#ion exchange resins
Text
Ion Exchange Resins for Water Purification: Effective Solutions for Clean Water

Ion Exchange Resins for Water Purification are essential in achieving high-quality, contaminant-free water. At Ion Exchange Global, we offer advanced resin solutions tailored for effective water treatment in various applications. Our resins efficiently remove impurities, ensuring safe and clean water for industrial and domestic use. For more information, visit us at https://id.ionexchangeglobal.com/
#ion exchange resins#water purification#water treatment#ion exchange technology#clean water solutions#water filtration#industrial water purification
0 notes
Text
#Total dissolved solids (TDS)#Drinking water quality#TDS measurement techniques#TDS reduction methods#Water purification systems#Reverse osmosis (RO) filtration#Activated carbon filters#Water softening systems#Deionization (DI) systems#Distillation processes#Ion exchange resins#TDS meter usage#Ideal TDS levels for drinking water#Importance of TDS testing in water quality#Health effects of high TDS levels in drinking water.#commercial ro plant manufacturer#commercial ro plant
0 notes
Text
Figure 24.7 shows the analysis of a polypeptide hydrolysate by ion-exchange chromatography.
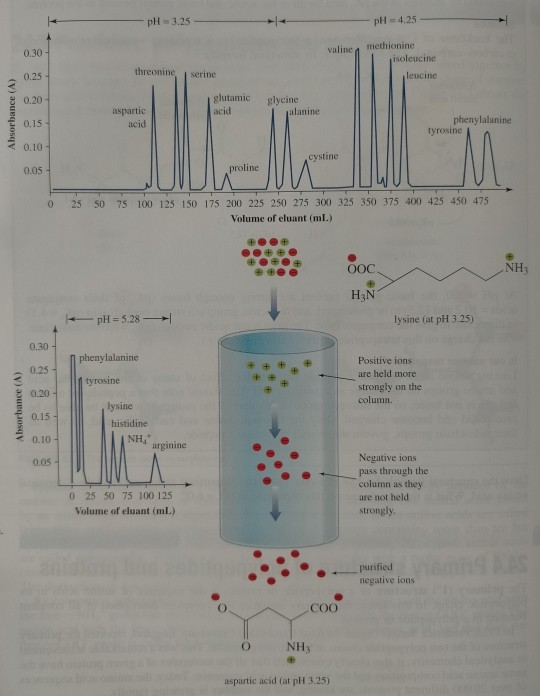
FIGURE 24.7 Analysis of a mixture of amino acids by ion-exchange chromatography using Amberlite IR-120, a sulfonated polystyrene resin. The resin contains phenyl-SO3-Na+ groups. The amino acid mixture is applied to the column at low pH (3.25), conditions under which the acidic amino acids (Asp, Glu) are weakly bound to the resin and the basic amino acids (Lys, His, Arg) are tightly bound. Sodium citrate buffers of two different concentrations and three different values of pH are used to elute the amino acids from the column. Cysteine is determined as cystine, Cy-S-S-Cys, the disulfide of cysteine.
"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quotes#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#polypeptide#hydrolysate#ion exchange#chromatography#resin#amino acid#aspartic acid#threonine#serine#glutamic acid#proline#glycine#alanine#cystine#valine#methionine#isoleucine#leucine#tyrosine#phenylalanine#cysteine#ions#amberlite
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
[ID: four large plastic totes overflowing with large black plastic funnels. Three of the totes are placed on a cart, and the fourth is next to the cart because the cart ran out of room. The funnels are not in organized stacks but instead piled haphazardly and look rather like they’re going to fall over at any moment. In a few places plastic tubes are visible connected to the bottom of each funnel - this is why they do not stack nicely. End ID]

#this image represents the single most insane project i have ever been involved in#say hello to my 216 funels! which corresponded to 216 1 liter bottles. 216 plants. 216 different samples under different conditions.#oh and 216 tubes full of microplastic ion exchange resin#this project was nuts. it also involved 2 whole days spent in a greenhouse. one of those was in summer.#anyways. madness.#i loved it but oh my god#it wasn't my project it was one of the plant scientists but as an undergrad i did A LOT of the prep work#i and one other person assembled all those funels and resin tubes. and we acid washed the resin tubes. i wish i had photos#of every available countertop covered in plastic boxes full of resin tubes and acid.#dilute acid but still#acid. so much acid. we made it in 3 liter batches.#too many batches to count#this also involved 74 liters of potassium chloride#which is like...#almost 20 gallons#i am never happier than when lab work gets this insane#hylian does science#biogeochemistry
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Resin for Commercial Water Treatment in Kenya: Efficient Solutions for Industrial Water Purification

Get high-quality resin for commercial water treatment in Kenya from Ion Exchange Global. Our ion exchange resins are designed for efficient industrial water purification, softening, and filtration. Trust us for reliable and sustainable water treatment solutions for your business in Kenya. For more information, visit us at https://ke.ionexchangeglobal.com/
#resin for commercial water treatment in Kenya#commercial water treatment resin#industrial water purification#water treatment solutions in Kenya#ion exchange resin for commercial use
0 notes
Text
Role of Ion Exchange Resins in Water Treatment

Water is a precious resource obtained from natural sources like rivers, streams, or wells. It can contain contaminants or pollutants that can be harmful for usage or consumption. While solid particles can be removed through filtration, soluble substances need special treatment. Ion exchange resins play a crucial selectively removing solutes from water. They are used to reduce dissolved impurities by selectively exchanging ions based on charges. This article shed light on the role of ion exchange resins in water treatment, emphasizing their importance in different industries.
What are Ion Exchange Resins?
Ion exchange resins are highly porous materials that selectively remove or exchange ions in water or other solutions. The primary role of ion exchange in water treatment is ion exchange. These are tiny beads that have charged particles known as ions. This helps remove hardness and contaminants like chromate, nitrate, and arsenic in water. Western Carbon & Chemicals is a leading ion exchange resin manufacturer in India, offering a comprehensive range of ion exchange resins for different water treatment processes. Our product is tested and approved by the power sector, fertilizers, textiles, and other industries for their need of high-quality water needs. Choose our range of high-quality ion exchange resins for your specific applications.
Role of Ion Exchange Resin in Water Treatment Process
Water Softening
Water softness involves reducing water hardness by removing magnesium and calcium ions. These components create scales in appliances and pipes. Hard water is passed through a bed of cationic ion exchange resin beads that grab calcium and magnesium ions and release sodium ions in exchange. This helps to produce softer water that reduces the chances of scale build-up.
Demineralization
This process removes specific ions like magnesium, chloride, calcium, and sulfate from water. Ion exchange resins are used in industries that need high-quality treated water. This process is a combination of anionic and cationic resins. The ion exchange resin suppliers can customize resin tailored to remove specific ions for water consisting of needed minerals.
Deionization
Deionization, a critical process in water treatment, involves the removal of all ions from water to produce the high-purity water that is indispensable in laboratories, electronics manufacturing, and various industrial processes. The use of cationic resins, followed by anionic resins, effectively removes ions from water, ensuring the high-purity water that is a necessity in these settings. This underscores the critical role of ion exchange resins in ensuring the quality and reliability of industrial processes.
In all these water treatment processes, ion exchange resins selectively remove specific ions to get the desired water quality. The versatility and effectiveness of ion exchange resins make them essential in water treatment processes in different industrial settings. Western Carbon & Chemicals is one of the most trusted ion exchange resin manufacturers in uae for water treatment. Whether you need ion exchange resins for high-purity water or water for industrial processes, we tailor our product to your application. Get in touch with us to discuss your water treatment requirements.
Also visit:- Choose the Right Garnet Abrasive for Your Waterjet Cutting
#ion exchange resin manufacturer in India#ion exchange resin suppliers#ion exchange resin manufacturers in India
0 notes
Text
What are Ion Exchange Resins? Properties, Types & Applications

Western Carbon & Chemicals is a leading ion exchange resin manufacturer in India. We offer different grades in gel micro-porous structures for water and other applications, and another popular ion exchange resins application is in the fruit beverage industry. For more information visit our blog.
#Ion Exchange Resin manufacturer in India#Ion Exchange Resin supplier in India#Ion Exchange resins materials#Ion Exchange resins applications#Ion Exchange Resin for water softener#Ion Exchange Resins water treatment#water softener Ion Exchange#high-capacity Ion Exchange Resin#Ion Exchange resin exporter
0 notes
Text
Ion Exchange Resins Market Share, Industry Trends, Forecast 2023-2030
BlueWeave Consulting, a leading strategic consulting and market research firm, in its recent study, estimated the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market size at USD 1.43 billion in 2023. During the forecast period between 2024 and 2030, BlueWeave expects the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market size to expand at a CAGR of 5.64% reaching a value of USD 2.1 billion by 2030. The Global Ion Exchange Resins Market is propelled by the thriving water treatment sector driven by the rising need for ultrapure water in the electronics and pharmaceutical industries. The growing utilization of mixed bed resins in water treatment, nuclear applications, and power generation is contributing to the increased demand for ion exchange resins. The rise in electricity demand in both industrial and residential sectors is also a key factor driving market growth. Also, the escalating use of these resins in various industries such as industrial water treatment, mining, power generation, and food & beverages is expected to enhance the overall global ion exchange resins market size during the forecast period. Market players are presented with promising growth opportunities through the expansion of manufacturing capacities. Key companies in the global ion exchange resins industry are strategically focusing on partnerships and collaborations to reinforce their global presence. Hence, such aspects are expected to boost the expansion of the global ion exchange resins market during the period in analysis.
Impact of Geopolitical Tensions on Global Ion Exchange Resins Market
The Global Ion Exchange Resins Market is impacted by increasing geopolitical tensions in several ways. The conflict has generated geopolitical tensions and economic disruptions, resulting in heightened uncertainty and volatility in global trade. It has adversely affected the production, supply chain, and distribution of anion-exchange resins, potentially leading to shortages and fluctuations in market prices. Also, the slowdown in industrial activities and reduced demand for products and services globally have contributed to a decline in the demand for ion-exchange resins. Despite these challenges, the ion-exchange resins market is expected to experience moderate growth during the forecast period. It can be attributed to factors, such as increased industrialization, expanding applications in water treatment, and rising environmental concerns. However, the exact growth expectations remain uncertain due to the aforementioned geopolitical tensions and the potential for further economic repercussions from the ongoing conflicts on the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market.
Sample Request @ https://www.blueweaveconsulting.com/report/ion-exchange-resins-market/report-sample
Global Ion Exchange Resins Market
Segmental Information
Global Ion Exchange Resins Market – By End User Industry
By end user industry, the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market is divided into Healthcare, Food & Beverages, Water and Wastewater Treatment, Mining, Power, Paper & Pulp, and Chemicals segments. The power segment is expected to hold the highest share in the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market by end user industry during the forecast period. It is primarily due to the burgeoning demand for ion exchange resins in the power industry. The heightened demand is particularly noteworthy in emerging economies, such as China, India, and the UAE. Ion exchange resins play a crucial role in the sector by facilitating the removal of toxic and heavy metal ions from hard water, a process wherein magnesium and calcium ions are substituted with sodium ions. As the power industry rapidly expands in these emerging economies, the reliance on ion exchange resins for effective water treatment contributes significantly to the projected dominance of the power segment in the global market.
Global Ion Exchange Resins Market – By Region
The in-depth research report on the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market covers the market in a number of major countries across five regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East and Africa. The Asia Pacific region is expected to hold the highest share of the Global Ion Exchange Resins Market during the forecast period. Rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India have led to an increased demand for water treatment solutions, where ion exchange resins play a significant role. The flourishing manufacturing and chemical industries in the region further amplify the need for purification and separation processes, contributing to the rising demand for ion exchange resins. Additionally, the region's large and growing population and heightened awareness of water scarcity and environmental concerns prompt investments in advanced water treatment technologies, fostering market growth. Favorable government policies supporting water conservation and environmental sustainability also contribute to the widespread adoption of ion exchange resins in the region.
Competitive Landscape
Major players operating in Global Ion Exchange Resins Market include Anhui Samsung Resin Co. Ltd, Bio-rad Laboratories Inc., Doshion Polyscience Pvt Ltd, Dupont, Ecolab, Eichrom Technologies LLC, Evoqua Water Technologies LLC, Ion Exchange (India) Ltd, Jacobi Carbons Group, Lanxess, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, and Novasep. To further enhance their market share, these companies employ various strategies, including mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, joint ventures, license agreements, and new product launches.
Contact Us:
BlueWeave Consulting & Research Pvt. Ltd
+1 866 658 6826 | +1 425 320 4776 | +44 1865 60 0662
0 notes
Video
youtube
all kinds of ion exchange resin & adsorption resin,Made in China.Sanxing...
#ion exchange resin#cation exchange resin#anion exchange resin#adsorption resin#watertreatment#mixed bed resin#purewater
1 note
·
View note
Text

One of the three letters written by Vlad Drăculea, Prince of Wallachia, and the historical predicate for the character Dracula, studied to diagnose his condition of hemolacria. :: [Robert Scott Horton]
+
A chemical analysis of the letters of the legendary historical figure reputed to have inspired fictional vampire Dracula has revealed Vlad Drăculea (aka Vlad the Impaler) may have cried tears of blood. Traces left behind on the paper by the 15th century ruler of Wallachia suggest he was afflicted by a condition known as hemolacria, which manifests as the presence of blood in tears. And he may have had skin and respiratory conditions besides.
"To our reckoning," writes a team led by chemist Maria Gaetana Giovanna Pittalà of the University of Catania in Italy, "this is the first time such research has been carried out and has helped to bring to the limelight the health status of Vlad Dracula the Impaler." Vlad Drăculea, also known as Vlad Țepeș, was certainly a towering figure in European history. His exploits as ruler of Wallachia are almost mythical; in particular, the extremely bloody lengths he went to in order to protect his land from multiple conflicts.
It's unknown how many deaths he is responsible for, but estimates put it at over 80,000 – and an estimated over 20,000 of those were impaled on wooden spikes. Not to mention all the other forms of torture of which he has been (disputedly) accused. Although his life and deeds have been well documented, and in many cases no doubt exaggerated, there are some details that we are likely never to know. But Pittalà and her colleagues thought there may be a way to find out – by studying objects that Drăculea is known to have touched. Namely, letters the man himself penned.
Letters are an absolute treasure trove for historians. In this case, however, it was not the contents of Drăculea's letters that interested the researchers, but what secrets may have been left behind on the paper: the molecules and proteins that may have been transferred by human touch. The letters are now over 500 years old, and extracting material from them could cause damage, which is not ideal for precious historical documents. But the recent development of a special film of ethylene-vinyl acetate, treated with ion exchangers and water-repelling resins, has been used to promising effect with ancient fabrics and papers.
When applied to any type of surface, this film is able to extract proteins and molecules without damaging the surface. The team used these films on three of the Vlad Drăculea letters, one dated 1457, the other two 1475, and used mass spectrometry to analyze the results. They found thousands of peptides and proteins. They focused on signals of human biology; and, because many people have handled the letters over the centuries, only the human material with the most advanced degradation.
[Dracula Letters]
* * * *
“How blessed are some people, whose lives have no fears, no dreads; to whom sleep is a blessing that comes nightly, and brings nothing but sweet dreams.”
― Bram Stoker, Dracula
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, science Tumblr, question.
Dishwashers have this water softening system: a special ion exchange resin, that attracts certain minerals, which prevents the buildup of limescale. It needs to be reset periodically, and that's what the dishwasher salt is for - it's mostly regular salt, just purer and bigger (for a reason!).
Water jug filtering cartridges usually contain active carbon and ion exchange resin. With the resin handling minerals responsible for limescale.
If the main reason why I'm using water filters is to handle limescale, would giving a cartridge a salt bath reset it? Can I reuse it then?!
#science tumblr#save me science tumblr#I have some old cartridges I haven't thrown out yet#so I'm gonna grab some water tests from the shop#and actually run some tests#and you know actually test it#and yes I get that mold can be an issue#but it's for science!#hag talks
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ion Exchange Resins Types

Indion Resins, a product of Ion Exchange (India) Ltd., offers a wide range of ion exchange resins for various applications:
Cation Exchange Resins: These resins remove positively charged ions (e.g., calcium, magnesium) from water, commonly used in softening and demineralization.
Anion Exchange Resins: Designed to remove negatively charged ions (e.g., chloride, sulfate), used in water purification and deionization processes.
Mixed Bed Resins: A combination of cation and anion resins, typically used for high-purity water applications like in electronics or pharmaceuticals.
Specialty Resins: Tailored for specific applications such as metal recovery, sugar refining, or wastewater treatment.
Indion resins are widely used across industries such as water treatment, power generation, and food processing.
Read more here
0 notes
Note
*asks about job*
Anon you are my favorite.
Okay, so, I'm a laboratory and field technician in a soil and water science lab.
I love my job so goddamn much. I get to work with fancy machines like the gas chromatograph and spectrometer! (The spectrometer is actually really boring but shhh.) I get to go outside and watch birds while I collect water samples! I am getting paid for this! I get to learn data processing and engineering and wilderness safety precautions and how to explain complex science to people whose careers are Not This.
Also, research labs are chaos and I delight in it. Okay maybe not ALL research labs, I'm informed the chemistry department does not look like this. BUT this is an environmental science lab. It is full is bizarre, deeply nerdy, deeply passionate people. Who do things like eat baked potatoes like apples, improvise experimental setups with mason jars and duct tape, and nickname every instrument either a human name or a Pixar reference. I love them so much I have no words.
Crazy and fun things I've done for this job:
Freezer jenga followed by freezer tetris (had to take all the things out of a the freezer, put them in coolers to keep them cold, defrost the freezer, and put them back in except organized this time. I was delighted by this for no logical reason, my boss thought I was nuts).
Okay you know in scifi movies where they have some weird mystery substance and they put it in a box with gloves attatched so they can work with it without actually touching it? I've done that! Not because of hazardous substances, we just needed to put stuff in jars without exposing it to oxygen. But still! It was cool!
Shopping trip to get food for like half a dozen people for three days (I had weird dreams about being overwhelmed with tortilla chips afterwards, this doesn't sound that crazy but I promise you it felt like it).
Taped plastic tubing to 200+ funels until the boxes we were storing them in overflowed and there was no longer floorspace to walk (AFTER cutting the plastic tubing into 200+ equally sized pieces and stuffing it with ion exchange resin, which is like evil microplastic sand. Between all those things, this took WEEKS. It got really boring).
Dissolved like 10kg of KCl (KCl my behated, its very harmless but hell to get off glassware) in water to make 80 LITERS OF KCL SOLUTION (that's over 20 pounds of solid KCl and over 20 gallons of solution! My coworker and I were sort of laughing hysterically over this entire process because come on! 80 liters! For reference most lab protocols need like, a liter or less of whatever solution.) Fun fact about solid KCl, it tends to stick together into a giant brick. We were chiseling at it with scoops, spoons, whatever was on hand (i really wanted to attack it with a screwdriver but it would introduce dirt into the chemicals so i couldn't) and eventually we got so frustrated we went outside and dropped the thing off a second floor balcony. After wrapping it in like 3 layers of plastic bags because we knew at least one bag was gonna break. This did not actually help much but it was very cathartic.
There was a project once where we had to take sealed mason jars and replace all the air in them with nitrogen gas. Repeatedly. For over a hundred jars. My PI (principle invesitgator, means the scientist in charge of a project and usually a lab) is good at building things, so of course he assembled this manifold thing so we could pump nitrogen through a dozen jars at once. Which was great, except it involved two dozen needles, half of them attatched to flexible plastic tubing so they'd kinda bounce around when you pulled them out of the jars. It looked like a very stabby centipede-slash-octopus monster. Impressively, we only stabbed ourselves a couple times each with this thing (and changed the needles of course, we are aware of the risks of transmitting blood diseases).
Actually one of the craziest things about this job in my opinion is how many fucking needles we work with. You see, we study atmospheric gases. And to do that, we need to transfer gases between sealed containers, which means needles and septa (the rubber things they put on vials so you can poke needles through them). So. Many. Needles. Did you know you can only use a needle four times before it gets too dull? It's extremely noticeable as you're using them - not as they get dull, but when you discard an old needle and get out a new one it is a huge difference. I don't know why I find this so fascinating, but working with needles is honestly so fun. I feel like a mad scientist or something. Also, for the first couple months I kept poking myself on accident so I was just walking around with these pinpricks and papercut looking wounds. It felt a bit like a badge of honor, somehow, like a rite of passage for working in the gas lab. Another thing about needles, if you get scratched with one horizontally instead of stabbed, they look like papercuts. It's weird. Also weird is how good you get after a while at not stabbing yourself.
I think I like working with needles because they're something that used to make me nervous. Not horribly, but I have more than typical anxiety and I get nervous about everything. And yet I am now totally chill about needles, because I work with them all the time. It's... freeing I guess. Maybe empowering, even. I am scared of so many things, but I am not scared of this. Ditto large quantities of acid, once you've had to work with dozens of liters of the stuff you stop being scared of it - this was for the same project as the KCl and yes it was equally ridiculous. Dilute acid, thankfully, but to make dilute acid you have to mix the really concentrated stuff with water. It does not come as dilute acid, that would be too easy. So we spent multiple days in a row diluting acid and soaking things in it, there were plastic boxes full of the stuff on every available counter space with handmade warning labels, it was A Thing™️.
Anyways, I'm a person who's scared of everything, except weird stuff like hydrochloric acid, needles, and wasps. I can blame all three of those things on this job, which I love dearly. I love to learn new things, pretend I'm in a scifi movie, be surrounded by crazy people (affectionate), and apparently overcome my numerous fears. You absolutely did not sign up for this big puddle of feelings, anon, but thank you for inspiring it nevertheless.
#something something personal growth and overcoming fears. maybe that's part of why i love this job.#the wasp thing is because i have a field site at a bridge that's basically got wasp nests all over the underside#the wasps like to watch me work#i am genuinely having personal realizations while answering this ask#thank you anon sorry this got out of control i hope my exploits amuse you#some of it i think you just had to be there#also if anyone recognizes these stories shh you didn't see anything#my coworkers had better not see this it would be so embarassing#hylian rambles#hylian does science#anon#asks#thanks anon!#needles tw#i promise proper safety protocols were being followed in all of these stories#the acid involved so. much. ppe.
1 note
·
View note
Text
PFAS Water Filters: Protecting Your Health from Forever Chemicals

In recent years, PFAS contamination has become a growing concern for communities around the world. Known as "forever chemicals," Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) are synthetic chemicals that do not break down easily in the environment or the human body, leading to potential health risks. As awareness of PFAS increases, many are looking for ways to protect themselves from these harmful chemicals, and one of the most effective solutions is using PFAS water filters.
This blog will explore the dangers of PFAS, the benefits of using PFAS water filters, and how to choose the right filter to ensure your drinking water is safe.
What are PFAS?
PFAS are a group of man-made chemicals used in various industries since the 1940s. They are commonly found in products like non-stick cookware, water-repellent clothing, firefighting foams, and certain food packaging. While their resistance to heat, water, and oil makes them useful in many applications, these same qualities mean they persist in the environment and our bodies for long periods.
Some of the health risks associated with PFAS exposure include:
Increased risk of cancer
Immune system suppression
Liver damage
Thyroid hormone disruption
Developmental issues in children
How Do PFAS Get into Drinking Water?
PFAS can enter water sources through industrial discharges, firefighting foam runoff, and even landfill leachate. Since they are highly mobile in water, PFAS can spread over large areas and contaminate groundwater, rivers, and lakes, eventually reaching our taps.
Drinking water contaminated with PFAS is a major exposure route for many people. Unfortunately, conventional water treatment plants are not always equipped to remove these chemicals, making it essential for individuals to take extra steps to filter PFAS from their water supply.
How Do PFAS Water Filters Work?
Not all water filters can remove PFAS. Filters designed specifically for this purpose often use activated carbon, reverse osmosis, or a combination of filtration technologies to effectively capture and eliminate PFAS compounds.
Activated Carbon Filters: These filters trap PFAS molecules on the surface of carbon granules. While highly effective, activated carbon filters require regular replacement to maintain their efficiency.
Reverse Osmosis Systems: These systems use a semi-permeable membrane to remove PFAS along with other contaminants. Reverse osmosis is one of the most effective methods for filtering PFAS, but it can be more expensive and may waste more water compared to other methods.
Ion Exchange Filters: Some advanced filtration systems use ion exchange resins to specifically target and remove PFAS compounds. These filters are highly effective for long-chain PFAS chemicals, such as PFOA and PFOS.
Benefits of PFAS Water Filters
Protection Against Health Risks
The most significant benefit of PFAS water filters is the protection they offer against the harmful effects of these chemicals. By removing PFAS from your drinking water, you reduce your risk of cancer, hormonal disruptions, and other serious health conditions linked to PFAS exposure.
Improved Water Quality
Beyond just PFAS, many of these filtration systems also remove other common contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and chlorine, improving the overall quality and taste of your drinking water.
Peace of Mind
Knowing that your water is free from toxic chemicals can provide peace of mind, especially for families with young children who are more vulnerable to the effects of PFAS.
Choosing the Right PFAS Water Filter
When selecting a PFAS water filter, it’s essential to choose one that has been tested and certified for PFAS removal. Look for filters certified by reputable organizations, such as the NSF International or Water Quality Association (WQA), for the reduction of PFOA and PFOS levels.
Here are a few factors to consider:
Type of Filter: Decide whether an activated carbon filter, reverse osmosis system, or another filtration method is right for your household based on your budget, water usage, and filtration needs.
Filter Maintenance: Consider how often the filter needs to be replaced and whether you can easily maintain the system.
Size and Installation: Choose between whole-house filtration systems or under-sink filters, depending on whether you want to filter all the water in your home or just your drinking water supply.
Final Thoughts
PFAS contamination is a serious environmental and health issue, but taking proactive steps to protect your family with a PFAS water filter can reduce your exposure. Whether you choose an activated carbon filter, reverse osmosis system, or a combination of technologies, investing in the right filter is an important step toward safer, cleaner water.
By staying informed and choosing a reliable water filtration system, you can safeguard your health and minimize the impact of these harmful "forever chemicals" on your household.
0 notes
Text
PFAS Water Filters: Protecting Your Health from Forever Chemicals

In recent years, PFAS contamination has become a growing concern for communities around the world. Known as "forever chemicals," Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) are synthetic chemicals that do not break down easily in the environment or the human body, leading to potential health risks. As awareness of PFAS increases, many are looking for ways to protect themselves from these harmful chemicals, and one of the most effective solutions is using PFAS water filters.
This blog will explore the dangers of PFAS, the benefits of using PFAS water filters, and how to choose the right filter to ensure your drinking water is safe.
What are PFAS?
PFAS are a group of man-made chemicals used in various industries since the 1940s. They are commonly found in products like non-stick cookware, water-repellent clothing, firefighting foams, and certain food packaging. While their resistance to heat, water, and oil makes them useful in many applications, these same qualities mean they persist in the environment and our bodies for long periods.
Some of the health risks associated with PFAS exposure include:
Increased risk of cancer
Immune system suppression
Liver damage
Thyroid hormone disruption
Developmental issues in children
How Do PFAS Get into Drinking Water?
PFAS can enter water sources through industrial discharges, firefighting foam runoff, and even landfill leachate. Since they are highly mobile in water, PFAS can spread over large areas and contaminate groundwater, rivers, and lakes, eventually reaching our taps.
Drinking water contaminated with PFAS is a major exposure route for many people. Unfortunately, conventional water treatment plants are not always equipped to remove these chemicals, making it essential for individuals to take extra steps to filter PFAS from their water supply.
How Do PFAS Water Filters Work?
Not all water filters can remove PFAS. Filters designed specifically for this purpose often use activated carbon, reverse osmosis, or a combination of filtration technologies to effectively capture and eliminate PFAS compounds.
Activated Carbon Filters: These filters trap PFAS molecules on the surface of carbon granules. While highly effective, activated carbon filters require regular replacement to maintain their efficiency.
Reverse Osmosis Systems: These systems use a semi-permeable membrane to remove PFAS along with other contaminants. Reverse osmosis is one of the most effective methods for filtering PFAS, but it can be more expensive and may waste more water compared to other methods.
Ion Exchange Filters: Some advanced filtration systems use ion exchange resins to specifically target and remove PFAS compounds. These filters are highly effective for long-chain PFAS chemicals, such as PFOA and PFOS.
Benefits of PFAS Water Filters
Protection Against Health Risks
The most significant benefit of PFAS water filters is the protection they offer against the harmful effects of these chemicals. By removing PFAS from your drinking water, you reduce your risk of cancer, hormonal disruptions, and other serious health conditions linked to PFAS exposure.
Improved Water Quality
Beyond just PFAS, many of these filtration systems also remove other common contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and chlorine, improving the overall quality and taste of your drinking water.
Peace of Mind
Knowing that your water is free from toxic chemicals can provide peace of mind, especially for families with young children who are more vulnerable to the effects of PFAS.
Choosing the Right PFAS Water Filter
When selecting a PFAS water filter, it’s essential to choose one that has been tested and certified for PFAS removal. Look for filters certified by reputable organizations, such as the NSF International or Water Quality Association (WQA), for the reduction of PFOA and PFOS levels.
Here are a few factors to consider:
Type of Filter: Decide whether an activated carbon filter, reverse osmosis system, or another filtration method is right for your household based on your budget, water usage, and filtration needs.
Filter Maintenance: Consider how often the filter needs to be replaced and whether you can easily maintain the system.
Size and Installation: Choose between whole-house filtration systems or under-sink filters, depending on whether you want to filter all the water in your home or just your drinking water supply.
Final Thoughts
PFAS contamination is a serious environmental and health issue, but taking proactive steps to protect your family with a PFAS water filter can reduce your exposure. Whether you choose an activated carbon filter, reverse osmosis system, or a combination of technologies, investing in the right filter is an important step toward safer, cleaner water.
By staying informed and choosing a reliable water filtration system, you can safeguard your health and minimize the impact of these harmful "forever chemicals" on your household.
0 notes