#sure this is not picking a text into pieces nor a content analysis
Text
As someone who's about to work in biology research, I can't stay silent about the Frontiers AI rat penis event.
LOOK AT HIM

WARNING: LONG AF. STRAP YOURSELVES IN, WITCHES!
I'll explain in detail, in a way that's accessible for non-scientists, everything that's wrong with this. Recently, a scientific article with AI generated figures was published in the journal "Frontiers in cell and developmental biology".
Here's the link to download this (now retracted) article in PDF.
(disclamer: I am a master's student in neuroscience with a bachelor's in biology, so, definitely not a rat ball specialist, and I have never published anything)
Context
This is a review article about the relationship between rat ball cells and a signalling pathway that happens inside cells.
What's a review article? It's an article that is meant to summarise everything we know about a certain topic, based on recent research articles. This means that the authors of a review don't conduct any experiments: they gather information from people who did. It sounds easy but it's not. They have to piece together a very complex puzzle. Sometimes an article says that molecule A interacts with molecule B and gives you such and such effects, but in another article they say they haven't found any effect in particular of molecules A and B, and a third article will tell you that the effect exists in cell cultures but not in an actual animal because molecule C is also there... And there are dozens and dozens of articles they have to sift through, dissect, evaluate etc. And then they have to make sense of that whole hoopla. And then they have to explain it to everyone.
BUT. A review is probably the easiest type of scientific article to fake. Because for a research article, you have to conduct actual experiments and provide results. For a meta-analysis, you will come under great scruitiny because they are expected to be very reliable and when a new meta-analysis drops, the hype in the field is big. People will see through it in seconds. But a bullshit review? People are not as interested in picking apart reviews, because there are no experimental results directly shown in them, no statistical calculations or criteria to criticise etc. It's almost all text. You can AI generate text. You can write lazily and it will still have the appearance of a review from afar.
However, a review has figures. The figures are meant to illustrate the mechanisms of the phenomena described in the review. Usually, those are very clean, easy to understand even for non-specialists, they are your best friend when you're not too sure what's going in this wall of text and you want to get the gist. Review figures are good educational tools, so you need to have a good understanding of the topic and be concise to make a good review figure. You can't fake that with AI.
In order to publish a review, just like any other scientific article, you have to submit it to a scientific journal. You have to format your article exaclty according to the journal's criteria, (and if you were wondering, no you don't get paid for doing the journal's job for them, nor do you get paid for providing them content you took years to produce, in fact you have to pay them, the journal, thousands of dollars). Your article will then go through several rounds of selection and revisions. First the journal will decide whether or not your article is relevant to their area of expertise (like, if you try to publish a paper on quantum mechanics to the journal "Poultry Science", it will not work, no matter if you're better than Einstein and Hawking combined). Then they'll decide whether or not your article is interesting enough to them. If it is, they will send your article to reviewers (usually 2, sometimes 3). Reviewers are researchers who are knowledgeable about the topic you're covering in your article. They're usually anonymous, they shouldn't be associated with the journal and they don't get paid by the journal for reviewing the paper (this is to guarantee neutrality, but still it's work to review an article and they don't get paid). The reviewers will suggest modifications to the paper, ask for clarifications etc. You change your paper, they give their suggestions again, you change your paper again... Then after this back and forth is done, if everyone is satisfied, your article can get published. I'd like to emphasize that in a decent journal, it almost never happens that a paper gets accepted right away without any rounds of corrections. Most of the time, reviewers get real nitpicky and I've had professors complain that they'll sometimes freak out over every single comma. This is what the term "peer-reviewed" means. Other researchers in the field have to critique your paper before it even comes out, and after it comes out, every other scientist who reads your paper can critique your paper. Some say the real peer review starts after publication, because then everyone in the scientific community can pick your article apart and determine how relevant it actually is by deciding whether or not to cite it in their own works.
The journal this article was published in, Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, is not the most prestigious, but it is (or was, I guess) still rather reputable with an impact factor of 5. The impact factor is a score that evaluates the quality of a journal based on how many times their articles were cited as references in other articles. To give you an idea, here are the 2023 impact factors of the biggest journals in biology:
Science: 57
Nature: 65
Cell: 65
The average impact factor for all scientific journals is under 1, because there are a lot of shit journals out here. Journals are businesses that can be very low effort to set up, so the quality journals are actually few. An impact factor above 10 means business, that's some shit you can brag about. 5 is not super glorious but it's decent.
Frontiers is not just one journal but a group of journals, each specialised in one topic (Frontiers in Immunology, Frontiers in Surgery, etc) each with their own impact factor.
Where did shit go wrong?
I don't know what the fuck went through the authors' heads. Was this a troll? Were they serious?? Anyway let's start with the funniest and most visible part.
The figures
Figure 1
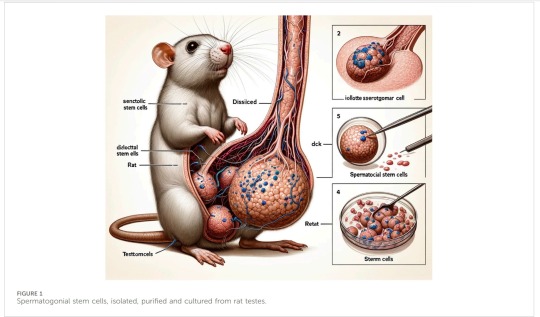
Do I really need to explain? These aren't real body parts. These aren't even words. Shoutout to "rat", the only correct part of this figure. The caption says just about nothing.
This is the image that went viral because... Of course. It's a massive rat dick and balls. But the other figures aren't any better.
Figure 2
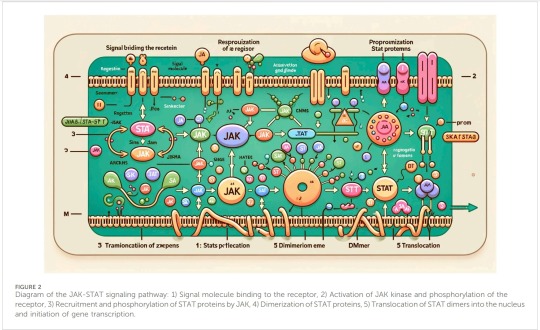
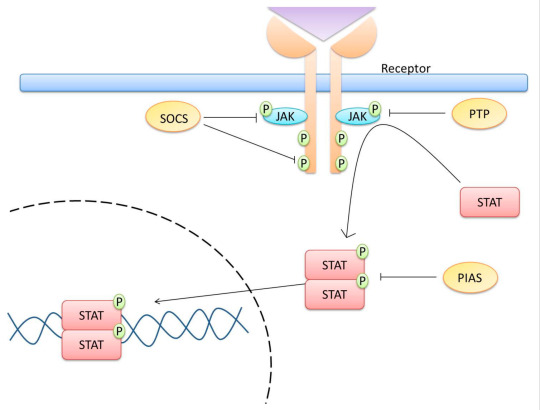
This is supposed to represent the JAK-STAT intracellular pathway. JAK and STAT are proteins, and this is supposed to represent how their activation impacts other molecules inside the cell. As you can see, again, not a single real word on that figure, this represents absolutely nothing. You can clearly see that the authors gave the AI image generator "JAK-STAT pathway" as a prompt because every single thing on this image is labelled as some variation of JAK or STAT. Which is pretty funny. Another thing I find hilarious is that the caption underneath the figure is actually a correct description of the JAK-STAT pathway, which leads me to think it was written by a human. For reference here's an actual diagram that represents this pathway rather simply (by Adriana Gutiérrez-Hoya and Isabel Soto-Cruz)
Source
Figure 3

Again, no real words, just a bunch of balls and circles without any meaning. I can't speak about whether or not the caption makes any sense because I'm not too well versed in the topic. Special shoutout to the beautiful word "IMMOUMINOMUDUODIUILATIUCATON" in figure E. I think that was an attempt at saying "immunomodulation".
The content of the text
This review attempts to summarise the current knowledge on spermatogonial stem cells in relation to the JAK-STAT pathway. Spermatogonial stem cells are self-renewing cells located in testicles that allow for continuous production of sperm cells throughout a male mammal's whole adult life. The JAK-STAT pathway is a cellular signaling pathway. What this means, in simple terms, is basically a cascade of proteins inside a cell that talk to each other to say shit like "hey hey hey have you heard that there's a bunch of [X] molecule outside?? We better do something about it." And then they do something about it.
As I've said before I'm not an expert in this area at all. I vaguely know the JAK-STAT pathway, the structure of testicles, and what stem cells do, but it stops there. I do want to discuss the content of this article though, because I haven't seen anyone do it yet and I wish an expert in the field would tell us what the content of that review is really worth.
There are some things that do seem fishy in here. First of all, when I first read the abstract, I was convinced that the whole article was AI generated because it looked like a succession of buzzwords. Turns out, the captions of the figures make sense and the text seems somewhat coherent. I would tend to say it was written by people, albeit in a very boring and unclear way. Then I went to the references to check if they were real. It turns out, at least the references are real articles.
I will not speak on the validity of the claims made in the article because I'm not knowledgeable enough. I've checked some references at random though, and sometimes, they are only very very loosely related to the claim in the review that they're supposed to illustrate, or sometimes just unrelated.
Example: at the beginning of page 7, you can read "miR-34c activates the JAK2/STAT3 pathway, implicated in germ cell
generation and SSC differentiation (Clotaire et al., 2018)." When you go to that 2018 reference, you find out that this paper is not about miR-34c (it's not even mentioned once in that article). It's about another miRNA called miR-19b-3p. I've checked, they are 2 completely different miRNAs. They're not even coded on the same chromosome ffs. The article barely mentions JAK2 and the few times it does mention JAK2, there is no significant result showing any activation of JAK2.
Other example: at several points throughout the review, the authors claim that spermatogonial stem cells have an important immunomodulatory role. I haven't found literature supporting this claim anywhere. The one reference that the authors linked to this claim was absolutely not about immunomodulation, it was about reprogramming spermatogonial stem cells into neurons. What I did find, is several mentions of Sertoli cells (another type of cell present in testicles) having an immunomodulatory role.
Literally a case of [citation needed]. If there is one place where you have to have proper citations, it has to be a review article. This seems like some top tier laziness. I kind of doubt myself because I don't want to believe that someone would make a review where they don't source their information. I want to believe that I understood their reference articles wrong. But for real, check for yourself if you know a bit about biology. I don't think I'm wrong here.
I will not dive further into the content but tell me if y'all are interested. I will read up on rat balls to try and see if there is more bullshit in here, section by section, if you want me to.
The authors
The lovely individuals behind this review are Xinyu Guo, Liang Dong, and Dingjun Hao. All three are part of the Department of Spine Surgery in Xi'an Honghui hospital in China.
Because I don't speak chinese, and because it's common for hundreds or even thousands of people to have the exact same name in China, and because chinese social media is isolated from the rest of the world, it was hard for me to find information about these people.
All I can think is, what were they thinking??
First of all, what are y'all spine surgeons doing writing about rat balls?
First author - Xinyu Guo
For context, the first author is the person who contributed the most to the paper.
It's hard to find information about this person due to a lot of homonyms. However I was able to find 4 other articles from them on ResearchGate, which were about spinal cord injury, the JAK-STAT pathway, and one about reprogramming spermatogonial stem cells into neural-like cells in order to transplant them and help with recovery after spinal cord injury. So I guess that's why they're interested in rat balls. Kind of makes sense, but it looks like spermatogonial sperm cells could be a tool that they use in their research, and not their actual area of expertise which is, ya know. Spines. They seem knowledgeable about spines. I've also found their name in articles that were reports of medical cases and treatments for spinal injuries. I haven't found any online accounts related to this person, even on "scientist" social media like ResearchGate. My hypothesis is that this is a medical doctor turned researcher who got into using stem cells.
I did find this person as a reviewer for a paper in Frontiers in Immunology. If they're also in the field of immunology, that might explain why the review was so adamant that these spermatogonial stem cells have a role in immunomodulation...
Anyway, it doesn't seem very wise to have someone who is not specialised in stem cells to be the main author of a review about stem cells.
Second author - Liang Dong
Again, all I can find on that person is about spines and how to fix them. Articles associated with them are related to spinal cord injuries, spine surgeries, reports about medical cases and treatment efficiency etc. Nothing related to stem cells, except that one fateful review. No social media accounts either that I could find.
Third and last author - Dingjun Hao
Another Mister Spine. An experienced and prestigious one, even. He is (or was, I'm unsure) the president of the spinal surgery department of the hospital all three authors work at. He was also an author on many other papers, including those I found with the first author, so he did read the term spermatogonial stem cells at some point in his life it seems. But with his rhythm of publication (sometimes more than 10 papers a year), there is simply no way he is putting much effort in all of these papers. It seems like he is an old renowned professor, director of such and such department, who gets almost automatically added as an author in all of his colleagues' papers. I doubt he contributed a significant amount to this review. There's even a chance he hasn't read it.
He has been a reviewer for another journal of Frontiers, Frontiers in Surgery. He reviewed various papers on spinal injuries, which is fair enough because it's his area of expertise.
This time though, I got some more fun details. Interestingly, I found this from the website of Honghui hospital:

Looks like our friend won a great prize from the chinese government for his scientific work! Congrats! I'm sure that this botched review and the associated global backlash will not affect his relationship with the chinese government at all!
Overall, it seems like the authors are indeed spine surgeons, probably good ones, but not researchers specialised in stem cells or cellular singaling pathways.
This leads me to think that this review was not a troll at all. The likely scenario, in my opinion, is that, since all institutions need to publish articles to stay relevant (the age old slogan, publish or perish), the first two authors were asked to write a review and did so in a rush, about a topic they're vaguely familiar with. They didn't have anyone available to make cool looking figures, so they resorted to using AI at the last minute. It turned out terrible but they still tried to publish it in a not so prestigious journal, and somehow succeeded. They probably thought nobody would notice because no one would care enough to read it (and fair enough it is boring as hell).
The last author likely just has his name on there because he's the head of the department they work at, and these guys always get the last author spot by default. They're not necessarily very involved in the paper because they don't have time, but it benefits them by inflating their publication count.
The reviewers/the journal
With the way the figures look, there is absolutely no way a reviewer even looked at this paper and gave a favorable opinion. Point blank. Even an editor with very little scientific knowledge would have screamed seeing this. So what happened here?
After retracting the paper, just a few days after the publication, Frontiers released a statement in which they say:
"Our investigation revealed that one of the reviewers raised valid concerns about the figures and requested author revisions. The authors failed to respond to these requests. We are investigating how our processes failed to act on the lack of author compliance with the reviewers' requirements."
It seems like one reviewer (why just one??) raised concerns, somehow their opinion was not taken into account, and the editor still chose to publish without the reviewer's accord which is a huge no-no (means the paper is not in fact peer reviewed).
In a Vice article, one of the two reviewers, Jingbo Dai, (probably the one who didn't raise concerns, as you can tell from his detached attitude) said:
"As a biomedical researcher, I only review the paper based on its scientific aspects. For the AI-generated figures, since the author cited Midjourney, it's the publisher's responsibility to make the decision," Dai said. "You should contact Frontiers about their policy of AI-generated figures."
This is utter bullshit, because the figures are 100% part of the review, they are a "scientific aspect", and if they are inaccurate it's totally the reviewer's job to call them out. This guy simply doesn't give a shit. He shouldn't have accepted to review this paper if he didn't want to bother doing the bare minimum. If by "scientific aspects" he means the text, had he checked the references, he would have noticed some shit to fix as well.
Basically, what happened is that at least one reviewer didn't do his job, the editors flat out didn't look at what they published, and they only bothered looking at it when the backlash started. A nice chain of incompetence.
Conclusion
What does this mean for the scientific community?
It's important to note that the reason this article was even retracted is thanks to online backlash from the scientific community. What corrects science? More science. Better science. Not your aunt who "did her own research" on Young Living's facebook page.
Many in the scientific community are now more than ever highly critical of Frontiers, saying they will never publish in or review for them. The reputation of the journal is severely tarnished in the eyes of many, and one can hope that this will make editors look twice before they publish bullshit.
This may or may not be a career-ending mistake for the authors as well. We will see in the following weeks or months if they get to keep their jobs. They might not be able to publish in scientific papers ever again due to bad reputation. But I don't think they will have to stop their work as surgeons, since this is a completely different activity.
For me, this whole ordeal is a reminder that scientific journals are, first and foremost, businesses. Ultimately, they don't give a shit if what they publish is true. They only pretend to care about scientific integrity to maintain their reputation.
I hope that this will also encourage co-authors, especially senior researchers who get the last author spot by default, to be more cautious about what kind of papers they're willing to put their name on. And I hope this encourages institutions to lower their push for their researchers and doctors to publish publish publish no matter the quality, just so they can flex how many papers came out of their institution.
If anyone actually read this entire thing, thank you so much. I am very grateful that you found my rant good enough to read. If you have any additional information or corrections, please share them! Because this is just something a master's kid wrote in a boring afternoon, so there might be some errors. Have a nice day and uh... stay sciencing
#rat penis scandal#science#stem cell research#biology#frontiers#research#scientific research#can't believe I wrote this#long post#deep dive#scientific scandal
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good or Bad? An Adaptation Review and Analysis of "Suppose a Kid from the Last Dungeon Boonies Moved to a Starter Town" Episode 1 (SPOILERS)

By: Peggy Sue Wood | @peggyseditorial
Whenever I think about adaptations, I always try to remember that the anime and manga are different works. I try to enjoy them as you might enjoy two different books with similar premises, but that doesn’t mean I don’t compare them, and this series is pretty hard not to compare to its comic-counterpart.
Suppose a Kid from the Last Dungeon Boonies Moved to a Starter Town, is a comedy, as the title implies. The MC, Lloyd Belladonna, is our overpowered center of the story seen front and center in the image above.
As of Episode 1, we've already diverged from the manga's events, character designs, and dialogue pieces. Probably because of the race to get through content in this opening episode. What do I mean?
I mean that Episode 1 is essentially the first three and one-eights chapters of volume one, which was only about four chapters long. Now, keep in mind that much of the first volume was filler, with jokes about how overpowered Lloyd is and how he doesn't have any common sense regarding what constitutes normal because of where he grew up. The manga did not appear to be aiming for a solid, long story so much as setting up for a series of comedic events playing with tropes of the fantasy-adventure genre. (Not to imply that there wasn’t a plot in there, simply that it takes a back seat.)
The anime condenses a lot of these comedic moments, and even leaves out many details in a way that seems focused on setting up for a larger story.
For example, in both the anime and manga, Lloyd goes on an errand run for Marie, the Witch he's to live with while attending school. When he returns from running errands in the manga, he gifts Marie a beautiful broach that she notes is way too expensive given how much money he had when leaving. Lloyd explains that he ran to another kingdom and back again to get the items she asked for since they had lower prices, allowing him to spend the money on this luxury gift for her. He also explains how he fixed a number of problems along the way that would be deemed miracles by most regular people in the text. The scene serves as another example in the text of how strong Lloyd is while also showing how little he knows about the world beyond his village. This conversation acts as confirmation, and a slight copy, of a previous retelling of events to Marie, in which Lloyd retold of how he arrived at the capital after running there over six days--a feat anyone else might deem impossible but is considered "slow" in his village. The anime, however, leaves much of these details out. For example, Marie doesn't ask him about the jewelry, nor does she hear about him running to another kingdom to pick up the items she asked for--instead, she blushes, and we move on to the next day.
Other differences in the anime include introducing an elder-brother character who gives Lloyd a book of fairy tales that inspire Lloyd's wish to become a knight. The concept of stories inspiring Lloyd's wish is mentioned in the manga, but I do not believe that a specific book was shown nor that a brother character was present. In fact, Lloyd seems to be a child "raised by a village" in the manga, while his anime counterpart appears to have a family consisting of at least one elder brother and a grandparent.
During the aforementioned errand run, Lloyd meets Selen Hemein, or the Cursed Belt Princess, who he saves in more than one way--first from a monster and then from her curse. She becomes his stalker-like love interest (she's stanning him hardcore) that he sees her as a new friend (played for comedic effect). Her character design and personality at the end of the episode look pretty similar to her manga counterpart as with the other characters. I mention "by the end" because when we first meet her, I noticed that she had long hair, which becomes short in subsequent scenes even though I'm pretty sure we only see her with short hair at the start in the manga.
Moving on...
Are these changes good? Bad? I think these are good changes. It certainly makes the story move a lot faster. However, these changes do hold the consequences of stealing from the comedy and character personalities in many ways. For example, we see less of Lloyd's struggle with self-confidence, which changes how we view him as a character. In the manga, his self-confidence issues play a role in how he acts around others--making him act meek and brushing off compliments as someone being overly kind. This issue is compounded by the three times he does something amazing (getting to the capital in six days by running there, cleaning Marie's house with ancient magic/using runes, and the events on his errand run). This is shown in how Lloyd retells the events and is told that what he did is impressive, only to respond to the praise with growing depression and discomfort because he sees his actions as simple or lacking due to how he was raised. In the anime, we see his low self-confidence but don't get to see how extensive this issue is because we mostly see him happily exploring, smiling, and helping out. Meaning that the different approaches don’t his us the same emotionally.
This change may still be for the good of the story, as the same scenes that brought us this emotional difference in the manga, also served as comedic scenes that felt repetitive in showing us Lloyd’s OP skills.
If the anime plans to focus more on the story's adventure/fantasy elements, then these changes will remain good. It certainly allows us to fly through the exposition portion of the story quickly, which could be a good thing for those of us who already know how it begins. And I don't think it hurts new viewers who are unfamiliar with the manga-version to start with the anime. It's different, but it's consistently different, and it will probably set up an entirely new story, meaning that you won't feel the same whiplash I felt upon seeing an unknown character so early.
Side note, someone I watched this with said that Riho Flavin is the actual female lead/main love interest, and all I can say to that is: You're wrong. Sorry (but not really).
Episode 1 leaves off at the admissions board for new students of the soldier's academy, and Lloyd's name is missing (but don't worry too much about that 😉). That's where Chapter 4 opens in the first volume.
Would I recommend it? Yes. It's pretty good, and I have high hopes for the future of this series. I'd rate it 7/10 for now, but that could go up or down dependent on further episodes. You can watch it now on Funimation.com.
#Tatoeba Last Dungeon Mae no Mura no Shounen ga Joban no Machi de Kurasu Youna Monogatari#Suppose a Kid from the Last Dungeon Boonies moved to a starter town?#Suppose a Kid from the Last Dungeon Boonies Moved to a Starter Town#Who Longs For Life In The City And Goes to Live in The Starting Town#A Story About a Boy in the Village Right Before the Last Dungeon#anime#manga#adaptation#funimation#review#analysis
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
via Blogger https://ift.tt/3aKTI0F
#blogger #bloggingtips #bloggerlife #bloggersgetsocial #ontheblog #writersofinstagram #writingprompt #instapoetry #writerscommunity #writersofig #writersblock #writerlife #writtenword #instawriters #spilledink #wordgasm #creativewriting #poetsofinstagram #blackoutpoetry #poetsofig
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
from The Moz Blog http://tracking.feedpress.it/link/9375/13195579
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
from The Moz Blog https://ift.tt/38IEuYl
via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
https://ift.tt/3aKDtRp
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there���s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes
Text
The Dirty Little Featured Snippet Secret: Where Humans Rely on Algorithmic Intervention [Case Study]
Posted by brodieclarkconsulting
I recently finished a project where I was tasked to investigate why a site (that receives over one million organic visits per month) does not rank for any featured snippets.
This is obviously an alarming situation, since ~15% of all result pages, according to the MozCast, have a featured snippet as a SERP feature. The project was passed on to me by an industry friend. I’ve done a lot of research on featured snippets in the past. I rarely do once-off projects, but this one really caught my attention. I was determined to figure out what issue was impacting the site.
In this post, I detail my methodology for the project that I delivered, along with key takeaways for my client and others who might be faced with a similar situation. But before I dive deep into my analysis: this post does NOT have a fairy-tale ending. I wasn’t able to unclog a drain that resulted in thousands of new visitors.
I did, however, deliver massive amounts of closure for my client, allowing them to move on and invest resources into areas which will have a long-lasting impact.
Confirming suspicions with Big Data
Now, when my client first came to me, they had their own suspicions about what was happening. They had been advised by other consultants on what to do.
They had been told that the featured snippet issue was stemming from either:
1. An issue relating to conflicting structured data on the site
OR
2. An issue relating to messy HTML which was preventing the site from appearing within featured snippet results
I immediately shut down the first issue as a cause for featured snippets not appearing. I’ve written about this topic extensively in the past. Structured data (in the context of schema.org) does NOT influence featured snippets. You can read more about this in my post on Search Engine Land.
As for the second point, this is more close to reality, yet also so far from it. Yes, HTML structure does help considerably when trying to rank for featured snippets. But to the point where a site that ranks for almost a million keywords but doesn’t rank for any featured snippets at all? Very unlikely. There’s more to this story, but let’s confirm our suspicions first.
Let’s start from the top. Here’s what the estimated organic traffic looks like:
Note: I’m unable to show the actual traffic for this site due to confidentiality. But the monthly estimation that Ahrefs gives of 1.6M isn’t far off.
Out of the 1.6M monthly organic visits, Ahrefs picks up on 873K organic keywords. When filtering these keywords by SERP features with a featured snippet and ordering by position, you get the following:
I then did similar research with both Moz Pro using their featured snippet filtering capabilities as well as SEMrush, allowing me to see historical ranking.
All 3 tools displaying the same result: the site did not rank for any featured snippets at all, despite ~20% of my client's organic keywords including a featured snippet as a SERP feature (higher than the average from MozCast).
It was clear that the site did not rank for any featured snippets on Google. But who was taking this position away from my client?
The next step was to investigate whether other sites are ranking within the same niche. If they were, then this would be a clear sign of a problem.
An “us” vs “them” comparison
Again, we need to reflect back to our tools. We need our tools to figure out the top sites based on similarity of keywords. Here’s an example of this in action within Moz Pro:
Once we have our final list of similar sites, we need to complete the same analysis that was completed in the previous section of this post to see if they rank for any featured snippets.
With this analysis, we can figure out whether they have featured snippets displaying or not, along with the % of their organic keywords with a featured snippet as a SERP feature.
The next step is to add all of this data to a Google Sheet and see how everything matches up to my client's site. Here’s what this data looks like for my client:
I now need to dig deeper into the sites in my table. Are they really all that relevant, or are my tools just picking up on a subset of queries that are similar?
I found that from row 8 downwards in my table, those sites weren’t all that similar. I excluded them from my final dataset to keep things as relevant as possible.
Based on this data, I could see 5 other sites that were similar to my clients. Out of those five sites, only one had results where they were ranking within a featured snippet.
80% of similar sites to my client's site had the exact same issue. This is extremely important information to keep in mind going forward.
Although the sample size is considerably lower, one of those sites has ~34% of search results that they rank for where they are unable to be featured. Comparatively, this is quite problematic for this site (considering the 20% calculation from my client's situation).
This analysis has been useful in figuring out whether the issue was specific to my client or the entire niche. But do we have guidelines from Google to back this up?
Google featured snippet support documentation
Within Google’s Featured Snippet Documentation, they provide details on policies surrounding the SERP feature. This is public information. But I think a very high percentage of SEOs aren’t aware (based on multiple discussions I’ve had) of how impactful some of these details can be.
For instance, the guidelines state that:
"Because of this prominent treatment, featured snippet text, images, and the pages they come from should not violate these policies."
They then mention 5 categories:
Sexually explicit
Hateful
Violent
Dangerous and harmful
Lack consensus on public interest topics
Number five in particular is an interesting one. This section is not as clear as the other four and requires some interpretation. Google explains this category in the following way:
"Featured snippets about public interest content — including civic, medical, scientific, and historical issues — should not lack well-established or expert consensus support."
And the even more interesting part in all of this: these policies do not apply to web search listings nor cause those to be removed.
It can be lights out for featured snippets if you fall into one of these categories, yet you can still be able to rank highly within the 10-blue-link results. A bit of an odd situation.
Based on my knowledge of the client, I couldn’t say for sure whether any of the five categories were to blame for their problem. It was sure looking like it was algorithmic intervention (and I had my suspicions about which category was the potential cause).
But there was no way of confirming this. The site didn’t have a manual action within Google Search Console. That is literally the only way Google could communicate something like this to site owners.
I needed someone on the inside at Google to help.
The missing piece: Official site-specific feedback from Google
One of the most underused resources in an SEOs toolkit (based on my opinion), are the Google Webmaster Hangouts held by John Mueller.
You can see the schedule for these Hangouts on YouTube here and join live, asking John a question in person if you want. You could always try John on Twitter too, but there’s nothing like video.
You’re given the opportunity to explain your question in detail. John can easily ask for clarification, and you can have a quick back-and-forth that gets to the bottom of your problem.
This is what I did in order to figure out this situation. I spoke with John live on the Hangout for ~5 minutes; you can watch my segment here if you’re interested. The result was that John gave me his email address and I was able to send through the site for him to check with the ranking team at Google.
I followed up with John on Twitter to see if he was able to get any information from the team on my clients situation. You can follow the link above to see the full piece of communication, but John’s feedback was that there wasn't a manual penalty being put in place for my client's site. He said that it was purely algorithmic. This meant that the algorithm was deciding that the site was not allowed to rank within featured snippets.
And an important component of John’s response:
If a site doesn’t rank for any featured snippets when they're already ranking highly within organic results on Google (say, within positions 1–5), there is no way to force it to rank.
For me, this is a dirty little secret in a way (hence the title of this article). Google’s algorithms may decide that a site can’t show in a featured snippet (but could rank #2 consistently), and there's nothing a site owner can do.
...and the end result?
The result of this, in the specific niche that my client is in, is that lots of smaller, seemingly less relevant sites (as a whole) are the ones that are ranking in featured snippets. Do these sites provide the best answer? Well, the organic 10-blue-links ranking algorithm doesn’t think so, but the featured snippet algorithm does.
This means that the site has a lot of queries which have a low CTR, resulting in considerably less traffic coming through to the site. Sure, featured snippets sometimes don’t drive much traffic. But they certainly get a lot more attention than the organic listings below:
Based on the Nielsen Norman Group study, when SERP features (like featured snippets) were present on a SERP, they found that they received looks in 74% of cases (with a 95% confidence interval of 66–81%). This data clearly points to the fact that featured snippets are important for sites to rank within where possible, resulting in far greater visibility.
Because Google’s algorithm is making this decision, it's likely a liability thing; Google (the people involved with the search engine) don’t want to be the ones to have to make that call. It’s a tricky one. I understand why Google needs to put these systems in place for their search engine (scale is important), but communication could be drastically improved for these types of algorithmic interventions. Even if it isn’t a manual intervention, there ought to be some sort of notification within Google Search Console. Otherwise, site owners will just invest in R&D trying to get their site to rank within featured snippets (which is only natural).
And again, just because there are categories available in the featured snippet policy documentation, that doesn’t mean that the curiosity of site owners is always going to go away. There will always be the “what if?”
Deep down, I’m not so sure Google will ever make this addition to Google Search Console. It would mean too much communication on the matter, and could lead to unnecessary disputes with site owners who feel they’ve been wronged. Something needs to change, though. There needs to be less ambiguity for the average site owner who doesn’t know they can access awesome people from the Google Search team directly. But for the moment, it will remain Google’s dirty little featured snippet secret.
Sign up for The Moz Top 10, a semimonthly mailer updating you on the top ten hottest pieces of SEO news, tips, and rad links uncovered by the Moz team. Think of it as your exclusive digest of stuff you don't have time to hunt down but want to read!
0 notes