jay Stout, a 20-year-old in Wilmington, North Carolina, is one of those people. He was in good health until a head-on car collision nearly severed his arm and landed him in the hospital for more than a month. Surgeries and rehabilitation would have cost him hundreds of thousands of dollars that, as a community college student working part-time as a busboy, he could never have paid — if not for the Blue Cross plan that his mother had bought through the Affordable Care Act. When we spoke a few weeks ago, he told me the insurance has been “irreplaceable” and that losing it “would be totally devastating.”
Meenakshi Bewtra had never had a serious health problem until her first year at the University of Pennsylvania medical school, when she developed severe gastrointestinal problems — the kind that forced her into the hospital for two months and drove her to drop out of school. Her insurance lapsed, which meant that her GI issues became a pre-existing condition. She eventually found coverage and today she’s a professor of medicine at Penn, where she moonlights as an advocate for universal health insurance.
“For the first time, I truly understood what comprehensive health insurance meant,” Bewtra said, remembering what it was like to become fully covered. “I did not have to worry about how many times I saw a doctor, or how many lab tests I had to get, or having to ration out medications.”
Angela Eilers, who lives in Yorba Linda, California, isn’t worrying about her own health. It’s her daughter Myka who has a congenital heart condition called pulmonary stenosis, which makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood to the lungs. The little girl has required multiple surgeries and will need intensive medical treatment throughout her childhood.
In 2012, Angela’s husband, Todd, was laid off from his job at an investment firm. Since going without insurance was not an option, they took advantage of COBRA to stay on his old company’s health plan. It was expensive, and Eilers recalled panicking over the possibility they might not be able to pay the premiums. “I remember sitting at the table, thinking of plans. What would be our plan? One of them was … giving up our parents rights to my mom, because she has really good health insurance.”
Eventually her husband started his own consulting business, and that gave them the income to keep up with premiums until 2014 — when they were able to obtain coverage through the Affordable Care Act. Today they have a gold plan, one of the most generous available, for which they pay around $20,000 a year. Even though they make too much to qualify for financial assistance, they’re grateful for the coverage. Seven-year-old Myka has already run up more than a half-million dollars in medical bills. In the old days, before Obamacare, they would have worried about hitting their plan’s lifetime limit on benefits.
The family’s coverage has become..
from DIYS http://ift.tt/2lVz2x4
0 notes