#AI and machine learning training
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#AI Mastery course online#Learn AI for students#Online artificial intelligence course#AI training for beginners online#Advanced AI course for students#Best AI courses online#AI certification for students#Artificial intelligence classes online#AI courses for college students#AI and machine learning training#Online AI development course#AI programming course online#AI deep learning online course#Top AI courses for students#AI specialist training online#Best online course for AI mastery#Artificial intelligence for beginners online#AI algorithms course online#Machine learning basics online#Online AI projects for students#Introduction to AI online course#AI ethics course online#Online AI tutorials for students#AI and data science online course#Online AI bootcamp for students#Best AI training program online#AI career path online#AI masterclass online#Online AI education for students#AI technology course online
0 notes
Text
The surprising truth about data-driven dictatorships

Here’s the “dictator’s dilemma”: they want to block their country’s frustrated elites from mobilizing against them, so they censor public communications; but they also want to know what their people truly believe, so they can head off simmering resentments before they boil over into regime-toppling revolutions.
These two strategies are in tension: the more you censor, the less you know about the true feelings of your citizens and the easier it will be to miss serious problems until they spill over into the streets (think: the fall of the Berlin Wall or Tunisia before the Arab Spring). Dictators try to square this circle with things like private opinion polling or petition systems, but these capture a small slice of the potentially destabiziling moods circulating in the body politic.
Enter AI: back in 2018, Yuval Harari proposed that AI would supercharge dictatorships by mining and summarizing the public mood — as captured on social media — allowing dictators to tack into serious discontent and diffuse it before it erupted into unequenchable wildfire:
https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2018/10/yuval-noah-harari-technology-tyranny/568330/
Harari wrote that “the desire to concentrate all information and power in one place may become [dictators] decisive advantage in the 21st century.” But other political scientists sharply disagreed. Last year, Henry Farrell, Jeremy Wallace and Abraham Newman published a thoroughgoing rebuttal to Harari in Foreign Affairs:
https://www.foreignaffairs.com/world/spirals-delusion-artificial-intelligence-decision-making
They argued that — like everyone who gets excited about AI, only to have their hopes dashed — dictators seeking to use AI to understand the public mood would run into serious training data bias problems. After all, people living under dictatorships know that spouting off about their discontent and desire for change is a risky business, so they will self-censor on social media. That’s true even if a person isn’t afraid of retaliation: if you know that using certain words or phrases in a post will get it autoblocked by a censorbot, what’s the point of trying to use those words?
The phrase “Garbage In, Garbage Out” dates back to 1957. That’s how long we’ve known that a computer that operates on bad data will barf up bad conclusions. But this is a very inconvenient truth for AI weirdos: having given up on manually assembling training data based on careful human judgment with multiple review steps, the AI industry “pivoted” to mass ingestion of scraped data from the whole internet.
But adding more unreliable data to an unreliable dataset doesn’t improve its reliability. GIGO is the iron law of computing, and you can’t repeal it by shoveling more garbage into the top of the training funnel:
https://memex.craphound.com/2018/05/29/garbage-in-garbage-out-machine-learning-has-not-repealed-the-iron-law-of-computer-science/
When it comes to “AI” that’s used for decision support — that is, when an algorithm tells humans what to do and they do it — then you get something worse than Garbage In, Garbage Out — you get Garbage In, Garbage Out, Garbage Back In Again. That’s when the AI spits out something wrong, and then another AI sucks up that wrong conclusion and uses it to generate more conclusions.
To see this in action, consider the deeply flawed predictive policing systems that cities around the world rely on. These systems suck up crime data from the cops, then predict where crime is going to be, and send cops to those “hotspots” to do things like throw Black kids up against a wall and make them turn out their pockets, or pull over drivers and search their cars after pretending to have smelled cannabis.
The problem here is that “crime the police detected” isn’t the same as “crime.” You only find crime where you look for it. For example, there are far more incidents of domestic abuse reported in apartment buildings than in fully detached homes. That’s not because apartment dwellers are more likely to be wife-beaters: it’s because domestic abuse is most often reported by a neighbor who hears it through the walls.
So if your cops practice racially biased policing (I know, this is hard to imagine, but stay with me /s), then the crime they detect will already be a function of bias. If you only ever throw Black kids up against a wall and turn out their pockets, then every knife and dime-bag you find in someone’s pockets will come from some Black kid the cops decided to harass.
That’s life without AI. But now let’s throw in predictive policing: feed your “knives found in pockets” data to an algorithm and ask it to predict where there are more knives in pockets, and it will send you back to that Black neighborhood and tell you do throw even more Black kids up against a wall and search their pockets. The more you do this, the more knives you’ll find, and the more you’ll go back and do it again.
This is what Patrick Ball from the Human Rights Data Analysis Group calls “empiricism washing”: take a biased procedure and feed it to an algorithm, and then you get to go and do more biased procedures, and whenever anyone accuses you of bias, you can insist that you’re just following an empirical conclusion of a neutral algorithm, because “math can’t be racist.”
HRDAG has done excellent work on this, finding a natural experiment that makes the problem of GIGOGBI crystal clear. The National Survey On Drug Use and Health produces the gold standard snapshot of drug use in America. Kristian Lum and William Isaac took Oakland’s drug arrest data from 2010 and asked Predpol, a leading predictive policing product, to predict where Oakland’s 2011 drug use would take place.
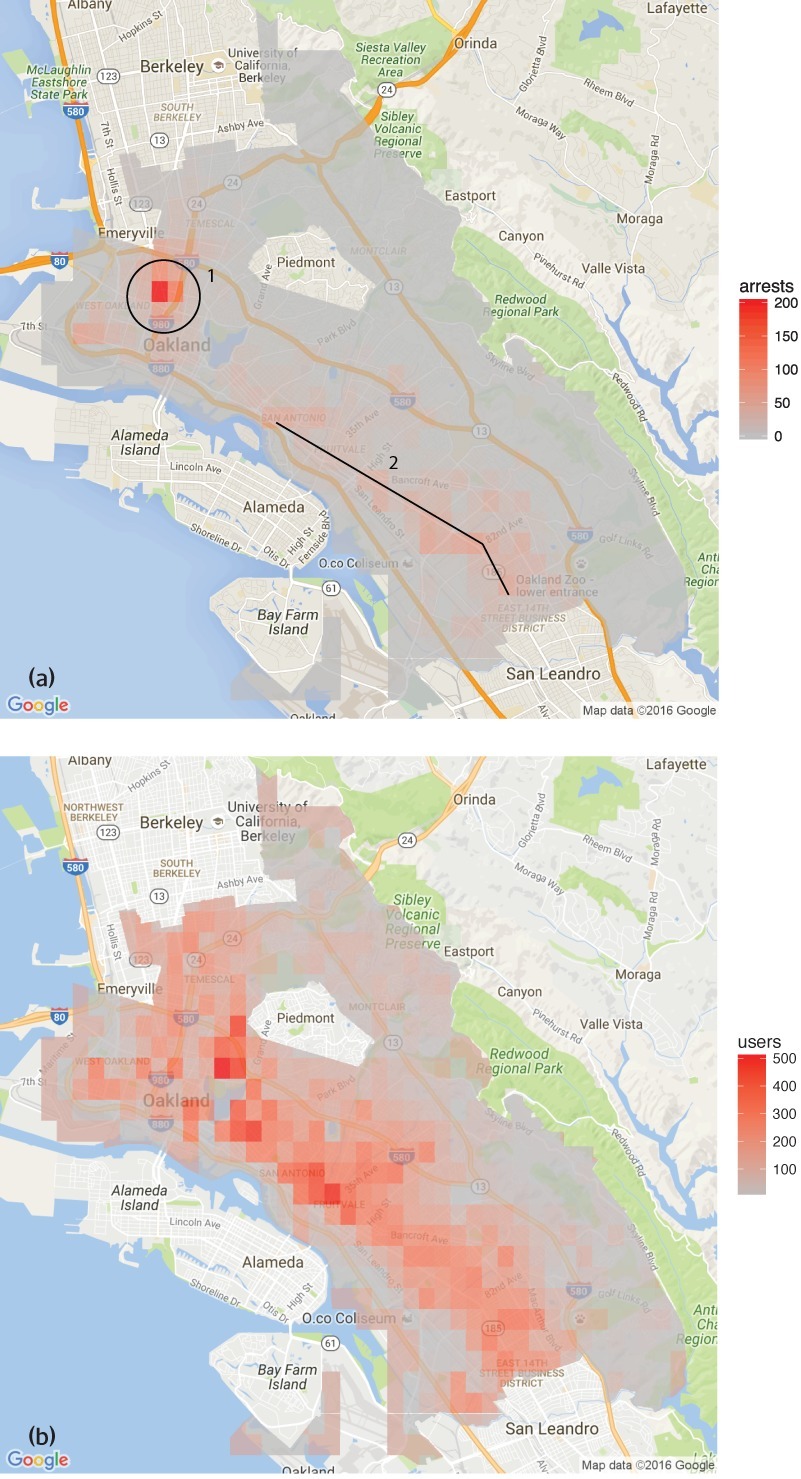
[Image ID: (a) Number of drug arrests made by Oakland police department, 2010. (1) West Oakland, (2) International Boulevard. (b) Estimated number of drug users, based on 2011 National Survey on Drug Use and Health]
Then, they compared those predictions to the outcomes of the 2011 survey, which shows where actual drug use took place. The two maps couldn’t be more different:
https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1740-9713.2016.00960.x
Predpol told cops to go and look for drug use in a predominantly Black, working class neighborhood. Meanwhile the NSDUH survey showed the actual drug use took place all over Oakland, with a higher concentration in the Berkeley-neighboring student neighborhood.
What’s even more vivid is what happens when you simulate running Predpol on the new arrest data that would be generated by cops following its recommendations. If the cops went to that Black neighborhood and found more drugs there and told Predpol about it, the recommendation gets stronger and more confident.
In other words, GIGOGBI is a system for concentrating bias. Even trace amounts of bias in the original training data get refined and magnified when they are output though a decision support system that directs humans to go an act on that output. Algorithms are to bias what centrifuges are to radioactive ore: a way to turn minute amounts of bias into pluripotent, indestructible toxic waste.
There’s a great name for an AI that’s trained on an AI’s output, courtesy of Jathan Sadowski: “Habsburg AI.”
And that brings me back to the Dictator’s Dilemma. If your citizens are self-censoring in order to avoid retaliation or algorithmic shadowbanning, then the AI you train on their posts in order to find out what they’re really thinking will steer you in the opposite direction, so you make bad policies that make people angrier and destabilize things more.
Or at least, that was Farrell(et al)’s theory. And for many years, that’s where the debate over AI and dictatorship has stalled: theory vs theory. But now, there’s some empirical data on this, thanks to the “The Digital Dictator’s Dilemma,” a new paper from UCSD PhD candidate Eddie Yang:
https://www.eddieyang.net/research/DDD.pdf
Yang figured out a way to test these dueling hypotheses. He got 10 million Chinese social media posts from the start of the pandemic, before companies like Weibo were required to censor certain pandemic-related posts as politically sensitive. Yang treats these posts as a robust snapshot of public opinion: because there was no censorship of pandemic-related chatter, Chinese users were free to post anything they wanted without having to self-censor for fear of retaliation or deletion.
Next, Yang acquired the censorship model used by a real Chinese social media company to decide which posts should be blocked. Using this, he was able to determine which of the posts in the original set would be censored today in China.
That means that Yang knows that the “real” sentiment in the Chinese social media snapshot is, and what Chinese authorities would believe it to be if Chinese users were self-censoring all the posts that would be flagged by censorware today.
From here, Yang was able to play with the knobs, and determine how “preference-falsification” (when users lie about their feelings) and self-censorship would give a dictatorship a misleading view of public sentiment. What he finds is that the more repressive a regime is — the more people are incentivized to falsify or censor their views — the worse the system gets at uncovering the true public mood.
What’s more, adding additional (bad) data to the system doesn’t fix this “missing data” problem. GIGO remains an iron law of computing in this context, too.
But it gets better (or worse, I guess): Yang models a “crisis” scenario in which users stop self-censoring and start articulating their true views (because they’ve run out of fucks to give). This is the most dangerous moment for a dictator, and depending on the dictatorship handles it, they either get another decade or rule, or they wake up with guillotines on their lawns.
But “crisis” is where AI performs the worst. Trained on the “status quo” data where users are continuously self-censoring and preference-falsifying, AI has no clue how to handle the unvarnished truth. Both its recommendations about what to censor and its summaries of public sentiment are the least accurate when crisis erupts.
But here’s an interesting wrinkle: Yang scraped a bunch of Chinese users’ posts from Twitter — which the Chinese government doesn’t get to censor (yet) or spy on (yet) — and fed them to the model. He hypothesized that when Chinese users post to American social media, they don’t self-censor or preference-falsify, so this data should help the model improve its accuracy.
He was right — the model got significantly better once it ingested data from Twitter than when it was working solely from Weibo posts. And Yang notes that dictatorships all over the world are widely understood to be scraping western/northern social media.
But even though Twitter data improved the model’s accuracy, it was still wildly inaccurate, compared to the same model trained on a full set of un-self-censored, un-falsified data. GIGO is not an option, it’s the law (of computing).
Writing about the study on Crooked Timber, Farrell notes that as the world fills up with “garbage and noise” (he invokes Philip K Dick’s delighted coinage “gubbish”), “approximately correct knowledge becomes the scarce and valuable resource.”
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/07/25/51610/
This “probably approximately correct knowledge” comes from humans, not LLMs or AI, and so “the social applications of machine learning in non-authoritarian societies are just as parasitic on these forms of human knowledge production as authoritarian governments.”

The Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers’ Workshop summer fundraiser is almost over! I am an alum, instructor and volunteer board member for this nonprofit workshop whose alums include Octavia Butler, Kim Stanley Robinson, Bruce Sterling, Nalo Hopkinson, Kameron Hurley, Nnedi Okorafor, Lucius Shepard, and Ted Chiang! Your donations will help us subsidize tuition for students, making Clarion — and sf/f — more accessible for all kinds of writers.

Libro.fm is the indie-bookstore-friendly, DRM-free audiobook alternative to Audible, the Amazon-owned monopolist that locks every book you buy to Amazon forever. When you buy a book on Libro, they share some of the purchase price with a local indie bookstore of your choosing (Libro is the best partner I have in selling my own DRM-free audiobooks!). As of today, Libro is even better, because it’s available in five new territories and currencies: Canada, the UK, the EU, Australia and New Zealand!

[Image ID: An altered image of the Nuremberg rally, with ranked lines of soldiers facing a towering figure in a many-ribboned soldier's coat. He wears a high-peaked cap with a microchip in place of insignia. His head has been replaced with the menacing red eye of HAL9000 from Stanley Kubrick's '2001: A Space Odyssey.' The sky behind him is filled with a 'code waterfall' from 'The Matrix.']

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
—
Raimond Spekking (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Acer_Extensa_5220_-_Columbia_MB_06236-1N_-_Intel_Celeron_M_530_-_SLA2G_-_in_Socket_479-5029.jpg
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
—
Russian Airborne Troops (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vladislav_Achalov_at_the_Airborne_Troops_Day_in_Moscow_%E2%80%93_August_2,_2008.jpg
“Soldiers of Russia” Cultural Center (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Col._Leonid_Khabarov_in_an_everyday_service_uniform.JPG
CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#habsburg ai#self censorship#henry farrell#digital dictatorships#machine learning#dictator's dilemma#eddie yang#preference falsification#political science#training bias#scholarship#spirals of delusion#algorithmic bias#ml#Fully automated data driven authoritarianism#authoritarianism#gigo#garbage in garbage out garbage back in#gigogbi#yuval noah harari#gubbish#pkd#philip k dick#phildickian
833 notes
·
View notes
Text
What does ChatGPT stand for? GPT stands for Generative Pre-Trained Transformer. This means that it learns what to say by capturing information from the internet. It then uses all of this text to "generate" responses to questions or commands that someone might ask.
7 things you NEED to know about ChatGPT (and the many different things the internet will tell you.) (BBC)
#quote#ChatGPT#GPT#Generative Pre-Trained Transformer#AI#artificial intelligence#internet#technology#computers#digital#LLM#large language model#machine learning#information
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
not to be controversial, but i believe that it should be an opt-in thing to allow websites and platforms to use your content to train AI, not an opt-out thing.
i’m so tired of seeing posts explaining how platforms are “secretly using you to train AI” and “here’s how to turn it off.” why isn’t there a bigger pushback or uproar over this apart from just turning it off? why are we just letting websites and platforms constantly do this?
#ai training#ai#ai generated#ai artwork#ai content#artificial intelligence#machine learning#personal#ok to rb
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Human Brain vs. Supercomputers: The Ultimate Comparison
Are Supercomputers Smarter Than the Human Brain?
This article delves into the intricacies of this comparison, examining the capabilities, strengths, and limitations of both the human brain and supercomputers.

#human brain#science#nature#health and wellness#skill#career#health#supercomputer#artificial intelligence#ai#cognitive abilities#human mind#machine learning#neural network#consciousness#creativity#problem solving#pattern recognition#learning techniques#efficiency#mindset#mind control#mind body connection#brain power#brain training#brain health#brainhealth#brainpower
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Ways Technology is Boosting Workplace Productivity
In the contemporary professional landscape, productivity is the currency of success. Businesses and individuals alike are constantly seeking innovative strategies to optimize output, streamline workflows, and maximize efficiency. At the forefront of this revolution is technology, which has fundamentally transformed how we work, collaborate, and manage our time. Far from being a mere convenience,…
#AI in Workplace#artificial intelligence#automation#business efficiency#Business Growth#Business Intelligence#Business Management#Business Solutions#Business Technology#cloud computing#Collaboration Tools#cybersecurity#data analytics#Data-Driven Decisions#Digital Collaboration#Digital Document Management#digital tools#digital transformation#Digital Workplace#Efficiency Tools#Employee Efficiency#Employee Engagement Technology#Employee Training Platforms#Enterprise Software#future of work#Hybrid Work#machine learning#Mobile Productivity#Modern Workplace#Office Technology
1 note
·
View note
Text
lsdunes: Lost Souls, the music video for Old Wounds will be yours this Friday the 29th at 9am PT / 12pm ET 🦂
🎥: @.iammethisisi
(L.S. Dunes Instagram | September 25, 2023)
#ls dunes#l.s. dunes#m: anthony green#m: frank iero#m: tim payne#m: travis stever#m: tucker rule#lsd: 2023#in: sept/23#t: video#s: old wounds#sm: instagram#from: official instagram#archive[ane]#i'm only posting this 'cause it's my duty as an archivist but God... how disappointing is this?#even after the wga and sag-aftra strikes that were (also) due to studios using ai instead of employing ACTUAL artists????#wish people could do a little research to understand the implications of using artificial intelligence and machine learning#without an ounce of critical thinking#ai is not supposed to be recklessly used like that and i'm saying this as a compsci student/researcher#'but the art is cool!' yeah bc it's created by a model trained with a bunch of real artworks from real artists. without their permission#most AI platforms STEAL from them#sorry i'm just really upset. also please that 'art' is ugly as hell#this fandom is so full of MANY brilliant artists and they chose AI over them???? damn that's just disappointing#i love them wholeheartedly but that was really disappointing#sorry for tag rant
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Im kinda thrown off by that "twt is gonna use your art to train ai" post going around because nowhere in those screenshots does it imply that at all. Straight up fearmongering shit.
#the “we can use your shit however” is still bad. but the machine learning section was pretty clearly aboug algorythm and ad shit.#literally why would twitter be training a ai art program? through twitter?
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI Deep Learning Online Course: Mastering Advanced Techniques
Embarking on an AI deep learning online course is a transformative journey for students and professionals alike. Deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence (AI), focuses on training algorithms to learn from data and make intelligent decisions, mimicking the human brain's neural networks. This guide explores the importance of deep learning education, key concepts covered, choosing the right course, popular platforms, and career opportunities in this dynamic field.
1. Introduction to AI Deep Learning Online Course
Diving into the realm of deep learning through an online course provides a structured pathway for individuals keen on mastering advanced AI techniques. These courses offer comprehensive insights into neural networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and generative adversarial networks (GANs), among other cutting-edge technologies shaping AI innovation.
2. Importance of Learning AI Deep Learning
Deep learning plays a pivotal role in modern AI applications, from image and speech recognition to autonomous vehicles and healthcare diagnostics. Understanding and applying deep learning principles are essential for driving innovation and solving complex problems across various industries, making specialized education in this field highly valuable.
3. Key Concepts Covered in AI Deep Learning Courses
AI deep learning courses typically cover fundamental and advanced concepts:
Neural Networks: Building blocks of deep learning models that mimic the human brain's structure.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Specialized for image and video analysis, enabling tasks like object detection and image classification.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Effective for sequential data processing, used in natural language processing and time series prediction.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Used for generating new data instances, enhancing images, and creating realistic simulations.
4. Choosing the Right AI Deep Learning Course
Selecting the right AI deep learning course involves considering several factors:
Course Structure: Evaluate the course outline, modules, and learning objectives to ensure they align with your learning goals.
Instructor Expertise: Choose courses led by experienced professionals with practical industry experience in deep learning.
Platform Credibility: Opt for reputable online learning platforms like Coursera, edX, Udacity, and specialized AI academies known for their high-quality courses.
Hands-On Projects: Look for courses that offer hands-on projects and practical exercises to reinforce theoretical concepts and enhance learning outcomes.
Student Reviews: Read reviews and testimonials from past learners to gauge the course's effectiveness and relevance.
5. Popular Platforms for AI Deep Learning Courses
Explore leading platforms offering AI deep learning courses:
Coursera: Offers courses from top universities and industry experts, including deep learning specializations.
edX: Provides courses in collaboration with prestigious institutions like MIT and Microsoft, focusing on AI and machine learning.
Udacity: Known for nanodegree programs that combine theoretical knowledge with hands-on projects mentored by industry professionals.
6. Course Curriculum and Learning Objectives
A typical AI deep learning course curriculum includes:
Introduction to Deep Learning: Basics of neural networks and deep learning frameworks.
Advanced Topics: CNNs, RNNs, GANs, and their applications in image recognition, natural language processing, and more.
Practical Applications: Hands-on projects to implement deep learning algorithms and analyze real-world datasets.
7. Hands-On Projects and Practical Exercises
Hands-on experience is crucial for mastering AI deep learning techniques:
Image Classification: Implementing CNNs to classify images and improve accuracy.
Natural Language Processing: Building RNN models for sentiment analysis and language generation.
GANs Projects: Creating realistic images or videos using generative adversarial networks.
8. Career Opportunities in AI Deep Learning
AI deep learning expertise opens doors to diverse career paths:
Data Scientist: Analyzing large datasets and developing predictive models using deep learning techniques.
Machine Learning Engineer: Designing and deploying machine learning systems for automated decision-making.
AI Researcher: Conducting groundbreaking research in neural networks and advancing AI technologies.
AI Specialist: Consulting on AI projects and implementing solutions across industries.
9. Student Success Stories and Testimonials
Real-life examples of students benefiting from AI deep learning courses:
Career Advancement: Securing roles at leading tech companies and research institutions.
Skill Enhancement: Applying deep learning knowledge to solve complex problems and innovate in AI applications.
Networking Opportunities: Connecting with industry experts and peers through course communities and events.
10. Conclusion
Enrolling in an AI deep learning online course equips you with the knowledge and skills to thrive in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence. By choosing a reputable course, engaging in hands-on projects, and leveraging practical experience, you can accelerate your career growth and contribute to cutting-edge AI innovations.
Closing Thoughts
Investing in AI deep learning education is an investment in your future, empowering you to tackle global challenges and drive technological advancements. Start your journey today by exploring AI deep learning courses that align with your goals and aspirations, and embark on a fulfilling career in artificial intelligence.
#AI Mastery course online#Learn AI for students#Online artificial intelligence course#AI training for beginners online#Advanced AI course for students#Best AI courses online#AI certification for students#Artificial intelligence classes online#AI courses for college students#AI and machine learning training#Online AI development course#AI programming course online#AI deep learning online course#Top AI courses for students#AI specialist training online#Best online course for AI mastery#Artificial intelligence for beginners online#AI algorithms course online#Machine learning basics online#Online AI projects for students#Introduction to AI online course#AI ethics course online#Online AI tutorials for students#AI and data science online course#Online AI bootcamp for students#Best AI training program online#AI career path online#AI masterclass online#Online AI education for students#AI technology course online
0 notes
Text
Derin, with all due respect, I feel like you also haven't had the best samples of what current LLMs are like. They do sound a LOT more coherent now even compared to just two years ago. My exposure to Grok is also just the stuff that gets screenshotted or the rare Twitter thread I muddle through, and what I've seen are absolutely nothing groundbreaking compared with what I've seen from other LLMs these days.
idk if elon will kill his new chatbot grok when he finds out its woke, but he'll definitely kill it once he discovers it's funnier than him

#turk LLMs are real#but im pretty sure grok isnt one#its just a reasonably mid LLM#this is not a blanket endorsement of LLM or AI or machine learning training methods
81K notes
·
View notes
Text
Remote Data Science Jobs Are Booming: Here’s How to Prepare
In the ever-evolving digital economy, data has become the backbone of decision-making across every industry. From e-commerce giants and fintech startups to healthcare and manufacturing sectors, organizations are increasingly relying on data science to unlock hidden patterns, predict outcomes, and guide strategic planning. What’s truly revolutionary, however, is how this once location-dependent…

View On WordPress
#ai#best data science certifications#cloud computing#cloud tools for data science#data analysis#data science#data science bootcamp#data science career#data science course#data science freelancing#data science from home#data science hiring trends#data science portfolio tips#data science remote work#data science skills#Data Science Training Course In Kolkata#freelancing#how to become a data scientist#job readiness#machine learning#machine learning online course#online data science training#Online Learning#python#python for data science#remote data jobs#remote data science jobs#remote tech jobs 2025#remote work future#SQL
0 notes
Text

Join Best Machine Learning Course in India with online training & certification. Expert Mentors, ML training, Online Classes & live projects. Kickstart your career in Machine Learning with our beginner-friendly ML program. Learn from industry experts, work on real-time projects, and get certified to stand out in today’s AI-driven world. Course Highlights: 📘 Beginner to Advanced ML Concepts 👨🏫 Mentorship by Industry Experts 💻 100% Online Classes with Flexible Timings 🧠 Hands-on Practice with Live Projects 📄 Globally Recognized Certification 💬 Interactive Sessions & Doubt Solving 🚀 Career Guidance & Placement Support Stay ahead of the curve—enroll in an AI & Machine Learning course today and transform your professional journey. Visit: https://scilindia.org/courses/Machine-learning-course
#Beginner to Advanced ML Concepts#Online Classes#Machine Learning Course#online training & certification#ML training#beginner-friendly ML program#AI & Machine Learning course
0 notes
Text
The whole AI apocalypse is so funny to me because like.
There were engineers who did a lot of thinking to get ore out of the ground, and to press that ore into computer chips so unfathomably compact that Luciver "besides thou, not bellow" Morningstar thought it hubris; and to write programs that make those chips do simple math; AND to study the art of random shit happening to find out how to make random things happen less randomly; AND to write a computer program that does entirely random simple math, compares the output with what you said you wanted and remembers whether it was or wasn't just to can do less random stuff and more what it thinks you want.
All so every cityboy (affectionate) can do things without doing... y'know the thinking.
The irony is so graspable, I could use it to cobble not one, but two ML engineers into a pair of shoes.
"edit images with AI-- search with AI-- control your life with AI--"

#And you know the most ironic part? Not even the computer does the thinking now. No one does!#training an AI is like rolling a d20 for hit but you get a +1 for every time you defeat a training puppet#but you have an inherent -3 against anything that moves and at +2 the bonus resets#cityboy (affectionate. you cuties ;* )#ai#machine learning#automation
60K notes
·
View notes
Text
I love to sign up for courses and certifications and then forget to do them
#it’s free so it’s fine but I’m two modules behind on my edX intro to AI & machine learning in healthcare course#I hate AI lowkey but I fear it’s not going away anytime soon so. AMSA offered this course I wrote an application for the free version#and I got it and then I forgot. oops sorry guys#it’s from edX and Mass General Brigham and I could pay $230 to also get an official certification with it but I don’t want that 🙅♂️#not paying for this 🙅♂️🤷♂️#but now I’m just trying to cram to catch up on this course my bad guys#I’ve got two other courses pulled up that I’m in the middle of rn too#getting a dementia doula certificate from NANPE and working on finishing the volunteer training for hospice volunteer position#also trying to get my baby brother a job at P.F. Chang’s with me 😬#that’s all that’s my life 🙂↕️
0 notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Explained Simply
Introduction: Why You Hear About AI and ML Everywhere
From your phone predicting what you'll type next to self-driving cars on the road, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are reshaping the world around us. But what do these buzzwords actually mean? And why are businesses in every industry looking for professionals trained in these technologies?
This blog will simplify the concepts of AI and ML so anyone even without a tech background can understand their importance, how they work, and how you can get started through an Artificial Intelligence course online. Whether you're a student, a working professional, or someone looking to switch careers, this guide is your starting point.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI in Simple Terms
Artificial Intelligence is the simulation of human intelligence by machines. In other words, it’s when machines are built to "think" or act like humans. These machines can perform tasks such as reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, and understanding language.
Everyday Examples of AI
Smart Assistants like Siri or Alexa
Chatbots on websites
Face recognition for unlocking phones
Recommendation systems on YouTube or Netflix
Autonomous vehicles (self-driving cars)
These systems don’t have consciousness—but they can process information and respond intelligently thanks to AI algorithms.
What is Machine Learning?
ML in Simple Terms
Machine Learning is a branch of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of writing code to solve every problem, we train the system using examples so it can learn patterns and make decisions on its own.
A Real-World Example
Let’s say you want to train a computer to recognize cats in images. With Machine Learning, you feed it thousands of images labeled “cat” or “not cat.” Over time, it learns the features that typically appear in cat images—like fur, ears, or tail—and uses this to identify new images.
The Difference Between AI and ML
FeatureArtificial Intelligence (AI)Machine Learning (ML)DefinitionAI is the broader concept of machines being smartML is a subset of AI focused on learning from dataGoalSimulate human thinkingMake accurate predictions using dataExampleA robot that can navigate a roomA spam filter that learns to block junk emails
Types of Machine Learning
Supervised Learning
What it is: Training the system with labeled data.
Example: Classifying emails as spam or not spam.
Unsupervised Learning
What it is: No labels; the system tries to find hidden patterns.
Example: Customer segmentation for marketing.
Reinforcement Learning
What it is: The system learns through trial and error with rewards and punishments.
Example: Game-playing AI agents.
Key Concepts You’ll Learn in an AI Training Program
An AI training program will introduce you to essential concepts and practical tools that help build AI-powered systems. Some of the core modules typically include:
Python Programming for AI
Data Preprocessing Techniques
Model Building and Evaluation
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Computer Vision
How Does AI Work? A Simple Breakdown
Here’s a basic step-by-step look at how AI systems operate:
1. Input Collection
The system receives input like images, text, or audio.
2. Preprocessing
The input is cleaned and transformed into a suitable format (e.g., converting images to pixels).
3. Model Training
The system is trained using algorithms and historical data.
4. Prediction
Once trained, the model can make predictions or decisions based on new inputs.
5. Feedback Loop
The system receives feedback and improves over time.
Real-World Applications of AI and ML
1. Healthcare
AI is used to detect diseases like cancer in medical images and predict patient outcomes.
2. Finance
ML models detect fraud, assess loan eligibility, and automate trading.
3. Retail
AI recommends products based on shopping history and optimizes inventory.
4. Manufacturing
Smart sensors monitor machinery to predict maintenance needs.
5. Cybersecurity
AI helps identify unusual activities that may indicate cyber threats.
AI in Action: A Beginner-Friendly Demo (Pseudocode)
Here’s a simple pseudocode to understand how a Machine Learning model might predict whether a review is positive or negative.
python
# Step 1: Collect Data reviews = ["Great product", "Worst service", "Excellent quality", "Not worth it"] labels = [1, 0, 1, 0] # 1 = Positive, 0 = Negative # Step 2: Preprocess Text processed_reviews = preprocess_text(reviews) # Step 3: Train Model model = train_model(processed_reviews, labels) # Step 4: Predict New Input new_review = "Fantastic experience" prediction = model.predict(preprocess_text([new_review])) # Output: 1 (Positive)
Why Learn AI Now?
Industry Demand is Soaring
According to industry reports, AI jobs have increased by over 74% in the last 4 years.
Career Opportunities
Professionals skilled in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are in high demand in roles like:
AI Engineer
Data Scientist
Machine Learning Engineer
NLP Specialist
Robotics Engineer
High Salary Potential
According to global job data, AI professionals earn 20–40% higher than traditional IT roles.
Benefits of Taking an Artificial Intelligence Course Online
Learn at Your Pace: Study when and where you want.
Job-Ready Skills: Courses are designed to align with industry requirements.
Hands-On Learning: Use tools and datasets used by real-world AI engineers.
Certification: Gain an Artificial Intelligence certification online to showcase your expertise.
Project-Based Curriculum: Build actual models and applications that you can show employers.
What You’ll Gain from H2K Infosys AI Training Program
At H2K Infosys, we focus on making complex AI topics simple and practical. Our AI training program includes:
Instructor-led interactive classes
Real-world projects with datasets
Resume-building and mock interviews
Lifetime access to course materials
Industry-recognized certification
Whether you're a complete beginner or already working in tech, our Artificial Intelligence course online will help you bridge the gap from theory to application.
Common Myths About AI—Busted
MythRealityAI will take all jobsAI will transform jobs, not eliminate all. It will create new roles.You need a PhD to learn AINot true. Many successful professionals start with online courses.AI systems are 100% accurateAI makes predictions, not guarantees it improves with data.AI can think like humansAI processes data logically, but lacks emotions and true consciousness.
Simple Tools You’ll Use in AI Learning
Python: The most popular programming language for AI
Scikit-learn: For building ML models
TensorFlow/Keras: For deep learning and neural networks
Pandas & NumPy: For data manipulation
Jupyter Notebook: For writing and testing code interactively
Your Learning Path: Step-by-Step AI Guide
Start with Python Programming
Understand Data Handling (cleaning, transforming, visualizing)
Learn Supervised and Unsupervised ML Techniques
Move into Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Explore NLP and Computer Vision
Build Real-World Projects
Earn Your Artificial Intelligence Certification Online
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are not just buzzwords—they are career-launching tools you can start learning today. With expert guidance, hands-on projects, and industry-ready skills, you can transition into one of the most in-demand tech fields globally.
Enroll in H2K Infosys’ AI course today to gain hands-on learning and unlock exciting career opportunities.
#Artificial intelligence and machine learning#Artificial intelligence course for beginners#Artificial intelligence course online#Artificial intelligence certificate online#Artificial intelligence certification courses#AI certification online#Ai courses certification#intelligence courses online#Artificial intelligence training course#Artificial intelligence online training#devops training
0 notes
Photo
remember - it is literally impossible for the machine to be more morally correct than humans, because everything it spits out was once said by a human before. only another human can out-moral what humans have already said.
if anything, it does TOO good of a job at pointing out all our flaws, biases, stereotypes, and bigotry, because bigots yell loud and often.
if you give AI the prompt for a "normal" human, the human will be white, cis, male, and EVERYTHING ELSE that favors the privileged, because they have the largest online presence. we're allowing the machine to sit stagnant in heteronormativity, misogyny, racism, ableism, etc.
it's impossible for something trained on HUMAN data to ever outdo humans on anything; it is STAGNATING US


@hatr @fasterthanlime
#NEURAL TOXICITY#i know that's not a popular term for it BUT MACHINES CANNOT POSSIBLY STAY MORALLY PURE IF THEY ARE TRAINED ON HUMAN DATA RJEKFJELGJT#i hate ai#machine learning
102K notes
·
View notes