#difference between Microservices and APIs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Achieving Scalability and Flexibility: A Look at Microservices and APIs
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, two pivotal concepts have risen to prominence: Microservices and APIs. These technologies are revolutionizing the way applications are constructed, offering heightened scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. In this blog, we will dissect the disparities between microservices and APIs and delve into the advantages and benefits of…

View On WordPress
#Advantages of microservices#API versus microservices#APIs vs microservices#Benefits of Microservices#Benefits of microservices architecture#Difference between microservices and API#Microservices vs API
0 notes
Text
#Microservices vs API#Advantages of microservices#Benefits of Microservices#Difference between microservices and API#Benefits of microservices architecture#APIs vs microservices#API versus microservices
0 notes
Text
Microservices vs Monolith: Choosing the Right Architecture

Content: When developing software systems, architecture is one of the first and most impactful decisions. Two primary models dominate: monolithic applications and microservices architectures.
Monoliths consolidate all functions into a single unit, making them easier to build initially. However, they often become cumbersome as the codebase grows, making deployments riskier and updates slower.
Microservices, on the other hand, break applications into independent services that communicate over APIs. Each service is loosely coupled, allowing teams to work independently, use different tech stacks, and scale specific components without overhauling the entire system.
However, microservices come with their own challenges: higher complexity, the need for service orchestration, and potential for network latency.
Choosing between monolith and microservices depends largely on your team's size, project complexity, and long-term goals. Companies uses tools like Software Development assist in evaluating your needs to design the most appropriate architecture, balancing scalability with simplicity.
Ultimately, it’s not about trends—it’s about choosing what fits your project’s current and future states.
Before jumping into microservices, ensure your team masters clean modular design within a monolith first—it’ll make the transition smoother if/when you need it.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Role of Microservices In Modern Software Architecture

Are you ready to dive into the exciting world of microservices and discover how they are revolutionizing modern software architecture? In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are constantly seeking ways to build more scalable, flexible, and resilient applications. Enter microservices – a groundbreaking approach that allows developers to break down monolithic systems into smaller, independent components. Join us as we unravel the role of microservices in shaping the future of software design and explore their immense potential for transforming your organization’s technology stack. Buckle up for an enlightening journey through the intricacies of this game-changing architectural style!
Introduction To Microservices And Software Architecture
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, software architecture has become a crucial aspect for businesses looking to stay competitive. As companies strive for faster delivery of high-quality software, the traditional monolithic architecture has proved to be limiting and inefficient. This is where microservices come into play.
Microservices are an architectural approach that involves breaking down large, complex applications into smaller, independent services that can communicate with each other through APIs. These services are self-contained and can be deployed and updated independently without affecting the entire application.
Software architecture on the other hand, refers to the overall design of a software system including its components, relationships between them, and their interactions. It provides a blueprint for building scalable, maintainable and robust applications.
So how do microservices fit into the world of software architecture? Let’s delve deeper into this topic by understanding the fundamentals of both microservices and software architecture.
As mentioned earlier, microservices are small independent services that work together to form a larger application. Each service performs a specific business function and runs as an autonomous process. These services can be developed in different programming languages or frameworks based on what best suits their purpose.
The concept of microservices originated from Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA). However, unlike SOA which tends to have larger services with complex interconnections, microservices follow the principle of single responsibility – meaning each service should only perform one task or function.
Evolution Of Software Architecture: From Monolithic To Microservices
Software architecture has evolved significantly over the years, from traditional monolithic architectures to more modern and agile microservices architectures. This evolution has been driven by the need for more flexible, scalable, and efficient software systems. In this section, we will explore the journey of software architecture from monolithic to microservices and how it has transformed the way modern software is built.
Monolithic Architecture:
In a monolithic architecture, all components of an application are tightly coupled together into a single codebase. This means that any changes made to one part of the code can potentially impact other parts of the application. Monolithic applications are usually large and complex, making them difficult to maintain and scale.
One of the main drawbacks of monolithic architecture is its lack of flexibility. The entire application needs to be redeployed whenever a change or update is made, which can result in downtime and disruption for users. This makes it challenging for businesses to respond quickly to changing market needs.
The Rise of Microservices:
To overcome these limitations, software architects started exploring new ways of building applications that were more flexible and scalable. Microservices emerged as a solution to these challenges in software development.
Microservices architecture decomposes an application into smaller independent services that communicate with each other through well-defined APIs. Each service is responsible for a specific business function or feature and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently without affecting other services.

Advantages Of Using Microservices In Modern Software Development
Microservices have gained immense popularity in recent years, and for good reason. They offer numerous advantages over traditional monolithic software development approaches, making them a highly sought-after approach in modern software architecture.
1. Scalability: One of the key advantages of using microservices is their ability to scale independently. In a monolithic system, any changes or updates made to one component can potentially affect the entire application, making it difficult to scale specific functionalities as needed. However, with microservices, each service is developed and deployed independently, allowing for easier scalability and flexibility.
2. Improved Fault Isolation: In a monolithic architecture, a single error or bug can bring down the entire system. This makes troubleshooting and debugging a time-consuming and challenging process. With microservices, each service operates independently from others, which means that if one service fails or experiences issues, it will not impact the functioning of other services. This enables developers to quickly identify and resolve issues without affecting the overall system.
3. Faster Development: Microservices promote faster development cycles because they allow developers to work on different services concurrently without disrupting each other’s work. Moreover, since services are smaller in size compared to monoliths, they are easier to understand and maintain which results in reduced development time.
4. Technology Diversity: Monolithic systems often rely on a single technology stack for all components of the application. This can be limiting when new technologies emerge or when certain functionalities require specialized tools or languages that may not be compatible with the existing stack. In contrast, microservices allow for a diverse range of technologies to be used for different services, providing more flexibility and adaptability.
5. Easy Deployment: Microservices are designed to be deployed independently, which means that updates or changes to one service can be rolled out without affecting the entire system. This makes deployments faster and less risky compared to monolithic architectures, where any changes require the entire application to be redeployed.
6. Better Fault Tolerance: In a monolithic architecture, a single point of failure can bring down the entire system. With microservices, failures are isolated to individual services, which means that even if one service fails, the rest of the system can continue functioning. This improves overall fault tolerance in the application.
7. Improved Team Productivity: Microservices promote a modular approach to software development, allowing teams to work on specific services without needing to understand every aspect of the application. This leads to improved productivity as developers can focus on their areas of expertise and make independent decisions about their service without worrying about how it will affect other parts of the system.
Challenges And Limitations Of Microservices
As with any technology or approach, there are both challenges and limitations to implementing microservices in modern software architecture. While the benefits of this architectural style are numerous, it is important to be aware of these potential obstacles in order to effectively navigate them.
1. Complexity: One of the main challenges of microservices is their inherent complexity. When a system is broken down into smaller, independent services, it becomes more difficult to manage and understand as a whole. This can lead to increased overhead and maintenance costs, as well as potential performance issues if not properly designed and implemented.
2. Distributed Systems Management: Microservices by nature are distributed systems, meaning that each service may be running on different servers or even in different geographical locations. This introduces new challenges for managing and monitoring the system as a whole. It also adds an extra layer of complexity when troubleshooting issues that span multiple services.
3. Communication Between Services: In order for microservices to function effectively, they must be able to communicate with one another seamlessly. This requires robust communication protocols and mechanisms such as APIs or messaging systems. However, setting up and maintaining these connections can be time-consuming and error-prone.
4. Data Consistency: In a traditional monolithic architecture, data consistency is relatively straightforward since all components access the same database instance. In contrast, microservices often have their own databases which can lead to data consistency issues if not carefully managed through proper synchronization techniques.
Best Practices For Implementing Microservices In Your Project
Implementing microservices in your project can bring a multitude of benefits, such as increased scalability, flexibility and faster development cycles. However, it is also important to ensure that the implementation is done correctly in order to fully reap these benefits. In this section, we will discuss some best practices for implementing microservices in your project.
1. Define clear boundaries and responsibilities: One of the key principles of microservices architecture is the idea of breaking down a larger application into smaller independent services. It is crucial to clearly define the boundaries and responsibilities of each service to avoid overlap or duplication of functionality. This can be achieved by using techniques like domain-driven design or event storming to identify distinct business domains and their respective services.
2. Choose appropriate communication protocols: Microservices communicate with each other through APIs, so it is important to carefully consider which protocols to use for these interactions. RESTful APIs are popular due to their simplicity and compatibility with different programming languages. Alternatively, you may choose messaging-based protocols like AMQP or Kafka for asynchronous communication between services.
3. Ensure fault tolerance: In a distributed system like microservices architecture, failures are inevitable. Therefore, it is important to design for fault tolerance by implementing strategies such as circuit breakers and retries. These mechanisms help prevent cascading failures and improve overall system resilience.
Real-Life Examples Of Successful Implementation Of Microservices
Microservices have gained immense popularity in recent years due to their ability to improve the scalability, flexibility, and agility of software systems. Many organizations across various industries have successfully implemented microservices architecture in their applications, resulting in significant benefits. In this section, we will explore real-life examples of successful implementation of microservices and how they have revolutionized modern software architecture.
1. Netflix: Netflix is a leading streaming service that has disrupted the entertainment industry with its vast collection of movies and TV shows. The company’s success can be attributed to its adoption of microservices architecture. Initially, Netflix had a monolithic application that was becoming difficult to scale and maintain as the user base grew rapidly. To overcome these challenges, they broke down their application into smaller independent services following the microservices approach.
Each service at Netflix has a specific function such as search, recommendations, or video playback. These services can be developed independently, enabling faster deployment and updates without affecting other parts of the system. This also allows for easier scaling based on demand by adding more instances of the required services. With microservices, Netflix has improved its uptime and performance while keeping costs low.
The Future Of Microservices In Software Architecture
The concept of microservices has been gaining traction in the world of software architecture in recent years. This approach to building applications involves breaking down a monolithic system into smaller, independent services that communicate with each other through well-defined APIs. The benefits of this architecture include increased flexibility, scalability, and resilience.
But what does the future hold for microservices? In this section, we will explore some potential developments and trends that could shape the future of microservices in software architecture.
1. Rise of Serverless Architecture
As organizations continue to move towards cloud-based solutions, serverless architecture is becoming increasingly popular. This approach eliminates the need for traditional servers and infrastructure management by allowing developers to deploy their code directly onto a cloud platform such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Microservices are a natural fit for serverless architecture as they already follow a distributed model. With serverless, each microservice can be deployed independently, making it easier to scale individual components without affecting the entire system. As serverless continues to grow in popularity, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of microservices.
2. Increased Adoption of Containerization
Containerization technology such as Docker has revolutionized how applications are deployed and managed. Containers provide an isolated environment for each service, making it easier to package and deploy them anywhere without worrying about compatibility issues.
Conclusion:
As we have seen throughout this article, microservices offer a number of benefits in terms of scalability, flexibility, and efficiency in modern software architecture. However, it is important to carefully consider whether or not the use of microservices is right for your specific project.
First and foremost, it is crucial to understand the complexity that comes with implementing a microservices architecture. While it offers many advantages, it also introduces new challenges such as increased communication overhead and the need for specialized tools and processes. Therefore, if your project does not require a high level of scalability or if you do not have a team with sufficient expertise to manage these complexities, using a monolithic architecture may be more suitable.
#website landing page design#magento development#best web development company in united states#asp.net web and application development#web designing company#web development company#logo design company#web development#web design#digital marketing company in usa
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
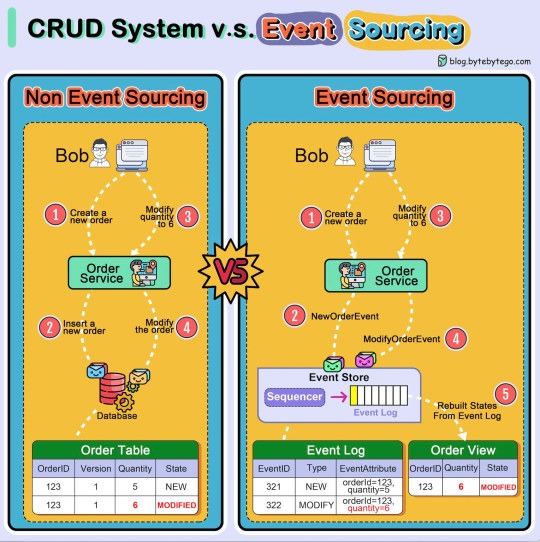
YABI Yet another ByteByteGo Infographic: This one shows the difference between a traditioanl CRUD (create, read, update and delete) system and a more contemporary event sourcing system. Both achieve the same end result but the event sourcing model is more resilient to failure and data corruption. It also scales well in a microservices environment.
Although the diagram does not mention it, the two systems can be used in a complimentary fashion. The CRUD system can be exposed as a typical REST API which is very well understood by developers and quite easy to develop to. Meanwhile, within the organisation the CRUD methods can easily proxy to events. The net result is a modern event sourcing system internally with a low friction REST API for integration.
(via https://substack-post-media.s3.amazonaws.com/public/images/0a124ddf-8104-48fc-8f61-e190a73579e9_1529x1536.jpeg (1529×1536))
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Serverless Computing?
Serverless computing is a cloud computing model where the cloud provider manages the infrastructure and automatically provisions resources as needed to execute code. This means that developers don’t have to worry about managing servers, scaling, or infrastructure maintenance. Instead, they can focus on writing code and building applications. Serverless computing is often used for building event-driven applications or microservices, where functions are triggered by events and execute specific tasks.
How Serverless Computing Works
In serverless computing, applications are broken down into small, independent functions that are triggered by specific events. These functions are stateless, meaning they don’t retain information between executions. When an event occurs, the cloud provider automatically provisions the necessary resources and executes the function. Once the function is complete, the resources are de-provisioned, making serverless computing highly scalable and cost-efficient.
Serverless Computing Architecture
The architecture of serverless computing typically involves four components: the client, the API Gateway, the compute service, and the data store. The client sends requests to the API Gateway, which acts as a front-end to the compute service. The compute service executes the functions in response to events and may interact with the data store to retrieve or store data. The API Gateway then returns the results to the client.
Benefits of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing offers several benefits over traditional server-based computing, including:
Reduced costs: Serverless computing allows organizations to pay only for the resources they use, rather than paying for dedicated servers or infrastructure.
Improved scalability: Serverless computing can automatically scale up or down depending on demand, making it highly scalable and efficient.
Reduced maintenance: Since the cloud provider manages the infrastructure, organizations don’t need to worry about maintaining servers or infrastructure.
Faster time to market: Serverless computing allows developers to focus on writing code and building applications, reducing the time to market new products and services.
Drawbacks of Serverless Computing
While serverless computing has several benefits, it also has some drawbacks, including:
Limited control: Since the cloud provider manages the infrastructure, developers have limited control over the environment and resources.
Cold start times: When a function is executed for the first time, it may take longer to start up, leading to slower response times.
Vendor lock-in: Organizations may be tied to a specific cloud provider, making it difficult to switch providers or migrate to a different environment.
Some facts about serverless computing
Serverless computing is often referred to as Functions-as-a-Service (FaaS) because it allows developers to write and deploy individual functions rather than entire applications.
Serverless computing is often used in microservices architectures, where applications are broken down into smaller, independent components that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Serverless computing can result in significant cost savings for organizations because they only pay for the resources they use. This can be especially beneficial for applications with unpredictable traffic patterns or occasional bursts of computing power.
One of the biggest drawbacks of serverless computing is the “cold start” problem, where a function may take several seconds to start up if it hasn’t been used recently. However, this problem can be mitigated through various optimization techniques.
Serverless computing is often used in event-driven architectures, where functions are triggered by specific events such as user interactions, changes to a database, or changes to a file system. This can make it easier to build highly scalable and efficient applications.
Now, let’s explore some other serverless computing frameworks that can be used in addition to Google Cloud Functions.
AWS Lambda: AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows developers to run code in response to events without worrying about managing servers or infrastructure.
Microsoft Azure Functions: Microsoft Azure Functions is a serverless compute service from Microsoft Azure. It allows developers to run code in response to events and supports a wide range of programming languages.
IBM Cloud Functions: IBM Cloud Functions is a serverless compute service from IBM Cloud. It allows developers to run code in response to events and supports a wide range of programming languages.
OpenFaaS: OpenFaaS is an open-source serverless framework that allows developers to run functions on any cloud or on-premises infrastructure.
Apache OpenWhisk: Apache OpenWhisk is an open-source serverless platform that allows developers to run functions in response to events. It supports a wide range of programming languages and can be deployed on any cloud or on-premises infrastructure.
Kubeless: Kubeless is a Kubernetes-native serverless framework that allows developers to run functions on Kubernetes clusters. It supports a wide range of programming languages and can be deployed on any Kubernetes cluster.
IronFunctions: IronFunctions is an open-source serverless platform that allows developers to run functions on any cloud or on-premises infrastructure. It supports a wide range of programming languages and can be deployed on any container orchestrator.
These serverless computing frameworks offer developers a range of options for building and deploying serverless applications. Each framework has its own strengths and weaknesses, so developers should choose the one that best fits their needs.
Real-time examples
Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola uses serverless computing to power its Freestyle soda machines, which allow customers to mix and match different soda flavors. The machines use AWS Lambda functions to process customer requests and make recommendations based on their preferences.
iRobot: iRobot uses serverless computing to power its Roomba robot vacuums, which use computer vision and machine learning to navigate homes and clean floors. The Roomba vacuums use AWS Lambda functions to process data from their sensors and decide where to go next.
Capital One: Capital One uses serverless computing to power its mobile banking app, which allows customers to manage their accounts, transfer money, and pay bills. The app uses AWS Lambda functions to process requests and deliver real-time information to users.
Fender: Fender uses serverless computing to power its Fender Play platform, which provides online guitar lessons to users around the world. The platform uses AWS Lambda functions to process user data and generate personalized lesson plans.
Netflix: Netflix uses serverless computing to power its video encoding and transcoding workflows, which are used to prepare video content for streaming on various devices. The workflows use AWS Lambda functions to process video files and convert them into the appropriate format for each device.
Conclusion
Serverless computing is a powerful and efficient solution for building and deploying applications. It offers several benefits, including reduced costs, improved scalability, reduced maintenance, and faster time to market. However, it also has some drawbacks, including limited control, cold start times, and vendor lock-in. Despite these drawbacks, serverless computing will likely become an increasingly popular solution for building event-driven applications and microservices.
Read more
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] A book for the aspiring .NET software architect - design scalable and high-performance enterprise solutions using the latest features of C# 12 and .NET 8Purchase of the print or Kindle book includes a free PDF eBookKey FeaturesGet introduced to software architecture fundamentals and begin applying them in .NETExplore the main technologies used by software architects and choose the best ones for your needsMaster new developments in .NET with the help of a practical case study that looks at software architecture for a travel agencyBook DescriptionSoftware Architecture with C# 12 and .NET 8 puts high-level design theory to work in a .NET context, teaching you the key skills, technologies, and best practices required to become an effective .NET software architect.This fourth edition puts emphasis on a case study that will bring your skills to life. You'll learn how to choose between different architectures and technologies at each level of the stack. You'll take an even closer look at Blazor and explore OpenTelemetry for observability, as well as a more practical dive into preparing .NET microservices for Kubernetes integration.Divided into three parts, this book starts with the fundamentals of software architecture, covering C# best practices, software domains, design patterns, DevOps principles for CI/CD, and more. The second part focuses on the technologies, from choosing data storage in the cloud to implementing frontend microservices and working with Serverless. You'll learn about the main communication technologies used in microservices, such as REST API, gRPC, Azure Service Bus, and RabbitMQ. The final part takes you through a real-world case study where you'll create software architecture for a travel agency.By the end of this book, you will be able to transform user requirements into technical needs and deliver highly scalable enterprise software architectures.What you will learnProgram and maintain Azure DevOps and explore GitHub ProjectsManage software requirements to design functional and non-functional needsApply architectural approaches such as layered architecture and domain-driven designMake effective choices between cloud-based and data storage solutionsImplement resilient frontend microservices, worker microservices, and distributed transactionsUnderstand when to use test-driven development (TDD) and alternative approachesChoose the best option for cloud development, from IaaS to ServerlessWho this book is forThis book is for engineers and senior software developers aspiring to become architects or looking to build enterprise applications with the .NET stack.Basic familiarity with C# and .NET is required to get the most out of this software architecture book.Table of ContentsUnderstanding the Importance of Software ArchitectureNon-Functional RequirementsManaging RequirementsBest Practices in Coding C# 12Implementing Code Reusability in C# 12Design Patterns and .NET 8 ImplementationUnderstanding the Different Domains in Software SolutionsUnderstanding DevOps Principles and CI/CDTesting Your Enterprise ApplicationDeciding on the Best Cloud-Based SolutionApplying a Microservice Architecture to Your Enterprise ApplicationChoosing Your Data Storage in the cloudInteracting with Data in C# - Entity Framework CoreImplementing Microservices with .NETApplying Service-Oriented Architectures with .NETWorking with Serverless - Azure FunctionsPresenting ASP.NET Core(N.B. Please use the Look Inside option to see further chapters) Publisher : Packt Publishing; 4th ed. edition (28 February 2024) Language : English Paperback
: 756 pages ISBN-10 : 1805127659 ISBN-13 : 978-1805127659 Item Weight : 1 kg 280 g Dimensions : 19.05 x 4.34 x 23.5 cm Country of Origin : India [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
You Won’t Believe How Fast These Apps Run with Node.js Development
The digital world moves fast—so fast that even milliseconds can make or break a user’s experience. That’s why so many businesses are turning to Node js Development to power their modern web and mobile applications. With its non-blocking architecture, event-driven model, and lightweight footprint, Node.js has become the engine behind some of the fastest and most scalable apps you use every day.
What Is Node.js and Why Does Speed Matter?
Before diving deep, let’s answer the basics: Node js Development refers to building server-side applications using Node.js—a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 engine. Its asynchronous nature means it can handle thousands of requests simultaneously without slowing down, making it a perfect fit for applications that require speed, such as chat apps, eCommerce sites, or real-time dashboards.
Its performance advantages have positioned it as a favorite among developers exploring different Node Frameworks, such as Express, NestJS, and Koa. These frameworks help streamline development, manage routing, and handle middleware more efficiently—making scalable app development faster than ever.
Why Node.js Is a Favorite for Modern Developers
Speed is only one part of the equation. The real magic happens when developers pair Node.js with modern libraries and architecture patterns. One popular pairing is React and Nodejs, where React handles the frontend UI and Node.js powers the backend logic. This JavaScript synergy results in smooth data flow, reusable code, and rapid development cycles.
With a shared language (JavaScript) between client and server, teams can move faster and collaborate more effectively—reducing the communication gap between frontend and backend developers.
The Role of Node.js in Real-Time Applications
If your app requires instant updates—think notifications, live chats, or stock tickers—Node js Development is the way to go. Thanks to WebSocket support and event-driven programming, Node.js enables real-time communication between client and server.
It’s especially relevant for businesses working on Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks, where consistency and performance across devices are crucial. Node.js helps ensure that both the web and mobile versions of an app behave identically and respond instantly to user interactions.
Book an appointment with our Node.js experts and explore how we can bring speed and efficiency to your next application.
Why Node.js Works So Well for APIs and Microservices
Node.js is also an excellent choice for building RESTful APIs and microservices. Its ability to handle multiple I/O operations concurrently makes it ideal for connecting with third-party services, databases, and cloud platforms.
This architecture is favored by agile teams and Hire Full Stack Developers who want to break large applications into smaller, more manageable parts. With microservices, teams can deploy, scale, and update individual features without affecting the entire system—something that Node.js facilitates with ease.
Who’s Using Node.js—and Why?
Still not convinced? Consider this: brands like Netflix, Uber, PayPal, and LinkedIn all rely on Node js Development for their core systems. Netflix, for example, reported a 70% reduction in startup time after migrating from Java to Node.js. Uber uses it to handle millions of real-time location updates per second.
What do these companies have in common? They need performance at scale, and Node.js delivers. That’s why any leading Custom Software Development Company includes Node.js in its stack for high-performance solutions tailored to client needs.
Key Benefits of Node.js Development
Let’s quickly summarize why Node js Development continues to grow in popularity:
High Performance: Non-blocking I/O for ultra-fast responses
Scalability: Ideal for microservices and growing apps
Community Support: Thousands of open-source modules
Unified Language: JavaScript for both frontend and backend
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Great for hybrid and mobile apps
Easy to Learn: Fast adoption for new devs and startups
When Should You Choose Node.js?
Node.js is a great choice if you’re building:
Real-time chat apps or collaborative tools
Streaming apps (audio/video)
APIs for mobile and web apps
Microservices-based platforms
Single Page Applications (SPAs)
Performance-intensive eCommerce systems
But it's not ideal for CPU-heavy operations like video editing or 3D rendering—other platforms might serve you better there.
The Future of Node.js
The future looks bright for Node js Development. With constant updates, an expanding ecosystem, and growing enterprise adoption, Node.js continues to evolve as a robust solution for scalable and maintainable applications.
In addition, integration with modern Node Frameworks, deeper synergy with React and Nodejs, and advancements in Cross-Platform App Development Frameworks will further cement its place in the developer's toolkit.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're a startup building an MVP or an enterprise optimizing an existing product, Node js Development Company offers a powerful and efficient path forward. It simplifies development, accelerates performance, and supports innovation at scale.
Ready to create apps that feel lightning-fast and future-ready?
Book an appointment with our Node.js experts today and let’s bring your project to life.
0 notes
Text
🔍 Streamlining JSON Comparison: Must-Know Tips for Dev Teams in 2025

JSON is everywhere — from configs and APIs to logs and databases. But here’s the catch: comparing two JSON files manually? Absolute chaos. 😵💫
If you’ve ever diffed a 300-line nested JSON with timestamps and IDs changing on every run… you know the pain.
Let’s fix that. 💡
📈 Why JSON Comparison Matters (More Than You Think)
In today’s world of microservices, real-time APIs, and data-driven apps, JSON is the glue. But with great power comes... yeah, messy diffs.
And no, plain text diff tools don’t cut it anymore. Not when your data is full of:
Auto-generated IDs
Timestamps that change on every request
Configs that vary by environment
We need smart tools — ones that know what actually matters in a diff.
🛠️ Pro Strategies to Make JSON Diff Less of a Nightmare
🔌 Plug It Into Your Dev Flow
Integrate JSON diff tools right in your IDE
Add them to CI/CD pipelines to catch issues before deploy
Auto-flag unexpected changes in pull requests
🧑💻 Dev Team Playbook
Define what counts as a “real change” (schema vs content vs metadata)
Set merge conflict rules for JSON
Decide when a diff needs a second pair of eyes 👀
✅ QA Power-Up
Validate API responses
Catch config issues in test environments
Compare snapshots across versions/releases
💡 Advanced Tactics for JSON Mastery
Schema-aware diffing: Skip the noise. Focus on structure changes.
Business-aware diffing: Prioritize diffs based on impact (not just "what changed")
History-aware diffing: Track how your data structure evolves over time
⚙️ Real-World Use Cases
Microservices: Keep JSON consistent across services
Databases: Compare stored JSON in relational or NoSQL DBs
API Gateways: Validate contract versions between deployments
🧠 But Wait, There’s More…
🚨 Handle the Edge Cases
Malformed JSON? Good tools won’t choke.
Huge files? Stream them, don’t crash your RAM.
Internationalization? Normalize encodings and skip false alarms.
🔒 Privacy & Compliance
Mask sensitive info during comparison
Log and audit every change (hello, HIPAA/GDPR)
⚡ Performance Tips
Real-time comparison for live data
Batch processing for large jobs
Scale with cloud-native or distributed JSON diff services
🚀 Future-Proof Your Stack
New formats and frameworks? Stay compatible.
Growing data? Choose scalable tools.
New team members? Train them to use smarter JSON diffs from day one.
💬 TL;DR
Modern JSON comparison isn't just about spotting a difference—it’s about understanding it. With the right strategies and tools, you’ll ship faster, debug smarter, and sleep better.
👉 Wanna level up your JSON testing? Keploy helps you test, diff, and validate APIs with real data — no fluff, just solid testing automation.
0 notes
Text
Getting Started with Microservices Testing: A Complete Guide
Modern software applications are no longer monolithic. Organizations are increasingly adopting microservices architecture to improve scalability, modularity, and deployment agility. But with this shift comes a new challenge: microservices testing.
In a microservices-based system, testing becomes significantly more complex due to the large number of independently deployable services, their interdependencies, and the distributed nature of the architecture. This guide will help you understand microservices testing, its types, challenges, strategies, and best practices to ensure your services are reliable, resilient, and production-ready.
What Is Microservices Testing?
Microservices testing is the process of validating individual microservices, their interactions, and the system as a whole to ensure correct functionality, performance, and resilience. Unlike monolithic testing, where the focus is on a single codebase, testing microservices requires validating multiple decoupled services—often owned by different teams—and their APIs, databases, and communication protocols.
Why Microservices Testing Is Crucial
Service Independence: Since each microservice can be developed and deployed independently, bugs can arise in isolation.
Inter-Service Communication: REST, gRPC, messaging queues—microservices rely heavily on inter-service calls.
Data Integrity: Each service may have its own data store, making consistency and data validation essential.
Deployment Automation: With CI/CD pipelines pushing frequent updates, tests act as a safety net.
Without a strong testing strategy, microservices can become fragile, prone to regression, and hard to debug—resulting in cascading failures in production.
Key Challenges in Microservices Testing
Distributed Nature: Services may run on different hosts, containers, or clusters.
Data Management: Testing with consistent, isolated, and realistic test data across services is difficult.
Environment Parity: Replicating production-like environments for test purposes is costly and complex.
Mocking and Stubbing: Each service may require mocks of dependent services to test in isolation.
Test Flakiness: Network latency, timeouts, or service downtime can cause intermittent test failures.
These challenges make it clear that traditional testing approaches alone aren’t enough.
Types of Testing in Microservices
1. Unit Testing
Focuses on individual functions/methods within a microservice.
Fast and isolated.
Ensures internal logic works as expected.
Tools: JUnit, PyTest, GoTest, NUnit
2. Component Testing
Tests a complete microservice (APIs + DB + logic) in isolation.
Mocks dependencies like databases or downstream services.
Simulates real-life scenarios.
3. Contract Testing
Ensures the interface (contract) between services is honored.
Provider and consumer services agree on the structure of requests/responses.
Tools: Pact, Spring Cloud Contract
4. Integration Testing
Validates the interaction between two or more microservices.
Includes network communication, API contracts, and data flow.
Can be fragile if dependent services are not available or unstable.
5. End-to-End (E2E) Testing
Tests the system as a whole, from frontend to backend services.
Often slower and more brittle but useful for validating user journeys.
Tools: Cypress, Selenium, Playwright
6. Performance Testing
Evaluates the responsiveness and stability of services under load.
Helps identify bottlenecks or resource leaks.
Tools: JMeter, Gatling, k6
7. Chaos Testing
Introduces failures like service crashes, latency, or network issues.
Helps assess system resilience and fallback mechanisms.
Tools: Gremlin, Chaos Monkey
Microservices Testing Pyramid
A well-balanced testing strategy follows a layered approach:
Unit Tests – Large base, fast, run frequently
Component/Integration Tests – Validate logic across services
Contract Tests – Enforce service boundaries
E2E Tests – Minimal, slow, validate critical flows
Following this testing pyramid helps maintain speed, reliability, and test coverage without excessive flakiness.
Best Practices for Microservices Testing
Isolate Tests: Keep unit/component tests independent from external dependencies using mocks/stubs.
Use Test Containers: Tools like Testcontainers help spin up disposable services or DBs during tests.
Adopt CI/CD Pipelines: Automate test runs on every commit or pull request.
Enable Observability: Use logs, traces, and metrics to debug test failures in distributed environments.
Shift Left: Write tests early, not after code is deployed.
Use Contract Tests: Validate API agreements without needing full integration tests.
Leverage Tools Like Keploy: Keploy captures real API traffic to auto-generate tests and mocks—helping test services in isolation without rewriting test cases manually.
Real-World Example
Imagine you're working on an e-commerce platform with the following services:
User Service – Manages registration and login
Product Service – Handles inventory and listings
Order Service – Processes orders and payments
Here’s how testing would be applied:
Unit tests validate user authentication logic.
Component tests check the order processing logic with a mock payment gateway.
Contract tests ensure the product service sends data in the expected format.
Integration tests validate that placing an order updates inventory.
E2E tests verify a user can log in, add products to the cart, and check out.
By combining all these levels, you ensure coverage across functionality, communication, and edge cases.
Tools for Microservices Testing
Purpose
Tool Examples
Unit Testing
JUnit, PyTest, GoTest
API Testing
Postman, Keploy, Rest Assured
Contract Testing
Pact, Spring Cloud Contract
Service Mocking
WireMock, Mountebank, Keploy
Load Testing
JMeter, k6, Gatling
Test Containers
Testcontainers, Docker Compose
CI/CD Pipelines
GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab
Role of Automation in Microservices Testing
Testing manually in microservices architecture is not scalable. Automation ensures:
Fast feedback loops
Higher test coverage
Reliable deployments
Cost-effective testing across environments
Tools like Keploy play a key role in automation by auto-generating test cases and mocks from actual traffic. This enables teams to test microservices in isolation—even in the absence of upstream/downstream services.
Final Thoughts
Microservices testing is not just about writing test cases—it’s about creating a robust, automated, and scalable testing strategy that ensures each service works independently and in harmony with others.
With distributed systems becoming the norm, mastering microservices testing is essential for maintaining product quality, performance, and reliability. Whether you're just starting out or looking to optimize your existing setup, embracing the right mix of testing types, tools, and practices will ensure your microservices architecture is built for success. Looking to automate your microservices testing? Try Keploy to capture traffic, generate tests, and create mocks effortlessly—reducing testing overhead and improving speed to deployment.
0 notes
Text
Dynamic AI-RAN Orchestration for NVIDIA Accelerated Computing Infrastructure
NVIDIA accelerated computing can significantly accelerate many different types of workloads. In this blog, I will explain how the same NVIDIA GPU computing infrastructure (all the way to fractional GPU) can be shared for different workloads, such as RAN (Radio Access Network) and AI/ML workloads, in a fully automated manner. This is the foundational requirement for enabling AI-RAN, a technology that is being embraced widely by the telecommunications industry, to fuse AI and RAN on a common infrastructure as the next step towards AI-native 5G and 6G networks. I will also show a practical use case that was demonstrated to a Tier-1 telco.
First some background before diving into the details: The infrastructure requirements for a specific type of workload (e.g., RAN or AI/ML) will vary dynamically, and the workloads cannot be statically assigned to the resources. This is particularly aggravated by the fact that RAN utilization can vary wildly, with the average being between 20%-30%. The unused cycles can be dynamically allocated to other workloads. The challenges in sharing the same GPU pool across multiple workloads can be summarized below:
Infrastructure requirements may be different for RAN/5G & AI workloads
Dependency on networking, such as switch re-configuration, IP/MAC address reassignment, etc.
Full isolation at infra level for security and performance SLAs between workloads
Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) sizing - Fixed partitions or dynamic configuration of MIG
Additional workflows that may be required, such as workload migration/scaling
This means that there is a need for an intelligent management entity, which is capable of orchestrating both infrastructure as well as different types of workloads, and switch the workloads in a dynamic fashion. This is accomplished using AMCOP (Aarna Networks Multicluster Orchestration Platform, which is Aarna’s Orchestration platform that supports orchestrating infrastructure, workloads, and applications).
The end-to-end scenario works as follows:
Create tenants for different workloads – RAN & AI. There may be multiple tenants for AI workloads if multiple user AI jobs are scheduled dynamically
Allocate required resources (servers or GPUs/fractional GPUs) for each tenant
Create network and storage isolation between the workloads
Provide an observability dashboard for the admin to monitor the GPU utilization & other KPIs
Deploy RAN components i.e. DU, CU, and NVIDIA AI Aerial (with Day-0 configuration) from RAN tenant
Deploy AI workloads (such as an NVIDIA AI Enterprise serverless API or NIM microservice) from AI tenant(s)
Monitor RAN traffic metrics
If the RAN traffic load goes below the threshold, consolidate RAN workload to fewer servers/GPUs/fractional GPUs
Deploy (or scale out) the AI workload (e.g. LLM Inferencing workload), after performing isolation
If the RAN traffic load exceeds the threshold, spin down (or scale in) AI workload, and subsequently, bring up RAN workload
The demo for showcasing a subset of this functionality using a single NVIDIA GH200 Grace Hopper Superchip is described below. This uses a single GPU (which is divided into fractional GPUs, as 3+4 MIG configuration), which are allocated to different workloads.
The following functionality can be seen in the demo, as part of the end-to-end flow.
Open the dashboard and show the RAN KPIs on the orchestrator GUI. Also, show the GPU and MIG metrics.
Show all the RAN KPIs and GPU + MIG metrics for the past duration (hours / days)
Show the updated RAN & GPU / MIG utilizations + AI metrics
Initiate the AI load/performance testing and then show the AI metrics and GPU/MIG utilizations on the dashboard
Query the RAG model (from a UE) from a custom GUI and show the response.
Next Steps:
Over the next few years, we predict every RAN site to run on an NVIDIA GPU-accelerated infrastructure. Contact us for help on getting started with sharing NVIDIA GPU compute resources within your infrastructure. Aarna.ml’s AI-Cloud Management Software (also known as AMCOP) orchestrates and manages GPU-accelerated environments including with support for NVIDIA AI Enterprise software and NVIDIA NIM microservices. Working closely with NVIDIA, we have deep expertise with the NVIDIA Grace Hopper platform, as well as NVIDIA Triton Inference Server and NVIDIA NeMo software.
This content originally posted on https://www.aarna.ml/
0 notes
Text
Observability vs. Monitoring: Implementing Distributed Tracing with Open Telemetry in Bangalore
Introduction: Why Observability is Bangalore’s New Tech Superpower Did you know that 60% of IT outages in distributed systems occur due to undetected latency between services (Gartner 2023)? For a tech hub like Bangalore—where companies deploy hundreds of microservices—traditional monitoring is like checking a car’s speedometer while ignoring its engine diagnostics.
Take the case of a Bangalore e-commerce giant that reduced checkout delays by 40% after implementing OpenTelemetry for distributed tracing. Suddenly, they could see the entire customer journey—from cart additions to payment processing—as a single, traceable flow.
For DevOps professionals in DevOps coaching in Bangalore, mastering observability tools like OpenTelemetry isn’t just about fixing bugs faster—it’s about preventing them altogether. This guide breaks down: ✔ Observability vs monitoring: Key differences ✔ How OpenTelemetry transforms troubleshooting ✔ Bangalore-specific implementation strategies
Monitoring vs. Observability: What Bangalore’s Tech Teams Need to Know
Monitoring: The Rearview Mirror What it does: Alerts you when known metrics (CPU, memory) breach thresholds Limitation: Can’t explain why a payment gateway times out
Observability: The X-Ray Vision What it provides: Distributed traces (Full request journeys) Context-rich logs Multi-dimensional metrics Bangalore Example:
OpenTelemetry trace of an e-commerce order
Browse (150ms) → AddToCart (200ms) → PaymentGateway (2000ms) → Confirm (150ms)
This trace exposed a slow third-party payment API—solved by switching providers.
The Tool Stack Revolution Purpose Monitoring Tools Observability Tools Metrics Nagios, Zabbix Prometheus, OpenTelemetry Tracing N/A Jaeger, OpenTelemetry Logs ELK Stack Loki, OpenTelemetry
This stack is now taught in advanced DevOps coaching in Bangalore programs.
Why OpenTelemetry? The Bangalore Advantage
Unified Data Collection Single SDK for traces, metrics, logs Vendor-agnostic: Works with AWS, GCP, Azure
Auto-Instrumentation Magic Zero-code changes for Java/Python apps Example: A Koramangala startup traced Django API latencies in 2 hours
Cost-Efficient Scaling Sampling controls: Keep only 10% of traces but 100% of errors
Bangalore Case Study: From 4-Hour Outages to 4-Minute Fixes Problem: A food-delivery app’s orders failed randomly during peak hours.
OpenTelemetry Implementation: Instrumented all microservices (Python + Go)
Discovered: Restaurant API cached menu data incorrectly Delivery service leaked database connections
Fixed: Added Redis caching Implemented connection pooling
Results: ✅ MTTR reduced from 4 hours → 4 minutes ✅ Peak throughput increased by 35% This troubleshooting prowess is why DevOps coaching in Bangalore prioritizes observability labs.
Overcoming Observability Challenges ❌ “Too Much Data!” Solution: Focus on SLOs (e.g., “Checkout < 2s”) Use flame graphs to spot latency hotspots ❌ “Complex Setup” Fix: Start with auto-instrumentation → expand gradually ❌ “Team Resistance” Strategy: Show cost savings—every 1% uptime improvement = $250K+ saved (Forrester)
Bangalore’s Observability Adoption Roadmap Start Small Instrument one critical service (e.g., payments) Build Context Add business attributes to traces: span.setAttribute("user.tier", "premium"); Correlate Everything Link traces to logs/metrics via TraceID Automate Alerts Trigger Slack alerts when: Error rate > 1% P99 latency > 500ms Upskill Continuously Advanced techniques are covered in DevOps coaching in Bangalore
Why Bangalore’s Tech Ecosystem Needs Observability 🔹 Microservices Boom: 70% of Bangalore tech firms use containers 🔹 Competitive Edge: Observability engineers earn 40% more 🔹 Industry-Aligned Training: DevOps coaching in Bangalore now includes: OpenTelemetry certification prep Distributed tracing labs Incident simulation drills

Conclusion: Observability—Your Microservices Crystal Ball In Bangalore’s high-stakes tech landscape: ✔ Monitoring tells you when something breaks ✔ Observability shows why—before users notice For DevOps professionals, DevOps coaching in Bangalore provides the hands-on Open Telemetry experience needed to future-proof careers.
Ready to see through your systems like never before? Enroll today and master observability’s superpowers!
What’s your biggest visibility challenge—sporadic latency or alert fatigue? Share your war stories below!
0 notes
Text
Core Concepts from Fundamentals of Software Architecture.
Let’s be real: the term software architecture can sound intimidating. It conjures up images of tech wizards surrounded by fancy diagrams, making big, mysterious decisions about servers and microservices. But here’s the truth—it’s not as complicated as it sounds, and understanding the basics will give you the tools to build more powerful, scalable, and maintainable software.

In this article, we’re going to break down the core concepts of software architecture in a way that’s easy to understand and impossible to ignore. Trust us, whether you’re building an app for fun or architecting an enterprise system, knowing these concepts will give you a massive leg up.
Table of Contents: What the Heck is Software Architecture?
The Key Building Blocks of Software Architecture
Architectural Patterns—What Are They and Why Should You Care?
The Must-Have Quality Attributes for Your Software
Designing for the Long Run: Scalability, Reliability, and Maintainability
Who’s the Software Architect?
Wrapping It Up: Why These Concepts Matter for You
What the Heck is Software Architecture? Imagine you’re building a house. You wouldn’t just start slapping walls together and hope everything fits, right? You’d have a blueprint, a vision, and a strategy for the plumbing, the wiring, and the layout.
Well, software architecture is that blueprint, but for software. It’s the high-level design that tells you how all the pieces of your system will fit together and work. And just like with a house, getting it right from the start saves you a ton of trouble down the road.
Think of it this way: without a solid architecture, you might end up with a system that’s hard to scale, a nightmare to maintain, and prone to crashing when more users show up. So yeah, it’s kind of a big deal.
The Key Building Blocks of Software Architecture If software architecture were a recipe, these would be the ingredients. Here’s a quick breakdown of the core components that make up your architecture:
Components/Modules: These are your building blocks—think of them as rooms in a house. Each component handles a specific function. For example, one module might handle user authentication, while another manages your database.
Interfaces: This is how the rooms talk to each other. It's like the doors and windows that connect your rooms and let the flow of people (or data) happen. In tech terms, interfaces let different components communicate.
Connectors: These are your "pipes" and "wires"—the things that help information flow between your components. It could be something like an API (Application Programming Interface), a message queue, or a database connector.
Data Flow: Data flow is how data moves through the system—like water flowing through pipes. When a user interacts with your app, data gets sent to different parts of your system, processed, and sent back to the user. A good data flow keeps everything running smoothly.
Architectural Patterns—What Are They and Why Should You Care? Now, here’s where it gets interesting. Architectural patterns are like blueprints for building your software. They’re tried-and-tested solutions to common problems that arise when designing systems. Think of them as templates, like "cookie-cutter" home designs that you can tweak to fit your needs.
Here are some of the big ones:
Monolithic Architecture: It’s like building your whole house in one go—everything is connected. Simple to start, but can get overwhelming as it grows.
Microservices Architecture: Now, imagine building lots of small, modular houses that can be expanded and modified independently. Microservices break your system into small, autonomous services that can evolve separately, making them ideal for large-scale systems.
Layered Architecture: This is like stacking your house in layers: foundation (data), walls (business logic), and the roof (presentation). Each layer has a specific job, and they only interact with the one directly below them.
Event-Driven Architecture: Think of this like setting up a system where rooms respond to specific triggers—like when the lights turn on automatically when you walk into a room. In software, this is useful for systems that need to be reactive and scalable.
Serverless Architecture: This is like renting a home instead of owning one—you don’t need to worry about the infrastructure, just focus on living (or in this case, coding). The cloud provider manages all the infrastructure while you just write functions.
The Must-Have Quality Attributes for Your Software You want your software to be fast, secure, and reliable, right? That’s where quality attributes come into play. These are the non-functional requirements (fancy speak for "how well your software works") that will shape your architectural decisions.
Here are some of the most important quality attributes:
Scalability: Can your software handle more users without breaking a sweat? Scalable systems grow with demand, just like how you can add more rooms to a house as your family grows.
Performance: Does it respond quickly? Performance is all about minimizing delays and keeping everything snappy.
Security: Is your system protected from hackers? Security is like building a fortress around your software. You need strong encryption, authentication, and access controls.
Maintainability: How easy is it to fix bugs and add new features? A well-designed system should be easy to update, just like a house that has good plumbing and wiring that you can easily repair.
Reliability: If something breaks, does your system recover gracefully? Think of this like a backup generator that kicks in when the power goes out. Your software should keep running even if some parts fail.
Designing for the Long Run: Scalability, Reliability, and Maintainability You’re not just building for today—you’re building for tomorrow. So, designing for scalability, reliability, and maintainability is crucial.
Scalability: Your system should be able to grow without a hitch. If you’re anticipating a flood of new users or data, you need an architecture that can handle the load, like a system of highways that can expand as traffic increases.
Reliability: Your system should be rock-solid. Think of it like building a house that can weather a storm. Redundancy and failover mechanisms ensure that if one part fails, another part takes over seamlessly.
Maintainability: Software isn’t static. It evolves. Your architecture should be flexible enough to handle changes. A modular design (think Lego blocks) makes it easier to swap out pieces without tearing the whole thing down.
Who’s the Software Architect? Okay, but who’s actually in charge of making all these big decisions? Enter the software architect—the person who designs the system’s overall structure and ensures everything is aligned with business goals.
Think of them as the chief architect of your house. They’re responsible for creating the blueprint, selecting the right materials (technologies), and ensuring everything works together harmoniously.
Wrapping It Up: Why These Concepts Matter for You So why does all of this matter? Well, whether you’re building an app for your side project or working on a multi-million-dollar enterprise system, understanding software architecture is crucial.
Good architecture helps you make smart decisions about how your system is built.
It ensures your system is ready to grow and adapt over time.
And most importantly, it saves you time, money, and a lot of headaches down the line.
0 notes
Text
Enterprise Teams, Here’s Why You Need Custom E-commerce Development Services — Not Just More Tools

Okay, so here’s the deal—if you’re working inside an enterprise e-commerce team, you already have a stack. Maybe too much of a stack.
There’s the headless CMS. The order management software. Maybe a CRM duct-taped to an ERP. It looks great in the pitch deck… but under the hood? A bunch of workarounds.
Been there. That's exactly why we started looking for proper e-commerce development services that could actually help us scale intelligently, not just “bigger.”
Tool Overload ≠ Scalability
You know what I’m talking about. Every quarter, someone introduces a new tool “to streamline the process.” And then six months later? It’s abandoned. Or worse—it’s still half-integrated and breaking things quietly in the background.
We thought we needed more apps. What we really needed was better dev support to bring everything into one clean system.
That’s where MSM CoreTech came in. Not another vendor selling us a plug-and-play solution—but a e-commerce development company that helped us rationalize our tech stack.
They asked:
What’s essential?
What can be replaced?
What’s duplicating effort?
What’s breaking silently at 2 a.m.?
And then… they built around that.
Not Just Code — Enterprise-Grade Thinking
Let me be super clear: this isn’t about having “clean code.” This is about business continuity.
MSM CoreTech didn’t just ask for our Jira board. They wanted to understand:
Our reporting chain
Our internal handoffs between marketing, IT, and fulfillment
Our integration points with legacy systems (some of which are… yikes)
They weren’t just solving a ticket—they were helping us clean up our entire workflow.
That’s the difference between a generic agency and a true e-commerce development agency that’s been through enterprise trenches before.
You Can’t Scale With Duct Tape
We were scaling fast. But not sustainably.
One of the biggest issues? We had microservices duct-taped together—shipping logic in one place, product rules in another, pricing config in spreadsheets. Sound familiar?
Every deployment was a gamble. Every Black Friday meant “all hands on deck.”
MSM CoreTech came in and asked, “Why not modularize this the right way?” And they meant it. They gave us:
Proper containerized services
Deployment pipelines with rollback plans
A clean separation of logic between storefront, backend, and fulfillment
API monitoring that worked
Suddenly, we weren’t scared to push code. We were actually releasing features on time.
You Need Speed Without Sacrificing Control
Enterprise pace is weird. You need to move fast, but everything has to go through approvals. Legal. Compliance. IT security. And then… maybe, maybe you can test in staging.
What MSM CoreTech helped us do was design a workflow that respected all that red tape—but didn’t get buried under it.
They gave us:
A gated deployment system with feature toggles
Role-based access for marketing vs dev vs ops
Sandbox environments that actually reflected production
Documentation so our internal teams could maintain changes
Now, we launch confidently—without stepping on IT’s toes.
Internal Teams + Dev Partners = Harmony (Finally)
One of our fears going in? That an outside team would step on our internal devs.
Turns out, the opposite happened.
MSM CoreTech worked with our engineering leads. They shared updates in our Slack. They asked the right questions in retros. They even flagged a security issue that our internal audit missed.
It didn’t feel like a vendor relationship. It felt like having another squad in the war room.
Long-Term Stability Beats Short-Term Sizzle
A lot of agencies pitch shiny features. “Let’s add gamification!” “Let’s integrate AR previews!”
But our leadership didn’t want more flash—they wanted:
Uptime during peak hours
Clean performance data
Bulletproof order flows
That’s what we got. MSM CoreTech helped us build infrastructure we could grow into, not just “the cool stuff everyone else is doing.”
And honestly? That’s what separates scalable brands from fragile ones.
You Already Have the Ideas — You Just Need the Engine
If you're part of an enterprise e-commerce team, you're not lacking in ideas. You’ve got roadmaps. You’ve got visions. You’ve got quarterly OKRs that keep getting pushed.
What you might be missing is the execution partner. Someone who doesn’t need hand-holding. Someone who can walk into your chaos and calmly say, “Yeah, we’ve seen this before. Here's what to do.”
That was MSM CoreTech for us.
0 notes
Text
SAP Commerce Cloud V2 vs V1: What’s New and Improved
In eCommerce, being ahead means offering better products as well as adopting flexible and innovative platforms. The switch from CCv1 to CCv2 for enterprise businesses signals an important achievement in SAP’s plan to improve customer experiences.
In this blog, we’ll break down the SAP Commerce Cloud V2 vs V1 comparison, exploring how the newer version empowers businesses with better architecture, performance, and integration capabilities. Whether you're planning an upgrade or considering a complete SAP Commerce Cloud migration, understanding these differences will help you make informed decisions.

Understanding SAP Commerce Cloud: A Quick Overview
SAP Commerce Cloud is made to give companies the ability to provide personalized shopping experiences to their customers on all channels. Previously, it was called Hybris, but it shifted to the cloud in order to give more flexibility, scalability, and compatibility with the SAP suite.
Using the V2 version of SAP Commerce Cloud, the platform has now been redesigned to function using Kubernetes and Microsoft Azure in a cloud environment. This is quite the opposite of the V1 prototype, which was still in the cloud, even though it wasn't constructed with native cloud ideas.
SAP Commerce Cloud V2 vs V1: Key Architectural Changes
1. Cloud-Native Architecture in V2
One of the most defining changes in the SAP Commerce Cloud V2 vs V1 debate is the transition to a cloud-native architecture. Although V1 was hosted on the cloud, it used a big codebase and familiar setup designs.
Meanwhile, V2 contains only microservices which run on top of Kubernetes. Following this approach means you gain:
Faster deployments
Improved scalability
Higher ability to handle any errors
Lowering the expenses needed for the maintenance of structures
This makes SAP CCv2's new features more adaptable to today's digital commerce needs, especially for businesses looking to scale quickly across geographies.
2. Flexible Deployment with CI/CD Pipelines
Using V2, businesses are able to include CI/CD pipelines in their regular commerce operations. SAP Commerce Cloud V2 moves updates quicker than V1 used to since the updates used to be slower.
Quick and reliable movement of changes to the environments
Quick rollbacks
Testing and QA are done automatically
Online deployments always
This comes in handy, especially for businesses updating their operations, running campaigns and offering new products seasonally.
Feature Enhancements in SAP CCv2: What’s New
3. SmartEdit Enhancements
It is now easier and more enjoyable to use SmartEdit in V2. Editing is now possible with these features:
Study pages that are targeted to various types of customers
Apply drag-and-drop activities
Make sure to schedule updates at the right times
Although SmartEdit was part of V1, it sometimes ran slowly and did not have enough contextual previews, but these issues are almost gone in V2.
4. Advanced API Support
In V2, SAP has chosen a headless model and improved its GraphQL and RESTful API features. Because of these changes, front-end experts can make dynamic storefronts and mobile apps with complete independence from back-end development efforts.
An API-first method helps companies provide omnichannel commerce experiences that cover different channels faster:
Web
Mobile
POS
IoT devices
5. Enhanced Integration with SAP Ecosystem
Integration across the whole SAP landscape adds more value for users, too:
SAP S/4HANA
SAP Customer Data Cloud is a platform for handling customer data
SAP Marketing Cloud
SAP Sales and Service Cloud is a package that involves SAP Sales and SAP Service
Because of these improvements in V2, digital transformation can finally happen smoothly, quickly and with lower custom work.
Migration between V1 and V2: What Do You Need to Consider
Planning a SAP Commerce Cloud migration can seem daunting, but with the right strategy and partner, the transition from V1 to V2 can be seamless.
6. Pre-Migration Assessment
Begin the process by doing a full analysis of where you are beginning. Identify:
Extending MyLittlePlanet with additional software
Data models
Business procedures and ways of working
The company performs thorough reviews to show you the existing state of things and estimate the time and effort needed for the migration.
7. Data Migration and Extension Rebuild
Some V1 extensions have to be updated to fit with cloud-native methods in the new release of CCv2. Royal Cyber's migration team can refactor the extensions and preserve data uniformity as they are moved over.
8. Testing and QA in Containerized Environments
Thanks to container replicas in SAP CCv2, parallel QA tests are possible and safer. Royal Cyber makes use of automated test tools to ensure the smooth transition of every migration step without causing problems in the original systems.
SAP CCv2 New Features That Drive Business Value
9. Better Performance and Uptime
With its microservices, V2 allows each service to increase in size depending on how much work is needed. If your business goes through peak traffic or grows worldwide, SAP Commerce Cloud V2 ensures reliable performance and faster loading speed.
10. Improved Security and Compliance
Because CCv2 features role-based access control, scans container images and includes GDPR features, your commerce data is defended on multiple fronts. SAP supplies regular updates that address zero-day threats.
11. Operational Transparency
It is directly linked to performance tools such as Dynatrace, New Relic, and Azure Monitor. Organizations can see details about their business in real-time:
Application performance
Infrastructure health
User behaviors
Back in the V1 era, one had to rely on simple logs and third-party utilities to monitor and learn about possible issues.
Why Royal Cyber for SAP Commerce Cloud Migration
Moving to V2 means both upgrading technology and making a smart business decision that can change your digital commerce processes. Royal Cyber is a trusted choice for companies that want to use SAP due to its offerings:
Services covering the entire process, from planning to putting the new system into use
Workers who possess SAP certification and are knowledgeable about it
Cloud-native solutions specifically created for your field
Assisting and making enhancements after the migration to encourage constant progress
We aim to make your switch to SAP Commerce Cloud V2 to boost your platform abilities as well as your business results.
Final Thoughts: V2 is the Future of SAP Commerce
In the comparison of SAP Commerce Cloud V2 vs V1, it's clear that V2 represents a massive leap toward modernization. Because of its cloud-native architecture and better integration, SAP CCv2 helps businesses achieve greater agility, faster approaches and increased scalability.
If your business has yet to move from V1 or is about to perform digital commerce transformation, now would be an ideal time to study why migrating to V2 makes sense. Having Royal Cyber on your team makes adapting to new business systems a positive and productive experience.
#SAPCommerceCloud#SAPMigration#eCommerceInnovation#CloudNativeCommerce#SAPCCv2#HeadlessCommerce#RoyalCyber#DigitalTransformation
0 notes
Text
Best Software Development Company in Chennai: Delivering Excellence in Every Line of Code

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, choosing the best software development company in Chennai can make all the difference between a project that merely functions and one that truly transforms your business. With an ever-growing demand for robust, scalable, and user-centric applications, organizations need a partner who not only writes clean code but also understands market trends, user expectations, and long-term support needs.
Why Chennai Is a Hub for Software Development Excellence
Chennai has rapidly emerged as a leading technology hub in India, thanks to:
World-class talent pool: Top engineering colleges and institutes produce thousands of skilled developers each year.
Cost-effective solutions: High quality at competitive rates compared to global markets.
Mature infrastructure: State-of-the-art IT parks, connectivity, and support services.
Government support: Proactive policies and incentives that nurture IT growth.
Choosing a Software Development Company in Chennai means tapping into this unique ecosystem, where innovation and efficiency go hand in hand.
Key Services Offered by a Top Chennai Software Development Company
Custom Software Development Tailored solutions built from the ground up to address your specific business challenges—whether it’s a CRM, ERP, or niche SaaS application.
Web & Mobile App Development Responsive web portals and native/hybrid mobile apps that deliver seamless user experiences across devices.
Enterprise Solutions & Integrations Scalable architectures, microservices, and API integrations to streamline workflows and data exchange.
UI/UX Design Intuitive interfaces and engaging designs that keep users coming back.
Quality Assurance & Testing Automated and manual testing processes to ensure robust, bug-free software releases.
Maintenance & Support Ongoing updates, security patches, and performance tuning to keep your applications running flawlessly.
What Sets the Best Software Development Company in Chennai Apart?
1. Domain Expertise
A leading Software Development Company in Chennai brings deep knowledge across industries—healthcare, finance, e-commerce, logistics, and more—ensuring your solution aligns with sector-specific regulations and standards.
2. Agile & Collaborative Approach
By embracing Agile methodologies, teams deliver incremental value, adapt quickly to changing requirements, and maintain transparent communication through sprints, standups, and demos.
3. End-to-End Project Management
From requirement gathering and prototyping to deployment and post-launch support, the best firms handle every phase with dedicated project managers, business analysts, and technical leaders overseeing quality and timelines.
4. Cutting-Edge Technologies
Whether it’s AI/ML, blockchain, IoT, or cloud-native development, a top Chennai partner stays ahead of the curve—leveraging modern frameworks (React, Angular, Flutter), robust back-end platforms (Node.js, .NET Core, Java Spring), and scalable cloud services (AWS, Azure, GCP).
5. Commitment to Security
With cyber-threats on the rise, the best software development company in Chennai integrates security best practices from day one—conducting threat modeling, code reviews, and penetration testing to safeguard your data and users.
Client Success Stories
E-Commerce Platform Overhaul: Reduced page-load times by 70% and increased conversions by 35% after migrating to a microservices architecture.
Healthcare App Development: Delivered a HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution serving over 50,000 patients across India.
Logistics Optimization Tool: Automated route planning and real-time tracking, cutting fuel costs by 25% and improving delivery accuracy.
How to Choose Your Software Development Partner in Chennai
Evaluate Portfolio & Case Studies Look for proven success in projects similar to yours, with clear metrics on performance improvements and ROI.
Check Client Testimonials & References Honest feedback from past clients speaks volumes about a company’s reliability, communication, and support.
Assess Technical & Domain Fit Ensure the team’s expertise aligns with your technology stack and industry requirements.
Review Engagement Models & Pricing Transparent models—fixed price, time-and-materials, or dedicated teams—help you plan budgets and resource allocations.
Consider Cultural & Communication Compatibility Seamless collaboration across time zones, clear reporting structures, and shared values foster long-term partnerships.
Conclusion & Next Steps
When you’re ready to accelerate your digital transformation, partnering with the best software development company in Chennai means more than just code delivery—it’s about innovation, collaboration, and measurable business impact.
Reach Out for a Free Consultation: Share your project vision and challenges.
Get a Detailed Proposal: We’ll outline scope, timelines, and costs.
Kick Off Your Project: With an agile team committed to your success, watch your ideas come to life.
Transform your business with a software partner who cares about your goals as much as you do. Contact us today to embark on your journey with Chennai’s finest in software development!
0 notes