#project and training in Embedded Linux with ARM
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Embedded Linux ARM
Embedded Linux: The Heart of Modern Devices Embedded Linux is a lightweight version of the Linux operating system, optimized for embedded systems- specially designed computing devices whose purpose is to be integrated into any hardware. Embedded Linux has been widely used in IoT devices, automotive systems, industrial automation, and more in the application mainly because of its elasticity and efficiency.

Embedded Linux is designed to run effectively within constrained resource environments unlike traditional operating systems. Another key advantage of Embedded Linux is that developers can customize the kernel and software stack according to specific hardware requirements. Its scalability and robust community support give access to a large number of libraries and tools, reducing development time and cost. Moreover, because of its real-time processing capabilities and multiple communication protocol support, it has received immense importance in robotics, medical appliances, and smart appliances. Through its Embedded Linux course, Emblogic offers comprehensive training to meet the ever-increasing demand for skilled professionals in this field. This hands-on program equips participants with the knowledge and skills required to work with Embedded Linux systems, covering essential topics like kernel programming, device drivers, and system optimization. Emblogic has designed its curriculum to be industry-aligned, ensuring students are adequately equipped to face real-world challenges in this exciting domain. Therefore, for fresh professionals, Embedded Linux and its training at Emblogic lead to richer career opportunities in developing embedded systems.
Embedded Linux with ARM, Embedded Linux with ARM training, Embedded Linux with ARM course, Embedded Linux with ARM online, Embedded Linux with ARM training online, Embedded Linux with ARM course online, Embedded Linux with ARM online training, Embedded Linux with ARM online course, project-based Training in Embedded Linux with ARM, project and training in Embedded Linux with ARM, Development Designing Embedded Linux with ARM, Learning Embedded Linux with ARM.
#Embedded Linux with ARM#Embedded Linux with ARM training#Embedded Linux with ARM course#Embedded Linux with ARM online#Embedded Linux with ARM training online#Embedded Linux with ARM course online#Embedded Linux with ARM online training#Embedded Linux with ARM online course#project-based Training in Embedded Linux with ARM#project and training in Embedded Linux with ARM#Development Designing Embedded Linux with ARM#Learning Embedded Linux with ARM
0 notes
Text
Transform Your Career with TechnoScripts’
Embedded Systems Training in Pune
Embedded systems are the backbone of upcoming modern technology, quietly running everything from your smartphone to the navigation system in your car. As industries like IoT, automotive, & healthcare expand, companies are seeking for engineers who can design, program, & troubleshoot these critical systems. But landing a role in this field or advancing in it needs a lot more knowledge. You need to stand out in interviews, build a strong online presence, and show employers you’re ready for real-world challenges. That’s where TechnoScripts, a leading embedded systems training institute in Pune, steps in. Their four-month Advance Career Track in Embedded Systems is built to equip both fresh graduates and seasoned professionals with the skills and tools to succeed. Here’s a look at the nine key features that make this program a standout: mock interviews, LinkedIn profile optimization, ATS-friendly resume crafting, 100% placement assistance, internship opportunities, flexible learning options, hands-on projects, professional profile building, and mentorship from industry veterans.
Why Choose Embedded Systems as a career?
Embedded systems make various technologies possible, & as innovation surges, so does the need for skilled engineers and Technoscripts is fulfilling that demand. In 2025, employers are finding talent who can tackle tasks like programming microcontrollers & integrating IoT solutions. But to get hired, you need to shine in 1000s of candidates. TechnoScripts’ program doesn’t just teach you the technical stuff it prepares you to navigate the job market with confidence.
Nine Features That Set TechnoScripts Apart
Mock Interviews: Sharpen Your Skills Job interviews for embedded systems roles can be intense, with questions ranging from embedded C coding to real-time operating systems. TechnoScripts offers mock interviews led by industry pros who’ve been on both sides of the table. These sessions feel like the real thing, covering technical challenges and HR-style questions. You’ll get feedback on how to explain your projects better or come across more confidently—think of it as a dress rehearsal for your dream job.
LinkedIn Optimization: Get Noticed Online Your LinkedIn profile is the 1st thing recruiters see. TechnoScripts helps you make it very sharp & professional, with a headline that gets attention (like “Embedded Systems Engineer Focused on IoT Innovation”) & a summary that tells your unique story & Skillset. You’ll learn to highlight skills like sensor integration or ARM programming and share project updates to build credibility. They even offer tips on connecting with industry folks, so your profile works for you 24/7.
ATS-Friendly Resumes: Pass the Digital Gatekeepers Ever sent out a resume and heard nothing back? Chances are, an Applicant Tracking System (ATS) filtered it out. TechnoScripts shows you how to create a resume that beats these systems by weaving in keywords like “embedded Linux” or “microcontroller design” naturally. They’ll guide you on structuring your experience to showcase projects and certifications clearly, ensuring your resume lands in front of a hiring manager.
100% Placement Assistance: Your Path to a Job TechnoScripts doesn’t just train you—they help you cross the finish line. Their placement team works tirelessly to connect you with top companies in the embedded systems space. From fine-tuning your resume to arranging campus recruitment drives, they’re your partner in the job hunt, giving you access to opportunities that match your skills and goals in Embedded Systems Course in Pune with Placement.
Internship Opportunities & the Real-World Experience Nothing impresses employers like hands-on experience. TechnoScripts provides internship letters that open doors to roles where you might code IoT software or debug hardware systems. These internships let you apply what you’ve learned and give you stories to share in interviews—like the time you fixed a tricky sensor issue. That kind of experience makes your resume pop.
Flexible Learning Options: Fit Training Into Your Life Whether you’re a student or a working professional, TechnoScripts makes learning accessible. You can attend in-person classes at their Pune facility, where you’ll work with real hardware and collaborate with peers, or opt for online sessions that are just as engaging. With early morning, evening, and weekend batches, you can balance training with your busy schedule.
Hands-On Projects: Build What Matters This program is all about doing. You’ll work on at least two live projects, like creating an IoT device or programming a microcontroller to manage sensors. These projects mirror real job tasks, teaching you how to solve problems under pressure. Plus, they give you something concrete to show employers, proving you can handle the challenges they care about.
Professional Profile Building: Stand Out in the Crowd In a competitive market, a polished professional profile can set you apart. TechnoScripts helps you craft one that highlights your skills, projects, and the certificate you’ll earn. They’ll coach you on presenting your work—like a project where you integrated a sensor array—in a way that catches employers’ eyes, making you a top candidate.
Mentorship from Industry Experts: Learn from the Best The instructors at TechnoScripts aren’t just teachers—they’ve built real products and solved real problems in the embedded systems world. They’ll guide you through complex topics like embedded C or IoT protocols, sharing insights you won’t find in textbooks. Their mentorship prepares you for the realities of the job, not just the theory.
Why TechnoScripts Stands Out
The Embedded Course in Pune covers 12 modules, from digital electronics to advanced IoT and embedded Linux, all taught through hands-on practice. With flexible training, real-world projects, and a strong placement record, TechnoScripts ensures you’re ready for the industry. Their mentors, who’ve worked on cutting-edge systems, bring practical knowledge that bridges the gap between learning and doing.
How to Get Started
Ready to jump in? Visit TechnoScripts’ website or reach out to their admissions team for details on batches, fees, and enrollment. They offer regular and fast-track options, plus schedules tailored for working professionals, so you can find what works for you.
Final Thoughts
The embedded systems industry is brimming with opportunity, but breaking in requires the right preparation. TechnoScripts’ Embedded Systems Course in Pune delivers the technical skills and career tools you need—from mock interviews to hands-on projects and expert mentorship. Enroll now to start building a career that makes an impact in this fast-growing field.
0 notes
Text

Top 10 Skills You’ll Learn in an Embedded System Development Course in India
Today, with advanced technology in every field, the world has taken a big step toward creating new industries and innovations. It is one of the most challenging and exciting fields, and it's worth investing in by enrolling in an embedded system development course in India. The knowledge and skills gained are useful for outstanding performance in various domains such as IoT, robotics, and automotive technology. Here, we look at the top 10 skills you would learn in an embedded system development course, including a fascinating project initiative, TechnosCOE.
1. Familiarity with Microcontrollers and Microprocessors
Microcontrollers and microprocessors are the foundation base for embedded systems. Courses include architecture, functioning, and programming, with hands-on experience in popular controllers such as Arduino, PIC, and ARM, which form the backbone of most embedded applications.
2. Programming Languages
One of the main emphases of an embedded system development course in India is acquiring skills in programming languages such as C and C++. These skills are essential to writing firmware and developing applications for embedded systems. It also makes some courses introduce Python for scripting and debugging purposes to improve a student's versatility.
3. Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS)
The creation of efficient and reliable systems is based on the understanding of how RTOS works. These courses cover the principles of multitasking, scheduling, and inter-process communication. By mastering RTOS concepts, students can develop systems for industries such as telecommunications and healthcare.
4. Circuit Design and PCB Development
These contain custom circuitry designs and a printed circuit board (PCB). The knowledge gained from developing circuitry robust and efficient within Eagle and Altium Designer gives immense value toward the prototyping and product development phase.
5. Sensor integration and data acquisition
Modern embedded systems interact with the physical world through sensors. Courses teach students how to integrate sensors, process their data, and use it in meaningful ways. Applications include temperature monitoring, motion detection, and environmental sensing, among others.
6. IoT (Internet of Things) Development
IoT has changed the face of industries, and at the center of this change is the concept of embedded systems. Students are taught to design devices that are internet-enabled, which can talk to other devices, and perform analytics in real-time data. The same skill can be applied to smart home automation and industrial applications.
7. Embedded Linux
Training on Embedded Linux is generally a part of an embedded system development course in India. It is a highly versatile and widely used open-source software in the world of embedded systems. A student learns how to develop applications, configure the kernel, and build custom distributions for different types of devices.
8. Debugging and Testing Techniques
Debugging is a key tool in embedded system development. Students become experts in using tools like JTAG debuggers and oscilloscopes to identify and debug those issues. Techniques on testing address all the requirements for the performance and safety of the system.
9. Communication Protocols
Understanding communication protocols is very important to the embedded engineers. The curriculum covers some popular protocols such as I2C, SPI, UART, CAN, and Ethernet, which are usually used in applications such as car systems and automation in industrial places.
10. Project Management and Documentation
Beyond technical skills, students also learn project management techniques and documentation practices. These soft skills ensure that they can efficiently collaborate with teams, manage timelines, and maintain accurate records of their work.
Role of TechnosCOE in Embedded Learning
Most embedded system courses include real-world projects that allow students to apply their skills practically. TechnosCOE is one such project, an initiative designed to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. TechnosCOE offers students opportunities to work on cutting-edge projects involving IoT, robotics, and smart devices.
This initiative focuses on teamwork, innovation, and problem-solving, ensuring learners are industry-ready. Through the TechnosCOE, students are exposed to real-world challenges and learn how to apply embedded system principles to develop effective solutions.
Why Choose an Embedded System Development Course in India?
India is turning out to be a fast-growing hub for embedded technology. Industries like automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics will have a vast number of opportunities. Embedded system development courses offered in India will ensure expert faculty members, state-of-the-art labs, and industrial collaborations. They also offer internship and placement support, which proves to be perfect for career growth.
Conclusion
The course on embedded system development course in India not only gives the students technical expertise but also prepares them for dynamic and rewarding careers. Mastering microcontrollers to developing IoT solutions, these skills are invaluable in today's technology-driven world. Initiatives like TechnosCOE further enhance the learning experience, making these courses a worthwhile investment for aspiring engineers.
0 notes
Text
Emertxe Embedded Systems Online Course – A Gateway to a Thriving Career

Are you looking to kickstart your career in embedded systems but don't have the time to attend traditional classroom-based courses? Emertxe's Embedded Systems Online Course offers the perfect solution to gain in-depth knowledge and practical experience in this rapidly growing field from the comfort of your home.
Why Choose Emertxe’s Embedded Systems Online Course?
Emertxe is a leading provider of embedded systems training, offering specialized online courses designed to bridge the gap between academic knowledge and industry requirements. With its embedded systems online program, you can gain expertise in key areas such as microcontrollers, real-time operating systems (RTOS), device drivers, communication protocols, and much more.
Here’s why Emertxe’s embedded systems online course stands out:
1. Industry-Recognized Curriculum
Emertxe’s course content is developed in collaboration with industry experts and aligned with the latest trends and technologies in embedded systems. The online embedded systems program includes everything from the basics to advanced topics, ensuring that you are well-prepared for industry challenges.
2. Hands-on Learning Experience
Emertxe’s online embedded systems course focuses heavily on practical learning. You will work on real-time projects, assignments, and simulations that help solidify your understanding and improve your problem-solving skills. Emertxe’s online platform makes it easy to access tutorials, lab sessions, and code examples anytime, anywhere.
3. Experienced Trainers
Learn from highly qualified instructors who have hands-on experience in embedded systems development. Emertxe’s trainers are industry veterans who share their insights and guide you through the complexities of embedded system design and implementation.
4. Flexible Learning Pace
One of the key advantages of the Emertxe embedded systems online course is the flexibility it offers. You can learn at your own pace, revisit lessons whenever needed, and balance your studies with personal and professional commitments.
5. Job Placement Assistance
Emertxe provides placement assistance to its students. With its strong industry connections and a network of partner companies, Emertxe helps students get placed in top tech companies. Graduates of the online embedded systems program are highly sought after for roles such as Embedded Engineer, Firmware Developer, and Hardware Design Engineer.
Key Topics Covered in Emertxe’s Embedded Systems Online Course
Introduction to Embedded Systems: Learn the fundamentals of embedded systems, including their applications in various industries like automotive, consumer electronics, healthcare, and more.
Microcontroller Programming: Get hands-on experience in programming microcontrollers like ARM and AVR to build embedded solutions.
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS): Dive into RTOS concepts such as task scheduling, inter-process communication, and memory management to design responsive embedded systems.
Embedded C and C++ Programming: Master the core languages used in embedded systems programming and develop efficient, resource-constrained applications.
Device Drivers and Communication Protocols: Learn to develop device drivers and implement protocols like UART, SPI, I2C, and CAN to ensure seamless communication between components in embedded systems.
Embedded Linux: Explore the power of Linux in embedded systems and understand how to work with Linux kernel, drivers, and file systems.
Career Opportunities After Completing Emertxe’s Embedded Systems Online Course
Graduating from Emertxe’s embedded systems online program opens the doors to a wide range of career opportunities. The demand for skilled embedded systems professionals is soaring in sectors like automotive, aerospace, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. Emertxe’s curriculum equips you with the expertise needed to take on roles such as:
Embedded Systems Engineer
Firmware Developer
Embedded Software Developer
Hardware Engineer
Embedded Systems Consultant
How to Enroll in Emertxe’s Embedded Systems Online Course
Enrolling in the Emertxe embedded systems online course is simple. Visit the Emertxe website, select the online course option, and follow the easy steps to complete your registration. With flexible payment plans and a dedicated support team, Emertxe ensures that the entire process is smooth and hassle-free.
Final Thoughts
Emertxe's embedded systems online course is the perfect way to build a solid foundation in embedded systems while balancing your existing commitments. With a comprehensive curriculum, hands-on projects, and job placement assistance, Emertxe ensures that you are ready to take on exciting career opportunities in embedded systems development.
Ready to kickstart your career in embedded systems? Visit Emertxe Embedded Systems Online Course and enroll today!
0 notes
Text
Mixtile Edge 2 Kit– AI based bee detection and tracking
Here I describe usage of Mixtile Edge 2 Kit in agriculture, bee detection, which can be essential for health and survival of bees.
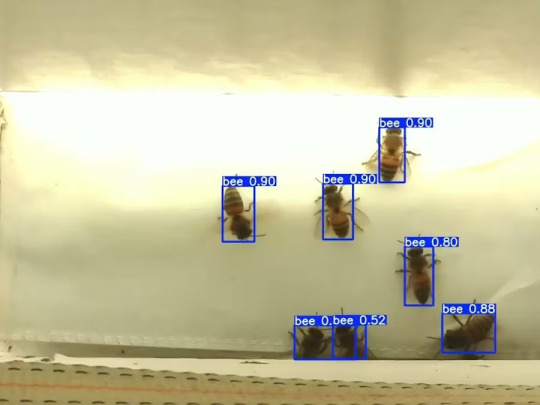

Story

Mixtile is professional IoT hardware solution provider specialized in Linux and Android-based embedded systems.Mixtile Edge 2 Kit is high-performance ARM single board computer. It comes in variants of 2GB of LPDDR4 DRAM and 16GB eMMC Flash storage, or 4GB of LPDDR4 DRAM and 32GB eMMC Flash storage. This single board computer comes with preinstalled Android 11, and it runs Ubuntu Linux operating system in Android container. It comes with large connectivity options (Bluetooth, 4G/5G Cellular, GPS, and Lora, Zigbee and Z-Wave). For those, you will need module, but it comes with default onboard Wi-Fi connectivity, Gigabit Ethernet Port (RJ45) and Serial Port (RS-485). Because it comes with RS-485 port, which is industrial standard, and it comes within a strong metal case, it seems to me that it can be really used in industrial projects. I used official Raspberry Pi 5 power supply in order to power up my Mixtile Edge 2 Kit.So, an idea came to me why not to use it in agriculture, bee detection, which can be essential for health and survival of bees.This project will cover setting up Mixtile Edge 2 Kit, and custom photo dataset form video in order to train custom YOLOv5 bee detection model. YOLOv5 models must be trained on labelled data in order to learn classes of objects in that data.I gathered data from video and trained model on my PC.To train a model, I used python and typed in command line:
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights best.pt
My training results are summarized in the following table:
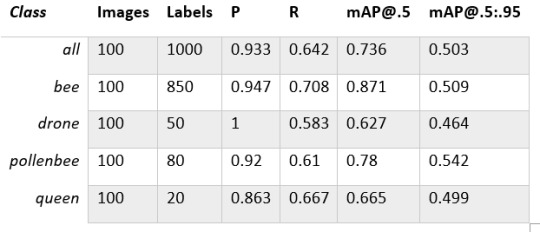
Training results
From this table you can see that images are divided into 4 detection classes:
Bee
Drone
Pollenbee
Queen
Example for each class is summarized in a table below:

Bee classes
1. Getting started
First, I will write about software part of the project, and later on steps of starting the recognition.
1.1 What is YOLOv5?
If you have been in the field of machine learning and deep learning for some time now, there is a high chance that you have already heard about YOLO. YOLO is short for You Only Look Once. It is a family of single-stage deep learning-based object detectors. It was written using Python language, and the framework used is PyTorch.
To ease control, I connected usb mouse to the one of three Mixtile Edge 2 Kit USB3 port. I used Ubuntu Linux for this project. Ubuntu on container is installed in Android system of Mixtile Edge 2 Kit by default. When you boot Mixtile Edge 2 Kit, you get Android OS. Since I wanted to access Edge 2 Kit remotely, and get easier control, I installed droidVNC server from this link:
It is an Android VNC server using Android 5+ APIs. It does not require root access.
I started the VNC server, connected with VNC Viewer and I got the following Android 11 screen:

Android 11
After that, I installed SimpleSSHD from this link:
SimpleSSHD is a SSH server Android app, based on Dropbear.It allows user access (user ssh) or full root access (by setting the login shell to /system/xbin/su) (if root is allowed).
After I installed SSH server, I connected to it via putty SSH terminal. Username and Password are root/root.
Com.hubware.ubuntu is ubuntu on a container and we are connected to it immidiately.
Now we are going to install required software.
First, you will need to upgrade Ubuntu by typing in the command: apt-get upgrade.
Second, I installed python by typing: apt-get install python.
You will also need pip, the package installer for Python.
2. Installing the YOLOv5 Environment
To start off we first clone the YOLOv5 repository and install dependencies. This will set up our programming environment to be ready to running object detection training and inference commands.
Install git: apt-get install git
Clone YOLOv5 repository:
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
Move to YOLOv5 folder:
cd yolov5
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Wait some time to download and install all requirement packages, I waited 25 minutes, because there are a lot of python packages to install besides YOLOv5. YOLOv5 needs numpy package, scipy, OpenCV, etc.
The putty connection and installation process looks like below:
I transferred my model best.pt to the yolov5 installation folder via SCP, with MobaXterm.
You can simply download my model immidiate by typing:
wget https://github.com/sdizdarevic/beedetectionyolov5/raw/main/best.pt
Also, download original video by typing:
wget https://sdizdarevic.typepad.com/cr/bees-orig.mp4
Now, the final step is detection, and we are interested in the “result” content video.
python3 detect.py --weights best.pt --source bees-orig.mp4
The process of detection looks like below:

In the last lines from last picture we can see the detected number of bees at any point in time.
The summarized short steps to follow are below:
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
cd yolov5
pip install -r requirements.txt
wget https://github.com/sdizdarevic/beedetectionyolov5/raw/main/best.pt
wget https://sdizdarevic.typepad.com/cr/bees-orig.mp4
python3 detect.py --weights best.pt --source
Demonstrated videos are on urls with detection finished completely on Mixtile Edge 2 Kit. Output video is in folder runs/detect/exp2.
Original video:
youtube
Result video:
youtube
Last, but not less important: If you want to safely turn off your Mixtile Edge 2 Kit, I recommend you to install Shutdown (no Root) application: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.samiadom.Shutdown&hl=en.
3.Conclusion:
After testing I found out that the Mixtile Edge 2 Kit is designed with wide range of applications, from industrial applications, IOT devices, smart home automation, to more than capable AI and edge detection. It is low powered device, with a lot of built-in connectivity options.
I would like to thank amazing Mixtile people for creating this amazing peace of hardware and especially for sending me the Mixtile Edge 2 Kit. Also, Mixtile nurtures the open source values and software, and I believe more people and companies will be involved in making projects with this board.
All in all, I recommend this board for implementing types of projects I described here.
0 notes
Text
Unlock Your Potential with Embedded Systems Training at IPCS Global
Introduction: In today’s tech-driven world, the demand for skilled professionals in embedded systems is constantly growing. From smartphones to medical devices, embedded systems play a crucial role in powering various electronic devices. If you’re looking to kickstart or advance your career in this exciting field, IPCS Global offers comprehensive embedded systems training programs designed to equip you with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Why Choose IPCS Global for Embedded Systems Training? 1. Industry Expertise: IPCS Global brings years of experience and expertise in providing training in embedded systems. With a team of seasoned professionals, you can rest assured that you’re learning from the best in the industry.
2. Hands-On Learning: Our training programs focus on practical, hands-on learning experiences. You’ll have access to state-of-the-art labs equipped with the latest hardware and software, allowing you to gain real-world experience and develop practical skills.
3. Customized Curriculum: At IPCS Global, we understand that one size doesn’t fit all. That’s why our training programs are tailored to meet the specific needs and requirements of our students. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional looking to upskill, we have a program for you.
4. Industry-Relevant Projects: As part of our training programs, you’ll have the opportunity to work on industry-relevant projects. This not only enhances your learning experience but also gives you valuable insights into the real-world applications of embedded systems.
5. Expert Faculty Support: Our team of expert faculty members are dedicated to helping you succeed. With their guidance and mentorship, you’ll be able to overcome challenges and achieve your goals in embedded systems.
Training Programs Offered: 1. Embedded Systems Design 2. Embedded C Programming 3. ARM Microcontroller Programming 4. IoT (Internet of Things) Development 5. Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) 6. Embedded Linux Development 7. PCB Design and Fabrication
Who Can Benefit from Our Training Programs? - Engineering Students - Electronics and Communication Professionals - IT Professionals looking to switch careers - Entrepreneurs looking to venture into the embedded systems domain
Conclusion: Embark on a rewarding career journey in embedded systems with IPCS Global. Our comprehensive training programs, industry expertise, and hands-on learning approach ensure that you’re well-equipped to meet the demands of the ever-evolving technology landscape. Take the first step towards unlocking your potential today!
For more information and to enroll in our training programs, visit our website or contact us directly. Let IPCS Global be your gateway to success in the exciting world of embedded systems.
0 notes
Text
This Week in Rust 528
Hello and welcome to another issue of This Week in Rust! Rust is a programming language empowering everyone to build reliable and efficient software. This is a weekly summary of its progress and community. Want something mentioned? Tag us at @ThisWeekInRust on Twitter or @ThisWeekinRust on mastodon.social, or send us a pull request. Want to get involved? We love contributions.
This Week in Rust is openly developed on GitHub and archives can be viewed at this-week-in-rust.org. If you find any errors in this week's issue, please submit a PR.
Updates from Rust Community
Official
Announcing Rust 1.75.0
Project/Tooling Updates
Rustdoc JSON in 2023
2023 in Review: Establishing Rust as a Godot 4 language
Rust9x update: Rust 1.76.0-beta
Announcing smol-macros, smol-hyper and smol-axum
Rust Language Bootstrap Team Progress Report 2023
gitoxide: The year in retrospective, and what's to come
Observations/Thoughts
A few fast solutions for Advent of Code 2023
An Update on Writing Memory Safety Bugs
Testing Your Embedded Rust
avatar.png
Arc vs String, is Arc really faster?
Iggy.rs - building message streaming in Rust
Getting Started with Loco in Rust: Part 1
Printing errors in Rust
[video] Rust 1.75.0: 54 highlights in 20 minutes!
Miscellaneous
Test command line application written in Rust
Open Source Applications written in Rust
Prompt - read input from Standard Input (STDIN) in Rust
Testing Your Embedded Rust (feat. embedded-hal-mock and explosions)
[video] Rust Release Train 1.75
[video] Rust 1.75.0: 54 highlights in 20 minutes
Crate of the Week
This week's crate is fast_pool, a fast async pool based on the flume channel crate.
Thanks to zhuxiujia for the self-suggestion!
Please submit your suggestions and votes for next week!
Call for Participation; projects and speakers
CFP - Projects
Always wanted to contribute to open-source projects but did not know where to start? Every week we highlight some tasks from the Rust community for you to pick and get started!
Some of these tasks may also have mentors available, visit the task page for more information.
* Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Implement Code cov for local system using makefile * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Setup code coverage for local tests & CI * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Add domain type for client secret * Hyperswitch - [FEATURE]: Have get_required_value to use ValidationError in OptionExt
If you are a Rust project owner and are looking for contributors, please submit tasks here.
CFP - Speakers
Are you a new or experienced speaker looking for a place to share something cool? This section highlights events that are being planned and are accepting submissions to join their event as a speaker.
If you are an event organizer hoping to expand the reach of your event, please submit a link to the submission website either through a PR to TWiR or on the [Rust-lang forums].[link TBD]
Updates from the Rust Project
194 pull requests were merged in the last week
rustc_lint: Enforce rustc::potential_query_instability lint
rustc_lint: Prevent triplication of various lints
unused_bindings: also walk bindings created by if-let guards
change rustc_codegen_ssa's atomic_cmpxchg interface to return a pair of values
coverage: avoid a possible query stability hazard in CoverageCounters
coverage: prepare mappings separately from injecting statements
coverage: unexpand spans with find_ancestor_inside_same_ctxt
don't drop a hir node after lowering
don't suggest writing a bodyless arm if the pattern can never be a never pattern
don't validate / lint MIR before each pass
enable profiler in dist-powerpc-linux
fix infinite loop in <BoundConstness as Display>
fix invalid check-cfg Cargo feature diagnostic help
fix parenthesization of subexprs containing statement boundary
fix: correct the args for disambiguate the associated function diagnostic
fix: diagnostic for casting reference to slice
introduce const Trait (always-const trait bounds)
simplify Parser::ident_or_error
simplify bootstrap --check-cfg arguments
solaris support on bootstrap lock
subtree sync for rustc_codegen_cranelift
suggest => → >= in comparisons
utilize the unused llvm-tools option
miri: fix integer overflow ICEs from round_up_to_next_multiple_of
miri: NaN non-determinism for intrinsics and libm functions
miri: support for tempfile crate on UNIX hosts
implement constant propagation on top of MIR SSA analysis
only store StableCrateId once in DefPathTable
shrink span encoding further
openbsd: available_parallelism: use the right API
cargo: cargo add - fix for adding features from repository with multiple packages
cargo: cargo fix: always inherit the jobserver
cargo: fix fix::fix_in_dependency to not rely on rustc
cargo: rustfix: support inserting new lines
rustdoc-search: count path edits with separate edit limit
rustdoc: treat query string + as space
clippy: check for redundant matches! with Ready, Pending, V4, V6
clippy: [doc_markdown]: Add "WebGL2", "WebGPU" to default doc_valid_idents
clippy: add external macro checks to iter_without_into_iter and into_iter_without_iter
clippy: don't lint default_numeric_fallback on return and local assigned macro calls with type stated
clippy: extend unconditional_recursion to check for ToString implementations
clippy: add manual_is_variant_and lint
clippy: add new lint pub_underscore_fields
clippy: suggest str.lines when splitting at hard-coded newlines
clippy: make mutex_atomic more type aware
clippy: new lint: empty_enum_variants_with_brackets
clippy: new lint: thread_local_initializer_can_be_made_const
clippy: new lint: eager_transmute
clippy: remove mitigations for incorrect node args
rust-analyzer: fix SyntaxContextID using incorrect self IDs
rust-analyzer: fix out-of-bounds panic in some macros due to unhandled self_ref
Rust Compiler Performance Triage
Overall, this week had very few regressions and a moderate amount of improvements. The two biggest improvements came in how metadata was being encoded including a change to only store StableCrateId once in DefPathTable which yielded a 0.3% average improvement across 79 different benchmarks.
Triage done by @rylev. Revision range: 1ab783112..67b6975
Summary:
(instructions:u) mean range count Regressions ❌ (primary) 0.7% [0.3%, 1.5%] 8 Regressions ❌ (secondary) 0.8% [0.2%, 1.3%] 23 Improvements ✅ (primary) -0.6% [-2.6%, -0.2%] 121 Improvements ✅ (secondary) -5.2% [-62.5%, -0.2%] 53 All ❌✅ (primary) -0.5% [-2.6%, 1.5%] 129
2 Regressions, 3 Improvements, 1 Mixed; 0 of them in rollups 46 artifact comparisons made in total
Full report here
Approved RFCs
Changes to Rust follow the Rust RFC (request for comments) process. These are the RFCs that were approved for implementation this week:
No RFCs were approved this week.
Final Comment Period
Every week, the team announces the 'final comment period' for RFCs and key PRs which are reaching a decision. Express your opinions now.
RFCs
No RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Tracking Issues & PRs
[disposition: merge] rustdoc: search for tuples and unit by type with ()
Language Reference
No Language Reference RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
Unsafe Code Guidelines
No Unsafe Code Guideline RFCs entered Final Comment Period this week.
New and Updated RFCs
RFC: New range types for Edition 2024
Add RFC to discuss RustConf 2024 Steering Committee
Call for Testing
An important step for RFC implementation is for people to experiment with the implementation and give feedback, especially before stabilization. The following RFCs would benefit from user testing before moving forward:
No RFCs issued a call for testing this week.
If you are a feature implementer and would like your RFC to appear on the above list, add the new call-for-testing label to your RFC along with a comment providing testing instructions and/or guidance on which aspect(s) of the feature need testing.
Upcoming Events
Rusty Events between 2024-01-03 - 2024-01-31 🦀
Virtual
2024-01-03 | Virtual (Indianapolis, IN, US) | Indy Rust
Indy.rs - with Social Distancing
2024-01-06 | Virtual (Kampala, UG) | Rust Circle
Rust Circle Meetup
2024-01-09 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Second Tuesday
2024-01-11 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-01-11 | Virtual (Nürnberg, DE) | Rust Nuremberg
Rust Nürnberg online
2024-01-16 | Virtual (Washington, DC, US) | Rust DC
Mid-month Rustful
2024-01-17 | Virtual (Vancouver, BC, CA) | Vancouver Rust
Rust Study/Hack/Hang-out
2024-01-21 | Virtual | Rust Maven
Web development with Rocket - In English
2024-01-23 | Virtual (Halifax, NS, CA) | Rust Halifax
Rust&Tell - Halifax
2024-01-24 | Virtual (Berlin, DE) | WeAreDevelopers Community
WeAreDevelopers LIVE - Rust Day
2024-01-25 | Virtual (Charlottesville, NC, US) | Charlottesville Rust Meetup
Crafting Interpreters in Rust Collaboratively
2024-01-28 | Virtual (Wrocław, PL) | Stacja IT Wrocław
Wprowadzenie do języka Rust
2024-01-30 | Virtual (Buffalo, NY, US) | Buffalo Rust User Group
Buffalo Rust User Group
2024-01-30 | Virtual (Dallas, TX, US) | Dallas Rust
Last Tuesday
Europe
2024-01-10 | Cologne, DE | Rust Cologne
Game development in Rust
2024-01-11 | Reading, UK | Reading Rust Workshop
Reading Rust Meetup at Browns
2024-01-11 | Wrocław, PL | Rust Wrocław
Rust Meetup #36
2024-01-13 | Tampere, FI | Finland Rust-lang Group
January Meetup
2024-01-16 | Leipzig, DE | Rust - Modern Systems Programming in Leipzig
Async in Rust
2024-01-17 | Praha / Prague, CZ | Rust Prague
Rust Meetup Renewed
2024-01-17 | Zurich, CH | Rust Zurich
How to Community - January Meetup
2024-01-23 | Aarhus, DK | Rust Aarhus
Hack and Learn
North America
2024-01-06 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Beacon Hill Rust Lunch
2024-01-08 | Chicago, IL, US | Deep Dish Rust
Rust Hack Night
2024-01-09 | Seattle, WA, US | Cap Hill Rust Coding/Hacking/Learning
Rusty Coding/Hacking/Learning Night
2024-01-09 | Minneapolis, MN, US | Minneapolis Rust Meetup
Minneapolis Rust Meetup Happy Hour
2024-01-09 | New York, NY, US | Rust NYC
Rust NYC Monthly Meetup: A Deep Dive into Tower by Adrien Guillo
2024-01-14 | Cambridge, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Alewife Rust Lunch
2024-01-16 | San Francisco, CA, US | San Francisco Rust Study Group
Rust Hacking in Person
2024-01-17 | Chicago, IL, US | Deep Dish Rust
Rust Happy Hour
2024-01-18 | Seattle, WA, US | Seattle Rust User Group
Seattle Rust User Group Meetup
2024-01-22 | Boston, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
North End Rust Lunch
2024-01-24 | Austin, TX, US | Rust ATX
Rust Lunch - Fareground
2024-01-30 | Cambridge, MA, US | Boston Rust Meetup
Harvard Square Rust Lunch
If you are running a Rust event please add it to the calendar to get it mentioned here. Please remember to add a link to the event too. Email the Rust Community Team for access.
Jobs
Please see the latest Who's Hiring thread on r/rust
Quote of the Week
Some people don't believe in life after death... Rust doesn't believe in magic after compilation.
– Stephan Sokolow on rust-users
Thanks to Todd Fleming for the suggestion!
Please submit quotes and vote for next week!
This Week in Rust is edited by: nellshamrell, llogiq, cdmistman, ericseppanen, extrawurst, andrewpollack, U007D, kolharsam, joelmarcey, mariannegoldin, bennyvasquez.
Email list hosting is sponsored by The Rust Foundation
Discuss on r/rust
1 note
·
View note
Text
IAR fully supports Infineon's latest TRAVEO T2G CYT6BJ body control MCU family products

According to the information received by Lansheng Technology, it has fully supported the latest CYT6BJ series in Infineon's TRAVEO™ T2G body control MCU family. IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm is a complete embedded development solution, equipped with highly optimized compiler and build tools, code analysis tools C-STAT and C-RUN, and powerful debugging functions. This enables developers working on complex automotive body electronics applications to take full advantage of the features of the TRAVEO™ T2G MCU to create innovative designs with high code quality. IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm supports AUTOSAR and provides a functional safety version to help customers accelerate product certification.
Clara Volkmar, Director Product Marketing Body and Driver Information, Infineon's Automotive Division, said: "Infineon's TRAVEO™ T2G microcontrollers provide a compact solution to meet the needs of modern automotive body electronics systems and can take advantage of IAR Professional and suitable third-party development tools such as Embedded Workbench for Arm to achieve efficient development. Thanks to such a powerful tool partner as IAR, developers can quickly realize their demanding automotive applications even with our latest CYT6BJ series chips project."
By supporting all available TRAVEO™ T2G series chips, including the latest CYT6BJ series, IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm ensures compatibility and provides developers with highly optimized build tools and advanced debugging features: such as complex code and data interrupts Points, runtime stack analysis, call stack visualization, code coverage analysis, and integrated monitoring of power consumption contribute to a seamless development experience. With the code analysis tools C-STAT and C-RUN, developers can fully control the code quality.
For companies with functional safety requirements, IAR Embedded Workbench for Arm offers a functional safety version certified by TÜV SÜD (certified according to ISO 26262 requirements). This functional safety version is also certified according to IEC 61508, IEC 62304, EN 50128, EN 50657, IEC 60730, ISO 13849, IEC 62061, IEC 61511 and ISO 25119. For companies using continuous integration (CI) workflows and automated build and test processes, IAR Build Tools is also available for Linux-based frameworks. In addition, IAR's professional technical support, training and flexible licenses enable all customers to find a solution that suits their specific needs.
Lansheng Technology Limited, which is a spot stock distributor of many well-known brands, we have price advantage of the first-hand spot channel, and have technical supports.
Our main brands: STMicroelectronics, Toshiba, Microchip, Vishay, Marvell, ON Semiconductor, AOS, DIODES, Murata, Samsung, Hyundai/Hynix, Xilinx, Micron, Infinone, Texas Instruments, ADI, Maxim Integrated, NXP, etc
To learn more about our products, services, and capabilities, please visit our website at http://www.lanshengic.com
0 notes
Text
TensorFlow Lite for microcontrollers
*Maybe I had better get used to this.
https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/microcontrollers
TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers is an experimental port of TensorFlow Lite designed to run machine learning models on microcontrollers and other devices with only kilobytes of memory.
It doesn't require operating system support, any standard C or C++ libraries, or dynamic memory allocation. The core runtime fits in 16 KB on an Arm Cortex M3, and with enough operators to run a speech keyword detection model, takes up a total of 22 KB.
There are example applications demonstrating the use of microcontrollers for tasks including wake word detection, gesture classification from accelerometer data, and image classification using camera data.
To try the example applications and learn how to use the API, read Get started with microcontrollers.
TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers is written in C++ 11 and requires a 32-bit platform. It has been tested extensively with many processors based on the Arm Cortex-M Series architecture, and has been ported to other architectures including ESP32.
The framework is available as an Arduino library. It can also generate projects for development environments such as Mbed. It is open source and can be included in any C++ 11 project.
There are example applications available for the following development boards:
Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense
SparkFun Edge
STM32F746 Discovery kit
Adafruit EdgeBadge
Adafruit TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers Kit
To learn more about the libraries and examples, see Get started with microcontrollers.
Microcontrollers are typically small, low-powered computing devices that are often embedded within hardware that requires basic computation, including household appliances and Internet of Things devices. Billions of microcontrollers are manufactured each year.
Microcontrollers are often optimized for low energy consumption and small size, at the cost of reduced processing power, memory, and storage. Some microcontrollers have features designed to optimize performance on machine learning tasks.
By running machine learning inference on microcontrollers, developers can add AI to a vast range of hardware devices without relying on network connectivity, which is often subject to bandwidth and power constraints and results in high latency. Running inference on-device can also help preserve privacy, since no data has to leave the device.
To deploy a TensorFlow model to a microcontroller, you will need to follow this process:
Create or obtain a TensorFlow model
The model must be small enough to fit on your target device after conversion, and it can only use supported operations. If you want to use operations that are not currently supported, you can provide your own implementations.
Convert the model to a TensorFlow Lite FlatBuffer
You will convert your model into the standard TensorFlow Lite format using the TensorFlow Lite converter. You may wish to output a quantized model, since these are smaller in size and more efficient to execute.
Convert the FlatBuffer to a C byte array
Models are kept in read-only program memory and provided in the form of a simple C file. Standard tools can be used to convert the FlatBuffer into a C array.
Integrate the TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers C++ library
Write your microcontroller code to collect data, perform inference using the C++ library, and make use of the results.
Deploy to your device
Build and deploy the program to your device.
TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers is designed for the specific constraints of microcontroller development. If you are working on more powerful devices (for example, an embedded Linux device like the Raspberry Pi), the standard TensorFlow Lite framework might be easier to integrate.
The following limitations should be considered:
Support for a limited subset of TensorFlow operations
Support for a limited set of devices
Low-level C++ API requiring manual memory management
Training is not supported
Read Get started with microcontrollers to try the example applications and learn how to use the API....
1 note
·
View note
Link
Are you planning to learn embedded domain? If Yes, then you are at the right place. Cranes Varsity is one among the Best Embedded Training Institutes in Bangalore with 100% guaranteed placement. Our Embedded Training Course includes Project designing and Development, PCB Designing and Fabrication and Embedded Software development and Testing. Start your career in embedded domain.
https://www.cranesvarsity.com/courses/pg-diploma-in-embedded-and-automotive-systems/
0 notes
Text
USB Device Driver Course Online
Learn Advanced Embedded Linux ARM USB Device Driver Course Online – Certified Training Available Worldwide.

Noida, India—Are you an engineering student or expert looking to learn Embedded Linux ARM device drivers? Join our Advanced Embedded Linux ARM Training and advance your skills! This path is designed to offer hands-on experience with Linux device drivers, ARM board convey-up, Linux internals, and real-world projects.
What You’ll Learn:
Embedded Linux fundamentals and ARM board setup
Linux device driver improvement and debugging
Working with hardware interfaces and peripherals
Practical ARM-based total tasks for palms-on getting to know
Our schooling is led by enterprise experts with years of experience in embedded structures and Linux development. The route gives an established mastering path to assist students in building information in embedded programming, kernel improvement, and device motive force implementation.
Who Can Join?
Engineering students (ECE, CSE, EE, etc.)
Professionals in embedded software program improvement
Anyone captivated by Linux and ARM-based structures
Why Choose Us?
✔ Live Online Classes & Self-Paced Learning
✔ Practical Hands-on Projects
✔ Certification Upon Completion
✔ Guidance for Industry-Oriented ARM Projects
We offer schooling in Noida, India, and global–overlaying cities like Texas, Cambridge, Chicago, Sydney, Perth, Tampa, Brisbane, Melbourne, New York, Quebec, British Columbia, Ontario, Calgary, Alberta, and Yorkshire.
Start your journey in Embedded Linux ARM development nowadays! Enroll now and gain the competencies needed to excel in the embedded industry.
📞 Contact us at +91-8527567776 for more details and registration.
Click to:Chat on WhatsApp
Mail Us: [email protected]
🌐 Visit: Emblogic - USB Device Driver Course Online
#embedded linux arm training#linux device drivers#linux internals#arm board bring up#arm projects#embedded linux course#embedded linux course noida#embedded linux arm course
0 notes
Text
Getting Started with Yocto: Meeting the challenge of Embedded Linux deployment

Toradex's partner, Doulos, brings forth an interesting training webinar, which delves into how a minimal Linux system can be extended to include custom, packaged software. Doulos demonstrates how standard Linux tools, such as gdbserver or the Target Communication Framework agent (TCF agent), drops out of the build system and can be used in a stand-alone SDK. In the process, key concepts of the Yocto Project build system such as recipes, tasks and layers will be introduced. A board from the Toradex Colibri Arm family of System on Modules will be used as an example platform.
The webinar covers the following topics:
Managed Linux distributions
The Yocto build system
Creating custom software packages
Application development and systems development SDKs
Example BSP support
Grab your free registrations now: https://www.doulos.com/content/events/intro_to_yocto_tdx.php?pk_campaign=TDXWB#sched
Date and Time:
Europe/Asia - Tuesday, November 26, 2019, 11:00 A.M. - 12:00 P.M. (CET)
Americas - Tuesday, November 26, 2019, 10:00 A.M. - 11:00 A.M. (PST)
Speaker:
Adrian Thomasset, Sr. Member Technical Staff, Doulos | Yocto Expert
Venue: Online Webinar
0 notes
Text
Fruit identification using Arduino and TensorFlow
By Dominic Pajak and Sandeep Mistry
Arduino is on a mission to make machine learning easy enough for anyone to use. The other week we announced the availability of TensorFlow Lite Micro in the Arduino Library Manager. With this, some cool ready-made ML examples such as speech recognition, simple machine vision and even an end-to-end gesture recognition training tutorial. For a comprehensive background we recommend you take a look at that article.
In this article we are going to walk through an even simpler end-to-end tutorial using the TensorFlow Lite Micro library and the Arduino Nano 33 BLE 33 Sense’s colorimeter and proximity sensor to classify objects. To do this, we will be running a small neural network on the board itself.

Arduino BLE 33 Nano Sense running TensorFlow Lite Micro
The philosophy of TinyML is doing more on the device with less resources – in smaller form-factors, less energy and lower cost silicon. Running inferencing on the same board as the sensors has benefits in terms of privacy and battery life and means its can be done independent of a network connection.
The fact that we have the proximity sensor on the board means we get an instant depth reading of an object in front of the board – instead of using a camera and having to determine if an object is of interest through machine vision.
In this tutorial when the object is close enough we sample the color – the onboard RGB sensor can be viewed as a 1 pixel color camera. While this method has limitations it provides us a quick way of classifying objects only using a small amount of resources. Note that you could indeed run a complete CNN-based vision model on-device. As this particular Arduino board includes an onboard colorimeter, we thought it’d be fun and instructive to demonstrate in this way to start with.
We’ll show a simple but complete end-to-end TinyML application can be achieved quickly and without a deep background in ML or embedded. What we cover here is data capture, training, and classifier deployment. This is intended to be a demo, but there is scope to improve and build on this should you decide to connect an external camera down the road. We want you to get an idea of what is possible and a starting point with tools available.
youtube
What you’ll need
Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense
A micro USB cable
A desktop/laptop machine with a web browser
Some objects of different colors
About the Arduino board
The Arduino Nano 33 BLE Sense board we’re using here has an Arm Cortex-M4 microcontroller running mbedOS and a ton of onboard sensors – digital microphone, accelerometer, gyroscope, temperature, humidity, pressure, light, color and proximity.
While tiny by cloud or mobile standards the microcontroller is powerful enough to run TensorFlow Lite Micro models and classify sensor data from the onboard sensors.

Setting up the Arduino Create Web Editor
In this tutorial we’ll be using the Arduino Create Web Editor – a cloud-based tool for programming Arduino boards. To use it you have to sign up for a free account, and install a plugin to allow the browser to communicate with your Arduino board over USB cable.
You can get set up quickly by following the getting started instructions which will guide you through the following:
Download and install the plugin
Sign in or sign up for a free account
(NOTE: If you prefer, you can also use the Arduino IDE desktop application. The setup for which is described in the previous tutorial.)
Capturing training data
We now we will capture data to use to train our model in TensorFlow. First, choose a few different colored objects. We’ll use fruit, but you can use whatever you prefer.
Setting up the Arduino for data capture
Next we’ll use Arduino Create to program the Arduino board with an application object_color_capture.ino that samples color data from objects you place near it. The board sends the color data as a CSV log to your desktop machine over the USB cable.

To load the object_color_capture.ino application onto your Arduino board:
Connect your board to your laptop or PC with a USB cable
The Arduino board takes a male micro USB
Open object_color_capture.ino in Arduino Create by clicking this link
Your browser will open the Arduino Create web application (see GIF above).
Press OPEN IN WEB EDITOR
For existing users this button will be labeled ADD TO MY SKETCHBOOK
Press Upload & Save
This will take a minute
You will see the yellow light on the board flash as it is programmed
Open the serial Monitor
This opens the Monitor panel on the left-hand side of the web application
You will now see color data in CSV format here when objects are near the top of the board
Capturing data in CSV files for each object
For each object we want to classify we will capture some color data. By doing a quick capture with only one example per class we will not train a generalized model, but we can still get a quick proof of concept working with the objects you have to hand!
Say, for example, we are sampling an apple:
Reset the board using the small white button on top.
Keep your finger away from the sensor, unless you want to sample it!
The Monitor in Arduino Create will say ‘Serial Port Unavailable’ for a minute
You should then see Red,Green,Blue appear at the top of the serial monitor
Put the front of the board to the apple.
The board will only sample when it detects an object is close to the sensor and is sufficiently illuminated (turn the lights on or be near a window)
Move the board around the surface of the object to capture color variations
You will see the RGB color values appear in the serial monitor as comma separated data.
Capture at a few seconds of samples from the object
Copy and paste this log data from the Monitor to a text editor
Tip: untick AUTOSCROLL check box at the bottom to stop the text moving
Save your file as apple.csv
Reset the board using the small white button on top.
Do this a few more times, capturing other objects (e.g. banana.csv, orange.csv).
NOTE: The first line of each of the .csv files should read:
Red,Green,Blue
If you don’t see it at the top, you can just copy and paste in the line above.
Training the model
We will now use colab to train an ML model using the data you just captured in the previous section.
First open the FruitToEmoji Jupyter Notebook in colab
Follow the instructions in the colab
You will be uploading your *.csv files
Parsing and preparing the data
Training a model using Keras
Outputting TensorFlowLite Micro model
Downloading this to run the classifier on the Arduino
With that done you will have downloaded model.h to run on your Arduino board to classify objects!
The colab will guide you to drop your .csv files into the file window, the result shown above

Normalized color samples captured by the Arduino board are graphed in colab
Program TensorFlow Lite Micro model to the Arduino board
Finally, we will take the model we trained in the previous stage and compile and upload to our Arduino board using Arduino Create.
Open Classify_Object_Color.ino
Your browser will open the Arduino Create web application:
Press the OPEN IN WEB EDITOR button
Import the model.h you downloaded from colab using Import File to Sketch:

Import the model.h you downloaded from colab
The model.h tab should now look like this
Compile and upload the application to your Arduino board
This will take a minute
When it’s done you’ll see this message in the Monitor:
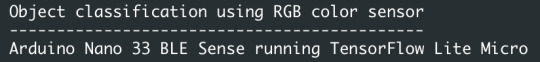
Put your Arduino’s RGB sensor near the objects you trained it with
You will see the classification output in the Monitor:
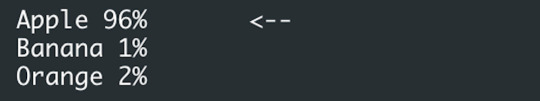
Classifier output in the Arduino Create Monitor
You can also edit the object_color_classifier.ino sketch to output emojis instead (we’ve left the unicode in the comments in code!), which you will be able to view in Mac OS X or Linux terminal by closing the web browser tab with Arduino Create in, resetting your board, and typing cat /cu/usb.modem[n].
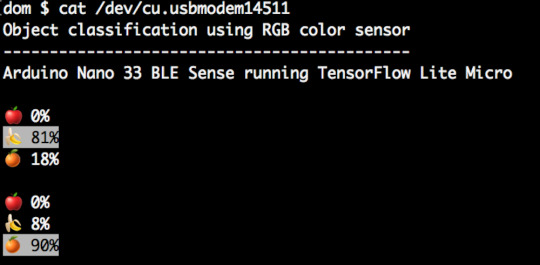
Output from Arduino serial to Linux terminal using ANSI highlighting and unicode emojis
Learning more
The resources around TinyML are still emerging but there’s a great opportunity to get a head start and meet experts coming up 2-3 December 2019 in Mountain View, California at the Arm IoT Dev Summit. This includes workshops from Sandeep Mistry, Arduino technical lead for on-device ML and from Google’s Pete Warden and Daniel Situnayake who literally wrote the book on TinyML. You’ll be able to hang out with these experts and more at the TinyML community sessions there too. We hope to see you there!
Conclusion
We’ve seen a quick end-to-end demo of machine learning running on Arduino. The same framework can be used to sample different sensors and train more complex models. For our object by color classification we could do more, by sampling more examples in more conditions to help the model generalize. In future work, we may also explore how to run an on-device CNN. In the meantime, we hope this will be a fun and exciting project for you. Have fun!
Fruit identification using Arduino and TensorFlow was originally published on PlanetArduino
0 notes
Text
Emertxe Embedded Systems Course with Placement in Bangalore
In today’s technology-driven world, embedded systems are the backbone of innovations ranging from IoT devices to automotive technologies. If you're looking for a career in this high-demand sector, Emertxe’s Embedded Systems Course in Bangalore is your perfect launchpad. With industry-recognized training and a strong placement program, Emertxe is helping aspiring engineers transition into successful embedded systems professionals.
Why Choose Emertxe for Embedded Systems Training?
As one of India’s top embedded systems training institutes, Emertxe stands out for its comprehensive curriculum, experienced faculty, and robust placement support. Here’s why Emertxe is a preferred choice:
1. Industry-Relevant Curriculum
Emertxe’s embedded systems course is meticulously designed to align with current industry trends. The curriculum covers:
Embedded C and Data Structures
Linux Systems Programming
ARM-based Embedded Systems Design
RTOS (Real-Time Operating System)
IoT Systems and Embedded Firmware
This hands-on learning approach ensures that you’re industry-ready by the time you complete the course.
2. 100% Placement Guarantee
One of the biggest benefits of enrolling in Emertxe is the institute’s strong placement support. Emertxe has a stellar track record of placing students in top companies. Through rigorous training and mock interviews, the placement team ensures you’re well-prepared for job opportunities. Some of the hiring partners include:
Intel
Bosch
Samsung
Qualcomm
With a 100% placement guarantee, Emertxe has helped numerous students achieve their dream jobs.
3. Experienced Faculty
The training at Emertxe is led by industry veterans with years of experience in embedded systems and IoT. The faculty provides not only theoretical knowledge but also valuable industry insights and project-based learning.
4. Real-World Projects
The best way to master embedded systems is through practical experience. Emertxe’s course includes hands-on projects like:
Designing Embedded IoT Devices
Building ARM Cortex-Based Applications
Real-Time Systems Development
These projects help you gain real-world skills that can be directly applied in your future career.
5. Bangalore – The Hub for Tech Jobs
Bangalore, often referred to as the Silicon Valley of India, offers immense opportunities for embedded systems professionals. Being located in Bangalore, Emertxe provides students with exposure to a thriving tech ecosystem, making it easier to connect with top companies during placement drives.
Course Highlights at Emertxe
Duration: 6 months
Mode of Learning: Classroom and online
Eligibility: Engineering graduates (ECE, EEE, CSE, and IT)
Certification: Upon course completion, you will receive an industry-recognized certification in embedded systems.
Success Stories of Emertxe Alumni
Many students have transformed their careers through Emertxe. From working in core embedded systems jobs to landing high-paying roles in MNCs, the opportunities are endless. Here are a few success stories from Emertxe alumni:
Sanjeev Kumar – Placed at Qualcomm with a package of 7 LPA
Meghana Reddy – Working as an Embedded Developer at Bosch
Rohan Sharma – Landed an IoT engineer role at Intel
Join Emertxe Today and Kickstart Your Embedded Systems Career!
If you're passionate about technology and want a rewarding career in embedded systems, Emertxe’s Embedded Systems Course with Placement in Bangalore is the ideal starting point. With cutting-edge training and unmatched placement support, you’ll be well-equipped to enter this lucrative field.
Enroll now and become part of a leading tech institute that transforms your career.
0 notes
Text
Professional Training Institute (PTI) is a Training organization, which is well known for providing quality education in advance fields such as Embedded System, C, Linux, CAN, Basic electronics, digital electronics, presently these are the hottest and best job-providing sectors. As the world changing fast, the technologies also changing day by day, we at Professional Training Instituteupdate our syllabus after every six months, we train the students according to the present using technologies in the industries. We at Professional Training Institute train our student such a way that, it’s easy for them to work in industries as they will have good practical knowledge. We at Professional Training Institute provide practical training such a way that our student getting an edge over others. Our main motto is to focus on practical and hands-on training to the student so that they are able to face any kind of interview in the embedded domain.

The Syllabus is Followed by Embedded Training Institute in Bangalore
This is a 4-5 month course for B.E/B. Tech/MTech/ ME/ MCA/M. Sc Candidates Pre-final & Final Year with a background preferably Electronics, Electrical, Instrumentation or Computer science.
1. With this students will be handling their Mini & Final year project by themselves independently. If already completed engineering then this course will help to get the job. 2. Our embedded training institute in Bangalore will provide 100% job assistance to our students. We give our full effort to get a job/place. We are having a dedicated team how is working with the placements. 3. Course Code: PTIESD0a – Comprehensive Embedded Systems Design Course is divided into following Major headings.
a) Basic Electronics and Digital Electronics. b) Basic C. c) Tools including S/W and H/W. d) Basic of Hardware Concepts. e) Basic Embedded. f) Advance C. g) Advance Embedded. h) Basic Linux. i) RTOS concepts. j) Linux Internal and Linux Device Drivers.
Details Description of Syllabus of Embedded Systems Courses in Bangalore
Basics of Electronics and Digital Electronic
Basic Electronics
Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors.
PN-Junction.
Diodes.
Transistor.
MOSFET/CMOS.
Interpretation Data Sheet.
Half-Wave Rectifiers/ Full-Wave Rectifier.
Power Supply 3.3V,5.0V,12.0V, Voltage Regulators.
Crystals
Switches, Relays.
7-Segment
555 Timers in AS/MS/BS
Digital Electronics
Number System – Binary, Hex, Decimal,BCD System.
Addition/Subtraction of binary, 2’s complements.
Interconversion of number system.
Logic Gates – AND/OR/NOR/EXOR.
Filip-flop, Memory element.
Mux- De-Mux, Decoders.
Shift Registers.
Counters.
Basics C
CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
What is C?
Data Types
Variables
Naming Conventions for C Variables
Printing and Initializing Variables
CHAPTER 2: SCOPE OF VARIABLES
Block Scope
Function Scope
File Scope
Program Scope
The auto Specifier
The static Specifier
The register Specifier
The extern Specifier
The register Specifier
The extern Specifier
CHAPTER 3: CONTROL FLOW CONSTRUCTS
if
if else
while
for
Endless Loops
do while
break and continue
switch
else if
CHAPTER 4: THE C PREPROCESSOR
#define
Macros
#include
Conditional Compilation
#ifdef
#ifndef
CHAPTER 5: MORE ON FUNCTIONS
Function Declarations
Function Prototypes
Returning a Value or Not
Arguments and Parameters
Organization of C Source Files
Extended Example
CHAPTER 6: BIT MANIPULATION
Defining the Problem Space
A Programming Example
Bit Wise Operators
Bit Manipulation Functions
Circular Shifts
CHAPTER 7: STRINGS & ARRAY
Fundamental Concepts
Aggregate Operations
String Functions
Array Dimensions
An Array as an Argument to a Function
String Arrays
Example Programs
CHAPTER 8: POINTERS (PART 1)
Fundamental Concepts
Pointer Operators and Operations
Changing an Argument with a Function
call
Pointer Arithmetic
String Functions with Pointers
Pointer Difference
Prototypes for String Parameters
Relationship Between an Array and a Pointer
The Pointer Notation *p++
CHAPTER 9: STRUCTURES
Fundamental Concepts
Describing a Structure
Creating Structures
Operations on Structures
Functions Returning Structures
Passing Structures to Functions
Pointers to Structures
Array of Structures
Functions Returning a Pointer to a Structure
Structure Padding
CHAPTER 9: STRUCTURES
typedef – New Name for an Existing Type
Bit Fields
unions
Non-Homogeneous Arrays
Enumerations
Tools Including S/W and H/W for Embedded Systems Training
KEIL
Making project in Keil.
Keil features/ tabs
Memory models in Keil.
Debugger setting in Keil.
Linker settings in Keil.
Multimeter
Measuring Voltage/Current/Registers
Measuring continuity
Introducing BBT – Baring Board Test.
CRO
Use of CRO.
What is Trigger?
How to do setting in CRO.
Measuring Voltage/current from CRO
Logic Analyzer
What is Logic Analyzer
How to use Logic Analyzer
What is the use of a logic analyzer
For which protocol we can use a logic analyzer.
Soldering Iron/Heat GUN/
How to use Soldering Iron.
Precaution needs to take.
Basic Hardware Concepts of Professional Training Institute
Designing Power supply
Design of power supply 5V.
Designing of 7 Segment Display Hardware
Study of 7 segment components
Designing Schematics of hardware implementation.
Hardware Design guidelines.
Important concepts during hardware Schematics design
Important concepts during hardware PCB lay-outing.
Active High/Active Low
Description of Active high and Active Low
EMI/EMC consideration
Use of Ground Plan
Use of De-coupling capacitor
Use of TVS Diode
Components Torrance and Data sheet study
Component Torrance study.
Consideration during designing.
Certification/Standard
CE/TUV/IC/ISI/IS/ISO
Basics of Embedded Systems
Microprocessor/Microcontroller
Basic Concepts and Review
Definition
Nomenclature
Buses – Address, Data, and Control
Architecture
Interfacing memory & I/O devices
Programming ( Assembly)
Monitor program
Micro-controller
Microcontroller Basic Concepts and Review
Architecture
Interfacing memory & I/O devices
Programming ( Assembly)
Assignments
Assembly Programming
Addition of two number.
Toggling Port with delay
Toggling Port with a timer.
Introduction of Interrupt.
Comparison interrupt and polling.
Communication with loopback.
Keyboard interface.
Controlling LED with Switches.
Embedded C
Embedded C & Integrated Development Environment
Embedded C Programming
Data types
Pointers
Arrays
Pointer functions
Loops
Introducing ARM Architecture
Induction of ARM Architecture
ARM7TDMI
Difference between ARM9/ARM11
Different ARM concepts
The advantage of ARM.
Advance C
Structure and union
Combination of Structure and union.
Bit fields in Structure.
Pointers to structure and union.
The advantage of Structure and union
Function Pointers
Microcontroller Basic Concepts and Review
Function pointers.
Callbacks
Advantage/use of functions pointers.
Dynamic memory allocation
Malloc
Calloc
free
re-alloc
File operations
Opening A file
Closing a file
Writing some data in a file and reading back and printing.
The different mode in which file can be open and write.
String operation
Srtcpy
strcmp
strcat
strlen
strstr
Pre-requisites for the Embedded Training in Bangalore:
1. B.E/B. Tech/MTech/ ME/ MCA/M.Sc Candidates Pre-final & Final Year with a background preferably Electronics, Electrical, Instrumentation or Computer science.
Professional Training Institute – Embedded Systems Training Institute in Bangalore
Our training method is different, our students get hands-on experience, they do experiments individually, which helps them to understand each part clearly like for example in embedded part we train them on UART protocol, we make them think and write a program for UART protocol, and we let them do communication between two devices using the UART protocol, by all these they will have good understanding of the UART protocol and they can easily use UART anytime in future. In this way, they get more interest to know about different technologies and we make them work and think.
We start our embedded system training from basic electronics, we teach the importance of electronics components, circuit design and we train them to design a power supply for different voltages. During c-programming classes we make our student think of the logic of each programmer, we never help them for write program, instead we help them to think and solve, this help them develop their logical skills and they can able to write any different programs.
We make student to discuss in class, and to give a seminar, which helps our students to develop the communication skills.
Learn More
More Tags: embedded training in Bangalore | embedded Linux training in Bangalore | best-embedded training institute in Bangalore | embedded training institute in Bangalore | list of embedded systems institute in Bangalore | embedded systems courses in Bangalore | embedded courses in Bangalore
#Embedded Training in Bangalore#embedded training institutes in bangalore#embedded systems courses in bangalore
0 notes
Text
Embedded Linux Kernel Internals using ARM and Device Drivers
"Embedded Linux Kernel Internals using ARM and Device Drivers" (ELKIADD) is an Ineffable, Comprehensive, Hands-on, project based career oriented, training program for BE, B Tech, ME, M Tech from the streams of Electronics, Computer Science, Information Technologies, Instrumentation or Master of Computer Applications.
This trainig aims at building your career with respect to innovative technologies related to Embedded Linux, ARM, Device Drivers, System Software, System Engineering.
The concepts absorbed during this training should help you in any domain where electro-mechanical, electronic devices are designed. You will be efficient with respect to incorporating intelligencs in the devices.
0 notes