#usb digital microscope
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

USB digital microscope
USB digital microscope is a easy to use portable unit with USB output interface. Software helps to observe magnified images, capture video and take snapshots. LED illumination with LED lamps for enhancing details in microscopic images. Adjustable brightness to control resolution and contrast.Compatible for PC usage with USB connection.
#usb digital microscope#usb microscope#annlov microscope#digital microscope 1000x#best usb microscope
0 notes
Text
So as a birthday present to myself this year I decided to get myself a second microscope.
If you want to see things up close, send me an ask and I will do my best.
In case you’re interested, I am using a Vision Scientific VS-2FZ Trinicular Zoom Stereo Microscope with a 5MP camera for pics.
Here is today’s fun image set.
We begin at MAXIMUM ZOOOOM!
[ID: Hard to tell what this is up close. But they’re white, shiny, and sharp looking, interspersed with teeny dark bits. Are those fibres? Crystals? Flakes? Skin? Is that dark stuff dirt? Ink? Bugs? Blood? /End ID]
Un-zooming up a notch:

[ID: Um, still a mess of…stuff. Kinda white. More little dark dots. Definitely fibrous. But is it paper? Plastic? Some third and mysterious thing starting with a P merely for the sake of alliteration? And…Is that a curve at the bottom? /End ID]
Ok, not too helpful, let’s back out some more.
[ID: Ok, now we’re getting somewhere. It’s round and it’s fibrous and it’s white with little black specks. There might be a flake there too, same material. Can’t tell if this is normal or out of the ordinary. But it’s really round, even up close, and the round thing looks raised. Like the top of a LEGO block, but…fibrous, thready. /END ID]
And another YOINK on the zoom knob (you heard me, I just yoinked my knob. If you can’t handle that without giggling like a twelve year old then at least keep it down so the other kids can learn something)
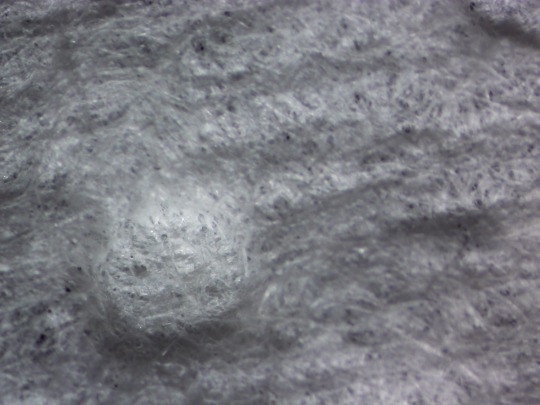

[ID: Thé zoomed has been dialled back far enough that we can now clearly see the little round indented thing. The surrounding terrain is flatter, with definite horizontal striations of some kind. Is this proof of life? Were these once channeling some great flood of water, millions of years ago? And…hey, up there. In the upper right hand corner. Is that a shadow cast by another ROUND THING? Quick Robin! To the Bat Zoom/Unzoom dial! /END ID]
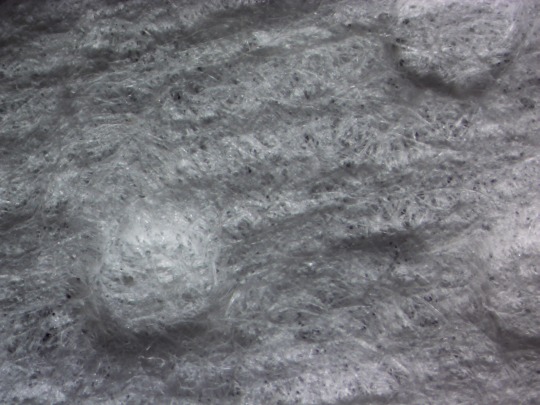

[ID: It is clear to me now from this vantage point at which I find myself that there are yet more of these round, fibrous masses. They are arranged in some geometric pattern whose ultimate purpose, for all my scientific knowledge, I cannot fathom. /END ID]

[ID: Thé image is the same, but an immense blade has descended from the heavens, its reflective point, glinting and metallic, pointing at the original target of our investigation. Perhaps if we zoom out fully we would have a better perspective. Quick Watson! The game is afoot! /END ID]

[ID: our perspective shifts beyond zooming, beyond the microscope. Returning to the macro-world, we find ourselves affixing our gaze upon an iPhone picture of an Xacto knife, blade pointing downward at a torn fragment of brightly illuminated absorbent paper towel. We can now see the circular, dotted landscape as the embossed dots making up the pattern on the paper towel fragment. /END ID]
Huh. The part I find nearest about this image set is the black dots. Totally can’t see them without the scope.
Oh yeah, and the fact that this entire time we’ve been looking at little dipped valleys as opposed to raised mountains. The final iPhone image of the microscope viewing area shows the paper roll dimples are all facing downwards.
Nifty!
Anyway, I’m going to do more of these. If you want to see the surface of something specific up close, feel free to ask.
At some point I’ll pull out the other microscope and my slides, because those are fun too, but right now I’m enjoying my new (early) birthday toy.
🥳🔬🧻

[ID: A final close-up shot of the paper towel fragment, brightly illuminated by LED light, dimples clearly facing away /END ID]
#microscope#zoom and enhance!#microscopy#Vision Scientific VS-2FZ Trinocular Zoom Stéréo Microscope#AMScope MD500 5MP USB Still Photo & Live Video Microscope Imager Digital Camera
0 notes
Text
Types of Microscopes
1. Simple Microscope
2. Compound Microscope
3. Phase Contrast Microscope
4. Fluorescence Microscope
5. Electron Microscope
6. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
7. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
8. Dark Field Microscope
9. Dissecting Microscope (Stereo Microscope)
10. Digital Microscope
11. Scanning Probe Microscope (SPM)
12. Atomic Force Microscope (ATM)
13. Inverted Microscope
14. Acoustic Microscope
15. X-Ray Microscope
16. Polarizing Microscope
17. Metallurgical Microscope
18. Pocket Microscope
19. USB Microscope
20. Confocal Microscope
21. Laser Scanning Microscope
22. Differential Interference Contrast Microscope (DIC)
23. Near-field Scanning Optical Microscope (NSOM)
24. Raman Microscope
25. Super-resolution Microscope
26. Cryo-electron Microscope
27. Time-lapse Microscope
There is a wide range of microscopy techniques and instruments used in various fields of science and research.
#forensic#forensics#criminology#forensic science#evidence#criminalistic#forensic field#crime#forensic science notes#crime scene investigation#electron microscope#microscope
8 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
How Lanoptik embedded camera works with Leica DM500 or DM750 Microscope? Digitizing Your Leica Microscope Without Sacrificing the Eyepiece If you've ever tried to upgrade a Leica DM500 or DM750 microscope for digital imaging, you probably ran into this issue: 👉 You have to replace the original binocular head with a costly trinocular head + adapter + camera. 👉 And once that happens, your original eyepiece? Gone. Wasted. Unusable.But what if you didn’t have to give that up at all?Introducing the Lanoptik Embedded Camera, custom-designed for Leica DM500/DM750.Unlike traditional solutions, this camera fits directly into the existing dovetail mount, with no adapter, no head replacement, and no disruption to your workflow. ✨ Why it matters: You keep the original eyepiece for direct optical observationYou gain digital outputs (HDMI, USB, WiFi, LAN) with no PC requiredYou avoid costly upgrades and reduce clutterYou get a lens tuned for Leica optics — full field of view, distortion-freePerfect for educators, clinics, and lab techs who want digital microscopy without losing what already works. 📩 Want to see it in action? Reach out at lanoptik.com for demo photos, specs, or test clips.#LanoptikEmbeddedCamera #LeicaDM500Camera #LeicaDM750Camera #MicroscopeUpgrade #DigitalMicroscopy #PCFreeImaging #AdapterFreeCamera #MicroscopyLab #ScientificImaging #EfficientDigitalWorkflow
#Digitizing Your Leica Microscope Without Sacrificing the Eyepiece If you've ever tried to upgrade a Leica DM500 or DM750 microscope for digi#youtube
0 notes
Text
Explore USB microscope(Uniglobal Business)

Check out the USB Digital Microscope (1000X Magnification) from Uniglobal Business! Whether you're into electronics, research, coin collecting, or just curious about the micro world, this microscope makes it super simple. Just plug it into your device, zoom up to 1000X, and capture clear, detailed images in no time. It’s compact, easy to use, and perfect for both professionals and hobbyists.
Visit: https://uniglobalbusiness.com/products/usb-digital-microscope-1000x-magnification
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
The Case of the Vanishing Mouse: When Chrome Eats Your USB Devices
You know that moment when you're 47 Chrome tabs deep into "research" (read: watching YouTube tutorials for hobbies you'll never start while simultaneously checking email, Reddit, and that one website where people draw mustaches on renaissance paintings), and suddenly your USB mouse decides it's had quite enough of this digital circus and ceremoniously disconnects itself?
It's not being dramatic. It's not mercury retrograde. It's a genuinely fascinating hardware quirk that exposes the precarious timing ballet happening inside your computer.
What's Actually Happening
What I've discovered through extensive analysis (and by "extensive analysis" I mean "becoming irrationally angry at my mouse and diving into kernel logs") is a delightful system architecture quirk:
When Chrome tabs consume significant CPU resources (mine were cheerfully gobbling ~44% each), the system experiences microscopic delays processing USB interrupts. For most devices, these delays are inconsequential—like being one person behind in line at the coffee shop. But USB mice, especially low-speed ones, are the technological equivalent of that person who checks their watch every 8 seconds while waiting for the elevator.
The error (-71 EPROTO) translates to: "I asked a question and didn't get an answer fast enough, so I'm disconnecting myself in protest."
The Class Divide of Input Devices
The most fascinating part? Your laptop's built-in touchpad continues working flawlessly during this mouse rebellion. This is because your touchpad lives on computing's equivalent of the Upper East Side—it connects through dedicated internal buses with VIP access to the kernel. When it speaks, the system listens.
Meanwhile, your USB mouse is essentially showing up to the party without being on the guest list, forced to communicate through the baroque bureaucracy of the USB stack, desperately hoping someone important notices its increasingly frantic message requests.
The Fix (Besides "Use Fewer Chrome Tabs" Which We Both Know Isn't Happening)
For those who refuse to close their 83 open tabs explaining why you should close your tabs:
#Tell your kernel to respect the mouse's feelings echo "options usbhid quirks=0x[your-vendor-id]:0x[your-product-id]:0x40" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/usbhid-mouse-fix.conf # Boost USB interrupt priority
echo "options xhci_hcd interrupt=7" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/usb-priority.conf # Refresh your kernel's perspective on life sudo update-initramfs -u
This essentially tells your system: "I don't care if Chrome is in the middle of rendering 47 JavaScript-heavy tabs about cryptocurrency—when this mouse speaks, you LISTEN."
The Broader Existential Crisis
The truly delightful thing about this issue is how it exposes the fragile assumptions underpinning our computing experience. We've built technological cathedrals on the digital equivalent of "well, it probably won't rain THAT hard."
So the next time your mouse vanishes while you're deep in a Chrome rabbit hole, know that you've stumbled upon one of computing's hidden fault lines—where timing-sensitive hardware protocols crash against the resource-hungry realities of modern web browsers.
And remember: your laptop isn't broken. It's just experiencing an existential crisis about resource allocation priorities. Aren't we all?
0 notes
Text
Microscope Digital Cameras Market Opportunities Expand with Technological Advancements and Sector-Wide Digital Adoption
The microscope digital cameras market is at the forefront of a significant digital transformation, driven by technological evolution, increased funding in research, and rising applications across diverse sectors. From biomedical research to electronics manufacturing and remote education, these digital imaging tools are rapidly becoming indispensable. As the demand for precise, real-time, and shareable microscopic visuals grows, so do the market’s opportunities.
In this article, we examine the expansive opportunities shaping the microscope digital cameras market—ranging from regional adoption and industry-specific needs to technology-driven innovations and strategic partnerships.

Current Market Overview
Microscope digital cameras are designed to capture and transfer high-resolution images or videos of specimens viewed through a microscope. These cameras are integral to modern microscopy applications and come in various formats—ranging from basic USB models to advanced 4K, AI-powered imaging systems.
As of 2024, the global microscope digital cameras market is valued at over USD 1.2 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7–10% through 2030. This growth is fueled by:
Digitalization across clinical, educational, and industrial environments
Rising demand for accurate and remote diagnostic capabilities
Advancements in imaging sensors and software
Increased emphasis on data sharing and automation in microscopy
Key Market Opportunities by Sector
1. Healthcare and Biomedical Research
One of the most promising areas for growth is in clinical diagnostics and life sciences research. Hospitals, pathology labs, and academic research centers rely on microscope digital cameras for:
Cancer screening and tissue imaging
Pathogen identification
Cell biology and genetic studies
The opportunity lies in developing AI-powered imaging systems that enhance diagnosis speed and precision, reduce human error, and support remote collaboration. Emerging markets with expanding healthcare infrastructure represent a major untapped opportunity for affordable, high-performance solutions.
2. Education and E-Learning Platforms
As education systems integrate more digital tools, microscope digital cameras have become essential in virtual science laboratories. These tools allow real-time viewing of biological or chemical specimens on screens during hybrid or remote learning.
Manufacturers that offer plug-and-play, cost-effective, and portable microscope cameras tailored for schools and universities can tap into a growing user base. The expansion of STEM education and global e-learning initiatives further expands this opportunity.
3. Industrial and Materials Inspection
Microscope digital cameras are used extensively in the inspection and quality assurance of semiconductors, electronics, automotive parts, and other precision-engineered components. With miniaturization in product design and tighter quality controls, manufacturers increasingly rely on digital cameras for:
High-resolution inspection
Defect detection
Process validation
Opportunities exist in developing robust camera systems integrated with image recognition, automation, and machine learning, tailored for industrial use.
Technological Innovations Driving Market Expansion
Innovation remains at the core of opportunity generation in the microscope digital cameras market. Key technological trends include:
AI and Deep Learning
AI integration offers powerful capabilities in imaging analysis, including:
Real-time object recognition
Automated cell counting
Anomaly detection in industrial workflows
Companies investing in AI-based software platforms that work seamlessly with their cameras can establish long-term value through data-driven insights and automation.
4K and Ultra HD Imaging
The demand for higher resolution imaging is growing in clinical diagnostics and scientific research. Cameras that offer 4K video, enhanced color reproduction, and faster frame rates provide clearer results and greater detail—particularly in histology, material science, and microelectronics.
Cloud-Based Data Management
Cameras integrated with cloud platforms allow instant sharing, storage, and access to microscopy data, enhancing remote collaboration and telepathology. This presents opportunities for SaaS-based business models, creating recurring revenue streams for camera manufacturers.
Modular and Portable Designs
Portable and modular digital camera systems that can adapt to various microscopes and environments provide flexibility, particularly in field research and mobile clinics. These compact systems are especially useful in emerging markets or resource-constrained environments.
Geographic Growth Opportunities
North America and Europe
While these regions are mature markets, opportunities exist in upgrading older systems with next-gen digital cameras featuring AI, 4K, and wireless capabilities. Demand is also growing in decentralized healthcare centers and educational institutions implementing smart classrooms.
Asia-Pacific
APAC offers significant growth potential due to rising government investments in biotechnology, education, and digital healthcare. China, Japan, South Korea, and India are leading demand, with local manufacturers also entering the market to provide affordable alternatives.
Latin America, Middle East, and Africa
These emerging markets offer untapped opportunities due to expanding healthcare networks and educational reforms. Companies offering budget-friendly, durable, and easy-to-use solutions are well-positioned for growth in these regions.
Strategic Partnerships and Distribution
Collaborations with microscope manufacturers, academic institutions, and software developers can accelerate market penetration. Key strategies include:
Bundling Solutions: Partnering with microscope manufacturers to offer complete imaging systems
OEM Partnerships: Providing camera modules to be embedded in other systems
Software Licensing: Offering image analysis and management tools as subscription services
Training and Support Services: Building brand loyalty through education, setup assistance, and remote diagnostics
Addressing Market Challenges
Even amid strong opportunities, companies must navigate certain barriers:
Cost Sensitivity: Especially in developing regions, affordability remains a concern.
Technical Skill Gaps: Lack of training and digital literacy can limit adoption.
Regulatory Hurdles: Compliance with healthcare and education standards varies by country and application.
Solutions lie in offering tiered product lines, investing in user education, and developing region-specific strategies for compliance and support.
Conclusion
The microscope digital cameras market is bursting with opportunity as digital transformation takes hold across healthcare, education, and industry. Whether through AI-driven software, high-resolution imaging, or portable, adaptable designs, manufacturers that prioritize innovation and accessibility are best positioned to lead the market forward.
By addressing sector-specific needs and expanding into underserved regions, stakeholders can unlock substantial long-term value in this evolving digital microscopy ecosystem.
0 notes
Text

Trademark Class 9: Computers, Software and Electronics
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the power of a strong brand is undeniable. Whether you're developing cutting-edge software, manufacturing innovative electronic devices, or providing essential computer hardware, protecting your brand identity is paramount. This is where trademark registration comes into play, and understanding the specific classifications, like Trademark Class 9, is crucial for securing the right protection.
Navigating the Trademark Landscape: The Importance of Classification
Before diving into the specifics of Trademark Class 9, it's essential to grasp the concept of trademark classification. The Nice Classification, an international system, categorizes goods and services into 45 distinct classes. This system helps streamline the trademark registration process by allowing applicants to specify the exact nature of their products or services. Choosing the correct class is vital because your trademark registration will primarily protect your brand in relation to the goods or services listed within that class.
Entering the Digital Domain: What Falls Under Trademark Class 9?
Trademark Class 9 is a broad and dynamic category encompassing a wide array of goods related to computers, software, and electronics. It essentially covers the technological backbone of our modern world. Understanding the scope of this class is the first step towards ensuring your innovative creations and brand names are adequately protected through trademark registration.
Here's a comprehensive breakdown of the types of goods typically included in Trademark Class 9:
1. Computers and Hardware:
Central processing units (CPUs)
Computer monitors
Keyboards
Mouse devices
Printers
Scanners
Computer memory devices (RAM, ROM, hard drives, SSDs)
Motherboards
Graphic cards
Sound cards
Network interface cards
Servers
Laptops
Tablets
Personal digital assistants (PDAs)
External hard drives and storage devices
USB flash drives
Modems
Routers
Networking hardware (switches, hubs)
2. Software:
Operating system software
Application software (for various purposes like business, productivity, entertainment, education)
Computer games software
Anti-virus software
Firewall software
Database management software
Programming software
Web design software
Mobile applications (apps)
Cloud computing software
Artificial intelligence (AI) software
Machine learning software
3. Electronic Devices and Equipment:
Smartphones
Televisions
Audio and video players
Cameras and camcorders
GPS devices
Wearable technology (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
Electronic sensors
Remote controls
Power supplies
Batteries
Electric cables and wires
Electronic circuit boards
Semiconductors
Integrated circuits (ICs)
Radio and television broadcasting apparatus
Radar apparatus
Navigation apparatus
4. Scientific and Laboratory Instruments:
Measuring instruments
Testing apparatus
Laboratory equipment for scientific research
5. Photographic, Cinematographic, and Optical Apparatus:
Cameras
Lenses
Projectors
Telescopes
Microscopes
6. Data Processing Equipment:
Data processing programs
Data storage devices
7. Teaching Apparatus and Instruments:
Electronic teaching devices
Simulators (for training purposes)
Important Considerations within Trademark Class 9
While Trademark Class 9 covers a vast range of technological goods, it's crucial to be precise when listing your specific products during the trademark registration process. Overly broad descriptions can lead to objections or limit the scope of your protection. For instance, instead of simply stating "software," you might specify "downloadable mobile application for managing personal finances."
Furthermore, it's important to note what Trademark Class 9 does not include. For example:
Electric tools and machines (Class 7)
Electrical apparatus for medical purposes (Class 10)
Electric lighting apparatus (Class 11)
Telecommunications services (Class 38)
Computer programming services (Class 42)
Understanding these distinctions is vital to ensure you apply for trademark registration in the correct class.
Securing Your Brand in the Digital Age: The Trademark Registration Process
The process of trademark registration in India involves several key steps:
Trademark Search: Before filing your application, conduct a thorough trademark search to ensure that your proposed brand name or logo is not already in use or similar to existing trademarks in Trademark Class 9 or related classes.
Filing the Application: Once you're confident in the uniqueness of your mark, you need to file a trademark application with the Indian Trademark Registry. This can be done online through the Intellectual Property India website. The application requires details about your business, the trademark itself (name, logo, or both), and a clear specification of the goods falling under Trademark Class 9 that your brand represents.
Examination: The Trademark Registry will examine your application to ensure it meets all the legal requirements and that there are no conflicting trademarks.
Publication in the Trademark Journal: If the examination report is favorable, your trademark will be published in the Trademark Journal, allowing third parties to raise objections within a specified period.
Opposition (if any): If any objections are raised, you will have an opportunity to respond and defend your application.
Registration: If there are no objections or if any objections are successfully overcome, your trademark will be registered, and you will receive a certificate of registration. This grants you exclusive rights to use your trademark in relation to the specified goods in Trademark Class 9.
Navigating the Legal Landscape with Online Legal India
The trademark registration process, while seemingly straightforward, can involve complexities and legal nuances. This is where professional guidance can be invaluable. Online Legal India provides comprehensive services to assist businesses in securing their trademarks, particularly within the crucial Trademark Class 9.
Online Legal India can help you with:
Thorough Trademark Search: Conducting comprehensive searches to identify potential conflicts and ensure the uniqueness of your brand.
Expert Application Filing: Accurately preparing and filing your trademark application, ensuring all necessary details and specifications for Trademark Class 9 goods are correctly included.
Handling Objections: Providing expert legal support in case of any objections raised by the Trademark Registry or third parties.
Ongoing Monitoring: Offering services to monitor your trademark and protect it against potential infringement.
General Trademark Advice: Providing expert consultation and guidance on all aspects of trademark registration and protection.
By leveraging the expertise of Online Legal India, businesses operating in the dynamic realm of computers, software, and electronics can navigate the trademark registration process with confidence, ensuring their valuable brand assets are effectively protected within Trademark Class 9. Their online platform and experienced professionals can streamline the process, saving you time and potential legal complications, allowing you to focus on innovation and growth in the digital marketplace.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Innovation in Trademark Class 9
In the fast-paced world of technology, your brand identity is a critical asset. Understanding Trademark Class 9 and navigating the trademark registration process effectively is essential for safeguarding your innovations in computers, software, and electronics. By taking the necessary steps and considering the expert assistance offered by platforms like Online Legal India, you can secure your brand and build a strong foundation for future success in the digital age. Don't let your valuable intellectual property go unprotected – take action today to secure your brand in Trademark Class 9.
0 notes
Text
Types of Digital Microscope
In today's world of advanced technology, digital microscopes have revolutionized the field of microscopy, offering enhanced imaging, precision, and ease of use. Unlike traditional optical microscopes, digital microscopes use a digital camera and a computer screen to display magnified images, making it easier to analyze and document samples. They have become essential tools in various industries, including healthcare, electronics, material science, and education. In this article, we will explore the different types of digital microscopes available, their unique features, and their applications.
1. USB Digital Microscopes
USB digital microscopes are among the most popular and widely used types of digital microscopes. They are compact, easy to use, and connect directly to a computer or mobile device via a USB cable. These microscopes are ideal for hobbyists, students, and professionals who need a portable and affordable solution for magnification and image capturing.
Key Features:
Direct connection to a computer or smartphone via USB.
High-resolution imaging (ranging from 2 MP to 14 MP).
Built-in LED lighting for enhanced visibility.
Easy to use with plug-and-play functionality.
Applications:
Educational purposes (biology, physics, and chemistry labs).
Jewelry inspection.
Coin and stamp collection analysis.
PCB and circuit board examination.
2. HDMI Digital Microscopes
HDMI digital microscopes are designed to provide high-quality, real-time imaging directly to an HDMI-compatible display. These microscopes offer high-resolution images and low latency, making them suitable for applications requiring real-time monitoring and precision.
Key Features:
Direct connection to a monitor or TV via HDMI.
High frame rates for smooth, real-time viewing.
High-definition resolution (up to 1080p or 4K).
Adjustable LED lighting for better illumination.
Applications:
Quality control in manufacturing.
Electronics repair and assembly.
Forensic examination.
Educational demonstrations.
3. Wireless Digital Microscopes
Wireless digital microscopes provide the convenience of wireless connectivity, allowing users to view and capture images on a smartphone, tablet, or computer without the hassle of cables. These microscopes are battery-operated and offer excellent portability.
Key Features:
Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connectivity.
High-resolution cameras (up to 5 MP).
Portable and lightweight design.
Long battery life for extended use.
Applications:
Outdoor biological research.
Mobile inspection of industrial equipment.
Educational fieldwork.
Dermatology and skin analysis.
4. Desktop Digital Microscopes
Desktop digital microscopes are larger, more powerful, and designed for high-precision tasks. They offer greater magnification levels, advanced image processing features, and a stable platform for accurate analysis.
Key Features:
Magnification power up to 1000x or more.
Adjustable stand for precise positioning.
Built-in measurement tools.
High-definition imaging and video recording.
Applications:
Material analysis in metallurgy.
Semiconductor and PCB inspection.
Medical research and pathology.
Biological sample examination.
5. Portable Handheld Digital Microscopes
Handheld digital microscopes are compact and designed for use on the go. They are battery-powered and lightweight, making them ideal for quick inspections and fieldwork.
Key Features:
Lightweight and easy to carry.
Battery-operated for enhanced portability.
High-resolution imaging with adjustable focus.
LED lighting for low-light conditions.
Applications:
Industrial inspections.
Environmental research.
Geological surveys.
Mobile forensic analysis.
6. Inverted Digital Microscopes
Inverted digital microscopes are designed for observing samples from below. This type of microscope is particularly useful for biological and medical research where samples are in petri dishes or liquid-filled containers.
Key Features:
High-quality optics for clear imaging.
Capability to observe live cell cultures.
Adjustable lighting and focus.
Compatibility with various imaging software.
Applications:
Cell culture and tissue analysis.
IVF and embryology research.
Microbiology and bacteriology.
Pharmaceutical development.
7. 3D Digital Microscopes
3D digital microscopes allow users to view samples in three dimensions, providing a more detailed and accurate analysis of the sample's surface structure. These microscopes use advanced imaging software to construct a 3D model of the sample.
Key Features:
High-resolution 3D imaging.
Advanced measurement and analysis tools.
Multiple lighting options for enhanced contrast.
User-friendly interface for data manipulation.
Applications:
Material surface analysis.
Forensic science.
Biological research.
Industrial quality control.
8. Confocal Digital Microscopes
Confocal digital microscopes use laser technology to capture high-resolution images at different depths. This type of microscope is ideal for analyzing complex structures and creating detailed 3D images.
Key Features:
Laser-based imaging system.
High-resolution, high-contrast imaging.
Ability to create 3D reconstructions.
Software integration for advanced analysis.
Applications:
Biological and medical research.
Material science and engineering.
Nanotechnology analysis.
Pharmaceutical research.
9. Polarized Light Digital Microscopes
Polarized light digital microscopes use polarized light to enhance contrast and detail in birefringent materials. They are widely used in material science and geology.
Key Features:
Polarized light system for enhanced detail.
High-resolution imaging.
Advanced contrast adjustment.
Compatible with various imaging software.
Applications:
Mineral and crystal analysis.
Textile and fiber inspection.
Pharmaceutical quality control.
Metallurgical studies.
10. Fluorescence Digital Microscopes
Fluorescence digital microscopes use specific wavelengths of light to excite fluorophores in the sample, producing highly detailed images with excellent contrast.
Key Features:
High sensitivity and resolution.
Multi-channel imaging capability.
Software-controlled image enhancement.
Compatibility with live cell imaging.
Applications:
Cellular and molecular biology.
Immunology research.
Cancer research.
Drug discovery and development.
Choosing the Right Digital Microscope
When selecting a digital microscope, it is essential to consider factors such as magnification power, resolution, lighting options, and software compatibility. The intended application, budget, and portability requirements should also guide your decision. For example, a USB or wireless digital microscope may be ideal for hobbyists and educators, while a 3D or confocal microscope would be more suitable for industrial and medical research.
Conclusion
Digital microscopes have transformed the way we examine and analyze samples. With various types available, including USB, HDMI, wireless, desktop, 3D, and confocal models, there is a suitable microscope for every application. Understanding the unique features and applications of each type will help you make an informed decision and enhance your research or inspection capabilities.
0 notes
Text

Portable digital microscope
Portable digital microscope is an independent and easy to operate handheld unit. It provides powers from 20X and 300X with 5.0MP Image sensor. LED illumination with LED lamps for enhancing details in microscopic images.Compatible for PC usage with USB connection
#portable digital microscope#handheld microscope#best handheld microscope#tinyscope#digital usb microscope#portable microscope 1000x
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] From the brand RuhZa Tech Provide everything you want!, Choose us, Choose the world! About RuhZa Tech: We are the market leader in providing technological supplies and solutions. With many years of experience, we completely understand what technology our customers demand. RuhZa Tech not only provides a wide range of innovative accessories, we also introduce the best products to consumers. RuhZa Wifi Digital Microscope USB MICROSCOPES What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! USB HUB DOCKING STATION USB HUB DOCKING STATION USB HUB DOCKING STATION USB HUB DOCKING STATION USB HUB DOCKING STATION USB HUB DOCKING STATION USB HUB DOCKING STATION
What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! What Are You Waiting For!!! This Device is Based on the high speed USB 2.0 technology; It can capture one signal channel HD HDMI video signal. Suitable for devices with HDMI output;such as Blu-ray Player;PS3/4;Xbox one;Wii U;Nintendo Switch;DVD;Camera;ZOSI security camera;DSLR and Set Top Box NO driver; and it is truly PnP. Low latency for game recording; meeting recording; live streaming.Let more Gamers know you. Compatible with Windows; Linux; Mac OS X Capture resolutions up to 1080p 60fps for 1080P video source with hardware accelerated up-scaling/down-scaling.The recorded video resolution depends on the original video; which is not changeable by capture Audio and Video Record ability from external devices via HDMI port; easy File Save and Share via Computer; Support live RTMP video streamin. compatible with popular streaming software and services like OBS Studio; VLC;PotPlayer;Vmix Capture Card Support 1080P 30P HDMI Input/Output.A fast; familiar; and way to share content in the conference room and into online meetings.Connect to present; no software required;Simply connect a laptop or tablet via HDMI to start sharing. with Yand H HDMI Game Capture Card;you can record the game more easily.Add your voice to the game through Mic [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
Digital Microscope LDM-C10
Labtron digital microscope, with a built-in USB camera and PC/monitor connectivity, provides high-resolution imaging via S-LED illumination and Scope Image 9.0 software. Its coaxial coarse and fine focusing enables sharp, clear visuals, ideal for fatigue-free viewing. Perfect for professional applications, this advanced microscope delivers precise and strain-free sample analysis.

0 notes
Text
Using 13MP USB Cameras for Accurate and Reliable Life Science Imaging
In the quickly developing life sciences, accurate imaging is essential for teaching, research, and diagnosis. The emergence of 13MP USB cameras has greatly improved the quality and dependability of life science imaging due to advancements in imaging technology. For academics, educators, and medical professionals, these high-resolution cameras are an indispensable tool since they provide clarity, detail, and ease of use. The advantages and uses of 13MP USB cameras in the life sciences will be discussed in this article, along with tips for putting them to good use for dependable and accurate photography.
Thirteen Megapixel USB Camera Benefits
High Definition for Added Intricacy
The great resolution that a 13MP USB camera provides is one of its main benefits. These cameras' 13 megapixels provide images with amazing clarity and detail. This is especially crucial for applications in life sciences where it's necessary to observe minute structures. Researchers can evaluate their subjects precisely thanks to the great resolution of a 13MP camera, whether they are photographing fine details of tissue samples or looking at cells under a microscope.
Flexibility and simplified connectivity
Another significant benefit of 13MP USB cameras is that they are plug-and-play devices. These cameras may be easily connected to a wide number of devices, including PCs, laptops, and Raspberry Pi systems, making them incredibly versatile for a wide range of applications. Researchers can easily set up their imaging systems without the need for complicated configurations thanks to its ease of use. Moreover, a multitude of software programs are compatible with the USB interface, facilitating the real-time capturing, storing, and analysis of photos.
Cost-Effectiveness
Financial limitations can be a major factor in the field of life science imaging. 13MP USB cameras provide an affordable option without sacrificing image quality. These cameras offer superior performance at a far lower cost when compared to more costly, specialized imaging systems, which makes them available to a wider range of organizations, including research labs and educational facilities.
13 Megapixel USB Camera Applications in the Life Sciences
Making use of microscopes
Microscopy is one of the most popular applications of 13MP USB cameras in the biological sciences. These cameras give researchers a digital imaging choice that can be easily mounted on a range of microscopes and capture high-resolution images of objects. This integration enables the thorough analysis and documentation of biological specimens, including microorganisms, tissues, and cells. A 13MP USB camera's clarity helps researchers spot structural traits and minute alterations in specimens that could be crucial to their research.
Laboratory Records
A scientific project must have accurate documentation. Researchers may quickly and conveniently take high-quality pictures of their experiments, processes, and outcomes with a 13MP USB camera. This feature is very helpful when writing research articles or keeping lab notebooks full of findings. The accurate documentation that can endure inspection during peer review or regulatory processes is made possible by the high resolution, which guarantees the preservation of even the smallest information.
Instruction and Practice
13MP USB cameras have the potential to greatly improve learning environments. In labs and schools, these cameras can be used to show intricate biological structures and processes. Teachers can help students grasp complex subjects by giving them access to high-quality visuals. These cameras can also help with remote learning by enabling students to watch experiments and demonstrations in real time from a distance.
Telemedicine and remote imaging
The emergence of telemedicine has revolutionized the way medical professionals give care. In remote imaging applications, 13MP USB cameras play a crucial role in enabling medical personnel to take high-quality patient photos for diagnosis and treatment planning. In underserved or rural locations, where access to specialized imaging equipment may be limited, this technique is very helpful. No matter where they are located, healthcare professionals can make educated judgments about patient care because of the clarity of photos captured by a 13MP USB camera.
Making Certain Dependable and Accurate Imaging
Taking into account a number of criteria, a 13MP USB camera can produce dependable and precise images:
Lighting Specifications
Good lighting is essential for taking pictures that are of a good caliber. It is important for researchers to make sure that their imaging environment is well-lit and that the right illumination strategies are used, such as fiber optic illuminators or LED ring lights. This can lessen shadows and improve the clarity of little details in the photos that are taken.
Adjustments and Configurations
To get the best results, the camera settings must be calibrated. It is important for researchers to modify factors like gain, exposure, and white balance according to the particular needs of their imaging assignments. Getting familiar with the software and functions of the camera can greatly improve the quality of the photographs that are captured.
Software for Image Processing
The quality of photographs taken with a 13MP USB camera can be further improved by using sophisticated image processing software. Researchers can enhance the quality of their photographs for more effective analysis and presentation by utilizing software tools that provide capabilities like noise reduction, contrast modification, and image stitching.
In summary
The advent of 13MP USB cameras, which offer a dependable and affordable means of obtaining excellent photos, has completely changed the field of life science imaging. They are a vital resource for academics, researchers, and medical professionals due to their adaptability, simplicity of usage, and remarkable resolution. The uses and advantages of these cameras in the biological sciences will only grow as technology develops, opening the door for fresh findings and advancements in the area. Accepting this technology is a leap into the future of precise and dependable life science imaging, not merely a step in the right direction.
https://www.vadzoimaging.com/product/ar1335-4k-autofocus-usb-3-0-camera
0 notes
Text
Digital Microscope 13mm
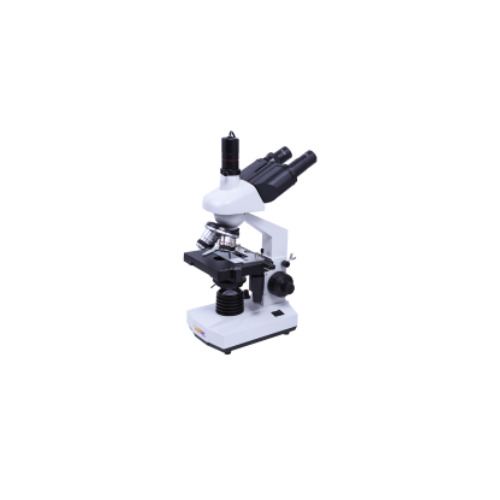

Labnic Digital Microscope features an achromatic optical system with a 40x-1600x magnification range, an outward quadruple nosepiece, and an Abbe-iris diaphragm 1.25 N condenser. It has a 23.2mm diameter, fine focusing with a safety stop screw and a 5.0-megapixel camera with USB output.
0 notes
Text
We have the top 5 reliable products from scientific lab equipment manufacturers in India.

Meta Description: Are you searching for the best scientific lab equipment manufacturers in India? Look no further than Educational Equipment India! As a leading name in the industry, we specialize in producing high-quality lab instruments designed to cater to the diverse needs of laboratories and research facilities around the world. Based in India, we are not only a trusted supplier but also a renowned exporter, ensuring that our top-notch scientific instruments meet global standards. Our cutting-edge equipment supports seamless research and educational experiences, making us the preferred choice for scientific lab equipment worldwide. Scientific Lab Equipment Supplier in India, Scientific Lab Manufacturer in India, Scientific Lab Equipment Supplier in India, Scientific Lab Equipment Manufacturers, Suppliers, and Exporters in India, Scientific Lab Equipment in India, Scientific Lab Equipment Exporter in India.
Mitosis & Meiosis Set, Microscope Slides:
Explore cellular division processes with our comprehensive mitosis and meiosis slide set.
Contains high-quality microscope slides illustrating various stages of mitosis and meiosis.
Ideal for educational purposes, including biology classes and research projects.
Clear labelling and detailed images provide a thorough understanding of cell division.
Enhance your microscopy studies with this essential slide collection.
Mitosis & Meiosis Slide Set
Set of 10 slides:
Astacus testis VS
Locust testis VS
Locust, testis, and squash
Locust embryo squash
Allium root tip (LS)
Lillium anthers TS early prophase
Lillium anthers, TS late prophase
Lillium anthers, TS metaphase
Lillium anthers, TS, late first division
Lillium anthers, TS second division.

How to use them and where:
Place the slides onto the stage of your microscope and focus on the specimens using the appropriate magnification. Observe and analyse the stages of mitosis and meiosis under the microscope to understand cellular division processes. Perfect for biology classrooms, colleges, and research laboratories.
Insect Anatomy Slide Set of 9:
Delve into the fascinating world of insect anatomy with our comprehensive slide set.
Features nine high-quality microscope slides showcasing different insect anatomical structures.
Perfect for educational purposes, entomology studies, and research projects.
Detailed images provide valuable insights into insect morphology and physiology.
Expand your knowledge of entomology with this essential slide collection.
Set of 9 microscope slides showing anatomical parts.
Technical Specifications:-
Apis (bee), legs E
Apis, spiracles E
Apis, head and eyes VS
Apis, wing E
Pieris, imago, proboscis E
Pieris (butterfly), imago, antenna E
Periplaneta (cockroach), trachea E
Periplaneta, mouthparts, disarticulated E
Musca (house fly) imago, proboscis E

How to use them and where:
Place the slides onto the microscope stage and adjust the magnification to examine the intricate details of insect anatomy. Study the different anatomical structures, such as wings, legs, and mouthparts, to gain a deeper understanding of insect biology. Ideal for biology classrooms, natural history museums, and research institutions.
Microscope Digital Camera:
Enhance your microscopy experience with our high-quality microscope digital cameras.
Capture precise images and videos of your specimens with ease.
Compatible with most microscopes for seamless integration.
Perfect for research, education, and documentation purposes.
Explore our range of microscope digital cameras for superior imaging solutions.
The USB Eyepiece Video Camera. Mid-resolution digital cameras for attaching to biological or stereo microscopes, with all you need for video capture via direct connection to a PC.
Direct connection into the eyepiece tube instead of one of the eyepieces (23mm, 30mm & 30.5mm diameter)
Technical Specifications:-
Digital camera resolution: 2 MP
Analogue camera resolution: No
Signal output: USB 2.0
Audio Signal: No
Sensor Size: 13.2
Sensor technology: CMOS
Image format: 43
White Balance: Auto
Gain Control: Auto
Back light control: Auto
Exposure control: Auto
C-Mount connection: No
CS-Mount connection: No
Full Image size: 1600 x 1200
Frame rate full resolution: 5 fps (1600×1200) / 7,5 fps (1280×1024) / 22fps (640×480)
ON board Memory: Auto
External Memory Card: No
External camera power: PC USB
How to use them and where:
Install the microscope digital camera onto the eyepiece or trinocular port of your microscope. Connect it to your computer or monitor using the provided software or cables. Adjust the settings for resolution and focus, then capture images or videos of your specimens. Ideal for laboratories, educational institutions, and research facilities.
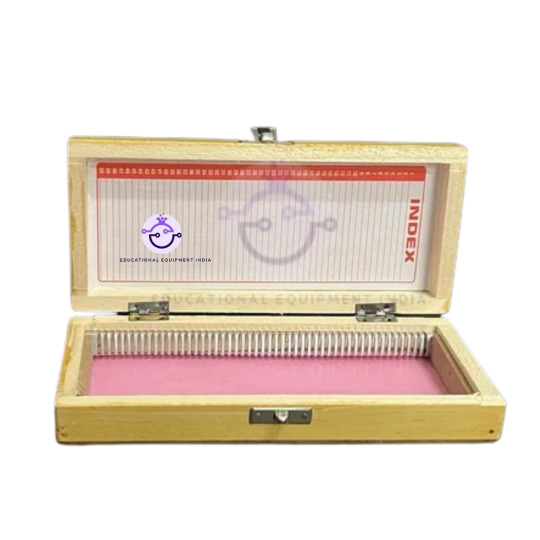
Wooden Slide Case:
Keep your microscope slides organised and protected with our premium wooden slide cases.
Crafted from durable wood for long-lasting use and protection,
Designed to hold standard-sized microscope slides securely in place.
Ideal for storing and transporting slides safely between locations.
Choose from various capacities to suit your needs.
The fully lined case is fitted with brass clips and an aluminium index cardholder.
This wooden slide case safely holds 100 (75 x 26 mm) glass microscope slides with good shock resistance characteristics.

How to use them and where:
Simply place your microscope slides into the designated slots within the wooden slide case. Ensure each slide is properly aligned and secured. Close the case securely before storing it in a dry, dust-free environment. Perfect for classrooms, laboratories, and fieldwork.
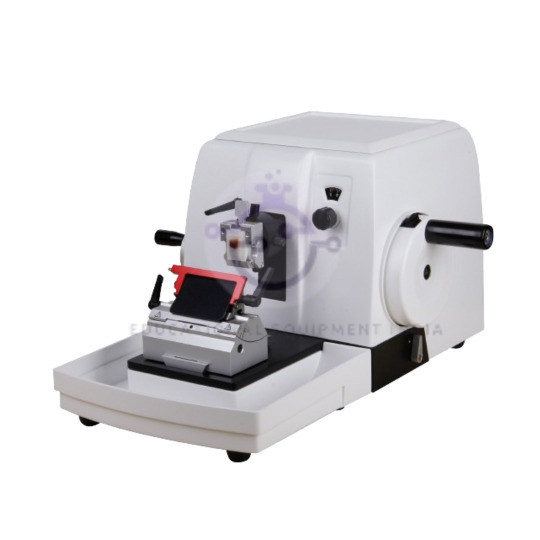
Microtome:
Achieve precision sectioning of biological specimens with our advanced microtomes.
Designed for cutting thin slices of tissue for microscopic examination.
Features adjustable cutting thickness for customised results.
Durable construction ensures reliability and longevity.
Suitable for histology, pathology, and research applications.
Hand cylinder microtome with a wide flat top to guide the sectioning razor and to protect the hand.
The feed screw has a 1 mm pitch and a wide milled flange so that the embedded material may be advanced very gradually and thin sections cut easily.
Dimensions: Cutting table, 50 mm in diameter. Central well is 16 mm in diameter.

How to use them and where:
Place the specimen onto the microtome's sample holder and adjust the cutting thickness according to your requirements. Use the handwheel to advance the specimen towards the cutting blade, producing thin sections for microscopy. Ideal for histology labs, medical facilities, and research institutions.
#scientific lab equipment manufacturers in India#scientific lab equipment manufacturers#scientific lab equipment in India#scientific lab equipment#labequipment
0 notes