Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Local Control Stations: An Essential Component in Industrial Automation
In the world of industrial automation, Local Control Stations (LCS) play a critical role in enhancing operational efficiency and safety. These devices, strategically located near machinery or equipment, provide operators with direct control over specific processes without needing to interact with a central control system. Their importance lies in offering real-time control and emergency shutdown options, making them indispensable in sectors like oil and gas, manufacturing, chemical processing, and power generation.
What is a Local Control Station?
A Local Control Station is an industrial control panel equipped with switches, push buttons, indicators, and other interface devices that allow operators to control equipment directly at the location of the process. These stations are usually enclosed in durable housings, often made of materials such as stainless steel or cast aluminum, ensuring they can withstand harsh environmental conditions like high temperatures, dust, moisture, and potential chemical exposure.
Local Control Stations can be custom-designed to suit the specific requirements of the application, including the number and type of buttons, lights, and other control components. They typically include:
Start/Stop switches: For basic operational control.
Emergency stop buttons: To instantly halt machinery in case of an emergency.
Indicator lights: Providing visual feedback on system status (e.g., power on, running, or fault conditions).
Selector switches: To toggle between operational modes (e.g., manual, automatic, maintenance).

These stations allow for localized manual control over equipment, which is essential in situations where central control systems might not be practical or fast enough to respond to immediate safety concerns.
The Role of Local Control Stations in Industrial Operations
Local Control Stations are designed to enhance the safety and efficiency of industrial operations. By placing control capabilities near the equipment, operators can quickly intervene when necessary, reducing the risk of delays in responding to machinery malfunctions or safety hazards. This proximity to equipment enables swift action, reducing downtime and potentially preventing costly accidents.
In addition to safety, LCS also contributes to process efficiency by offering real-time, localized control, meaning operators can fine-tune processes based on immediate feedback. This localized control is particularly useful in industries where process precision is vital, such as pharmaceuticals, chemical production, and food and beverage manufacturing.
Types of Local Control Stations
Depending on the industry and application, there are different types of Local Control Stations. Some of the most common types include:
Basic Push Button Stations: The simplest form of control stations, featuring start/stop buttons and emergency stops. These are often used in smaller installations or for straightforward operations.
Hazardous Area Control Stations: Designed to be explosion-proof or intrinsically safe, these stations are used in industries like oil and gas, where hazardous atmospheres may be present. These control stations are engineered to prevent ignition sources from causing explosions.
Multi-Function Control Stations: These stations feature multiple controls, including push buttons, switches, and indicators, all within one enclosure. They offer greater versatility and are often found in complex machinery or systems that require more comprehensive control.
Customized Local Control Stations: Many manufacturers offer customization options, enabling companies to tailor LCS solutions to their specific process needs. These stations can include any combination of control features and are often designed to integrate with existing automation systems.
Advantages of Using Local Control Stations
The use of Local Control Stations offers several key advantages to industrial operations:
Enhanced Safety: By allowing operators to control equipment directly at the site, LCS enables quick responses to emergency situations. The presence of emergency stop buttons is especially critical in high-risk environments, where immediate shutdowns can prevent accidents or equipment damage.
Operational Efficiency: LCS allows operators to make quick adjustments and real-time decisions without having to return to a central control room. This immediate interaction can optimize workflow and reduce the likelihood of production delays.
Flexibility and Customization: Local Control Stations can be configured to suit specific operational needs. Whether the requirements are for a simple start/stop function or more complex control options, LCS provides versatile solutions.
Durability in Harsh Environments: Built to withstand extreme temperatures, corrosive substances, and high-pressure environments, these control stations are well-suited for industries where conditions are less than ideal. Their robust design ensures reliable performance, even in challenging conditions.
Localized Control in Remote Areas: For industries such as oil and gas, where equipment is often spread out over large geographical areas, LCS serves as a practical solution for on-site control. This is particularly important in remote operations, where access to a central control room may be limited.
Key Industries Utilizing Local Control Stations
Several industries rely heavily on Local Control Stations for efficient and safe operations. These include:
Oil and Gas: In hazardous environments like offshore rigs or refineries, LCS provides immediate control over pumps, valves, and safety equipment, ensuring operational safety.
Manufacturing: LCS is used to control machinery in production lines, offering real-time feedback and control for efficiency and safety.
Chemical Processing: In plants where sensitive chemical reactions occur, LCS offers operators the ability to quickly adjust processes or shut down equipment to prevent accidents.
Power Generation: Local Control Stations are integral in controlling turbines, generators, and other equipment in power plants, allowing for quick adjustments to optimize output and maintain safety.
Conclusion
As industries continue to emphasize automation and safety, Local Control Stations remain a vital component of modern industrial setups. By providing operators with localized, real-time control over equipment, they ensure that processes run smoothly and safely. Whether for starting machinery, stopping operations during emergencies, or monitoring equipment status, LCS offers the reliability and control necessary in high-demand industries.
For businesses seeking robust and reliable Local Control Stations, Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd. offers a range of high-quality, customizable solutions designed to meet the specific needs of various industries. Buy Local Control Station from Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd. today to ensure efficient and safe industrial operations.
0 notes
Text
High Pressure Needle Valves: Precision Flow Control in Demanding Applications

In the realm of fluid control systems, high pressure needle valves stand out as indispensable components, offering precise regulation of flow in some of the most challenging industrial environments. These valves, characterized by their ability to withstand extreme pressures while providing accurate flow control, play a crucial role across various sectors, from oil and gas to chemical processing and hydraulic systems.
Understanding High Pressure Needle Valves
A high pressure needle valve is a type of linear motion valve designed to regulate flow with high precision, particularly in systems operating under significant pressure. The valve's name derives from its key component: a slender, tapered pin (the "needle") that moves in and out of a small orifice to control flow. This design allows for extremely fine adjustments, making needle valves ideal for applications requiring meticulous flow regulation.
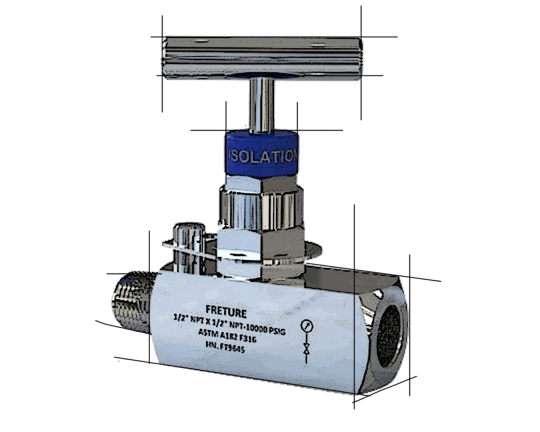
Key Features and Advantages
Precise Flow Control: The gradual taper of the needle and its fine-threaded stem allow for minute adjustments, enabling operators to achieve exact flow rates.
High Pressure Capability: Engineered to withstand pressures ranging from several hundred to thousands of bar, these valves maintain their integrity in extreme conditions.
Tight Shut-off: When fully closed, the needle forms a metal-to-metal seal with the seat, ensuring minimal to zero leakage.
Durability: Constructed from high-strength materials, these valves offer long service life even in harsh operating environments.
Compact Design: Despite their high pressure capabilities, needle valves are relatively small, making them suitable for installations with space constraints.
Versatility: Available in various configurations to suit different mounting requirements and flow directions.
Construction and Materials
The effectiveness of a high pressure needle valve largely depends on its construction and the materials used:
Body: Typically made from forged steel, stainless steel, or special alloys like Monel or Hastelloy for corrosive applications.
Needle (Stem): Usually constructed from hardened stainless steel or other wear-resistant alloys to ensure longevity and maintain a tight seal.
Seat: Often integrated into the valve body, but may be replaceable in some designs. Material choice depends on the application but is generally a hardened alloy compatible with the body material.
Packing: High-quality packing materials like PTFE or graphite are used to prevent leakage around the stem while allowing smooth operation.
Bonnet: Secures the packing and guides the stem. In high pressure applications, a bolted bonnet design is common for added strength.
The choice of materials is critical and depends on factors such as operating pressure, temperature, media compatibility, and environmental conditions.
Types of High Pressure Needle Valves
Several variations of high pressure needle valves exist, each designed to meet specific application requirements:
Standard Needle Valves: The most common type, suitable for a wide range of general applications.
Micro-Metering Valves: Feature an exceptionally fine needle taper for ultra-precise flow control, often used in laboratory or analytical equipment.
Multi-Port Needle Valves: Incorporate multiple inlets or outlets for complex flow control scenarios.
Angle Pattern Needle Valves: Designed with the inlet and outlet at right angles, useful in certain piping configurations.
Bar Stock Needle Valves: Machined from solid bar stock for maximum pressure handling capability.
Cryogenic Needle Valves: Specially designed to maintain functionality at extremely low temperatures.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility and precision of high pressure needle valves make them indispensable in numerous industrial applications:
Oil and Gas: Used in wellhead control panels, sampling systems, and pressure reduction stations.
Chemical Processing: Crucial for precise chemical injection and reactor feed control.
Hydraulic Systems: Employed in pressure control and hydraulic test benches.
Power Generation: Found in steam sampling systems and turbine control.
Aerospace: Used in fuel systems and hydraulic controls of aircraft.
Research and Development: Essential in high pressure testing equipment and experimental setups.
Water Jet Cutting: Control water flow in high pressure cutting systems.
Considerations for Selection and Installation
Choosing the right high pressure needle valve requires careful consideration of several factors:
Pressure Rating: Must exceed the maximum system pressure with an appropriate safety margin.
Temperature Range: Ensure compatibility with both the minimum and maximum expected temperatures.
Flow Coefficient (Cv): Select a valve with an appropriate Cv for the required flow rate and pressure drop.
Material Compatibility: Choose materials resistant to corrosion and degradation by the process media.
Connection Type: Consider the existing piping system (e.g., NPT threads, tube fittings, welded connections).
Actuation Method: Determine if manual operation is sufficient or if automated control is necessary.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations: Evaluate accessibility for maintenance and incorporate necessary safety features.
Installation best practices include proper alignment, use of appropriate thread sealants or gaskets, and adherence to torque specifications. In high pressure systems, it's crucial to follow proper start-up and shutdown procedures to prevent sudden pressure surges that could damage the valve or connected equipment.
Maintenance and Safety
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and safe operation of high pressure needle valves:
Regular Inspection: Check for signs of wear, leakage, or damage, particularly around the stem and seat area.
Lubrication: Periodically lubricate the stem threads to ensure smooth operation, using lubricants compatible with the process media.
Packing Adjustment: Tighten or replace packing as needed to prevent leakage around the stem.
Cleaning: Remove any debris or buildup that could affect valve performance or cause uneven wear.
Testing: Regularly verify proper operation and shut-off capability, especially in critical applications.
Safety is paramount when working with high pressure systems. Always follow proper lockout/tagout procedures before performing maintenance. When opening a high pressure needle valve, do so gradually to prevent sudden pressure release. Training personnel in the proper operation and maintenance of these valves is crucial to prevent accidents and ensure optimal performance.
Innovations and Future Trends
The field of high pressure needle valve technology continues to evolve, driven by industry demands for greater efficiency, safety, and control:
Advanced Materials: Development of new alloys and composites to enhance pressure capabilities and corrosion resistance.
Smart Valves: Integration of sensors and digital controls for real-time monitoring and remote operation.
Improved Sealing Technologies: Innovations in seat and stem designs to enhance shut-off capabilities and reduce wear.
Additive Manufacturing: Exploration of 3D printing techniques for producing complex valve geometries or custom solutions.
Miniaturization: Development of smaller, high-performance valves for space-constrained applications.
Enhanced Ergonomics: Redesigned handles and actuation mechanisms for improved operator comfort and precision.
As industries push the boundaries of pressure and flow control, high pressure needle valves will undoubtedly continue to play a critical role. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on expanding the operational limits of these valves while improving their longevity, ease of use, and integration with modern control systems.
Conclusion
High pressure needle valves represent a pinnacle of precision flow control technology, capable of operating under extreme conditions while providing the fine adjustments necessary for critical processes. Their importance across various industries underscores the need for continued innovation and refinement in valve design and materials.
For engineers and system designers working with high pressure applications, a thorough understanding of needle valve principles, selection criteria, and maintenance requirements is essential. By choosing the right valve and implementing proper care and operation procedures, industries can ensure safe, efficient, and reliable flow control in even the most demanding environments.
As we look to the future, high pressure needle valves will undoubtedly continue to evolve, incorporating new technologies and materials to meet the ever-increasing demands of modern industrial processes. Their role in ensuring precise, safe, and efficient fluid control remains as critical as ever, making them an indispensable component in the landscape of high pressure fluid systems.
0 notes
Text
The Power of Rotation: A Comprehensive Look at Rotary Actuators
Transform Pneumatic, Hydraulic, or Electric Energy to Mechanical Rotation
In the realm of industrial automation, precise control over movement is paramount. Rotary actuators play a vital role in achieving this control, converting various forms of energy into rotary motion to power a wide range of applications. From the delicate movements of robotic arms to the powerful operation of valves and gates, rotary actuators offer a versatile and efficient solution for driving rotational tasks. This article delves into the world of rotary actuators, exploring their types, working principles, functionalities, and their diverse applications across various industries.
Understanding Rotary Actuators:
At their core, rotary actuators are mechanical devices that translate energy into rotary motion, or torque, around a specific axis. This energy source can be electric, pneumatic, hydraulic, or even manual. By converting this energy, rotary actuators enable precise control of angular displacement and rotational force, making them ideal for applications requiring positioning, opening, closing, or rotating various mechanisms.

Types of Rotary Actuators:
The diverse world of rotary actuators encompasses various types, each catering to specific needs and applications:
Electric Rotary Actuators: Powered by electric motors, these actuators offer precise control and are well-suited for automated applications. They come in various configurations, including stepper motors, servo motors, and DC gear motors, each offering distinct torque and speed characteristics.
Pneumatic Rotary Actuators: Utilizing compressed air as the energy source, these actuators are known for their speed and force output. They are commonly used in applications requiring high-speed actuation or limited space availability. Rack and pinion and vane types are two common configurations of pneumatic rotary actuators.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: These actuators rely on hydraulic fluid for power, offering exceptional force and torque capabilities. They are ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high power output, such as operating large valves or manipulating massive machinery components.
Working Principles of Rotary Actuators:
The specific working principle of a rotary actuator depends on its type. Here's a simplified breakdown of the primary types:
Electric Rotary Actuators: An electric motor converts electrical energy into rotational motion of the motor shaft. This rotation can be geared down or up to achieve the desired output speed and torque. In stepper motors, the rotation occurs in discrete steps, offering precise positioning control. Servo motors provide continuous rotation with precise control over speed and position based on feedback signals.
Pneumatic Rotary Actuators: Compressed air enters the actuator body, pushing against a piston or vane, causing it to rotate. The direction of rotation is controlled by valves that direct the compressed air flow. Rack and pinion actuators convert the linear motion of the piston or vane into rotary motion using a gear rack and pinion gear. Vane actuators utilize the direct rotation of the vane within the actuator body.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: Hydraulic fluid, pressurized by a pump, enters the actuator body and exerts force on a piston or vane. The resulting linear motion is converted into rotary motion through a gear mechanism similar to pneumatic rotary actuators.
Functionalities of Rotary Actuators:
Rotary actuators perform a wide range of functions in various applications. Some key functionalities include:
Positioning: Rotary actuators can precisely position mechanical components or robotic arms to specific angles.
Opening and Closing: They can be used to open and close valves, gates, dampers, and other mechanisms requiring rotational movement.
Mixing and Stirring: Rotary actuators can power mixing blades or stirrers in various industrial processes.
Indexing and Material Handling: They can be used for precise indexing of materials in automated production lines or material handling equipment.
Clamping and Gripping: Rotary actuators can be used to clamp or grip objects in robotic applications or assembly lines.
Selection Considerations for Rotary Actuators:
Choosing the right rotary actuator for your application requires careful consideration of several factors:
Torque and Speed Requirements: The actuator's torque output and speed capabilities need to match the application's specific demands.
Power Source: Electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic power sources should be chosen based on available resources and desired control characteristics.
Duty Cycle: The frequency and duration of operation for the actuator must be considered to ensure proper sizing and prevent overheating.
Accuracy and Repeatability: The level of precision required for positioning or control should be factored in when selecting the actuator type.
Environmental Conditions: The operating environment, including temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to dust or liquids, should be considered to ensure proper material selection and protection for the actuator.
Applications of Rotary Actuators (Continued):
Building upon the previous section, here's a detailed look at some key industry applications of rotary actuators:
Oil & Gas: Rotary actuators are crucial in the oil & gas industry for:
Valve operation: Opening and closing valves for flow control in pipelines, refining processes, and wellheads.
Actuating blowout preventers (BOPs): Ensuring safety by closing wellbores in case of emergencies.
Positioning drilling equipment: Providing precise control over drilling heads and other downhole tools.
Power Generation: Rotary actuators are used in power plants for:
Valve actuation: Regulating fluid flow in cooling systems, boiler operations, and steam turbines.
Damper control: Adjusting air intake and exhaust dampers for combustion efficiency.
Positioning solar tracker systems: Optimizing the angle of solar panels to maximize sun exposure.
Food & Beverage: Rotary actuators contribute to automation in food processing by:
Operating valves for ingredient mixing, filling lines, and sterilization processes.
Positioning robotic arms for food handling, packaging, and palletizing.
Controlling conveyor belts for product movement within the production line.
Automotive Industry: Rotary actuators play a role in:
Robotic welding and painting applications: Precise movement of robotic arms for welding and painting car bodies.
Assembly line automation: Positioning and manipulation of components during vehicle assembly.
Climate control systems: Adjusting air flow dampers for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning within vehicles.
Aerospace & Defense: Rotary actuators find application in:
Aircraft control surfaces: Moving rudders, ailerons, and flaps for aircraft maneuverability.
Landing gear deployment and retraction: Precise actuation of landing gear mechanisms.
Radar positioning: Controlling the movement of radar antennae for target detection and tracking.
Construction: Rotary actuators contribute to automation in construction by:
Operating valves in concrete mixing trucks and other heavy machinery.
Positioning robotic arms for automated welding and material handling.
Controlling the movement of construction equipment attachments like excavator buckets and bulldozer blades.
Beyond these specific examples, rotary actuators are present in countless other applications across diverse industries. Their versatility, reliability, and ability to convert various energy sources into precise rotational motion make them a cornerstone of industrial automation.
Freture Techno: Your Partner in Rotary Actuator Solutions
Freture Techno Pvt. Ltd., a leading manufacturer of rotary actuators in Mumbai, India, offers a comprehensive range of high-quality electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic rotary actuators. With a commitment to innovation and engineering excellence, Freture Techno caters to diverse industry needs. Their team of experts can assist you in selecting the optimal rotary actuator for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency. Visit their website today to explore their product portfolio and discover how Freture Techno can be your trusted partner in rotary actuator solutions.
#valves#automation#Pneumatic#Hydraulic#Electric#Rotary Actuators#Freture Techno#Manufacturer#Mumbai#India
0 notes