#pancreatic cancer bilirubin
Text
Gallbladder Surgery in Basavanagudi, Bangalore — Comprehensive Care at Himas Hospital

What is Gallbladder Surgery (Cholecystectomy)?
Gallbladder surgery is a procedure performed to remove the gallbladder, typically due to the presence of gallstones or inflammation. Gallstones are hard deposits of cholesterol or bilirubin that can form in the gallbladder, causing pain, infection, or blockages in the bile ducts. Some common symptoms that indicate the need for gallbladder surgery include:
Severe abdominal pain, especially after eating fatty foods.
Nausea and vomiting.
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Fever and chills, indicating an infection.
The most common approach to gallbladder surgery today is laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which involves making small incisions and using a camera to guide the surgeon in removing the gallbladder. In more complicated cases, open surgery may be required, but laparoscopic surgery remains the preferred method due to its many benefits.
Types of Gallbladder Conditions Treated at Himas Hospital
At Himas Hospital, we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of various gallbladder-related conditions, including:
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis): Gallstones can block the bile ducts, leading to severe pain, infection, or pancreatitis. Surgery is often the best treatment option.
Cholecystitis: This is the inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by gallstones. It can lead to sharp pain and may require surgical intervention.
Biliary Dyskinesia: A condition where the gallbladder does not empty properly, causing chronic pain. Surgery is a common solution.
Gallbladder Polyps: Small growths in the gallbladder that can become cancerous, necessitating removal.
Gallbladder Cancer: Though rare, gallbladder cancer may require the removal of the gallbladder along with surrounding tissues.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Gallbladder Surgery
At Himas Hospital, we use the minimally invasive laparoscopic technique to perform most gallbladder surgeries. This advanced method offers numerous benefits over traditional open surgery, including:
Smaller Incisions: Laparoscopic surgery requires only a few small incisions, resulting in minimal scarring and less post-operative pain.
Faster Recovery: Patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy typically recover faster and can return to their daily activities within a week.
Shorter Hospital Stay: Most patients can go home on the same day or within 24 hours of the procedure, depending on their condition.
Lower Risk of Infection: The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery reduce the risk of post-operative infections.
Improved Precision: The high-definition camera used in laparoscopic surgery allows surgeons to have a clear, magnified view of the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
Why Choose Himas Hospital for Gallbladder Surgery?
Expert Surgical Team: At Himas Hospital, our experienced surgeons have successfully performed hundreds of gallbladder surgeries, ensuring the best outcomes for our patients.
Advanced Technology: We use cutting-edge technology and equipment to perform minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, reducing recovery times and improving patient comfort.
Personalized Care: Every patient receives individualized care from diagnosis through recovery. Our medical team takes the time to understand each patient’s unique condition and health needs.
Comprehensive Pre- and Post-Operative Care: Our services go beyond surgery. We offer comprehensive care, including thorough pre-operative assessments and post-operative support to ensure a smooth and comfortable recovery.
Affordable Healthcare: At Himas Hospital, we believe that everyone deserves access to high-quality healthcare. We offer cost-effective gallbladder surgeries without compromising on quality or patient care.
Gallbladder Surgery Process at Himas Hospital
Consultation and Diagnosis: Your journey begins with a consultation, where our specialists will evaluate your symptoms and recommend the best course of action. This may involve diagnostic tests like ultrasound or CT scans to confirm the presence of gallstones or other gallbladder issues.
Surgical Procedure: On the day of surgery, our team will guide you through every step of the process. Whether it’s laparoscopic or open surgery, you can trust our surgeons to provide expert care using the most effective techniques.
Post-Surgical Recovery: After the surgery, patients are closely monitored in a comfortable recovery environment. Our medical team will provide personalized post-operative care instructions to help speed up your recovery.
Conclusion:
If you’re suffering from gallbladder issues such as gallstones or cholecystitis, seeking timely medical intervention is crucial. At Himas Hospital in Basavanagudi, Bangalore, we offer expert gallbladder surgery performed by highly skilled surgeons using advanced laparoscopic techniques. Our focus on minimally invasive procedures ensures that you can recover quickly and with minimal discomfort. From the initial diagnosis to post-surgical care, we are committed to delivering comprehensive, patient-centered treatment.
Visit Us :- https://maps.app.goo.gl/aMfxCDtTNn9PJCvE7
0 notes
Text
Ayurveda and Yoga therapy treatment for Gall bladder stones
Gall bladder stones: Gall stones are the hard deposited digestive waste or fluids in the gall bladder. It is also named as cholelithiasis. Gall bladder is a pear shape of sac present in the right hypochondrium of abdomen just beneath the liver. The size and number of gall stones may vary from person to person.
Causes
The correct cause for gallstones is unknown, but experts mention that followings may lead to gall stones.
Digestive fluid (bile) may contains high cholesterol or bilirubin
Improper metabolism
Gall bladder doesn't get proper elimination
Family history of gallstones
Underlying liver disease
Antibiotics
Stress and emotional disturbance
Symptoms
Sudden and strong pain in the abdomen, more on right side
Nausea or vomiting
Loss of appetite
Pain in shoulder or upper back
Color of urine changes
Stomach upset
Fever or chills
Types of gallstones
Cholesterol gallstones - Undissolved cholesterol makes the yellow colored stones in gall bladder.
Pigment gallstones - Increased bilirubin of bile makes the dark colored stones.
Mixed composition stones.
Risk factors
Obesity
Wrong food habits
Increased intake of fat, cholesterol or animal products
High triglycerides
Women after 40 years
Sedentary lifestyle
Diabetes
Other metabolic disorders
Complications
Severe abdominal pain
Shoulder pain
Back pain
Chest pain
Nausea, vomiting
Bloating
Diagnosis
Imaging tests include. MRI, CT Scan, Ultrasound, cholescintigraphy etc.
Differential diagnosis
Appendicitis
Peptic ulcer disease
Pancreatic cancer
Gallbladder cancer
Chole cystitis
Bileduct strictures or tumors
Management Through Natural therapies
Heliotherapy or sun bath: Sun bath is one of the best methods to clear the bile retention, gall bladder hypertrophy and poor gallbladder emptying. It also reduces stress and helps in developing positive mental health.
Hydrotherapy: Gastro hepatic pack including the hot fomentation bag to abdomen and cold compress to back region is the effective method to relieve the pain and influence the function of abdominal organs.
Cold water enema is one of the detoxifying methods which relieves pain and other symptoms.
Mud bath: Mud is believed to dilute and absorb toxic substances of the body ultimately eliminate them from the body. Studies recommend mud application to influence bile secretion and assimilation of bile stones.
Fasting & Diet therapy: Fasting for 4-6 days has been shown to reduce the proportion of cholesterol in gall bladder bile. This indicates a possible lipotropic effect of fasting which can be effectively helped in treating gallstones. Fasting also will help in reducing the cholesterol production in the body.Increased intake of high fiber and other vegetables are very good to reduce the formation of gallstones. Dietary fiber also reduces the production of deoxycholic acid and thereby enhances the solubility of cholesterol in bile. Non-vegetarian food and animal products should be avoided to reduce the risk and complications.
Acupuncture: It is a traditional Chinese method which believes in Qi (energy) circulation. Some of the acupuncture points will help in energizing the Qi and blood circulation to gall bladder and remove the stasis. Acupuncture will also help in managing the abdominal pain.
Yoga therapy: Regular yoga practice is the one of the best methods to prevent gallstones and to restore the health of gall bladder. Postures like padahastasana, kati chakrasana, paschimottanasana, pawana muktasana, bhujangasana, bow pose(dhanurasana) and other twisting poses will help in improving the blood circulation & function of abdominal organs. Breathing exercises, relaxation techniques and Pranayama will always help in relaxing body, mind and their by reduces stress and depression
Ayurveda also offers treatment for Gall stones. Polyherbal combinations containing hers such as Katuki, Bhumyamalaki, Pashanabheda are very effective in the treatment of gall stones.They work on the basis of eliminating the excess pitta, reducing the metabolic waste (Ama) and thus providing relief in the signs and symptoms.
Article By :
Dr.Anitha
0 notes
Text
Understanding Jaundice: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment

What is Jaundice?
Jaundice is a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. This yellow color is due to an excess of bilirubin, a yellow-orange bile pigment, in the blood. Bilirubin is produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells and is usually processed by the liver. When there is a disruption in this process, jaundice can occur.
Causes of Jaundice
Jaundice can be caused by various underlying conditions, which are broadly categorized into pre-hepatic (before bile is made in the liver), hepatic (issues within the liver), and post-hepatic (after bile is made).
Pre-Hepatic Causes:
Hemolytic anemia: Accelerated breakdown of red blood cells increases bilirubin production.
Sickle cell anemia: Abnormal red blood cells break down more rapidly.
Malaria: Infection causes red blood cell destruction.
Hepatic Causes:
Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver reduces its ability to process bilirubin.
Cirrhosis: Chronic liver damage from various causes leads to scarring and liver dysfunction.
Liver cancer: Malignant cells impair liver function.
Genetic disorders: Conditions like Gilbert's syndrome affect bilirubin metabolism.
Post-Hepatic Causes:
Gallstones: Block the bile ducts, preventing bilirubin excretion.
Pancreatic cancer: Tumors can compress the bile ducts.
Biliary atresia: Congenital condition where bile ducts are absent or blocked.
Symptoms of Jaundice
Yellowing of the skin and eyes
Dark urine
Pale stools
Itchy skin
Fatigue
Abdominal pain
Weight loss
Vomiting
Diagnosis of Jaundice
Diagnosing jaundice involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests:
Physical Examination: A doctor will look for signs of jaundice and other related symptoms.
Laboratory Tests:
Bilirubin Levels: Blood tests to measure total and direct (conjugated) bilirubin.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): To check for hemolytic anemia.
Liver Function Tests (LFTs): To assess the liver's health and functioning.
Viral Hepatitis Panel: To detect hepatitis viruses.
Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound: To visualize the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
CT Scan/MRI: For more detailed imaging.
Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a small tissue sample from the liver may be examined to determine the cause of liver dysfunction.
Treatment of Jaundice
The treatment of jaundice focuses on addressing the underlying cause:
Pre-Hepatic Jaundice:
Treating the underlying hemolytic disorders or infections.
Hepatic Jaundice:
Hepatitis: Antiviral or immunosuppressive drugs.
Cirrhosis: Lifestyle changes, medications, or possibly a liver transplant.
Liver Cancer: Surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
Post-Hepatic Jaundice:
Gallstones: Medications to dissolve stones or surgery to remove them.
Tumors: Surgical removal, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
Biliary Atresia: Surgery to reconstruct bile ducts or liver transplant.

Managing Jaundice
Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can support liver health.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps maintain kidney function and aids in the excretion of bilirubin.
Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can exacerbate liver damage.
Medication Management: Some medications can cause liver damage; consult a doctor before taking new medications.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you notice symptoms of jaundice, especially if accompanied by severe abdominal pain, confusion, or blood in vomit or stool, as these could indicate a serious underlying condition.
Understanding jaundice and its underlying causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment is crucial for effective management and recovery. If you suspect jaundice, it's important to seek medical attention promptly.
Important Information:
Conference Name: 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference
Short Name: 14GHUCG2024
Dates: December 17-19, 2024
Venue: Dubai, UAE
Email: [email protected]
Visit: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/
Call for Papers: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/submit-abstract/
Register here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/registration/
Exhibitor/Sponsor: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/exhibit-sponsor-opportunities/
Call Us: +12073070027
WhatsApp Us: +442033222718
0 notes
Text
Introduction
Jaundice is a condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin and eyes, caused by an excess of bilirubin in the blood. It can be a sign of an underlying liver or gallbladder problem. The aim of this guide is to provide a comprehens...
#Mirari #MirariDoctor #MirariColdPlasma #ColdPlasma
0 notes
Text
What is the main causes of Jaundice?
Discover the comprehensive guide on What is the main causes of Jaundice? Understand the key factors leading to yellowing skin. Uncover expert insights and FAQs for a detailed understanding.
Introduction:
Jaundice, a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, can be alarming. Understanding the main causes is crucial for early detection and effective management. In this article, we'll delve into the intricate details of What is the main causes of Jaundice?, exploring 15 crucial aspects to provide you with a comprehensive guide.
What is Jaundice?
Jaundice occurs when there is an excess buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. This condition manifests as yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Now, let's explore the specific causes contributing to this phenomenon.
Hepatitis: The Silent Culprit
Jaundice often results from viral hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver. Various hepatitis viruses, including Hepatitis A, B, and C, can lead to jaundice. These viruses impair the liver's ability to process bilirubin, causing it to accumulate in the bloodstream.
Understanding Hepatitis A, B, and C:
Hepatitis A: Contracted through contaminated food or water, this virus affects the liver, leading to jaundice.
Hepatitis B and C: Transmitted through infected blood and bodily fluids, these chronic infections can cause prolonged jaundice.
Liver Cirrhosis: Scarring the Vital Organ
Cirrhosis, a condition where the liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue, is another significant cause of jaundice. The impaired liver function hinders bilirubin processing, contributing to its buildup in the body.
Alcohol and Liver Cirrhosis:
Excessive alcohol consumption is a leading factor in liver cirrhosis, emphasizing the importance of moderation for liver health.
Gilbert's Syndrome: A Genetic Quirk
Some individuals experience jaundice due to Gilbert's Syndrome, a genetic condition affecting bilirubin processing. While not harmful, it can cause intermittent jaundice episodes.
Medication-induced Jaundice: Balancing Risks and Benefits
Certain medications, including antibiotics, antivirals, and anti-seizure drugs, can cause jaundice as a side effect. It's crucial to be aware of potential risks and consult with a healthcare professional when prescribed such medications.
Common Medications Linked to Jaundice:
Acetaminophen: In high doses, this common pain reliever can contribute to jaundice.
Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, like erythromycin and tetracycline, may induce jaundice in susceptible individuals.
Hemolytic Anemia: Unleashing the Power of Destruction
Jaundice can result from hemolytic anemia, a condition where red blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can replace them. The breakdown of these cells releases excess bilirubin into the bloodstream.
Identifying Hemolytic Anemia Causes:
Genetic Conditions: Conditions like sickle cell anemia and thalassemia contribute to hemolytic anemia and subsequent jaundice.
Bile Duct Disorders: Obstructing the Flow
Disorders affecting the bile ducts, such as gallstones or tumors, can obstruct the flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine. This obstruction leads to a buildup of bilirubin, causing jaundice.
Gallstones and Jaundice:
Gallstones can block the bile ducts, triggering jaundice. Timely intervention is crucial to prevent complications.
Pancreatic Cancer: Unveiling the Connection
Pancreatic cancer can contribute to jaundice as tumors obstruct the bile ducts. Understanding this link is vital for early detection and improved prognosis.
What is the main causes of Jaundice? Unraveling the Complexities
Jaundice is a multifaceted condition with various underlying causes. From viral infections to genetic quirks, understanding the intricacies allows for better prevention, management, and treatment.
Alcoholic Hepatitis: The Consequence of Excess
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, contributing to jaundice. Acknowledging the risks and seeking help for alcohol dependence is crucial for preventing further complications.
Autoimmune Hepatitis: When the Body Turns Against Itself
In autoimmune hepatitis, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the liver, leading to inflammation and jaundice. Timely diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention are vital for managing this condition.
Navigating Autoimmune Hepatitis:
Understanding the immune system's role in liver health is essential for comprehending autoimmune hepatitis and its impact on jaundice.
Wilson's Disease: The Copper Conundrum
Wilson's disease, a rare genetic disorder, can cause copper to accumulate in the liver, leading to jaundice. Early detection and management are crucial for individuals with this condition.
Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Balancing the Risks
Certain drugs, including statins and anti-seizure medications, can induce liver injury, resulting in jaundice. Careful monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential for those on these medications.
Statins and Liver Health:
While statins are widely prescribed for cholesterol management, understanding their potential impact on the liver is vital for overall health.
Congenital Disorders: Addressing Early Challenges
Some infants may exhibit jaundice due to congenital disorders affecting bilirubin metabolism. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications and ensure the child's well-being.
Neonatal Jaundice:
Understanding the difference between physiological jaundice and underlying congenital disorders is crucial for parents and healthcare providers.
Having ulcer or ulcer bleeding issues and have severe abdominal pain then must book an appointment with Dr. Sushil Kumar Jain, He is a highly experienced gastroenterologist in Jaipur who provide the best and most advanced treatment for ulcer bleeding at ACE Gastro Super-Speciality Clinic. He has more than 16+ years of experience and provides the best treatment for gastro and liver disease with a hundred percent success rate.
What is the main causes of Jaundice? Addressing Common Questions
Q.1 Can Jaundice be Prevented?
Ans. Preventing jaundice involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including moderate alcohol consumption, vaccination against hepatitis, and regular medical check-ups.
Q.2 Is Jaundice Contagious?
Ans. No, jaundice itself is not contagious. It results from underlying causes such as viral infections or genetic factors.
Q.3 How is Jaundice Diagnosed?
Ans. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging studies, and a thorough medical history review by healthcare professionals to identify the underlying cause.
Q.4 What Role Does Diet Play in Jaundice Management?
Ans. A balanced diet, low in fatty and processed foods, can support liver health and aid in the management of jaundice.
Q.5 Can Herbal Remedies Alleviate Jaundice Symptoms?
Ans. While some herbal remedies may claim to help jaundice, it's crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before trying alternative treatments.
#gastroenterologist#gastroenterologistindia#drsushilkumarjain#liver specialist in jaipur#endoscopic#gastro doctor in jaipur#acegastro#gastroenterologist in jaipur
0 notes
Text
Decoding the Whispering Assassin: Unveiling Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms

Pancreatic cancer is often referred to as the "whispering assassin" because it tends to hide in the shadows, silently advancing before manifesting noticeable symptoms. Understanding the subtleties of these symptoms is crucial for early detection, as pancreatic cancer is notorious for its late-stage diagnosis and high mortality rate. In this article, we will delve deep into the enigmatic world of pancreatic cancer symptoms, shedding light on its covert nature and the importance of recognizing these signs. Let's embark on this journey to decipher the whispers of pancreatic cancer and raise awareness about the critical need for vigilance.
1. The Unseen Intruder: Pancreatic Cancer Unveiled
Pancreatic cancer, a malignant disease that affects the pancreas, can be insidious in its onset. The pancreas, a vital organ located behind the stomach, plays a crucial role in digestion and hormone regulation. However, when cancer invades this organ, it can disrupt its normal functions and lead to a cascade of symptoms.
2. The Silent Onset: Early Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms
Early-stage pancreatic cancer often proceeds without any conspicuous symptoms, making it challenging to detect. Nevertheless, some subtle signs may give an inkling that something is amiss within the pancreas.
2.1. Unexplained Weight Loss
Sudden, unexplained weight loss is a common early indicator of pancreatic cancer. When cancer disrupts the pancreas's ability to produce digestive enzymes, the body struggles to absorb nutrients, leading to unintended weight loss.
2.2. Abdominal Pain
Pancreatic cancer can cause discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen or back. This pain may be dull and persistent, worsening after meals or when lying down. It is often mistaken for other less severe conditions.
2.3. Jaundice
Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, can occur when pancreatic cancer obstructs the bile duct. This obstruction leads to a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream, resulting in the classic yellow hue associated with jaundice.
3. The Hidden Culprit: Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms
As pancreatic cancer advances, the symptoms become more pronounced and alarming, demanding immediate attention.
3.1. Dark Urine and Pale Stools
The blockage of the bile duct due to pancreatic cancer can also cause changes in urine and stool color. Dark urine and pale stools may signal an issue with the pancreas or bile duct, which should be investigated promptly.
3.2. Loss of Appetite and Nausea
Advanced pancreatic cancer can further disrupt the digestive process, leading to a loss of appetite and persistent nausea. This can make it difficult for individuals to maintain their normal eating habits.
3.3. Blood Clots
Pancreatic cancer can increase the risk of blood clots, leading to conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE). If you experience sudden pain, swelling, or redness in your limbs, seek medical attention immediately.
3.4. Diabetes Onset or Worsening
In some cases, pancreatic cancer can affect the production of insulin, resulting in the development of diabetes or the worsening of pre-existing diabetes. This sudden change in blood sugar levels should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
4. The Elusive Diagnosis: Pancreatic Cancer and its Mimickers
One of the challenges in diagnosing pancreatic cancer is its ability to mimic other, less severe conditions. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Let's explore some conditions that may be mistaken for pancreatic cancer.
4.1. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas, shares symptoms such as abdominal pain and nausea with pancreatic cancer. A careful evaluation by a healthcare provider is necessary to differentiate between the two.
4.2. Gallstones
Gallstones can also cause abdominal pain and jaundice, making it easy to confuse their symptoms with those of pancreatic cancer. Imaging studies can help determine the underlying cause.
4.3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or gastritis can lead to weight loss and digestive discomfort, similar to early pancreatic cancer symptoms. A thorough examination is essential to rule out cancer.
5. The Importance of Early Detection: Pancreatic Cancer Screening
Given the elusive nature of pancreatic cancer symptoms, early detection becomes paramount for improving survival rates. While there is no routine screening test for pancreatic cancer, certain individuals with risk factors should consider regular check-ups and discussions with their healthcare providers.
5.1. Family History
Individuals with a family history of pancreatic cancer are at an increased risk. Close relatives, such as parents, siblings, or children, who have had pancreatic cancer may indicate a hereditary predisposition. Genetic counseling and screening may be recommended in such cases.
5.2. Inherited Genetic Syndromes
Certain genetic syndromes, such as Lynch syndrome and familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome, are associated with an elevated risk of pancreatic cancer. Those with a family history of these syndromes should undergo regular screenings.
5.3. Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis, especially if it develops at a young age, can increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer. Patients with chronic pancreatitis should be closely monitored.
5.4. Smoking and Obesity
Smoking and obesity have been linked to an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. Lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight, can help reduce this risk.
6. The Detective Work: Diagnosis and Treatment
When pancreatic cancer is suspected, a series of diagnostic tests are conducted to confirm the presence of the disease and determine its stage. These tests may include:
6.1. Imaging Scans
CT scans, MRI scans, and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can provide detailed images of the pancreas, helping doctors assess the tumor's size, location, and spread.
6.2. Biopsy
A biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the pancreas for examination under a microscope. It is the definitive way to confirm the presence of cancer.
6.3. Blood Tests
Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of specific tumor markers, such as CA 19-9, which can indicate the presence of pancreatic cancer.
7. The Battle Plan: Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
The treatment approach for pancreatic cancer depends on its stage, location, and the patient's overall health. Common treatment options include:
7.1. Surgery
Surgery aims to remove the tumor and, in some cases, a portion of the pancreas. Surgical options may include a Whipple procedure, distal pancreatectomy, or total pancreatectomy.
7.2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other particles to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery or in combination with chemotherapy.
7.3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It can be administered before or after surgery or as a standalone treatment for advanced cases.
7.4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy drugs are designed to target specific molecules involved in cancer growth. They may be used in conjunction with chemotherapy.
8. The Outlook: Living with Pancreatic Cancer
A diagnosis of pancreatic cancer can be daunting, but it's essential to remember that advances in medical research and treatment options continue to improve the outlook for patients. Support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family is invaluable during this journey.
8.1. Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies that may offer hope for improved outcomes.
8.2. Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from the symptoms and side effects of cancer treatment. It can enhance the quality of life for individuals living with advanced pancreatic cancer.
9. The Final Word: Awareness Saves Lives
In the realm of pancreatic cancer, awareness is the key to early detection and improved survival rates. Understanding the subtle signs and risk factors associated with this disease empowers individuals to take action and seek timely medical attention.
Conclusion
Pancreatic cancer may be a silent intruder, but with knowledge and vigilance, its whispers can be heard. Recognizing the subtle symptoms and risk factors associated with this disease is the first step towards early detection and effective treatment. By shedding light on the enigmatic world of pancreatic cancer symptoms, we hope to inspire awareness, encourage early diagnosis, and ultimately save lives. In the battle against the "whispering assassin," knowledge is our most potent weapon.
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How to detect pancreatic cancer symptoms ?
Detecting pancreatic cancer symptoms can be challenging because they often appear in the later stages of the disease when it's more difficult to treat. However, one key sign to watch for is:

Unexplained and Persistent Jaundice: If you notice yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, along with symptoms like dark urine, pale stools, and abdominal pain, it could be a sign of pancreatic cancer. Jaundice occurs when the tumor blocks the bile duct, leading to a buildup of bilirubin in the body.
If you or someone you know experiences persistent jaundice or any other concerning symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel habits, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Early detection can significantly improve the prognosis for pancreatic cancer.
Read more helpful information about health & fitness :
#cancer#pancreatic cancer#nutrition#health and fitness#healthy#healthy lifestyle#healthy eating#healthy living#exercise#workout#healthy food#spiritual development
1 note
·
View note
Text
Gallbladder Stone Treatment in Delhi: Expert Care by Dr. Neeraj Goel

Gallbladder Stone Treatment in Delhi
Gallbladder stones, medically known as cholelithiasis, can lead to significant discomfort and health concerns. Finding the right treatment for gallbladder stone removal is of utmost importance, and in Delhi, patients can rely on the expertise of Dr. Neeraj Goel, a distinguished GI Surgeon specializing in gallbladder stone treatment. In this blog, we will delve into the various aspects of gallbladder stones, the need for treatment, and the comprehensive care offered by Dr. Neeraj Goel, a renowned medical professional.
Gallbladder Stone Surgery In Delhi
Gallstone is not an uncommon problem and with the availability of ultrasonography the diagnosis is increasing, and so does the number of gallbladder stone surgeries. Certain questions come to one’s mind when diagnosed with gallstones.
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
Typical symptoms of gallstones are pain in the right upper abdomen which radiates to the back and may be associated with vomiting. The pain is typically aggravated by fatty food intake. A minority of the patients present with symptoms of hyperacidity. Sometimes if the stone slips into the bile duct patient may have jaundice or acute pancreatitis.
Stomach Cancer Treatment In Delhi
Stomach Cancer is one of the malignancies which remain difficult to treat as it spreads fast. So it becomes important that we are aware of it and respond at the earliest to any particular symptoms.
Understanding Gallbladder Stones and the Need for Treatment:
Gallbladder stones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder due to the accumulation of cholesterol or bilirubin materials. These stones can cause distressing symptoms, including severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloating. When conservative approaches fail to relieve symptoms or complications arise, treatment becomes necessary. The primary goal of gallbladder stone treatment is to remove the stones and restore normal gallbladder function, thus alleviating the discomfort.
What Are Colorectal Diseases?
The colon and rectum combine to form the bowel. The purpose of the bowel is to eliminate the waste material after digestion. There are several conditions that affect the functioning of the colon and rectum. If the disease is confined to the colon, the condition is known as colon disease. A disease confined only to the rectum is known as rectal disease. However, some diseases affect both the colon and the rectum. Such diseases are termed colorectal diseases. Some examples of colorectal diseases include colorectal cancer, colon polyps, Ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease. Patients with colorectal diseases experience several symptoms. These are abdominal pain, blood in the stool, rectal bleeding, and prolonged constipation and diarrhea.
Meet Dr. Neeraj Goel: A GI Surgeon with Exceptional Expertise:
Dr. Neeraj Goel is a highly qualified GI Surgeon, acclaimed for his extensive surgical experience and dedication to providing excellent patient care. He is the first GI Surgeon in East Delhi & adjoining NCR to offer comprehensive GI surgical and GI Oncologic care. With training from the coveted GB Pant Hospital and a fellowship in HPB Surgery from South Korea, Dr. Goel is at the forefront of gallbladder stone treatment in Delhi.
Liver Disorders
Liver disorders are the diseases of liver. The liver is a vital organ and performs several necessary functions. Liver diseases may be mild, moderate, or severe. There are several causes of liver disease and the treatment depends upon the disease. Do not ignore the symptoms of liver disease as it may result in the progression of the disease leading to lengthening the treatment, irreversible damage, or causing complications.
Symptoms of Gallstones and Diagnosis:
Typical symptoms of gallstones include pain in the right upper abdomen, which may radiate to the back and be associated with vomiting. Pain worsens after consuming fatty foods. A minority of patients may present with symptoms of hyperacidity. Accurate diagnosis is crucial to determine the presence and severity of gallbladder stones. Diagnostic tests, such as ultrasounds, play a crucial role in confirming the condition and guiding the treatment approach.
Key Considerations for Gallbladder Stone Treatment in Delhi:
When seeking gallbladder stone treatment in Delhi, several factors should be considered:
1. Diagnosis: Accurate diagnosis is essential through medical testing and consultation with a specialist.
2. Treatment Options: The recommended approach may vary based on the patient's condition, ranging from laparoscopic procedures to traditional open surgery.
3. Preoperative Preparation: Patients receive instructions on dietary restrictions, medication management, and necessary tests to ensure a smooth surgical procedure.
4. Surgical Procedure: Dr. Neeraj Goel chooses the most appropriate surgical approach based on the patient's condition, utilizing the latest technology and techniques.
5. Postoperative Care: Patients receive guidance on pain management, incision care, dietary adjustments, and gradual resumption of daily activities.
6. Recovery and Follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor recovery, address concerns, and ensure optimal healing.
Conclusion:
Dr. Neeraj Goel's expertise in gallbladder stone treatment in Delhi has earned him accolades as a leading GI Surgeon in the region. With a commitment to advanced surgical techniques and cutting-edge technology, Dr. Goel provides comprehensive care for patients with gallbladder stones, ensuring improved health and quality of life. For those seeking the best gallbladder stone surgery in Delhi, Dr. Neeraj Goel's clinic stands as a symbol of excellence and a compassionate approach to healthcare.
Contact Information:
Name: Gastro Delhi
Address: D-1, Hakikat Rai Rd, Block D, Adarsh Nagar, Delhi, 110033
Phone: +91–9667365169, +91–9599294453
Website: www.gastrodelhi.com
#Esophagus Surgeon in Delhi#Colorectal Surgery in Delhi#Robotic Surgeon in Delhi#HIPEC Surgery in Delhi#Laparoscopic Hepatobiliary Surgeon in Delhi#Stomach Cancer Surgeon in Delhi#Gallbladder stone Treatment in Delhi#Pancreatic Cancer Treatment in Delhi#Pancreatic Surgery in Delhi#Gastrointestinal Cancer Doctor in Delhi
1 note
·
View note
Text

Pancreatic cancer often does not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. As the disease progresses, the signs and symptoms may include:
Abdominal or back pain: This is one of the most common symptoms. The pain may start in the upper abdomen and radiate to the back.
Unintentional weight loss: A sudden and unexplained loss of weight can be a sign of pancreatic cancer.
Jaundice: The yellowing of the skin and eyes occurs when pancreatic cancer affects the bile ducts, leading to a buildup of bilirubin.
Loss of appetite: Pancreatic cancer can cause a loss of appetite and a feeling of fullness even after eating small amounts of food.
Digestive problems: Some people with pancreatic cancer may experience nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or pale, greasy stools.
Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak is a common symptom of many types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer.
New-onset diabetes: Pancreatic cancer can interfere with insulin production, leading to the onset of diabetes in people who have never had it before.
Blood clots: The occurrence of blood clots, particularly in the veins of the legs, can be a sign of pancreatic cancer.
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. However, if you experience persistent or unexplained symptoms, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. There are best gastroenterologists in Mumbai like Dr Amit Maydeo who can give you the most accurate diagnosis of pancreatic cancer and treatment plan. Dr Amit Maydeo is associated with H N Reliance hospital Mumbai.
#pancreatic cancer#stomach ulcer#stomach cancer treatment#stomach cancer#stomach surgery#stomach pain#peptic ulcer#gastric ulcer
0 notes
Text
Unraveling the Signs of Liver Metastasis Symptoms
Liver metastasis refers to the spread of cancerous cells from another part of the body to the liver. It is a common occurrence in advanced stages of various types of cancers, including colorectal, breast, lung, and pancreatic cancers. Recognizing the symptoms of liver metastasis is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. In this article, we will explore the common signs and symptoms associated with liver metastasis.
Abdominal Discomfort and Pain:
One of the primary symptoms of liver metastasis is abdominal discomfort or pain. The pain may vary in intensity and can be felt as a dull ache, tenderness, or sharp twinges. The discomfort may be localized to the upper right side of the abdomen, where the liver is situated, or it may radiate to the back or right shoulder.
Jaundice:
Jaundice is a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes. Liver metastasis can obstruct the bile ducts, leading to a buildup of bilirubin in the body. This excess bilirubin can result in jaundice. Symptoms of jaundice include yellow skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, and itching.
Fatigue and Weakness:
Liver metastasis can cause fatigue and weakness due to the compromised liver function. The liver plays a vital role in metabolizing nutrients and removing toxins from the body. When cancer cells invade the liver, it hampers its ability to perform these functions efficiently, leading to fatigue, weakness, and a general decline in energy levels.
Unexplained Weight Loss:
Unintentional weight loss is a common symptom associated with advanced stages of cancer, including liver metastasis. Cancer cells can alter metabolism, leading to a loss of appetite and difficulty in maintaining a healthy weight. If you experience significant weight loss without a clear explanation, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Enlarged Liver:
As cancer spreads to the liver, it can cause hepatomegaly, or an enlarged liver. An enlarged liver may be palpable during a physical examination or observed through medical imaging tests. It can contribute to abdominal swelling or a feeling of fullness.
Nausea, Vomiting, and Digestive Issues:
Liver metastasis can disrupt normal digestion, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. The liver produces bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats. When the liver is affected by metastatic cancer, bile production may be impaired, resulting in gastrointestinal disturbances.
Fluid Buildup:
Liver metastasis can disrupt the liver's ability to maintain fluid balance in the body. As a result, fluid may accumulate in the abdomen, causing a condition called ascites. Symptoms of ascites include abdominal bloating, discomfort, and a visibly distended abdomen.
Liver metastasis can present with a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the extent of the cancer spread and the underlying primary cancer. Early detection and prompt medical intervention are crucial for better treatment outcomes. If you experience any persistent or concerning symptoms associated with liver metastasis, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate management.
0 notes
Text
Gallbladder and Biliary Diseases: Understanding, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Common Gallbladder and Biliary Diseases
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones):
Types: Cholesterol stones (most common), pigment stones (bilirubin).
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic; can cause biliary colic, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, and acute pancreatitis.
Risk Factors: Obesity, female gender, age, rapid weight loss, pregnancy, certain medications, and genetic predisposition.
Cholecystitis:
Acute Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder, usually due to gallstones blocking the cystic duct.
Chronic Cholecystitis: Long-standing inflammation, often associated with gallstones.
Symptoms: Severe right upper quadrant abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness over the gallbladder (Murphy's sign).
Choledocholithiasis:
Gallstones in the common bile duct.
Symptoms: Similar to cholelithiasis but can also cause bile duct obstruction, leading to jaundice and biliary colic.
Cholangitis:
Infection of the bile ducts, often due to obstruction by gallstones.
Symptoms: Charcot’s triad (fever, jaundice, right upper quadrant pain), and in severe cases, Reynolds’ pentad (Charcot’s triad plus hypotension and altered mental status).
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC):
Chronic disease causing inflammation and scarring of bile ducts.
Symptoms: Fatigue, pruritus (itching), jaundice, and complications like cirrhosis or liver failure.
Associations: Often linked with inflammatory bowel disease (especially ulcerative colitis).
Biliary Atresia:
A congenital condition where bile ducts are abnormally narrow, blocked, or absent.
Symptoms: Jaundice in newborns, dark urine, pale stools, and failure to thrive.
Treatment: Kasai procedure (hepatoportoenterostomy) and potentially liver transplantation.
Gallbladder Cancer:
Rare but often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Symptoms: Similar to gallbladder disease but can include weight loss, anorexia, and more persistent pain.

Diagnosis
Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound: First-line for detecting gallstones and assessing gallbladder inflammation.
CT Scan and MRI: Used for more detailed imaging, particularly in complicated cases.
HIDA Scan (Cholescintigraphy): Evaluates gallbladder function and bile flow.
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): Combines endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat bile duct disorders.
MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography): Non-invasive imaging of the biliary and pancreatic ducts.
Laboratory Tests:
Liver Function Tests: Elevated bilirubin, ALP, GGT, AST, and ALT suggest bile duct obstruction or liver involvement.
Complete Blood Count (CBC): Can indicate infection or inflammation.
Blood Cultures: Useful in cases of suspected cholangitis.
Treatment
Medications:
Antibiotics: For bacterial cholangitis or cholecystitis.
Pain Management: NSAIDs or opioids for pain relief.
Ursodeoxycholic Acid: May help dissolve certain types of gallstones.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures:
Cholecystectomy: Surgical removal of the gallbladder, often laparoscopic.
ERCP: Can remove stones from the common bile duct and place stents.
Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiography (PTC): Used for drainage or to relieve obstruction.
Biliary Bypass Surgery: For palliative treatment of biliary obstructions, often in cancer.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes:
Dietary Modifications: Low-fat diet to reduce symptoms.
Weight Management: Gradual weight loss to reduce risk of gallstones.
Conclusion
Gallbladder and biliary diseases can range from benign to serious conditions. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are vital to prevent complications and improve patient outcomes. If you experience any symptoms related to gallbladder or biliary issues, consult your healthcare provider promptly. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for managing chronic conditions and maintaining overall digestive health.
Important Information:
Conference Name: 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference
Short Name: 14GHUCG2024
Dates: December 17-19, 2024
Venue: Dubai, UAE
Email: [email protected]
Visit: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/
Call for Papers: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/submit-abstract/
Register here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/registration/
Exhibitor/Sponsor: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/exhibit-sponsor-opportunities/
Call Us: +12073070027
WhatsApp Us: +442033222718
1 note
·
View note
Text
When does Pancreatic Cancer show its early warning signs?
The development of malignant cells in the tissues of the pancreas, an organ in the abdomen that is essential for digestion and blood sugar management, results in pancreatic cancer. With only a 10% five-year survival rate, it is a very dangerous kind of cancer. Unfortunately, because pancreatic cancer sometimes doesn't show symptoms until it has progressed to other body areas, it is frequently difficult to diagnose early.
However, being aware of the early indicators of pancreatic cancer can assist raise the likelihood of early discovery, providing greater options for treatment and better results. The finest country in the world for treating pancreatic cancer is India. Understanding pancreatic cancer's early warning symptoms and its consequences in India are crucial.
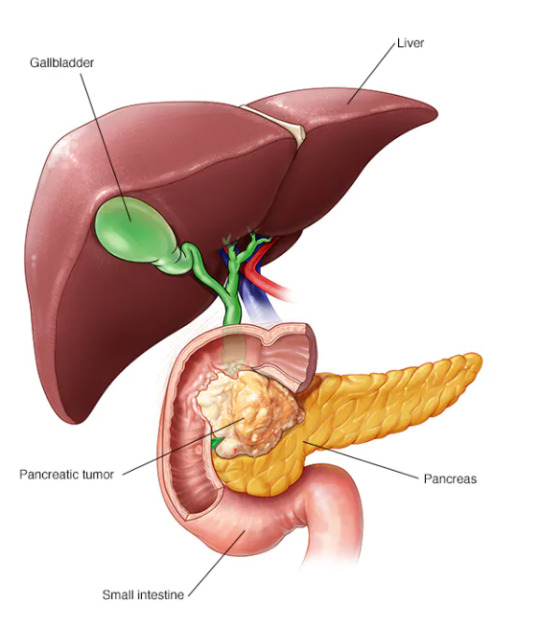
Pancreatic Cancer: An Overview
Your pancreas is around 6 inches or 15 centimetres long and resembles a pear flipped on its side. Your body produces (secretes) chemicals like insulin to help it metabolise the sugar in the meals you eat. It also produces digestive juices to help in the digestion of meals and nutrient absorption.
The Functions of the Pancreas
The pancreas generates enzymes that aid in the digestion of food and hormones such as insulin that regulate blood sugar levels. It is deep within the abdomen, behind the stomach.
Different Kinds Pancreatic Cancer
There are two forms of pancreatic cancer:
Exocrine tumors
Endocrine tumors
Out of which Exocrine tumours, account for around 95% of cases, grow in cells that manufacture digestive enzymes. Endocrine tumours, also known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (PNETs), arise from cells that create hormones.
The Cause of Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is the outcome of DNA alterations (mutations) in pancreatic cells. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell it what to do. These mutations give the cells the instructions to proliferate out of control and continue to exist after normal cells would die. As they accumulate, these cells may become a tumour.
The pancreas, a vital organ in the belly, is affected by pancreatic cancer, a dangerous and sometimes fatal condition. The likelihood of effective therapy increases with earlier pancreatic cancer detection. The importance of early detection and the early warning signals of pancreatic cancer will be covered in this blog.
Progression of Pancreatic Cancer
Although the primary aetiology of pancreatic cancer is unclear, various risk factors have been discovered. Age, family history, smoking and tobacco use, obesity and poor nutrition, chronic pancreatitis, and diabetes are all risk factors.
The Advantages of Early Detection
Early identification of pancreatic cancer can considerably improve treatment outcomes. When pancreatic cancer is detected early, it is more likely to be localised and treatable. Patients with early-stage pancreatic cancer have a substantially better chance of surviving than those with advanced illness.
Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection Challenges
One of the difficulties in detecting pancreatic cancer early is that the disease's early stages frequently do not present any symptoms. When symptoms occur, cancer may have already migrated to other regions of the body, making treatment more difficult.
Screening's Role in Early Detection
Screening techniques, such as imaging scans and blood testing, can aid in the early detection of pancreatic cancer. However, there is no standard pancreatic cancer screening test, and screening is often only suggested for patients who are at high risk for the illness.
Typical Early Warning Signs
Jaundice
It is a disorder in which the skin and eyes become yellow owing to bilirubin accumulation in the body. If the tumour is positioned in the head of the pancreas, where it might block the bile duct, this can be a symptom of pancreatic cancer.
Pain in the abdomen
One of the most prevalent signs of pancreatic cancer is abdominal discomfort. The discomfort is felt in the upper abdomen and might be severe or continual.
Unusual Weight Loss
Even if the person is eating appropriately, unexplained weight loss might occur. It's also a prevalent side effect of pancreatic cancer.
Appetite Suppression
Another symptom of pancreatic cancer is loss of appetite, which can be caused by a combination of causes such as pain and nausea.
Digestive Problems
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and constipation are all symptoms of pancreatic cancer.
Back Ache
If the tumour is in the body or the pancreas tail, back discomfort is a common symptom.
Pancreatic Cancer comes with multiple Risk Factors
Age: Pancreatic cancer risk increases with age, with most instances occurring in those over 60.
History of the Family: Those with a family history of pancreatic cancer are more likely to get the illness.
Tobacco Use and Smoking: Tobacco use and smoking are key risk factors for pancreatic cancer, with smokers being two to three times more likely than nonsmokers to get the illness.
Obesity and poor dietary habits: Obesity and a high-fat, processed-food diet have been related to an increased risk of pancreatic cancer.
Chronic pancreatitis: Prolonged pancreas inflammation increases the chance of developing pancreatic cancer.
Diabetes: Diabetics are at a slightly increased risk of acquiring pancreatic cancer.
Why is India the best place to seek treatment for pancreatic cancer?
India is well-known for having one of the greatest healthcare systems in the world. Indian Hospitals are outfitted with cutting-edge facilities and medical equipment, making them a popular destination for people seeking superior medical care. This is especially true for patients with pancreatic cancer, since India is home to some of the world's top pancreatic cancer treatment centres and specialists.
India is also recognised for valuing interdisciplinary treatment. This implies that patients are treated by a multidisciplinary team of professionals, including medical and surgical oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, and dietitians. This interdisciplinary approach guarantees that patients receive complete, individualised treatment that is customised to their specific need.
Furthermore, India is at the forefront of pancreatic cancer research, with many of its healthcare facilities conducting clinical trials and studies to create new and creative therapies. In India, patients have access to cutting-edge therapies like immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
Conclusion
India is one of the greatest places for pancreatic cancer treatment, with world-class hospitals, top doctors, and cutting-edge technology. Patients receive thorough and individualised therapy as a result of the emphasis on interdisciplinary care, while continuing research and clinical trials enable access to cutting-edge therapies. While the cost of therapy may be greater in India than in other countries, the quality of care and likelihood of success make it a top choice for patients seeking advanced pancreatic cancer treatment.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options
Pancreatic cancer affects the pancreas, and symptoms such as abdominal pain and weight loss may not appear until the cancer has spread. Risk factors include smoking, obesity, and family history. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
SYMPTOMS OF PANCREATIC CANCER
• Blood clots: Pancreatic cancer can increase the risk of developing blood clots, which can cause swelling, pain, and redness in the affected area.
• Dark urine: This can be a symptom of jaundice, which can occur when pancreatic cancer blocks the bile duct, leading to a buildup of bilirubin in the body.
• Pain in the abdomen: Pancreatic cancer can cause pain in the upper abdomen or back, which may be constant or intermittent.
• Digestive problems: These can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and loss of appetite, which can occur due to pancreatic cancer affecting the digestive system.
• Light-colored stools: This can be another symptom of jaundice, as it can cause the stools to become pale or clay-colored due to the lack of bilirubin being passed through the digestive system.
If you are experiencing the symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer and searching for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment in meerut, consider visiting Valentis Cancer Hospital. They provide top-notch treatment and services for cancer patients.

0 notes
Text
Gallstones:Facts and Definition
The hardening of the deposition of the digestive fluid in your gallbladder forms gallstones. The gold bladder is a pear-shaped organ on your abdomen's right side, just below your liver. The gallbladder releases a digestive fluid called bile into the small intestine.
Some gallstones can be significant as a golf ball or small as a grain of sand. Depending on the person, some may develop just one call stone or many gallstones. Treatment for gallstones Singapore is very simple.
Symptoms
The gallstones show no signs or symptoms during the early stage. However, if a stone causes a blockage in a duct, then there can be the following symptoms last from several minutes to a few hours.
• Sudden and immense pain in the upper right portion of the abdomen and the center of your abdomen just below the breastbone.
• Back pain between your shoulder blades.
• Pain in your right shoulder.
• Nausea or vomiting.
When to see a Doctor
If you have any doubts, you should immediately make an appointment with your doctor. Some of the gallstone complications include abdominal pain that is so intense that you cannot find a comfortable position. Yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes and high fever with chills also is an area of concern. Treatment of gallstones Singapore is common and does not require much time if there are no complications.
Causes
• Too much cholesterol: the cholesterol excreted by the liver is dissolved by the chemicals in the bile. If your liver excretes more cholesterol, the dissolving capacity of the bile, then the excess cholesterol crystallizes and forms stones.
• Too much bilirubin: bilirubin is also present in the gallbladder, which breaks down red blood cells. Under certain circumstances and conditions liver may produce axis bilirubin which contributes to gallstone formation.
• Gallbladder doesn't empty correctly: if your gallbladder is not empty entirely or if it does not empty as often as it should, then the bile concentration becomes dense, leading to the formation of gallstones.
Types of Gallstones
Cholesterol: cholesterol gallstones are the most common type that appears yellow. The composition of these stones is mainly dissolved in cholesterol but may also have other components.
Pigment: these types of gallstones appear brown or black, resulting from too much bilirubin in the bile.
Complications
• Gallstones that block the neck of the gallbladder cause bladder inflammation.
• It can even block the tubes or ducks through which the bile flows from the liver or gallbladder to your small intestine.
• Inflammation of the pancreas can occur due to the blockage of the pancreatic duct, leading to constant and immense abdominal pain that requires hospitalization and gallstone surgery Singapore.
• Those with a history of gallstones have an elevated risk of gallbladder cancer. But the chance is scarce.
Prevention
• The risk of the formation of gallstones can be reduced if the following preventive measures are taken:
• No skip of meals.
• If you want to lose weight, make it a slow process rather than a rapid one.
• Your diet should have fiber-rich food.
• Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as obese people have a higher chance of gallstone formation.
Gallstone surgery Singapore is ubiquitous in today's time. The surgery has zero to minimum complications that can be avoided if proper prevention and a healthy lifestyle are maintained.
0 notes
Text
What is pancreatic cancer? What are the symptoms and treatment methods? 2023
New Post has been published on https://bankakredin.com/what-is-pancreatic-cancer-what-are-the-symptoms-and-treatment-methods-2023/
What is pancreatic cancer? What are the symptoms and treatment methods? 2023
The pancreas is an organ that has very important functions in the body, located at the back of the abdomen and adjacent to the stomach, duodenum and large intestine, which is about 15 cm long. The pancreas ensures the digestion of the consumed foods and keeping the glucose obtained from these foods at the required levels in the blood. Apart from this, the smallest damage to the pancreas, which has many vital functions, can lead to consequences that affect the whole body.
What is pancreatic cancer?
Malignant masses that tend to proliferate in any part of the pancreas are called pancreatic cancer. Although cancers formed in this organ can develop in all parts of the organ, they most commonly spread in the head region. The most common type of pancreatic cancer is adenocarcinoma. Since adenocarcinoma originates from aggressive cells, it can progress rapidly and metastasize to surrounding tissues.
What are the symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
Pancreatic cancer can progress insidiously without any symptoms in its initial stages. However, the most common pancreatic cancer symptoms that started to appear in the later stages are; symptoms such as weight loss, abdominal pain, jaundice, loss of appetite, nausea-vomiting, weakness, fatigue, diarrhea, indigestion, back pain, glass paste-colored stools, pallor, sudden onset diabetes and depression without a family history. Rapid weight loss is seen in patients as a result of malnutrition along with bloating, indigestion and loss of appetite. One of the earliest and most common symptoms is jaundice. Initially, jaundice appears in the eyes, then yellowing of the skin, darkening of the urine color and turning into ‘tea-colored urine’, and finally results in an abnormal lightening of the stool color, defined as ‘glass paste’. The cause of jaundice is the inhibition of the excretion of bilirubin produced by the liver to the duodenum as a result of obstruction of the biliary tract by pancreatic cancer. While the pain is a mild discomfort, which is defined as vague abdominal pain, it takes the form of abdominal pain in the back in the future. It is blunt in nature. It is often associated with symptoms of bloating and indigestion. in the future, it takes the form of abdominal pain that hits the back. It is blunt in nature. It is often associated with symptoms of bloating and indigestion. in the future, it takes the form of abdominal pain that hits the back. It is blunt in nature. It is often associated with symptoms of bloating and indigestion.
What are the causes of pancreatic cancer?
Although the cause of the disease is unknown, it is more common in smokers and obese individuals. In almost 30% of patients, the cause of pancreatic cancer is smoking. Pancreatic cancer associated with adult diabetes is controversial. Having a family history of cancer is also among the causes of pancreatic cancer. The disease is more common in men than women, and the risk of developing this disease increases with age. The average age at catching pancreatic cancer worldwide is 63 for men and 67 for women.
How is pancreatic cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis can be difficult, especially in the early stages, as the disease presents with insidious symptoms. In patients who apply to the health institution in the early period, it is of great importance that the patient is well examined by the physician and that the necessary diagnostic tests are applied in order to diagnose the disease.
Ultrasonography: Ultrasonography is the first examination method to be applied in the suspicion of pancreatic cancer. The presence of a hard or cystic mass in the pancreas gives information about the size of the mass, its relationship with other surrounding structures, and its proximity to vascular structures.
Laboratory tests: Serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, liver transaminases and values such as CEA, CA19-9 and CA-125 were increased. Bilirubin in the urine is positive.
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MR): CT gives very important information about pancreatic tumors when taken orally and intravenously with contrast medication. It has a diagnostic feature of approximately 95% or more. MR imaging is also important in the differential diagnosis of the tumor. These two examinations can be used together when necessary, ensuring the correct results for the surgery decision to be given to the patient and the correct staging of the tumor.
Individuals diagnosed with the disease as a result of the tests should be evaluated in detail in terms of pancreatic cancer stages, and the treatment process should be started immediately after the stage of the disease is determined.
How is pancreatic cancer treated?
At the beginning of the process for pancreatic cancer treatment, at the end of physical examination, laboratory and radiological examinations, the stage of the pancreatic tumor, its relationship with neighboring organs, especially whether it has spread to adjacent vessels and/or distant organs, and the chance of surgical removal are evaluated. Surgery cannot be performed in advanced stage tumors. Along with the chemotherapy to be applied to these patients, some interventions can be applied to improve the comfort of life by correcting the existing jaundice, providing nutritional support and reducing pain. For this purpose, placing a tube (stent) that provides passage to the bile duct with endoscopy from the mouth through the stomach, draining the bile out with the help of a needle placed from the abdominal skin to the intrahepatic biliary tract with the help of a needle, advanced pain relief techniques,
Surgical Treatment: If the tumor is suitable for surgical removal, ‘Whipple surgery’ is performed. In addition, if the tumor is located in the body and tail of the pancreas, relatively easier resection methods can be applied. Surgical removal of the tumor is the only cure for these patients. In pancreatic head tumors, surgery is more complicated since it is not possible to surgically remove only the head of the pancreas. In Whipple surgery; Together with the head of the pancreas, the gallbladder, part of the main bile duct, duodenum, part of the stomach and surrounding lymph nodes are removed as a block.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy, also called radiotherapy, involves using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy only affects cells in the area being treated. Radiotherapy is applied alone or in combination with chemotherapy, especially if the location and size of the tumor complicates the surgery or in cases where surgery cannot be performed. Radiotherapy can be combined with chemotherapy to shrink the tumor before surgery. In some cases, radiotherapy may be given to prevent recurrences after surgery.
Chemotherapy: It is the use of anticancer drugs to kill cancer cells. In pancreatic cancers, drug treatment called chemotherapy can be applied, taking into account the general conditions of the patients before or after surgery. Chemotherapy may be used in conjunction with radiotherapy to shrink the tumor prior to surgery or as a primary treatment in place of surgery. Surgery and radiotherapy have no place in extensive advanced disease. By administering chemotherapy to this group of patients, their quality of life can be significantly improved.
after treatment
Survival: The chance of full recovery after surgery with early diagnosis is less than 50%. Anticancer drugs and radiation therapy increase the rate of recovery. However, survival rates are not good after surgeries that leave cancer cells behind or in cases where there is spread to neighboring organs.
Prevention: In order to prevent pancreatic cancer, it is necessary to stay away from tobacco, eat a balanced diet, do regular exercise and get rid of excess weight.
NOTE: The text here is a general information and may vary depending on the patient and the condition of the disease, so consult with a Medical Oncology specialist for personal evaluation.
what is pancreatic cancer,what are the signs that pancreatic cancer is getting worse,who is pancreatic cancer most common in,does pancreatic cancer,is pancreatic rest cancer,can you have pancreatic cancer without a tumor,can you have pancreatic cancer without symptoms,can you have pancreatic cancer for years without knowing,can you have pancreatic cancer and not know it,can you have pancreatic cancer without pancreatitis,how did i get pancreatic cancer,what type of pancreatic cancer is the worst,what is the end of pancreatic cancer like,what type of pancreatic cancer is curable,what is pancreatic cancer and how do you get it,how do i know what stage my pancreatic cancer is,how do you know what stage pancreatic cancer is,what happens when diagnosed with pancreatic cancer,has anyone cured pancreatic cancer,what do you die of with pancreatic cancer,
#can you have pancreatic cancer and not know it#can you have pancreatic cancer for years without knowing#can you have pancreatic cancer without a tumor#can you have pancreatic cancer without pancreatitis#can you have pancreatic cancer without symptoms#does pancreatic cancer#has anyone cured pancreatic cancer#how did i get pancreatic cancer#how do i know what stage my pancreatic cancer is#how do you know what stage pancreatic cancer is#is pancreatic rest cancer#what are the signs that pancreatic cancer is getting worse#what do you die of with pancreatic cancer#what happens when diagnosed with pancreatic cancer#what is pancreatic cancer#what is pancreatic cancer and how do you get it#what is the end of pancreatic cancer like#what type of pancreatic cancer is curable#what type of pancreatic cancer is the worst#who is pancreatic cancer most common in
0 notes
Text
Pencil thin stool

Infection with giardia lamblia produces a characteristic yellow diarrhea. Yellow stool can be the result of gallbladder dysfunction which causes improper handling of bile. Green can also be a sign of Crohn's disease, antibiotic use, ingestion of leafy greens or iron therapy. Green stool can occur with rapid transit through the intestines where bile doesn't have a chance to be broken down to its final brown color. While it should always be reported, it's not always an ominous sign. Red stool can also be caused by ingesting red food coloring or beets. Red stool is most worrisome as it indicates bleeding in the lower GI tract from conditions like hemorrhoids or diverticulosis, or more serious conditions like rectal cancer. Normal stool is brown due to its composition: bacteria, water, bile, bilirubin, broken-down red blood celIs and indigestible plant matter like cellulose, along with small amounts of protein and fat. The color of stool can vary dramatically and can also be a clue as to whether various disease states are present. For most people, smelly stool is simply a byproduct of the beans they had for dinner the night before. New onset of diarrhea associated with a foul odor should prompt an evaluation for infection, whereas fat in the stool associated with a foul odor should raise concerns about malabsorption or pancreatic disorders. Infection with parasites such as giardia lamblia can cause stool to have a very unpleasant odor. Both these conditions can result in floating, foul-smelling stool with an oily sheen.ĭiseases that cause malabsorption of nutrients like Crohn's, celiac disease and cystic fibrosis can also lead to foul-smelling stool. More lethal causes of malodorous stool, and fortunately much less common, include inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) and pancreatic cancer. Antibiotics can also change the smell of stool and give it a medicinal odor. The most common cause of smelly stool is bacterial fermentation of the food in your intestines that produces foul-smelling sulfide compounds. Bacterial imbalance (dysbiosis) in the GI tract and undigested fat can also lead to a change in odor. The odor of your stool is highly dependent on a number of factors, including how long it's been sitting in your colon, your diet, medications you may be taking and, in some cases, the presence of infection. Even though a fiber-deficient diet is the most likely culprit, colon cancer is again on the list as most lethal. A high-fiber diet or regular use of a bulking agent like psyllium husk will lead to larger, softer stools in most people, making defecation easier. Constipation is often associated with small, difficult-to-pass stools, and people suffering from constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are particularly prone to having small stools. Small, hard stools are typical in people eating a low-fiber Western diet, and are associated with a higher risk for ultimately developing diverticulosis and colon cancer. Colon cancer definitely needs to be excluded by a colonoscopy in anyone experiencing new onset of pencil-thin stools, which can occur as a tumor gets larger and grows inward, reducing the colonic diameter. Endometriosis, uterine fibroids, masses in the abdomen or tumors in other organs, like the ovaries or bladder, can cause thin stools due to external compression of the colon. Other associated symptoms of diverticulosis include a dull ache in the lower abdomen, a feeling of incomplete evacuation even though you may be having multiple bowel movements, and lots of gas and bloating. The result is narrow, pellet-like stools that often fall apart in the bowl and can be difficult to expel. Diverticulosis causes pothole-like craters in the lining of the colon, as well as a narrowing of the internal diameter of the colon due to wall thickening. Insufficient fiber in the diet, diverticulosis, bowel spasm or excessive straining are common causes of a change in stool shape. Here's a guide to some of the most likely – and most lethal – conditions that can lead to changes in the shape, size, smell and shade of your stool.

1 note
·
View note