#javabasic
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Vòng Lặp While trong Java | Cách Hoạt Động và Ví Dụ
Vòng lặp while trong Java là một trong những cấu trúc điều khiển luồng quan trọng, được sử dụng rộng rãi trong lập trình để thực hiện các tác vụ lặp đi lặp lại khi điều kiện vẫn còn đúng. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu chi tiết về cách hoạt động của vòng lặp while, cú pháp, các ví dụ minh họa và một số lưu ý quan trọng để sử dụng hiệu quả.
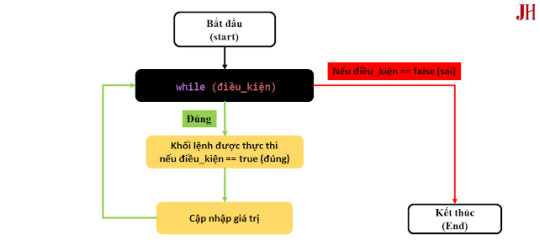
Ảnh mô tả cách hoạt động của vòng lặp while.
Vòng lặp while trong Java là gì?
Vòng lặp while là một cấu trúc lặp trong ngôn ngữ lập trình Java, cho phép thực thi một khối mã nhiều lần miễn là điều kiện được chỉ định vẫn đúng. Đây là loại vòng lặp đơn giản nhưng mạnh mẽ, thường được sử dụng khi số lần lặp không xác định trước.
Cú pháp cơ bản của vòng lặp while trong Java:
while (điều_kiện) {
// Khối mã được thực thi
}
điều_kiện: Một biểu thức boolean trả về giá trị true hoặc false. Nếu điều kiện là true, khối mã bên trong sẽ được thực thi. Nếu là false, vòng lặp sẽ dừng.
Khối mã: Các câu lệnh sẽ được thực thi lặp đi lặp lại cho đến khi điều kiện trở thành false.
Cách hoạt động của Vòng lặp while trong Java
Vòng lặp while hoạt động theo các bước sau:
Kiểm tra điều kiện: Trước mỗi lần lặp, Java sẽ kiểm tra điều kiện trong dấu ngoặc (). Nếu điều kiện trả về true, khối mã bên trong sẽ được thực thi.
Thực thi khối mã: Nếu điều kiện đúng, các câu lệnh trong khối mã sẽ được thực hiện.
Cập nhật điều kiện: Sau mỗi lần lặp, điều kiện sẽ được kiểm tra lại. Nếu điều kiện vẫn đúng, vòng lặp tiếp tục; nếu sai, chương trình thoát khỏi vòng lặp.
Lưu ý: Nếu điều kiện luôn đúng, vòng lặp while có thể dẫn đến vòng lặp vô hạn, gây treo chương trình. Vì vậy, cần đảm bảo điều kiện sẽ trở thành false tại một thời điểm nào đó.
Ví dụ về Vòng lặp while trong Java
Dưới đây là một số ví dụ minh họa cách sử dụng vòng lặp while trong các tình huống thực tế.
Ví dụ 1: In các số từ 1 đến 5
public class WhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
Kết quả:
1
2
3
4
5
Giải thích:
Biến i được khởi tạo với giá trị 1.
Điều kiện i <= 5 được kiểm tra trước mỗi lần lặp.
Nếu điều kiện đúng, chương trình in giá trị i và tăng i lên 1.
Khi i đạt 6, điều kiện trở thành false, vòng lặp dừng.
Ví dụ 2: Tính tổng các số từ 1 đến n
public class SumExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
int sum = 0;
int i = 1;
while (i <= n) {
sum += i;
i++;
}
System.out.println("Tổng các số từ 1 đến " + n + " là: " + sum);
}
}
Kết quả:
Tổng các số từ 1 đến 10 là: 55
Giải thích:
Biến sum lưu tổng, ban đầu bằng 0.
Vòng lặp while cộng dồn giá trị của i vào sum cho đến khi i vượt quá n.
So sánh Vòng lặp while và Vòng lặp do-while
Một cấu trúc tương tự vòng lặp while là vòng lặp do-while. Sự khác biệt chính là:
Vòng lặp while: Kiểm tra điều kiện trước khi thực thi khối mã. Nếu điều kiện sai ngay từ đầu, khối mã không được thực thi lần nào.
Vòng lặp do-while: Thực thi khối mã ít nhất một lần trước khi kiểm tra điều kiện.
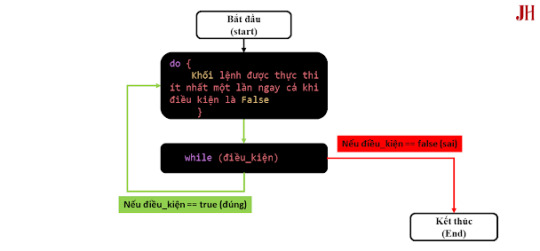
Ảnh mô tả cách hoạt động của vòng lặp do-while.
Cú pháp do-while:
do {
// Khối mã
} while (điều_kiện);
Ví dụ do-while:
int i = 1;
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (i <= 5);
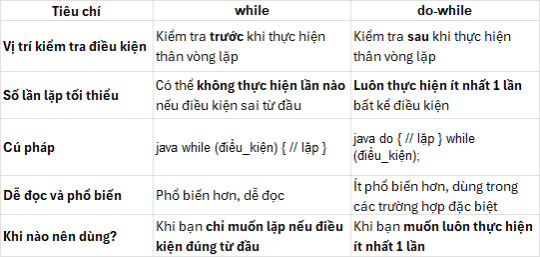
Bảng so sánh while và do-while
Một số lưu ý khi sử dụng Vòng lặp while trong Java
Tránh vòng lặp vô hạn: Luôn đảm bảo điều kiện của vòng lặp while sẽ trở thành false tại một thời điểm. Ví dụ, luôn tăng hoặc giảm biến điều khiển.
Khởi tạo biến: Biến điều khiển vòng lặp cần được khởi tạo trước khi vào vòng lặp.
Hiệu suất: Vòng lặp while phù hợp khi số lần lặp không xác định. Nếu số lần lặp đã biết, hãy cân nhắc sử dụng vòng lặp for.
Kiểm tra điều kiện: Đảm bảo điều kiện được viết chính xác để tránh lỗi logic.
Ứng dụng thực tế của Vòng lặp while trong Java
Vòng lặp while được sử dụng trong nhiều tình huống thực tế, chẳng hạn:
Xử lý dữ liệu đầu vào: Đọc dữ liệu từ người dùng cho đến khi nhập giá trị hợp lệ.
Xử lý vòng lặp không xác định: Ví dụ, chờ phản hồi từ server hoặc xử lý danh sách dữ liệu động.
Trò chơi: Kiểm tra trạng thái trò chơi (ví dụ: nhân vật còn sống hay không).
Kết luận
Vòng lặp while trong Java là một công cụ mạnh mẽ để xử lý các tác vụ lặp lại một cách linh hoạt. Với cú pháp đơn giản và khả năng ứng dụng đa dạng, vòng lặp while là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho nhiều tình huống lập trình. Hy vọng bài viết này đã giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách hoạt động, cách sử dụng và các ví dụ thực tế của vòng lặp while. Hãy thử áp dụng vào dự án của bạn và đừng quên tối ưu hóa mã để tránh các lỗi như vòng lặp vô hạn!
Nếu bạn có thắc mắc hoặc cần thêm ví dụ về vòng lặp while trong Java, hãy để lại câu hỏi dưới phần bình luận!
🌀 Vòng Lặp While trong Java | Cách Hoạt Động và Ví Dụ Thực Tế Tìm hiểu cách sử dụng vòng lặp while trong Java để thực hiện các thao tác lặp lại điều kiện. Hướng dẫn dễ hiểu kèm ví dụ minh họa rõ ràng giúp bạn nắm chắc cú pháp và logic vòng lặp.
🌐 Website: Java Highlight
#JavaHighlight#WhileLoop#JavaLoop#JavaBasic#LapTrinhJava#JavaTutorial#VongLapJava#JavaLearning#CodeJava#HocJava#Vòng Lặp While trong Java
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Unveiling Java: Exploring the Fundamentals

Java Programming Unveiled: Embark on Your Journey into the Basics! Discover the fundamentals of Java programming and lay a strong foundation for your coding journey. LSET's beginner-friendly course offers hands-on practice and expert guidance to help you grasp key concepts easily. Plus, with the London School of Emerging Technology (LSET) Java Programming Course, you'll receive comprehensive education and personalised support to become a proficient Java developer, ready to tackle real-world challenges in the ever-evolving tech industry. Enrol @ https://lset.uk/ for admission.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Kickstart Your Coding Career with Java

In today’s tech-driven world, mastering programming languages like Java is not just an advantage—it’s a career necessity. Java remains one of the most powerful, versatile, and in-demand programming languages in the software industry. Whether you aspire to become a software developer, Android app creator, or backend engineer, the first step is enrolling in thebest Java institute in Laxmi Nagar.
Why Java?
Java is a platform-independent, object-oriented programming language used across industries—from mobile applications to enterprise-level software. Its wide application and long-term relevance make it a smart choice for beginners and professionals alike. With real-time project applications, community support, and high-paying job prospects, Java is a gateway to a successful tech career.
Why Choose Laxmi Nagar?
Laxmi Nagar has become a popular educational and IT training hub in East Delhi. With its convenient metro connectivity, student-friendly atmosphere, and affordable learning options, it's the ideal location to kickstart your programming journey. And when it comes to learning Java, you need nothing less than the best Java course in Laxmi Nagar to stay ahead of the curve.
What Makes the Best Java Institute in Laxmi Nagar?
Choosing the right institute can make all the difference. The best Java institute in Laxmi Nagar should offer:
Comprehensive Course Structure: Covering Core Java, Advanced Java, JDBC, JSP, Servlets, and more.
Experienced Trainers: Industry professionals who provide practical insights and coding techniques.
Live Projects: Hands-on training with real-world coding challenges.
Certification: Recognized credentials that boost your job profile.
Placement Assistance: Support in resume building, interviews, and job connections.
Enroll in the Best Java Course in Laxmi Nagar
Whether you're a beginner or want to upgrade your skills, enrolling in the best Java course in Laxmi Nagar will provide you with a strong foundation in object-oriented programming, logical thinking, and application development. The course should be tailored for both academic excellence and job-readiness.
Final Thoughts
If you’re serious about building a successful career in tech, it’s time to take the right step with Java. Enroll in the best Java institute in Laxmi Nagar and gain access to quality training, expert guidance, and career opportunities that put you on the path to success. Your journey to becoming a Java professional starts here!
0 notes
Text
Binary Search in Java (Made Super Simple)
Hey folks!
If you're new to programming or just getting started with Java, you might’ve come across the term Binary Search. It might sound a little intimidating at first, but trust me, once you get the hang of it, it’s actually a pretty neat and efficient way to search through data.
Let’s break it down in a super simple way.
Imagine you have a sorted list of numbers — something like [2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 45, 56, 72, 91]. Now, let’s say you want to find out if the number 23 is in that list. You could go one by one, checking each number (this is called linear search), but that would take time — especially if the list is super long.
Enter Binary Search. Instead of checking each number, binary search cuts the list in half, checks the middle value, and then decides whether to go left or right, depending on whether the number you’re looking for is smaller or bigger than the middle value. This continues until the number is found, or until the list can’t be split anymore.
It’s kind of like playing a number guessing game. Say you’re told to guess a number between 1 and 100, and after every guess, you're told whether your guess was too high or too low. Instead of guessing randomly, you’d usually go for the middle, like 50, then adjust based on the feedback. That’s basically how binary search works!
In Java, writing a binary search algorithm is pretty straightforward. It usually involves using a while loop, checking the middle index of the array, and updating the start and end points based on your comparisons. With just a few lines of code, you get a fast and efficient way to search.
If you want a clear and beginner friendly explanation along with the Java code, do check out this page: Binary Search in Java.
It explains the logic step-by-step, and the example makes it easy to follow even if you're just starting out with coding. Practicing small programs like this is a great way to build your confidence and understanding of how algorithms work.
So yeah, binary search isn’t scary at all. Give it a shot, play around with the code, and see how it works in action. Once you get it, you’ll feel pretty good about adding it to your programming toolbox.
1 note
·
View note
Text
"Java in a Nutshell" by Benjamin J. Evans and David Flanagan is a concise yet comprehensive guide to the Java programming language. It serves as both a tutorial for beginners and a reference for experienced developers. The book covers the core features of Java, along with advanced topics, making it a valuable resource for anyone looking to master Java. Below is a user-friendly, step-by-step breakdown of the key outcomes and takeaways from the book, designed to help readers understand and apply Java effectively.
#Java#JavaProgramming#JavaInANutshell#JavaDevelopment#SoftwareDevelopment#ProgrammingBooks#JavaTutorial#JavaCode#TechBooks#JavaResources#JavaGuide#JavaBestPractices#JavaBasics#TechEducation#ProgrammingLanguages#JavaLearning#Java3#SoftwareEngineering#JavaProjects#JavaTips#JavaJVM#Coding#TechTutorial#JavaCommunity#JavaDevelopmentTools
0 notes
Text
Java vs Kotlin in 2025: Is Java Still Worth Learning?
In a world charmed by shiny tools and swift transitions, dismissing what came before is easy. The tech landscape is always humming—louder than it ever did. And in that rush, Java, the stalwart, gets nudged into the wings as Kotlin walks center stage.

But in 2025, something quiet is happening—Java remains. And not just remains, but serves.
Let’s anchor this in something real: Core Java Training in KPHB is still in demand, still shaping the futures of developers, still grounding newcomers in the fundamentals of software craftsmanship. In this hub of learning, what’s being taught isn't obsolete—it's foundational.
Why Java Holds Ground
Java offers something that doesn't waver with trends: stability. It’s the kind of language that helps you understand the spine of programming logic. And in today’s ecosystem—where microservices, cloud, and data-heavy applications thrive—Java continues to power robust backends, massive systems, and enterprise solutions.
Kotlin, though elegant and concise, leans heavily on Java's shoulders. Without Java, Kotlin wouldn’t stand as tall. It complements, yes. But it does not replace.
The KPHB Perspective
In KPHB, a locality brimming with institutes, tech aspirations, and the rhythms of ambitious learners, Java is more than a language. It’s a rite of passage. Core Java Training in KPHB is not about resisting change—it’s about beginning at the root.
Think of it this way: a tree doesn’t shed its roots just because it’s grown new leaves.
Why Employers Still Respect Java
Look through the job boards in Hyderabad, and you'll see something telling: Java is still there. Required. Expected. Especially in companies where legacy systems coexist with modern frameworks. If you're job-ready in Java, you're already ahead in versatility.
Java is also the first language for many global certification paths. Oracle’s ecosystem, Spring Framework, Android—these remain deeply connected to Java.
What Learners Say
The learners walking through the doors of KPHB’s training centers aren’t chasing trends. They’re seeking direction. They often start with a question: "Should I learn Kotlin instead?" But by the end of their Core Java modules, they understand that this isn’t a choice between old and new—it’s about building a base before climbing.
Looking Ahead
The future doesn't cancel the past. It includes it. Kotlin will continue to rise, especially in Android development and cross-platform spaces. But Java’s rhythm won’t fade—it will deepen.
If you’re in KPHB, wondering where to begin—know this: Core Java Training in KPHB isn’t just a course. It’s a compass.
🧠 Previous Year Questions - Core Java
1. What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM? Answer:
JDK (Java Development Kit) is a software development kit used to develop Java applications.
JRE (Java Runtime Environment) provides the environment to run Java applications.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) executes Java bytecode and provides platform independence.
2. Explain the concept of inheritance in Java. Answer: Inheritance is an OOP concept where one class (child) acquires properties and behavior from another class (parent) using the extends keyword. It promotes code reusability.
3. What is the difference between method overloading and method overriding? Answer:
Overloading occurs within the same class with different parameter lists.
Overriding occurs in a subclass, redefining a superclass method with the same signature.
4. What are access specifiers in Java? Answer: Access specifiers define the scope of access:
private – within the class only
default – within the same package
protected – within the same package or subclasses
public – accessible from everywhere
5. Explain the use of the ‘final’ keyword. Answer: The final keyword is used to declare constants, prevent method overriding, and prevent inheritance of classes.
6. What is the difference between an abstract class and an interface? Answer:
Abstract class can have both abstract and non-abstract methods; supports constructors.
Interface contains only abstract methods (prior to Java 8) and multiple inheritance of type.
7. What is multithreading in Java? Answer: Multithreading allows concurrent execution of two or more parts of a program for maximum CPU utilization using the Thread class or Runnable interface.
8. What is garbage collection in Java? Answer: Garbage collection is the process of automatically reclaiming memory by destroying unused objects to free space.
9. How does exception handling work in Java? Answer: It uses five keywords: try, catch, throw, throws, and finally to handle run-time errors, improving program stability.
10. What is the use of the ‘this’ keyword? Answer: The this keyword refers to the current object of a class, often used to distinguish between instance and local variables.
#CoreJava#JavaTraining#JavaInterviewQuestions#JavaBasics#KPHBTraining#JavaForBeginners#JavaLearning#JavaDevelopment#JavaCertification#JavaConcepts#KPHBJava#JavaClassesHyderabad#SoftwareTraining#TechSkillsIndia#JavaPYQs
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Java Equals Method: String Comparison Made Easy
Understand the Java Equals Method and its role in comparing object equality in Java programming. Learn how to effectively use equals for precise comparisons between Java objects.
0 notes
Video
youtube
How to remove a sublist from a list in java | java inspires
0 notes
Text
Core Java training near me
Embark on a journey of Java excellence with Sunbeam Institute for Java Training. Our comprehensive Core Java training program is designed to equip you with the essential skills to become a proficient Java developer. Whether you're a beginner or looking to level up your Java expertise, we've got you covered.
Why Choose Sunbeam Institute for Java Training?
✨ Expert Instructors: Learn from seasoned Java developers and industry experts with years of practical experience.
✨ Hands-on Learning: Dive into the world of Java through hands-on projects and real-world applications.
✨ Personalized Attention: Benefit from small class sizes and personalized attention to ensure a conducive learning environment.
✨ Updated Curriculum: Stay ahead in the Java landscape with a curriculum that covers the latest advancements and best practices.
#CoreJava#JavaTraining#JavaDevelopment#ProgrammingEducation#LearnJava#CodeWithJava#JavaProgramming#JavaClasses#TechTraining#JavaSkills#JavaBootcamp#CodingInstitute#JavaBasics#ProgrammingSkills#JavaLearning#ObjectOrientedProgramming#JDBC#JavaAPIs#CodingJourney#TechCareer
0 notes
Text
Vòng Lặp for Trong Java - Hướng Dẫn Chi Tiết
Vòng lặp for trong Java là một trong những cấu trúc điều khiển luồng quan trọng, được sử dụng rộng rãi để lặp lại một khối mã lệnh với số lần xác định. Nếu bạn đang học lập trình Java hoặc muốn nâng cao kỹ năng lập trình, việc hiểu rõ cách sử dụng vòng lặp for là điều không thể thiếu. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ cùng tìm hiểu chi tiết về vòng lặp for, cách hoạt động, các dạng của nó, ví dụ minh họa và mẹo tối ưu hóa khi sử dụng.
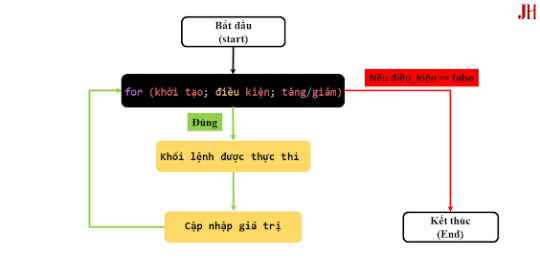
Ảnh mô tả cách hoạt động của vòng lặp for.
Vòng lặp for trong Java là gì?
Vòng lặp for là một cấu trúc lặp được sử dụng khi bạn biết trước số lần lặp cần thực hiện. Nó giúp thực thi một khối mã lệnh nhiều lần dựa trên một điều kiện cụ thể. Cú pháp cơ bản của vòng lặp for trong Java như sau:for (khởi_tạo; điều_kiện; cập_nhật) { // Khối mã cần thực thi }
Khởi tạo: Thiết lập giá trị ban đầu cho biến điều khiển lặp (thường là một biến đếm).
Điều kiện: Kiểm tra điều kiện trước mỗi lần lặp. Nếu điều kiện đúng, khối mã được thực thi.
Cập nhật: Thay đổi giá trị của biến điều khiển sau mỗi lần lặp (thường là tăng hoặc giảm).
Ví dụ đơn giản:
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Lần lặp thứ: " + i);
}
Kết quả sẽ in ra:
Lần lặp thứ: 0
Lần lặp thứ: 1
Lần lặp thứ: 2
Lần lặp thứ: 3
Lần lặp thứ: 4
Các dạng của vòng lặp for trong Java
1. Vòng lặp for cơ bản
Đây là dạng phổ biến nhất, như ví dụ đã đề cập ở trên. Nó phù hợp khi bạn biết chính xác số lần lặp hoặc phạm vi của biến đếm.
Ví dụ:
In các số chẵn từ 0 đến 10:
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i += 2) {
System.out.println(i);
}
2. Vòng lặp for lồng nhau
Vòng lặp for lồng nhau là khi một vòng lặp for được đặt bên trong một vòng lặp for khác. Loại này thường được sử dụng để xử lý các bài toán liên quan đến mảng hai chiều hoặc các cấu trúc dữ liệu phức tạp.
Ví dụ:
In bảng cửu chương:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
System.out.println(i + " * " + j + " = " + (i * j));
}
}
3. Vòng lặp for cải tiến (Enhanced for loop)
Còn được gọi là for-each loop, đây là dạng vòng lặp for được sử dụng để duyệt qua các phần tử của mảng hoặc tập hợp (Collection) mà không cần chỉ số.
Cú pháp:
for (Kiểu_dữ_liệu phần_tử : tập_hợp) {
// Khối mã cần thực thi
}
Ví dụ:
Duyệt qua một mảng:
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int num : numbers) {
System.out.println(num);
}
Khi nào nên sử dụng vòng lặp for?
Vòng lặp for phù hợp trong các trường hợp sau:
Bạn biết trước số lần lặp cần thực hiện.
Bạn cần kiểm soát chính xác giá trị của biến đếm.
Bạn đang làm việc với mảng hoặc danh sách có kích thước cố định.
Ngược lại, nếu số lần lặp không xác định, bạn có thể cân nhắc sử dụng vòng lặp while hoặc do-while.
Mẹo tối ưu hóa khi sử dụng vòng lặp for
Tránh tính toán lặp lại trong điều kiện: Nếu điều kiện lặp liên quan đến một phép tính phức tạp, hãy tính trước và lưu vào biến. Ví dụ: int length = array.length; // Tính trước for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // Thực thi mã }
Sử dụng break và continue hợp lý: break: Thoát hoàn toàn khỏi vòng lặp khi đạt điều kiện nhất định. continue: Bỏ qua lần lặp hiện tại và chuyển sang lần lặp tiếp theo. Ví dụ: for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if (i == 5) break; // Thoát vòng lặp khi i = 5 if (i % 2 == 0) continue; // Bỏ qua số chẵn System.out.println(i); }
Hạn chế lồng quá nhiều vòng lặp: Vòng lặp for lồng nhau quá nhiều có thể làm giảm hiệu suất. Nếu có thể, hãy tìm cách tối ưu hóa thuật toán.
Các lỗi phổ biến khi sử dụng vòng lặp for
Vô tình tạo vòng lặp vô hạn: Nếu điều kiện lặp không bao giờ sai, chương trình sẽ chạy mãi mãi.for (int i = 0; i >= 0; i++) { // Vòng lặp vô hạn System.out.println(i); }
Truy cập ngoài giới hạn mảng: Khi sử dụng vòng lặp for để duyệt mảng, hãy đảm bảo chỉ số không vượt quá kích thước mảng. int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) { // Lỗi: arr.length gây ra ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException System.out.println(arr[i]); }
Quên cập nhật biến điều khiển: Nếu không cập nhật biến, vòng lặp có thể không hoạt động như mong muốn.
Kết luận
Vòng lặp for trong Java là một công cụ mạnh mẽ, linh hoạt và không thể thiếu trong lập trình. Từ vòng lặp for cơ bản, vòng lặp for lồng nhau đến for-each loop, mỗi dạng đều có ứng dụng riêng trong các tình huống khác nhau. Bằng cách hiểu rõ cách hoạt động, tối ưu hóa mã và tránh các lỗi phổ biến, bạn có thể sử dụng vòng lặp for một cách hiệu quả để giải quyết các bài toán lập trình.
Hãy thực hành các ví dụ trong bài viết này và áp dụng vòng lặp for vào d�� án của bạn. Nếu bạn có bất kỳ thắc mắc nào về vòng lặp for trong Java, đừng ngần ngại để lại câu hỏi!
Java Highlight – Hướng dẫn chi tiết về vòng lặp for trong Java dành cho người mới bắt đầu. Tìm hiểu cách sử dụng vòng lặp for, cú pháp, ví dụ minh họa và ứng dụng thực tế trong lập trình Java. 🌍 Website: Java Highlight
#JavaHighlight#Java#VongLapFor#ForLoopJava#Javalearning#LapTrinhJava#JavaTutorial#JavaBasic#CodeJava#JavaForBeginners#Vòng lặp for trong Java
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Java Programming: Basics

Embarking on Your Java Journey: Introduction to Java Programming Basics. Delve into the world of Java programming and lay a solid foundation in the basics of Java. LSET comprehensive guide covers essential topics such as syntax, data types, control structures, and object-oriented programming principles, providing a strong starting point for beginners. Plus, with London School of Emerging Technology (LSET) Java Programming Course, you'll receive expert-led instruction and hands-on experience to master Java programming from beginner to advanced levels. Join us and unlock the potential of Java, equipping yourself with the skills to develop robust and scalable software applications.
Enrol @ https://lset.uk/ for admission.
0 notes
Text
🧩 Day 11 of Java Mastery: Relational Operators Want your code to make decisions? Read Blog: https://wp.me/paNbWh-6A #Java #JavaMastery #Day11 #RelationalOperators #LearnJava #100DaysOfCode #CodeNewbie #JavaBasics #LogicBuilding
#>#>=#<#app development#architecture of java#arithmetic#backend#beginner#calculations#datastructures#execution flow#frontend#fullstack#fullstackdeveloper#greater than#greater than or equal to#Java#less than#less than or equal to#operators#output#print#relational
0 notes