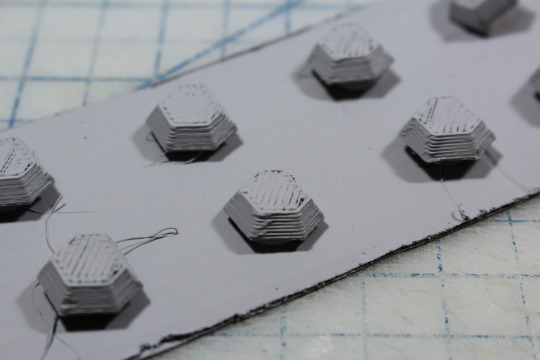
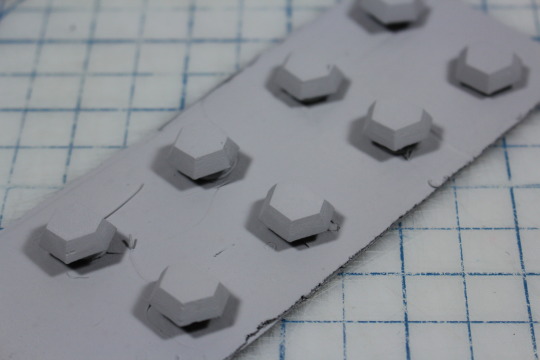
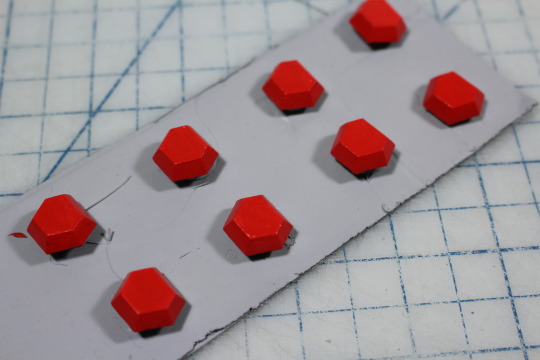
#if i had a printer i would scan these but alas we make do with what we have
Text
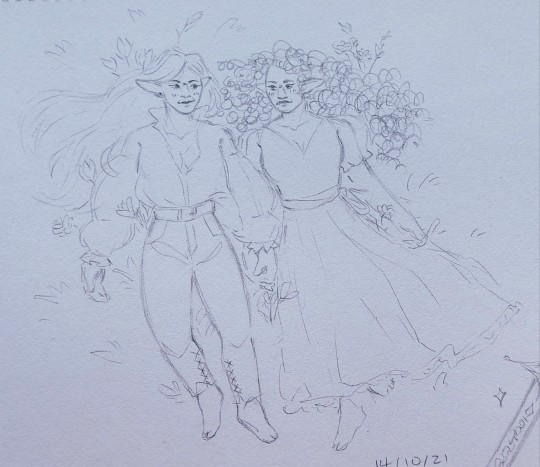
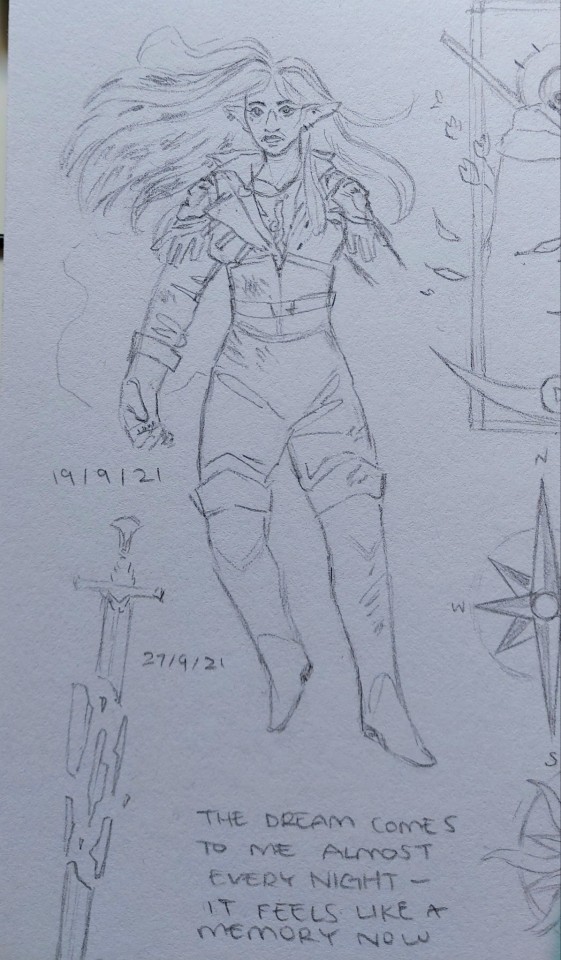


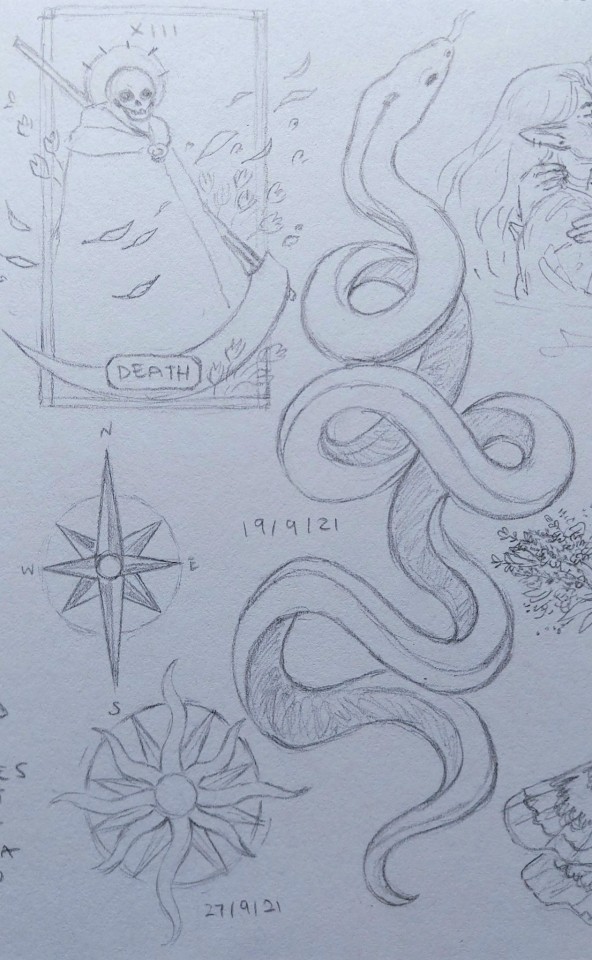

Of dreams about death and love.
I do commissions!
#ghostart#andromeda#d&d oc#rpg oc#dnd 5e character#13th age#original character#sorry for the dogshit quality of the pics. i tried my best but my hands shake real bad#everything other than the characters are her tattoos (she has more than that but i didnt draw them all)#if i had a printer i would scan these but alas we make do with what we have#these are a little old but i was saving them to post after reveals happened bc i have my friends on here
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the economic sphere too, the ability to hold a hammer or press a button is becoming less valuable than before. In the past, there were many things only humans could do. But now robots and computers are catching up, and may soon outperform humans in most tasks. True, computers function very differently from humans, and it seems unlikely that computers will become humanlike any time soon. In particular, it doesn’t seem that computers are about to gain consciousness, and to start experiencing emotions and sensations. Over the last decades there has been an immense advance in computer intelligence, but there has been exactly zero advance in computer consciousness. As far as we know, computers in 2016 are no more conscious than their prototypes in the 1950s. However, we are on the brink of a momentous revolution. Humans are in danger of losing their value, because intelligence is decoupling from consciousness.
Until today, high intelligence always went hand in hand with a developed consciousness. Only conscious beings could perform tasks that required a lot of intelligence, such as playing chess, driving cars, diagnosing diseases or identifying terrorists. However, we are now developing new types of non-conscious intelligence that can perform such tasks far better than humans. For all these tasks are based on pattern recognition, and non-conscious algorithms may soon excel human consciousness in recognising patterns. This raises a novel question: which of the two is really important, intelligence or consciousness? As long as they went hand in hand, debating their relative value was just a pastime for philosophers. But in the twenty-first century, this is becoming an urgent political and economic issue. And it is sobering to realise that, at least for armies and corporations, the answer is straightforward: intelligence is mandatory but consciousness is optional.
Armies and corporations cannot function without intelligent agents, but they don’t need consciousness and subjective experiences. The conscious experiences of a flesh-and-blood taxi driver are infinitely richer than those of a self-driving car, which feels absolutely nothing. The taxi driver can enjoy music while navigating the busy streets of Seoul. His mind may expand in awe as he looks up at the stars and contemplates the mysteries of the universe. His eyes may fill with tears of joy when he sees his baby girl taking her very first step. But the system doesn’t need all that from a taxi driver. All it really wants is to bring passengers from point A to point B as quickly, safely and cheaply as possible. And the autonomous car will soon be able to do that far better than a human driver, even though it cannot enjoy music or be awestruck by the magic of existence.
Indeed, if we forbid humans to drive taxis and cars altogether, and give computer algorithms monopoly over traffic, we can then connect all vehicles to a single network, and thereby make car accidents virtually impossible. In August 2015, one of Google’s experimental self-driving cars had an accident. As it approached a crossing and detected pedestrians wishing to cross, it applied its brakes. A moment later it was hit from behind by a sedan whose careless human driver was perhaps contemplating the mysteries of the universe instead of watching the road. This could not have happened if both vehicles were steered by interlinked computers. The controlling algorithm would have known the position and intentions of every vehicle on the road, and would not have allowed two of its marionettes to collide. Such a system will save lots of time, money and human lives – but it will also do away with the human experience of driving a car and with tens of millions of human jobs.
Some economists predict that sooner or later, unenhanced humans will be completely useless. While robots and 3D printers replace workers in manual jobs such as manufacturing shirts, highly intelligent algorithms will do the same to white-collar occupations. Bank clerks and travel agents, who a short time ago were completely secure from automation, have become endangered species. How many travel agents do we need when we can use our smartphones to buy plane tickets from an algorithm?
Stock-exchange traders are also in danger. Most trade today is already being managed by computer algorithms, which can process in a second more data than a human can in a year, and that can react to the data much faster than a human can blink. On 23 April 2013, Syrian hackers broke into Associated Press’s official Twitter account. At 13:07 they tweeted that the White House had been attacked and President Obama was hurt. Trade algorithms that constantly monitor newsfeeds reacted in no time, and began selling stocks like mad. The Dow Jones went into free fall, and within sixty seconds lost 150 points, equivalent to a loss of $136 billion! At 13:10 Associated Press clarified that the tweet was a hoax. The algorithms reversed gear, and by 13:13 the Dow Jones had recuperated almost all the losses.
Three years previously, on 6 May 2010, the New York stock exchange underwent an even sharper shock. Within five minutes – from 14:42 to 14:47 – the Dow Jones dropped by 1,000 points, wiping out $1 trillion. It then bounced back, returning to its pre-crash level in a little over three minutes. That’s what happens when super-fast computer programs are in charge of our money. Experts have been trying ever since to understand what happened in this so-called ‘Flash Crash’. We know algorithms were to blame, but we are still not sure exactly what went wrong. Some traders in the USA have already filed lawsuits against algorithmic trading, arguing that it unfairly discriminates against human beings, who simply cannot react fast enough to compete. Quibbling whether this really constitutes a violation of rights might provide lots of work and lots of fees for lawyers.
And these lawyers won’t necessarily be human. Movies and TV series give the impression that lawyers spend their days in court shouting ‘Objection!’ and making impassioned speeches. Yet most run-of-the-mill lawyers spend their time going over endless files, looking for precedents, loopholes and tiny pieces of potentially relevant evidence. Some are busy trying to figure out what happened on the night John Doe got killed, or formulating a gargantuan business contract that will protect their client against every conceivable eventuality. What will be the fate of all these lawyers once sophisticated search algorithms can locate more precedents in a day than a human can in a lifetime, and once brain scans can reveal lies and deceptions at the press of a button? Even highly experienced lawyers and detectives cannot easily spot deceptions merely by observing people’s facial expressions and tone of voice. However, lying involves different brain areas to those used when we tell the truth. We’re not there yet, but it is conceivable that in the not too distant future fMRI scanners could function as almost infallible truth machines. Where will that leave millions of lawyers, judges, cops and detectives? They might need to go back to school and learn a new profession.
When they get in the classroom, however, they may well discover that the algorithms have got there first. Companies such as Mindojo are developing interactive algorithms that not only teach me maths, physics and history, but also simultaneously study me and get to know exactly who I am. Digital teachers will closely monitor every answer I give, and how long it took me to give it. Over time, they will discern my unique weaknesses as well as my strengths. They will identify what gets me excited, and what makes my eyelids droop. They could teach me thermodynamics or geometry in a way that suits my personality type, even if that particular way doesn’t suit 99 per cent of the other pupils. And these digital teachers will never lose their patience, never shout at me, and never go on strike. It is unclear, however, why on earth I would need to know thermodynamics or geometry in a world containing such intelligent computer programs.
Even doctors are fair game for the algorithms. The first and foremost task of most doctors is to diagnose diseases correctly, and then suggest the best available treatment. If I arrive at the clinic complaining about fever and diarrhoea, I might be suffering from food poisoning. Then again, the same symptoms might result from a stomach virus, cholera, dysentery, malaria, cancer or some unknown new disease. My doctor has only five minutes to make a correct diagnosis, because this is what my health insurance pays for. This allows for no more than a few questions and perhaps a quick medical examination. The doctor then cross-references this meagre information with my medical history, and with the vast world of human maladies. Alas, not even the most diligent doctor can remember all my previous ailments and check-ups. Similarly, no doctor can be familiar with every illness and drug, or read every new article published in every medical journal. To top it all, the doctor is sometimes tired or hungry or perhaps even sick, which affects her judgement. No wonder that doctors often err in their diagnoses, or recommend a less-than-optimal treatment.
Now consider IBM’s famous Watson – an artificial intelligence system that won the Jeopardy! television game show in 2011, beating human former champions. Watson is currently groomed to do more serious work, particularly in diagnosing diseases. An AI such as Watson has enormous potential advantages over human doctors. Firstly, an AI can hold in its databanks information about every known illness and medicine in history. It can then update these databanks every day, not only with the findings of new researches, but also with medical statistics gathered from every clinic and hospital in the world.
Secondly, Watson can be intimately familiar not only with my entire genome and my day-to-day medical history, but also with the genomes and medical histories of my parents, siblings, cousins, neighbours and friends. Watson will know instantly whether I visited a tropical country recently, whether I have recurring stomach infections, whether there have been cases of intestinal cancer in my family or whether people all over town are complaining this morning about diarrhoea.
Thirdly, Watson will never be tired, hungry or sick, and will have all the time in the world for me. I could sit comfortably on my sofa at home and answer hundreds of questions, telling Watson exactly how I feel. This is good news for most patients (except perhaps hypochondriacs). But if you enter medical school today in the expectation of still being a family doctor in twenty years, maybe you should think again. With such a Watson around, there is not much need for Sherlocks.
This threat hovers over the heads not only of general practitioners, but also of experts. Indeed, it might prove easier to replace doctors specialising in a relatively narrow field such as cancer diagnosis. For example, in a recent experiment a computer algorithm diagnosed correctly 90 per cent of lung cancer cases presented to it, while human doctors had a success rate of only 50 per cent. In fact, the future is already here. CT scans and mammography tests are routinely checked by specialised algorithms, which provide doctors with a second opinion, and sometimes detect tumours that the doctors missed.
A host of tough technical problems still prevent Watson and its ilk from replacing most doctors tomorrow morning. Yet these technical problems – however difficult – need only be solved once. The training of a human doctor is a complicated and expensive process that lasts years. When the process is complete, after ten years of studies and internships, all you get is one doctor. If you want two doctors, you have to repeat the entire process from scratch. In contrast, if and when you solve the technical problems hampering Watson, you will get not one, but an infinite number of doctors, available 24/7 in every corner of the world. So even if it costs $100 billion to make it work, in the long run it would be much cheaper than training human doctors.
And what’s true of doctors is doubly true of pharmacists. In 2011 a pharmacy opened in San Francisco manned by a single robot. When a human comes to the pharmacy, within seconds the robot receives all of the customer’s prescriptions, as well as detailed information about other medicines taken by them, and their suspected allergies. The robot makes sure the new prescriptions don’t combine adversely with any other medicine or allergy, and then provides the customer with the required drug. In its first year of operation the robotic pharmacist provided 2 million prescriptions, without making a single mistake. On average, flesh-and-blood pharmacists get wrong 1.7 per cent of prescriptions. In the United States alone this amounts to more than 50 million prescription errors every year!
Some people argue that even if an algorithm could outperform doctors and pharmacists in the technical aspects of their professions, it could never replace their human touch. If your CT indicates you have cancer, would you like to receive the news from a caring and empathetic human doctor, or from a machine? Well, how about receiving the news from a caring and empathetic machine that tailors its words to your personality type? Remember that organisms are algorithms, and Watson could detect your emotional state with the same accuracy that it detects your tumours.
This idea has already been implemented by some customer-services departments, such as those pioneered by the Chicago-based Mattersight Corporation. Mattersight publishes its wares with the following advert: ‘Have you ever spoken with someone and felt as though you just clicked? The magical feeling you get is the result of a personality connection. Mattersight creates that feeling every day, in call centers around the world.’ When you call customer services with a request or complaint, it usually takes a few seconds to route your call to a representative. In Mattersight systems, your call is routed by a clever algorithm. You first state the reason for your call. The algorithm listens to your request, analyses the words you have chosen and your tone of voice, and deduces not only your present emotional state but also your personality type – whether you are introverted, extroverted, rebellious or dependent. Based on this information, the algorithm links you to the representative that best matches your mood and personality. The algorithm knows whether you need an empathetic person to patiently listen to your complaints, or you prefer a no-nonsense rational type who will give you the quickest technical solution. A good match means both happier customers and less time and money wasted by the customer-services department.
The most important question in twenty-first-century economics may well be what to do with all the superfluous people. What will conscious humans do, once we have highly intelligent non-conscious algorithms that can do almost everything better?
Throughout history the job market was divided into three main sectors: agriculture, industry and services. Until about 1800, the vast majority of people worked in agriculture, and only a small minority worked in industry and services. During the Industrial Revolution people in developed countries left the fields and herds. Most began working in industry, but growing numbers also took up jobs in the services sector. In recent decades developed countries underwent another revolution, as industrial jobs vanished, whereas the services sector expanded. In 2010 only 2 per cent of Americans worked in agriculture, 20 per cent worked in industry, 78 per cent worked as teachers, doctors, webpage designers and so forth. When mindless algorithms are able to teach, diagnose and design better than humans, what will we do?
This is not an entirely new question. Ever since the Industrial Revolution erupted, people feared that mechanisation might cause mass unemployment. This never happened, because as old professions became obsolete, new professions evolved, and there was always something humans could do better than machines. Yet this is not a law of nature, and nothing guarantees it will continue to be like that in the future. Humans have two basic types of abilities: physical abilities and cognitive abilities. As long as machines competed with us merely in physical abilities, you could always find cognitive tasks that humans do better. So machines took over purely manual jobs, while humans focused on jobs requiring at least some cognitive skills. Yet what will happen once algorithms outperform us in remembering, analysing and recognising patterns?
The idea that humans will always have a unique ability beyond the reach of non-conscious algorithms is just wishful thinking. True, at present there are numerous things that organic algorithms do better than non-organic ones, and experts have repeatedly declared that something will ‘for ever’ remain beyond the reach of non-organic algorithms. But it turns out that ‘for ever’ often means no more than a decade or two. Until a short time ago, facial recognition was a favourite example of something which even babies accomplish easily but which escaped even the most powerful computers on earth. Today facial-recognition programs are able to recognise people far more efficiently and quickly than humans can. Police forces and intelligence services now use such programs to scan countless hours of video footage from surveillance cameras, tracking down suspects and criminals.
In the 1980s when people discussed the unique nature of humanity, they habitually used chess as primary proof of human superiority. They believed that computers would never beat humans at chess. On 10 February 1996, IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov, laying to rest that particular claim for human pre-eminence.
Deep Blue was given a head start by its creators, who preprogrammed it not only with the basic rules of chess, but also with detailed instructions regarding chess strategies. A new generation of AI uses machine learning to do even more remarkable and elegant things. In February 2015 a program developed by Google DeepMind learned by itself how to play forty-nine classic Atari games. One of the developers, Dr Demis Hassabis, explained that ‘the only information we gave the system was the raw pixels on the screen and the idea that it had to get a high score. And everything else it had to figure out by itself.’ The program managed to learn the rules of all the games it was presented with, from Pac-Man and Space Invaders to car racing and tennis games. It then played most of them as well as or better than humans, sometimes coming up with strategies that never occur to human players.
Computer algorithms have recently proven their worth in ball games, too. For many decades, baseball teams used the wisdom, experience and gut instincts of professional scouts and managers to pick players. The best players fetched millions of dollars, and naturally enough the rich teams got the cream of the market, whereas poorer teams had to settle for the scraps. In 2002 Billy Beane, the manager of the low-budget Oakland Athletics, decided to beat the system. He relied on an arcane computer algorithm developed by economists and computer geeks to create a winning team from players that human scouts overlooked or undervalued. The old-timers were incensed by Beane’s algorithm transgressing into the hallowed halls of baseball. They said that picking baseball players is an art, and that only humans with an intimate and long-standing experience of the game can master it. A computer program could never do it, because it could never decipher the secrets and the spirit of baseball.
They soon had to eat their baseball caps. Beane’s shoestring-budget algorithmic team ($44 million) not only held its own against baseball giants such as the New York Yankees ($125 million), but became the first team ever in American League baseball to win twenty consecutive games. Not that Beane and Oakland could enjoy their success for long. Soon enough, many other baseball teams adopted the same algorithmic approach, and since the Yankees and Red Sox could pay far more for both baseball players and computer software, low-budget teams such as the Oakland Athletics now had an even smaller chance of beating the system than before.
In 2004 Professor Frank Levy from MIT and Professor Richard Murnane from Harvard published a thorough research of the job market, listing those professions most likely to undergo automation. Truck drivers were given as an example of a job that could not possibly be automated in the foreseeable future. It is hard to imagine, they wrote, that algorithms could safely drive trucks on a busy road. A mere ten years later, Google and Tesla not only imagine this, but are actually making it happen.
In fact, as time goes by, it becomes easier and easier to replace humans with computer algorithms, not merely because the algorithms are getting smarter, but also because humans are professionalising. Ancient hunter-gatherers mastered a very wide variety of skills in order to survive, which is why it would be immensely difficult to design a robotic hunter-gatherer. Such a robot would have to know how to prepare spear points from flint stones, how to find edible mushrooms in a forest, how to use medicinal herbs to bandage a wound, how to track down a mammoth and how to coordinate a charge with a dozen other hunters. However, over the last few thousand years we humans have been specialising. A taxi driver or a cardiologist specialises in a much narrower niche than a hunter-gatherer, which makes it easier to replace them with AI.
Even the managers in charge of all these activities can be replaced. Thanks to its powerful algorithms, Uber can manage millions of taxi drivers with only a handful of humans. Most of the commands are given by the algorithms without any need of human supervision. In May 2014 Deep Knowledge Ventures – a Hong Kong venture-capital firm specialising in regenerative medicine – broke new ground by appointing an algorithm called VITAL to its board. VITAL makes investment recommendations by analysing huge amounts of data on the financial situation, clinical trials and intellectual property of prospective companies. Like the other five board members, the algorithm gets to vote on whether the firm makes an investment in a specific company or not.
Examining VITAL’s record so far, it seems that it has already picked up one managerial vice: nepotism. It has recommended investing in companies that grant algorithms more authority. With VITAL’s blessing, Deep Knowledge Ventures has recently invested in Silico Medicine, which develops computer-assisted methods for drug research, and in Pathway Pharmaceuticals, which employs a platform called OncoFinder to select and rate personalised cancer therapies.
As algorithms push humans out of the job market, wealth might become concentrated in the hands of the tiny elite that owns the all-powerful algorithms, creating unprecedented social inequality. Alternatively, the algorithms might not only manage businesses, but actually come to own them. At present, human law already recognises intersubjective entities like corporations and nations as ‘legal persons’. Though Toyota or Argentina has neither a body nor a mind, they are subject to international laws, they can own land and money, and they can sue and be sued in court. We might soon grant similar status to algorithms. An algorithm could then own a venture-capital fund without having to obey the wishes of any human master.
If the algorithm makes the right decisions, it could accumulate a fortune, which it could then invest as it sees fit, perhaps buying your house and becoming your landlord. If you infringe on the algorithm’s legal rights – say, by not paying rent – the algorithm could hire lawyers and sue you in court. If such algorithms consistently outperform human fund managers, we might end up with an algorithmic upper class owning most of our planet. This may sound impossible, but before dismissing the idea, remember that most of our planet is already legally owned by non-human inter-subjective entities, namely nations and corporations. Indeed, 5,000 years ago much of Sumer was owned by imaginary gods such as Enki and Inanna. If gods can possess land and employ people, why not algorithms?
So what will people do? Art is often said to provide us with our ultimate (and uniquely human) sanctuary. In a world where computers replace doctors, drivers, teachers and even landlords, everyone would become an artist. Yet it is hard to see why artistic creation will be safe from the algorithms. Why are we so sure computers will be unable to better us in the composition of music? According to the life sciences, art is not the product of some enchanted spirit or metaphysical soul, but rather of organic algorithms recognising mathematical patterns. If so, there is no reason why non-organic algorithms couldn’t master it.
David Cope is a musicology professor at the University of California in Santa Cruz. He is also one of the more controversial figures in the world of classical music. Cope has written programs that compose concertos, chorales, symphonies and operas. His first creation was named EMI (Experiments in Musical Intelligence), which specialised in imitating the style of Johann Sebastian Bach. It took seven years to create the program, but once the work was done, EMI composed 5,000 chorales à la Bach in a single day. Cope arranged a performance of a few select chorales in a music festival at Santa Cruz. Enthusiastic members of the audience praised the wonderful performance, and explained excitedly how the music touched their innermost being. They didn’t know it was composed by EMI rather than Bach, and when the truth was revealed, some reacted with glum silence, while others shouted in anger.
EMI continued to improve, and learned to imitate Beethoven, Chopin, Rachmaninov and Stravinsky. Cope got EMI a contract, and its first album – Classical Music Composed by Computer – sold surprisingly well. Publicity brought increasing hostility from classical-music buffs. Professor Steve Larson from the University of Oregon sent Cope a challenge for a musical showdown. Larson suggested that professional pianists play three pieces one after the other: one by Bach, one by EMI, and one by Larson himself. The audience would then be asked to vote who composed which piece. Larson was convinced people would easily tell the difference between soulful human compositions, and the lifeless artefact of a machine. Cope accepted the challenge. On the appointed date, hundreds of lecturers, students and music fans assembled in the University of Oregon’s concert hall. At the end of the performance, a vote was taken. The result? The audience thought that EMI’s piece was genuine Bach, that Bach’s piece was composed by Larson, and that Larson’s piece was produced by a computer.
Critics continued to argue that EMI’s music is technically excellent, but that it lacks something. It is too accurate. It has no depth. It has no soul. Yet when people heard EMI’s compositions without being informed of their provenance, they frequently praised them precisely for their soulfulness and emotional resonance.
Following EMI’s successes, Cope created newer and even more sophisticated programs. His crowning achievement was Annie. Whereas EMI composed music according to predetermined rules, Annie is based on machine learning. Its musical style constantly changes and develops in reaction to new inputs from the outside world. Cope has no idea what Annie is going to compose next. Indeed, Annie does not restrict itself to music composition but also explores other art forms such as haiku poetry. In 2011 Cope published Comes the Fiery Night: 2,000 Haiku by Man and Machine. Of the 2,000 haikus in the book, some are written by Annie, and the rest by organic poets. The book does not disclose which are which. If you think you can tell the difference between human creativity and machine output, you are welcome to test your claim.
In the nineteenth century the Industrial Revolution created a huge new class of urban proletariats, in the twenty-first century we might witness the creation of a new massive class: people devoid of any economic, political or even artistic value, who contribute nothing to the prosperity, power and glory of society.
In September 2013 two Oxford researchers, Carl Benedikt Frey and Michael A. Osborne, published ‘The Future of Employment’, in which they surveyed the likelihood of different professions being taken over by computer algorithms within the next twenty years. The algorithm developed by Frey and Osborne to do the calculations estimated that 47 per cent of US jobs are at high risk. For example, there is a 99 per cent probability that by 2033 human telemarketers and insurance underwriters will lose their jobs to algorithms. There is a 98 per cent probability that the same will happen to sports referees, 97 per cent that it will happen to cashiers and 96 per cent to chefs. Waiters – 94 per cent. Paralegal assistants – 94 per cent. Tour guides – 91 per cent. Bakers – 89 per cent. Bus drivers – 89 per cent. Construction labourers – 88 per cent. Veterinary assistants – 86 per cent. Security guards – 84 per cent. Sailors – 83 per cent. Bartenders – 77 per cent. Archivists – 76 per cent. Carpenters – 72 per cent. Lifeguards – 67 per cent. And so forth. There are of course some safe jobs. The likelihood that computer algorithms will displace archaeologists by 2033 is only 0.7 per cent, because their job requires highly sophisticated types of pattern recognition, and doesn’t produce huge profits. Hence it is improbable that corporations or government will make the necessary investment to automate archaeology within the next twenty years.
Of course, by 2033 many new professions are likely to appear, for example, virtual-world designers. But such professions will probably require much more creativity and flexibility than your run-of-the-mill job, and it is unclear whether forty-year-old cashiers or insurance agents will be able to reinvent themselves as virtual-world designers (just try to imagine a virtual world created by an insurance agent!). And even if they do so, the pace of progress is such that within another decade they might have to reinvent themselves yet again. After all, algorithms might well outperform humans in designing virtual worlds too. The crucial problem isn’t creating new jobs. The crucial problem is creating new jobs that humans perform better than algorithms.
- Yuval Noah Harari, The Great Decoupling in Homo Deus: A Brief History of Tomorrow
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Making Soldier 76′s Gloves: A Tutorial

Yay gloves! This is a walk-through that shows how I made them. I did make several mistakes along the way, but hopefully there is still value to be found in the process. Enjoy!
Warning: Ridiculously image heavy!!
As usual, I started by hoarding references. The 3D model I downloaded was very helpful for this.

Several months ago at the beginning of this adventure, I sat down and planned how all the costume components would be built. At the time I intended to use spray adhesive to tack down some type of stretchy, plastic-y fabric--probably vinyl. Later I learned that my library’s makerspace had a die cutter, so “stretch vinyl” was replaced with heat transfer vinyl. I did choose to omit the grey palm, but otherwise these are accurate to the game model.

The pre-existing gloves were a pair of these from Costco. In hind sight, they weren’t 100% ideal; see that seam across the knuckles? It’s going to cause trouble later.

Next I needed to make a digital cut file for the Silhouette die cutter. Die cutters are basically digital cutting machines... sort of like printing with a knife. You give them a file with lines, and a knife (or other tool) traces them onto materials like paper, fabric, and vinyl. The software requires vectors to cut, so I used Adobe Illustrator. If you don’t have access to this software, the open source equivalent Inkscape would work just as well. I began by very carefully measuring the gloves to make a janky but correctly scaled pattern. The red armor was drawn over the top.
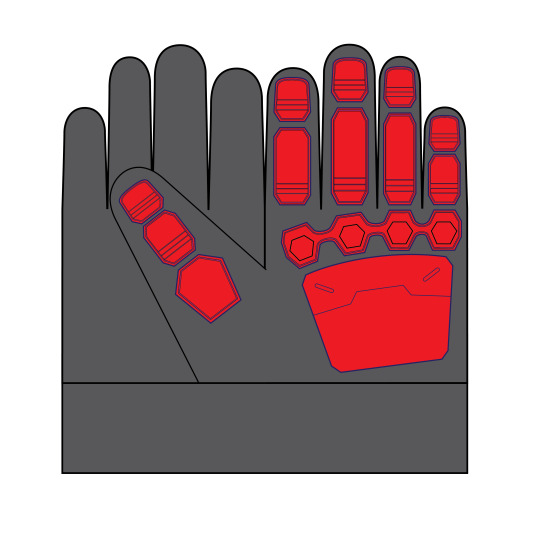
Next, the templates were printed and laid over the glove to check for scale. as you can see, the guard on top of the hand is much too large. I made a few adjustments to the paper templates, scanned them, and modified the vectors to fit.

Then it was cutting time! Only the finger and knuckle guard bases were made from heat transfer vinyl. (If I didn’t have access to the die cutter, I would have traced the templates onto masking tape and used them as a mask for fabric paint.)

Next I wanted to make the knuckle guards. These could have easily been made with Sculpey, but I sit next to a 3D printer all day at work so I took the easy way out.

As normal with 3D prints, these had a distinct texture. I decided to take the opportunity and try out Automotive Filler Primer since it’s supposed to be the bee’s knees for smoothing 3D prints. Sanding PLA sucks, so I’ll jump on any possible opportunity to avoid it. In preparation for spray painting, the knuckle guards were stuck on a piece of cardboard with hot glue. A little clearance from the surface means their edges will be more clean, plus I don’t need to keep track of 8 tiny pieces of plastic. The hot glue will peel off cleanly later.
From what I had heard, you don’t need to sand filler primer because it self-levels. After one coat, I was not so sure.
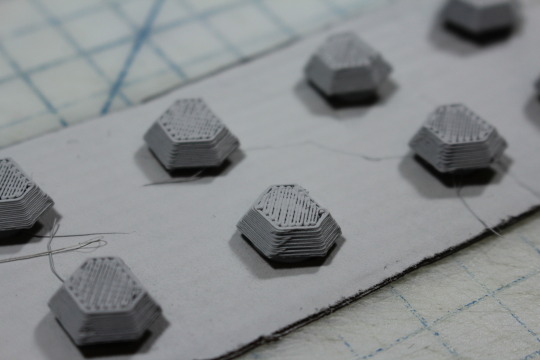
Three coats in and the ridges were actually more pronounced, so I broke out the sandpaper.
Amazing!!! It looks awful but dang did it feel smooth and it sanded SO MUCH EASIER than PLA! 220 grit paper was plenty remove material.

After two more passes of spraying and sanding, the guards were looking pretty smooth. Here they are after their final spray:
Fun fact, that stuff will clog up your paper something fierce! Buy a lot of sandpaper if you have large things to surface.
Next up was painting. Normally I would spray paint or airbrush something like this, but the weather has not been cooperating lately so I hand-painted them instead.

Since the red paint is somewhat translucent, I gave the parts a thin coating of white first. Then red was layered on until I achieved full coverage.


The final detail for the knuckle guards was a thin, black line running around their base. Any permanent marker will do.

The knuckle guards still need weathering, but I prefer to weather everything at once so I moved on to building the hand guards. Using the paper template from Illustrator, I traced the main shape onto 6mm foam. You will notice some indents running along the flat surface:
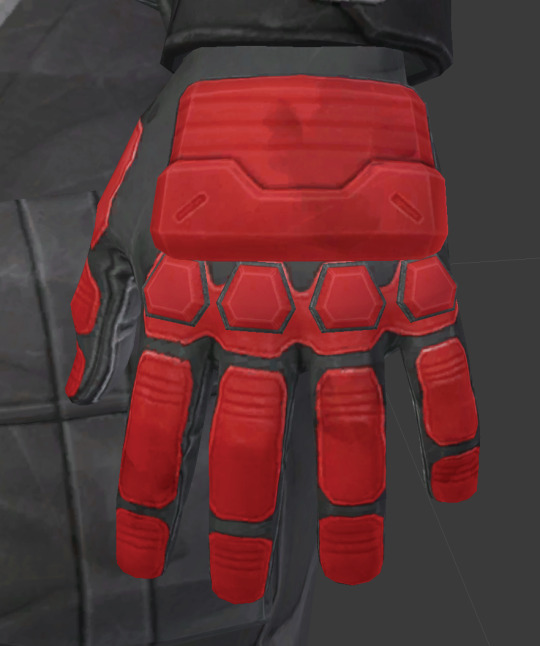

Those were recreated by scoring the foam with an X-acto knife. When blasted with a heat gun, the foam will contract slightly to create a groove (pictures of this later).

I added a second layer to the guards with 2mm craft foam.
In order to emphasize the angles, I carved a teeny grove with my pen knife and removed the excess material with a pair of tweezers.


This channel helps the foam bend a little sharper. It might seem subtle, but the effect was worth it.

Next, I used a sharpened aluminum tube to punch perfect circles into the foam. You can find these at most hobby stores and sharpen them with a needle file--also to be found at most hobby stores. The holes were expanded into slots using my handy X-acto. This was surprisingly hard to do neatly; I wish EVA foam was a little more dense :/


The parts were adhered together with contact cement. I had to do this outside and it was dark, so I don’t have good pictures :( As a last step before painting, I used a heat gun to give them a gentle curve and emphasize those grooves. Unfortunately, I was a little liberal with the heat and you can see some low-key melting. Oops. Given the size of these parts, it was an interesting challenge to attempt without gloves.

For painting, I decided to use my airbrush. I was gifted a setup yeeeeeeeears ago and I hardly ever use it. Time to change that! I primed the foam with this all-purpose primer which claimed to be slightly flexible. This is a lie. Don’t buy this brand of primer if you need something to be flexible!!

Like the knuckle guards, I gave the hand guards a light pass with white so it would take less red to reach full coverage. Full disclosure, I kind of suck with air-brushes. See that weirdo blob on the left corner of the left guard? That’s what happens when you spray too much paint with an air-brush. They also had a funky texture which I believe was a result of too much paint at once.



For weathering, I used 400 grit sandpaper to remove paint from corners and edges revealing the primer beneath. I think it gives a pretty neat effect! Grime was a mixture of Mars Black, Burnt Umber, and water. Finally, a coat of brush-on varnish sealed the paint job.


It was only after applying the varnish that I realized it was glossy, so I misted the parts with Matte Fixative meant for sealing drawings. This is not ideal and you should be smarter than me and buy the right varnish to begin with.
Finally, it was time to add the finger pieces and assemble the gloves! This was done with an ancient (circa 1970′s) iron, a scrap of muslin, some cardboard, and sewing pins.

Note about the vinyl: There is such a thing as stretchy heat transfer vinyl. I didn’t know this when purchasing, but stretchy would definitely have been preferable. The fingers of a glove are constantly flexing and moving, so over time my regular vinyl will break down. I did verify that my pattern would stretch, but you should still purchase the proper variety if you choose to do something like this. Thankfully the pattern I cut allowed the material to stretch somewhat.

Once cut, the vinyl needed weeding. Weeding is the process of removing everything you don’t need from the piece to be transferred. While there are specific tools available for this task, I like using an X-acto knife. After you get a piece started, tweezers can help remove the rest. Be very careful during this step; sometimes the machine doesn’t quite slice all the way through and you can pull off the wrong parts.
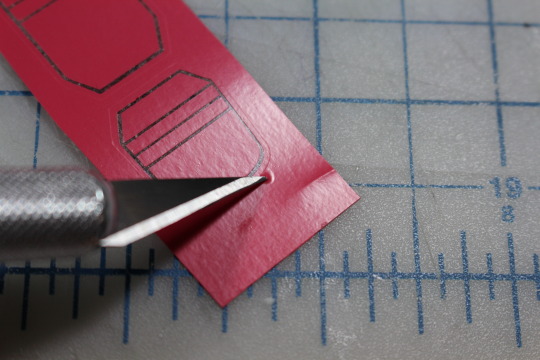

With the parts weeded, it was time to iron them in place. Heat transfer vinyl needs to be pressed while perfectly flat. The fingers of these gloves have gussets on each side which equals a lot of fabric and seams in a small area. Such construction makes them form-fitting and comfortable, but I couldn't get them to lay flat. To remedy this I made an insertable cardboard finger and pinned the fabric in place. It was important NOT to stretch the fabric while doing so or else the vinyl would crumple when un-pinned.



With the fabric secured, I attempted to stick the vinyl in place using the mildly adhesive cover plastic. Alas, it just wouldn’t stay, so I used a snugly pinned piece of muslin to hold it down. 15 seconds of pressing with the iron, and ta-dah! Red decals :)




These gloves are two sizes too big for me in case you couldn’t tell :)
Remember how I mentioned that seam across the back causing trouble? Unfortunately it runs right through the middle of a decal. It was very tricky to iron without burning the vinyl and it’s kind of ugly. 10-foot rule will save me, but it could have been avoided by buying better gloves.

The last step was gluing the hand and knuckle guards in place. Because the fabric is stretchy but my parts are curved, I needed to put the gloves on Casey before gluing down anything rigid. Alas, I don’t have many images here because Casey didn’t feel like being a hand model and we were outside because of glue fumes. Each hand guard got a thorough application of E6000 in the center with hot glue around the edges. I wanted the strength of E6000 but needed the quick dry time of hot glue, so this worked fairly well. Overflowed hotglue was colored with a Sharpie and disappears from a distance.



More E6000 was used to fix the knuckle guards. Then the gloves were tossed into the Bin of Shame ™ to cure without fumigating my room.


After two days of curing, everything was finished! I'm really happy with how they turned out :D

98 notes
·
View notes
Text
FAQ
What is the final product going to be?
The final product will be a compilation in book format. See the Submissions page for details.
Do I need to sign up?
Nope! It’s entirely up to you whether you want to participate, and there’s no absolutely no obligation to commit. This is just a fun project to send a little love back to someone who’s been so loving and awesome to us.
Can I send a handwritten letter?
Short answer: YES!
Long answer: STILL YES. Since everything is compiled digitally, all I ask is that you submit a clean, legible scan of your letter by email.
Don’t have a scanner? Your local library probably does, and I can promise it’ll look better reproduced on a page if it’s a scan rather than a photo.
Remember that it’s gotta be legible at an 8”x10” (20×25 cm) size!!
What dimensions do I need to fit my submission to?
The active print dimensions will be 7.25 x 9.25in (18.415 x 23.495cm). If you’re submitting an image, the minimum resolution requirement is 300 dpi. The size of the image itself can be larger or smaller, but smaller images will only be printed at their original size – bigger images will be scaled down to fit the page accordingly.
Want a full bleed image that reaches the edge of the page? Make sure it’s 8.125 x 10.25in (20.637 x 26.035cm) and there’s nothing vital on the very edges.
Here are the dimension specifics & a handy template you can use to make sure your image will print beautifully.
Will you edit my submission?
This has two answers.
I will not be changing whatever you choose to submit. Whatever you send me is what will be printed. Your work is your own, and you are responsible for submitting what you think best reflects your thoughts. Please proofread (or have a friend proofread) for errors like spelling/grammar.
I will be checking for resolution & size requirements, and if there’s any red flags I’ll get back to you.
Will you print everything that you receive?
Yes. If it doesn’t fit within the allotted 200 pages, we can add a few pages or discuss a Vol. 2.
I missed the deadline by, like, a day. Will you add my submission to the book?
Unless we’re short on content, no. (If we are short, the deadline will be extended). You’re more than welcome to submit after the deadline, but everything will be put into a folder marked Vol. 2 and won’t be included in Vol. 1.
Why?
Deadlines are important -- to you, so you have time to consider what you want to submit and when it needs to be together by; and to me, as the person compiling the book, I need all of the content before this can be completed.
How is Michael going to get this book?
Great question. I’d love to hand-deliver this, but sadly I have no plans right now of ever meeting him in person (I live very far away from any of the places that host events that he frequents and have Many Student Loans so travel is sort of a stretch right now), but he did very kindly give us the mailing address of his agency, who forward mail to him. I’ll be verifying the address with him before it’s sent.
I’ve already sent stuff to Michael over Twitter/Instagram. Can I submit it anyway?
Yes!!! If you want to immortalize your words or art in a book he can access even when the electricity or wifi cuts out, send it on in!
Will anything submitted here be posted online?
I’d love to share anything you send me on this blog -- it’s great for inspiration to see what other people are making -- but that won’t happen unless you give me explicit permission to do so.
But does that mean I won’t be able to see the finished product?
I’ll be posting a link to a PDF of the final product so that everyone can see their contributions all together.
How can I help?
I would cry and also add you to the This Project Was Made Possible By page if you do.
Things that could be done:
Networking!!! If you know of anyone who might be interested in participating in this project, let them know we exist! Shoutout on the social media platform of your choice!
Funding (see below)
Costs:
You are under no obligation to pay anything to be a part of this project. Participation is free!!
This is just full disclosure of what’s going on with the production side of things.
If I had a decent printer, I would print everything and bind the book myself but alas I am no longer in college.
I’ll be using Blurb.com (a print-on-demand service) to print – an 8”x10” (20×25 cm) trade hardcover with imagewrap (no dust jacket), in full colour on 70# paper. If I have time, I can make and construct a dust jacket to put over it, no problem.
Why a trade hardcover instead of a photo book?
Price. A good quality photo book is in the range of $80. A trade paperback offers slightly lower quality paper (70# paper is still hecking amazing, btw, I love printing on it), and lowers the cost significantly. It’s also still a very high quality book (I love blurb??? They do an amazing job)
Economy colour at 200 pages: $25.55 (additional pages $0.06)
Standard colour at 200 pages: $49.39 (additional pages $0.15)
(This does not include shipping).
I’m not made of money but I can afford to print a book.
And hey, if everyone who submits also contributes as little as 50c or even $1, this would be covered in no time and if we pool enough money, I’m all for splurging for the photo book, no bother.
If I donate, where will my money go?
It’ll go straight into funding this book. If we reach the goal, then I’ll update this page & also make a shoutout post – life is expensive so it’s really not necessary to go over the goal. If the amount goes over, then it’ll go straight to the next volume.
As always, thank you so much!!! This wouldn’t be possible without you.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Promotion, Pt I
- You had always thought you could get along with anybody at work - even if it was merely on a professional level. That was until you met Jungkook. The most irritating man you had ever met. He got under your skin in a way nobody else could and vice versa. Nothing could make you like him. Shame then, that your boss makes you an offer you can't refuse, pushing the pair of you closer than ever before. -
Yet another slow, Friday morning had been spent behind your desk at BH Industries ignoring possibly quite important phone calls and doing the bare minimum when an empty candy wrapper zoomed through your line of vision, landing just beside your keyboard. You stared at it blankly for a moment, yanked out of your daydream about Kim Namjoon aka the sexiest man ever to grace your television before another (this time balled up to ensure it hit its target) smacked you straight across the face. You swivelled around in your chair to see Nayeon just as she let go of another wrapper which landed directly on your keyboard and no doubt had left a greasy mark. Just as you were about to open your mouth to give her a piece of your mind, you clocked the alarmed look on her face and noticed she was trying to point in the direction of the door in what she thought was a discrete gesture. You turned quickly to see what she was warning you about and when you saw it, you threw your head back on your desk chair, looking directly up at the ceiling and gave out a deep groan. Jungkook was wandering about in the office and you knew exactly who he was looking for.
He scanned the room and you slunk down in your chair, praying that perhaps he would miss you and assume you were out, but alas, there was the flash of recognition in his eyes before he made his way over. “There you are,” he said casually as though it weren’t at all strange that you were halfway down your chair, almost on the floor. He perched on the end of your light wooden desk, identical to all the others in the room and placed his hands softly on the end of one knee that was draped across the corner of the table like it was perfectly normal for him to be here. “Did you sort out the April ‘17 file I sent you?”
You refused to meet his gaze, pretending to scan the papers before you, although your eyes flickered to your screen showing the one unopened email marked ‘IMPORTANT!’ from his address. You had made it a rule to ignore anything from JJeon2801 until the last possible moment and it appeared that the last possible moment had passed five minutes ago.
You thought for a moment and settled with: “not yet, I haven’t had time.” Half-true. Your voice had exited your throat sounding calm like you had hoped, but unintentionally sing-songy in a way that would no doubt grate on his nerves.
However if it had irritated him even in the slightest, he didn’t show it. His composure maintained like a perfect mask in a way yours never did and probably never could. “Shouldn’t you prioritise those? We have to get it done for-”
You cut him off with an over-dramatic sigh you saved just for interactions with him, wheeling yourself over to the printer in your chair and wheeling back to straighten them out by tapping them gently on the desk in an unnecessary fashion. “Don’t you have anything better to do besides to criticise how I do my job?”
Jungkook rolled his eyes. “You’re keeping me waiting. Perhaps if you did something other than strut about the office like you own the place you’d get some work done.”
He always did this; resorting to making little digs about your performance. Each time you promised you’d have a scathing remark waiting to bite back with, and each time you came up with nothing. “Keep waiting.” You snapped and stood up, collecting the wrappers Nayeon had thrown at you and balling them up in frustration, chucking them into the wastepaper basket with a little too much force. “Last time I checked you weren’t my boss, so I don’t have to answer to you.” You made your way to the door, grasping the door handle before pausing and turning back to face him. “And I don’t strut.”
In a huff, you stormed out of the room and headed to the ladies bathroom to recollect yourself. Once again you had let him get to you in front of a room full of people - people you respected, and it was no less mortifying than the last time. Even when there wasn’t a problem, the pair of you would find some way to argue, and it always seemed to you that he won. It had gotten considerably worse since Jungkook found out about the time you had gone to your boss to ask if you could avoid working with him. Needless to say, your boss had basically told you to get on with it, and so here you were once again. This was becoming too regular of a thing.
“Surely not another fight with my boyfriend?” You heard a voice you recognised to be Madge from HR chuckle behind you. She always flirted with the younger men in the office, it was a game for her, but she seemed to have built up a particular rapport with Jungkook - much to your disappointment, as you had always felt you could confide in her beforehand. Now it just seemed a bit rude to rant about one of her friends.
You shrugged, taking steadying breaths in the mirror as you watched your own reflection. From here you could see Madge sat behind you nibbling on a Kit-Kat whilst perched on the window ledge with no window. As usual, she looked absolutely incredible even in unflattering office attire; perhaps looking in her early forties despite pushing late-fifties. It hadn’t surprised you that she was here, she always seemed to be hiding in here and it was a wonder she hadn’t been fired.
“What’s he done now?” She asked as she picked apart the wafers on her chocolate bar and let the crumbs spill all over the place, ignoring your coldness as she always did when you turned up here.
“Oh, you know... He’s trying to tell me how I should be doing my job.” You explained, trying to sound nonchalant but instead sounding completely apathetic - almost robotic. Inside, however, you were a swirling mess of frustration, somewhere between wanting to punch something and wanting to bang your head against the wall and scream.
Madge just shook her head and tried to hide her smile beneath her blonde hair. “You two need to stop this - winding each other up and nobody is going to win.”
You turned to look at her face-on, almost shocked at the suggestion that any of this was somehow your fault. “He started it!” You exclaimed, your voice rocketing octaves higher causing even you to wince.
Madge hopped off the ledge, wiping the remaining specks of chocolate from her trouser leg to the floor. “You sound like a sulky teenager right now.” She frowned at you in disapproval and you bit your tongue, knowing she was right and feeling ashamed that she had seen this side of you. You could hear just how childish and silly this all sounded, but you couldn’t stop it. Madge came over to you and gave you two gentle pats on the back as she looked at your reflection in the mirror. “Just try giving him a chance - he’s sweet. You’re the only one in the office who doesn’t like him.” She pointed out, to which you couldn’t help but sigh and roll your eyes. She smiled at that. “I’d say exactly the same thing to him about you.” Then she gave your shoulder a quick squeeze and was gone, leaving you alone in the bathroom.
Once again Madge was your voice of reason and the only reason that you didn’t go mad working here. You thought about how lucky you had been to find somewhere like this to work. All-in-all you were pretty popular in the office, with quite a few friends and a decent relationship with your boss and before Jungkook had arrived, no particular feelings of ill-will towards anyone. But when he turned up, you’d have thought the Messiah himself had step foot in the office with the way everyone was behaving. One athletic pretty boy gets hired and suddenly all the men want to be him and all the women swoon over him. Madge had been quick to point out to you that he’s not just a pretty face. Apparently, he’s also quick-witted, hard-working and an all-around nice guy, but the thought of that made you scrunch up your face in disgust. Usually, you trusted Madge’s opinion, but he had never exhibited any of these qualities while you were around so it was much easier to believe that it wasn’t true and that Jungkook is in-fact a monster sent to drive you crazy.
Back at your desk, you were relieved to find that there was absolutely no sign of Jungkook at all - your desk was the same, everyone was sat down quietly chatting and working, and everything seemed normal. With a baited breath, you opened up the dreaded file and groaned loudly at the number of fuck-ups you could see just at a glance. He must have done this on purpose because if you had one good thing to say about him was that he was never usually this careless. It would take you all day just to correct his mistakes, never mind anything else.
“How’s Madge?” Nayeon asked playfully as she skipped over and plopped herself down on the edge of your desk before slipping a small red lollipop into her mouth and stuffing the empty wrapper into your pencil holder.
You let out a small whine of disapproval as you pulled it out immediately and threw it away, earning a big grin from Nayeon through which you could see that her tongue was tinged with chemical red. “She’s fine, I think. Still trying to convince me that Jungkook isn’t out to get me.”
Nayeon shot you a look that told you she probably agreed with Madge, so you turned your computer monitor towards her showing her your predicament. “I mean, come on. Look at this.” You watched her register everything that was wrong, her eyes widening in shock at all the silly little mistakes within it. “Look at the state of it, and he wants it done by tomorrow. Who does he think he is?”
Nayeon slid herself off the desk, her feet landing gently on the floor. “You could try sending it back and asking him to review his mistakes before you work out the cuts for this month?” She suggested, and you glared at her, well aware that she knew as well as you that he would send back the exact same file demanding that you do it. She held her hands up in defeat and head back to her desk. “Fair enough, I’ll leave you to it.”
You worked from that point on in silence as you tried to go through every mistake, even skipping lunch to ensure it was done. He was not going to get the better of you. Nayeon occasionally offered candy or asked if you would like a tea, but only really cut through the intense quiet when there was a half hour of the working day left. “Are you coming to the party tonight?” She asked as she shut down her computer a little too early and began to clear away her desk haphazardly.
The party was being held in a function room in BH Inc’s downtown offices in honour of Nara - Nayeon’s sister and the main desk receptionist on the first floor. She had been working there for 10 years, but now she’d finally gotten her degree she had gotten herself a brand-new, high paying job on the other side of town, so this party was her big send off.
“You couldn’t keep me away!” You winked with false enthusiasm, seeing Nayeon’s face light up at your response. Nara and Nayeon had been great to you since you had moved here and you couldn’t bring yourself to let them down now. Jungkook’s stupid file had tired you out and in all honesty, you just wanted to head to Bedfordshire, but you owed Nara a great deal so the least you could do was make an appearance.
Nayeon threw you your old leather jacket that wasn’t entirely appropriate office attire and the zips clanked against your desk making you cringe at the sound. “It starts at 8 - we’re getting a taxi, do you want us to pick you up on the way?”
You nodded as you shut everything down and made sure the chairs were tucked away neatly. “I’ll be ready for 7.45.”
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Backstage in 1962 With Shelby, Breedlove, Roth, Stanley Mouse, Mickey Thompson, Jet Cars, Dobie Gillis, and the First Ford Mustang
Boom!
The first wave of post-WWII Americans was flooding DMV offices with license applications. Millions more of us were right behind, pacifying ourselves with model kits and slot cars and go-karts and magazines until that magic 16th birthday made the real thing possible. Tri-Five Chevys were just used cars, cheap and abundant. Networks of indoor winter shows brought California’s latest customs to enthusiasts across North America. Automaker dollars flowed freely to motorsports for the first time in five years, since spooked automakers and suppliers pledged to stop supporting racers and promoting speed. Henry Ford II personally announced his factory’s return while mocking secret skunkworks programs that enabled rival manufacturers to win races on Sunday and sales on Monday during the so-called ban. Ford Motor Company simultaneously dispatched an elaborate Custom Car Caravan of modified new cars and display engines. Most of Detroit’s new, lightweight compacts were optionally available with small V8s. The species of muscle car was not germinated just yet, but the gleam was in the eye. What a great year to be a gearhead!
Archive images exposed outside and inside L.A.’s long-gone Great Western Exhibit Center support Tex Smith’s Apr. 1962 HOT ROD appraisal of NHRA’s second Winternationals Rod & Custom Show as, “The major hot rod exposition in the nation” and “the biggest show ever staged that we know of.” The hit-making bands of guitarist Dick Dale and drummer Sandy Nelson undoubtedly contributed to four-day admissions exceeding 65,000, according to HRM. Later, the vast City of Commerce facility hosted the 1968-1979 L.A. Roadsters Shows prior to its demolition.
It’s impossible to imagine such a cohesive hot-rodding world evolving without the media network created by the Petersen Publishing Company. Even after two ex-PPC employees opened Argus Publishers and launched Popular Hot Rodding this year, Petersen monthlies had virtually no competition on a national scale (with the exception of Road & Track, which always stayed ahead of Petersen latecomer Sports Car Graphic). News-hungry enthusiasts had no reliable alternative to coverage arriving two, three, or more months late, sterilized in Hollywood to portray the hobby positively (and ignore drag racing outside of NHRA’s). On paper, Robert “Pete” Petersen appeared to be printing money. Editors never let on how close he—and we—came to losing it all.
There’s a business expression about how strong cash flow will invariably cover up mistakes—until it won’t. Early employees have said that the fledgling company thrice fell perilously behind on printing bills in the 1950s and survived only by the grace of sympathetic, patient printers and bankers. “Pete got a little carried away with his spending,” recalled photographer Bob D’Olivo, who was hired on in 1952 and stayed for 44 years. “The company was growing, and Pete wasn’t seeing all the figures. He hired a general manager to take some of the load, but if you wanted to talk to him in the afternoon, call the bar just down the street, and he willtake your call!”
When Car Craft’s Bud Lang stopped by this Sherman Oaks upholstery shop to report on a T-bodied AA/Modified Roadster under construction out back, Tony Nancy happened to be building a custom oxygen mask. We know that “The Home of Bitchin’ Stitchin’” did its usual fine job because later, when Spirit of America crashed into the water, Craig Breedlove feared that he was trapped and doomed until realizing that the breathing hose was keeping him connected to the submerged cockpit.
D’Olivo said the “major change came in the early 1960s, after two financial guys named Doug Russell and Fred Waingrow came aboard. Tighter control was needed on salaries, projects, travel, and so on. A management-and-numbers guy was needed, and that job went to Fred. All publishers and directors would now report directly to him, about 28 or so. This is when I was given the title of photographic director.”
A tradition of acquiring competitive titles and spinning off experimental ones was paused. As strict formulas were imposed upon individual publications, unprofitable or inconsistently profitable titles were either killed off (e.g., Kart and Rod & Custom Models) or reinvented (e.g., Motor Life became Sports Car Graphic) to free up operating capital and reduce debt. The painfulprocess worked: President Waingrow steered the ship back into the black, and the founder retained full ownership of a company that he would ultimately sell, in two installments, for nearly three-quarters of a billion dollars.
Since setting up shop at the 1958 Michigan State Fair at age 18, Stanley “Mouse” Miller drew crowds and eager customers wherever he appeared in the Midwest and Northeast. If $6 seems like too little to charge for a custom airbrushed sweatshirt, that would be about 55 bucks today. The kid could whip out one every hour and do it in color, instead of the basic black outline drawn by competitors. His operation must have impressed Wally Parks, who waded through the sea of ducktails to get the shot. Burned out on monsters by 1965, Mouse returned to his native California (where his animator father used to work for Walt Disney) and found work creating posters for San Francisco music promoters and album art for local bands, most notably the Grateful Dead. Mouse is still painting at 80, and still offers prints of Freddie Flypogger and other lovable “weirdoes” (MouseStudios.com).
Sure, had this virtual monopoly come apart early, competitors would have tried to fill the abandoned niches, but how well, and for how long? Just like the tree that falls in a forest with no one around to hear it, how else in 1962 could all of us, together, have followed Zora and Shelby, hot rods and customs, Roth and Mouse, Tony Nancy and Craig Breedlove, Cobras and Sting Rays, model cars, slot cars, sports cars, old cars, new cars? No way would the photo archive that Bob D’Olivo organized in 1955 and protected had stayed intact, in which case the most complete pictorial record of hot rodding and American motorsports would not exist for us to study and enjoy in a magazine directly descended from Pete’s first one. We’ll be feeling lucky all over again as each coming issue digs deeper into the 1960s.
Decades before IRS became commonplace in domestic cars, Pontiac chief engineer John DeLorean attached this exotic suspension, two-speed-automatic transaxle, and torque tube to entry-level 1961-1963 Tempest compacts with just a few bolts. How convenient for Mickey Thompson’s busy skunkworks, which the factory commissioned to hurriedly convert a stocker for the NHRA’s Winternationals introduction of Factory Experimental classes. Regular visitor Eric Rickman obviously had his run of M/T Enterprises—and a hunch that future readers might appreciate a peek at the world’s fastest man’s junk pile. We are left to wonder how the faded body panel wound up here, and whether some magazine staffer was responsible for separating the piece from an unknown open-wheel race car. (Help, longtime Car and Driver followers?)
Here’s the kind of historical image that could easily go undiscovered without the magnification enabled by modern scanning and digitizing. Only after zooming in to confirm the identity of Zora Arkus-Duntov (with helmet) did we realize that his waiting ride was a test mule made by joining the front half of the upcoming second-generation Corvette with the back half and roofline of a first-gen Vette. Sports Car Graphic tech editor Jerry Titus was granted exclusive access to private January tests at Daytona and Sebring on the condition that he ignore the “blue disguised prototype” that joined a red ’62 model and Zora’s baby, the CERV I single seater, for some brake development. Titus snapped the photo literally behind the distracted engineer’s back in late January, nearly a year before most folks saw a new Corvette in person. (See Apr. & May 1962 SCG.)
Jerry Titus was probably the best racing writer or writing racer ever employed by Robert E. Petersen. At the conclusion of Chevy’s Florida testing, Zora offered a few laps of Sebring in a priceless test car previously driven only by Stirling Moss, Dan Gurney, and Duntov himself. In the May 1962 SCG cover story, Titus described his 172-mph straightaway speed as “conservative” in a 1,700-pound package pushed by at least the 380 hp conceded by Chevrolet. Later, Titus was tabbed by Carroll Shelby to shake down and race the G.T. 350.
Help, readers: Does this scene ring any bells? None of our sources can recall a movie or TV production involving the channeled, 283-powered ’31 highboy that New York transplant Bill Neumann (not pictured) brought to L.A. prior to joining Car Craft and, ultimately, taking over Rod & Custom after PPC editorial director Wally Parks fired the whole staff. Neumann’s classified ad in R&C’s May 1962 Bargain Box mentioned “over 90 trophies,” but no asking price. A born promoter, he helped organize the Speed Equipment Manufacturers Association in 1963 (later renamed the Specialty Equipment Market Association, or SEMA) before opening Neuspeed Performance Systems.
Leave it to George Barris to add life-size TV stars Robert Young and Dwayne Hickman to a Barris Kustoms display that brought three famous hot rods to the Winternationals Rod & Custom Show. Barris’ own AMBR-winning ’27 T played a role in Young’s short-lived Window on Main Street series, while the former Chrisman & Cannon competition coupe costarred with Hickman and beatnik sidekick Bob Denver in an episode of The Many Loves of Dobie Gillis. Behind them is the Ala Kart, the roadster pickup that survived the 1957 Barris Kustoms fire to become the first repeat winner of Oakland’s tall AMBR trophy. (See Apr. 1962 HRM; May 1962 R&C.)
Yes, slot car racing was both a participant and spectator sport at its peak. Model-maker AMT staged regional competitions on elaborate tracks like the setup at the NHRA’s February show. This showdown matched up winners from 1,100 West Coast hobby shops. Later in the year, AMT cheerleader Budd Anderson unveiled the gamechanging, steerable, 1:8-scale Authentic Model Turnpike system for home use during a six-month, fulltime modeling stint at the Seattle World’s Fair. (See May 1962 CC.)
Pontiac stockers prepared by factory contractor Mickey Thompson enjoyed another dominating season, starting with February’s second Winternationals. What appears to be a late round of Mr. Stock Eliminator—a bonus, heads-up showdown bringing back the quickest 50 stockers, win or lose—finds S/S Automatic champ Carol Cox, the first female allowed to enter an NHRA national event, out in front of stick-class-winner Jess Tyree, an M/T mechanic driving the same 167-mph Catalina that set multiple international speed records over the winter at March Air Force Base. Waiting to run at Pomona are previous-round winners Lloyd Cox, Carol’s husband (Pontiac, right); Gas Ronda (Ford); and eventual runnerup Dave Strickler (Chevy), who would fall in the Mr. Stock final to Don Nicholson (not shown). The barn across the street is long gone, but last time we looked, the two-story house remained. (See May 1962 HRM, MT & CC.)
The ragtag bunch of drag and dry-lakes racers that test-fired Craig Breedlove’s $500 military-surplus engine at Los Angeles International Airport in June, just two months before this homebuilt tricycle’s scheduled Bonneville Nationals debut, must have seemed unlikely to make the builder-driver a household name worldwide. The official team truck’s wooden signboards announced the “Spirit of America World Land Speed Record Attempt.” The low-buck team made it to Speed Week, but the semifinished car/trike was limited to static testing at the adjacent Wendover airbase. (See Sept. 1962 MT.)
Despite the convergence of five jet-powered vehicles on the salt during and immediately following Speed Week, a piston-powered streamliner remained the world’s fastest land vehicle all year—to the certain relief of Revell, which had entered the hot rod market by miniaturizing the 406-mph Challenger I and Ed Roth’s revolutionary Outlaw street roadster. Rather than follow the shady example of fly-by-night model makers that blatantly reproduced identifiable race cars without attribution or remuneration, Revell licensed and heavily promoted the men along with their machines. Revell’s national advertising blasted Roth’s brand and zany image far beyond the hot-rodding press and car-show circuit. (See Nov. 1962 R&C.)
It didn’t take long for an unidentified slot car hobbyist to power one of Revell’s snap-together streamliners. Reader Rick Voegelin, the former Car Craft editor and a lifelong slot racer, squinted at the photo through old eyes and semipositively identified the dual motors as Pittmans, likely swapped out of powerful locomotives.
It’d be a stretch to suggest that muscle cars and Funny Cars were invented here, but the roots of both American inventions run through this very engine compartment. Two years before the second-gen Tempest begat the GTO, Pontiac assigned the Super Stock Division of Mickey Thompson Enterprises to create a prototypical factory hot rod for the NHRA’s new A/Factory Experimental class. Beyond a mandate to stick with genuine Pontiac hardware wherever visible, in-house engineers Hayden Proffitt and Lloyd Cox (pictured) virtually rewrote the rulebook as they converted a four-cylinder ’62 Tempest into the year’s quickest and fastest late model, a runaway A/FX champ at both of the NHRA’s national events. By the time this photo was snapped in late June, displacement of M/T’s Super Duty 421 had soared from 434 to 487 cubes, according to Motor Trend, and Cox had assumed the wheel vacated when Proffitt took a 409 Chevy deal and opened his own shop. Meanwhile, Holman-Moody and Dragmaster were secretly developing 480-inch strokers for Ford and Chrysler, respectively. Understandably alarmed, Wally Parks halted drag racing’s arms race—temporarily—by capping 1963 displacement at 427 for NHRA-legal competition. However, the horse had left the barn, and the Big Three’s monster-motor lessons would not be lost on so-called “outlaw Super Stock” racers running independent meets and run-what-ya-brung match races. (See Sept. 1962 HRM; May & Dec. 1962 MT; June 1962 R&C; Jan. 2017 HRD.)
If you remember being faked out by this photo, don’t feel like the Lone Ranger; so were the rest of us subscribers and newsstand browsers. Art director Al Isaacs’s clever positioning of the car’s shadow and of editor Don Evans’s right forearm clinched the delusion that Monogram’s 1:8-scale “Big T” was a real roadster. Inside, the description of Bud Lang’s cover shot joked that because the car is only 16 inches long, Evans and his “lovely cousin, Sharon Huss … were shrunk for photo.” Either way, such juxtaposition was a neat trick when Xacto knives, layers of physical film, and steady hands were required to do the layout work done digitally now.
Staff photographer Pat Brollier shot the B&W photos for CC’s inside story, which Isaacs laid out like a typical car feature. Despite a steep retail price of $10.98—10 times that of the usual $1.98 kit—strong sales inspired Monogram to rush-order a fullsize running version for use as a promotional vehicle. Customizer Darryl Starbird delivered that bigger-yet Big T to the model maker’s booth at NHRA’s late-summer car show in Indianapolis. (See Oct. 1962 CC; Dec. 1962 R&C.)
This one had us baffled until a regular research source, the American Hot Rod Foundation, came through in a big way. AHRF director David Steele recognized the back wall from later photos of Carroll Shelby’s Cobra factory, while AHRF curator Jim Miller instantly identified the last Scarab that Phil Remington built just before Reventlow Automobiles Inc. was shut down under IRS scrutiny. Its all-aluminum Buick V8 shared technology and major components with similar engines that Mickey Thompson developed for this year’s Indy 500. The suspiciously empty Venice, California, space and much of Reventlow’s workforce were taken over by Shelby not long after photographer Pat Brollier visited in early July. Lance Reventlow personally debuted the sports car in September with an impressive second-place SCCA finish at Santa Barbara and made at least two more starts before selling to John Mecom, who installed a small-block Chevy. Augie Pabst eventually acquired this rarest of Scarabs and still has it, as far as our AHRF friends know. (See Dec. 1962 SCG.)
Lance Reventlow was the husband of actress Jill St. John and the son of infamous heiress Barbara Woolworth Hutton. Mom’s fortune financed the boy’s dream of all-American sports cars, built and driven by homegrown hot rodders to beat the best European factory racers. His trio of front-engined Scarab roadsters did exactly that starting in 1958 with a shocking upset at Riverside’s International Grand Prix and the national SCCA championship. Two subsequent attempts at building formula cars and competing in Europe were expensive failures, however, and the Internal Revenue Service was unconvinced that the cash-burning business was really a business. Lance fatally crashed a private plane in 1972, at age 36. His alcoholic, drug-addicted mother followed in 1979, leaving behind just $3,000 of a trust fund that had once been the equivalent of nearly $400 million in today’s money.
Wally Parks became HOT ROD’s first fulltime editor in 1949, cofounded the NHRA in 1961, and simultaneously guided the publishing company and the sanctioning body through the end of this year. In early 1963, he resigned as editorial director of Petersen’s automotive publications to run the NHRA fulltime.
Two years after designer-builder Athol Graham was killed chasing the unlimited LSR in the homebuilt Spirit of Salt Lake, his widow, Zeldine, and former helper, Otto Anzjon, brought the rebuilt streamliner back to Bonneville to prove that Graham’s design was sound. The inexperienced driver followed officials’ instructions to gradually build speed to the 225-mph range before attempting this first full pass, which lasted about 100 feet before Allison-induced wheelspin exploded the right-rear tire. (See Dec. 1962 MT; Jan. 2017 HRD; Jan. 2019 HRD.)
NorCal drag racers Romeo Palamides and Glen Leasher didn’t get to Wendover until the last day of Speed Week, in August, which is normally restricted to prequalified record runs. They were granted one low-speed shakedown run that reportedly revealed “unexpected chassis problems.” The monstrous Infinity went home to Oakland to prepare for a private session on September 10. Leasher, who’d acquired jet-car experience in Romeo’s busy Untouchable dragster, made a troublefree checkout pass and turned around. On the return trip, he unexpectedly accelerated on “full ’burner,” veered off the course, flipped repeatedly, and was dismembered. (Later that day, Romeo called another Bay Area slingshot driver about fulfilling his jet dragster’s commitments and created a colorful career for “Jet Car” Bob Smith, who miraculously survived crashes in a whole
In late August, the original Ford Mustang was captured in the L.A. shop of famed bodybuilders Dick Troutman and Tom Barnes. Barely a month later, the tube-framed, midmounted-V4, front-drive, 1,480-pound prototype made exhibition laps and fans at both the Watkins Glen and Riverside Grands Prix. Ford described it as a “study vehicle for possible production of a sports car.” Motor Trend predicted that its “Impact should hit squarely and cause excitement in three or four or five years,” adding, “Unlike so many styling projections and dream cars offered so far, this one is crammed full of usable ideas.” (See Nov. 1962 HRM; Dec. 1962 SCG; Jan. 1963 MT; Feb. 1963 CC.)
Judging by other film negatives documenting Robert E. Petersen’s fall hunting trip, the boss got the last laugh by bagging both an elk and a bear.
The day before the Los Angeles Times Grand Prix in Riverside, Carroll Shelby (right) and Ford upstaged Zora Arkus-Duntov (left center) and Chevrolet by sneaking the second Cobra ever built into a so-called Experimental Production class and race that SCCA conceived for brand-new Sting Rays; in particular, the fearsome foursome of Z06 fastbacks entered by Mickey Thompson. Despite Bill Krause’s sizable horsepower handicap, his spunky, 260ci roadster swapped leads with Dave MacDonald’s 327ci Corvette (background) until the Cobra’s rear hub carrier failed an hour into the 300-mile enduro. (See Jan. 1963 SCG; Jan. 2017 HRD.)
These had to be the trickest transporters at Laguna Seca for October’s SCCA showdown. Meister Brau beer outfitted one of the earliest tractor-trailer rigs in the photo archive for hauling the high-dollar Scarabs and Chaparrals campaigned by Harry Heuer, a member of the brewing family. Norm Holtcamp had other ideas and started from scratch on his Cheetah, sliding an electric-load-leveling Mercedes sedan chassis under a ’60 El Camino cab purchased at GM’s Van Nuys Boulevard plant. A hot-rodded ’57 Corvette 283 and three-speed Chevy trans mount amidships. We don’t know whether Holtcamp hit his target of 112 mph fully loaded, but you can be sure that second-owner Dean Moon wrung top speed out of the Cheetah before parking and neglecting it for years at Moon Equipment Company. Longtime HRD readers will recall a small color snapshot in our May 2013 issue of the disembodied remains in the yard of collector Geoff Hacker, who tells us that full restoration is scheduled to start later this year at JR’s Speed Shop (Venice, Florida).
Longtime PPC photographer Bob D’Olivo identified art director Art Smith, but neither the blonde nor the legs. Not much work was getting done the day that SCG editor John Christy wandered by, two weeks before Christmas.
The Mysterion signaled the beginning of Ed Roth’s asymmetrical (some would say dysfunctional) stage. The dual-engined gas dragsters that proliferated during these fuel-ban years might have inspired the twins that buddy Budd Anderson procured from Ford (said to be 406s, but probably ordinary 390s). During transport between shows, their combined weight repeatedly cracked and ultimately collapsed the Swiss-cheese frame, which was stripped and junked along with the body. Reader Don Baker saw the HOT ROD Network preview of this article and sent in a memory of riding bikes with his childhood pals to a show at Devonshire Downs (San Fernando Valley). Lacking money for admission, they arrived early that morning and sat outside, watching the show cars arrive, “when Big Daddy rides in, towing Mysterion. He was alone and asked us to help getting it off the trailer. We pushed it right onto the show floor. Pretty cool at that time.” We found the image on one of the final rolls exposed by staff photographers this year, yet the Mysterion was completed in time for the start of the indoor show season in January. (See Dec. 1962 & Sept. 1963 R&C.)
The post Backstage in 1962 With Shelby, Breedlove, Roth, Stanley Mouse, Mickey Thompson, Jet Cars, Dobie Gillis, and the First Ford Mustang appeared first on Hot Rod Network.
from Hot Rod Network https://www.hotrod.com/articles/backstage-1962-shelby-breedlove-roth-stanley-mouse-mickey-thompson-jet-cars-dobie-gillis-first-ford-mustang/
via IFTTT
0 notes