#looking at that Tudors still is insane like they really will go to any lengths to not make men feel like they've got bare legs XD
Text
So I accidentally almost got into an argument on Twitter, and now I'm thinking about bad historical costuming tropes. Specifically, Action Hero Leather Pants.
See, I was light-heartedly pointing out the inaccuracies of the costumes in Black Sails, and someone came out of the woodwork to defend the show. The misunderstanding was that they thought I was dismissing the show just for its costumes, which I wasn't - I was simply pointing out that it can't entirely care about material history (meaning specifically physical objects/culture) if it treats its clothes like that.
But this person was slightly offended on behalf of their show - especially, quote, "And from a fan of OFMD, no less!" Which got me thinking - it's true! I can abide a lot more historical costuming inaccuracy from Our Flag than I can Black Sails or Vikings. And I don't think it's just because one has my blorbos in it. But really, when it comes down to it...
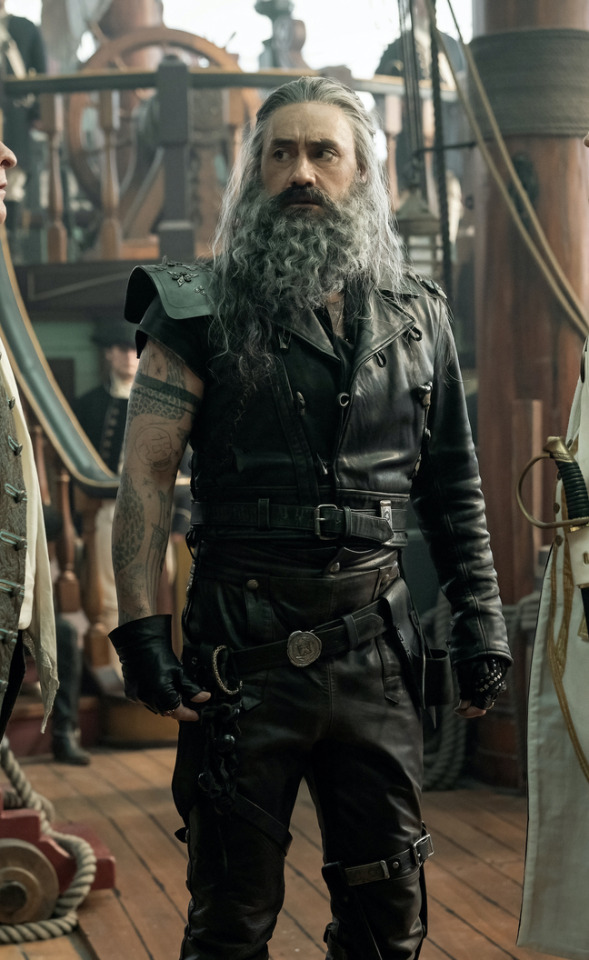
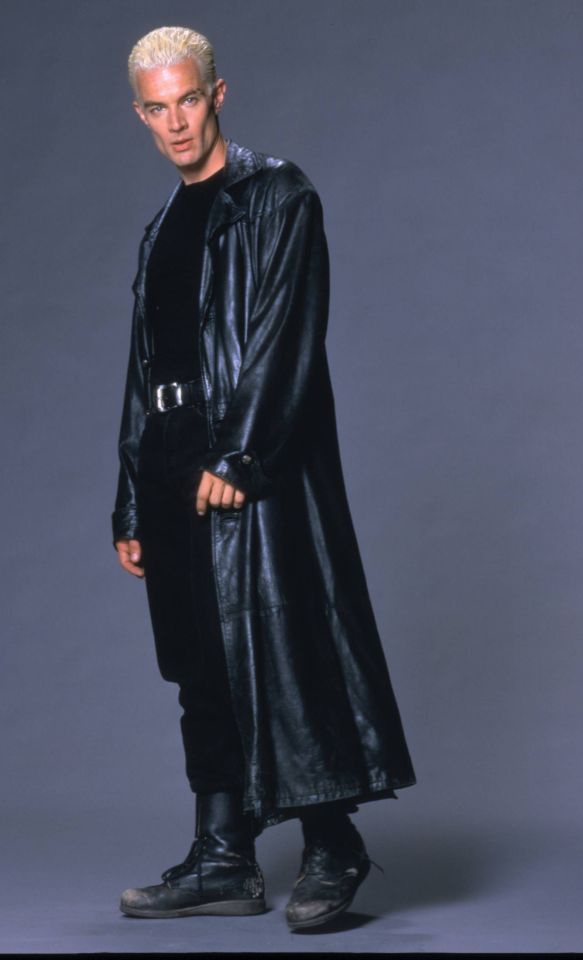
What is the difference between this and this?
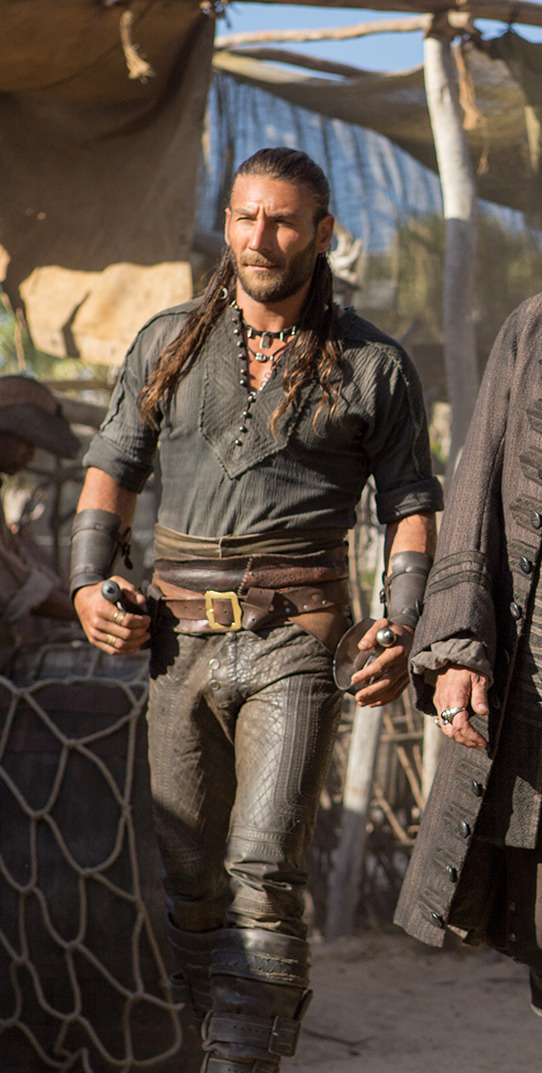

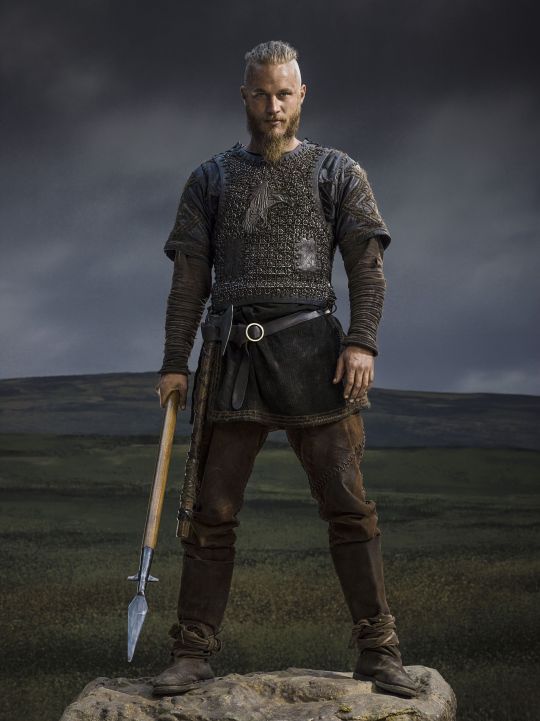
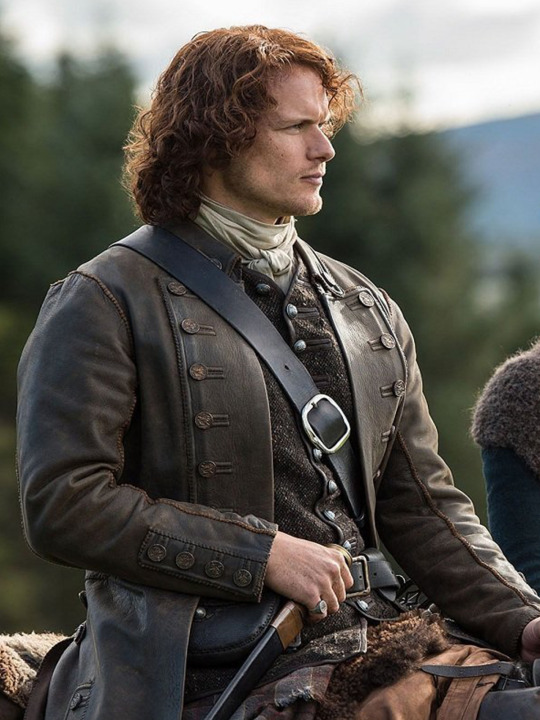
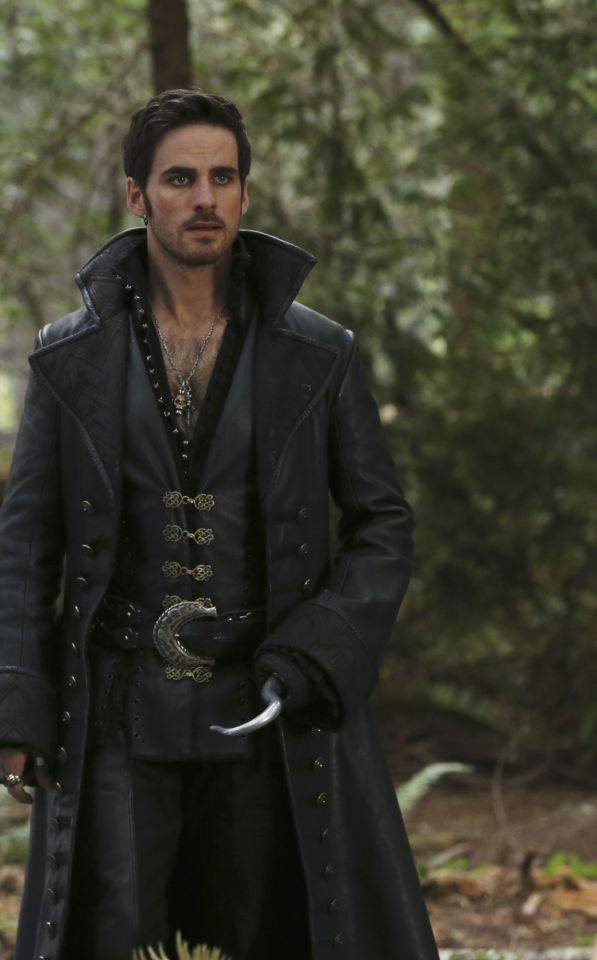
Here's the thing. Leather pants in period dramas isn't new. You've got your Vikings, Tudors, Outlander, Pirates of the Caribbean, Once Upon a Time, Will, The Musketeers, even Shakespeare in Love - they love to shove people in leather and call it a day. But where does this come from?








Obviously we have the modern connotations. Modern leather clothes developed in a few subcultures: cowboys drew on Native American clothing. (Allegedly. This is a little beyond my purview, I haven't seen any solid evidence, and it sounds like the kind of fact that people repeat a lot but is based on an assumption. I wouldn't know, though.) Leather was used in some WWI and II uniforms.
But the big boom came in the mid-C20th in motorcycle, punk/goth, and gay subcultures, all intertwined with each other and the above. Motorcyclists wear leather as practical protective gear, and it gets picked up by rock and punk artists as a symbol of counterculture, and transferred to movie designs. It gets wrapped up in gay and kink communities, with even more countercultural and taboo meanings. By the late C20th, leather has entered mainstream fashion, but it still carries those references to goths, punks, BDSM, and motorbike gangs, to James Dean, Marlon Brando, and Mick Jagger. This is whence we get our Spikes and Dave Listers in 1980s/90s media, bad boys and working-class punks.


And some of the above "historical" design choices clearly build on these meanings. William Shakespeare is dressed in a black leather doublet to evoke the swaggering bad boy artist heartthrob, probably down on his luck. So is Kit Marlowe.
But the associations get a little fuzzier after that. Hook, with his eyeliner and jewellery, sure. King Henry, yeah, I see it. It's hideously ahistorical, but sure. But what about Jamie and Will and Ragnar, in their browns and shabby, battle-ready chic? Well, here we get the other strain of Bad Period Drama Leather.
See, designers like to point to history, but it's just not true. Leather armour, especially in the western/European world, is very, very rare, and not just because it decays faster than metal. (Yes, even in ancient Greece/Rome, despite many articles claiming that as the start of the leather armour trend!) It simply wasn't used a lot, because it's frankly useless at defending the body compared to metal. Leather was used as a backing for some splint armour pieces, and for belts, sheathes, and buckles, but it simply wasn't worn like the costumes above. It's heavy, uncomfortable, and hard to repair - it's simply not practical for a garment when you have perfectly comfortable, insulating, and widely available linen, wool, and cotton!
As far as I can see, the real influence on leather in period dramas is fantasy. Fantasy media has proliferated the idea of leather armour as the lightweight choice for rangers, elves, and rogues, a natural, quiet, flexible material, less flashy or restrictive than metal. And it is cheaper for a costume department to make, and easier for an actor to wear on set. It's in Dungeons and Dragons and Lord of the Rings, King Arthur, Runescape, and World of Warcraft.
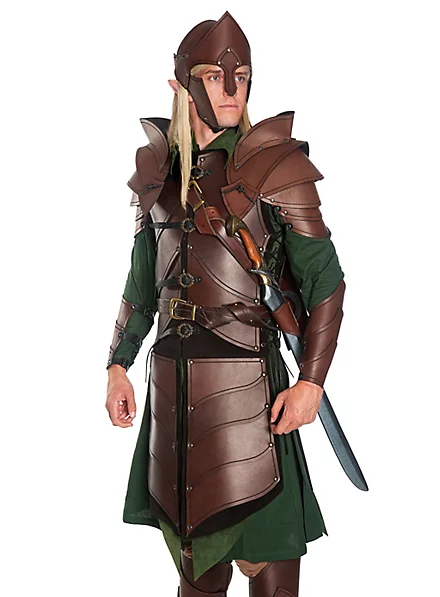
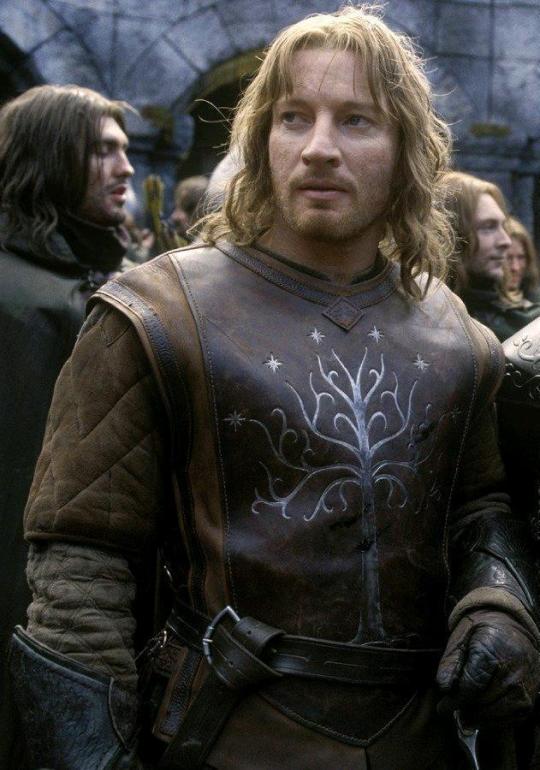
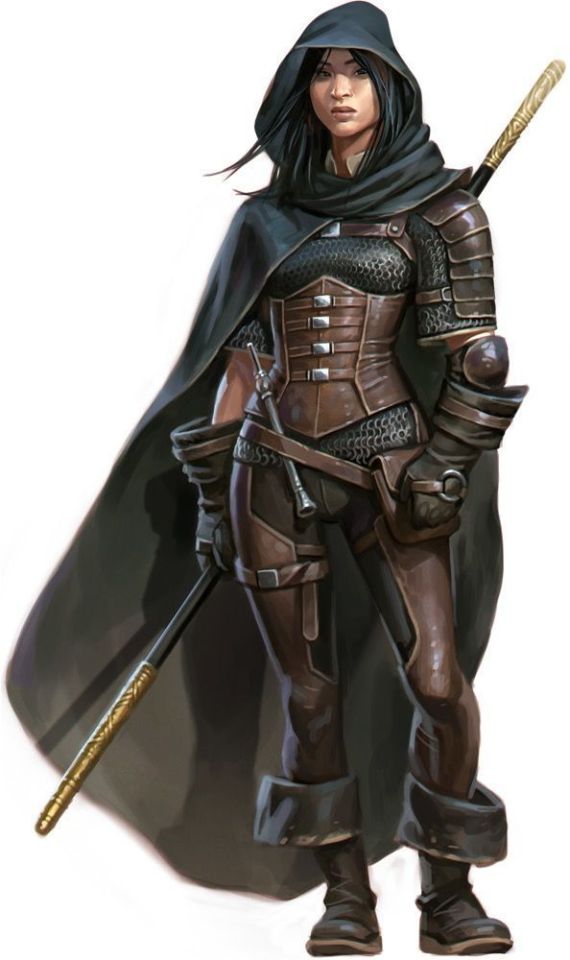





And I think this is how we get to characters like Ragnar and Vane. This idea of leather as practical gear and light armour, it's fantasy, but it has this lineage, behind which sits cowboy chaps and bomber/flight jackets. It's usually brown compared to the punk bad boy's black, less shiny, and more often piecemeal or decorated. In fact, there's a great distinction between the two Period Leather Modes within the same piece of media: Robin Hood (2006)! Compare the brooding, fascist-coded villain Guy of Gisborne with the shabby, bow-wielding, forest-dwelling Robin:
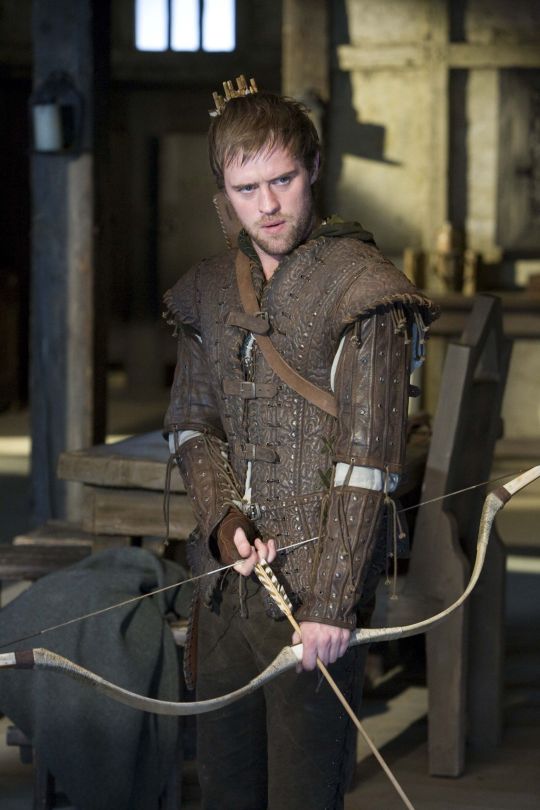


So, back to the original question: What's the difference between Charles Vane in Black Sails, and Edward Teach in Our Flag Means Death?
Simply put, it's intention. There is nothing intentional about Vane's leather in Black Sails. It's not the only leather in the show, and it only says what all shabby period leather says, relying on the same tropes as fantasy armour: he's a bad boy and a fighter in workaday leather, poor, flexible, and practical. None of these connotations are based in reality or history, and they've been done countless times before. It's boring design, neither historically accurate nor particularly creative, but much the same as all the other shabby chic fighters on our screens. He has a broad lineage in Lord of the Rings and Pirates of the Caribbean and such, but that's it.
In Our Flag, however, the lineage is much, much more intentional. Ed is a direct homage to Mad Max, the costuming in which is both practical (Max is an ex-cop and road warrior), and draws on punk and kink designs to evoke a counterculture gone mad to the point of social breakdown, exploiting the thrill of the taboo to frighten and titillate the audience.
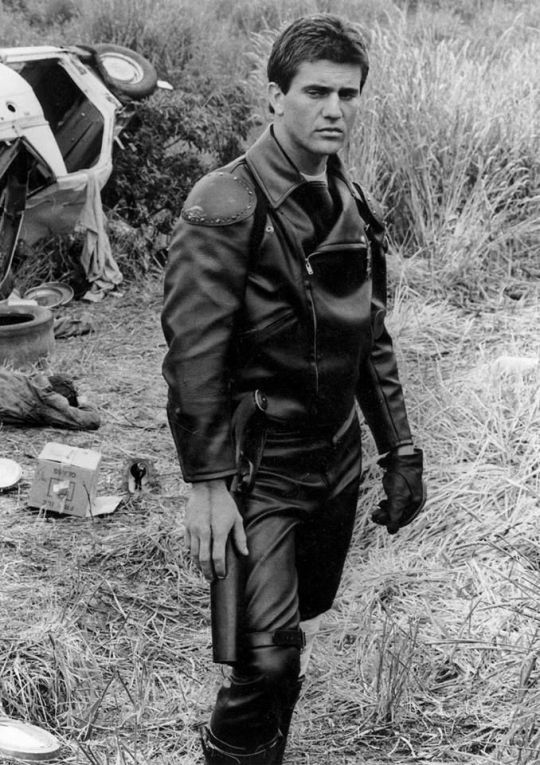


In particular, Ed is styled after Max in the second movie, having lost his family, been badly injured, and watched the world turn into an apocalypse. He's a broken man, withdrawn, violent, and deliberately cutting himself off from others to avoid getting hurt again. The plot of Mad Max 2 is him learning to open up and help others, making himself vulnerable to more loss, but more human in the process.
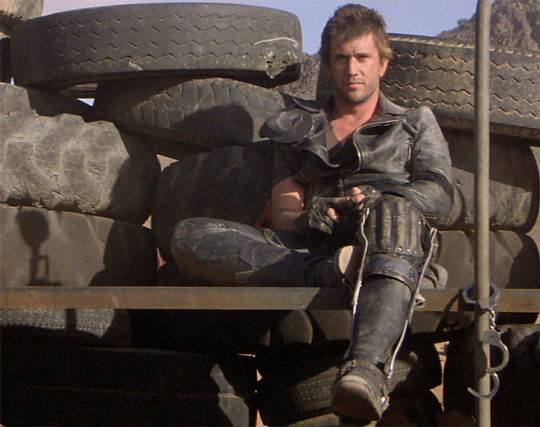

This ties directly into the themes of Our Flag - it's a deliberate intertext. Ed's emotional journey is also one from isolation and pain to vulnerability, community, and love. Mad Max (intentionally and unintentionally) explores themes of masculinity, violence, and power, while Max has become simplified in the popular imagination as a stoic, badass action hero rather than the more complex character he is, struggling with loss and humanity. Similarly, Our Flag explores masculinity, both textually (Stede is trying to build a less abusive pirate culture) and metatextually (the show champions complex, banal, and tender masculinities, especially when we're used to only seeing pirates in either gritty action movies or childish comedies).
Our Flag also draws on the specific countercultures of motorcycles, rockers, and gay/BDSM culture in its design and themes. Naturally, in such a queer show, one can't help but make the connection between leather pirates and leather daddies, and the design certainly nods at this, with its vests and studs. I always think about this guy, with his flat cap so reminiscient of gay leather fashions.
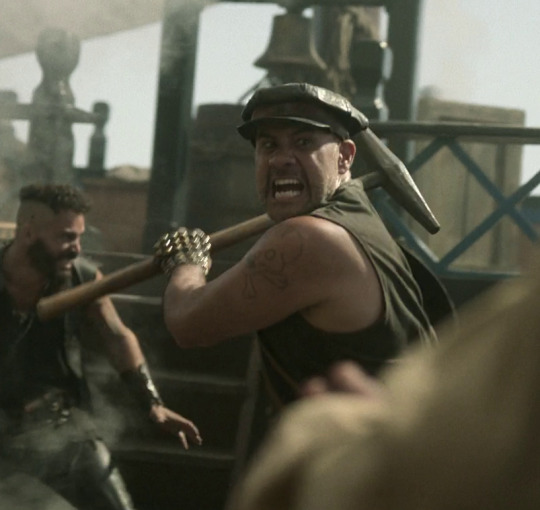

More overtly, though, Blackbeard and his crew are styled as both violent gangsters and countercultural rockstars. They rove the seas like a bikie gang, free and violent, and are seen as icons, bad boys and celebrities. Other pirates revere Blackbeard and wish they could be on his crew, while civilians are awed by his reputation, desperate for juicy, gory details.
This isn't all of why I like the costuming in Our Flag Means Death (especially season 1). Stede's outfits are by no means accurate, but they're a lot more accurate than most pirate media, and they're bright and colourful, with accurate and delightful silks, lace, velvets, and brocades, and lovely, puffy skirts on his jackets. Many of the Revenge crew wear recognisable sailor's trousers, and practical but bright, varied gear that easily conveys personality and flair. There is a surprising dedication to little details, like changing Ed's trousers to fall-fronts for a historical feel, Izzy's puffy sleeves, the handmade fringe on Lucius's red jacket, or the increasing absurdity of navy uniform cuffs between Nigel and Chauncey.
A really big one is the fact that they don't shy away from historical footwear! In almost every example above, we see the period drama's obsession with putting men in skinny jeans and bucket-top boots, but not only does Stede wear his little red-heeled shoes with stockings, but most of his crew, and the ordinary people of Barbados, wear low boots or pumps, and even rough, masculine characters like Pete wear knee breeches and bright colours. It's inaccurate, but at least it's a new kind of inaccuracy, that builds much more on actual historical fashions, and eschews the shortcuts of other, grittier period dramas in favour of colour and personality.
But also. At least it fucking says something with its leather.
#everyone say 'thank you togas' for not including a long tangent about evil rimmer in red dwarf 5x05#Our Flag Means Death#Togas does meta#and yes these principles DO fall apart slightly in s2 and i DON'T like those costumes as much#don't get me wrong they're fun and gorgeous - but generally a bit less deep and more inaccurate. so. :(#I'm not sure this really says anything new about Our Flag but I just needed to get my thoughts out#i hate hate hate Gritty Period Drama costumes they're so boring and so ugly and so wrong#god bless OFMD for using more than 3 muted colours and actually putting men in heels (and not as a shorthand for rich/foppish villainy) <3#looking at that Tudors still is insane like they really will go to any lengths to not make men feel like they've got bare legs XD#image descriptions in alt text#and yes i DID just sink about two hours into those so you'd better appreciate them
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Worldbuilding June Day 18: Fashion
But that’s when I remember that we all want
We all need
Fashion
Jon Bellion, anyone? Nah? Alrighty then.
Unfortunately for this prompt, I’ve been watching a bit too many videos about historical fashion lately. I just find it really fascinating how fashion changes through history: what stays the same, what stays constant. For example, I did not realize how little women’s undergarments (as in the next-to-skin layer, not corsets and drawers and padding and all that) changed between the 1300s and like the 1920s. It’s a chemise or shift and maybe some stockings, depending on your economic status and how easy stockings were to make at the time. For six centuries. That’s insane! Also, the evolution of toe length in English men’s fashionable shoes from the beginning of the 14th century to the end of it is simply astonishing.
All this research has had the opposite effect of what one might expect, however; instead of being inspired and full of ideas, I’m stumped. I’m so overwhelmed with historical fashions that I have no idea where to even start at designing my own. So I think I’m gonna stick to general trends, especially in the upper classes. This might be an entry full of rather obvious conclusions. Sorry about that.
Lower class fashions are strongly driven by practicality. Most people, regardless of gender, wear some variety of a tunic and (maybe) breeches or hose, if they’re decently upper lower class. The tunic is usually belted at the waist and might be dyed blue or red with various naturally occurring dyes, or might be left its natural color. It’s usually made of linen, cotton, or wool, hand-woven. People might roll up the sleeves and belt the tunic tighter to keep it out of the way while working, or might even strip down to their drawers if it’s hot out. Shoes are simple, and again not dependent on gender. Depending on the skill of whoever made them, they may not even differentiate between left and right. They’re usually made of leather, and may or may not have a solid sole (might be more of a leather foot bag than a shoe). A sole usually consists of several pieces of tough, stiffened leather, pressed together then sewn to the rest of the shoe. Shoes are cheaply made and don’t last long.
Upper class fashions are, as one might imagine, quite different. Seeing as they never have to do any real work, upper class clothing is driven by trends, not practicality. It is always in fashion to show off one’s wealth, and one of the best ways to do this is to wear clothes that look just like the ones Intelligence Werner and his wife wore last week. This is exacerbated by the fact that since the barrier went up, Urbemonte’s large-scale economy has completely died. Most of the upper class are from merchant families, and since they are unable to trade with the mainland and unwilling to trade with the rest of the island, that leaves their monetary prospects at a bit of a loss. Therefore, they turn to trends. They have nothing else to do but gamble. (Damn, I still have to build that game.)
Look at Tudor (Henrician-ish) fashion for my inspiration for the upper class trend, at least at the moment the PCs will arrive in the city. I realize I said in an earlier entry that I was going for a late Renaissance feel, and this is a bit early, but that doesn’t mean I have to take fashion inspiration from there. Plus, trends are changing so rapidly that although the basic layers will probably remain the same, fashion could be in the Elizabethan period of clothing within less than a year. Or could completely diverge from what happened in real life fashion. I don’t know. It’s 11 pm. I gotta work tomorrow.
0 notes