#democracy or bust
Text
My parents: Oh, it's not so bad! Sure, the next four years are going to be rough, but the next election...
Me internally: There aren't going to be next election, you stupid slut.
#slovakia#ťumbľr#the fear of coming subversion of democracy is real#are we going to have to use violence?#i am ready to bust some heads#are you?
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The unexpected upside of global monopoly capitalism

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me TODAY (Apr 10) at UCLA, then Chicago (Apr 17), Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

Here's a silver lining to global monopoly capitalism: it means we're all fighting the same enemy, who is using the same tactics everywhere. The same coordination tools that allow corporations to extend their tendrils to every corner of the Earth allows regulators and labor organizers to coordinate their resistance.
That's a lesson Mercedes is learning. In 2023, Germany's Supply Chain Act went into effect, which bans large corporations with a German presence from using child labor, violating health and safety standards, and (critically) interfering with union organizers:
https://www.bafa.de/EN/Supply_Chain_Act/Overview/overview_node.html
Across the ocean, in the USA, Mercedes has a preference for building its cars in the American South, the so-called "right to work" states where US labor law is routinely flouted and unions are thin on the ground. As The American Prospect's Harold Meyerson writes, the only non-union Mercedes factories in the world are in the US:
https://prospect.org/labor/2024-04-08-american-workers-german-law-uaw-unions/
But American workers – especially southern workers – are on an organizing tear, unionizing their workplaces at a rate not seen in generations. Their unprecedented success is down to their commitment, solidarity and shrewd tactics – all buoyed by a refreshingly pro-worker NLRB, who have workers' backs in ways also not seen since the Carter administration:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/14/prop-22-never-again/#norms-code-laws-markets
Workers at Mercedes' factory in Vance, Alabama are trying to join the UAW, and Mercedes is playing dirty, using the tried-and-true union-busting tactics that have held workplace democracy at bay for decades. The UAW has lodged a complaint with the NLRB, naturally:
https://www.commondreams.org/news/alabama-mercedes-benz
But the UAW has also filed a complaint with BAFA, the German regulator in charge of the Supply Chain Act, seeking penalties against Mercedes-Benz Group AG:
https://uaw.org/uaw-files-charges-in-germany-against-mercedes-benz-companys-anti-union-campaign-against-u-s-autoworkers-violates-new-german-law-on-global-supply-chain-practices/
That's a huge deal, because the German Supply Chain Act goes hard. If Mercedes is convicted of union-busting in Alabama, its German parent-company faces a fine of 2% of its global total revenue, and will no longer be eligible to sell products to the German government. Chomp.
Now, the German Supply Chain Act is new, and this is the first petition filed by a non-German union with BAFA, so it's not a slam dunk. But supermajorities of Mercedes workers at the Alabama factory have signed UAW cards, and the election is going to happen in May or June. And the UAW – under new leadership, thanks to a revolution that overthrew the corrupt old guard – has its sights set on all the auto-makers in the American south.
As Meyerson writes, the south is America's onshore offshore, a regulatory haven where corporations pay minimal or no tax and are free to abuse their workers, pollute, and corrupt local governments with a free hand (no wonder American industry is flocking to these states). Meyerson: "The economic impact of unionizing the South, in other words, could almost be placed in the same category as reshoring work that had gone to China."
The German Supply Chain Act was passed with the help of Germany's powerful labor unions, in an act of solidarity with workers employed by German companies all over the world. This is that unexpected benefit to globalism: the fact that Mercedes has extrusions into both the American and German political spheres means that both American and German workers can collaborate to bring it to heel.
The same is true for antitrust regulators. The multinational corporations that are in regulators' crosshairs in the US, the EU, the UK, Australia, Japan, South Korea and beyond use the same playbook in every country. That's doubly true of Big Tech companies, who literally run the same code – embodying the same illegal practices – on servers in every country.
The UK's Competition and Markets Authority has led the pack on convening summits where antitrust enforcers from all over the world gather to compare notes and collaborate on enforcement strategies:
https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/cma-data-technology-and-analytics-conference-2022-registration-308678625077
And the CMA's Digital Markets Unit – which boasts the the largest tech staff of any competition regulator in the world – produces detailed market studies that turn out to be roadmaps for other territories' enforces to follow – like this mobile market study:
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/63f61bc0d3bf7f62e8c34a02/Mobile_Ecosystems_Final_Report_amended_2.pdf
Which was extensively referenced in the EU during the planning of the Digital Markets Act, and in the US Congress for similar legislation:
https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/senate-bill/2710
It also helped enforcers in Japan:
https://asia.nikkei.com/Business/Technology/Japan-to-crack-down-on-Apple-and-Google-app-store-monopolies
And South Korea:
https://www.reuters.com/technology/skorea-considers-505-mln-fine-against-google-apple-over-app-market-practices-2023-10-06/
Just as Mercedes workers in Germany and the USA share a common enemy, allowing for coordinated action that takes advantage of vulnerable flanks wherever they are found, anti-monopoly enforcers are sharing notes, evidence, and tactics to strike at multinationals that are bigger than most countries – but not when those countries combine.
This is an unexpected upside to global monopolies: when we all share a common enemy, we've got endless opportunities for coordinated offenses and devastating pincer maneuvers.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/10/an-injury-to-one/#is-an-injury-to-all
#pluralistic#monopoly#labor#nlrb#germany#harold meyerson#supply chain act#right to work#onshore offshore#uaw#vance alabama#vance#alabama#bafa#mercedes#antitrust#trustbusting
688 notes
·
View notes
Text
🗣️ Please pay attention

Amazon argues that national labor board is unconstitutional, joining SpaceX and Trader Joe’s
Amazon is arguing in a legal filing that the 88-year-old National Labor Relations Board is unconstitutional, echoing similar arguments made this year by Elon Musk’s SpaceX and the grocery store chain Trader Joe’s in disputes about workers’ rights and organizing.
The Amazon filing, made Thursday, came in response to a case before an administrative law judge overseeing a complaint from agency prosecutors who allege the company unlawfully retaliated against workers at a New York City warehouse who voted to unionize nearly two years ago.
In its filing, Amazon denies many of the charges and asks for the complaint to be dismissed. The company’s attorneys then go further, arguing that the structure of the agency — particularly limits on the removal of administrative law judges and five board members appointed by the president — violates the separation of powers and infringes on executive powers stipulated in the Constitution.
The attorneys also argue that NLRB proceedings deny the company a trial by a jury and violate its due-process rights under the Fifth Amendment. (source)
ICYMI, this is a case of corporations going, “7th Amendment Protections for me, but not for thee.”
It is strongly worth noting that in 2018 the John Roberts Court ruled 5-4 that companies can use forced arbitration clauses to stop people from joining together to fight workplace abuses - in effect denying individuals their 7th Amendment protections.
Subsequently, binding arbitration clauses used by corporations has proliferated; sneaking into all manner of common legal documents: personal banking applications, ordinary car loan applications, furniture purchases, and more. This is, unsurprisingly, a direct violation of the 7th Amendment that guarantees HUMAN BEINGS AND PEOPLE the right to a jury trial in certain civil cases and inhibits courts from overturning a jury's findings of fact. Republicans and SCOTUS are perfectly okay with corporations having more rights than workers and using forced arbitration to block people from having access to jury trials—but God forbid if corporations don’t have their right to a jury trial.

This legislative push to bestow corporations with more rights than people, while simultaneously taking away rights from human beings, has been nothing if not thoroughly and methodically done. At this rate, no corporation will ever need to fear a class action lawsuit again.
Amazon, SpaceX and Trader Joe’s are union busting.
But this latest case against the NLRB isn’t just an attack on labor and worker’s rights, it’s a fascistic attack on the very heart of fairness and democracy itself.
#politics#amazon#7th amendment#forced arbitration#spacex#trader joes#nlrb#workers rights#class action lawsuits#labor unions#union busting#collective bargaining#labor law#labor rights#scotus#john roberts court#john roberts#republicans are evil
100 notes
·
View notes
Note
Any recommended reading for a newbie to anarchism?
David Graeber truly is the best entry point into the pipeline i feel. Reading his work doesn't feel like "reading theory", it feels like learning more about a specific aspect of the world from an engaging, open-minded author who makes history and anthropology accessible, and then simply realizing somewhere along the line that you've become a lot more radical than you realized you'd always been.
Bullshit Jobs is his easiest and most approachable read -- start with this if you're not a big reader of dense books, or if my book Laziness Does Not Exist particularly spoke to you. It's about how the majority of reasonably well-paying jobs today are completely meaningless, and why important, fulfilling jobs that are actually necessary to run society are so often thankless and poorly paid.
If you have student loan or credit card debt out the ass or you grew up hearing the myth that the earliest human societies relied on trading and bartering, pick up Debt: The First 5000 Years. This one is a bit of a tougher read than Bullshit Jobs, but still approachable, talking about the history of human commerce, debt forgiveness, enslavement, and where that history has left us today. You'll learn a lot about history but Graeber will also always lead you back to the present.
If you were a follower of the Occupy Wallstreet movement and wonder why it failed (or whether it failed), pick up The Democracy Project. This is a slimmer, faster read! And it focuses a lot more on the practical tactics and bylaws of Occupy organizing. In it, Graeber illustrates how human groups can be run without hierarchy and just how well that can work! It's perhaps the most explicitly anarchist book of his in that sense at least, yet it's also very conversational and easy to follow, with lots of lessons learned and specific examples from real-life organizing meetings.
If you hate rules and bureaucracy, pick up Utopia of Rules. What Debt is for bursting basic, widespread myths about economics, Utopia of Rules is for challenging mainstream knowledge about the role of the state. This one is actually an essay collection, and that makes it a quicker, easier read than many of the others -- in each chapter, Graeber tackles one specific aspect of irritating modern-day bureaucracy, and its full of relatable gripes about going to the DMV or applying for unemployment, but then it zooms out to make a larger point about how societies now function (and fail to function).
If you're interested in Indigenous cultures and how various human societies have approached governance, start with Dawn of Everything, which he co-wrote with David Wengrow. Now this is a MUCH denser book that I recommend taking chapter by chapter, pausing to savor all the new information and paradigm-busting that they've just showered you with. A chapter before bed each night and then some time laying down and simply reflecting about the diversity of human social potential is a great way to slowly work your way through it.
If you read any of these, you'll be left with a lot of ideas as to where to look next -- Graeber was widely read in a great many fields himself, so he'll leave you a trail of breadcrumbs to follow.
The Anarchist Library online is also a great place to find shorter, more explicitly anarchist theory work, once you're ready to delve in. The r/debateanarchism subreddit is also something you should subscribe to and thumb through every once in a while!
112 notes
·
View notes
Note
Which federal laws and policies would you get rid of or modify in order to help the American labor movement.
I was looking through the labor law tag on my blog and your ask reminded me I haven't actually written a comprehensive post about this on Tumblr. (Indeed, you'd have to go back to my old, old policy blog from 2009...it's been a while.)
One silver lining of the Sisyphean struggle to restore American labor law that's been going on since the 1970s is that the labor movement and their allies in Congress, academia, think tanks, and progressive media have been thinking through this very issue of "what reforms would make a real difference" for a long time. I'm not going to say it's a solved question, but the research literature is pretty robust.

For the purposes of this post, I'm going to focus on the three most recent reform packages: the Employee Free Choice Act that was the main vehicle during the Obama years, Bernie Sanders' Workplace Democracy Act (which was introduced repeatedly between 1992 and 2018), and the Richard L. Trumka Protecting the Right to Organize Act (PRO Act) that is the current proposal of the Democratic legislative caucuses. There's going to be quite a bit of overlap between these proposals, because it's very much an iterative process where allies in the same movement are trading ideas with one another and trying to stay abreast of new developments, but I'll try to tease out some of the similarities and differences.
EFCA
While EFCA contained a number of provisions that sought to close various loopholes in U.S labor law, the three main provisions largely target the flaws that have made it extremely difficult to win a union through the National Labor Relations Act process devised in 1935 that has turned into a Saw-style gauntlet thanks to the professionalization of union-busting and the Federalist Society's strategy of death-by-a-thousand-cuts:
"Card check." Probably the most common pattern of union-busting in the workplace today is a war of attrition by management waged by an industry of specialized law firms. Generally what happens is that the union files for election with a super-majority of ~70% workers having signed union cards, then management delays the vote as long as possible to give their hired "union-avoidance" firm to systematically intimidate, surveil, propagandize, and divide workers, up to and including illegally firing pro-union workers pour encouragez les autres. Over several months, what happens is that the initial 70% of pro-union support starts to erode as workers decide it's just too dangerous to stick their necks out, until the vote happens and the union loses either by a squeaker or a landslide.
Card check short-circuits this process by just saying that if the union files with a majority of cards, you skip the election and the union is recognized. And for all the pearl-clutching by the right, this is actually how labor law works in many democratic countries, because the idea of a fair election that lets management participate is an oxymoron.
Arbitrated first contract. In the event that enough workers keep the faith and actually vote for a union, management's next move is to draw out collective bargaining for a year or more. After a year, the original vote is no longer considered binding and employers can push for a "decertification" vote, which they usually win because workers either give up hope or change jobs. So this provision says that if the two sides can't reach an agreement on a first contract within 120 days, a Federal arbitrator will just impose one, so that at least for two years there will be a union contract no matter what management wants.
Strengthening enforcement. As I said above, one of the problems with existing labor law is that there are basically no penalties for management knowingly breaking the law; companies literally just budget in a line-item and do it anyway. This provision would allow unions to file an injunction against employers for unfair labor practices or ULPs (at present, injunctions are only required for violations done by unions), and would add triple back pay for illegal firings and fines of $20,000 for each ULP. This would make union-busting much more expensive, because companies routinely rack up hundreds and hundreds of them during a campaign.
Workplace Democracy Act
Sanders' proposal includes the main proposals from EFCA, and adds a bunch of additional reforms, like mis-classifying workers as independent contractors, banning captive audience meetings, making "joint employers" liable for labor law violations by franchisees, legalizing secondary boycotts, and requiring employers to report to the NLRB on all anti-union expenditures during a campaign and barring anyone convicted of an unfair labor practice from being hired for anti-union campaigns and making "union-avoidance" consultants liable for fines for ULPs (which would kill the "union-avoidance" industry, because they commit ULPs for a living).
PRO Act
The PRO Act is very much an updating of the previous efforts we've talked about. It bans captive audience meetings, allows for secondary strikes and boycotts, massively increases fines and allows for compensatory damages, ends mis-classification, speeds up the election process, etc.
It also contains a couple new and ambitious proposals:
it allows unions to sue management in court instead of having to complain to the NLRB, which opens management up to a very expensive legal proceeding and discovery.
it bans "right-to-work" as established by the Taft-Hartley Act.
it requires that any worker who's fired for pro-union activity be immediately reinstated while their unfair labor practice process or civil lawsuit is going through the process. This would be enormous just on its own, because it changes the entire veto structure of illegal firing. As it stands, employers fire people and maybe maybe have to pay some back wages in a couple years when the worker has found another job and is unlikely to come back. This would reverse the balance of power, such that the worker is immediately back and other workers can see that they can speak up without getting fired, which makes illegal firings a giant waste of time and money for management.
In terms of stuff that's not on this list that I would add, I would say that an enormous difference could be made by simply making it illegal for management to lock-out their workers or hire scabs. You do that, and unions can win almost every strike.
75 notes
·
View notes
Text

The struggle for civil rights in the United States has a murderous history. William Lewis Moore was a staunch advocate for civil rights; he was raised in Mississippi but on the white side of town.
After being institutionalized with a diagnosis of schizophrenia, Williambecame an activist for the mentally ill. He soon became involved with the civil rights movement and fought for the rights of African Americans. William would often organize demonstrations for civil rights and became a member of the Congress of Racial Equality which was a vital ark of activism at the time.
While working as a postman, William came up with the idea that he would hand deliver a letter to Ross Barnett, the governor of Mississippi. He wanted Barnett to fundamentally change Mississippi’s racial hierarchy. In this letter, Moore warned “do not go down in infamy as one who fought the democracy for all which you have not the power to prevent.” Tragically, William never got a chance to deliver the letter; he would be shot dead while walking to his destination.
On the 21st of April, 1963, William set off alone on a 342 mike walk from Chattanooga, Tennessee, to Jackson, Mississippi, to deliver his letter. He was wearing a sandwich board which proudly read: “Equal rights for all & Mississippi or Bust”. Throughout his trek, he was offered drives to his destination but each time he refused; he was determined to march right to the governor’s front door. Around 70 miles into his journey, he was shot dead.
Floyd Simpson, a Ku Klux Klan member, was suspected of being the killer. The gun ownership was traced to Floyd Simpson, whom William had an argument with earlier on in the day. Nevertheless, charges were never brought upon him and the murder still remains technically unsolved.
181 notes
·
View notes
Text
ms appleton was nowhere close to having total control over soy sauce: perspectives on food and postwar japan
there's a popular post going around this month by @inneskeeper about how a single person changed japanese soy sauce forever. i've made my own post showing why this the story is incomplete and based on some factual inaccuracies, but i will be honest in saying that i would not be so engaged in responding to this post if it were not wrapped in a shockingly reductive narrative. i'll use this quote from op as a summary of the general idea they're trying to convey:
[...] I think that it is incredibly important that more people in the world are aware that leading into the Cold War, Japan was forcibly coerced into giving total power over a significant cultural touchstone/ingredient/way of life to a single foreigner who had a complete lack of respect for what shoyu is, even going so far as to say "I want to change Japan's taste preferences". I cannot imagine a more direct and blunt parallel to settler-colonialism mindset. I truly cannot. [link]
i will attempt give a larger view of that era and convey why this singular view is at best oversimplifying and at worst an incorrect projection of other trends upon what is an almost unique event in history.
note: i am not an academic historian; i will do my best to provide sources, but they will mostly be secondary.
i will use the three i's presented by prof. ian shapiro of yale, interests, institutions, and ideals, as lenses through which i will provide a more holistic view of the events at hand:
tl;dr:
the united states did not have uniform interests entering the cold war and the occupiers had a varying set of visions for japanese society and economy.
both the japanese public, the american occupation, and the japanese civil government had a more important goal: preventing hunger. japan was not coerced into handing over a tradition; it was suffering the consequences of its own colonial empire-building.
both countries were interested in building a healthy consumer economy, and ultimately the tastes of the public held most sway.
the idea of "a guy" being in charge of things has been a common theme in american foreign policy, but the idea that "the guy" was singularly responsible for massive change belies american perspectives and biases that often misrepresent the truth abroad.
i - ideals
i think this lens is maybe the most sympathetic to @inneskeeper's narrative: it makes sense that a settler-colonial nation with a deep root of anglo-protestant self-righteousness and evangelical tendencies would want to impose its vision of society upon a defeated foe. that said, it is not the only ideology at play in this situation, from both japan and the usa.
let's talk about main value the united states likes to impose upon foreign societies: democracy capitalism. i think what is interesting here is that this single word can have multiple interpretations in practice, and we can use this soy sauce story to look at the diversity in opinion of what capitalism means.
first, a capitalism tied to liberal ideals: a free and open market without monopolies as a promoter of egalitarianism. this concept was brought to japan by many of the administrators in the american occupation that have previously observed or enacted roosevelt's new deal in the aftermath of the great depression. [1, p.57-58; 2, p.98] we see a focus on trust-busting and a strong aversion to any significantly concentrated capital. pre-war japan was dominated by structures known as 財閥 zaibatsu, vertically integrated groups that are helmed by a family-controlled holding company owning a set of subsidiaries in banking and industry with interlocking stock ownership and directorship. the zaibatsu structures, emerging since the late edo and early meiji periods, have become inextricably linked to building the japanese imperial war machine (though somewhat forcibly). [3] on the american side, as a result, certain american elements viewed trust-busting as a way to democratize japan through the economy. [2, p.34; 4, p.19; 5, IV-2b] this included maj. gen. marquat, ms. appleton's boss at the ghq/scap economic and scientific section (ess). [4, p.31] japan's first postwar prime minister, shigeru yoshida, and his ministry of foreign affairs, seemed to agree with the deconcentration of capital. [4, p.20] this is not to say that the americans were particularly sympathetic, as gen. macarthur and others were quite convinced of the japanese population's inability to shed its feudal tendencies; rather, the americans found an opportunity to build a new liberal, democratic society to their liking. and yes, there was some punitive intent; the united states and allies did just finish fighting an 8-year-long war against an expanding empire. [4, p.30]
opposite the liberal view is the conservative, if not pragmatic, ideal of capitalism: as a bulwark against communism. japan was an industrialized nation with a developed economy, and as far as the looming cold war is involved, the united states wants both a healthy consumer economy and one that is integrated in the new world economy (i.e. one with american interests as stakeholders). [4, p.31-32, 44] if "deconcentration" of capital, as it was called by the occupiers, were to run its course, some americans (and lobbyists linked to japanese industry) feared that japanese society would be thrown into chaos, or worse, the rapprochement with the soviets under a socialist economy. [4, p.22, 32] the victors did initially break up many of the tightly-woven zaibatsu, but the overall health of the economy was eventually prioritized as a bulwark against communism, thus the number of zaibatsu slated for dismantling was reduced, and the main deconcentration proposal (FEC-230) was disavowed. [4, p. 32]
all this debate within the american occupation, plus some interjections from the japanese business community, about the nature of the rebuilding japanese market and economy was held from 1946 to 1948. this culminated in the "reverse course," in which cold war objectives won out in occupation policy, though the free market as a liberalizing principle was not discarded. [4, p.44-46] in the same space, there existed both a punitive drive to disperse the old japanese economic engine and a desire to build a new, genuinely local, consumer society as a protection against communism.
“Nothing will serve better to win the Japanese people over to a peaceful, democratic way of life than the discovery that it brings rewards in the way of better living and increasing economic security.” - col. r.m. cheseldine, u.s. war department [4, p.44]
it is important to distinguish this from the colonialist drive, which is to capture markets and resources for the sole benefit of the homeland.
in the context of soy sauce, the release by ghq/scap of american soybeans to japan was announced in 1948, after the reverse course has taken hold. [6, p.157] in addition, kikkoman was not even a zaibatsu, it was a company with roots in family ownership, vertically-integrated structures, and eventually found to engage in monopolistic practices, but was not of a large enough scale or diversification to qualify. [7, ch.3] the list of zaibatsu is actually quite limited. [wiki] all this meant that the anti-trust case brought against noda shōyu k.k. (kikkoman's predecessor) in 1954 in the tokyo high court is an entirely domestic affair (scap handed over power in 1949 and the position was abolished in 1952). [8, p.53] that said, the 1957 ruling against noda in noda shōyu k.k. v. japan fair trade commission (jftc) was the result of an aberrant and unfavourable reading of the act on prohibition of private monopolization and maintenance of fair trade, article 3; the act was passed in 1947, when scap was in power. [8, p.53] since article 3 is quite short ("an enterprise must not effect private monopolization or unreasonable restraint of trade."), it was open to wide interpretation, leading to the argument by the jftc that price-fixing as a leading player in an industry constituted monopolistic behaviour. [9] in that sense, we can see echoes of the debate around monopolies from the occupation era.
through the lens of ideals, we can see that in the periphery of this story, there is a friction between competing visions of capitalism in practice. in that sense, while it agrees that the usa had some desire to reshape a foreign country to its own ideals, it also shows how @inneskeeper's narrative unduly reduces the american occupation to a singular actor with singular motives, and one that is akin to colonial empires in other parts of history.
research questions:
did american attitudes towards monopolies affect the free distribution of semichemical fermentation methods? [6, p.160]
what direct links can we make between occupation-era attitudes towards monopolization and japanese governance regarding the food industry?
ii - institutions
from the point of view of institutions (i use the term loosely), it's a lot more apparent how the situation has a lot more factors flowing in many directions. i will largely focus on three structures: the japanese food industry, the allied victors, and the japanese civil government.
when discussing the food industry, it's important to note that this is what sustains the inhabitants of a place; while condiments are a trivial part of sustenance, the way it is made and its ebbs and flows and shed a lot of light onto the needs of people. japan, since the early 20th century, had been a country that could not sustain itself off the resources of its home islands. as a colonial empire, it relied on food imports from korea and taiwan, and in the 20s and 30s pursued the low-lying plains of manchuria (northeastern china). this reflects in its soybean consumption as well: japan consumed about 1 million tons of soy each year in the 1930s, and at least two-thirds of it was imported from the colonies or manchukuo (the puppet régime ruling machuria). [10] within what we now call the "home islands" of japan, hokkaido, the one remaining settler-colony of japan to this day, produces the most out of all regions. [11, p.4]
(time for some math: [10] states that about 949 000 tons of soy sauce was consumed in japan per year in the mid-1930s. a quick look at soy sauce recipes reveals that 1kg of soy produces about 4 litres (and assuming about 4kg due to density of water) of sauce. with the 4:1 ratio, we can therefore estimate that about 237 000 tons of soy was used per year to make sauce immediately before the war.)
the end of the japanese empire meant losing direct access to those production areas: manchuria was returned to china, and korea and taiwan were placed under various allied (usa, china, ussr) administrations. with japan needing to supply its troops over an ever-growing front line, caloric intake by the average japanese already dropped well below necessary levels for an adult by 1944. [12] by 1946, the defeated nation was at the brink of starvation. american analysis towards the end of wwii determined that soybean production in the home islands could not rise beyond its pre-war levels without sacrificing other land use. [11, p.5] in order to survive, the soy industry needed to replace about 70% of its sources in short order without encroaching upon other agricultural sectors necessary to sustain life. there was immense pressure.
regarding the allies: the japanese empire was largely carved up by three victors, china, the ussr, and the usa. the ussr, having been the least active in the defeat of japan, with its most important contribution being the verbal threat of invasion, was not actively threatening aside from the spectre of spreading communism (as mentioned in part i). china, on the other hand, regained the lands that produced much of the food japan was consuming. while the republic of china (ruled by the kmt) was still in power, it was able to continue supplying food to neighbouring nations. [14] however, civil war broke out between the kmt government and the communists almost immediately after the end of wwii. [13] 1948 saw active fighting in northern china, thus hampering any exports of food; the kmt régime collapsed and fled to taiwan in 1949, and the communist government stopped all trade with the western bloc at the outbreak of the korean war in 1950. [14] with china being unable to supply japan, there is only one remaining option for food imports: the usa. soybean imports in the usa was generally coordinated by the garioa program and through private trade. american exports of soybean to japan skyrocketed from 6000 tons in 1946 and 34600 tons in 1947 to 119500 tons (about 12% of pre-war consumption) in 1948, 152500 tons in 1949 (almost all imports to japan that year), and 305000 tons in 1950. [15, p.67, 69] japan itself likely produced between 300 000 and 450 000 tons of soybeans each year, which meant that in 1947-48 japan was consuming definitively less than two-thirds of its pre-war consumption. the soy industry as a whole, and certainly the soy sauce industry, was in a desperate state.
unlike the collapsed german and italian régimes, the japanese government retained a functioning structure after the rapid end to hostilities in the pacific theatre. [16, p.194] this meant that instead of being tasked with the groundwork of running a country, the allied powers had an existing civil government to administer directives and policies; the u.s. eighth army served as an enforcement and reporting arm of scap. [16, p.195-197] during the war, from 1939 to 1942, the imperial government instituted various food control laws that collected and distributed food from producers under a quota system. [17, p.221] such quotas, as as well as rationing, persisted in the immediate months after allied victory. however, with the surrender of japan, public confidence in the government plummeted, significantly hampering its ability to administer food. the average caloric value of rations in tokyo could only fulfill about a third of an adult's needs; hungry city-dwellers increasingly opted to buy on the black market (which had poached imperial military stock) or physically go to the countryside to acquire food directly from farmers outside of government rationing. [18, p.30-31; 19, p.835, 843] scap policy directed the japanese government to "reinstate" agricultural quotas, and in 1946, it issued the emergency imperial food ordinance which empowered government expropriation of food for the production quota and enforcement of such policies; the u.s. eighth army participated in enforcing the policy within the civil administration. [17; 18] the yoshida government,the first democratically elected administration in the new state of japan, was keenly aware of the necessity of food in rehabilitating japan, as well as the importance of competing against the black market in order to once again establish the rule of law. [18] as such, the tight government control of domestic food production lasted much longer than in other industries, causing pressure for "non-essential" segments like the seasoning industry.
(as an aside, in line with certain ideas discussed in part i, scap directed land reform which redistributed much of the arable land in japan, increasing productivity of land and eliminating the interest of large landowners thought to be threatening to democracy. [18])
as discussed in my previous post, chemical alternatives to fermented soy sauce have been developed since the early 20th century. [6] during the war, substitute methods (especially amino acid-based ones, e.g. hvp or mixed hvp-honjozo) replaced fermented honjozo* methods as resources became more scarce. [20]
*honjōzō (本醸造) means "genuinely fermented".
in early 1948, it was announced that 20 000 tons of soybean meal would be made available by the eroa fund for the purpose of making seasonings, to be allocated by ms appleton at ghq/scap. [14; 6, p.159] this amount is only about 10% of the soybean consumption of soy sauce manufacturers before the war. on the surface, for an industry marginalized by the need to stave off starvation and maintain social stability, securing the imported soybean meal can be seen as a life-or-death situation. however, given the wartime state of sauce production, the struggle to acquire the soybean meal is more akin to an attempt to return to fully soy-based fermentation methods. the invention of the semichemical #2 method which increased soy usage productivity and secured most of the soybean meal for the soy sauce industry can be seen as a faster intermediate step to return to traditional fermented methods used before the war. it's also important to note that over 80% of soy sauce in japan has returned to traditional honjozo production, and that large companies such as kikkoman and yamasa have attempted to return to honjozo methods as early as the late 1950s. [20]
from this point of view, it does not seem particularly apparent that a single administrator had the power to change an industry, but rather her decisions were the impetus for developments to happen within the domestic industry. ultimately, japan's soy sauce industry was suffering the consequences of its industrialization and the failure of its colonial experiment. in a wider view, we can see this as a detail in the friction between two imperial projects. (consider this: out of the major parties involved, japan, china, usa, ussr, and other minor players in the pacific war, gb, netherlands, france, all of them entered the 20th century with imperial projects.)
research questions:
are there japanese sources that can verify production and imports during the 1940s?
there was a soy sauce control corporation formed by the imperial government in 1942 (��国醤油統制株式会社) that dictated resource allocation and quotas for the soy sauce industry. it seemed to have only been dissolved in 1948. what was its role after the war and what relationship did it have with scap?
iii - interests
as for interests, i will limit its scope to answering "who materially benefits." the groups at play are generally the same as the previous part, so i will be brief in elaboration.
the most obvious interest is that of the japanese public: their main material benefit in the late 1940s is to be nourished enough to stay alive (see part ii). while soy sauce is an important part of japanese cuisine, as a condiment, it is a nutritionally trivial part of its diet. it is then understandable, that japanese society and scap would be willing to temporarily sacrifice an immediate return to traditional production in favour of methods that would leave more food for direct consumption.
the next interest to discuss is that of the soy sauce industry, and its desire to return to honjozo (traditionally fermented) production after a period of scarcity during and after the war. it is important to note that regarding the 20 000 tons of soybean meal to be allocated by scap in 1948, the competitor to the soy sauce industry for those resources is the amino acid industry (msg, etc.). [6, p.159] with soybeans hard to come by, the soy sauce industry would have been under immense pressure to aquire the soybean meal distributed as aid. with kikkoman's development of semichemical #2 method, the scap decisionmakers reconsidered an earlier uneven distribution of soybean meal in favour of the amino acid producers. [6, p.160] what resulted next was talk between representatives of the two competing industries, facilitated by the americans. [6, p.160] it is important that taste trials were conducted, with wide support for the new semi-chemical method by the polled public. [6, p.160] at every step of the decision-making process, japanese interests were consulted by scap.
it is also important to mention the "japan lobby" in washington a set of interest groups and lobbyists representing japanese business as to illustrate the bidirectionality of influence in postwar japan. [21] this group arose from the aftermath of the first zaibatsu dissolutions. some key achievements of their advocacy activities include the disavowal of the fec-230 policy proposal from the allied powers (against gen. macarthur's wishes!), and adding revisions to scap's economic deconcentration program. it is plausible that this lobbying set had influence with scap and washington regarding soy sauce, given the tight-knit nature of the japanese business class. that said, the direct link between the japan lobby and soy sauce, should it exist, necessitates further research.
i think it is necessary to analyze from the lens of interests @inneskeeper's claim of the united states occupation forcibly seizing and making changes to a traditional food industry. it is known that the united states seeks to build a strong consumer economy that is open to american investment and imports of american products. [18, p.40] given that the soybean meal managed by scap in 1948 was aid, it would've been in the american interest to support either industry, since they would both eventually rely on american imports once the period of scarcity ends (china would soon cease ot be a reliable exporter of food). there is nothing related to soy sauce that would've been against american interests, business or political, whereas food scarcity has been a real problem facing the japanese and allied administration. in this case, the chief american interest is to stabilize japan as a society against two perceived social enemies: communism on the left and a renewed militarism borne of resentment on the right. with the task of placating a hungry and defeated populace, producing large amounts of soy sauce that is palatable to the public using minimal aid material would be an interest in and of itself for the americans. i think it could be argued whether comments made by americans about how easily japanese tastes can be swayed are insensitive and out of line, but it is also true that the public had much more pressing needs than condiment purity.
@inneskeeper also mentioned the yakuza in some of their posts as a possible interest group involved. the informal economy grew to encompass all strata near the end of the war and immediately afterwards; most urbanites were forced to use the black market to stave off hunger. [19] the yakuza, mafia-like organizations that would operate somewhat openly in the decades before the war, entered the fray as groups that managed informal vendors. [22, p.632] racketeering became rampant in the years immediately after japanese surrender due to shortages and irregular flows of necessities such as food, but as the economy recovered entering the 1950s, the yakuza moved to more conventional underworld enterprises such as as gambling, prostitution, and nightlife. [22, 23] it also moved towards the underbelly of political life, becoming an actor in anti-left politics. [22] we know that the changes to soy sauce production happened in the small window between the end of the war and the earnest start of economic recovery, so it is possible that parties involved would have to deal with the yakuza as a necessary source of material. however, since their sights are set on the industries traditionally associated with the underworld, it would be a stretch to say that they had any real say in the proceedings of this development beyond being one additional obstacle to the soy sauce industry in acquiring ingredients. that said, using a singular product can be very useful as a window into how the yakuza may have coerced informal food distribution channels.
research questions:
what specific outcomes were agreed upon at the "shoda-ouchi conference" between the soy sauce and amino acid manufacturing industries? [6, p.160]
how did the japan lobby affect or facilitate changes in the soy sauce industry?
how did the yakuza affect the informal food economy?
iv - individuals
one thing that made the original story by @inneskeeper so appealing to the tumblr public is the proposition that a single person may have changed japanese soy sauce forever.
it bears repeating that major industrial changes (and i would challenge the categorization of this soy sauce happening as "major" in comparison to the general state of japan in the 1940s) are often the culmination of many small decisions from a wide set of actors. what is interesting about the idea of a singular "manipulator" is that it mirrors a common trope in american foreign policy: the idea of "our guy" (e.g. "our guy in afghanistan" [24, p.277], "our guy in panama" [25], etc.), that is, a singular handler for american interests in a foreign theatre of operations. in this case, since the country at hand is managed by an american occupation, "our guy" in the japanese soy sauce industry is an american, ms. blanche appleton. while american policy sometimes prefers to use this paradigm, it does not necessarily mean it works, not is the wishful american imagination correct when it comes to situations on the ground (see citations above). this trope may also possibly be borne of the oft-cited concept of "american individualism," a value that is as much a contradiction (how can a single person be free to change the world as they see fit, while also live in a world free from the will of others?) as it is a real part of american culture.
in the faulty narrative of ms. appleton, we also see a similar contradiction: how can a foreign woman who is allegedly willingly unfamiliar (as it turns out, probably not true [6, p.160]) with the native culture be in total control of an entire element of its cuisine? what is the meaning of "total power": did she personally decide taste profile of the condiment to her tastes, coerce various native parties to the will of the americans (what will?), or facilitate the solution to a complex resource distribution problem? in any case (except the fancifully implausible first case), what is the singular role of ms appleton? did power flow from her, or through her? perhaps a more interesting way to look at this problem is to ask what would have happened if someone else were in ms. appleton's place. would their personal influence be significant enough as to change the outcome? if so, what would have been the extent of the changes? (we can maybe look at the facilitation of the "shoda-ouchi conference" as one point. [6, p.160]) conversely, what would have remained the same as the various parties involved influenced the situation?
a more helpful view is to see the balance between the ideas, institutions, and interests behind each decision that would paint a more complete picture of this historical era. perhaps it is not as flashy to break down a chapter in culinary history as the convergence of multiple influences, but it is the one that does history most justice.
discussion questions
this is for the test
how significant was the dearth of food in late 1940s japan to this situation, and what similar adaptations of food cultures occurred in other post-wwii nations?
what factors from imperial japan, whether before the sino-japanese war or during the war, influenced this situation?
is there any part of this development that forshadows the economic rehabilitation and subsequent growth of japan in the latter half of the 20th century? if so, how?
what american attitudes were at play in this situation, and what japanese attitudes (if you're familiar) were involved as well?
what influence did china, as the originator of soy sauce, a major source of food in east asia, and a significant allied power, have on postwar japan and how did it influence the development of the japanese variants of soy sauce?
what was the influence of the japanese public's tastes?
bibliography:
apologies for the weird mix of ieee inline and mla bibliography formats, ieee works best with hypertext but doesnt make much sense for non-stem subjects.
Allinson, G. D. Japan's postwar history, Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 2004. [link]
Moore, R. A., & D. L. Robinson. Partners for Democracy : Crafting the New Japanese State under MacArthur, Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, Incorporated, 2002. [avail. at libraries]
Okazaki, T. “The Japanese Firm Under the Wartime Planned Economy,” in The Japanese Firm: Sources of Competitive Strength, edited by M. Aoki and R. Dore, Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1994. [link, requires academic access]
Sugita, Y. Pitfall or panacea : the irony of US power in occupied Japan 1945-1952, New York: Routledge, 2003. [avail. at libraries]
State-War-Navy Coordinating Committee. United States Initial Post-Surrender Policy for Japan (SWNCC150/4), 1945. [link]
Oguri, T. "醤油製造技術の系統化調査 Development of Soy sauce Manufacturing Technologies" in 国立科学博物館技術の系統化調査報告, Tokyo: National Museum of Nature and Science, 2008.
[link; translation of excerpts in an earlier post]
Fruin, W. M. The Japanese Enterprise System: Competitive Strategies and Cooperative Structures, Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 1994. [link]
Haley, J. O. "Marketing and Antitrust in Japan" in Hastings Int'l & Comp.L. Rev. 51 Vol. 2 No. 1, San Francisco: UC Hastings Law, 1979. [link]
Japan, National Diet. Act on Prohibition of Private Monopolization and Maintenance of Fair Trade (Act No. 54 of April 14, 1947), Tokyo: National Diet, 14 Apr. 1947 [link]
Nakamura, H. "The Japanese Soybean Market" in Illinois Agricultural Economics Vol. 1, No. 2, Milwaukee, WI: Agricultural & Applied Economics Association, 1961. [link]
United States of America, Tariff Commission. Japanese trade studies : special industry analysis no. 13, Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1944-45. [link]
United States of America, Strategic Bombing Survey. Summary Report (Pacific War), Washington, DC: Government Printing Office, 1946. [link]
Crisis, Time, 1944. [link]
Hirano, M. "Using American Soybeans in the Japanese Economy" in The Soybean Digest Vol. 12 Iss. 11, Cleveland, OH: Penton, 1952. [link]
United States of America, Department of Agriculture, Foreign Agricultural Service. United States Farm Products In Foreign Trade, Statistical Bulletin No. 112, Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture, 1953. [link]
General Staff of Gen. D. MacArthur. Reports of General MacArthur - MacArthur in Japan: The Occupation: Military Phase Volume I Supplement, Washington, DC: Center for Military History, 1966, reprinted 1994. [link]
Smith, H.F. (Chief, Food Branch, Price and Distribution Division, ESS, SCAP) "Food Controls in Occupied Japan" in Agricultural History Vol. 23, No. 3, Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 1949 [link]
Fuchs, S. J. "Feeding the Japanese: Food policy, land reform, and Japan’s economic recovery" in Democracy in Occupied Japan: The U.S. Occupation and Japanese Politics and Society, edited by M. E. Caprio and Y. Sugita, New York: Routledge, 2007. [link]
Griffiths, O. "Need, Greed, and Protest in Japan's Black Market, 1938-1949" in Journal of Social History Vol. 35, No. 4, Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2002. [link]
Oya, Y. "みそ製造業の構造変化とその要因" in 食品経済研究 第30号 (Bulletin of the Department of Food Economics, Nihon University), Tokyo: Nihon University, 2002. [link]
Schonberger, H. "The Japan Lobby in American Diplomacy, 1947-1952" in Pacific Historical Review Vol. 46, No. 3, Oakland, CA: University of California Press, 1977. [link]
Siniawer, E. M. "Befitting Bedfellows: Yakuza and the State in Modern Japan" in Journal of Social History Vol. 45, No. 3, The Hidden History of Crime, Corruption, and States, Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2012. [link]
Hill, P. B. E. The Japanese Mafia: Yakuza, Law, and the State, Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2003. [link]
Blaxland, J., M. Fielding, and T. Gellerfy, Niche Wars: Australia in Afghanistan and Iraq, 2001–2014, Canberra: ANU Press, 2020. [link]
Kornheiser, T. "Noriega Our Bountiful Nation" The Washington Post, Dec. 22, 1989. [link]
604 notes
·
View notes
Text
Musk should be jailed or at the least deported for the damage he has caused democracy in this country. Another immigrant/refugee who wants to pull the ladder up behind him. He fled South Africa to dodge the draft, was let into Canada, and somehow made his way here and now practically runs the country. MAGA assholes think he’s some great scientist and futurist. He’s Jack shit who inherited a fortune from his parents and then bought all the businesses he claims to have founded. He’s no scientist either, he only has a simple bachelors degree in economics which qualifies him to be an assistant manager at Taco Bell. He tells people he has another in physics but his college says no. Even if he did have it a bachelors degree doesn’t make you a scientist, in fact you can’t even teach elementary school with just a bachelors let alone colonize Mars.
He’s such a Nazi incel dweeb. A cancer on this country. A union busting sack of fascist feces that’s been festering in the hot sun of some failed confederate red state.
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
☝️
Highly recommend. A glimpse into the right-wing network of conservative think tanks and non-profits working to promote a pro-business culture, weaken all social programs, and undermine democracy.
Everything from weakening child labor laws to writing Trump’s Project 2025, although the authors refused to use the term “Project 2025” in their description of it.
Republican politicians never come up with legislation on their own. All Republican policy is crafted and written by right-wing political associations and then handed to Republicans stooges to sign and introduce into Congress. It is this behind the scenes network of oligarch dark money funded think tanks that are waging war against us.
You protest individual Republican politicians and their policies but neglect the oligarchs like Koch, Walton, Crow, and DeVos that actually write those policies. Then you support those same oppressive oligarchs by buying Koch products, shopping at Walmart, and sending your kids to charter schools operated by DeVos.
Thousands of us have been calling for a boycott of Walmart since the 90’s but the majority refuse because it would be inconvenient. I don’t want to drive an extra few miles to the store or I don’t want to spend and extra dollar at another store. Common refrains whenever a boycott is broached. Walmart is the most obvious target because they are not diversified like other oligarch families. A short boycott would change their tune real fast.
You know what’s really inconvenient; black people being executed in the streets by cops and denied the right to vote. You know what else, trans people being eliminated and lgbt being stripped of legal rights as citizens. How about bounties being placed on women who have abortions and women who have to travel across country to have those abortions and often having lost the right yo safely return to their home state at all. Migrants being held in camps and being separated permanently from their children is also inconvenient as is the human trafficking of them. How about the re-introduction of child labor without parental consent being required. Maybe unions being busted, pensions and health insurance being stripped, minimum wage being reduced and full-time jobs arbitrarily being turned into part-time jobs. I could go on and on here.
STOP USING YOUR DOLLARS TO SUPPORT THE OLIGARCHS AND CORPORATIONS THAT OPPRESS YOU.
#Searles pharmaceutical#project 2025#vast right-wing conspiracy#Koch network#boycott Walmart#cato institute#federalist society#ALEC#Koch family oligarchs#Walton family oligarchs#Harlan Crow Neo-Nazi oligarch#Betsy DeVos oligarch#Leonard Leo#Mackinac Center#dark money#Conservative oligarchs creating a fascist America#RESIST#Citizens United#reproductive freedom#gun lobby#voter suppression#voter disenfranchisement#lgbt persecution#Black Lives Matter#republican assholes#Republican oligarchs#republican values#evangelical Taliban#Theocracy#Dominionism
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
commies are catching strays over calling Biden fascist. Biden is a liberal, fascism is a political ideology, etc.
the commie line on fascism is that it is capitalism in crisis and the capitalist use the weight of the state and markets to bring working class to heel to quick fix the economy.
We see this with Biden busting the rail strike, the never ending waves of layoffs which coincide with increased interest in unionization, states legalizing & encouraging child labor, the rise in prison labor, the contradiction between the necessity of undocumented labor and build the wall — which as we’ve seen multiple times over recently Biden has the same line on this as far rightists (“he was an illegal”; offering to build the wall and other border measures per republican doctrine). the economy is booming according to gdp (the capitalist measuring stick of economic success) but nobody can afford groceries.
the genocide in gaza is a manifestation of this as well. much has been written on israel and the us not having a game plan. there’s no strategic victory just death and destruction for its own sake. all while weapons manufacturers get paid.
the proxy war with russia and posturing toward china hints to this as well; both challengers in some way to us imperialism. But we see the weakness exposed bc the comedian president who used to get gold saucers is now begging for scraps. can’t fund ukraine an israel infinitely.
yemen and ansarallah also expose how stretched the empire is when it seized 3 ships back in october, along with the hilarious fallout of the initial phase of prosperity guardian and the fact that the us has yet to open the red sea.
and insofar as liberalism is opposed to fascism… well we won’t look too closely at the transfer of power in Germany say around january 1933. nor how obama expanded repressive state apparatuses like surveillance, militarized police, unilateral presidential powers, setting a public precedent of extrajudicially killing us citizens and handing it off peacefully to trump, who is evidently a unique existential threat to democracy. nor how in every fascist regime the liberals, who are capitalists, sell out the commies, who are anti capitalists, to the fascists, who are capitalists.
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frank Vyan Walton at Dark Skies on the Horizon:
Among the many MAGA myths, this may be one of the most enduring and at the same time the most ridiculous. Even though they have deliberately chosen not to watch the January 6 hearings, they have plenty of opinions about them. Antifa implemented the attack, it was part of a false-flag plot by the FBI using informants, it was all Nancy Pelosi’s fault because she didn’t call the National Guard. And the hearings are a “Which Hunt” with a “Narrative.”
They have no regrets for the Insurrection, they have no apologies to give. They think that they are the ones who have been wronged, they believe that they were justified. [Even though they totally weren’t.]
[...]
There is no way that Trump didn’t know that these people did not “Stay” peaceful, thousands of them weren’t peaceful at all. This was part of him constructing a narrative, he had said at the ellipse we're going to “peacefully march” but that was bullshit because he already knew there were weapons in the crowd. He already knew how angry they were. His saying “Stay peaceful” here was part of his plot to blame that violence on Antifa, or whoever — which he did during a phone call with Kevin McCarthy — and pretend that his supporters didn’t enter the Capitol and didn't fight with police.
But they did.
Trump supporters were the ones who gave Officer Fanone a concussion, a heart attack and tased him repeatedly. They were the ones who attacked Sgt Gonell and gave him a permanent shoulder injury. They were the ones who caused Officer Sicknick to have a stroke, and several other officers to commit suicide. They were the ones who injured 150 Officers leading to five of them dying, and also four protestors dying during the attack.
This is the final straw, with this statement he made it clear that he was on the same side as the rioters. And they were on his side.
He initiated the rally. He instigated the attack. He picked the time, date and place. He used the people and the MAGA members of Congress as tools in his two-pronged assault on democracy. He didn't care that they were armed and dangerous. He didn't lift a finger to *stop* the attack while it was in progress until he was satisfied that they had stopped the vote and couldn't accomplish anything more.
He said “Peacefully” just to cover his ass and set up the narrative that the violence was from someone else.
But then if it really was Antifa, why is it that he’s since offered to pardon and offer a governmental apology to the rioters if he gets re-elected. Why would he do that for the “Violent Leftists?”
And he’s not just offering this pardon to the people who were actually “peaceful” and stood outside the Capitol. [Even though just being past the sidewalk and on the Capitol grounds was a crime, since the facility was closed to the public at that time.] He wants to pardon the people who are currently in jail for violent acts, who fought with the police, who vandalized the building and smashed their way inside, who were trying to hunt down and kill Nancy Pelosi, who wanted to “Hang Mike Pence.” This is a reward, and those the people he wants to give it too.
He’s on the side of the worst of the crowd, the Proud Boys, the Oath Keepers, the III Percenters, the racists and the domestic terrorists.
And they’re on his side.
This was not a boating accident. None of this happens, not the rally, not the march, not the attack, not the attempt to implement the fake electors, without Trump being behind all of it.
Every step of the way.
Frank Vyan Walton debunks the myths MAGA extremist spew out in regards to the Donald Trump-incited January 6th Insurrection.
#Capitol Insurrection#Donald Trump#Oath Keepers#Proud Boys#Women For America First#The Big Lie#Cassidy Hutchinson#Zachary Rehl#Enrique Tarrio#Amy Kremer#Frank Vyan Walton
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
National personification
The UK has Britannia. France has Marianne. The US have Uncle Sam. National personifications, summing up supposed collective qualities and passing on a message, both to citizens and foreigners alike. Instantly recognizable by just about anyone. To be found everywhere, from city halls (busts, frescoes, tapestries) to subway walls (Army conscription posters - of course it rings a bell!).
Romania has this:

This is Revolutionary Romania, as seen by C.D. Rosenthal, an Austrian painter who found both friendship and an avid clientele among the Romanian young rebels who tried and failed to overthrow the corrupted Ottoman rule, in 1848. Following them in exile and probably also spying on their behalf, Rosenthal was finally arrested in Budapest and tortured to death by the Imperial authorities: a normal occurrence in troubled times. His memory went on and on and on, because the same friends were soon to come back home and become ministers, bankers, newspaper owners: a modern democracy slowly emerged.
This is his most famous portrait and it quickly became our Britannia of sorts. Ceaușescu had it placed in his office, for inspiration - it did not help much, though.
The woman painted by Rosenthal holds the red, yellow and blue flag and is dressed in a Southern peasant costume, as it was worn at the time. She gazes with strength, determination and confidence towards a future that spells free press, parliamentary elections, industrialization and capitalist speculation. In real life, she is Maria Rosetti, a personal friend and sponsor of his. The wife of C.A. Rosetti, an authentic Prince of Genoese and Greek stock, one of the leaders of both the rebellion and the future Liberal Party. Also a many times removed relative of this blogger - but let's not insist. 😉
There is a catch, however, in all this fine and dandy story. Our national personification, the woman I just mentioned, is Scottish. Her life begins in Guernsey in 1819, as Marie Grant, the daughter of Captain Edward Grant, a ship-owner businessman and member of the Clan Grant of Carron and Spey and Marie La Lacheur, a French Huguenot woman.
These people, who fought as Jacobites at Prestonpans and Culloden and whose motto was 'Stand Fast':


Marie came to Wallachia, or what is now the Southern part of Romania, around 1837, following her younger brother, Effingham Grant, who just managed to find a lucrative job as the private secretary of another Scot (Glaswegian, even), Robert Gilmour Colquhoun, the newly appointed British Consul-General. At the time, these were long term postings, not unlike a long sojourn on a space station of sorts: Colquhoun remained in Bucharest from 1835 to 1854, when he eventually was posted to Bosnia.
Because she needed to support herself, Marie found a well paid live-in job as a governess for the family of Ion Odobescu, a high ranking Police honcho (also a far removed relative, this time on my maternal grandmother's side - the world is really, really small). The rest was easy enough: having met Rosetti through her brother, they fell in love, eloped to Plymouth and got married there, for what was to become a life long equal political and business partnership. Because they owned several newspapers, she is our first female journalist. A truly remarkable woman, a philanthropist and an indispensable voice advocating for the dispossessed. Effingham went on to establish the biggest foundry in the country, along with a real estate company, a tobacco manufacture, an orchid greenhouse and a bread factory - all prospered beyond any expectations. A heavy traffic steel bridge in Bucharest still bears his name. Enduring legacies.
For those brave enough or bored enough to look for more, here is the best detailed account on her I could find, based on Guernsey sources (but not only): https://www.priaulxlibrary.co.uk/node/386 .
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
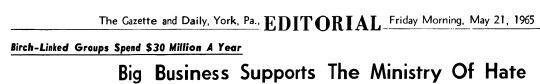











May 21, 1965.
"Radical reactionaries are literally undermining American democracy … to achieve that end the right-wing propaganda apparatus now spends upwards of $30 million annually … The money that greases the hate-machine of the right comes mainly from the coffers of big business, industry and union-busting employers."
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
SOTU - 2024
Well, I'm forcing myself to watch the State of the Union while I grade speeches, so I figured I'd record my reactions and thoughts here.
Do I hope for the words "Immediate Ceasefire"? Absolutely. Will we get them? Looking at the track record, probably not. But I remain optimistic because otherwise I'd be six feet under by now; ANYWHO here is a list of my reactions/thoughts/general feelings of the evening's watch.
I do want to give a point of clarity: I technically am identified as a democrat; truly, I'm a socialist, but seeing as how the U.S. is stuck in this godforsaken two-party-system, that is where I am. Though both sides have me feeling very french-revolutionary-esque.
Of course the first thing I see if MTG rifling through her purse on screen. I quite literally despise her.
AP is discussing Ukraine's need for weapons and funding; I would truly rather us align with Ukraine than Isr@el. I will stand unapologetically firm for Palestine and Ukraine.
Who is actually in the cabinet? I know Blinken, Garland, and Buttiegeg. Damn, wish he was running again. Would rather have him than Biden.
How insane is it that the Sec. of Defense didn't even let the White House know that he had to go in for surgery because of cancer. Like, that's just bonkers to me.
Republicans truly look like fucking robots right now. No warm greetings, no hellos, simple nods.
Republicans out here wasting fucking time with that impeachment of Mayorkas. Like how about we house the homeless populations with the money they wasted on this circus.
Oh funky fresh look at the Ultra-Mormon(TM) Mitt Romney.
MTG with that stupid fucking MAGA hat on is just... disgusting. Like this bitch is crazy.
Okay Joe, speed it up down the fucking aisle please. I got papers to grade.
Lowkey Joe looks like he might have had a five-hour energy drink with that big-ole look in his eyes.
I do appreciate that Joe still smiles and is kind to MTG. She truly doesn't deserve it.
Okay this is getting just a wee bit too monarchy for me.
MTG holds up a button saying "Laken Riley..." (couldn't read the rest). Riley was a 14 year old girl murdered by a man who was an illegal immigrant of venezuela, and instead of handling this situation with grace, empathy, and love; MTG and others seem to be capitalizing on her death to push their anti-immigration rhetoric.
Okay, cool selfie skills Joe, but let's get on with it.
ALSO HOW IS JOE BIDEN GONNA BE SO IN DEPTH WITH TECH AND "Savvy" WITH IT WHEN MOTHERFUCKER WANTS TO BAN TIKTOK!? Hello?!
BERNIE AND RAPHAEL! I feel like I haven't seen these guys in 10 million years.
Oh thank god we're starting.
Aww the little hand shake thingy he does with Kamala makes my heart happy.
Did Joe just yell "tony"?!
Wow, even got some republicans clapping for him (probs not a good thing but here we are)
Okay, good bit of humor at the top; and a throwback to the 40s. Funky fresh.
Yeah we ain't living in ordinary times for damn sure.
Interesting point of democracy being attacked here in the U.S. AND Internationally. (Mentions Ukraine and Putin; no word on Gaza yet).
Someone busted out a Ukrainian flag and shook it; rock on.
OH SHIT HE GOT MIKE JOHNSON TO CLAP!
Appreciate the insistance that the U.S. won't send troops to UKR.
Good use of Reagan to connect with the Repubs; and compare to the predecessor (aka Tr*mp).
Mike Johnson nodding instead of clapping about the predecessor comment, trying to save his ass in Orange Man's eyes.
Welcome to NATO, Sweden!
If there is one thing that should connect Democrats and Republicans; it's hatred for Putin. Yet there's a mix of Repubs standing in agreement and sitting to back up the predecessor's comment on Putin doing "whatever the hell he wants"
Talking about Jan 6. What breaks my heart? My parents still believe it wasn't an insurrection. Yikes on Bikes for me.
The line "You can't love your country only when you win" hits hard and even got Mike Johnson to applaud in agreement.
Foreign AND Domestic. Need a hefty focus on that with the right-wing republican group (@ MTG, Gaetz, Cruz, etc.)
Discussing IVF in Alabama; good connection to the overturning of Rowe v. Wade. It sucks that Republicans HAVE THE POWER to protect IVF nationally but shot the damn bill down not even a week ago.
ABORTION IS A HUMAN RIGHT. BODILY AUTONOMY IS A HUMAN. FUCKING. RIGHT. (@ The Missouri Senators who support taking away bodily autonomy).
WOMEN AREN'T WITHOUT ELECTORAL AND POLITICAL POWER; WE ABOUT TO TURN UP IN FORCE MOTHERFUCKERS!!! Bring back the strats from the 1900s; time to use our power and go bonkers.
Someone get Joe a glass of water please. Motherfucker looks a bit parched and keeps coughing. I get that when my throat goes dryyy
Can Biden not restore RvW? Can he not by an executive order make RvW the law of the land already?
Revisiting COVID's start from 2020 (Next week is the four year anniversary since the global pandemic).
PFFT idk who just yelled "LIES" but that was comical AF.
Well, the pandemic still controls a big part of our lives... so...don't agree with that shit.
Man, everyone sitting-and-standing must be getting a HELLA calf work out.
Sure, unemployment is down and new jobs are built; but corporate greed is quite literally killing us. Can Congress or Biden do something, damn it?!
Are we beginning to feel it, though? Are we feeling good economics? I doubt we are.
Good job pointing out how both parties have failed to buy american products, but how this admin has established that.
There's a good two rows of Republicans who stand in applause; but the rest just... sit there. Like robots. It's freaky as fuck.
Joe is actually doing pretty great with the flow of this speech. Only a couple of stumbles, but overall pretty gucci. (He'd get a 9/10 on delivery in my public speaking class).
God these fuckers are really gonna make me run for office at this damn point.
Removing poisonous lead pipes... but there's still a water crisis in Flint, Biden. Like, what the fuckeroni do you mean?
Yes, let's invest in family farms; lets stop selling our farmland (especially in Missouri) to foreign countries (@ China buying up TONS of Missouri Farmland).
I love that the UAW president is here, because he straight up is my kind of people. Dude wears eat-the-rich shirts and calls out the unethical-ness of billionaires.
UAW President pointing to Biden saying "It's you!"; nah dawg, it's you Sean.
MIDDLE CLASS DID BUILD THE COUNTRY AND UNIONS BUILT THE MIDDLE CLASS MOTHER FUCKERS!!!
Yes we get back up but right now...we might be getting more french revolutionary-esque if y'all don't stop PLAYING WITH OUR LIVES.
Oh jesus not the 4-more-years chants.
Oh now we talking about the future
YES PLEASE END TRICKLE DOWN ECONOMIES.
Says he's not anti-corp; but points out how trickle down economics has only helped the wealthy.
Yeah, how the fuck does it hurt the wealthy to pay just a weeee bit more in taxes? Like dawg, what are you gonna do with another million? What's the point?
Ooooh is Biden about to rope the repubs into some bipartisan shit? Please do.
What is Republicans huge issue with capping insulin? Truly? Who does it harm? Billionaires still get billions.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Book Review 64 – Poverty, by America by Mathew Desmond

I read Desmond’s Evicted a while back and found it a really excellent bit of sociology/journalism about the specifics and mechanisms of housing inequality and how modern slumlords exploit the poor. So this has been vaguely on my list for a decent while. Sadly, I found it a bit of a disappointment – more listing of facts and statistics that I already basically knew to support a manifesto than anything new or enlightening to me. Not that it’s bad, but if it was 20 pages instead of 200 I’m not sure much of value would really have been lost. Many such cases, I suppose.
The book is about exactly what it says is, a polemic decrying and investigation into why the United State’s poverty rates, and why extremes of material want are so much more common there than in comparable (poorer, even) western democracies. Refreshingly, Desmond has a clear thesis he doesn’t beat around the bush before saying – self-interest, essentially. The affluent benefit from having an underclass to extract resources from, and from excluding its members from the amenities they share, so they do. The book spends most of its wordcount enumerating and describing what Desmond considers the main problems: direct exploitation (underpayment, predatory financiers, slums, etc), an underresourced and misdirected wellfare state (compare the cost of middle/upper-class targeted programs like the mortgage interest deduction or tax-exempt savings accounts to the cost of adequately ending hunger or providing healthcare) and segregation (both spatial/residential and in terms of access to public or semi-public services).
It’s pretty traditional for a book like this to spend 90% of its wordcount diagnosing problems and then end with some publisher-mandated optimism and a chapter of solutions with a fraction of the care put into them as in the diagnosis. Desmond, to his credit, avoids this – each chapter includes both the problems and he considers the most feasible solutions to them to be. He actually makes a point of it, arguing that having practical, winnable goals that will actually improve things when achieved (and then celebrating them when they are) is a key part of any political organizing with a chance of actually working. Now, what I think of those solutions varies quite wildly, but they’re there and exactly what you’d expect for his politics – and speaking as someone whose been renting my entire life I wholly endorse fucking all the tax benefits you get essentially for having the cash on hand to make a down payment. (Relatedly, the book has a great deal of scorn for comfortable, affluent people whose progressive politics amount to lots of critiquing and zero actual positive action.)
Desmond is clearly writing this from the point of view of a(n inspirational) public intellectual; that is, by writing this he’s trying to call an audience and movement based around it into being. He likes the label Poverty Abolitionist and the central project of the book is basically trying to make it happen as an umbrella term people identify with – especially the affluent well-heeled people who read books like this, and might be persuaded to start boycotting companies for underpaying their employees or union-busting, or campaigning against government subsidies that benefit them instead of the poor. I did appreciate the relative hopeful tone, given the usual coverage of American politics – or, well, is ‘Washington was at least this fucked when it passed the Civil Rights Act or the New Deal” optimistic? Whatever the right word is.
Now, I’m summarized all this in ~500 words, obviously actually making the argument needs more space than that. But it really did not need to be as long as it was – a huge fraction of the wordcount is spent either restating arguments or just throwing around numbers and statistics without really contextualization (anyone who spends so much time comparing expenses and budgets across the decade should be legally required to adjust for inflation imo). There’s a good, well-cited (excessively cited, if anything. The footnotoes are like a fifth of the book) persuasive essay in here, but there is so much fat to cut around it.
Anyway yes, disappointing reading experience, given I was hoping for more sociology and less polemic. But as far as American political polemic goes, it’s pretty decent.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi there! @look-at-those-niceass-rocks and I are back on our bullshit with some unhinged movie-night quotes, this time with the first Descendants film. Previously, we've had some shit to say about Rise of the Pink Ladies and Julie and the Phantoms. This is the first actual movie we've watched for these movie-night quotes, so it's a long one. Buckle up, and enjoy the ride!
Bee: "Elected king"? That's not how democracy works.
Bee: How is he inheriting the crown if his dad is still alive???
(Note: For those not aware, hi, I'm a costume designer and technician, I usually have Things To Say about costumes, including the following Several Minute Rant)
Me, two minutes into the movie: PAUSE, okay I have opinions here
Bee: Okay?
Me: Okay so this is a fitting, right? I appreciate the big stitch lengths, that's accurate, but this should be a mock-up, with muslin! Why is it made of the fashion fabric???
Bee: This is riveting
Me: Why are his sleeves finished off? Where are the pins? Is that a hand back stitch???
Bee: *cackling*
Bee: YOU CANNOT BELIEVE IN THE DIVINE RIGHT OF KINGS AND DEMOCRACY
Me: Why did they give Ben a bust dart? Does he have tiddies???
Bee: TRANS BEN???
Bee: I'm gonna take a drink every time you go on a costume rant.
Me: LISTEN
Bee (@Evie and Mal): So they're lesbians, right?
Me: OH HO HO, YOU'D THINK SO WOULDN'T YA
Bee: You said Kenny Ortega did this, right?
Me: Yep!
Bee: That. SO very tracks.
Evie: *flirting*
Bee: Ahhh, performative heterosexuality!
Me: Her love interest is so [HUSBAND]-coded; you're gonna lose your mind
Bee: Ah yep, Kenny Ortega choreography
Bee: IS THAT FUCKING KRISTEN CHENOWETH???
Me: YOU DIDN'T KNOW THAT???
Both of us, anytime Carlos is on screen: He Baby
Bee: I bet AO3 had a field day with this franchise
Bee: Ohhhh, look at that shitty marching band, let me at 'em- NONE OF THOSE PEOPLE ARE PLAYING THOSE INSTRUMENTS
Me: *wheeze*
Bee @ Audrey: Oh THATS a lesbian
Me: I COULD GO ON A RANT and I won't until we have more context!
Me: Look, Evie's love interest is a dude but I choose to believe that he's a he/him lesbian so it works
Mal: And I totally don't blame your grandparents for inviting everyone in the whole world but my mother to their stupid christening!
Me: Look, christenings were public events! They had to go out of their way to tell Maleficent not to come!
Bee: Right! Like it was more work to have someone find her to tell her not to come! She would've stayed away if you just kept your mouths shut!
Me: Not to victim blame, but don't fuck with the fae if you don't want the fae to fuck with you
Bee: No I'm victim blaming in this one instance, that was fucking stupid
Doug: Hi-ho...
Bee: Oh god he is [HUSBAND]-coded
Carlos: Die, suckers!
Me: Let Carlos say fuck!
Bee: He would say it constantly
Jay: *ninja kick through the door*
Bee: Dumbass
Carlos: *trying to help Jay up*
Me: *sobbing* He baby!!!
Bee: He wants to help his brother!!!
Bee, already tipsy: I think every time we say "he baby" I need to drink water
Me: Hnng I remember being obsessed with Mal's outfits as a 14yo but looking at it now as a costume designer, I can't tell if I still love it or if I kinda hate it.
Bee: Lemme take a drink and you elaborate.
Me: There's something kinda off-putting about it and I can't tell if it's because it reeks of 2015 Disney Channel-which is not a bad thing!-or if I just don't think the design works.
Bee: It looks like they were going for scene but didn't really know what scene was
Me: I think we should also take a drink whenever we say "that's gay"
Both: STOP BEING MEAN TO JANE SHE'S SO CUTE
Ben: *trying to convince Carlos Dude won't hurt him*
Me: For the trans!Ben headcanon, I know that's just a weird fuckin' seam on his shirt, but it looks like a binder
Honorable mention: Us constantly screaming at evie that she's allowed to be smart
Bee: Hey, [HUSBAND], Wanna come see a character that's you coded???
Evie: *making clothes*
Me: THAT SEWING MACHINE IS SEXY
Me @ Lonnie: I wouldn't call that cool hair
Bee: Oh now she's cool, she ripped her skirt
Mal: I think it's time Benny Boo got himself a new girlfriend
Bee: Girl he is right behind that door
Mal: *wipes Lonnie's tear*
Bee: LOOK AT HER FACE, see that? That was a gay awakening
Me during Did I Mention: Guess what
Bee: Huh?
Me: That's not him singing
Bee: *gasp* They Troy Bolton'ed that man
Bee: There are. Not enough trumpets in this band
Me: Nerd
Talking about the Maleficent movie and how I've never seen it
Bee: Oh god, you would've been like. 12
Me: Or 13 depending on the time of year!
Bee: It came out in May
Me: ...Okay yeah I would've been 12
Bee: I can do math!
[HUSBAND], distantly: Citation needed!
Bee: HEY!!!
Ben: Is this your first time?
Bee: HUH???
Me: What was he trying to accomplish here? Like he didn't tell her they were going somewhere they might need swimsuits, was he trying to get her in her underwear???
Bee: If it wasn't a Disney movie I'd say yes
Me: Horny teenage boy
Ben: *shirtless on the cliff*
Me: Good for him, he's had top surgery since the last scene
Maleficent: Still doing tricks with eggplants?
Bee: Idk, ask her husband
After the cover of Be Our Guest
Bee: What. Was that.
Me: I know
Bee: That was so bad!
Me: I promise the other covers are better
Me: I hate Mal's costume in this scene
Bee: Drink!
Me: The purple on her blazer matches too perfectly with her hair, there's no break in the silhouette
Bee: Oh yeah, I see what you mean
Me: I get what they're trying to do with the lighter palette, but I'd swap the blue and purple, personally
Queen Leah: My daughter was raised by fairies
Me: That was your own fault
Bee: Nowhere in that curse did it say you couldn't raise her
Insert the TEN MINUTE interlude of me dying over the obscene fit of Ben's suit:

(Please note: A) his jacket sleeve is caught on his elbow, which is what's causing that FOUR INCH exposed sleeve, B) who wears a pocket square and no tie? C) the buttons are STRAINING because the suit hasn't been tailored properly, it's way too small, you're the future king and I expect better from you okay you CANONICALLY have people tailoring your clothes, and while we're on buttons, D) NEVER button both buttons on a suit jacket! If the jacket has two buttons, the top is buttoned and the bottom isn't. If it's three, top is button sometimes, middle is always buttoned, and the bottom is never. Also: Unbutton when sitting or doing physical activity, such as croquet. This has been Levi's useless button PSA)
Honorable mention: I showed my mentor this picture the next day and he gasped like he'd been shot
Jane: He's never gonna make a villain a queen
Me: WE WERE ROOTING FOR YOU!
Bee: WE WERE ALL ROOTING FOR YOU!
Me: she's not ugly, she just has a fuck ass bob
Bee @ Beast: Oh why'd they give him glasses, now he's hot
Mal: How do you know that??
Ben: because I'm listening to my heart!
Bee: Gay
Mal: I'm listening to mine too
Bee: DOUBLE gay
Bee: I love how you can soo very see all these frozen people moving
Maleficent: *Dragon Time (tm)*
Bee: FOUND THE BUDGET
Jane: Guess I did get pretty lucky in the mother department
Me: Speaking of mothers can someone please catch the lizard
Bee: PLEASE
Side note, my internet was wigging out and the stream kept freezing, particularly during Set It Off
Me, struggling with the connection: And what if I cry
Bee: Limping toward the finish line
Me: What if I cry and commit arson
Mal: You didn't think that was the end of the story, did you?
Bee: Well that was fucking ominous
#disney descendants#descendants#mal bertha#evie descendants#carlos de vil#jay descendants#ben florian#unhinged quotes
8 notes
·
View notes