#learnblockchain
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top 10 Blockchain Project Ideas For Students
Exploring blockchain technology opens up exciting project opportunities for students in 2025. Top ideas include cryptocurrency wallets, supply chain tracking, voting systems, NFT marketplaces, and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. These projects not only enhance technical skills but also offer practical exposure to real-world blockchain applications Read More...

0 notes
Text
Smart Contracts: The Self-Executing Code Behind Blockchain Magic

Imagine a contract that doesn't need lawyers, middlemen, or paper trails. A contract that executes itself automatically when predefined conditions are met — no questions, no delays. That’s exactly what smart contracts do on the blockchain.
In Episode 6 of Unpacking Blockchain Technology with Thabiso Njoko, we dive deep into one of the most powerful innovations in the blockchain ecosystem: Smart Contracts.
What Is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing program stored on the blockchain. It runs automatically when specific rules or conditions — written in code — are fulfilled.
In short: “If X happens, then do Y.”
They eliminate the need for intermediaries by ensuring that agreements are carried out exactly as programmed.
Key Features of Smart Contracts
Here’s what makes them revolutionary:
Autonomous – Executes automatically without human intervention Immutable – Once deployed, they can’t be altered Trustless – Parties don't need to trust each other, only the code Transparent – The contract code is visible and verifiable by anyone Secure – Stored across decentralized networks, making them resistant to tampering
Real-World Use Cases
Smart contracts are the building blocks of Web3, powering decentralized applications across industries:
1. Finance (DeFi)
Lending & Borrowing Platforms like Aave and Compound use smart contracts to automate collateralized loans.
Yield farming and staking protocols distribute rewards via code.
2. NFTs
When you mint or sell an NFT, smart contracts ensure:
Ownership is transferred
Royalties are sent to the creator
The transaction is recorded immutably
3. DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations)
Governance rules and treasury management are coded into smart contracts.
Members vote and make proposals through transparent on-chain mechanisms.
4. Supply Chain
Contracts trigger actions like payments or shipment releases when sensors confirm product delivery or conditions are met.
5. Gaming
In blockchain games, smart contracts manage in-game assets, rewards, and upgrades.
“Smart contracts are not just digital agreements — they’re trustless executors. Whether it’s splitting revenue among collaborators or automating donations, these lines of code are changing how we do business online.”
He further explains how Ethereum popularized smart contracts, and why other chains like Solana, BNB Chain, and Avalanche are optimizing them for scale and performance.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Written in code (often Solidity for Ethereum)
Deployed on the blockchain with a unique address
Triggered by users or other smart contracts when specific inputs or events occur
Execute predefined actions and update the state on-chain
Think of them as digital vending machines — you insert the input (e.g. crypto), the machine checks conditions (e.g. amount received), and then it delivers the output (e.g. an NFT or a token).
Limitations & Risks
While powerful, smart contracts are not foolproof:
Bugs in code can lead to costly exploits (e.g., The DAO Hack in 2016)
No flexibility once deployed unless designed with upgrade paths
Scalability issues on some blockchains
Legal grey areas in traditional regulatory systems
“Code is law — but that comes with responsibility,”
“Audit your contracts. Test everything.”
Why Smart Contracts Matter
Smart contracts are key to decentralization. They remove gatekeepers, increase transparency, and allow anyone, anywhere, to build trustless systems.
From splitting royalties for a music collaboration to powering decentralized insurance — smart contracts put control in the hands of creators, developers, and communities.
Tune In Now
Listen to Episode 6 of Unpacking Blockchain Technology with Thabiso Njoko on your favorite podcast platform to explore the world of smart contracts — and discover how they’re quietly transforming everything from banking to digital art.
#SmartContracts#BlockchainTechnology#Web3Education#Ethereum#DeFi#DAOs#NFTs#BlockchainAfrica#UnpackingBlockchain#ThabisoNjoko#CryptoDevelopment#Web3Tools#blockchaineducation#blockchain#blockchainforgood#bitcoin#blockchaininnovation#eswatini#EswatiniTech#AfricanInnovation#TechInAfrica#Web3Africa#DigitalAfrica#EswatiniBlockchain#BlockchainPodcast#Web3Podcast#PodcastSeries#LearnBlockchain#EducationalContent#BlockchainForBeginners
0 notes
Text
How To Become A Blockchain Developer
How To Become A Blockchain Developer In the dynamic realm of technology, blockchain has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing industries from finance to supply chain management. As the demand for blockchain expertise surges, more professionals are aspiring to transition into this domain. In "How To Become A Blockchain Developer," we provide a comprehensive roadmap for aspiring developers, covering essential skills, educational pathways, and practical steps to take in order to excel in this burgeoning field. Our guide aims to demystify the process, offering valuable insights and actionable advice to navigate the complexities of blockchain development efficiently and effectively.
Learn more at: https://ckbtino.com/how-to-become-a-blockchain-developer/

#BlockchainDeveloper#LearnBlockchain#Web3#CryptoJobs#BlockchainCareer#SmartContracts#DecentralizedApps#Solidity#EthereumDeveloper#FutureOfTech#BlockchainTechnology#Cryptocurrency#BlockchainLearning
0 notes
Text
Learn Blockchain Technology: Discover step-by-step guides, top resources, and practical tips to master blockchain technology for beginners and professionals alike.
#learnblockchain#blockchaintutorial#blockchaintechnologycourse#blockchaineducation#blockchaintraining
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Photo

Crowdfunding made easier, Money made easy. Thank you Blockchain!! Join the revolution- referral program 📲 launching in less than 30 days ✅ are you all excited? The Blockchain School is an e-learning freemium platform dedicated towards education on Blockchain Technology Join the disruption and be a part of the future with our courses and variety of materials on Blockchain, tailored specially for you. Learn Blockchain And Beyond 📚 #staytuned 🙌 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . #blockchain #blockchaintechnology #blockchains #blockchainfacts #blockchainrevolution #tbsnation #techiescoops #blockchain #blockchaintechnology #elearning #freemium #bitcoin #cryptocurrency #cryptoindia #india #globallaunch #tbs #theblockchainschool #blockchaincourses #learnblockchain #newtrends #technology #technologyeducation #techfacts #newwebsitelaunch #blockchainproject #hyperledger #freelance #blockchainjobs #learnblockchainandbeyond https://www.instagram.com/theblockchainschool/p/ByaTOFQj2ZG/?igshid=18nftefg0wfri
#staytuned#blockchain#blockchaintechnology#blockchains#blockchainfacts#blockchainrevolution#tbsnation#techiescoops#elearning#freemium#bitcoin#cryptocurrency#cryptoindia#india#globallaunch#tbs#theblockchainschool#blockchaincourses#learnblockchain#newtrends#technology#technologyeducation#techfacts#newwebsitelaunch#blockchainproject#hyperledger#freelance#blockchainjobs#learnblockchainandbeyond
1 note
·
View note
Text
Fintech and blockchain - A complete guide

Fintech is the combination of Financial technology. As we move ahead, we realize the power of technology. We also learn how it can make so many day-to-day activities easier in spaces we had never imagined. Fintech uses its specialized software and algorithms on computers and smartphones to assist businesses, business owners, and individuals. It aims to manage its financial operations, processes, and lives in a better manner. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Blockchain Project Ideas For Students
Exploring blockchain technology opens up exciting project opportunities for students in 2025. Top ideas include cryptocurrency wallets, supply chain tracking, voting systems, NFT marketplaces, and decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. These projects not only enhance technical skills but also offer practical exposure to real-world blockchain applications Read More..

0 notes
Text
Understanding the Four Types of Blockchains

Public, Private, Consortium & Hybrid — Which One Powers What?
Blockchain technology isn’t one-size-fits-all. As the technology evolves, we’re seeing different flavors of blockchain emerge — each tailored to specific use cases and governance models. In Episode 4 of Unpacking Blockchain Technology with Thabiso Njoko, we break down the four main types of blockchains and explain how each one functions in the real world.
If you’ve ever wondered why some blockchains are open and others are gated, this episode is your gateway to clarity.
The Four Main Types of Blockchains
Whether you're launching a cryptocurrency, managing a supply chain, or modernizing government services, choosing the right type of blockchain is critical. Here's how they compare:
1. Public Blockchains
These are fully decentralized and open to anyone. Anyone can read, write, or participate in the network. Popular examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana.
Features:
Open-source
Transparent and secure
Powered by consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS)
Use Cases:
Cryptocurrencies
NFTs
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Open-access Web3 applications
“Public blockchains are the backbone of the trustless Web3 world,” says Thabiso.
2. Private Blockchains
These are permissioned systems controlled by a single organization. Only selected participants can access the network or validate transactions.
Features:
High speed and scalability
Restricted access
Centralized authority and governance
Use Cases:
Internal business operations
Financial institutions
Healthcare data management
Think of private blockchains as enterprise-grade solutions for data security and control.
3. Consortium Blockchains
Also known as federated blockchains, these are governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. Each participant in the consortium has certain rights.
Features:
Semi-decentralized
Shared control among participants
Collaborative governance
Use Cases:
Supply chain tracking
Trade finance between banks
Joint ventures between corporations
These are ideal for industries that rely on shared infrastructure but don’t want to go fully public.
4. Hybrid Blockchains
As the name suggests, hybrid blockchains combine features of both public and private systems. This offers flexibility—you can keep some data public while keeping sensitive data private.
Features:
Controlled access + transparency
Combines the best of both worlds
Complex but powerful
Use Cases:
Government records (public data + confidential citizen info)
Healthcare systems (open research + private patient data)
Real estate platforms
Hybrid blockchains are perfect when trust, control, and openness need to co-exist.
How Do You Choose the Right One?
Thabiso emphasizes that context determines the blockchain. Ask:
Who needs access?
Who verifies the data?
How sensitive is the information?
What are the trust assumptions?
Each blockchain type serves a purpose. The key is understanding your goals before choosing the structure.
Real-World Examples
A public blockchain like Ethereum is widely used for DeFi and NFTs, while a private blockchain such as Hyperledger Fabric powers IBM's supply chain solutions. In the banking and finance sector, a consortium blockchain like R3 Corda is commonly used. Meanwhile, XinFin (XDC) serves as a hybrid blockchain, particularly effective in trade finance applications.
Final Thoughts from Thabiso
“Not every blockchain has to be open to the world. Some need privacy, speed, and control. But understanding why each model exists helps us build smarter systems.”
As blockchain adoption grows, knowing the differences between these models will shape how we design solutions, collaborate with others, and build trust across systems.
Tune In Now
Catch Episode 4 of Unpacking Blockchain Technology with Thabiso Njoko to hear the full breakdown and use-case comparisons.
Join the Discussion
Which blockchain type best fits your project or organization? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments — let’s unpack it together.
#BlockchainTechnology#Web3#CryptoEducation#DigitalTransformation#FutureOfTech#Decentralization#BlockchainRevolution#CryptoExplained#BlockchainInnovation#TechForAfrica#BlockchainPodcast#Web3Podcast#ThabisoNjoko#UnpackingBlockchain#PodcastSeries#LearnBlockchain#EducationalContent#BlockchainForBeginners#CryptoForEveryone#BlockchainAfrica#EswatiniTech#AfricanInnovation#TechInAfrica#Web3Africa#DigitalAfrica#EswatiniBlockchain
0 notes
Photo

Build your skills and get hands-on experience on Blockchain.
Hurry up! Register now
Contact: 9677781155
0 notes
Text
Blockchain in Agriculture
Blockchain in Agriculture

Did you know that the total number of deaths in the world is due to hunger? This is not at all because of the food shortage. Of course, the food shortage increases along with the increase in the population. We also waste a significant amount of food on a daily basis. Food is wasted for a number of reasons and many factors affect it. One of the reasons is that food is only spoiled because of the inefficient food supply chain.
The food supply chain is inefficient with current technology, and most of the work is still done manually. With numerous middlemen running the supply chain, food producers are struggling to get fair prices for their food. Consumers are unsure about the whereabouts of the food they buy. They are not sure if what they eat is organic. A sticker on the food product does not ensure that it is actually organic food. Those who enjoy the profit are middlemen.
Food fraud is very common and often undetectable. Consumers are very concerned about this because they affect health. And they have no way of checking the quality of the food they buy. For this reason, the scammers make a lot of money by exploiting innocent consumers.
These issues must be resolved with the highest priority because there are no compromises when it comes to health.
The solution :
Blockchain. As simple as it sounds and yes, it has the ability to revolutionize the way our food supply chain works. Food waste can be eliminated and avoided by making the food supply chain efficient. This can be a solution in many ways. The farmer benefits by getting the fair price for his products by eliminating middlemen, hunger can be satisfied and food fraud can be eliminated.
How is it possible?
Blockchain offers transparency;
it shows what is happening in the blocks so that everyone in the block can see where the product comes from;
and whether it's organic by using smart IoT devices in the farm that recognize the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers.
By eliminating the middlemen, farmers can effectively send their agricultural products directly to the grocer or consumer, making profits.
In the case of food fraud, no one can fool blockchain technology because of its decentralized nature. Since the blockchain network is distributed across the networks, the data in the network cannot be manipulated. In this way, integrity can be preserved and food fraud can be eliminated.
There are many other problems in agriculture and farming, blockchain has solutions to most problems. Identify it, build a blockchain in agriculture, and transform your business with agriculture and human health.
#blockchain#blockchaindevelopment#cryptocurrencies#learnblockchain#blockchaininagriculture#supplychain#smartcontract#blockchaindevelopmentcompany
0 notes
Text
What Is Blockchain?

What is blockchain?
Blockchain is actually simply a sequence of sections, yet not in the conventional perception of all those terminology. Whenever most of us mention the terms “block” and “chain” in this particular circumstance, we are basically discussing about digital information (the “block”) saved in a public database (the “chain”). “Blocks” on the blockchain are usually developed up of digital bits of data. Particularly, they have three parts: Blocks save data related to transactions such as the date, time, and money quantity of your almost all latest order from Amazon online marketplace. (NOTE: This particular Amazon example is for illustrative buys; Amazon retail does not function on a blockchain theory) Blocks save data regarding who is taking part in trades. A block for your shop buy from Amazon might capture your name along with Amazon.com, Inc. Instead of using your real name, your buy is saved without having any discovering details using a special “digital signature,” sort of just like an user name. Read about What Is Bitcoin? Complete Guide For Beginners Blocks save data that differentiates all of them from different blocks. Much like you and I have names to differentiate all of us from one another, each and every block saves a special code known as a “hash” that enables us to inform it apart from every single other block. Let’s tell you a person made your shop buy on Amazon, but when it’s in transit, you come to a decision you simply can’t avoid and require a 2nd one. Actually although the information of your fresh transaction might appear almost similar to your previous order, all of us can still inform the blocks separately mainly because of their special codes. Although the block in the example of this above is being utilized to save a single order from Amazon, the fact is a tiny unique. A individual block on the blockchain can truly store up to 1 MB of information. Based on the size of the orders, that indicates a single block can store a few thousand transactions within one block. Read the full article
#Bitcoinblockchain#BitcoinBlockchainTechnology#Blockchainacademy#blockchainadoption#blockchainexplained#blockchaintutorial#blockchainwithexample#learnblockchain#whatisblockchain
0 notes
Photo

Learn from experts.. Learn with The Blockchain School.. Join the revolution- referral program 📲 launching in less than a week ✅ are you all excited? The Blockchain School is an e-learning freemium platform dedicated towards education on Blockchain Technology. Learn Blockchain And Beyond 📚 #staytuned 🙌 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . #tbsnation #techiescoops #blockchain #blockchaintechnology #elearning #freemium #learnblockchain #blockchainquotes #blockchainquote #bitcoin #cryptocurrency #cryptoindia #globallaunch #theblockchainschool #blockchaincourses #learnblockchain #newtrends #technology #technologyeducation #techfacts #newwebsitelaunch #blockchainproject #hyperledger #blockchainjobs #learnblockchainandbeyond https://www.instagram.com/theblockchainschool/p/ByrqIZEDQqk/?igshid=cz4pxr6j05mi
#staytuned#tbsnation#techiescoops#blockchain#blockchaintechnology#elearning#freemium#learnblockchain#blockchainquotes#blockchainquote#bitcoin#cryptocurrency#cryptoindia#globallaunch#theblockchainschool#blockchaincourses#newtrends#technology#technologyeducation#techfacts#newwebsitelaunch#blockchainproject#hyperledger#blockchainjobs#learnblockchainandbeyond
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Places To Learn Blockchain In 2020
A blockchain defined by two distinct words block and chain is a growing list of records, called blocks. Hеrе is a list of Bеѕt Places To Learn Blockchain. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How Blockchain Works (Simplified)

Unpacking the Magic Behind the Chain
Blockchain may sound like a complicated tech buzzword, but at its core, it’s a beautifully simple concept. In Episode 3 of Unpacking Blockchain Technology with Thabiso Njoko, we break down how blockchain works—without the jargon or the confusion. Whether you're a creative, an entrepreneur, a student, or simply curious about Web3, this guide helps demystify the fundamentals.
So… What Is a Blockchain Really?
Imagine a notebook that everyone in a village can write in, but no one can erase or secretly edit. This notebook is visible to everyone, and once you write something, it’s there forever. That’s essentially how blockchain works.
In more technical terms, a blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and immutable way. It’s like a digital record book that's shared across a network of computers.
Each new transaction is grouped into a block, and once verified, that block is added to the chain of previous transactions—hence the name blockchain.
Breaking It Down: The Building Blocks of Blockchain
1. Blocks
A block contains three key elements:
Data (like a transaction or a contract)
A unique hash (digital fingerprint)
The hash of the previous block (linking it to the chain)
This linking of hashes is what makes the blockchain secure—if you tamper with one block, you break the chain.
2. The Chain
Each block is permanently connected to the one before it. This forms an unchangeable timeline of data. If someone tried to alter any information, the change would be obvious because the hashes wouldn’t match anymore.
3. Decentralization
Instead of one central authority controlling the blockchain, it is decentralized across a network of computers (also called nodes). Everyone in the network has a copy of the entire blockchain.
4. Consensus Mechanisms
Before a block is added to the chain, the network must agree that the transaction is valid. This process is known as achieving consensus. Common methods include:
Proof of Work (PoW) — solving complex puzzles (used by Bitcoin)
Proof of Stake (PoS) — validating based on ownership (used by Ethereum 2.0)
This ensures that no single entity can cheat the system.
Security Through Transparency
Here’s the twist: Blockchain is public by design, but also secure. Even though everyone can see the ledger, no one can alter the past records. And even though transactions are transparent, users can remain anonymous thanks to wallet addresses and cryptographic techniques.
This combination of transparency + immutability + decentralization is what makes blockchain so revolutionary. It builds trust without needing a central authority.
Real-World Analogy: A Community Ledger
Let’s say you and your neighbors start a community fund. Instead of trusting one person to manage the money, you all decide to log every transaction in a shared ledger. Anyone can write in it, but every entry must be verified by the majority before it's added.
You now have a trustless, transparent, and tamper-proof system.
That’s blockchain, in real life.
Why Should You Care?
Understanding how blockchain works is the first step to grasping its potential. It powers cryptocurrencies, underpins smart contracts, enables Web3 platforms, and is already transforming finance, art, music, identity, and more.
If you’re an innovator, creator, or entrepreneur, blockchain can empower you to:
Own your data
Sell directly to fans/customers
Build trust with no middlemen
Create secure digital products or contracts
Listen & Learn More
In the episode, Thabiso Njoko uses simple metaphors and real-world comparisons to make blockchain approachable. If you want to dive deeper and truly understand what makes blockchain tick, this episode is a great starting point.
Keep Exploring
Subscribe to the podcast Unpacking Blockchain Technology with Thabiso Njoko on your favorite platform and catch the rest of Season 1: The Foundations—the perfect beginner's guide to blockchain and Web3.
Join the Conversation
What part of blockchain is still confusing to you? Drop your questions and thoughts in the comments or message us directly. Let's unpack it together.
#BlockchainTechnology#Web3#CryptoEducation#DigitalTransformation#FutureOfTech#Decentralization#BlockchainRevolution#CryptoExplained#BlockchainInnovation#TechForAfrica#BlockchainPodcast#Web3Podcast#ThabisoNjoko#UnpackingBlockchain#PodcastSeries#LearnBlockchain#EducationalContent#BlockchainForBeginners#CryptoForEveryone#BlockchainAfrica#EswatiniTech#AfricanInnovation#TechInAfrica#Web3Africa#DigitalAfrica#EswatiniBlockchain
0 notes
Text
How Blockchain Works?
What is blockchain?
A blockchain (meaning "blockchain") is a special type of database, such as a digital accounting book although this simple explanation does not describe the genius behind how this technology records values and transactions.
Until recently, people had to rely on third parties (such as banks, governments and companies) to store their valuable assets, and their transaction information.
For example, when you make a purchase with your credit card, you trust that the credit card company and your bank will keep your personal information and your transaction details safe.
This trust towards institutions does not only apply to financial transactions: A car rental service also maintains a central database with your personal details, your address, the vehicles you have rented, and when you need to return them.
You trust that they will keep all this information private and secure. The information was always kept centralized in these establishments, and each of them had to maintain their own records and systems. But not anymore!
How Blockchain Works?
The blockchain is able to record all the transactions of the participants in the blockchain network. He stores and shares them publicly.
When people who want to make an online transaction are asked, what matters most to them in that movement, most stress security and transparency. And this is the main attraction that Blockchain has: the security and trust it generates.
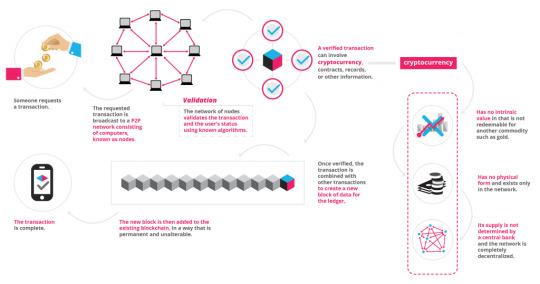
The blockchain consists of strong cryptography. It is an extremely intelligent software that protects documents and data ensuring that they cannot be hacked. This technology means being able to make a transfer abroad in a matter of seconds and without any associated commission. In this way, banks and stock markets are the most affected by this new transaction system. The elimination of intermediaries means that banks have to put the batteries. For example, in our country, specifically in Galicia, they already have their first bitcoin cashier . But Blockchain doesn't just affect the banking landscape. It could change the way it works, is regulated and operated on the Internet. Other alternatives have recently emerged. These New protocols built on the basis of such technology give rise to services and products that provide an amount of information stored in a database that cannot be altered, nor is it owned by a single entity.
A Blockchain technology with these characteristics could be the future of electronic voting, for example. Since, due to the nature of its operation, it could guarantee a system in which identities and voting would be protected at a very low cost and would be in falsifiable.
An example will serve to understand its operation and the steps that occur to perform these transactions. But there is the premise that blockchain must have several users so that they will validate the transactions and will be recorded in that book to which the authors refer.
1. Someone wants to send money, ship a product, or sign a contract.
2. A notification of the action is sent to all users who are within the network (which could be global).
3. If the transaction is valid, everyone approves it.
4. After approval, the record is updated (that is, a block is added to blockchain ).
5. The action occurs, and, if it is a payment, the money changes hands.
6. An unmodifiable record closes the transaction.
Do you want to learn more information about blockchain:
https://www.blockchainx.tech
#cryptocurrency#blockchain development#blockchain#coin marketing#ico development#sto development#bitcoin#learnblockchain
0 notes