#manually import updates in WSUS
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
WSUS Import The Underlying Connection Was Closed New PowerShell Script
WSUS Import The Underlying Connection Was Closed New PowerShell Script #homelab #vmwarecommunities #WSUSServerTroubleshooting #WSUSImportErrors #ResolvingWSUSIssues #UnderlyingConnectionErrorsInWSUS #TLS1.2InWSUS #.NETFrameworkAndWSUS #WSUSErrorLogs
Microsoft recently announced that the WSUS import updates feature in the WSUS console would no longer be used. Instead, admins need to use a PowerShell script provided by Microsoft to import updates into WSUS. However, in my recent testing of the script on a Windows Server 2022 server with WSUS installed, after following the steps exactly from the Microsoft KB, I received the error, “The…

View On WordPress
#.NET framework and WSUS#manually import updates in WSUS#resolving WSUS issues#TLS 1.2 in WSUS#underlying connection errors in WSUS#WSUS and internet explorer#WSUS error logs#WSUS import errors#WSUS PowerShell commands#WSUS server troubleshooting#powershell#powershellscripting
0 notes
Text
Server Patching Best Practices for Enterprise Patch Management
What Is Server Patching?
Server patching is the process of updating and applying security fixes, bug fixes, and performance improvements to server operating systems and applications. Effective enterprise patch management ensures that IT environments remain secure, stable, and compliant with industry regulations.
Why Is Server Patching Important?
✅ Enhances Security – Fixes vulnerabilities and prevents cyberattacks. ✅ Improves System Stability – Reduces crashes, bugs, and performance issues. ✅ Ensures Compliance – Meets regulatory standards (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, etc.). ✅ Reduces Downtime Risks – Prevents disruptions from outdated or vulnerable software.
Best Practices for Enterprise Patch Management
1. Establish a Patch Management Policy 📋
✔ Define clear roles and responsibilities for patching. ✔ Set patching schedules for critical, high, and low-priority updates. ✔ Include compliance requirements in the patching policy.
2. Conduct a Patch Risk Assessment ⚠️
✔ Identify high-risk vulnerabilities that need immediate attention. ✔ Evaluate the impact of patches on mission-critical systems. ✔ Test patches in a staging environment before deployment.
3. Automate Patch Deployment ⚙️
✔ Use patch management tools (e.g., WSUS, SCCM, Ansible, Ivanti, Automox). ✔ Automate patch scanning, testing, and deployment to reduce manual effort. ✔ Schedule updates outside peak business hours to minimize disruptions.
4. Prioritize Critical Security Updates 🔒
✔ Apply patches for zero-day vulnerabilities as soon as possible. ✔ Follow security bulletins from Microsoft, Linux, VMware, and other vendors. ✔ Ensure endpoint security tools are also updated.
5. Monitor Patch Compliance & Reporting 📊
✔ Track patching success rates and failed updates. ✔ Generate audit logs to meet regulatory requirements. ✔ Use SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools for monitoring.
6. Have a Rollback & Contingency Plan 🔄
✔ Backup systems before applying patches to prevent data loss. ✔ Implement rollback procedures in case a patch causes system instability. ✔ Test recovery strategies in a disaster recovery (DR) plan.
7. Keep Third-Party Software Updated 🖥️
✔ Patch browsers, databases, and applications alongside OS updates. ✔ Use vendor patch management solutions for consistency. ✔ Regularly audit and remove unsupported or end-of-life (EOL) software.
Common Challenges in Server Patching & Solutions
ChallengeSolutionDowntime ConcernsSchedule patches during off-peak hours and use rolling updates.Patch FailuresTest patches in a staging environment before deployment.Lack of AutomationUse patch management software to streamline updates.End-of-Life (EOL) SoftwareUpgrade or replace legacy systems to avoid security risks.Compliance AuditsMaintain detailed patch logs for regulatory reporting.
Final Thoughts: Strengthening Enterprise Security with Patching
A well-structured patch management strategy reduces security risks, improves system performance, and ensures compliance. By automating updates, prioritizing critical patches, and maintaining backups, businesses can protect their IT infrastructure from cyber threats.
Need Help with Enterprise Patch Management?
Tell me your server environment (Windows, Linux, hybrid cloud), compliance needs, and security concerns, and I’ll recommend the best patching strategy for your business!

0 notes
Text
Windows Update Cleanup
Verify the boxes to choose the items that you wish to cleanup and click OK. Disk cleanup is neat and quick. Click the files you wish to have Disk Cleanup delete. With it, you don't need to fret about Windows unworkable Disk Cleanup whatsoever.
The WinSxS folder can frequently be numerous Gigabytes in size as it has a copy of all of the Windows Updates applied to the computer, effectively a comprehensive copy if Windows so that you're ready to roll back an update if you want to. Thus, even when you believe that you have update files that you don't need anymore, Windows could think'' different. You could find that a whole lot of files are removed from your system or you can find that hardly any files are removed from your system. The files are in fact stored in different locations. So now ssh will observe that it has extra permissions and it will complain. Afterward, specify the kind of files which you want to remove and select OK. There is yet another way to take out the backup files for SP1 in Windows 7 and help it become permanent.

Most folks prefer deleting temporary files that are not supposed to be kept too long anyway. You understand how to delete temporary files manually and you also understand how to do away with old Windows versions. Manually deleting temporary files might help you fix the issue. To begin with, you are going to want to eliminate the damaged files.
Click OK' then choose the tick boxes of the files you need to delete. You'll have to transfer your regional files from 1 account to the other in all circumstances, though. When the archived files are removed you cannot remove SP2. So that you can readily Delete previous installation files who have any permission Error.
The Foolproof Windows Update Cleanup Strategy
After the Disk Cleanup utility has loaded, click the Cleanup system files button below the Description section. The Disk Cleanup tool has been in existence for quite a while. Following are a few of the qualities of Combo Cleaner that is thought to be the ideal Chrome cleanup tool for Mac in 2018.
Selling a computer where the operating system can't be kept-up-to-date is insane. The system doesn't use the previous files in any manner. The Windows operating system constantly wants a high excellent service with the aid of third-party applications.
Facts, Fiction and Windows Update Cleanup
The absolute most current version of each driver package is going to be kept. Indeed, it is possible to readily get your updates back on course. In order to be sure the updates don't lead to compatibility issues, all types of duplicate files become stored in the WinSxS folder so that everything can continue to work correctly. To make sure that they don't cause compatibility problems, all kinds of duplicate files get stored in the WinSxS folder so that everything can continue to function correctly. If you've got automatic updates enabled, you most likely already have it installed. You should observe an app named Suppressant.
An integral point to consider while using Chrome cleanup tool is that it's a one-time thing. The issue becomes compounded by how the WinSxS folder is utilized to store so many files. You may run that which will resolve the issue around Windows 10 Update which may be causing the cleanup tool to receive stuck. The primary problem is, its causes aren't confined to one particular mishap. If you have issues with temporary files on your computer, you may be able to remove them using a third-party application. For this reason, you ought to keep your drivers updated to be able to keep update issues at bay. Driver Manager drivers are a rather important portion of the Windows system.
Running Disk Cleanup will often make your system somewhat snappier and it is also possible to free up a huge amount of used disk space. Not having the ability to get rid of temporary files might be big problem at times, but you need to be in a position to repair it with one of our solutions. What's more, you can take advantage of the File History option as a way to carry out a backup. 1 common use for offline updates is to make sure a system is completely patched against security vulnerabilities before being on the web or a different network. Then you will realize that it is the very best alternative for Cleanup Disk. Or in the instance of Windows 10, you also receive the option togo back to your prior version of the operating system within the very first month in case you don't like it. In CB, there's a choice to schedule the WSUS cleanup whilst preparing the SUP site system role.
youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Adobe flash all versions

#ADOBE FLASH ALL VERSIONS INSTALL#
#ADOBE FLASH ALL VERSIONS UPDATE#
#ADOBE FLASH ALL VERSIONS WINDOWS 10#
Launch the WSUS console, expand your server and click Updates.
#ADOBE FLASH ALL VERSIONS UPDATE#
You can either visit Microsoft Update Catalog site and search 4577586 update or directly access the update. I will use the same steps to import the 4577586 update. In the past I had published a guide on importing the updates into WSUS. Import the KB 4577586 Update in WSUSįirst of all we must import the update in WSUS because it is an optional update. Ensure you download the update for the right version of Windows OS. The update is applicable for multiple products. Click the following link to download KB4577586 Update. You can download the KB 4577586 Update from the Microsoft Update Catalog.
Method 2: Reinstall your Windows operating system and do not apply the update KB 4577586.
Furthermore a system restore point must be created on your Windows device before you apply this update. Note that system restore feature must be explicitly enabled.
Method 1 – You can reset your device to an earlier system restore point.
However if you wish to use the Adobe Flash player again on your windows device, you can try the below methods.
#ADOBE FLASH ALL VERSIONS INSTALL#
The answer is no because once you install the update KB4577586, it cannot be uninstalled. Can I use the Adobe Flash Player again ?. However if you have installed Adobe Flash Player manually from another source, it will not be removed. The update KB 4577586 uninstalls the flash player.
#ADOBE FLASH ALL VERSIONS WINDOWS 10#
Note – When you install Windows 10 on a device, you also get the Adobe Flash Player installed. After this update has been applied, it cannot be uninstalled. However after few months the update will be termed as recommended update. Installing the update KB 4577586 will permanently remove Adobe Flash Player as a component of the Windows OS devices.įor now the update KB 4577586 will be optional on Windows Update and WSUS. The title of this update is Update for Removal of Adobe Flash Player. An update will be made available via Microsoft Update Catalog, Windows Update and WSUS. Microsoft recently published an article on removal of Adobe Flash Player: October 27, 2020. Update for Removal of Adobe Flash Player – KB4577586 Uninstall Adobe Flash Player using SCCM KB4577586.Download Update for Removal of Adobe Flash Player.Synchronize the KB4577586 Update in SCCM.Can I use the Adobe Flash Player again ?.Update for Removal of Adobe Flash Player – KB4577586.

0 notes
Text
Window critical updates

#WINDOW CRITICAL UPDATES INSTALL#
Windows Enterprise LTSC versions are not meant for gaming PCs, therefore we do not usually support them, although the most recent LTSC builds should still work without any issues.
#WINDOW CRITICAL UPDATES INSTALL#
You will need to find a way to install updates or install a legitimate version. The code that makes up the Windows operating system contains security loop. Includes all new security fixes for the month and will only be published to Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and the. Such as download but let me choose when to install, or notify only etc etc. Click Start, type Windows update in the search box, and then click Windows Update in the Programs list. Click on Security Updates checkbox to install windows security update or click on the checkbox based on the severities such as Critical, Important, Moderate, Low and Unrated. If you have a modified/cracked version of Windows where you are unable to install updates, we can not support such versions. 3 Reasons Why You Should Be Running The Latest Windows Security Patches & Updates. BTW - you can always change WU settings so as not to automatically install updates or download them -. Under Microsoft Updates, you'll find Security Updates. Workaround: Either the Windows logo key or Windows key + X can be used instead of the. You will need to use a supported build of Windows which still receives security updates from Microsoft. If youre having any issues with your console update, see. Otherwise, you can also try to upgrade by using the Media Creation Tool.Īlternatively, you can try to download updates manually from Microsoft website: If Windows update is not working for you or does not find any updates, please check solutions on Microsoft website. Make sure you apply the latest security updates from Windows update.

0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://techcrunchapp.com/microsoft-windows-security-updates-june-2020-overview/
Microsoft Windows Security Updates June 2020 overview

Welcome to the overview of Microsoft’s June 2020 security patch day. Microsoft releases security updates for all its products on the second Tuesday of the month. This overview provides you with detailed information on the released patches.
It includes links to the security patches as well as an Excel spreadsheet that lists all released security updates. You find direct download links of the latest cumulative updates for supported versions of Windows, the list of known issues, and other information that are useful when it comes to the released patches.
If you have missed out last month’s Patch Day overview, check it out here.
Microsoft Windows Security Updates June 2020

Download the linked Excel spreadsheet to your local system: it contains a list of released security updates that Microsoft released on the June 2020 Patch Day. Click on the following link to download the file to your system: microsoft-windows-security-updates-june-2020
Executive Summary
Microsoft released security updates for all supported versions of Windows (client and server).
Security updates are also available for Microsoft Edge (classic and Chromium), Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office, Windows Defender, Visual Studio, Microsoft Apps for Android, Windows App Store, System Center, and other Microsoft products.
The following Windows products have known issues: Windows 10 version 1607, 1809, 1903, and 1909, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server version 1903 and 1909.
Operating System Distribution
Windows 7 (extended support only): 30 vulnerabilities: 3 critical and 27 important
Windows 8.1: 37 vulnerabilities: 3 rated critical and 34 rated important
same critical vulnerabilities as Windows 7
Windows 10 version 1803: 78 vulnerabilities: 4 critical and 74 important
Windows 10 version 1809: 82 vulnerabilities: 4 critical and 78 important
same critical vulnerabilities as Windows 10 version 1803
Windows 10 version 1903: 91 vulnerabilities: 5 critical and 73 important
same as Windows 10 version 1803 plus
CVE-2020-1248 | GDI+ Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Windows 10 version 1909:
same as Windows 10 version 1903
Windows 10 version 2004:
Windows Server products
Windows Server 2008 R2 (extended support only): 30 vulnerabilities: 3 critical and 27 important
Windows Server 2012 R2: 37 vulnerabilities: 3 critical and 34 important.
same as Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2016: 60 vulnerabilities: 3 critical and 57 important.
same as Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2019: 81 vulnerabilities: 4 critical and 77 are important
Other Microsoft Products
Internet Explorer 11: 7 vulnerability: 3 critical, 4 important
Microsoft Edge: 4 vulnerabilities: 2 critical, 2 important
CVE-2020-1073 | Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability
CVE-2020-1219 | Microsoft Browser Memory Corruption Vulnerability
Microsoft Edge on Chromium:
see here (latest security patches from the Chromium project)
Windows Security Updates
Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2
Fixes and improvements
Fixed an issue that prevented users from updating .msi files from a network folder. (Monthly Rollup only)
Security Updates.
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2008 R2
Fixes and improvements
Fixed an issue that prevented users from updating .msi files from a network folder. (Monthly Rollup only)
Security Updates.
Windows 10 version 1803
Fixes and improvements
Fixed an issue that prevented users from updating .msi files from a network folder.
Security updates
Windows 10 version 1809
Fixes and improvements
Fixed an issue that prevented users from updating .msi files from a network folder.
Fixed an issue that caused the promotion of a server to a domain controller to fail.
Security updates.
Windows 10 version 1903 and 1909
Fixes and improvements
Fixed an issue that prevented users from updating .msi files from a network folder.
Security updates
Windows 10 version 2004
Fixes and improvements
Fixed an issue that prevented users from updating .msi files from a network folder.
Fixed an issue that prevented users from using voice commands in Windows Mixed Reality if the display language was set to English (Canada) or English (Australia).
Improved the reliability of voice assistants that use Windows voice activation for keywords.
Improved the reliability of Cortana’s voice activation on devices that support low-power keywords.
Security updates
Other security updates
KB4561603 — Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: June 9, 2020
KB4561600 — 2020-06 Security Update for Adobe Flash Player for Windows Server, version 2004 and Windows 10 Version 2004
KB4561612 — 2020-06 Security Monthly Quality Rollup for Windows Embedded 8 Standard and Windows Server 2012
KB4561645 — 2020-06 Security Only Quality Update for Windows Server 2008
KB4561670 — 2020-06 Security Monthly Quality Rollup for Windows Server 2008
KB4561674 — 2020-06 Security Only Quality Update for Windows Embedded 8 Standard and Windows Server 2012
KB4557957 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows Server, version 2004 and Windows 10 Version 2004
KB4561602 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1709
KB4561605 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1703
KB4561616 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 Version 1607
KB4561649 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1507
Servicing Stack Updates
KB4560366 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Server, version 2004 and Windows 10 Version 2004
KB4560959 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Server, version 1909, Windows 10 Version 1909, Windows Server 2019 (1903), and Windows 10 Version 1903
KB4562030 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Embedded Standard 7, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 R2
KB4562031 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Server 2008
KB4562249 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows 10 Version 1507
KB4562561 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10 Version 1607
KB4562250 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows 10 Version 1703
KB4562560 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows 10 Version 1709
KB4562251 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows 10 Version 1803
KB4562562 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 Version 1809
KB4562252 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows Embedded 8 Standard and Windows Server 2012
KB4562253 — 2020-06 Servicing Stack Update for Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2
Known Issues
Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2
Error “Failure to Configure Windows Updates. Reverting Changes. Do not Turn off your computer. “may be displayed.
Expected behavior if the update is installed on non-ESU joined devices.
Windows 10 version 1809
Devices with some Asian language packs installed may display the error “0x800f0982 – PSFX_E_MATCHING_COMPONENT_NOT_FOUND”.
Workaround 1: uninstall and install recently added language packs. Select check for updates.
Workaround 2: Reset the PC.
Windows 10 version 1903 and 1909
Internet connectivity may not be available after installing the update on devices with wireless wide area network LTE modems. The Network Connectivity Status Indicator may still show that the device is connected to the Internet.
Microsoft is working on a resolution.
Security advisories and updates
ADV200009 | Windows DNS Server Denial of Service Vulnerability
ADV200010 | June 2020 Adobe Flash Security Update
Non-security related updates
Microsoft Office Updates
You find Office update information here.
How to download and install the June 2020 security updates
Microsoft releases security updates for Windows via Windows Updates and other update management services such as WSUS. Administrators may download updates directly as well to install them manually.
It is advised to back up the system before updates are applied.
If you don’t want to wait, do the following to run an update check on Windows.
Do the following to check for new updates:
Open the Start Menu of the Windows operating system, type Windows Update and select the result.
Select check for updates in the application that opens. Updates may be installed automatically when they are found or offered by Windows; this depends on the operating system and version that is used, and update settings.
Direct update downloads
Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2
KB4561643 — 2020-06 Security Monthly Quality Rollup for Windows 7
KB4561669 — 2020-06 Security Only Quality Update for Windows 7
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2
KB4561666 — 2020-06 Security Monthly Quality Rollup for Windows 8.1
KB4561673 — 2020-06 Security Only Quality Update for Windows 8.1
Windows 10 (version 1803)
KB4561621 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1803
Windows 10 (version 1809)
KB4561608 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1809
Windows 10 (version 1903)
KB4560960 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1903
Windows 10 (version 1909)
KB4560960 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 1909
Windows 10 (version 2004)
KB4557957 — 2020-06 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 2004
Additional resources
Summary
Article Name
Microsoft Windows Security Updates June 2020 overview
Description
Microsoft’s June 2020 Patch Day; Microsoft released security updates and non-security updates for all supported versions of Windows — both client and server versions — on June 9, 2020.
Author
Martin Brinkmann
Publisher
Ghacks Technology News
Logo

Advertisement
0 notes
Text
Windows Server vNext Preview Build 18917 released

Windows Server vNext Preview Build 18917 released. There also released Windows Admin Center Preview 1906. What’s New: Thanks for staying up-to-date on the Windows Admin Center journey! As our first preview release following the last generally available release in April, Windows Admin Center preview 1906 includes several new preview features: Updates tool: you can now select individual Windows updates to install. Windows Admin Center connectivity settings: We’ve heard from users that are in completely disconnected environments that they would prefer to have a setting in Windows Admin Center where they can specify they are offline, so there will be no notifications about Azure hybrid functionality, extensions updates, or other actions that require public internet access. To give this a try, enter msft.sme.shell.connectivity as an experiment key in Settings-> Development -> Advanced, then visit the new Connectivity settings item. You can select Gateway to restrict online access, or Azure and Gateway if you want to access Azure features only, but nothing else on the public internet. In a future release, this menu item will also provide you with a complete list of URLs so that you can configure your firewall to block all traffic by default and explicitly allow only specific traffic to known services. Virtual machines tool: Import/Export VM – We’ve added Import/Export buttons to the Virtual Machines tool for importing VMs from and exporting VMs to a local volume or remote file share. When importing VMs, you have the option to create a new VM ID, and copy the VM files or use them in-place. When importing a VM and creating a copy of the VM files, if you choose a local volume or cluster shared volume as the destination, it will be saved to the volume’s root folder instead of under the “Hyper-V” folder. This will be fixed in the next release. For now, you can use the Browse button to manually navigate to the actual folder you want to import the VM to. VM tagging – Similar to the UI for tagging connections in Windows Admin Center, you can now tag VMs on a Hyper-V server! In the Virtual machines tool’s Inventory tab, an “Edit tags” button has been added to manage tags. These tags are saved on the Hyper-V host server and can be accessed by other admins. VM tagging is not supported in the Failover Cluster or Hyper-Converged Cluster UI yet. Tags will not show up in the clustered VM view and managing tags from this view may unintentionally overwrite or delete existing tags. Performance improvements – Significant performance improvements have been made to reduce page load time in the Virtual machines tool. Improvements to Azure integration functionality: The Azure Hybrid services tool now loads content from a feed, so that new services can be added at any time without an update of the entire tool.From the Account menu in setting, you can now switch between multiple Azure accounts.When adding a server or Windows PC to your connection list, you have a new option to log in to Azure and browse your Azure resources for the specific server or PC. At this time, Windows Admin Center only enumerates your Azure resources, but cannot guarantee connectivity. Windows Admin Center ecosystem developers: you’ll find a new menu item: Performance Profile, in the Windows Admin Center settings under the Development heading. This new tool will record your browsing session, tracking the times of each request and page load, so that you can identify opportunities to improve performance. Known issues -Windows Admin Center Preview 1906 Network – If you have configured an Azure Network Adapter, the value under Microsoft Azure Virtual Network Gateway Address will be formatted as a hyperlink but leads to an invalid address. Azure Update Management onboarding – If you have already installed the MMA agent, or install the agent using the new integration for Azure Monitor, you will not be able to onboard the server to Azure Update Management through the UI in Windows Admin Center. If Azure Update Management is already configured (whether through Admin Center or another way), you can still onboard the server to the Azure Monitor Virtual Machines Insights solution using the Windows Admin Center UI.Chrome users may see 403 Forbidden response from WAC after upgrading. The workaround is to close *all* open chrome tabs (make sure there are no chrome.exe processes running). After restarting chrome, everything will function normally. We have an error message that makes this clear, but chrome users with multiple windows admin center tabs open during upgrade will not see the message. Windows Server Bug Fixes Fixed an issue where a local user’s last logon time output from “net user username” may not be recorded even when the user has accessed the server’s network share.Fixed an issue when attempting to update Server Standard to Server Datacenter, results in error “Error: 1168. An error occurred while applying target edition component setting. The upgrade cannot proceed.”Fixed an issue when domain trust was broken when the recycle bin configured on the domains carrying the trust.Fixed an issue where an invalid file was being created in %Systemroot%\System32\LogFiles\Sum by User Access Logging. Windows Server Known Issues Using ntdsutil.exe to move of the Active Directory database files may fail with error: “Move file failed with source and Destination with error 5 (Access is denied.)”Auto-logon configured by login scripts may fail to work properlyStatus of online/offline files icon and status bar may not display an accurate status. OfflineFiles event manager logs will show the actual state of the files.PowerShell may report an incorrect NdisPhysicalMedium result on IPoIB adapterApplies to App Compat FOD MMC.exe only: Multiple Active Directory Users and Computers snap-ins added to the same MMC.exe instance could show inconsistent or no data on part of the snap-ins after adding extra columns to the UI view. Wokaround: for UI user management, use a separate MMC for each ADUC (DSA.MSC) snap-in.Scheduled startup tasks may fail to run. An event is logged, ID 101 with the error code ERROR_LOGON_FAILURE when the failure occurs.DCPromo fails if the interface metric of the physical NIC is larger than Loopback InterfaceRenaming a domain controller may update incorrect attributes in Active Directory (msDS-AdditionalDnsHostName, msDS-AdditionalSamAccountName and servicePrincipalName attributes) leaving orphaned data behind (ValidateSPNsAndDNSHostNameActual)Domain Controller rename updates incorrect attributes in AD leaving orphaned data behind (ValidateSPNsAndDNSHostNameActual). This can be reproduced by adding a new FQDN, setting it as primary, restarting the domain controller, then removing the current FQDN. Checking the msDS-AdditionalDnsHostName, msDS-AdditionalSamAccountName and servicePrincipalName attributes will incorrect values.Self-service users cannot install Feature on Demand (FOD) packages and Language Packs for Windows Server Update Service (WSUS), System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), and Autopilot scenarios.After disabling and re-enabling SR-IOV capability on a NIC on Linux VM, Windows may report “Error applying Network Adapter changes.” Details will show “The Hyper-V Virtual Machine Management service encountered an unexpected error: Call was canceled by the message filter. (0x80010002).” A side effect of this failure is that the VM will remain in a stopping state when shutting down the VM, and cannot be restarted without a power resetWhen deploying a controller VM, after the last reboot in the deployment process the controller VM is not visible. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained
New Post has been published on https://www.articletec.com/faq-windows-10-ltsb-explained-3/
FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained
Windows 10 powered to its third anniversary this year, but one branch, identified by the initials L-T-S-B, remained an enigma to most corporate users.
LTSB, which stands for “Long-term Servicing Branch,” was among the pillars of Windows 10 in the months leading up to, and for months after, the mid-2015 roll-out of the operating system. For a time, it seemed that it had a shot at becoming the Windows 10 for enterprise because it was seen as a calm port in a storm of radical change.
That hasn’t happened, in part because Microsoft has steered customers away from LTSB.
Just what is LTSB? And what has Microsoft done to make it an afterthought?
We have answers.
So what is Windows 10 LTSB?
Officially, LTSB is a specialized edition of Windows 10 Enterprise that promises the longest intervals between feature upgrades of any version of the operating system.
Where other Windows 10 servicing models push feature upgrades to customers every six months, LTSB does so only every two or three years. That means fewer changes during a set timeline, a less-involved upgrade effort, and fewer disruptions as well as fewer possibilities for applications breaking because of a modification of the OS.
If LTSB stands for ‘Long-term Servicing Branch,’ what’s this ‘LTSC’ acronym I’ve seen?
When Microsoft dropped multiple labels for Windows 10’s release tracks – those now retired included “Current Branch” and the unwieldy “Current Branch for Business” – for the single “Semi-Annual Channel” (SAC) it also debuted “Long-term Servicing Channel” (LTSC) to match.
Although LTSC could be viewed as the mechanism that updated and upgraded the actual operating system, which went by the LTSB moniker, Microsoft has shifted to using the former exclusively and ditching the latter. Yes, it’s confusing. But then, it is Microsoft we’re talking about.
(Note: Computerworld intends to continue using LTSB, at least in the short run, as it, not LTSC, is the better-known acronym.)
How often does the LTSC update Windows 10 LTSB?
That’s a question so good it comes with more than one answer.
Windows 10 LTSB does receive the usual monthly security updates.
The twice-annual feature upgrades delivered to other channels will not be offered to LTSB systems.
Microsoft upgrades the LTSB “build” every two to three years. Those upgrades, however, are optional, or at least optional to some degree (more on that later).
Each LTSB build is supported with security updates for a decade, the same 10-year lifespan Microsoft has designated and maintained for ages. The decade is split into two equal halves: “Mainstream” support for the first five years, “Extended” for the second. For Windows 10 Enterprise 2016 LTSB, Mainstream support ends in October 2021 and Extended stops in October 2026.
What’s the current Windows 10 LTSB? When is the next one supposed to show up?
This question’s a tough one.
The current LTSB should be Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2019, which was introduced Oct. 2. But it’s not.
That’s because just four days later, on Oct. 6, Microsoft pulled all versions of Windows 10 1809 – the moniker in Microsoft’s yymm naming convention – and has not yet restored access to what it also calls “Windows 10 October 2018 Update.” (Microsoft yanked 1809 due to a very nasty bug that deleted user files on some customers’ PCs during the upgrade.)
Microsoft bases LTSB on a specific Windows 10 build, in the case of LTSC 2019, the 1809 code. Essentially, Microsoft picks a feature upgrade and labels it LTSB. So when the Redmond, Wash. developer withdrew Windows 10 1809 from the Windows Update service and manual download websites, it also revoked access to LTSC 2019. The firm has given users no new information about progress in re-releasing 1809 in more than a month.
For the time being, then, Windows 10 Enterprise 2016 LTSB, which was based on the mid-2016 Windows 10 1607, remains the latest available version. The even earlier Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB – based on the July 2015 debut version of the operating system – still receives security updates, of course.
Note: Although Microsoft said in May 2017 that the next LTSB would ship sometime in 2019, it changed its mind in early 2018, saying in February that a LTSB would launch in the fall.
What’s missing from LTSB?
A lot that makes Windows 10, well, Windows 10. Eschewing the regular feature upgrades means that LTSB does not include Edge nor any Microsoft Store (Universal Windows Platform, or UWP) apps, whether Redmond-made or third-part, because the browser and those apps constantly change and need updating. Also AWOL: the Cortana voice-activated digital assistant and access to the Microsoft Store.
That said, LTSB looks and runs just like any other Windows 10 edition. No one will be fooled into thinking it’s Windows 7.
Can we defer security updates if we’re on LTSB?
Yes.
Servicing tools such as Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) let administrators delay the monthly security updates – which Microsoft calls quality updates – just as they can postpone those same patches reaching machines running other versions of Window 10.
Why does Microsoft make LTSB available to customers?
Plainly put, it was a sop to the criticism very early on about Windows 10’s accelerated development and release tempo.
Customers had become accustomed to upgrading Windows every three or more years, with the emphasis on more in the enterprise. The announcement that that would change to multiple releases each year – initially, three annually – was a shock.
Microsoft tried to soften the blow by offering a schedule very similar to the slower cadence familiar to IT: Upgrades that appeared every three years or so, with little or no feature changes in between, and an update model that provided only security fixes. In a nutshell, that’s how Microsoft described Windows 10 LTSB at the start.
Although Microsoft always opined that LTSB was suitable only as a minority choice – one for special situations, such as machines that simply should not be frequently touched, like those that control industrial systems or ATMs – early in Windows 10, there was significant talk among IT administrators about choosing LTSB for broad swaths of their PC inventory.
Why? Because they weren’t convinced they could, or even should, snap to and adapt to Microsoft’s pitch of “Windows as a service” (WaaS).
Okay, so which PCs should be running LTSB? Here’s what Microsoft says on that:
“Specialized systems – such as PCs that control medical equipment, point-of-sale systems, and ATMs – often require a longer servicing option because of their purpose,” the company’s primary Windows-as-a-service documentation states. “These devices typically perform a single important task and … [i]t’s more important that these devices be kept as stable and secure as possible than up to date with user interface changes.”
and…
“As a general guideline, a PC with Microsoft Office installed is a general-purpose device, typically used by an information worker, and therefore it is better suited for the [non-LTSB servicing channels].”
Has Microsoft changed the support rules for LTSB since Windows 10’s debut?
Yes, and in a way that makes it difficult, if not impossible, to widely deploy the edition.
Over a year and a half ago, Microsoft added another law to the Windows 10 support scene, one that analysts contended invalidated LTSB’s advantages over the shifting features that mark the other versions.
Originally, Microsoft promised to support each LTSB edition for a full decade. But in early 2017, the company ruled that “LTSBs will support the currently released silicon at the time of release of the LTSB [emphasis added],” and that as new processors appeared from the likes of Intel and AMD, “support will be created through future Windows 10 LTSB releases that customers can deploy for those systems.”
The bland language disguised a huge change. Rather than be able to stick with a single LTSB edition for five, even 10, years, enterprises will need to adopt virtually every LTSB version as they buy new PCs powered by newser processors.
Can we upgrade one LTSB to another LTSB?
Yes. But there are conditions and stipulations. No surprise, really, what with Microsoft’s overall attitude toward the long-term build.
“Long-term Servicing Branch can be upgraded, one to another,” said Todd Furst, a Microsoft technical architect, in a presentation last year at his firm’s Ignite conference. “You can upgrade it in place, but there’s some caveats. You basically have to do a full OS deployment. There’s no special tools that say, ‘Just do the upgrade for me.’ You have to push the whole OS down. If you want to do the servicing rings inside of Config Manager or Windows Update for Business, that’s only for Current Branch.”
In other words, LTSB/LTSC requires full-size media to upgrade and new versions of the build are not published to Windows Update or available through WSUS (Windows Server Update Services).
Where do you get the next LTSC then? At the Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC).
What’s one of the least-understood aspects of LTSB?
We couldn’t stop at just one, so we highlighted a pair of points about LTSB.
First, although IT admins can switch PCs from LTSB to plain Windows 10 Enterprise – so those machines can receive feature upgrades, for instance – such a change is only supported when moving to the same or later SAC. If an enterprise has been running Windows 10 Enterprise 2016 LTSB, for example, it can shift only to Windows 10 Enterprise 1607 or later (meaning 1703, 1709 or 1803).
(And you’d better hurry if you plan to switch from 2016 LTSB to SAC 1607, since that version’s support expires in April 2019.)
Second, starting Jan. 14, 2020, the locally-installed applications included with an Office 365 subscription – they’re called “Office 365 ProPlus” – will not be supported on any version of Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB. Instead, LTSB systems must run Office 2016 or 2019, the perpetual license counterparts to ProPlus. (Office 2019 is supported on Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2019 only, not earlier versions.)
How long is LTSB supported?
Ten years is usually the answer you see to that one. But it would be, if not wrong, then misleading.
Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB is guaranteed only five years of support – from the time of its release, not its installation – if the underlying license does not have SA attached. With SA, a specific LTSB edition is supported for the full 10 years.
We run Windows 10 Enterprise and pay for Software Assurance, but we may drop SA. Anything we should know?
Yes, indeed.
When a company drops SA at the end of a contract period, it is entitled to roll out only the current Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB. It cannot later upgrade that version to a newer LTSB when one is released. Customers have a 90-day window to switch the current operating system from Windows 10 Enterprise to Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB. Note: To do that, Windows 10 Enterprise must be uninstalled before deploying LTSB.
Source link
0 notes
Text
Microsoft grants enterprises 6 more months of support for Windows 10 1511
Microsoft has reversed the retirement of Windows 10 version 1511, extending support for the 2015 feature upgrade by six months for commercial customers.
"To help some early enterprise adopters that are still finishing their transition to Windows as a service, we will be providing a supplemental servicing package for Windows 10, version 1511, for an additional six months, until April 2018," said Michael Niehaus, director of product marketing for Windows, in a post to a company blog.
The additional support, which Niehaus indicated would be limited to patches for security vulnerabilities rated "Critical" or "Important" -- Microsoft's two top categories in its four-level system -- will be distributed "via all normal channels," including Windows Update, Windows Server Update Service (WSUS), System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) and the for-manual-download Microsoft Update catalog.
To read this article in full, please click here
from Computerworld https://www.computerworld.com/article/3237667/microsoft-windows/microsoft-grants-enterprises-6-more-months-of-support-for-windows-10-1511.html#tk.rss_all
0 notes
Text
Microsoft grants enterprises 6 more months of support for Windows 10 1511
Microsoft has reversed the retirement of Windows 10 version 1511, extending support for the 2015 feature upgrade by six months for commercial customers.
"To help some early enterprise adopters that are still finishing their transition to Windows as a service, we will be providing a supplemental servicing package for Windows 10, version 1511, for an additional six months, until April 2018," said Michael Niehaus, director of product marketing for Windows, in a post to a company blog.
The additional support, which Niehaus indicated would be limited to patches for security vulnerabilities rated "Critical" or "Important" -- Microsoft's two top categories in its four-level system -- will be distributed "via all normal channels," including Windows Update, Windows Server Update Service (WSUS), System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) and the for-manual-download Microsoft Update catalog.
To read this article in full, please click here
from Computerworld https://www.computerworld.com/article/3237667/microsoft-windows/microsoft-grants-enterprises-6-more-months-of-support-for-windows-10-1511.html#tk.rss_all
0 notes
Text
Fix Zero Day Patch Missing from SCCM? How to Import into WSUS?
[New Post by Kannan @kannan_c_s ] FIX/Workaround Zero-Day Patch Missing from SCCM? How to Import into WSUS? #SCCM #ConfigMgr #Windows #ZeroDay #IE
Whenever you have a Zero Day patch and you don’t have the patches in WSUS? What are the options you have as an SCCM admin to patch your Windows 10 devices? How to Fix the issue of latest Zero Day patch missing from SCCM. How to import them into WSUS console manually?
KB4522014 for win10 1803
KB4522015 for win10 1809
Introduction
In General, most of the time Microsoft will release the update…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Microsoft grants enterprises 6 more months of support for Windows 10 1511
Microsoft has reversed the retirement of Windows 10 version 1511, extending support for the 2015 feature upgrade by six months for commercial customers.
"To help some early enterprise adopters that are still finishing their transition to Windows as a service, we will be providing a supplemental servicing package for Windows 10, version 1511, for an additional six months, until April 2018," said Michael Niehaus, director of product marketing for Windows, in a post to a company blog.
The additional support, which Niehaus indicated would be limited to patches for security vulnerabilities rated "Critical" or "Important" -- Microsoft's two top categories in its four-level system -- will be distributed "via all normal channels," including Windows Update, Windows Server Update Service (WSUS), System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) and the for-manual-download Microsoft Update catalog.
To read this article in full, please click here
from Computerworld https://www.computerworld.com/article/3237667/microsoft-windows/microsoft-grants-enterprises-6-more-months-of-support-for-windows-10-1511.html#tk.rss_all
0 notes
Text
Update rollup KB4019926 for System Center Configuration Manager current branch


Update rollup KB4019926 for System Center Configuration Manager current branch, version 1702.
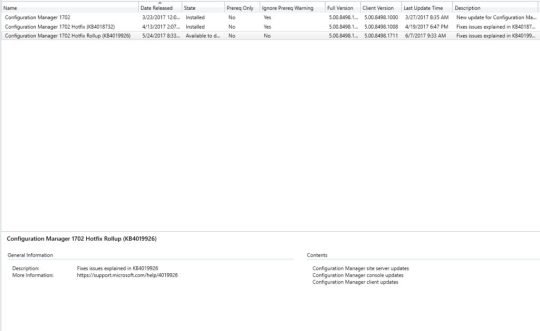
Operating system deployment Starting with System Center Configuration Manager, version 1702, unknown computers that are started from media or PXE may not find task sequences targeted to them. This issue may occur if the Previous button on the "Select a task sequence to run" page is selected on the unknown computer. The ImportMachineEntry method in the Configuration Manager Software Development Kit (SDK) fails when a computer record already exists, even if the OverwriteExistingRecord property is set to True. The Data Source page of the Operating System Upgrade Package properties does not load in the Configuration Manager console, and you receive an error message that resembles the following: Notice: System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException Index was out of range. Must be non-negative and less than the size of the collection. Parameter name: startIndex Multiple improvements were made to the client and the task sequence engine to ensure a more consistent transition into and out of provisioning mode. Windows 10 mobile Enterprise devices are not upgraded by a Windows 10 edition upgrade policy. The Create Task Sequence Media operation may fail if the Configuration Manager version 1702 client is installed on the computer being captured. If the final restart step does not complete, the computer can be manually restarted to complete the operation. The Install Applications task sequence step fails for HTTPS-only workgroup clients after you upgrade to Configuration Manager, version 1702. Additionally, errors that resemble the following are recorded in the smsts.log file on the client: Software distribution and content management After a secondary site is recovered, all packages are redistributed to the secondary site if any of the package contents contained invalid metadata. The distmgr.log file contains excessive entries for skipped drives on distribution points with many volumes when the NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS file is present. This could lead to problems in troubleshooting issues, as important information can roll out of the logs more quickly. Messages that resemble the following are logged in the distmgr.log file: Ignoring drive E:\. File E:\NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS exists. Ignoring drive F:\. File F:\NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS exists. Ignoring drive L:\. File L:\NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS exists. Ignoring drive C:\. File C:\NO_SMS_ON_DRIVE.SMS exists. Device-targeted Volume Purchasing Program (VPP) applications that require an associated mobile application management (MAM) policy are not installed. The status of the deployment is listed as "Remediation failed" in the Configuration Manager console. Site systems Internet-based clients may not scan for software updates when they connect to a Software Update Point through the Cloud Management Gateway (CMG). This issue occurs when the CMG encounters an internal server error during communication with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). Errors that resemble the following are recorded in the scanagent.log on the client: ScanJob({job_guid}): CScanJob::OnScanComplete -Scan Failed with Error=0x8024401f The Delete Orphaned Client Deployment State Records task is not removed at the Central Administration Site (CAS) following an upgrade from Configuration Manager version 1602 to a later version. Clients do not register with Management Point replicas. Errors resembling the following are recorded in the MP_ClientIDManager.log file: Parse a client ID request CMPDBConnection::ExecuteSQL(): ICommandText::Execute() failed with 0x80040E14 ======================================= MP_ClientIDManager MPDB ERROR - CONNECTION PARAMETERS SQL Server Name : Server.Domain.Label SQL Database Name : CM_P01_REPLICA Integrated Auth : True MPDB ERROR - EXTENDED INFORMATION MPDB Method : ExecuteSP() MPDB Method HRESULT : 0x80040E14 Error Description : Could not find stored procedure 'spGetLockState'. OLEDB IID : {guid} ProgID : Microsoft SQL Server Native Client 11.0 MPDB ERROR - INFORMATION FROM DRIVER SQL Server Name : {sql_server} Native Error no. : 2812 Error State : 62 Class (Severity) : 16 Line number in SP : 1 Mobile device management and Microsoft Intune Warning Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might require that you reinstall the operating system. Microsoft cannot guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your own risk. International station mobile equipment identity (IMEI) data for existing devices is not updated in Microsoft Intune-connected environments when their discovery data records are processed. Deleting an obsolete or decommissioned device that is superseded during re-enrollment removes the capacity to manage the new device. Additionally, the Exchange allow/block state cannot be changed. This issue occurs because the Exchange Active Sync (EAS) device ID is the same for both the removed and superseding device. An Exchange Connector full resync will restore management of the new device. If a managed device is not compliant with conditional access policies, a notification is sent to the user. If the user takes no action to make the device compliant (such as by enrolling in Microsoft Intune), the device is blocked from Microsoft Exchange access after 10 minutes. This 10-minute period is now configurable by creating the following registry value on the site server: Registry location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\SMS\COMPONENTS\SMS_EXCHANGE_CONNECTOR DWORD name: CAGracePeriodInMinutes DWORD value: number_of_minutes Configuration Manager console The username font driver host\umfd-# is listed as a potential primary user when you edit the user device affinity for Windows 10 Creators Update computers. The summary data that is displayed in the Distribution Point Configuration Status window is inconsistent between a CAS and Primary site. However, the details of the data are correct. To recover the Distribution Point that has this problem, run the following script: exec spRebuildContentDistribution 1 Device Health Attestation information is not updated for clients when double-byte character set languages are used. Update information for System Center Configuration Manager, version 1702 This update is available for installation in the Updates and Servicing node of the Configuration Manager console. If the service connection point is in offline mode, you must reimport the update so that it is listed in the Configuration Manager console. See Install in-console Updates for System Center Configuration Manager for detailed information. After you install this update on a primary site, pre-existing secondary sites must be manually updated. To update a secondary site in the Configuration Manager console, click Administration, click Site Configuration, click Sites, click Recover Secondary Site, and then select the secondary site. The primary site then reinstalls that secondary site by using the updated files. Configurations and settings for the secondary site are not affected by this reinstallation. The new, upgraded, and reinstalled secondary sites under that primary site automatically receive this update. Run the following SQL Server command on the site database to check whether the update version of a secondary site matches that of its parent primary site: select dbo.fnGetSecondarySiteCMUpdateStatus ('SiteCode_of_secondary_site') Note If a value of 1 is returned, the site is up to date, with all the hotfixes applied on its parent primary site. If a value of 0 is returned, the site has not installed all the fixes that were applied to the primary site, and you should use the Recover Secondary Site option to update the secondary site. Click to Post
0 notes