#zehnder modern radiators
Text
Shop an exclusive range of designer radiators online at Bathroom Shop UK! Our range of affordable, stylish and modern designer radiators come in both horizontal and vertical styles! We have a wide range of Designer Radiators including slimline, flat panel, traditional and striking modern designs. Quick delivery in Midlands, Yorkshire, Lancashire and all over England! All available from top brands such as Bisque radiators, Zehnder radiators, Vogue designer towel warmers and, more!
#Bisque radiators#Zehnder radiators#Vogue designer towel warmers#shop luxury bathrooms online#luxury bathrooms#best bathroom deals#best bathroom brands#bathroom discounts online#quality bathrooms#bathrooms midlands#bathrooms yorkshire#bathrooms lancashire#buy bathrooms cheaper online#vertical designer radiators#horizontal designer radiators#designer radiators#zehnder modern radiators#bisque radiators#designer radiators on sale
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Correlating Astrology , with Astronomy and Quantum mechanics.
There are many arguments about the relevance of astrology in the modern world so I'd like to present you with some resources so that you can find relevance.
P.S. : I am just a novice , so feel free to correct my mistakes.
Light emission in humans
So first of all I would like to tell you about a research done by scientists in Japan , they chose 5 healthy male volunteers for the examination of the presence of photon , they installed photon sensitive camaras . A photon is a sub - atomic particle of an atom or a particle representing a quantum of light or other electromagnetic radiation. A photon carries energy proportional to the radiation frequency but has zero rest mass.
They were asked to be bare chested for this in completely darkened rooms for 20 minutes every three hours from 10 a.m. to 10 p.m. for three days.The researchers found the body glow rose and fell over the day, with its lowest point at 10 a.m. and its peak at 4 p.m., dropping gradually after that.The face glowed more than the body due to the presence of more melanin , which has fluorescent components , they have linked this phenomenon to the rhythms of the body . The body image was captured with a camara that detected heat , the emissions were infrared and the images were thermal . We cannot normally see it because these are 1000 less sensitive than our visual capabilities .
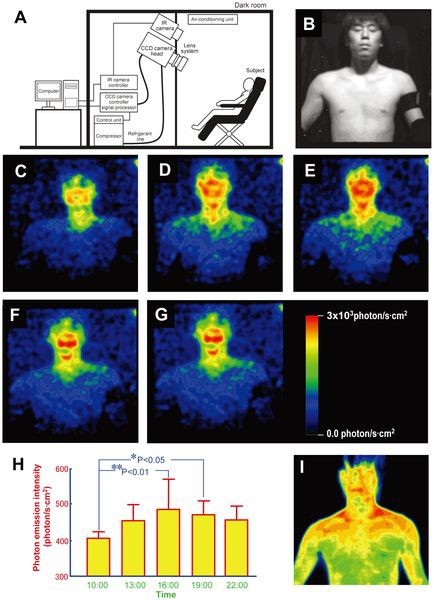
Aura's : an aura or human energy field is a colored emanation said to enclose a human body or any animal or object .
Aura photography : an object on a photographic plate is connected to a high-voltage source, an image is produced on the photographic plate.
This proves the presence of light emission from our human body.
Planets do not emit their own light , they rather reflect the rays of the sun , true emission of lights are produced as a result of nuclear fusion , which creates radiation and makes stars glow .
Young's double slit experiment
This experiment belongs to a general class of "double path" experiments, in which a wave is split into two separate waves that later combine into a single wave. Changes in the path-lengths of both waves result in a phase shift, creating an interference pattern. Another version is the Mach–Zehnder interferometer, which splits the beam with a beam splitter.
In the basic version of this experiment, a coherent light source, such as a laser beam, illuminates a plate pierced by two parallel slits, and the light passing through the slits is observed on a screen behind the plate. The wave nature of light causes the light waves passing through the two slits to interfere, producing bright and dark bands on the screen – a result that would not be expected if light consisted of classical particles. However, the light is always found to be absorbed at the screen at discrete points, as individual particles (not waves); the interference pattern appears via the varying density of these particle hits on the screen. Furthermore, versions of the experiment that include detectors at the slits find that each detected photon passes through one slit (as would a classical particle), and not through both slits (as would a wave).
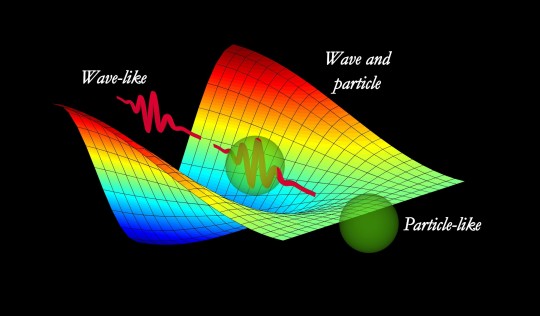
Image of light as a Particle as well as a wave .
A research team led by Fabrizio Carbone at EPFL has now carried out an experiment with a clever twist: using electrons to image light. The researchers have captured, for the first time ever, a single snapshot of light behaving simultaneously as both a wave and a stream of particles.
The experiment is set up like this: A pulse of laser light is fired at a tiny metallic nanowire. The laser adds energy to the charged particles in the nanowire, causing them to vibrate. Light travels along this tiny wire in two possible directions, like cars on a highway. When waves traveling in opposite directions meet each other they form a new wave that looks like it is standing in place. Here, this standing wave becomes the source of light for the experiment, radiating around the nanowire.
While this phenomenon shows the wave-like nature of light, it simultaneously demonstrates its particle aspect as well . The scientists shot a stream of electrons close to the nanowire, using them to image the standing wave of light. As the electrons interacted with the confined light on the nanowire, they either sped up or slowed down. Using the ultrafast microscope to image the position where this change in speed occurred, Carbone's team could now visualize the standing wave, which acts as a fingerprint of the wave-nature of light.
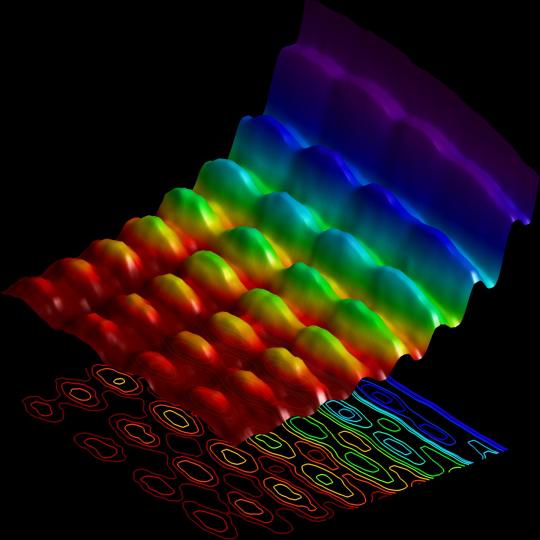
Wave and wave interaction :
Two wave paddles, generating waves of different frequencies and directions, are placed in two corners along one side of a tank of constant water depth. The resulting waves create a diamond pattern of crests and troughs, which has its own wave length, speed, and direction. This diamond pattern would interact with a third-wave component, if this third wave had the same wave length, speed, and direction as the diamond pattern.
The reflective waves of planets and our body emissions interact in a way of wave wave interaction and thus influence our lives, now the thing about wonder is that , why don't we have an influence on them , well we do but in a very negligible amount , this can be explained with the help of the third law of Newtonian physics , " Every action has an equal and opposite reaction " , this statement is actually incomplete , the original statement goes "To every Action there is always an equal Reaction: or the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary parts" .
For example , an elephant is trying to push you , but you are also pushing the elephant but obviously the elephant will overpower you because the elephant has more matter in its body than you , but that doesn't mean your efforts are in vain , they are just negligible enough to be overlooked , in the same way , when our auric fields , interact with the radiation of planets , the planets influence us more than we influence them .
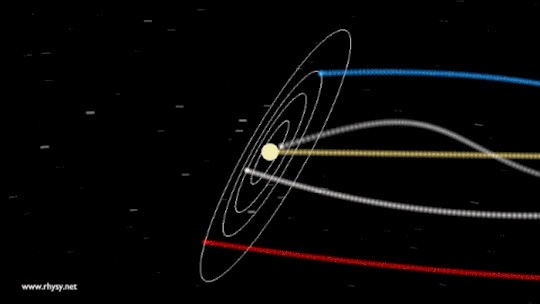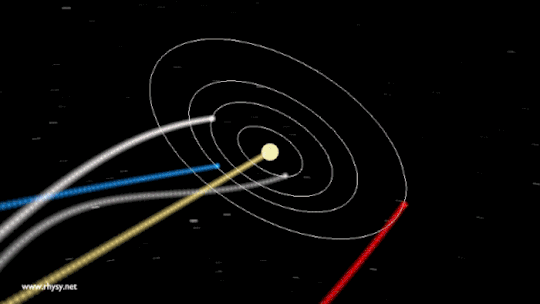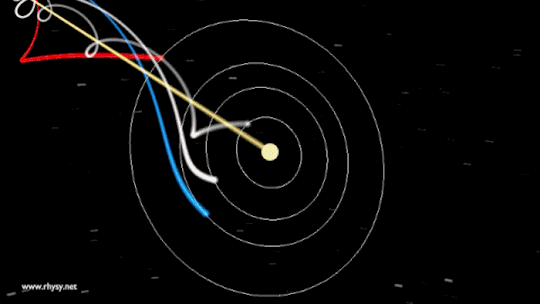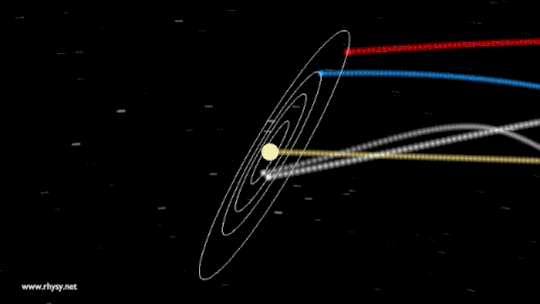
You can visualise wave -wave interaction through these images :


Planets
But if the same planets influence us why aren't we all the same? That's because during different period of the cycle of earth rotation their are different planets reflecting more than the other.
When you are born , the time , date and geographical location effects us , this leads to the formation of the innermost core our true self , but does that mean we can never change our circumstances ?
Our planet and all the planets orbit the Sun in a plane, and the entire plane moves in an elliptical orbit through the galaxy. Since every star in the galaxy also moves in an ellipse, we see ourselves appear to pass in-and-out of the galactic plane periodically, on timescales of tens of millions of years, while it takes around 200-250 million years to complete one orbit around the Milky Way. The other cosmic motions all contribute, too: the Milky Way within the Local Group, the Local Group in our Supercluster, and all of it with respect to the rest-frame of the Universe.The Solar System isn’t a vortex, but rather the sum of all our great cosmic motions.
A traditional birth chart shows where the sun, moon, and planets were on the Wheel of the Zodiac at the moment you were born. It can offer an astrological explanation for your communication style, how you process emotions, who you're attracted to, and more — think of it like a snapshot of your personalityFor example, it's believed that the sun moves one degree forward on the Wheel of the Zodiac for every year after your birthday. And every sign occupies 30 degrees of the Wheel, so, by the time you hit your 30s, if not earlier, the sun could very well have moved onto the next sign on your progressed chart. By comparison, the moon will move on from your natal moon sign much sooner, as it changes signs about every three years in a progressed chart. This can also relate to the d9 charts .

Sources:
Feel free to add up your points or theories .
Thank you for reading 🤍
Have a great day/night 💫.
#astrology#astro community#vedic astrology#sidereal astrology#sidereal zodiac#astrology community#thoughts#astronomy#quantum#quantum physics#quantum mechanics#planets#auras#spirituality
45 notes
·
View notes
Link
We stock a full range of horizontal and vertical designer radiators in different sizes and finishes from top brands such as Zehnder Heating. Zehnder Roda is the best range you can explore here at the lowest online prices with an excellent guarantee. Each modern radiator within this range is sure to enhance your home's interior. The UK Designer Radiators Shop.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems Market: Strong Distribution Channels Expected To Provide More Convenience To Various End Users In The Global Market 2027
Global Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems Market: Introduction
Radiant heating and cooling systems are used to regulate heat of a building by circulating water or air through building walls and floors. These systems can transfer nearly 50% of heat generated by radiation and convection heat exchange processes.
The radiant heat system circulates hot air from flue gas under building floors or in walls
This system can exchange heat with the surrounding environment through convection and radiation.
Global Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems Market: Dynamics
Rising demand and consumption of energy in different end-user sectors as well as high cost of energy is expected to create multiple issues for users. Manufacturers are focused on the development of innovative products to reduce the consumption of energy and to balance the high cost of energy. For instance, radiant systems can efficiently perform heating and cooling functions through radiation.
Radiant heating and cooling systems provide uniform energy-efficient heating and cooling. These systems are relatively cost-effective to achieve high levels of energy efficiency of buildings.
Rising demand for energy-efficient cooling and heating systems is a key factor driving the market
In the radiant cooling process, chilled water is circulated through floors and beams. The capacity of the radiant cooling system depends on different factors such as floor construction, pipe spacing, fluid flow rates, and insulation.
In radiant heating process, warm fluid is circulated through pipes or PEX integrated in the floor structure. The radiant heating system provides exceptional comfort at relative low temperatures and hence, it is more cost-effective and energy-efficient for consumers.
Planning To Lay Down Future Strategy? Request Sample https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=S&rep_id=74190
Technological advancement in radiant heating and cooling systems is expected to boost the demand for these systems and thereby, propel the market in the next few years
Increasing demand from residential and commercial building as well as advanced technologies associated with the use of radiant heating and cooling systems are key factors that are expected to propel the demand for radiant heating and cooling systems
Environment-friendly residential projects or modern green buildings are adopting various technologies as energy-efficient systems including thermal energy storage, heat pumps, and radiant heating and cooling systems.
However, the high cost associated with the installation of radiant heating and cooling systems is a major factor that is estimated to hamper the radiant heating and cooling systems market in the near future
Global Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems Market: Segmentation Analysis
Based on type, the global radiant heating and cooling systems market can be segmented into capillary surface systems, embedded surface systems, radiant panels, and thermally active building systems
In terms of technology, the global radiant heating and cooling systems market can be bifurcated into hydronic and electric
The hydronic segment accounted for a major share of the market in 2018, as hydronic systems drive more heat and incur low operating costs. This segment is projected to maintain its dominance of the global radiant heating and cooling systems market during the forecast period.
Based on end-user, the radiant heating and cooling systems market can be segmented into residential, commercial, and others
Request For COVID19 Impact Analysis Across Industries And Markets - Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems Market
Europe to Lead Global Market for Radiant Heating and Cooling Systems
In terms of region, the global radiant heating and cooling systems market can be divided into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and Middle East & Africa
Europe is likely to dominate the global radiant heating and cooling systems market from 2019 to 2027, followed by North America and Asia Pacific. Developed economies and increasing awareness and adoption of energy-efficient systems in increasing number of modern smart homes especially in developed countries, such as the U.S., in North America are key factors that are likely to drive the radiant heating and cooling systems market in the region in the next few years.
The radiant heating and cooling systems market in Asia Pacific and Middle East & Africa is expected to expand significantly in the next few years. Consumers in these regions tend to equip their homes with high-end safety and comfort devices and systems to ensure a good living experience. This is expected to propel the radiant heating and cooling market in the next few years.
Key Manufacturers Operating in Market
The global radiant heating and cooling systems market was moderately concentrated in 2018, owing to the presence of several regional and global players who have occupied prominent share of the radiant heating and cooling systems market. These vendors are engaged in offering varied products to end-users and adopt different technologies and strategies to compete in this competitive environment. Key manufacturers operating in the global market are:
Danfoss Group
Emerson Electric Co.
Radiant Cooling Corporation
Uponor Oyj
MrPEX Systems
REHAU
Zehnder Group AG
More Trending Reports by Transparency Market Research –
Shared Mobility Market https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-shared-mobility-market-to-grow-at-a-cagr-of-8-over-the-period-between-2018-and-2026-reaching-a-value-of-us-608-bn-by-2026-transparency-market-research-300998575.html
0 notes
Text
7 Facts About Designer Radiators
Designer radiators are interesting things; striking shapes, exciting colours and the warmth needed to keep you comfy. But today we’ve got a neat infographic for you with 7 fantastic facts about designer radiators which will keep you on your toes.
Designer radiators are interesting things; striking shapes, exciting colours and the warmth needed to keep you comfy. But today we’ve got a neat infographic for you with 7 fantastic facts about designer radiators which will keep you on your toes.
For more information, read on below for expanded descriptions of each of the 7 facts!
1 – The 1st Designer Radiator Was Invented in 1930!
In the early 1900s, Zehnder was a manufacturer of light motorcycles with a reputation for quality built up over several decades. Because they already manufactured steel tubes fort their motorcycles, they had the opportunity at that time in 1930 to make the Zehnder Charleston column radiator and expand into an emerging radiator market which at that time was populated by heavy, unwieldy and in some cases unsightly cast-iron heaters.
We are coming close now to a century on since that point and Zehnder have since revolutionised the way we think about our heating, and to this day sell the one and only Zehnder Charleston as one of the most flexible and popular designer radiators in the world.
2 – The Radiator Revolution
The ‘Radiator Revolution’ is the industry drive to help the world understand that the monotony of white compact radiators is no longer a problem you must cover up or resign yourself to.
Through the 70s and 80s the moment started to gain traction, and through the 90s and naughties modern hotels and the luxury homes of celebrities and socialites became the starting point for the nation-wide allure and fascination with the designer radiator, which today has become a the standard in at least one or two rooms in each modern home.
3 – Designer Radiator Materials
Most designer radiators are manufactured from steel; it’s cheap, strong, convects thermal energy satisfactorily and can be finished in hundreds of ways which also protect it from corrosion. Aluminium however is more costly to manufacture for heating, and it’s softer too, but it is an excellent convector of heat.
Cast Iron goes the other way and takes a long time to heat up, but looks absolutely tremendous in a contemporary setting, but especially in a period home. Stainless steel is step up from your run-of-the-mill steel, and typically lasts 4-5 times longer, but you can’t finish it with paint, you can only treat the metal itself and polish it or brush it to a satin finish.
Brass is used for the super high-quality traditional towel rails you see in classical bathrooms, the kind of elaborate rails you might see in Buckingham Palace and Chatsworth House. It is a long lasting, high quality metal which is suitable for any heating system, making it a brilliant luxury product.
Chrome is the last conventional finish on the market. Chrome radiators are in fact made from steel, and then chromium is electro-plated to the outside of the steel. The finish is a bright, reflective surface which is visually similar to polished stainless steel, but at a considerably better price.
Glass and mirrors are used in a lot of cases on designer radiators to pushing the boundaries of what is possible with heating, and while this might just sound like attaching a mirror to a normal radiator, it’s often more complex than that. Glass designer radiators can be made in vivid colours which often can’t quite be pulled off with paint, and additionally on glass you can print high-resolution images and create picture radiators!
By making specific fascia for a basic radiator, a lot of manufacturers can make efficient gorgeous radiators without having to extrude metals into hundreds of different shapes. Using marble and natural stone, wood, brass, copper and even the aforementioned glass, mirrors, stainless steel and aluminium, amazing covers can be made which create visual effects which would otherwise be completely unattainable.
4 - Radiators; LIES AND DECEIT
Okay, that might be a bit dramatic, but genuinely… Radiators… aren’t.
That is to say radiators don’t actually warm your rooms through radiation, it’s all an elaborate ruse! Depending on the radiator model, thermal radiation can make up as little as 20% of its overall heat output.
Convection is what actually does most of the work, in other words your radiators hold hot water, heat is passed through to the metal which heats up the surrounding air (which is why the surface area of a radiator is a big factor in how much heat it can produce) and then that air begins to circulate around the room.
The air heats up and begins to rise, and when it does that cool air is drawn in at the bottom of the radiator to replace it, this new air is heated and push upwards as more cool air is pulled upwards to take its place. As this happens, the hot air is being pushed further and further towards the centre of the room and reaches the furthest parts it can before beginning to cool and fall.
With enough time the air is warmed more and more quickly, and the result is that the whole room has become warm, nearly entirely by the convection of heat through the particles in the air.
The 20% radiation that we talked about before? That is direct-type heating. If on November 5th you stand 50 feet from a roaring bonfire you can feel thermal radiation making your face, your eyes and fingertips hot, even while the cool winter air whips around you, that’s because this type of direct heating warms surfaces directly.
So in your living room your walls, coffee table, sofas, paintings and curtain will all be directly heated to different degrees, and form there those surfaces raise the temperature of the air slightly, but with nowhere near the efficiency of the bulk convection.
5 – Best Heating
While we are on the topic of heating up the air efficiently, aluminium does a terrific job of just that. So much so that it can be designed not only to hold much less water than a steel counterpart, but also in a way which actively promotes the hot air currents we just talked about.
Aluminium designer radiators are now commonly manufactured so that they feature a large cavity inside, and only a small chamber for hot water to flow through. This means that in addition to the air surrounding the radiator being heated, the air inside the radiator is being heated, nearly doubling the surface area.
Two-fold, the air inside the radiator is heated up more quickly and is shot out the top of the radiator’s cavity, more quickly drawing the cool air in from beneath.
6 – Worst Heating
Doing a complete 180°, Chrome radiators are essentially a normal steel model, but with a layer of insulation on the outside. The chrome on the outside serves to look gorgeous, but sadly traps in nearly all of the radiation type heating, and even prevents some of the convection as well. You both need to pick a larger size if ordering chrome, and over the years it will cost you more as it needs to hold a good amount of hot water too, especially when put side-by-side next an aluminium model.
7 – Designer Radiator Shapes
The amazing thing about designer radiators is that they are only limited by imagination. We have products which can be sat on comfortably in bench form, perfect for spa or taking the chill out of a cold boot room.
How about a radiator entrenched under your feet, into the floor? Trench heating is completely unique, offering warmth in a discrete way that saves you valuable space by burying your heating under the floor, with only a hyper-stylish grille (available in a range of finish options) on show.
They can be shaped to fit gently curving walls as well as angled ones, like the Zehnder Charleston which we talked about earlier, meaning that no part of the home is off limits for heating. Most commonly this is used under bay windows which either curve or angle inwards, but they can even be used on outer angles.
Most mind-bogglingly, there are now designer radiators which can move! The Vogue Stendy is a sturdy towel rail which can be used as standard like any other gorgeous rail to dry your cosy towels on, but then like transformers-in-disguise can spring open to give you hot shelves to resting your folded towels or bath robes!
As interesting as these facts all are about designer radiators, the most exciting thing is that all of our brilliant and innovative designs are right at your fingertips, more affordable than you think and ready for delivery on the next day, so take a few minutes to imagine what you might fit into your dream interior today;
Source: https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/blog/7-facts-about-designer-radiators/
from Designer Radiator Showroom - Blog http://designeradiators.weebly.com/blog/7-facts-about-designer-radiators
0 notes
Text
7 Facts About Designer Radiators
Designer radiators are interesting things; striking shapes, exciting colours and the warmth needed to keep you comfy. But today we’ve got a neat infographic for you with 7 fantastic facts about designer radiators which will keep you on your toes.
Share this Image On Your Site
</p>
<p><strong>Please include attribution to DesignerRadiatorShowroom.co.uk with this graphic.</strong></p>
<p><a href=”><img src=’https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/wp/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/DRS-7-Facts-About-Designer-Radiators-new.jpg’ alt=’Designer radiator infographic by the Designer Radiator Showroom’ 540px border=’0′ /></a></p>
<p>
For more information, read on below for expanded descriptions of each of the 7 facts!
1 – The 1st Designer Radiator Was Invented in 1930!
In the early 1900s, Zehnder was a manufacturer of light motorcycles with a reputation for quality built up over several decades. Because they already manufactured steel tubes fort their motorcycles, they had the opportunity at that time in 1930 to make the Zehnder Charleston column radiator and expand into an emerging radiator market which at that time was populated by heavy, unwieldy and in some cases unsightly cast-iron heaters.
We are coming close now to a century on since that point and Zehnder have since revolutionised the way we think about our heating, and to this day sell the one and only Zehnder Charleston as one of the most flexible and popular designer radiators in the world.
2 – The Radiator Revolution
The ‘Radiator Revolution’ is the industry drive to help the world understand that the monotony of white compact radiators is no longer a problem you must cover up or resign yourself to.
Through the 70s and 80s the moment started to gain traction, and through the 90s and naughties modern hotels and the luxury homes of celebrities and socialites became the starting point for the nation-wide allure and fascination with the designer radiator, which today has become a the standard in at least one or two rooms in each modern home.
3 – Designer Radiator Materials
Most designer radiators are manufactured from steel; it’s cheap, strong, convects thermal energy satisfactorily and can be finished in hundreds of ways which also protect it from corrosion. Aluminium however is more costly to manufacture for heating, and it’s softer too, but it is an excellent convector of heat.
Cast Iron goes the other way and takes a long time to heat up, but looks absolutely tremendous in a contemporary setting, but especially in a period home. Stainless steel is step up from your run-of-the-mill steel, and typically lasts 4-5 times longer, but you can’t finish it with paint, you can only treat the metal itself and polish it or brush it to a satin finish.
Brass is used for the super high-quality traditional towel rails you see in classical bathrooms, the kind of elaborate rails you might see in Buckingham Palace and Chatsworth House. It is a long lasting, high quality metal which is suitable for any heating system, making it a brilliant luxury product.
Chrome is the last conventional finish on the market. Chrome radiators are in fact made from steel, and then chromium is electro-plated to the outside of the steel. The finish is a bright, reflective surface which is visually similar to polished stainless steel, but at a considerably better price.
Glass and mirrors are used in a lot of cases on designer radiators to pushing the boundaries of what is possible with heating, and while this might just sound like attaching a mirror to a normal radiator, it’s often more complex than that. Glass designer radiators can be made in vivid colours which often can’t quite be pulled off with paint, and additionally on glass you can print high-resolution images and create picture radiators!
By making specific fascia for a basic radiator, a lot of manufacturers can make efficient gorgeous radiators without having to extrude metals into hundreds of different shapes. Using marble and natural stone, wood, brass, copper and even the aforementioned glass, mirrors, stainless steel and aluminium, amazing covers can be made which create visual effects which would otherwise be completely unattainable.
4 – Radiators; LIES AND DECEIT
Okay, that might be a bit dramatic, but genuinely… Radiators… aren’t.
That is to say radiators don’t actually warm your rooms through radiation, it’s all an elaborate ruse! Depending on the radiator model, thermal radiation can make up as little as 20% of its overall heat output.
Convection is what actually does most of the work, in other words your radiators hold hot water, heat is passed through to the metal which heats up the surrounding air (which is why the surface area of a radiator is a big factor in how much heat it can produce) and then that air begins to circulate around the room.
The air heats up and begins to rise, and when it does that cool air is drawn in at the bottom of the radiator to replace it, this new air is heated and push upwards as more cool air is pulled upwards to take its place. As this happens, the hot air is being pushed further and further towards the centre of the room and reaches the furthest parts it can before beginning to cool and fall.
With enough time the air is warmed more and more quickly, and the result is that the whole room has become warm, nearly entirely by the convection of heat through the particles in the air.
The 20% radiation that we talked about before? That is direct-type heating. If on November 5th you stand 50 feet from a roaring bonfire you can feel thermal radiation making your face, your eyes and fingertips hot, even while the cool winter air whips around you, that’s because this type of direct heating warms surfaces directly.
So in your living room your walls, coffee table, sofas, paintings and curtain will all be directly heated to different degrees, and form there those surfaces raise the temperature of the air slightly, but with nowhere near the efficiency of the bulk convection.
5 – Best Heating
While we are on the topic of heating up the air efficiently, aluminium does a terrific job of just that. So much so that it can be designed not only to hold much less water than a steel counterpart, but also in a way which actively promotes the hot air currents we just talked about.
Aluminium designer radiators are now commonly manufactured so that they feature a large cavity inside, and only a small chamber for hot water to flow through. This means that in addition to the air surrounding the radiator being heated, the air inside the radiator is being heated, nearly doubling the surface area.
Two-fold, the air inside the radiator is heated up more quickly and is shot out the top of the radiator’s cavity, more quickly drawing the cool air in from beneath.
6 – Worst Heating
Doing a complete 180°, Chrome radiators are essentially a normal steel model, but with a layer of insulation on the outside. The chrome on the outside serves to look gorgeous, but sadly traps in nearly all of the radiation type heating, and even prevents some of the convection as well. You both need to pick a larger size if ordering chrome, and over the years it will cost you more as it needs to hold a good amount of hot water too, especially when put side-by-side next an aluminium model.
7 – Designer Radiator Shapes
The amazing thing about designer radiators is that they are only limited by imagination. We have products which can be sat on comfortably in bench form, perfect for spa or taking the chill out of a cold boot room.
How about a radiator entrenched under your feet, into the floor? Trench heating is completely unique, offering warmth in a discrete way that saves you valuable space by burying your heating under the floor, with only a hyper-stylish grille (available in a range of finish options) on show.
They can be shaped to fit gently curving walls as well as angled ones, like the Zehnder Charleston which we talked about earlier, meaning that no part of the home is off limits for heating. Most commonly this is used under bay windows which either curve or angle inwards, but they can even be used on outer angles.
Most mind-bogglingly, there are now designer radiators which can move! The Vogue Stendy is a sturdy towel rail which can be used as standard like any other gorgeous rail to dry your cosy towels on, but then like transformers-in-disguise can spring open to give you hot shelves to resting your folded towels or bath robes!
As interesting as these facts all are about designer radiators, the most exciting thing is that all of our brilliant and innovative designs are right at your fingertips, more affordable than you think and ready for delivery on the next day, so take a few minutes to imagine what you might fit into your dream interior today;
Source: https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/blog/7-facts-about-designer-radiators/
from Designer Radiator Showroom https://designeradiators.wordpress.com/2017/08/24/7-facts-about-designer-radiators/
0 notes
Text
7 Facts About Designer Radiators
Designer radiators are interesting things; striking shapes, exciting colours and the warmth needed to keep you comfy. But today we’ve got a neat infographic for you with 7 fantastic facts about designer radiators which will keep you on your toes.
Share this Image On Your Site
</p>
<p><strong>Please include attribution to DesignerRadiatorShowroom.co.uk with this graphic.</strong></p>
<p><a href=“><img src=‘https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/wp/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/DRS-7-Facts-About-Designer-Radiators-new.jpg’ alt='Designer radiator infographic by the Designer Radiator Showroom’ 540px border='0’ /></a></p>
<p>
For more information, read on below for expanded descriptions of each of the 7 facts!
1 – The 1st Designer Radiator Was Invented in 1930!
In the early 1900s, Zehnder was a manufacturer of light motorcycles with a reputation for quality built up over several decades. Because they already manufactured steel tubes fort their motorcycles, they had the opportunity at that time in 1930 to make the Zehnder Charleston column radiator and expand into an emerging radiator market which at that time was populated by heavy, unwieldy and in some cases unsightly cast-iron heaters.
We are coming close now to a century on since that point and Zehnder have since revolutionised the way we think about our heating, and to this day sell the one and only Zehnder Charleston as one of the most flexible and popular designer radiators in the world.
2 – The Radiator Revolution
The ‘Radiator Revolution’ is the industry drive to help the world understand that the monotony of white compact radiators is no longer a problem you must cover up or resign yourself to.
Through the 70s and 80s the moment started to gain traction, and through the 90s and naughties modern hotels and the luxury homes of celebrities and socialites became the starting point for the nation-wide allure and fascination with the designer radiator, which today has become a the standard in at least one or two rooms in each modern home.
3 – Designer Radiator Materials
Most designer radiators are manufactured from steel; it’s cheap, strong, convects thermal energy satisfactorily and can be finished in hundreds of ways which also protect it from corrosion. Aluminium however is more costly to manufacture for heating, and it’s softer too, but it is an excellent convector of heat.
Cast Iron goes the other way and takes a long time to heat up, but looks absolutely tremendous in a contemporary setting, but especially in a period home. Stainless steel is step up from your run-of-the-mill steel, and typically lasts 4-5 times longer, but you can’t finish it with paint, you can only treat the metal itself and polish it or brush it to a satin finish.
Brass is used for the super high-quality traditional towel rails you see in classical bathrooms, the kind of elaborate rails you might see in Buckingham Palace and Chatsworth House. It is a long lasting, high quality metal which is suitable for any heating system, making it a brilliant luxury product.
Chrome is the last conventional finish on the market. Chrome radiators are in fact made from steel, and then chromium is electro-plated to the outside of the steel. The finish is a bright, reflective surface which is visually similar to polished stainless steel, but at a considerably better price.
Glass and mirrors are used in a lot of cases on designer radiators to pushing the boundaries of what is possible with heating, and while this might just sound like attaching a mirror to a normal radiator, it’s often more complex than that. Glass designer radiators can be made in vivid colours which often can’t quite be pulled off with paint, and additionally on glass you can print high-resolution images and create picture radiators!
By making specific fascia for a basic radiator, a lot of manufacturers can make efficient gorgeous radiators without having to extrude metals into hundreds of different shapes. Using marble and natural stone, wood, brass, copper and even the aforementioned glass, mirrors, stainless steel and aluminium, amazing covers can be made which create visual effects which would otherwise be completely unattainable.
4 - Radiators; LIES AND DECEIT
Okay, that might be a bit dramatic, but genuinely… Radiators… aren’t.
That is to say radiators don’t actually warm your rooms through radiation, it’s all an elaborate ruse! Depending on the radiator model, thermal radiation can make up as little as 20% of its overall heat output.
Convection is what actually does most of the work, in other words your radiators hold hot water, heat is passed through to the metal which heats up the surrounding air (which is why the surface area of a radiator is a big factor in how much heat it can produce) and then that air begins to circulate around the room.
The air heats up and begins to rise, and when it does that cool air is drawn in at the bottom of the radiator to replace it, this new air is heated and push upwards as more cool air is pulled upwards to take its place. As this happens, the hot air is being pushed further and further towards the centre of the room and reaches the furthest parts it can before beginning to cool and fall.
With enough time the air is warmed more and more quickly, and the result is that the whole room has become warm, nearly entirely by the convection of heat through the particles in the air.
The 20% radiation that we talked about before? That is direct-type heating. If on November 5th you stand 50 feet from a roaring bonfire you can feel thermal radiation making your face, your eyes and fingertips hot, even while the cool winter air whips around you, that’s because this type of direct heating warms surfaces directly.
So in your living room your walls, coffee table, sofas, paintings and curtain will all be directly heated to different degrees, and form there those surfaces raise the temperature of the air slightly, but with nowhere near the efficiency of the bulk convection.
5 – Best Heating
While we are on the topic of heating up the air efficiently, aluminium does a terrific job of just that. So much so that it can be designed not only to hold much less water than a steel counterpart, but also in a way which actively promotes the hot air currents we just talked about.
Aluminium designer radiators are now commonly manufactured so that they feature a large cavity inside, and only a small chamber for hot water to flow through. This means that in addition to the air surrounding the radiator being heated, the air inside the radiator is being heated, nearly doubling the surface area.
Two-fold, the air inside the radiator is heated up more quickly and is shot out the top of the radiator’s cavity, more quickly drawing the cool air in from beneath.
6 – Worst Heating
Doing a complete 180°, Chrome radiators are essentially a normal steel model, but with a layer of insulation on the outside. The chrome on the outside serves to look gorgeous, but sadly traps in nearly all of the radiation type heating, and even prevents some of the convection as well. You both need to pick a larger size if ordering chrome, and over the years it will cost you more as it needs to hold a good amount of hot water too, especially when put side-by-side next an aluminium model.
7 – Designer Radiator Shapes
The amazing thing about designer radiators is that they are only limited by imagination. We have products which can be sat on comfortably in bench form, perfect for spa or taking the chill out of a cold boot room.
How about a radiator entrenched under your feet, into the floor? Trench heating is completely unique, offering warmth in a discrete way that saves you valuable space by burying your heating under the floor, with only a hyper-stylish grille (available in a range of finish options) on show.
They can be shaped to fit gently curving walls as well as angled ones, like the Zehnder Charleston which we talked about earlier, meaning that no part of the home is off limits for heating. Most commonly this is used under bay windows which either curve or angle inwards, but they can even be used on outer angles.
Most mind-bogglingly, there are now designer radiators which can move! The Vogue Stendy is a sturdy towel rail which can be used as standard like any other gorgeous rail to dry your cosy towels on, but then like transformers-in-disguise can spring open to give you hot shelves to resting your folded towels or bath robes!
As interesting as these facts all are about designer radiators, the most exciting thing is that all of our brilliant and innovative designs are right at your fingertips, more affordable than you think and ready for delivery on the next day, so take a few minutes to imagine what you might fit into your dream interior today;
from Designer Radiator Showroom https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/blog/7-facts-about-designer-radiators/
from Designer Radiator Showroom https://designerradiators.tumblr.com/post/164552764556
0 notes
Text
7 Facts About Designer Radiators
Designer radiators are interesting things; striking shapes, exciting colours and the warmth needed to keep you comfy. But today we’ve got a neat infographic for you with 7 fantastic facts about designer radiators which will keep you on your toes.
Share this Image On Your Site
</p>
<p><strong>Please include attribution to DesignerRadiatorShowroom.co.uk with this graphic.</strong></p>
<p><a href=''><img src='https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/wp/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/DRS-7-Facts-About-Designer-Radiators-new.jpg' alt='Designer radiator infographic by the Designer Radiator Showroom' 540px border='0' /></a></p>
<p>
For more information, read on below for expanded descriptions of each of the 7 facts!
1 – The 1st Designer Radiator Was Invented in 1930!
In the early 1900s, Zehnder was a manufacturer of light motorcycles with a reputation for quality built up over several decades. Because they already manufactured steel tubes fort their motorcycles, they had the opportunity at that time in 1930 to make the Zehnder Charleston column radiator and expand into an emerging radiator market which at that time was populated by heavy, unwieldy and in some cases unsightly cast-iron heaters.
We are coming close now to a century on since that point and Zehnder have since revolutionised the way we think about our heating, and to this day sell the one and only Zehnder Charleston as one of the most flexible and popular designer radiators in the world.
2 – The Radiator Revolution
The ‘Radiator Revolution’ is the industry drive to help the world understand that the monotony of white compact radiators is no longer a problem you must cover up or resign yourself to.
Through the 70s and 80s the moment started to gain traction, and through the 90s and naughties modern hotels and the luxury homes of celebrities and socialites became the starting point for the nation-wide allure and fascination with the designer radiator, which today has become a the standard in at least one or two rooms in each modern home.
3 – Designer Radiator Materials
Most designer radiators are manufactured from steel; it’s cheap, strong, convects thermal energy satisfactorily and can be finished in hundreds of ways which also protect it from corrosion. Aluminium however is more costly to manufacture for heating, and it’s softer too, but it is an excellent convector of heat.
Cast Iron goes the other way and takes a long time to heat up, but looks absolutely tremendous in a contemporary setting, but especially in a period home. Stainless steel is step up from your run-of-the-mill steel, and typically lasts 4-5 times longer, but you can’t finish it with paint, you can only treat the metal itself and polish it or brush it to a satin finish.
Brass is used for the super high-quality traditional towel rails you see in classical bathrooms, the kind of elaborate rails you might see in Buckingham Palace and Chatsworth House. It is a long lasting, high quality metal which is suitable for any heating system, making it a brilliant luxury product.
Chrome is the last conventional finish on the market. Chrome radiators are in fact made from steel, and then chromium is electro-plated to the outside of the steel. The finish is a bright, reflective surface which is visually similar to polished stainless steel, but at a considerably better price.
Glass and mirrors are used in a lot of cases on designer radiators to pushing the boundaries of what is possible with heating, and while this might just sound like attaching a mirror to a normal radiator, it’s often more complex than that. Glass designer radiators can be made in vivid colours which often can’t quite be pulled off with paint, and additionally on glass you can print high-resolution images and create picture radiators!
By making specific fascia for a basic radiator, a lot of manufacturers can make efficient gorgeous radiators without having to extrude metals into hundreds of different shapes. Using marble and natural stone, wood, brass, copper and even the aforementioned glass, mirrors, stainless steel and aluminium, amazing covers can be made which create visual effects which would otherwise be completely unattainable.
4 - Radiators; LIES AND DECEIT
Okay, that might be a bit dramatic, but genuinely… Radiators… aren’t.
That is to say radiators don’t actually warm your rooms through radiation, it’s all an elaborate ruse! Depending on the radiator model, thermal radiation can make up as little as 20% of its overall heat output.
Convection is what actually does most of the work, in other words your radiators hold hot water, heat is passed through to the metal which heats up the surrounding air (which is why the surface area of a radiator is a big factor in how much heat it can produce) and then that air begins to circulate around the room.
The air heats up and begins to rise, and when it does that cool air is drawn in at the bottom of the radiator to replace it, this new air is heated and push upwards as more cool air is pulled upwards to take its place. As this happens, the hot air is being pushed further and further towards the centre of the room and reaches the furthest parts it can before beginning to cool and fall.
With enough time the air is warmed more and more quickly, and the result is that the whole room has become warm, nearly entirely by the convection of heat through the particles in the air.
The 20% radiation that we talked about before? That is direct-type heating. If on November 5th you stand 50 feet from a roaring bonfire you can feel thermal radiation making your face, your eyes and fingertips hot, even while the cool winter air whips around you, that’s because this type of direct heating warms surfaces directly.
So in your living room your walls, coffee table, sofas, paintings and curtain will all be directly heated to different degrees, and form there those surfaces raise the temperature of the air slightly, but with nowhere near the efficiency of the bulk convection.
5 – Best Heating
While we are on the topic of heating up the air efficiently, aluminium does a terrific job of just that. So much so that it can be designed not only to hold much less water than a steel counterpart, but also in a way which actively promotes the hot air currents we just talked about.
Aluminium designer radiators are now commonly manufactured so that they feature a large cavity inside, and only a small chamber for hot water to flow through. This means that in addition to the air surrounding the radiator being heated, the air inside the radiator is being heated, nearly doubling the surface area.
Two-fold, the air inside the radiator is heated up more quickly and is shot out the top of the radiator’s cavity, more quickly drawing the cool air in from beneath.
6 – Worst Heating
Doing a complete 180°, Chrome radiators are essentially a normal steel model, but with a layer of insulation on the outside. The chrome on the outside serves to look gorgeous, but sadly traps in nearly all of the radiation type heating, and even prevents some of the convection as well. You both need to pick a larger size if ordering chrome, and over the years it will cost you more as it needs to hold a good amount of hot water too, especially when put side-by-side next an aluminium model.
7 – Designer Radiator Shapes
The amazing thing about designer radiators is that they are only limited by imagination. We have products which can be sat on comfortably in bench form, perfect for spa or taking the chill out of a cold boot room.
How about a radiator entrenched under your feet, into the floor? Trench heating is completely unique, offering warmth in a discrete way that saves you valuable space by burying your heating under the floor, with only a hyper-stylish grille (available in a range of finish options) on show.
They can be shaped to fit gently curving walls as well as angled ones, like the Zehnder Charleston which we talked about earlier, meaning that no part of the home is off limits for heating. Most commonly this is used under bay windows which either curve or angle inwards, but they can even be used on outer angles.
Most mind-bogglingly, there are now designer radiators which can move! The Vogue Stendy is a sturdy towel rail which can be used as standard like any other gorgeous rail to dry your cosy towels on, but then like transformers-in-disguise can spring open to give you hot shelves to resting your folded towels or bath robes!
As interesting as these facts all are about designer radiators, the most exciting thing is that all of our brilliant and innovative designs are right at your fingertips, more affordable than you think and ready for delivery on the next day, so take a few minutes to imagine what you might fit into your dream interior today;
from Designer Radiator Showroom https://www.designerradiatorshowroom.co.uk/blog/7-facts-about-designer-radiators/
0 notes
Text
Keep your towels warm and dry with our range of Zehnder and Bisque contemporary heated towel rails on available at Bathroom Shop UK Yorkshire! Contamporary Heated towel rails provide enough heat output to not only dry your towels but also warm your bathroom when the central heating comes on. Make a statement with our range of contemporary designs that are leading the way in modern towel rail and radiator innovation.
#heatedtowelrails#buytowelrails#heating#bathroomshopuk#shopbathroomsuk#buybathroomsonline#heatedtowelrailsuk#electricheatedtowelrails#contemporary heated towel rails
0 notes