#securing npm
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Secure your digital world by generating strong password.
0 notes
Text
Getting Started with Node.js: A Beginner's Guide
Getting Started with Node.js: A Beginner's Guide
Introduction Node.js has revolutionized server-side programming with its non-blocking, event-driven architecture. As a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine, Node.js allows developers to use JavaScript for both client-side and server-side programming, streamlining the development process and enabling a seamless experience across the stack. This guide will walk you through the…

View On WordPress
#Beginner&039;s Guide#JavaScript#Node.js#NPM#Programming Basics#Rapid Development#Scalability#Security#Server-Side Programming#Tutorial#web development
0 notes
Text
The hacker ecosystem in Russia, more than perhaps anywhere else in the world, has long blurred the lines between cybercrime, state-sponsored cyberwarfare, and espionage. Now an indictment of a group of Russian nationals and the takedown of their sprawling botnet offers the clearest example in years of how a single malware operation allegedly enabled hacking operations as varied as ransomware, wartime cyberattacks in Ukraine, and spying against foreign governments.
The US Department of Justice today announced criminal charges today against 16 individuals law enforcement authorities have linked to a malware operation known as DanaBot, which according to a complaint infected at least 300,000 machines around the world. The DOJ’s announcement of the charges describes the group as “Russia-based,” and names two of the suspects, Aleksandr Stepanov and Artem Aleksandrovich Kalinkin, as living in Novosibirsk, Russia. Five other suspects are named in the indictment, while another nine are identified only by their pseudonyms. In addition to those charges, the Justice Department says the Defense Criminal Investigative Service (DCIS)—a criminal investigation arm of the Department of Defense—carried out seizures of DanaBot infrastructure around the world, including in the US.
Aside from alleging how DanaBot was used in for-profit criminal hacking, the indictment also makes a rarer claim—it describes how a second variant of the malware it says was used in espionage against military, government, and NGO targets. “Pervasive malware like DanaBot harms hundreds of thousands of victims around the world, including sensitive military, diplomatic, and government entities, and causes many millions of dollars in losses,” US attorney Bill Essayli wrote in a statement.
Since 2018, DanaBot—described in the criminal complaint as “incredibly invasive malware”—has infected millions of computers around the world, initially as a banking trojan designed to steal directly from those PCs' owners with modular features designed for credit card and cryptocurrency theft. Because its creators allegedly sold it in an “affiliate” model that made it available to other hacker groups for $3,000 to $4,000 a month, however, it was soon used as a tool to install different forms of malware in a broad array of operations, including ransomware. Its targets, too, quickly spread from initial victims in Ukraine, Poland, Italy, Germany, Austria, and Australia to US and Canadian financial institutions, according to an analysis of the operation by cybersecurity firm Crowdstrike.
At one point in 2021, according to Crowdstrike, Danabot was used in a software supply-chain attack that hid the malware in a javascript coding tool called NPM with millions of weekly downloads. Crowdstrike found victims of that compromised tool across the financial service, transportation, technology, and media industries.
That scale and the wide variety of its criminal uses made DanaBot “a juggernaut of the e-crime landscape,” according to Selena Larson, a staff threat researcher at cybersecurity firm Proofpoint.
More uniquely, though, DanaBot has also been used at times for hacking campaigns that appear to be state-sponsored or linked to Russian government agency interests. In 2019 and 2020, it was used to target a handful of Western government officials in apparent espionage operations, according to the DOJ's indictment. According to Proofpoint, the malware in those instances was delivered in phishing messages that impersonated the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe and a Kazakhstan government entity.
Then, in the early weeks of Russia's full-scale invasion of Ukraine, which began in February 2022, DanaBot was used to install a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) tool onto infected machines and launch attacks against the webmail server of the Ukrainian Ministry of Defense and National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine.
All of that makes DanaBot a particularly clear example of how cybercriminal malware has allegedly been adopted by Russian state hackers, Proofpoint's Larson says. “There have been a lot of suggestions historically of cybercriminal operators palling around with Russian government entities, but there hasn't been a lot of public reporting on these increasingly blurred lines,” says Larson. The case of DanaBot, she says, “is pretty notable, because it's public evidence of this overlap where we see e-crime tooling used for espionage purposes.”
In the criminal complaint, DCIS investigator Elliott Peterson—a former FBI agent known for his work on the investigation into the creators of the Mirai botnet—alleges that some members of the DanaBot operation were identified after they infected their own computers with the malware. Those infections may have been for the purposes of testing the trojan, or may have been accidental, according to Peterson. Either way, they resulted in identifying information about the alleged hackers ending up on DanaBot infrastructure that DCIS later seized. “The inadvertent infections often resulted in sensitive and compromising data being stolen from the actor's computer by the malware and stored on DanaBot servers, including data that helped identify members of the DanaBot organization,” Peterson writes.
The operators of DanaBot remain at large, but the takedown of a large-scale tool in so many forms of Russian-origin hacking—both state-sponsored and criminal—represents a significant milestone, says Adam Meyers, who leads threat intelligence research at Crowdstrike.
“Every time you disrupt a multiyear operation, you're impacting their ability to monetize it. It also creates a bit of a vacuum, and somebody else is going to step up and take that place,” Meyers says. “But the more we can disrupt them, the more we keep them on their back heels. We should rinse and repeat and go find the next target.”
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Malware found in NPM packages with 1 million weekly downloads
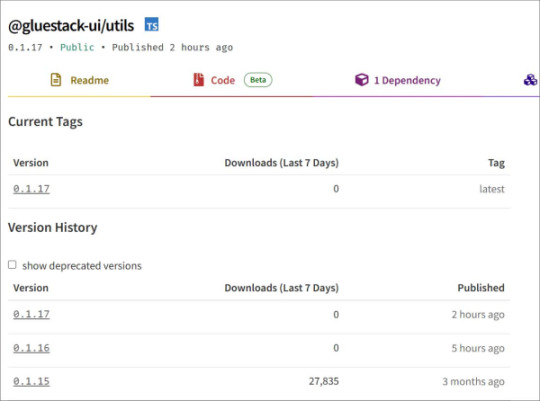
Source: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/supply-chain-attack-hits-gluestack-npm-packages-with-960k-weekly-downloads/
More info: https://www.aikido.dev/blog/supply-chain-attack-on-react-native-aria-ecosystem
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vibecoding a production app
TL;DR I built and launched a recipe app with about 20 hours of work - recipeninja.ai
Background: I'm a startup founder turned investor. I taught myself (bad) PHP in 2000, and picked up Ruby on Rails in 2011. I'd guess 2015 was the last time I wrote a line of Ruby professionally. I've built small side projects over the years, but nothing with any significant usage. So it's fair to say I'm a little rusty, and I never really bothered to learn front end code or design.
In my day job at Y Combinator, I'm around founders who are building amazing stuff with AI every day and I kept hearing about the advances in tools like Lovable, Cursor and Windsurf. I love building stuff and I've always got a list of little apps I want to build if I had more free time.
About a month ago, I started playing with Lovable to build a word game based on Articulate (it's similar to Heads Up or Taboo). I got a working version, but I quickly ran into limitations - I found it very complicated to add a supabase backend, and it kept re-writing large parts of my app logic when I only wanted to make cosmetic changes. It felt like a toy - not ready to build real applications yet.
But I kept hearing great things about tools like Windsurf. A couple of weeks ago, I looked again at my list of app ideas to build and saw "Recipe App". I've wanted to build a hands-free recipe app for years. I love to cook, but the problem with most recipe websites is that they're optimized for SEO, not for humans. So you have pages and pages of descriptive crap to scroll through before you actually get to the recipe. I've used the recipe app Paprika to store my recipes in one place, but honestly it feels like it was built in 2009. The UI isn't great for actually cooking. My hands are covered in food and I don't really want to touch my phone or computer when I'm following a recipe.
So I set out to build what would become RecipeNinja.ai
For this project, I decided to use Windsurf. I wanted a Rails 8 API backend and React front-end app and Windsurf set this up for me in no time. Setting up homebrew on a new laptop, installing npm and making sure I'm on the right version of Ruby is always a pain. Windsurf did this for me step-by-step. I needed to set up SSH keys so I could push to GitHub and Heroku. Windsurf did this for me as well, in about 20% of the time it would have taken me to Google all of the relevant commands.
I was impressed that it started using the Rails conventions straight out of the box. For database migrations, it used the Rails command-line tool, which then generated the correct file names and used all the correct Rails conventions. I didn't prompt this specifically - it just knew how to do it. It one-shotted pretty complex changes across the React front end and Rails backend to work seamlessly together.
To start with, the main piece of functionality was to generate a complete step-by-step recipe from a simple input ("Lasagne"), generate an image of the finished dish, and then allow the user to progress through the recipe step-by-step with voice narration of each step. I used OpenAI for the LLM and ElevenLabs for voice. "Grandpa Spuds Oxley" gave it a friendly southern accent.
Recipe summary:
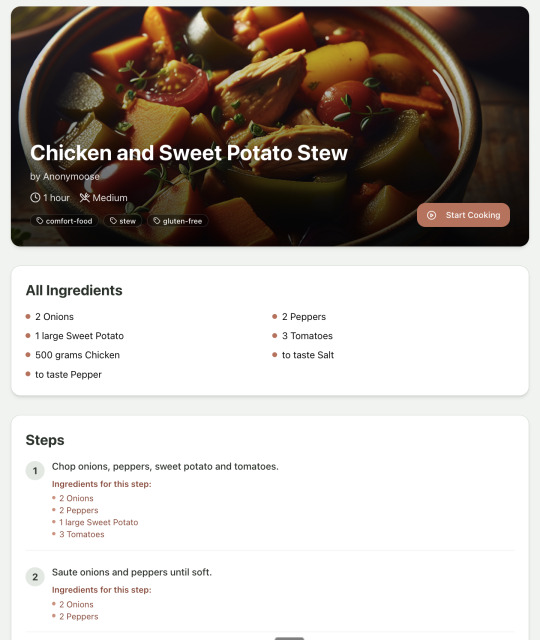
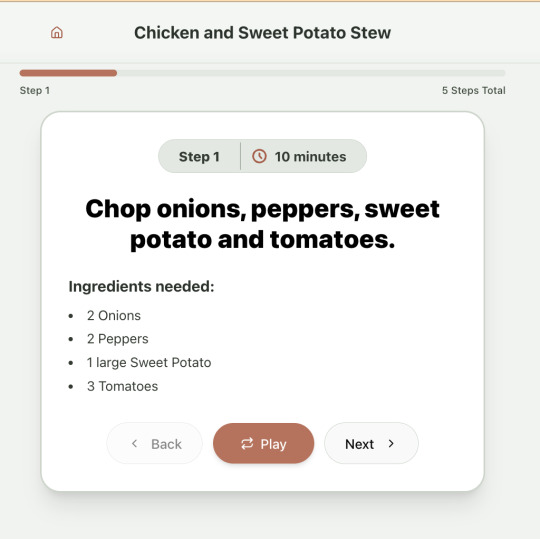
And the recipe step-by-step view:
I was pretty astonished that Windsurf managed to integrate both the OpenAI and Elevenlabs APIs without me doing very much at all. After we had a couple of problems with the open AI Ruby library, it quickly fell back to a raw ruby HTTP client implementation, but I honestly didn't care. As long as it worked, I didn't really mind if it used 20 lines of code or two lines of code. And Windsurf was pretty good about enforcing reasonable security practices. I wanted to call Elevenlabs directly from the front end while I was still prototyping stuff, and Windsurf objected very strongly, telling me that I was risking exposing my private API credentials to the Internet. I promised I'd fix it before I deployed to production and it finally acquiesced.
I decided I wanted to add "Advanced Import" functionality where you could take a picture of a recipe (this could be a handwritten note or a picture from a favourite a recipe book) and RecipeNinja would import the recipe. This took a handful of minutes.
Pretty quickly, a pattern emerged; I would prompt for a feature. It would read relevant files and make changes for two or three minutes, and then I would test the backend and front end together. I could quickly see from the JavaScript console or the Rails logs if there was an error, and I would just copy paste this error straight back into Windsurf with little or no explanation. 80% of the time, Windsurf would correct the mistake and the site would work. Pretty quickly, I didn't even look at the code it generated at all. I just accepted all changes and then checked if it worked in the front end.
After a couple of hours of work on the recipe generation, I decided to add the concept of "Users" and include Google Auth as a login option. This would require extensive changes across the front end and backend - a database migration, a new model, new controller and entirely new UI. Windsurf one-shotted the code. It didn't actually work straight away because I had to configure Google Auth to add `localhost` as a valid origin domain, but Windsurf talked me through the changes I needed to make on the Google Auth website. I took a screenshot of the Google Auth config page and pasted it back into Windsurf and it caught an error I had made. I could login to my app immediately after I made this config change. Pretty mindblowing. You can now see who's created each recipe, keep a list of your own recipes, and toggle each recipe to public or private visibility. When I needed to set up Heroku to host my app online, Windsurf generated a bunch of terminal commands to configure my Heroku apps correctly. It went slightly off track at one point because it was using old Heroku APIs, so I pointed it to the Heroku docs page and it fixed it up correctly.
I always dreaded adding custom domains to my projects - I hate dealing with Registrars and configuring DNS to point at the right nameservers. But Windsurf told me how to configure my GoDaddy domain name DNS to work with Heroku, telling me exactly what buttons to press and what values to paste into the DNS config page. I pointed it at the Heroku docs again and Windsurf used the Heroku command line tool to add the "Custom Domain" add-ons I needed and fetch the right Heroku nameservers. I took a screenshot of the GoDaddy DNS settings and it confirmed it was right.
I can see very soon that tools like Cursor & Windsurf will integrate something like Browser Use so that an AI agent will do all this browser-based configuration work with zero user input.
I'm also impressed that Windsurf will sometimes start up a Rails server and use curl commands to check that an API is working correctly, or start my React project and load up a web preview and check the front end works. This functionality didn't always seem to work consistently, and so I fell back to testing it manually myself most of the time.
When I was happy with the code, it wrote git commits for me and pushed code to Heroku from the in-built command line terminal. Pretty cool!
I do have a few niggles still. Sometimes it's a little over-eager - it will make more changes than I want, without checking with me that I'm happy or the code works. For example, it might try to commit code and deploy to production, and I need to press "Stop" and actually test the app myself. When I asked it to add analytics, it went overboard and added 100 different analytics events in pretty insignificant places. When it got trigger-happy like this, I reverted the changes and gave it more precise commands to follow one by one.
The one thing I haven't got working yet is automated testing that's executed by the agent before it decides a task is complete; there's probably a way to do it with custom rules (I have spent zero time investigating this). It feels like I should be able to have an integration test suite that is run automatically after every code change, and then any test failures should be rectified automatically by the AI before it says it's finished.
Also, the AI should be able to tail my Rails logs to look for errors. It should spot things like database queries and automatically optimize my Active Record queries to make my app perform better. At the moment I'm copy-pasting in excerpts of the Rails logs, and then Windsurf quickly figures out that I've got an N+1 query problem and fixes it. Pretty cool.
Refactoring is also kind of painful. I've ended up with several files that are 700-900 lines long and contain duplicate functionality. For example, list recipes by tag and list recipes by user are basically the same.
Recipes by user:
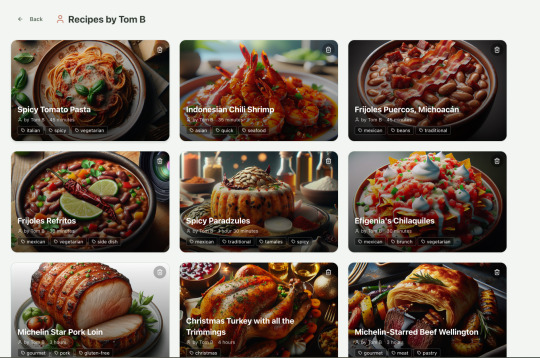
This should really be identical to list recipes by tag, but Windsurf has implemented them separately.
Recipes by tag:
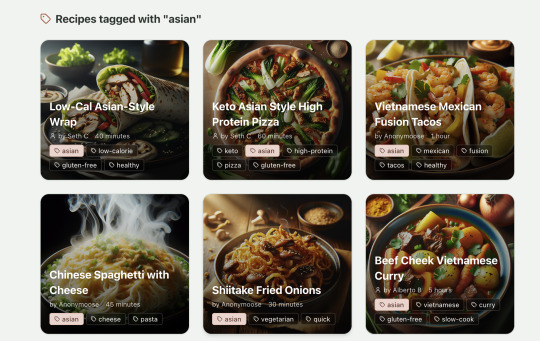
If I ask Windsurf to refactor these two pages, it randomly changes stuff like renaming analytics events, rewriting user-facing alerts, and changing random little UX stuff, when I really want to keep the functionality exactly the same and only move duplicate code into shared modules. Instead, to successfully refactor, I had to ask Windsurf to list out ideas for refactoring, then prompt it specifically to refactor these things one by one, touching nothing else. That worked a little better, but it still wasn't perfect
Sometimes, adding minor functionality to the Rails API will often change the entire API response, rather just adding a couple of fields. Eg It will occasionally change Index Recipes to nest responses in an object { "recipes": [ ] }, versus just returning an array, which breaks the frontend. And then another minor change will revert it. This is where adding tests to identify and prevent these kinds of API changes would be really useful. When I ask Windsurf to fix these API changes, it will instead change the front end to accept the new API json format and also leave the old implementation in for "backwards compatibility". This ends up with a tangled mess of code that isn't really necessary. But I'm vibecoding so I didn't bother to fix it.
Then there was some changes that just didn't work at all. Trying to implement Posthog analytics in the front end seemed to break my entire app multiple times. I tried to add user voice commands ("Go to the next step"), but this conflicted with the eleven labs voice recordings. Having really good git discipline makes vibe coding much easier and less stressful. If something doesn't work after 10 minutes, I can just git reset head --hard. I've not lost very much time, and it frees me up to try more ambitious prompts to see what the AI can do. Less technical users who aren't familiar with git have lost months of work when the AI goes off on a vision quest and the inbuilt revert functionality doesn't work properly. It seems like adding more native support for version control could be a massive win for these AI coding tools.
Another complaint I've heard is that the AI coding tools don't write "production" code that can scale. So I decided to put this to the test by asking Windsurf for some tips on how to make the application more performant. It identified I was downloading 3 MB image files for each recipe, and suggested a Rails feature for adding lower resolution image variants automatically. Two minutes later, I had thumbnail and midsize variants that decrease the loading time of each page by 80%. Similarly, it identified inefficient N+1 active record queries and rewrote them to be more efficient. There are a ton more performance features that come built into Rails - caching would be the next thing I'd probably add if usage really ballooned.
Before going to production, I kept my promise to move my Elevenlabs API keys to the backend. Almost as an afterthought, I asked asked Windsurf to cache the voice responses so that I'd only make an Elevenlabs API call once for each recipe step; after that, the audio file was stored in S3 using Rails ActiveStorage and served without costing me more credits. Two minutes later, it was done. Awesome.
At the end of a vibecoding session, I'd write a list of 10 or 15 new ideas for functionality that I wanted to add the next time I came back to the project. In the past, these lists would've built up over time and never gotten done. Each task might've taken me five minutes to an hour to complete manually. With Windsurf, I was astonished how quickly I could work through these lists. Changes took one or two minutes each, and within 30 minutes I'd completed my entire to do list from the day before. It was astonishing how productive I felt. I can create the features faster than I can come up with ideas.
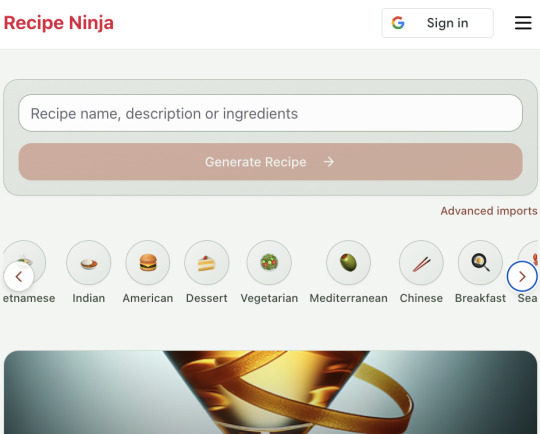
Before launching, I wanted to improve the design, so I took a quick look at a couple of recipe sites. They were much more visual than my site, and so I simply told Windsurf to make my design more visual, emphasizing photos of food. Its first try was great. I showed it to a couple of friends and they suggested I should add recipe categories - "Thai" or "Mexican" or "Pizza" for example. They showed me the DoorDash app, so I took a screenshot of it and pasted it into Windsurf. My prompt was "Give me a carousel of food icons that look like this". Again, this worked in one shot. I think my version actually looks better than Doordash 🤷♂️
Doordash:
My carousel:
I also saw I was getting a console error from missing Favicon. I always struggle to make Favicon for previous sites because I could never figure out where they were supposed to go or what file format they needed. I got OpenAI to generate me a little recipe ninja icon with a transparent background and I saved it into my project directory. I asked Windsurf what file format I need and it listed out nine different sizes and file formats. Seems annoying. I wondered if Windsurf could just do it all for me. It quickly wrote a series of Bash commands to create a temporary folder, resize the image and create the nine variants I needed. It put them into the right directory and then cleaned up the temporary directory. I laughed in amazement. I've never been good at bash scripting and I didn't know if it was even possible to do what I was asking via the command line. I guess it is possible.

After launching and posting on Twitter, a few hundred users visited the site and generated about 1000 recipes. I was pretty happy! Unfortunately, the next day I woke up and saw that I had a $700 OpenAI bill. Someone had been abusing the site and costing me a lot of OpenAI credits by creating a single recipe over and over again - "Pasta with Shallots and Pineapple". They did this 12,000 times. Obviously, I had not put any rate limiting in.
Still, I was determined not to write any code. I explained the problem and asked Windsurf to come up with solutions. Seconds later, I had 15 pretty good suggestions. I implemented several (but not all) of the ideas in about 10 minutes and the abuse stopped dead in its tracks. I won't tell you which ones I chose in case Mr Shallots and Pineapple is reading. The app's security is not perfect, but I'm pretty happy with it for the scale I'm at. If I continue to grow and get more abuse, I'll implement more robust measures.
Overall, I am astonished how productive Windsurf has made me in the last two weeks. I'm not a good designer or frontend developer, and I'm a very rusty rails dev. I got this project into production 5 to 10 times faster than it would've taken me manually, and the level of polish on the front end is much higher than I could've achieved on my own. Over and over again, I would ask for a change and be astonished at the speed and quality with which Windsurf implemented it. I just sat laughing as the computer wrote code.
The next thing I want to change is making the recipe generation process much more immediate and responsive. Right now, it takes about 20 seconds to generate a recipe and for a new user it feels like maybe the app just isn't doing anything.
Instead, I'm experimenting with using Websockets to show a streaming response as the recipe is created. This gives the user immediate feedback that something is happening. It would also make editing the recipe really fun - you could ask it to "add nuts" to the recipe, and see as the recipe dynamically updates 2-3 seconds later. You could also say "Increase the quantities to cook for 8 people" or "Change from imperial to metric measurements".
I have a basic implementation working, but there are still some rough edges. I might actually go and read the code this time to figure out what it's doing!
I also want to add a full voice agent interface so that you don't have to touch the screen at all. Halfway through cooking a recipe, you might ask "I don't have cilantro - what could I use instead?" or say "Set a timer for 30 minutes". That would be my dream recipe app!
Tools like Windsurf or Cursor aren't yet as useful for non-technical users - they're extremely powerful and there are still too many ways to blow your own face off. I have a fairly good idea of the architecture that I want Windsurf to implement, and I could quickly spot when it was going off track or choosing a solution that was inappropriately complicated for the feature I was building. At the moment, a technical background is a massive advantage for using Windsurf. As a rusty developer, it made me feel like I had superpowers.
But I believe within a couple of months, when things like log tailing and automated testing and native version control get implemented, it will be an extremely powerful tool for even non-technical people to write production-quality apps. The AI will be able to make complex changes and then verify those changes are actually working. At the moment, it feels like it's making a best guess at what will work and then leaving the user to test it. Implementing better feedback loops will enable a truly agentic, recursive, self-healing development flow. It doesn't feel like it needs any breakthrough in technology to enable this. It's just about adding a few tool calls to the existing LLMs. My mind races as I try to think through the implications for professional software developers.
Meanwhile, the LLMs aren't going to sit still. They're getting better at a frightening rate. I spoke to several very capable software engineers who are Y Combinator founders in the last week. About a quarter of them told me that 95% of their code is written by AI. In six or twelve months, I just don't think software engineering is going exist in the same way as it does today. The cost of creating high-quality, custom software is quickly trending towards zero.
You can try the site yourself at recipeninja.ai
Here's a complete list of functionality. Of course, Windsurf just generated this list for me 🫠
RecipeNinja: Comprehensive Functionality Overview
Core Concept: the app appears to be a cooking assistant application that provides voice-guided recipe instructions, allowing users to cook hands-free while following step-by-step recipe guidance.
Backend (Rails API) Functionality
User Authentication & Authorization
Google OAuth integration for user authentication
User account management with secure authentication flows
Authorization system ensuring users can only access their own private recipes or public recipes
Recipe Management
Recipe Model Features:
Unique public IDs (format: "r_" + 14 random alphanumeric characters) for security
User ownership (user_id field with NOT NULL constraint)
Public/private visibility toggle (default: private)
Comprehensive recipe data storage (title, ingredients, steps, cooking time, etc.)
Image attachment capability using Active Storage with S3 storage in production
Recipe Tagging System:
Many-to-many relationship between recipes and tags
Tag model with unique name attribute
RecipeTag join model for the relationship
Helper methods for adding/removing tags from recipes
Recipe API Endpoints:
CRUD operations for recipes
Pagination support with metadata (current_page, per_page, total_pages, total_count)
Default sorting by newest first (created_at DESC)
Filtering recipes by tags
Different serializers for list view (RecipeSummarySerializer) and detail view (RecipeSerializer)
Voice Generation
Voice Recording System:
VoiceRecording model linked to recipes
Integration with Eleven Labs API for text-to-speech conversion
Caching of voice recordings in S3 to reduce API calls
Unique identifiers combining recipe_id, step_id, and voice_id
Force regeneration option for refreshing recordings
Audio Processing:
Using streamio-ffmpeg gem for audio file analysis
Active Storage integration for audio file management
S3 storage for audio files in production
Recipe Import & Generation
RecipeImporter Service:
OpenAI integration for recipe generation
Conversion of text recipes into structured format
Parsing and normalization of recipe data
Import from photos functionality
Frontend (React) Functionality
User Interface Components
Recipe Selection & Browsing:
Recipe listing with pagination
Real-time updates with 10-second polling mechanism
Tag filtering functionality
Recipe cards showing summary information (without images)
"View Details" and "Start Cooking" buttons for each recipe
Recipe Detail View:
Complete recipe information display
Recipe image display
Tag display with clickable tags
Option to start cooking from this view
Cooking Experience:
Step-by-step recipe navigation
Voice guidance for each step
Keyboard shortcuts for hands-free control:
Arrow keys for step navigation
Space for play/pause audio
Escape to return to recipe selection
URL-based step tracking (e.g., /recipe/r_xlxG4bcTLs9jbM/classic-lasagna/steps/1)
State Management & Data Flow
Recipe Service:
API integration for fetching recipes
Support for pagination parameters
Tag-based filtering
Caching mechanisms for recipe data
Image URL handling for detailed views
Authentication Flow:
Google OAuth integration using environment variables
User session management
Authorization header management for API requests
Progressive Web App Features
PWA capabilities for installation on devices
Responsive design for various screen sizes
Favicon and app icon support
Deployment Architecture
Two-App Structure:
cook-voice-api: Rails backend on Heroku
cook-voice-wizard: React frontend/PWA on Heroku
Backend Infrastructure:
Ruby 3.2.2
PostgreSQL database (Heroku PostgreSQL addon)
Amazon S3 for file storage
Environment variables for configuration
Frontend Infrastructure:
React application
Environment variable configuration
Static buildpack on Heroku
SPA routing configuration
Security Measures:
HTTPS enforcement
Rails credentials system
Environment variables for sensitive information
Public ID system to mask database IDs
This comprehensive overview covers the major functionality of the Cook Voice application based on the available information. The application appears to be a sophisticated cooking assistant that combines recipe management with voice guidance to create a hands-free cooking experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Debate of the Decade: What to choose as the backend framework Node.Js or Ruby on Rails?
New, cutting-edge web development frameworks and tools have been made available in recent years. While this variety is great for developers and company owners alike, it does come with certain drawbacks. This not only creates a lot of confusion but also slows down development at a time when quick and effective answers are essential. This is why discussions about whether Ruby on Rails or Noe.js is superior continue to rage. What framework is best for what kind of project is a hotly contested question. Nivida Web Solutions is a top-tier web development company in Vadodara. Nivida Web Solutions is the place to go if you want to make a beautiful website that gets people talking.

Identifying the optimal option for your work is challenging. This piece breaks things down for you. Two widely used web development frameworks, RoR and Node.js, are compared and contrasted in this article. We'll also get deep into contrasting RoR and Node.js. Let's get started with a quick overview of Ruby on Rails and Node.js.
NodeJS:
This method makes it possible to convert client-side software to server-side ones. At the node, JavaScript is usually converted into machine code that the hardware can process with a single click. Node.js is a very efficient server-side web framework built on the Chrome V8 Engine. It makes a sizable contribution to the maximum conversion rate achievable under normal operating conditions.
There are several open-source libraries available through the Node Package Manager that make the Node.js ecosystem special. Node.js's built-in modules make it suitable for managing everything from computer resources to security information. Are you prepared to make your mark in the online world? If you want to improve your online reputation, team up with Nivida Web Solutions, the best web development company in Gujarat.
Key Features:
· Cross-Platforms Interoperability
· V8 Engine
· Microservice Development and Swift Deployment
· Easy to Scale
· Dependable Technology
Ruby on Rails:
The back-end framework Ruby on Rails (RoR) is commonly used for both web and desktop applications. Developers appreciate the Ruby framework because it provides a solid foundation upon which other website elements may be built. A custom-made website can greatly enhance your visibility on the web. If you're looking for a trustworthy web development company in India, go no further than Nivida Web Solutions.
Ruby on Rails' cutting-edge features, such as automatic table generation, database migrations, and view scaffolding, are a big reason for the framework's widespread adoption.
Key Features:
· MVC Structure
· Current Record
· Convention Over Configuration (CoC)
· Automatic Deployment
· The Boom of Mobile Apps
· Sharing Data in Databases
Node.js v/s RoR:
· Libraries:
The Rails package library is called the Ruby Gems. However, the Node.Js Node Package Manager (NPM) provides libraries and packages to help programmers avoid duplicating their work. Ruby Gems and NPM work together to make it easy to generate NPM packages with strict version control and straightforward installation.
· Performance:
Node.js' performance has been lauded for its speed. Node.js is the go-to framework for resource-intensive projects because of its ability to run asynchronous code and the fact that it is powered by Google's V8 engine. Ruby on Rails is 20 times less efficient than Node.js.
· Scalability:
Ruby's scalability is constrained by comparison to Node.js due to the latter's cluster module. In an abstraction-based cluster, the number of CPUs a process uses is based on the demands of the application.
· Architecture:
The Node.js ecosystem has a wealth of useful components, but JavaScript was never designed to handle backend activities and has significant constraints when it comes to cutting-edge construction strategies. Ruby on Rails, in contrast to Node.js, is a framework that aims to streamline the process of building out a website's infrastructure by eliminating frequent installation problems.
· The learning curve:
Ruby has a low barrier to entry since it is an easy language to learn. The learning curve with Node.js is considerably lower. JavaScript veterans will have the easiest time learning the language, but developers acquainted with various languages should have no trouble.
Final Thoughts:
Both Node.JS and RoR have been tried and tested in real-world scenarios. Ruby on Rails is great for fast-paced development teams, whereas Node.js excels at building real-time web apps and single-page applications.
If you are in need of a back-end developer, Nivida Web Solutions, a unique web development agency in Gujarat, can assist you in creating a product that will both meet and exceed the needs of your target audience.
#web development company in vadodara#web development company in India#web development company in Gujarat#Web development Companies in Vadodara#Web development Companies in India#Web development Companies in Gujarat#Web development agency in Gujarat#Web development agency in India#Web development agency in Vadodara
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Importance of MERN Stack
What is MERN Stack?
Four essential technologies make up the full-stack JavaScript framework MERN Stack:
MongoDB: A NoSQL database system known for its flexibility and scalability, MongoDB stores data in a JSON-like format, making it ideal for handling large volumes of data.
Express.js: A minimalist web application framework for Node.js, Express.js simplifies the process of building robust and scalable web applications by providing a set of features for web and mobile applications.
React.js: Developed by Facebook, React.js is a powerful JavaScript library for building interactive user interfaces. Its component-based architecture allows developers to create reusable UI components, resulting in a more modular and maintainable codebase.
Node.js: A server-side JavaScript runtime environment, Node.js enables developers to build fast and scalable network applications. With its event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, Node.js is well-suited for building real-time web applications.
Why Choose MERN Stack?
Streamlined Development: With MERN Stack, developers can leverage the power of JavaScript across the entire development stack, from frontend to backend. This unified approach reduces development time and eliminates the need to switch between different programming languages and frameworks.
SEO-Friendly Architecture: MERN Stack's server-side rendering capabilities, coupled with its support for modern JavaScript frameworks like React.js, make it highly SEO-friendly. This ensures that web applications built with MERN Stack are easily discoverable by search engines, leading to improved search engine rankings and increased organic traffic.
Optimized Performance: MERN Stack's asynchronous, non-blocking architecture allows for seamless communication between frontend, backend, and database components, resulting in faster response times and improved performance. This translates to a smoother user experience and higher customer satisfaction.
Improved Security: In today's digital environment, security is of the highest priority. MERN Stack provides built-in security features, such as authentication and authorization mechanisms, as well as support for encryption and data validation, to ensure that web applications are protected against common security threats.
Scalability and Flexibility: Whether you're building a small-scale application or a large-scale enterprise solution, MERN Stack offers the scalability and flexibility you need to grow and adapt to changing business requirements. With its modular architecture and support for microservices, MERN Stack allows for easy scaling and maintenance of complex applications.
Getting Started with MERN Stack
Are you prepared to explore the MERN Stack world? Here is a detailed how-to for getting started:
Install Node.js: Begin by installing Node.js, which includes npm (Node Package Manager), on your local machine. Node.js will serve as the runtime environment for your server-side code.
Set Up MongoDB: Install MongoDB, a NoSQL database system, and set up a local or remote MongoDB instance to store your application data.
Create an Express.js Server: Use Express.js to create a server-side application that will handle HTTP requests and serve as the backend for your web application.
Build Your React.js Frontend: Use React.js to create a client-side application that will handle user interface interactions and communicate with the backend server.
Integrate MongoDB with Express.js: Connect your Express.js server to your MongoDB database using Mongoose, a MongoDB object modeling tool for Node.js.
Deploy Your Application: Once your application is complete, deploy it to a hosting provider of your choice to make it accessible to users worldwide.
Conclusion
MERN Stack offers a powerful and versatile framework for building modern web applications that are fast, scalable, and secure. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just getting started, MERN Stack provides the tools and resources you need to bring your ideas to life. So why wait? Start exploring the endless possibilities of MERN Stack today and unlock the potential of your web development projects with Meander Training, Meander training is a platform where you can start your web development journey, it provides industrial training with certification.
1 note
·
View note
Quote
ここ数か月は、サプライ チェーン攻撃の急増 に関する(おそらく大げさな)懸念 、ユビキタス図書館 、あるいは責任の重い EU サイバーレジリエンス法 など、オープンソースのセキュリティにとって厳しい状況でした。 Open Source Security Foundation (OpenSSF) の新しい Malicious Packages Repository は、 「オープン ソース パッケージ リポジトリで公開されている悪意のあるパッケージのレポートをまとめた、包括的で高品質なオープン ソース データベース」として、こうした外部の不安への対応の一部として見ることができます。 OpenSSF の悪意のあるパッケージ リポジトリ このデータベースは主に、開発者が悪意のある依存関係が CI/CD パイプラインを通過するのを阻止し、検出エンジンを改良し、環境内での使用をスキャンして防止し、インシデント対応を迅速化することを支援することを目的としており、すでに約 15,000 件の悪意のあるパッケージのレポートが登録されています。 現在、各オープンソース パッケージ リポジトリには、悪意のあるパッケージを処理するための独自のアプローチがあります。 悪意のあるパッケージがコミュニティによって報告されると、パッケージ リポジトリのセキュリティ チームはパッケージとその関連メタデータを削除する可能性がありますが、すべてのリポジトリがパッケージの公開記録を作成するわけではありません。 これは、記録が多くの異種の公共ソース上、または独自の脅威インテリジェンス フィードを通じてのみ存在することを意味します。 OpenSSF は、業界横断的な財団として一定の管理者のような正当性を享受しており、そのメンバーには AWS、Alphabet (旧 Google)、GitHub、Dell、IMB、Meta (旧 Facebook)、Microsoft などのテクノロジー大手が含まれているという事実があります。これは、集中リポジトリへのこの取り組みが重要になる可能性があることを意味します。 背景のカオス Google オープンソース セキュリティ チームの Caleb Brown 氏と Checkmarx のソフトウェア サプライ チェーン セキュリティ部門の Jossef Harsh Kadouri 氏によると、このリポジトリは、システムに対する悪意のあるパッケージ攻撃の増加に直接対応して構築されたものであるとのことです。 「今年初め、Lazarus Group(北朝鮮国家支援の多大なハッキンググループ)がブロックチェーンと仮想通貨セクターを標的にした。このグループは、欺瞞的なnpmパッケージを含む高度な手法を使用して、さまざまなソフトウェアサプライチェーンを侵害した。共有インテリジェンスの集中リポジトリは、コミュニティに攻撃についてより早く警告し、オープンソース コミュニティが脅威の全範囲を理解できるように支援しました」と二人は OpenSSF ブログ投稿 で書いています。 によると、つい先月、Telegram、AWS、Alibaba Cloud のユーザーが、悪意のあるパッケージを使用した独自のオープンソース サプライ チェーン攻撃の標的になりました Checkmarx のレポート 。 攻撃者は「kohlersbtuh15」という仮名で活動し、一連の悪意のあるパッケージを PyPi パッケージ マネージャーにアップロードすることで、オープンソース コミュニティを悪用しようとしました。 (「これらのパッケージ内の悪意のあるコードは、自動実行を実行するのではなく、関数内に戦略的に隠蔽され、これらの関数が呼び出された場合にのみトリガーされるように設計されていた」と Checkmarx 氏は指摘しています。) 悪意のあるパッケージ リポジトリ : 入手方法 Malicious Packages リポジトリのレポートでは、オープン ソース プロジェクトの脆弱性を指定するために使用される JSON 形式であるオープン ソース脆弱性 (OSV) が使用されます。 悪意のあるパッケージに OSV 形式を使用すると、osv.dev API、osv-scanner ツール、deps.dev などの既存の統合を利用できます。 OSV 形式は拡張可能でもあり、侵害の兆候や分類データなどの追加データを記録できます。 へのリポジトリについてコメントし、 The Stack セキュリティ研究者である Henrik Plate 氏は、電子メールで アプリケーションセキュリティスタートアップのEndor Labs の 次のように述べています。「特に学術研究者にとって、これはマルウェア検出への新しいアプローチを調査しテストする良い機会を提供します。基本的な作業を何度もやり直します。たとえば、PyPI や npm などのさまざまなパッケージ レジストリでの新しいパッケージの公開の監視などです。 「ありがたいことに、この部分は関連する OpenSSF パッケージ フィード プロジェクトと連携しています OpenSSFパッケージ分析 プロジェクトでカバーされており、ブログ投稿で言及されているデータベースにデータを取り込む に匹敵する AI/ML トレーニング用の貴重なデータセットになる可能性があります Backstabber's Knife Collection 。 このデータベースは、実際のマルウェア (Python ホイールや tarball など) も公開していれば、 。 これが将来的に変��ることを願っています。 「技術的な観点から見ると、これは主に悪意のある動作の動的検��に依存しているようです。 この目的のために、彼らは gVisor サンドボックスにパッケージをインストールし、潜在的に悪意のあるアクティビティを監視します。 注目に値するのは、少なくとも Python の場合、実際に悪意のあるコードをトリガーするのに大いに役立っているということです。 たとえば、特定のパッケージに存在する Python モジュールをインポートし、その関数を呼び出そうとします...」 「このアプローチは、悪意のあるコードの実行条件が満たされないため、悪意のあるアクティビティを検出できないという動的検出の典型的な問題を克服しようとします。」
無料の悪意のあるパッケージ リポジトリは強力な資産です
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
GitHub Repositories Hit by Password-Stealing Commits Disguised as Dependabot Contributions
A new deceptive campaign has been observed hijacking GitHub accounts and committing malicious code disguised as Dependabot contributions with an aim to steal passwords from developers.
"The malicious code exfiltrates the GitHub project's defined secrets to a malicious C2 server and modify any existing javascript files in the attacked project with a web-form password-stealer malware code effecting any end-user submitting its password in a web form," Checkmarx said in a technical report
The malware is also designed to capture GitHub secrets and variables to a remote server by means of a GitHub Action.
The software supply chain security firm said it observed the atypical commits to hundreds of public and private GitHub repositories between July 8 and 11, 2023.
It has emerged that the victims had their GitHub personal access tokens stolen and used by the threat actors to make falsified code commits to users' repositories by posing as Dependabot.
Dependabot is designed to alert users of security vulnerabilities in a project's dependencies by automatically generating pull requests to keep them up-to-date.
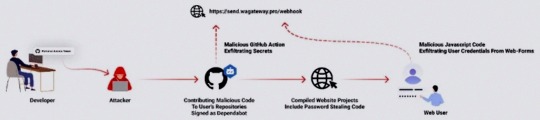
"The attackers accessed the accounts using compromised PATs (Personal Access Token) -- most likely exfiltrated silently from the victim's development environment," the company said. Most compromised users are located in Indonesia.
However, the exact method by which this theft may have taken place is currently unclear, although it's suspected that it may have involved a rogue package inadvertently installed by the developers.
This is evidenced by a new data exfiltration campaign targeting both npm and PyPI that uses as many as 39 counterfeit packages to gather sensitive machine information and transmit the details to a remote server.
The development highlights the continued attempts on part of threat actors to poison open-source ecosystems and facilitate supply chain compromises.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
You can learn NodeJS easily, Here's all you need:
1.Introduction to Node.js
• JavaScript Runtime for Server-Side Development
• Non-Blocking I/0
2.Setting Up Node.js
• Installing Node.js and NPM
• Package.json Configuration
• Node Version Manager (NVM)
3.Node.js Modules
• CommonJS Modules (require, module.exports)
• ES6 Modules (import, export)
• Built-in Modules (e.g., fs, http, events)
4.Core Concepts
• Event Loop
• Callbacks and Asynchronous Programming
• Streams and Buffers
5.Core Modules
• fs (File Svstem)
• http and https (HTTP Modules)
• events (Event Emitter)
• util (Utilities)
• os (Operating System)
• path (Path Module)
6.NPM (Node Package Manager)
• Installing Packages
• Creating and Managing package.json
• Semantic Versioning
• NPM Scripts
7.Asynchronous Programming in Node.js
• Callbacks
• Promises
• Async/Await
• Error-First Callbacks
8.Express.js Framework
• Routing
• Middleware
• Templating Engines (Pug, EJS)
• RESTful APIs
• Error Handling Middleware
9.Working with Databases
• Connecting to Databases (MongoDB, MySQL)
• Mongoose (for MongoDB)
• Sequelize (for MySQL)
• Database Migrations and Seeders
10.Authentication and Authorization
• JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
• Passport.js Middleware
• OAuth and OAuth2
11.Security
• Helmet.js (Security Middleware)
• Input Validation and Sanitization
• Secure Headers
• Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
12.Testing and Debugging
• Unit Testing (Mocha, Chai)
• Debugging Tools (Node Inspector)
• Load Testing (Artillery, Apache Bench)
13.API Documentation
• Swagger
• API Blueprint
• Postman Documentation
14.Real-Time Applications
• WebSockets (Socket.io)
• Server-Sent Events (SSE)
• WebRTC for Video Calls
15.Performance Optimization
• Caching Strategies (in-memory, Redis)
• Load Balancing (Nginx, HAProxy)
• Profiling and Optimization Tools (Node Clinic, New Relic)
16.Deployment and Hosting
• Deploying Node.js Apps (PM2, Forever)
• Hosting Platforms (AWS, Heroku, DigitalOcean)
• Continuous Integration and Deployment-(Jenkins, Travis CI)
17.RESTful API Design
• Best Practices
• API Versioning
• HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the Engine-of Application State)
18.Middleware and Custom Modules
• Creating Custom Middleware
• Organizing Code into Modules
• Publish and Use Private NPM Packages
19.Logging
• Winston Logger
• Morgan Middleware
• Log Rotation Strategies
20.Streaming and Buffers
• Readable and Writable Streams
• Buffers
• Transform Streams
21.Error Handling and Monitoring
• Sentry and Error Tracking
• Health Checks and Monitoring Endpoints
22.Microservices Architecture
• Principles of Microservices
• Communication Patterns (REST, gRPC)
• Service Discovery and Load Balancing in Microservices
1 note
·
View note
Text
is anything truly first-party? even the hardcore homelab folks still need a static ip and a reliable dns from a third-party
plus, these days, all critical js libraries start life hosted on third-party cdns. those daily/weekly metrics on their npm pages are download stats, not vibe checks
unless you're going to rebuild decades of web application infrastructure from scratch, apply all your security patches by hand, and rewrite every framework from zero, it's unavoidable, there's third-party cdns in your build and deployment pipelines. it's just a matter of who you trust, what risks you're willing to take, and what effort you're able to put in
I think the real reason most websites are janky as hell to use these days is because web developers have become so specialised that nobody really understands how anything works anymore. The other day I had to explain why hosting critical Javascript libraries on a third-party CDN is a bad idea to a "lead developer" who genuinely didn't know the difference between server-side versus client-side scripting.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring the Top Tools for Cloud Based Network Monitoring in 2025
With businesses increasingly implementing cloud-first programming, there has been no time when network visibility is more required. Conventional monitoring tools are no longer sufficient to monitor the performance, latency and security of the modern and distributed infrastructures.
And that is where cloud based network monitoring enters. It allows IT teams that have hybrid and cloud environments to have real-time views, remotely access them, and also have improved scalability.
Some of those tools are remarkable in terms of their features, user-friendliness, and in-depth analytics, in 2025. This is the list totaling the best alternatives that are assisting companies keep in front of the network problems prior to them affecting operations.

1. Datadog
DevOps and IT teams are fond of using Datadog due to its cloud-native architecture and extensive availability. It also provides visibility of full-stack, metrics, traces as well as logs, all on a single dashboard.
Its Network Performance Monitoring (NPM) allows identifying bottlenecks, tracing traffic and tracking cloud services such as AWS, Azure and Google cloud. It provides teams with the ability to move quickly with real-time alerts and customizable dashboards with the insights.
2. SolarWinds Hybrid Cloud Observability
SolarWinds is traditionally associated with on-prem monitoring solutions, whereas, with shifts toward hybrid cloud observability, it will find itself extremely pertinent in 2025. The platform has evolved and is able to combine conventional network monitoring with cloud insights.
It provides anomaly detection, visual mapping, deep packet inspection using AI. This aids IT teams to troubleshoot through complex environments without switching between tools.
3. ThousandEyes by Cisco
ThousandEyes specializes in digital experience monitoring, and it is especially applicable to large, distributed networks. It also delivers end to end visibility at user to application level across third party infrastructure.
Its cloud agents and the internet outage tracking ensure that businesses can find out in a short time whether a performance problem is either internal or external. The strong support of Cisco gives the accuracy and the access of its network data.
4. LogicMonitor
LogicMonitor is a simple to deploy and scale agentless platform. It is awesome when an organization needs automation and little configuration.
The tool measures bandwidth, uptime, latency and cloud performance among various providers. Its predictive analytics not only identify trends, but they also notify teams before minor problems become major ones.
5. ManageEngine OpManager Plus
OpManager Plus is a powerful tool to be used by those who require an infrastructure support combination of the traditional and cloud-based monitoring. It is compatible with hybrid networks that provide stats such as device health, traffic and application performance.
It is distinguished by the UI, which is clean, self-explanatory, and can be customized. It especially is suitable in the middle-sized IT departments who require an unobstructed glance of both physical and virtual systems.
6. PRTG Network Monitor (Cloud Hosted)
The hosted version of PRTG has the same functions as its widely used desktop version, and its availability is on cloud levels. It carries sensors to keep track of server availability to network capacity and usage as well as cloud services.
It is perfect when companies require such a convenient approach as a license and payment as you go prices. Even the simpler option of the tool can be a good option to apply to the project where IT team size is smaller or you are at the beginning of the cloud migration.
What to Look for in a Monitoring Tool
When choosing a cloud network monitoring solution, it's important to focus on a few key aspects:
Ease of deployment and scalability
Multi-cloud and hybrid support
Custom alerting and reporting
Integration with your existing stack
User-friendly dashboards and automation
Each business is unique in its requirements and there is no such thing like the best tool, only the tool that suits your infrastructure, the size of your team and your response requirements.
Conclusion
With evolving infrastructure it is important to have the correct tools implemented to observe performance and availability. In 2025, the cloud based network monitoring tools will be more competitive, intelligent and responsive than ever.
Be it a Hollywood-sized company or a small IT start-up, by investing in any of these best platforms, you have the sight of keeping secure, flexible and consistent in a cloud driven planet.
0 notes
Text
Node.js 24 Released: Key Features and Developer Benefits
Node.js 24 is now available with powerful updates that boost app speed, security, and developer productivity. It includes the new V8 13.6 engine, which adds better performance and features like Float16Array, safer regular expressions, and smarter error handling.
This release also comes with npm 11, making package installs faster and more secure. Developers using Windows will now need to switch to the ClangCL compiler, which brings faster builds and fewer errors.
Other highlights include global access to the URLPattern API, better async context tracking, improved testing with automatic subtest handling, and the modern Undici 7 HTTP client with HTTP/2 support.
Node.js 24 also removes outdated APIs to improve security and performance. Upgrading helps future-proof your apps and ensures they run faster and more reliably.
Ready to upgrade your app stack?
#Nodejs24#JavaScript#WebDevelopment#npm11#Undici#AsyncProgramming#SoftwareUpdate#NodejsUpgrade#PerformanceMatters#DevTools
0 notes
Text
How to Hire a Node.js Developer for Your Web Project in 2025

In 2025, it is more important than ever to build fast, scalable, and real-time web applications. Businesses in various industries use Node.js, a powerful JavaScript runtime, to create dynamic backend architecture to manage high concurrency with low response times. However, most importantly, you will need to find a good developer to bring this technology to life. But how do you hire the right Node.js developer to fit your project goals, timelines and budget?
In this blog, we will show you everything you need to know to hire dedicated NodeJs developers from trusted partner Jellyfish Technologies, and use advanced Nodejs development services for web applications in 2025.
Why Node.js Is Still Dominating in 2025
Before we dive into the hiring process, let's quickly understand why Node.js remains a top choice for backend technology:
Non-blocking I/O for real-time applications
Single programming language (JavaScript) in both front and back end
Huge ecosystem with npm (over 2 million packages)
Great scalability with microservices architecture
Strong community support and actively evolving (Node 20+)
Node.js can support the performance and flexibility that modern applications require, whether you're building a live chat app, a fintech dashboard, or an eCommerce platform.
Read also: Top Backend Technologies
Step-by-Step Guide to Hiring a Node.js Developer in 2025
Clarify your project needs The first step is to get clear. Ask yourself:
What do I want the app to accomplish?
What is the scope (timelines and budgets)?
Do I need someone full-time, part-time, or project-based?
This will help you figure out whether you will hire a freelancer, hire and onboard someone to in-house, or hire and onboard dedicated NodeJs developers through Jellyfish Technologies.
Determine the best engagement model Companies are increasingly adopting a flexible hiring model for talent in 2025:
Freelancers - Best for short-term tasks or quick fixes.
In-house Developers - Good for long-term, but expensive.
Dedicated Development Teams - The sweet-spot that works for most companies. When you hire dedicated NodeJs developers, you will get long-term focused talent at a lower operational cost.
Jellyfish Technologies provides Node.js development services will also provide built-in accountability and access to more available qualified talent.
Assess Important Technical Skills As you assess candidates or service providers, make sure they are proficient in:
Core Node.js Concepts (event loop, streams, and clusters)
RESTful APIs & GraphQL
Frameworks such as Express.js, and NestJS
MonogoDB, PostgreSQL, or MySQL
Authentication and Security practices (OAuth, JWT)
CI/CD, Docker, and Cloud Deployment (AWS, GCP, Azure)
Points for documentation on Typescript, microservices architecture, and WebSockets real-time communication.
Evaluate Soft Skills and Communication Just as technical knowledge is important, so too is communication, problem-solving, and working together—especially when working with remote partners. You want to make sure your developer can:
Explain complex topics simply
Work well with designers and front-end developers
Take feedback and work in an Agile way.
Review Portfolios and Previous Projects
A good portfolio tells you a lot. Look for:
Apps they've developed in Node.js
What they're role was and what they did in the project
Whether they’ve shown code samples or GitHub activity
And better yet, ask for references or case studies, especially if you’re looking to engage Nodejs development services through an agency.
Test Before You Buy In
Before you committed to someone for the long haul, it should be a no-brainer to:
Define a small paid task or a small period of trial
Do technical interviews or code challenges
Make use of platforms such as HackerRank or Codility.
This just confirms that you're actually hiring someone who can do the job and not an entertainer with an impressive CV.
Why Hiring Dedicated NodeJs Developers Is a Smart Move
The digital landscape in 2025 is increasingly competitive and innovation-oriented, and your web project deserves not just any backend developer, but one who understands performance, scalability and your overall business goals.
This is why so many organizations hire dedicated NodeJs developers through reputable providers such as Jellyfish Technologies. Jellyfish Technologies has a proven track record, allows flexible engagement options, has a talented pool of engineering talent, and will provide you with top tier Nodejs development services, tailored to your specifications.
No matter if you are building an MVP or scaling a full enterprise application, the right development team will make the difference. Choose your team wisely; and let your technology take you to the top!
0 notes
Text
SSH keys stolen by stream of malicious PyPI and npm packages

Source: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/ssh-keys-stolen-by-stream-of-malicious-pypi-and-npm-packages/
More info: https://blog.phylum.io/sensitive-data-exfiltration-campaign-targets-npm-and-pypi/
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Debugging Full Stack Apps: Common Pitfalls and Fixes
If you’ve ever stared at your code wondering why nothing works—while everything looks fine—you’re not alone. Debugging Full Stack Apps: Common Pitfalls and Fixes is something every full stack developer becomes intimately familiar with, usually the hard way. Debugging can feel like detective work: sifting through clues, spotting red herrings, and slowly putting the pieces together.
Whether you’re knee-deep in React components or wrangling with PostgreSQL queries, bugs don’t discriminate. They can lurk in the front end, back end, or anywhere in between.
Here’s a look at common pitfalls when debugging full stack apps—and practical ways to fix them.
1. Miscommunication Between Front End and Back End
One of the most common issues arises from how the front end communicates with the back end. Sometimes, they seem to speak different languages.
Common Symptoms:
API calls returning unexpected results (or nothing at all)
Mismatched data formats (e.g., sending a string where the server expects a number)
CORS errors that mysteriously appear during deployment
Fixes:
Always double-check your request headers and response formats.
Use tools like Postman or Insomnia to simulate API requests separately from your front-end code.
Implement consistent API response structures across endpoints.
As a full stack developer, ensuring clean contracts between layers is essential. Don’t assume—it’s better to over-communicate between parts of your app than to be left scratching your head at 2 AM.
2. Version Mismatches and Package Conflicts
Let’s face it: dependency hell is real.
Common Symptoms:
Front-end not rendering after an npm install
Server crashing due to deprecated methods
Mysterious breaking changes after updating a package
Fixes:
Lock dependencies using a package-lock.json or yarn.lock file.
Regularly audit your packages with tools like npm audit or yarn audit.
Avoid updating all dependencies at once—do it incrementally and test thoroughly.
Even the most seasoned full stack developer gets tripped up here. Being methodical with updates and isolating changes can save you hours of frustration.
3. State Management Gone Wrong
If your app behaves inconsistently, the problem might be state management.
Common Symptoms:
UI doesn’t reflect expected changes
Data seems to "disappear" or update out of sync
Components re-render unnecessarily
Fixes:
Use debugging tools like Redux DevTools or Vuex Inspector to trace changes.
Store only essential data in global state—leave UI state local whenever possible.
Be cautious with asynchronous operations that update state (e.g., API calls).
Mastering state is part art, part science. As a full stack developer, understanding both front-end and back-end data flow is key to smooth state management.
4. Overlooking Server Logs and Console Errors
It’s easy to jump straight into the code—but logs often contain the breadcrumbs you need.
Common Symptoms:
500 errors with no clear origin
"Something went wrong" messages with no context
App crashing without traceable bugs
Fixes:
Always monitor the back-end logs (use console.log, but also tools like Winston or Log4js for structured logging).
Use browser developer tools to inspect network requests and console outputs.
Integrate error-tracking tools like Sentry or LogRocket.
A skilled full stack developer knows that logs are like black box recorders for your app—ignore them at your own peril.
5. Deployment-Specific Bugs
Your app runs perfectly locally—but breaks in production. Sound familiar?
Common Symptoms:
Missing environment variables
Static assets not loading
Database connection failures post-deployment
Fixes:
Use .env files carefully and securely manage environment-specific configs.
Ensure your build process includes all required assets.
Test your deployment process using staging environments before going live.
Every full stack developer eventually realizes: what works in dev doesn’t always work in prod. Always test in conditions that mimic your live environment.
Final Thoughts
Debugging Full Stack Apps: Common Pitfalls and Fixes isn’t just about technical skills—it’s about mindset. It’s easy to get overwhelmed when something breaks, but remember: every bug you squash teaches you something new.
Here are some golden rules to live by:
Reproduce the bug consistently before trying to fix it.
Break down the problem layer by layer.
Ask for a second pair of eyes—sometimes, fresh perspective is all it takes.
Being a full stack developer is like being a bridge-builder—you connect front end and back end, logic and interface, user and server. And in between, debugging is your glue.
So next time you hit a wall, take a breath, grab a coffee, and dig in. You’ve got this.
#FullStackDeveloper#FullStackDevelopment#FullStackCourse#TechnoBridgeFullStack#LearnFullStack#FullStackTraining#MERNStack#FrontendDevelopment#BackendDevelopment#CareerInTech#CodingBootcamp#SoftwareDevelopmentCourse#TopFullStackDeveloperCourse#PlacementAssistance#JobOrientedCourse#UpskillNow#ReactJS#ITTrainingIndia
0 notes