#Augmented Reality (AR) Integration
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
Next-Gen AR Development: Bringing Ideas to Life - Atcuality
Augmented reality is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s here, transforming industries and enhancing real-world applications. At Atcuality, we specialize in custom AR solutions designed to create interactive, engaging, and scalable experiences for businesses of all sizes. Our augmented reality development services cater to diverse industries, including retail, tourism, real estate, and automotive, helping brands deliver unforgettable user experiences. Whether you need AR-powered product visualization, training simulations, or interactive storytelling, our expert team ensures a seamless, high-quality solution tailored to your needs. Elevate your business with Atcuality’s cutting-edge AR technology and shape the future of digital interaction today!
#website development#ai applications#artificial intelligence#augmented and virtual reality market#web development#information technology#emailmarketing#augmented reality#web design#digital marketing#augmentative and alternative communication#augmented intelligence#virtual reality#ar vr technology#digital consulting#digital services#iotsolutions#iot#iot platform#iot applications#iot development services#technologynews#iot solutions#iot integration#automation#software company#software development#software engineering#software testing#cash collection application
0 notes
Text
The Transformative Power of AI Devices: Driving Toward an AI-First Future
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/the-transformative-power-of-ai-devices-driving-toward-an-ai-first-future/
The Transformative Power of AI Devices: Driving Toward an AI-First Future
AI-driven devices have evolved from novelty to necessity. AI assistants that manage tasks, cameras with real-time object detection, wearables tracking health and behavioral metrics, and similar devices are no longer futuristic concepts—they’re reshaping how companies operate across nearly every industry. But with this rapid advancement comes a critical question: How do organizations integrate AI in ways that maximize innovation without sacrificing security?
Businesses are increasingly split in their approach. Some adopt an AI-First mindset, prioritizing rapid adoption and innovation. Others lean toward an AI-Safe approach, in which risk management and security take precedence, sometimes at the expense of agility and progress. The challenge lies in finding the balance between these two stances—a balance that enables businesses to embrace the future responsibly.
The Immediate Impact of AI Devices
AI-powered devices have already revolutionized operations across industries, especially for organizations embracing an AI-First mindset. These companies are experiencing significant gains in efficiency, productivity, and autonomous decision-making capabilities.
For instance, AI-enhanced cameras are used from manufacturing to retail. In manufacturing, they monitor assembly lines and worker activities in real time, detecting issues early to prevent costly downtime. In retail, AI cameras track customer foot traffic and optimize store layouts based on behavior analysis, providing a smarter approach to inventory and product placement. This real-time, data-driven decision-making provides companies a significant competitive edge.
Wearables are transforming industries from healthcare to logistics. Smart devices monitor patient vital signs continuously, providing real-time data that alerts medical professionals to changes before they become critical issues. Wearables allow logistics managers to track employee movements and optimize task assignments for efficiency and safety, making these technologies essential for risk management and operational control.
Multimodal AI assistants like Google Gemini are reshaping project management and workflow automation. These tools don’t just handle repetitive tasks—they actively support decision-making by generating insights, identifying patterns, and forecasting potential outcomes. AI assistants can analyze project timelines, suggest resource reallocation, and notify teams of potential delays or risks. For leaders, this means quicker access to valuable information, allowing them to make faster and better-informed decisions.
In contrast, organizations that over-prioritize risk management under an AI-Safe framework often delay adoption and lose out on these operational advantages, risking stagnation in a market increasingly driven by AI. To stay competitive, businesses must adopt a balanced perspective, understanding that both risks and innovation can be managed contemporaneously.
Enhancing Operations and Managing Risk
AI’s transformative impact is particularly clear in high-stakes sectors like finance. AI-driven trading platforms and real-time analytics enable institutions to gain insights and respond to market changes at speeds previously unattainable. For example, trading algorithms can analyze market data in milliseconds, maximizing profit potential and allowing firms to adapt instantly to micro-shifts and emerging opportunities.
AI’s role in security is equally critical. AI-enabled cameras on trading floors and in banks can monitor physical activity, using behavior analysis to flag unusual actions that may indicate security threats, strengthening protection against both internal and external risks.
However, the push to innovate in sectors like finance and healthcare is tempered by strict regulations and the potentially life-altering consequences of even minor failures. In healthcare, for example, AI-powered diagnostic tools can lead to earlier disease detection and improved patient outcomes. But improper AI deployment can expose institutions to significant privacy risks, such as unauthorized access to sensitive patient data, with possible legal consequences. An effective AI-First approach in these fields demands rigorous security measures, from encrypting patient information to ensuring privacy law compliance.
A robust risk management framework is essential, encompassing secure development practices, regular vulnerability assessments, and continuous data monitoring. Such measures enable organizations to harness AI’s potential responsibly, balancing innovation with the strict standards of highly regulated industries.
Democratizing AI: Making Advanced Technology Accessible
One of the most exciting developments is the potential for AI devices to democratize AI capabilities. From wearables and augmented reality (AR) headsets to smart cameras, smaller businesses now have access to powerful tools previously reserved for industry giants, enabling them to compete more effectively.
For example, engineers and developers using AI-powered smart glasses can collaborate remotely, overlaying data and solving complex problems in real time. These glasses can also connect specialists to technicians in the field, enabling them to guide repairs or adjustments as if they were there in person. The result is faster issue resolution, reduced costs, and more efficient project completion.
However, with accessibility comes responsibility. As AI becomes more democratized, companies must ensure their workforce is well-prepared to use these devices responsibly. Investment in generative AI (GenAI) education is essential, equipping employees to understand both the opportunities and risks AI devices bring to the work environment. By educating employees on topics like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and cybersecurity best practices, companies can build a workforce capable of using AI responsibly and effectively. This democratization of AI knowledge mitigates risk and positions employees to contribute proactively to their organizations’ AI strategies.
The AI-First Future: Balancing Innovation with Responsible Risk Management
As AI becomes increasingly ubiquitous in business operations, the debate between AI-First and AI-Safe approaches will only intensify. The companies that thrive will be those that embrace an AI-First approach without sacrificing safety. A true AI-First strategy doesn’t ignore security—it contextualizes it, applying risk management where it’s most needed without stifling growth.
For organizations in pursuit of a sustainable AI-powered future, the path forward includes several essential steps:
Develop a Comprehensive Risk Management Strategy: Companies must ensure their security protocols are robust and adaptable to the fast-evolving AI landscape, particularly in regulated industries. Regularly updating cybersecurity measures and conducting AI-specific risk assessments will help mitigate potential threats.
Prioritize Workforce Training: GenAI education must be a cornerstone of AI integration. Knowledgeable employees are essential to safely implementing and managing AI systems. Investing in their training equips them to handle AI tools responsibly.
Adopt an Agile Mindset: Organizations must be open to adjusting their strategies as technology and regulatory landscapes evolve. This adaptability will enable businesses to capitalize on opportunities and prepare to address new security challenges as they appear.
Monitor and Evaluate AI Performance: Regularly reviewing AI systems’ performance and effect on operations will provide insights into their effectiveness. Monitoring can reveal areas for improvement and inform strategies for remaining competitive while managing risks.
Ultimately, success in an AI-driven future will depend on how well organizations prepare their teams to leverage these technologies responsibly. The choice is clear: embrace an AI-First mindset that balances transformative power with responsible risk management or risk being left behind by competitors and the market as a whole.
The future belongs to those who can integrate AI thoughtfully and effectively, making innovation and security equally foundational to their strategy. By embracing an approach that combines forward-thinking with responsible management, companies position themselves to lead in an AI-powered world.
#Accessibility#adoption#agile#ai#AI integration#AI systems#ai tools#AI-powered#alerts#Algorithms#Analysis#Analytics#approach#ar#augmented reality#automation#autonomous#banks#Behavior#Bias#Business#CalypsoAI#Cameras#challenge#collaborate#Companies#compliance#comprehensive#continuous#Critical Issues
0 notes
Text
What Are the Latest Breakthroughs in Wearable Tech?
In 2024, the world of wearable technology is evolving faster than ever. With advancements spanning health, fitness, productivity, and even entertainment, wearable tech has become an integral part of daily life. But what are the latest breakthroughs in wearable tech, and how are they shaping the future? From AI-driven health monitors to augmented reality (AR) devices, new innovations are pushing…
#AI#AI-driven#air quality#Apple Watch#AR Glasses#AR integration#augmented reality#biofeedback#biometric authentication#biometric payments#body temperature#brain sensors#contactless payments#digital health#e-textiles#ECG#emerging tech#environmental sensors#fitness tracking#future tech#glucose monitoring#Google Glass#health monitoring#HoloLens#innovation#IoT#medical wearables#Mental Health#mindfulness tech#mixed reality
0 notes
Text
Neue Online-Plattformen bieten spezialisierte KI-Weiterbildungen für das Gesundheitswesen an
Die Digitalisierung des Gesundheitswesens schreitet unaufhaltsam voran, und Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) spielt dabei eine Schlüsselrolle. Um den wachsenden Anforderungen an Fachkräfte im Gesundheitswesen gerecht zu werden, entstehen immer mehr spezialisierte Online-Plattformen, die gezielte Weiterbildungsangebote im Bereich KI bereitstellen. Diese innovativen Lernformate bieten den Mitarbeitenden…
#Algorithmen#Augmented Reality#Augmented Reality (AR)#CAD#Digitalisierung#EdTech#Gesundheitswesen#Integration#Intelligenz#KI#Künstliche Intelligenz#Lernplattformen#Medizin#Medtech#Online-Kurse#SEM#Verantwortung#Virtual Reality (VR)#Webinare
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Potential of Augmented Reality in Education
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR VR) Software
Explore the world of Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR VR) software, its evolution, applications, benefits, and future trends in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, offering immersive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds seamlessly. In this article, we delve into the world of AR VR software, exploring its evolution, types, features, industries, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Evolution of AR VR Software
AR and VR technologies have come a long way since their inception. From early experiments to sophisticated applications, the evolution of AR VR software has been marked by significant technological advancements. Innovations in hardware and software have propelled AR VR from niche domains to mainstream adoption across various industries.
Types of AR VR Software
AR VR software encompasses a diverse range of applications tailored to different needs and industries. Consumer-oriented AR VR apps cater to entertainment, gaming, and social experiences, while enterprise solutions focus on training, simulation, and visualization tools for businesses.
Key Features and Functions
At the core of AR VR software are its immersive experiences and interactive capabilities. Users can explore virtual environments, manipulate objects, and engage with digital content in real-time, blurring the lines between the physical and virtual worlds.
Industries Utilizing AR VR Software
AR VR technology finds applications in a wide array of industries, including gaming, healthcare, education, and architecture. From immersive gaming experiences to surgical simulations, AR VR software is transforming how we learn, work, and interact with information.
Benefits of AR VR Software
The adoption of AR VR software brings forth a multitude of benefits. In education, students can engage in immersive learning experiences, while businesses leverage VR for training simulations and product visualization. Enhanced customer engagement and experiential marketing further amplify the impact of AR VR technology.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, AR VR software faces several challenges and limitations. High hardware requirements, user comfort issues, and content quality concerns pose barriers to widespread adoption. Addressing these challenges is crucial for unlocking the full potential of AR VR technology.
Future Trends in AR VR Software
Looking ahead, the future of AR VR software is promising. Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable new applications and experiences. Advancements in hardware, such as lightweight headsets and haptic feedback devices, will further enhance the immersive capabilities of AR VR technology.
Conclusion
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR VR) software represents a paradigm shift in how we interact with digital content and the world around us. As technology continues to evolve, AR VR software will play an increasingly integral role in various industries, shaping the way we learn, work, and communicate.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between AR and VR?
2. How does AR VR technology enhance training simulations?
3. Which industries benefit the most from AR VR software?
4. What are the primary challenges associated with AR VR adoption?
5. What advancements can we expect in AR VR hardware?
#Augmented Reality#Virtual Reality#AR VR technology#Immersive experiences#Training simulations#Gaming industry#Healthcare applications#Educational technology#Enterprise solutions#AI integration
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
The Future of Office Desks: Smart and Connected Workstations
The traditional office desk is transforming, ushering in the era of intelligent and connected workstations. As technological advancements continue to reshape how we work, office desks are becoming more than just static furniture. In this article, we will explore the future of office desks, delving into the innovative features and technologies that make workspaces smarter, more efficient, and…

View On WordPress
#Augmented Reality (AR) Integration#Biometric Security and Personalization#Embedded Touch screen Displays#Health Monitoring and Well-being Features#Internet of Things (IoT) Integration#Wireless Charging Capabilities
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unveiling the Power of 3D Visualization: Revolutionizing Engineering Applications
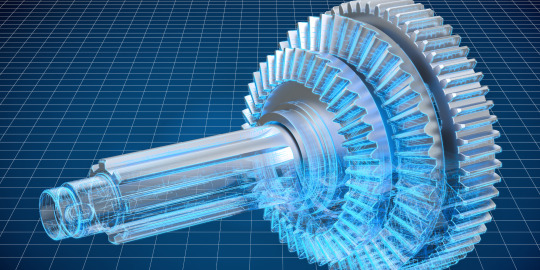
In the world of engineering, complex concepts and intricate designs often require effective means of communication to convey ideas, identify potential issues, and foster innovation. 3D visualization has emerged as a powerful tool that not only aids in comprehending intricate engineering concepts but also fuels creativity and enhances collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. This blog dives deep into the realm of 3D visualization for engineering applications, exploring its benefits, applications, and the technologies driving its evolution.
The Power of 3D Visualization
1. Enhanced Understanding: Traditional 2D drawings and diagrams can sometimes fall short in capturing the full complexity of engineering designs. 3D visualization empowers engineers, architects, and designers to create realistic and immersive representations of their ideas. This level of detail allows stakeholders to grasp concepts more easily and make informed decisions.
2. Identification of Design Flaws: One of the primary advantages of 3D visualization is its ability to identify potential design flaws before physical prototyping begins. Engineers can simulate real-world conditions, test stress points, and analyze the behavior of components in various scenarios. This process saves both time and resources that would have been wasted on rectifying issues post-construction.
3. Efficient Communication: When working on multidisciplinary projects, effective communication is essential. 3D visualization simplifies the sharing of ideas by presenting a clear visual representation of the design. This reduces the chances of misinterpretation and encourages productive discussions among team members from diverse backgrounds.
4. Innovation and Creativity: 3D visualization fosters creativity by enabling engineers to experiment with different design variations quickly. This flexibility encourages out-of-the-box thinking and exploration of unconventional ideas, leading to innovative solutions that might not have been considered otherwise.
5. Client Engagement: For projects involving clients or stakeholders who might not have technical expertise, 3D visualization serves as a bridge between complex engineering concepts and layman understanding. Clients can visualize the final product, making it easier to align their expectations with the project's goals.
Applications of 3D Visualization in Engineering
1. Architectural Visualization: In architectural engineering, 3D visualization brings blueprints to life, allowing architects to present realistic walkthroughs of structures before construction. This helps clients visualize the final appearance and make informed decisions about design elements.
2. Product Design and Prototyping: Engineers can use 3D visualization to create virtual prototypes of products, enabling them to analyze the functionality, ergonomics, and aesthetics. This process accelerates the design iteration phase and reduces the number of physical prototypes required.
3. Mechanical Engineering: For mechanical systems, 3D visualization aids in simulating motion, stress analysis, and assembly processes. Engineers can identify interferences, optimize part arrangements, and predict system behavior under different conditions.
4. Civil Engineering and Infrastructure Projects: From bridges to roadways, 3D visualization facilitates the planning and execution of large-scale infrastructure projects. Engineers can simulate traffic flow, assess environmental impacts, and optimize structural design for safety and efficiency.
5. Aerospace and Automotive Engineering: In these industries, intricate designs and high-performance requirements demand rigorous testing. 3D visualization allows engineers to simulate aerodynamics, structural integrity, and other critical factors before manufacturing.
Technologies Driving 3D Visualization
1. Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software forms the foundation of 3D visualization. It enables engineers to create detailed digital models of components and systems. Modern CAD tools offer parametric design, enabling quick modifications and iterative design processes.
2. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies enhance the immersive experience of 3D visualization. VR headsets enable users to step into a digital environment, while AR overlays digital content onto the real world, making it ideal for on-site inspections and maintenance tasks.
3. Simulation Software: Simulation tools allow engineers to analyze how a design will behave under various conditions. Finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations help predict stress, heat transfer, and fluid flow, enabling design optimization.
4. Rendering Engines: Rendering engines create photorealistic images from 3D models, enhancing visualization quality. These engines simulate lighting, materials, and textures, providing a lifelike representation of the design.
Future Trends and Challenges
As technology evolves, so will the field of 3D visualization for engineering applications. Here are some anticipated trends and challenges:
1. Real-time Collaboration: With the rise of cloud-based tools, engineers worldwide can collaborate on 3D models in real time. This facilitates global teamwork and accelerates project timelines.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI could enhance 3D visualization by automating design tasks, predicting failure points, and generating design alternatives based on predefined criteria.
3. Data Integration: Integrating real-time data from sensors and IoT devices into 3D models will enable engineers to monitor performance, identify anomalies, and implement preventive maintenance strategies.
4. Ethical Considerations: As 3D visualization tools become more sophisticated, ethical concerns might arise regarding the potential misuse of manipulated visualizations to deceive stakeholders or obscure design flaws.
In conclusion, 3D visualization is transforming the engineering landscape by enhancing understanding, fostering collaboration, and driving innovation. From architectural marvels to cutting-edge technological advancements, 3D visualization empowers engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible. As technology continues to advance, the future of engineering will undoubtedly be shaped by the dynamic capabilities of 3D visualization.
#3D Visualization#Engineering Visualization#CAD Software#Virtual Reality (VR)#Augmented Reality (AR)#Design Innovation#Visualization Tools#Product Design#Architectural Visualization#Mechanical Engineering#Civil Engineering#Aerospace Engineering#Automotive Engineering#Data Integration#Real-time Visualization#Engineering Trends#Visualization Technologies#Design Optimization
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top 7 Trends in Salesforce to Watch in 2023
Salesforce has been a trailblazer in the world of customer relationship management (CRM) software for years, helping businesses connect with customers, streamline processes, and drive growth. As we step into 2023, the platform continues to evolve, introducing new features and capabilities to meet the ever-changing demands of businesses and consumers alike. In this blog, we'll explore the top seven trends in Salesforce that are shaping the CRM landscape in 2023 and beyond.
AI-Driven Personalization:
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way businesses engage with their customers, and Salesforce is no exception. In 2023, expect to see AI-driven personalization take center stage, allowing companies to tailor customer interactions based on their preferences, behavior, and historical data. This will not only enhance customer satisfaction but also boost conversion rates and drive customer loyalty.
Integration of IoT and Salesforce:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping various industries, and Salesforce is embracing this trend by integrating IoT data into its CRM platform. This integration will enable businesses to gather real-time insights from connected devices, optimize operations, and provide proactive customer support. Expect to see IoT-enabled Salesforce solutions gaining traction across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail.
Blockchain for Secure Data Management:
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns for businesses and consumers alike. In 2023, Salesforce is likely to incorporate blockchain technology to enhance data integrity and security. Blockchain can provide a tamper-proof, decentralized data storage mechanism, ensuring sensitive customer information remains safe from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Hyper-Personalization with Customer Data Platforms (CDPs):
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are becoming increasingly popular as they consolidate customer data from various sources into a unified profile. Salesforce is expected to leverage CDPs to achieve hyper-personalization in 2023. By understanding customer behavior across channels, businesses can deliver highly targeted and relevant marketing campaigns, fostering deeper customer connections.
Low-Code/No-Code Development:
In 2023, we will witness an acceleration in low-code/no-code development on the Salesforce platform. These user-friendly tools enable businesses to build custom applications and automate processes without extensive coding knowledge. This democratization of development will empower organizations to innovate and respond quickly to changing market demands.
Extended Reality (XR) for Enhanced Customer Experiences:
Extended Reality (XR), which includes Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), is gaining traction in the CRM space. Salesforce is likely to integrate XR capabilities to offer unique and immersive customer experiences. From virtual product demonstrations to AR-powered customer support, XR will redefine how businesses engage with their audiences.
Voice Technology Integration:
As voice-activated devices become increasingly popular, Salesforce is expected to integrate voice technology into its CRM platform. This integration will simplify user interactions, making it easier for sales representatives to access information on-the-go, analyze data through voice commands, and improve overall productivity.
Conclusion:
Salesforce continues to be at the forefront of CRM innovation, and 2023 promises to be an exciting year with these emerging trends. AI-driven personalization, IoT integration, blockchain-enabled security, and hyper-personalization through CDPs are all set to revolutionize customer engagement. Furthermore, low-code/no-code development, XR integration, and voice technology will shape the future of the Salesforce platform, making it more accessible, immersive, and efficient for businesses worldwide.
As these trends continue to evolve, businesses must stay agile and adapt their strategies to leverage the full potential of Salesforce and gain a competitive edge in the dynamic world of CRM. Embracing these trends will not only enhance customer experiences but also drive revenue growth and long-term success.
#Salesforce Trends#Customer-Centric Approach#AI and Automation#Data-driven Insights#Augmented Reality (AR) in CRM#Integration and Connectivity#IoT (Internet of Things) and CRM#Omni-channel Engagement#Blockchain in Salesforce#Sales and Marketing Alignment#Virtual Events and Conferences#AI-driven Chatbots#Cloud Computing Advancements
0 notes
Text
Are you confused about the differences between Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR)? You’re not alone! These terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct technologies that are shaping the way we interact with the world around us. At Simulanis Solutions, we’re excited to break it down for you!
#Difference Between AR#VR#MR#AR vs VR vs MR#Augmented Reality Definition#Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality#Mixed Reality Solutions#What is Virtual Reality?#AR and VR Technologies#Mixed Reality Applications#VR vs MR vs AR Technologies#AR/VR/MR Differences#Virtual Reality Experience#AR for Business#VR Immersive Technology#Mixed Reality Development#AR/VR/MR Integration#Augmented Reality Devices#MR vs AR vs VR Use Cases#Immersive Reality Technologies#MR Applications in Industry#Comparing AR
0 notes
Text

#digital transformation#technology#tech#retail industry#retail solutions#augmented reality#retail mobility solutions#ar integration#visual merchandising#technology consultant#technology trends
0 notes
Text
The Metaverse: A New Frontier in Digital Interaction

The concept of the metaverse has captivated the imagination of technologists, futurists, and businesses alike. Envisioned as a collective virtual shared space, the metaverse merges physical and digital realities, offering immersive experiences and unprecedented opportunities for interaction, commerce, and creativity. This article delves into the metaverse, its potential impact on various sectors, the technologies driving its development, and notable projects shaping this emerging landscape.
What is the Metaverse?
The metaverse is a digital universe that encompasses virtual and augmented reality, providing a persistent, shared, and interactive online environment. In the metaverse, users can create avatars, interact with others, attend virtual events, own virtual property, and engage in economic activities. Unlike traditional online experiences, the metaverse aims to replicate and enhance the real world, offering seamless integration of the physical and digital realms.
Key Components of the Metaverse
Virtual Worlds: Virtual worlds are digital environments where users can explore, interact, and create. Platforms like Decentraland, Sandbox, and VRChat offer expansive virtual spaces where users can build, socialize, and participate in various activities.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing user experiences through devices like smartphones and AR glasses. Examples include Pokémon GO and AR navigation apps that blend digital content with physical surroundings.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR provides immersive experiences through headsets that transport users to fully digital environments. Companies like Oculus, HTC Vive, and Sony PlayStation VR are leading the way in developing advanced VR hardware and software.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain plays a crucial role in the metaverse by enabling decentralized ownership, digital scarcity, and secure transactions. NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) and cryptocurrencies are integral to the metaverse economy, allowing users to buy, sell, and trade virtual assets.
Digital Economy: The metaverse features a robust digital economy where users can earn, spend, and invest in virtual goods and services. Virtual real estate, digital art, and in-game items are examples of assets that hold real-world value within the metaverse.
Potential Impact of the Metaverse
Social Interaction: The metaverse offers new ways for people to connect and interact, transcending geographical boundaries. Virtual events, social spaces, and collaborative environments provide opportunities for meaningful engagement and community building.
Entertainment and Gaming: The entertainment and gaming industries are poised to benefit significantly from the metaverse. Immersive games, virtual concerts, and interactive storytelling experiences offer new dimensions of engagement and creativity.
Education and Training: The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize education and training by providing immersive, interactive learning environments. Virtual classrooms, simulations, and collaborative projects can enhance educational outcomes and accessibility.
Commerce and Retail: Virtual shopping experiences and digital marketplaces enable businesses to reach global audiences in innovative ways. Brands can create virtual storefronts, offer unique digital products, and engage customers through immersive experiences.
Work and Collaboration: The metaverse can transform the future of work by providing virtual offices, meeting spaces, and collaborative tools. Remote work and global collaboration become more seamless and engaging in a fully digital environment.
Technologies Driving the Metaverse
5G Connectivity: High-speed, low-latency 5G networks are essential for delivering seamless and responsive metaverse experiences. Enhanced connectivity enables real-time interactions and high-quality streaming of immersive content.
Advanced Graphics and Computing: Powerful graphics processing units (GPUs) and cloud computing resources are crucial for rendering detailed virtual environments and supporting large-scale metaverse platforms.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI enhances the metaverse by enabling realistic avatars, intelligent virtual assistants, and dynamic content generation. AI-driven algorithms can personalize experiences and optimize virtual interactions.
Wearable Technology: Wearable devices, such as VR headsets, AR glasses, and haptic feedback suits, provide users with immersive and interactive experiences. Advancements in wearable technology are critical for enhancing the metaverse experience.
Notable Metaverse Projects
Decentraland: Decentraland is a decentralized virtual world where users can buy, sell, and develop virtual real estate as NFTs. The platform offers a wide range of experiences, from gaming and socializing to virtual commerce and education.
Sandbox: Sandbox is a virtual world that allows users to create, own, and monetize their gaming experiences using blockchain technology. The platform's user-generated content and virtual real estate model have attracted a vibrant community of creators and players.
Facebook's Meta: Facebook's rebranding to Meta underscores its commitment to building the metaverse. Meta aims to create interconnected virtual spaces for social interaction, work, and entertainment, leveraging its existing social media infrastructure.
Roblox: Roblox is an online platform that enables users to create and play games developed by other users. With its extensive user-generated content and virtual economy, Roblox exemplifies the potential of the metaverse in gaming and social interaction.
Sexy Meme Coin (SEXXXY): Sexy Meme Coin integrates metaverse elements by offering a decentralized marketplace for buying, selling, and trading memes as NFTs. This unique approach combines humor, creativity, and digital ownership, adding a distinct flavor to the metaverse landscape. Learn more about Sexy Meme Coin at Sexy Meme Coin.
The Future of the Metaverse
The metaverse is still in its early stages, but its potential to reshape digital interaction is immense. As technology advances and more industries explore its possibilities, the metaverse is likely to become an integral part of our daily lives. Collaboration between technology providers, content creators, and businesses will drive the development of the metaverse, creating new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Conclusion
The metaverse represents a new frontier in digital interaction, offering immersive and interconnected experiences that bridge the physical and digital worlds. With its potential to transform social interaction, entertainment, education, commerce, and work, the metaverse is poised to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. Notable projects like Decentraland, Sandbox, Meta, Roblox, and Sexy Meme Coin are at the forefront of this transformation, showcasing the diverse possibilities within this emerging digital universe.
For those interested in the playful and innovative side of the metaverse, Sexy Meme Coin offers a unique and entertaining platform. Visit Sexy Meme Coin to explore this exciting project and join the community.
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
Neue Tools zur Automatisierung von Datenanalysen mit KI vorgestellt
Die rasante Entwicklung der Künstlichen Intelligenz (KI) hat in den letzten Jahren zahlreiche Bereiche transformiert, und die Datenanalyse bildet da keine Ausnahme. Innovative KI-Tools, die zur Automatisierung von Datenanalysen entwickelt wurden, versprechen nicht nur eine erhebliche Effizienzsteigerung, sondern auch eine Verbesserung der Datenqualität und der Entscheidungsfindung. In diesem…
#Algorithmen#Augmented Reality#Augmented Reality (AR)#Automatisierung#Datenanalyse#Datenqualität#Datenschutz#Datensicherheit#Datenvisualisierung#Entscheidungsfindung#Führungskräfte#Innovation#Integration#Intelligenz#KI#Marketing#Marketingstrategien#Maschinelles Lernen#Natural Language Processing (NLP)#NLP#Produktentwicklung#SEM#Sicherheit#Verantwortung#Virtual Reality (VR)#Visualisierung
0 notes
Text

The augmented reality of the Pizzaplex is one of the marvels of the modern age. It acts as not only a separate layer of highways to traverse for Fazbear Entertainment technicians, but digital servers for the AI within the building's premises. In all respects, it is an attraction of its own, unable to be viewed fully by the hardware limitations of Virtual Augmented Neural Network Integration units. Being as it is made for exclusively artificial entities, the AR World also suppresses unwanted apparitions left over from previous incidents. Whether said apparitions are due to programming bugs or other glitches, the AR World effectively constricts their signals and ensures no harm is done in the physical world. In this way, the AR World is simultaneously a net for external interferences and a roof for internal instances. "Illusions" (mascot programs, e.g. Helpi) are coded in by Fazbear Ent. employees in order to further mask and obscure unwanted apparitions, among their other purposes.
#art#fnaf art#fnaf au#fnaf#five nights at freddy's#fnaf security breach#fnaf tony#tony becker#au#illusionary memory au#tales from the pizzaplex
30 notes
·
View notes