#CodeQuality
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
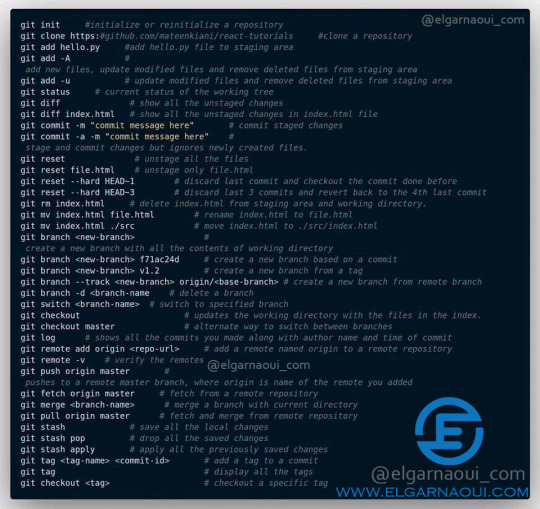
Git commands
#programming#git#gitlab#gitcommands#javaprogramming#java 21#javascript#web development#coding#codequality#software engineering#python#language#machine learning#artificial intelligence
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
#AITechnicalDebt#CodingAgents#SoftwareDevelopment#TechDebtCrisis#AIProgramming#CodeQuality#DeveloperProblems#AIAssistants#FutureOfCoding#AutomationPitfalls
0 notes
Text
From Chaos to Clarity: Transforming Messy API Logic into a Structured REST API with Flask
Creating APIs is a common task for developers, but without structure, the code can quickly become overwhelming and difficult to manage. Let’s dive into a before-and-after journey showcasing how messy API logic can be transformed into a clean, structured REST API using Flask.
Before Transformation: Initially, the API logic is often a tangled web of code—everything crammed into one file, functions overlapping, and no clear separation of concerns. This messy setup causes several pain points: debugging becomes a headache, adding new features risks breaking existing ones, and collaboration is nearly impossible. The codebase may contain redundant code and lack proper error handling, which can lead to unreliable API behavior.
After Transformation: Flask steps in as a lightweight, flexible framework that encourages best practices. By breaking the API into modular components, such as routes, controllers, and services, developers can create a clean separation of concerns. Each part of the API is responsible for a single task, which makes the code easier to read and maintain. Flask’s blueprint system allows organizing endpoints logically, while extensions provide easy ways to add features like authentication and database integration.
With this organized structure, testing becomes straightforward, and scaling the API to accommodate new features is simplified. The API now delivers consistent responses with improved error handling, making it more robust and user-friendly.
The takeaway? A well-structured Flask REST API transforms chaotic code into a scalable, maintainable, and efficient service—perfect for professional web development.
#FlaskAPI#RESTAPI#PythonDeveloper#CodeTransformation#APIRefactor#WebDevTips#SoftwareDevelopment#CleanCode#ProgrammingLife#PythonTips#BackendDevelopment#TechTips#Microservices#ModularCode#FlaskFramework#APIIntegration#DeveloperJourney#CodeQuality#WebAppDevelopment#TechGrowth#CodingBestPractices#APIProgramming#ScalableArchitecture#BuildInPublic#LearnToCode#TechCommunity
0 notes
Text
Advanced HTML Techniques: Multimedia, APIs, and Best Practices
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, mastering advanced HTML techniques is crucial for creating dynamic, engaging, and maintainable websites. This guide delves into embedding multimedia, leveraging HTML5 APIs, and adhering to best practices for modern HTML. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting, these techniques will enhance your web development skills.
HTML Techniques
Embedding Multimedia
Multimedia is an integral part of creating an engaging user experience on the web. From videos to audio files, multimedia elements can make your website more interactive and appealing.
Embedding Videos
Videos can significantly enhance the user experience by providing visual and auditory information. HTML5 introduced the <video> tag, making it easier to embed videos directly into web pages without relying on third-party plugins.
Here's how to embed a video using the <video> tag:
<video width="640" height="360" controls> <source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> Your browser does not support the video tag. </video>
Attributes:
width and height: Define the dimensions of the video player.
controls: Adds play, pause, and volume controls.
autoplay: Automatically starts playing the video when the page loads. Use with caution as it can be disruptive.
loop: Replays the video continuously.
muted: Mutes the video by default.
Embedding Audio
Just like videos, audio can be embedded using the HTML5 <audio> tag. This is especially useful for music, podcasts, or any sound effects.
Example:
<audio controls> <source src="audio.mp3" type="audio/mpeg"> Your browser does not support the audio element. </audio>
Attributes:
controls: Displays audio controls.
autoplay: Starts playing audio automatically.
loop: Plays the audio in a loop.
muted: Starts the audio muted.
Using HTML5 APIs
HTML5 introduced several APIs that provide powerful new features for web developers, enabling more dynamic and interactive websites.
Geolocation API
The Geolocation API allows web applications to access users’ location information with their permission. This can be used for location-based services, such as maps or localized content.
Example:
if (navigator.geolocation) { navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(showPosition); } else { console.log("Geolocation is not supported by this browser."); } function showPosition(position) { console.log("Latitude: " + position.coords.latitude + ", Longitude: " + position.coords.longitude); }
Web Storage API
The Web Storage API provides a way to store data on the client side. This includes localStorage and sessionStorage.
localStorage: Stores data with no expiration date.
sessionStorage: Stores data for the duration of the page session.
Example of using localStorage:
// Setting data localStorage.setItem('username', 'JohnDoe'); // Retrieving data var name = localStorage.getItem('username'); console.log(name);
Canvas API
The Canvas API provides a means for drawing graphics via JavaScript and the <canvas> element. It can be used for drawing shapes, creating games, or rendering complex visualizations.
Example:
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100" style="border:1px solid #000000;"> </canvas> <script> var canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas'); var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d'); ctx.fillStyle = '#FF0000'; ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 150, 75); </script>
HTML Techniques
Best Practices for Writing Modern, Maintainable HTML
Writing clean, maintainable HTML is essential for ensuring your code is easy to read, update, and scale. Here are some best practices to follow:
Semantic HTML
Use semantic HTML to improve code readability and accessibility. Semantic elements clearly describe their meaning in a human- and machine-readable way.
Use , , , , etc., instead of generic or elements.
Accessibility
Ensuring that websites are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, is crucial. Follow these practices to enhance accessibility:
Use alt attributes with descriptive text for images.
Ensure sufficient color contrast between text and background.
Use ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and properties where necessary.
Responsive Design
Design for a wide range of devices and screen sizes by using responsive design principles. Employ CSS media queries and flexible grid layouts to ensure your website looks good on any device.
Example of a simple media query:
@media only screen and (max-width: 600px) { body { background-color: lightblue; } }
Optimize Performance
Performance optimization is key to providing a fast and seamless user experience. Here are some tips:
Minimize HTTP requests by combining files and using CSS sprites.
Compress images and use modern formats like WebP.
Use asynchronous loading for scripts to avoid blocking rendering.
Keep HTML DRY
DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) is a principle that helps reduce repetition and redundancy in code. Use reusable components and templates to streamline your HTML.
HTML Techniques
Conclusion
By mastering these advanced HTML techniques, you can create more interactive, efficient, and accessible websites. Embedding multimedia, leveraging HTML5 APIs, and adhering to best practices will set you apart as a skilled web developer. Continue exploring new technologies and refining your skills to keep up with the ever-changing world of web development.
FAQs
What is the difference between localStorage and sessionStorage?
localStorage stores data with no expiration date, while sessionStorage stores data only for the duration of the page session. This means data in sessionStorage is cleared when the page session ends.
How can I ensure my website is accessible to users with disabilities?
Use semantic HTML, provide alt attributes for images, ensure good color contrast, and utilize ARIA roles and properties to enhance accessibility.
What are some best practices for optimizing website performance?
Minimize HTTP requests, compress images, use modern image formats like WebP, and load scripts asynchronously to optimize performance.
Why should I use semantic HTML elements instead of generic ones like <div>?
Semantic elements provide meaning and context to the content, improving both accessibility and SEO by making it easier for search engines and assistive technologies to understand your content.
How can I make my website responsive?
Use CSS media queries and flexible grid layouts to ensure your website adapts to different screen sizes and devices, providing a seamless experience across all platforms.
#AdvancedHTML#HTML5#HTMLTechniques#HTMLMultimedia#HTMLAPIs#HTMLBestPractices#WebDevelopment#FrontendDevelopment#FrontendTips#ResponsiveDesign#WebStandards#UIUXDesign#UXDesign#WebPerformance#WebAccessibility#CleanCode#CodeQuality#LearnHTML#LearnToCode#CodeNewbie#WebDevTips#ProgrammingTips#FrontendMasters#ModernWeb#WebCoding#SEOForDevelopers#AccessibleWeb#HTMLStructure#CleanCoding#BestPractices
0 notes
Text
Mastering Unit Testing: Essential Strategies for Modern Software Development
In the world of software development, unit testing is no longer optional — it's a necessity. As applications grow more complex, testing individual units of code ensures reliability, reduces bugs, and boosts confidence in your codebase.
What is unit testing in software testing?
Unit testing involves testing individual components of a program in isolation, ensuring each part functions as expected. By focusing on the smallest testable units (functions or methods), developers catch issues early, preventing them from snowballing into bigger problems.
The Evolution of Unit Testing:
Unit testing has shifted from a secondary consideration to a central part of the development process. It’s the foundation for creating scalable, maintainable, and reliable applications. Without it, teams risk costly production bugs and lost reputation.
Building a Robust Testing Strategy:
Testing Pyramid: Focus on a broad base of unit tests (70-80%), fewer integration tests, and minimal end-to-end tests to maintain speed and maximize coverage.
Test-Driven Development (TDD): Write tests before code. This improves design, ensuring your code is always testable and aligned with requirements.
Meaningful Test Cases: Don’t just test the happy path; test edge cases, error handling, and unexpected inputs for comprehensive coverage.
Advanced Unit Testing Techniques:
Mocking & Stubbing: Control external dependencies to test units in isolation.
Parameterized Testing: Run the same test logic with different input values to reduce duplication.
Property-Based Testing: Automatically generate random test cases to uncover edge cases you might miss.
Measuring Testing Effectiveness:
Code Coverage: Aim for high coverage, especially on critical business logic.
Mutation Testing: Check if your tests are catching bugs by deliberately introducing errors into the code.
Performance Testing: Set performance benchmarks for individual components to catch regressions early.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
Over-Testing & Under-Testing: Balance test coverage to avoid maintenance overhead while ensuring critical code paths are well-tested.
Brittle Tests: Make sure tests are resilient to minor code changes.
Test Data Management: Use test data builders and fixtures for reliable, repeatable tests.
Integration with Modern Development Workflows:
Continuous Integration: Automate unit tests within your CI pipeline to ensure code stays reliable.
IDE & Tooling: Leverage modern IDEs and test runners for efficient and seamless testing.
Team Collaboration: Make unit testing a team practice with shared knowledge and test reviews.
The Future of Unit Testing:
AI-Powered Test Generation: AI tools can help auto-generate unit tests, though human insight remains essential for comprehensive coverage.
Cloud-Native Testing: Unit testing must adapt to handle distributed systems and microservices as apps move to cloud environments.
Unit testing isn't just a practice; it’s a skill that separates professional developers from amateurs. By mastering it, your software will be more reliable, maintainable, and agile.
For teams looking to elevate their testing strategies, Keploy offers innovative solutions that streamline the testing process, ensuring comprehensive testing is more accessible than ever.
#UnitTesting#SoftwareTesting#TestDrivenDevelopment#TDD#TestAutomation#DeveloperTools#SoftwareDevelopment#CleanCode#TestingBestPractices#CodeQuality#Mocking#ContinuousIntegration#SoftwareEngineering#AgileDevelopment#PerformanceTesting#CI#TestCoverage#SoftwareDesign#TechTools#Keploy#DevelopmentStrategy#Debugging#TestStrategies
0 notes
Text
Error Handling in Node.js: Best Practices for Cleaner Code
Learn the best practices for handling errors effectively in Node.js to write cleaner, more reliable code. This guide covers common pitfalls, async error handling, and structured techniques to improve application stability.
#NodeJS#ErrorHandling#CleanCode#BackendDevelopment#JavaScriptTips#NodeBestPractices#AsyncProgramming#CodeQuality#WebDevelopment#NodeJSTips
0 notes
Text
🌱 Brownfields Development: What You Need to Know......
What Are Brownfields?
Brownfields are existing software systems or codebases that need changes, updates, or new features. Working on brownfields means programming within an existing project, making improvements or adding new parts. Sometimes, it involves removing old features, which can be tricky.
Greenfields vs. Brownfields
Greenfields = Starting a project from scratch, building something new.
Brownfields = Working on existing code, changing or expanding it.
Your Team Experience You'll usually work in teams on a brownfields project.
What to Expect
🕑 Iterations
Each lasts 2 weeks.
You’ll have specific goals to reach. Missed goals mean failure and need to be carried over.
After each iteration, you'll show your work to another team.
You’ll review and rate each other's work.
Teams will hold retrospectives to discuss what went well and what needs improvement.
🤝 Teamwork & Contribution
Everyone is expected to contribute fairly.
Your individual work is tracked via git logs (but don’t worry — quality matters more than quantity!).
Regular daily coding practice is encouraged.
🚀 Progress & Success
Progress is based on your code contributions and the team achieving goals.
Missing goals means no real progress for anyone.
Consistent effort and teamwork help catch up if goals are missed.
🎯 Responsibility
The whole team owns success or failure.
If a goal isn’t completed, the whole team is responsible for fixing it.
📂 The Codebase
Your focus is on understanding and improving the existing code, not deleting large parts.
Small, frequent code changes are best.
💡 Tips for Success
Work as a team.
Make small changes often.
Merge small chunks of working code daily.
Communicate well with team members for the best results.
Stay disciplined, focused, and collaborative — and you’ll become a high-performing developer! 🚀
Happy Coding....
Follow LorieNatalie for more content......
#BrownfieldsDevelopment#TeamProgramming#SoftwareDevelopment#CodingTips#IterativeDevelopment#CollaborativeCoding#AgileMethodology#CodeQuality#TeamWork#SoftwareEngineering#ProgrammingJourney#DevCommunity#CodeBetter#SmallStepsBigResults
0 notes
Text
How to Design and Build Scalable Microservices in Node.js
Microservices are becoming the go-to architecture for modern applications, and if you're just starting out with backend development, Node.js is a great place to begin. Known for its speed and lightweight nature, Node.js is an ideal choice for building services that need to grow and scale over time. If you're exploring Node.js web development, understanding how to create scalable microservices is a vital skill.
In this article, we’ll walk you through what microservices are, why they’re useful, and how you can design and build them using Node.js- even if you're new to backend programming.
What Are Microservices?
A microservices architecture breaks down a large application into smaller, independent services that each perform a specific task. These services communicate with each other through APIs, usually over HTTP or messaging queues.
For example, in an e-commerce platform:
One microservice might handle user authentication
Another handles orders
A third manages product listings
This approach is more flexible and maintainable than a traditional monolithic application, where everything is packed into one large codebase.
Why Choose Node.js for Microservices?
There are several reasons developers choose Node.js for microservices:
Fast and non-blocking I/O: Node.js handles multiple requests efficiently without waiting for previous ones to finish.
Lightweight and modular: Node’s package manager (npm) offers thousands of ready-to-use modules.
Easy to scale: Built-in tools like clustering and horizontal scaling make it easier to grow your services.
JavaScript everywhere: You can use the same language on both the frontend and backend.
Whether you're building your first API or planning a bigger system, many startups and enterprises rely on professional Node.js Development Services to set up clean and efficient architectures from the start.
Step-by-Step: Building Scalable Microservices in Node.js
Let’s break it down into manageable steps.
1. Define Your Services Clearly
Start by identifying the business functions of your app. Each microservice should be responsible for one feature or domain.
For example:
User Service for authentication
Order Service for handling transactions
Inventory Service for managing products
Keep each service focused. This improves performance and makes your app easier to maintain or scale.
2. Set Up a Basic Node.js Service
Here’s a very simple example using Express.js:
mkdir user-service cd user-service npm init -y npm install express
Create a server.js file:
jsCopy
const express = require('express'); const app = express(); app.get('/users', (req, res) => { res.json([{ id: 1, name: 'Alice' }]); }); app.listen(3000, () => { console.log('User service is running on port 3000'); });
This is your first microservice.
3. Use a Gateway or API Layer
In a microservices setup, each service has its own endpoint. But to avoid confusing your users with multiple URLs, you can use an API Gateway like Express Gateway, Kong, or Nginx to route traffic to the correct service.
The gateway can also handle:
Authentication
Rate limiting
Logging
Version control
If you want to save time and ensure best practices, it’s often a good idea to hire Node.js developers who already understand how to configure gateways and secure your APIs effectively.
4. Implement Inter-Service Communication
Microservices often need to talk to each other. This is done through APIs (HTTP) or message brokers (like RabbitMQ or Kafka).
In a simple HTTP example:
jsCopy
// order-service calls user-service const axios = require('axios'); axios.get('http://localhost:3000/users') .then(res => console.log(res.data));
As your system grows, switching to messaging queues improves performance and decouples services even further.
5. Use Docker to Containerize Your Services
To make your services easy to deploy, run, and scale, containerize them using Docker.
Here’s a simple Dockerfile for a Node.js service:
dockerfileCopy
FROM node:18 WORKDIR /app COPY . . RUN npm install CMD ["node", "server.js"]
This makes your service portable and predictable—key traits for scaling.
Most Node.js development companies containerize microservices and use orchestration tools like Docker Compose or Kubernetes to manage multiple services efficiently.
6. Add Monitoring and Logging
Don’t wait until something breaks. Add monitoring early.
Use tools like:
Winston or Morgan for logging
Prometheus and Grafana for monitoring performance
Logstash or Elasticsearch for log storage and search
This visibility helps you debug faster and scale more reliably.
7. Plan for Scaling
Node.js can scale vertically (more CPU/threads) and horizontally (more instances). Use built-in clustering or cloud platforms (like AWS ECS, Azure App Service, or Google Cloud Run) to scale your services based on demand.
Scalability is where many teams turn to expert Node.js Development Services to architect fault-tolerant and load-balanced systems that handle high traffic smoothly.
Tips for Beginners
Here are a few tips to make your microservices journey easier:
Start with two services and expand gradually
Keep services stateless (no shared memory or sessions)
Use environment variables for configuration
Maintain separate codebases for each service
Write clear API documentation for each microservice
Building scalable microservices doesn’t mean building everything at once. Take it step by step.
When to Seek Help
When your app grows in complexity or you need to handle production-level traffic, it might be time to bring in professional help.
A reputable Node.js development company can support you with:
System design and architecture
API security and versioning
Testing and CI/CD pipelines
Cloud deployment and scaling strategies
Or, if you’re looking for temporary expertise, you can hire Node.js developers to join your team on a freelance or contract basis. They’ll help speed up development, review your code for best practices, and guide your technical decisions.
Final Thoughts
Designing scalable microservices in Node.js is not as hard as it sounds—especially if you take a modular, step-by-step approach. With the right structure and tools, you can build systems that are easier to manage, faster to deploy, and ready to grow.
Whether you're building your first microservice or planning to scale a business application, Node.js has the flexibility and performance to help you succeed.
And when you're ready to move faster and scale smarter, don’t hesitate to reach out to a reliable Node.js development company or hire Node.js developers who can bring your vision to life with confidence.
#NodeJS#Microservices#BackendDevelopment#ScalableArchitecture#DistributedSystems#JavaScriptDevelopment#CloudNative#DevOps#Docker#Kubernetes#SystemDesign#WebDevelopment#TechArchitecture#HighAvailability#Serverless#APIDevelopment#SoftwareEngineering#CodeQuality#FullStackDevelopment
0 notes
Text
#TechnicalDebt#CustomSoftware#SoftwareDevelopment#CodeQuality#Refactoring#AgileDevelopment#TechDebtManagement#SoftwareEngineering#ProjectManagement#CleanCode
0 notes
Text
Study Finds AI Code Mutations Help Developers Catch Bugs Faster
The software development landscape is evolving rapidly, and a recent study finds AI code mutations are revolutionizing how developers identify and fix bugs. This groundbreaking research highlights the potential of artificial intelligence to enhance code quality, streamline debugging processes, and boost productivity. By introducing controlled changes to code, AI-driven mutation testing is proving to be a game-changer for developers striving to deliver robust applications in less time.
What Are AI Code Mutations?
AI code mutations involve using artificial intelligence to intentionally alter software code in small, controlled ways to test its resilience and uncover hidden bugs. Unlike traditional testing methods, which often rely on predefined test cases, mutation testing powered by AI generates dynamic variations of code to simulate potential errors. This approach allows developers to evaluate how their software responds to unexpected changes, revealing vulnerabilities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
The study finds AI code mutations offer a proactive way to stress-test applications. By mimicking real-world scenarios where bugs could emerge, AI helps developers catch issues early in the development cycle. This not only improves software reliability but also reduces the time spent on manual debugging, a process that can be tedious and error-prone.
Why Bug Detection Matters in Software Development
Bugs are the bane of every developer’s existence. Even a minor coding error can lead to significant issues, from application crashes to security vulnerabilities. Traditional debugging methods, while effective to an extent, often fail to catch complex or subtle bugs that only manifest under specific conditions. This is where AI-driven mutation testing shines, offering a more comprehensive approach to quality assurance.
The importance of early bug detection cannot be overstated. Catching issues during the development phase is far more cost-effective than addressing them after deployment. According to industry estimates, fixing a bug post-release can cost up to 30 times more than resolving it during the coding stage. By leveraging AI code mutations, developers can identify and address potential problems before they escalate, saving both time and resources.
How AI Code Mutations Work
AI code mutation tools analyze a program’s source code and introduce small, deliberate changes—known as mutations—to create multiple variants of the original code. These mutations might include altering a mathematical operator, modifying a conditional statement, or swapping variable values. The goal is to simulate potential errors and observe how the software behaves under these altered conditions.
Once the mutated code is generated, it is subjected to the existing test suite. If the tests fail to detect the introduced changes, it indicates gaps in the test coverage. Developers can then refine their tests or fix the underlying code to address these weaknesses. The study finds AI code mutations significantly improve test suite effectiveness, enabling developers to achieve higher code quality with fewer blind spots.
Benefits of AI Code Mutations for Developers
The adoption of AI code mutations offers several tangible benefits for developers and organizations alike. Here are some of the key advantages:
Faster Bug Detection
AI-driven mutation testing accelerates the bug detection process by automating the creation and evaluation of code variants. This reduces the reliance on manual testing, which can be time-consuming and inconsistent. Developers can quickly identify weak points in their code and address them before moving to the next development phase.
Improved Test Coverage
Traditional testing methods often focus on expected use cases, leaving edge cases untested. AI code mutations introduce a wider range of scenarios, ensuring that test suites are more comprehensive. This leads to more robust applications that can handle unexpected inputs or conditions.
Enhanced Code Quality
By identifying and fixing bugs early, AI code mutations contribute to higher-quality software. This is particularly valuable in industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, where reliability and security are paramount. The study finds AI code mutations help developers produce cleaner, more maintainable codebases.
Reduced Debugging Time
Debugging is often cited as one of the most time-intensive aspects of software development. AI-powered tools streamline this process by pinpointing issues with greater accuracy. Developers can focus on writing new features rather than spending hours—or even days—tracking down elusive bugs.
Cost Savings
Fixing bugs early in the development cycle is significantly cheaper than addressing them post-release. By catching issues before they reach production, AI code mutations help organizations save on maintenance costs and avoid potential reputational damage caused by software failures.
Real-World Applications of AI Code Mutations
The study finds AI code mutations are already making an impact across various industries. In web development, for example, AI-driven tools are being used to test complex JavaScript applications, ensuring they perform reliably under diverse conditions. In mobile app development, mutation testing helps developers catch bugs that could cause crashes on different devices or operating systems.
In the realm of cybersecurity, AI code mutations are proving invaluable for identifying vulnerabilities in software. By simulating potential exploits, these tools help developers strengthen their applications against attacks. This is particularly critical for industries handling sensitive user data, such as banking and healthcare.
Challenges and Limitations
While AI code mutations offer significant benefits, they are not without challenges. One potential drawback is the computational resources required to generate and test multiple code variants. For large-scale projects, this can lead to increased processing times and costs. Additionally, not all mutations are equally valuable—some may introduce trivial changes that do not meaningfully improve test coverage.
Another challenge is the learning curve associated with adopting AI-driven tools. Developers unfamiliar with mutation testing may require training to effectively integrate these tools into their workflows. However, as AI technology continues to advance, these challenges are likely to diminish, making mutation testing more accessible to teams of all sizes.
The Future of AI in Software Development
The study finds AI code mutations are just the beginning of AI’s transformative impact on software development. As machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated, we can expect even greater advancements in automated testing, code optimization, and bug detection. Future iterations of AI tools may integrate seamlessly with existing development environments, providing real-time feedback and suggestions to developers as they code.
Moreover, the rise of AI-driven development tools is likely to democratize access to high-quality software testing. Small startups and independent developers, who may lack the resources for extensive manual testing, can leverage AI to compete with larger organizations. This leveling of the playing field could spur innovation and lead to the creation of more reliable, user-friendly applications.
How Developers Can Get Started with AI Code Mutations
For developers eager to explore AI code mutations, the first step is to choose a mutation testing tool that aligns with their programming language and development environment. Popular tools include MutPy for Python, Pitest for Java, and Stryker for JavaScript. These tools offer robust features for generating and analyzing code mutations, with active communities providing support and updates.
Next, developers should integrate mutation testing into their existing workflows. This may involve updating test suites to account for mutated code or configuring CI/CD pipelines to run mutation tests automatically. Starting with small projects can help teams gain familiarity with the process before scaling up to larger codebases.
Finally, developers should stay informed about advancements in AI and mutation testing. The study finds AI code mutations are an evolving field, with new tools and techniques emerging regularly. By keeping up with the latest research and best practices, developers can maximize the benefits of AI-driven testing.
The study finds AI code mutations are transforming the way developers approach bug detection and software quality. By automating the creation of code variants and exposing weaknesses in test suites, AI is helping developers catch bugs faster and build more reliable applications. While challenges remain, the benefits of improved test coverage, reduced debugging time, and cost savings make AI code mutations a compelling tool for modern software development.
#AI#CodeMutations#BugDetection#SoftwareDevelopment#AICoding#DeveloperTools#CodeQuality#TechInnovation#Programming#BugFixing
0 notes
Text

🚀 Master the Art of Testing & Debugging in Python!
Are you struggling with bugs or want to improve code quality?
Here's your quick guide to essential tools every Python Full Stack Developer should know:
🔹 Pytest – For unit testing
🔹 Postman – For API testing
🔹 Logging – For efficient debugging
🔹 Black, Flake8 – For clean,linted code
✅ Learn these skills and boost your development speed and accuracy!
📞 Contact: +91 9704944488
🌐 Visit: www.pythonfullstackmasters.in
📍 Hyderabad
#PythonFullStack#TestingAndDebugging#PythonDeveloper#FullStackDevelopment#DebuggingTools#SoftwareTesting#CodeQuality#LintingTools#BlackFormatter#Flake8#PostmanTesting#LoggingInPython#BugFixing#CleanCodeMatters#FullStackTips#WebDevelopmentIndia#LearnToCode#CodeSmart#ITJobsIndia#HyderabadTech
0 notes
Text
"Working Effectively with Legacy Code" by Michael C. Feathers is a must-read for developers and software engineers who deal with legacy systems. Legacy code, often characterized by its complexity, lack of documentation, and resistance to change, can be daunting to work with. This book provides practical strategies and techniques to understand, refactor, and improve legacy codebases. Below is a user-friendly, step-by-step breakdown of the key outcomes and takeaways from the book.
#LegacyCode#Refactoring#SoftwareDevelopment#CleanCode#CodeRefactoring#TechBooks#SoftwareEngineering#WorkingWithLegacyCode#MichaelFeathers#LegacySystems#CodeQuality#TechTutorial#SoftwareMaintenance#DevelopmentBestPractices#TechEducation#SoftwareCraftsmanship#LegacyCodeTips#RefactorLegacyCode#ProgrammingBooks#TestDrivenDevelopment#AgileDevelopment#SoftwareDesign#TechLeadership#ProgrammingBestPractices#DeveloperTools#TechCommunity
0 notes
Text
🛠️ Not all code is created equal. At SDH, we build software that scales, adapts, and performs.
0 notes
Text
React Best Practices: Build Scalable & High-Performing Apps
Learn proven React best practices to build clean, efficient, and high-performing ReactJS apps. Explore tips on component structure, state management, and optimization.
#ReactJS#WebDevelopment#AppOptimization#FrontendDevelopment#JavaScriptTips#CodeQuality#ReactBestPractices#HireReactJSDevelopers
0 notes
Text
Semantic HTML: Writing Cleaner, More Accessible Code
In the evolving world of web development, the importance of writing clean, structured, and accessible code cannot be overstated. Semantic HTML plays a crucial role in achieving these goals. By using semantic tags, developers can create more meaningful and organized documents, enhancing both the user experience and accessibility for people with disabilities. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of semantic HTML, its benefits, and how to effectively use semantic elements like <header>, <article>, and <section> to improve the structure of your web pages.
What is Semantic HTML?
Semantic HTML refers to the use of HTML tags that convey meaning about the content they enclose. Unlike generic tags like <div> and <span>, semantic tags provide information about the role or purpose of the content. For example, <header> indicates the top section of a document or section, and <article> represents a self-contained piece of content.
Benefits of Using Semantic HTML
Improved Accessibility: Semantic HTML helps screen readers and other assistive technologies understand the structure and content of a webpage, making it more accessible to users with disabilities.
Better SEO: Search engines use the semantic structure of a webpage to better understand its content. Using semantic tags can improve your site's search engine ranking.
Enhanced Readability: Semantic HTML makes your code easier to read and maintain for other developers, as it provides a clear structure and purpose for each section of the document.
Future-Proofing: As web standards evolve, semantic HTML ensures better compatibility with future browsers and technologies.
Key Semantic Elements and Their Usage
The <header> Element
The <header> element is used to define introductory content or navigational links for a section or page. It typically contains a heading, logo, or other relevant information.
Usage Example:
<header> <h1>Welcome to My Blog</h1> <nav> <ul> <li><a href="#home">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#about">About</a></li> <li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li> </ul> </nav> </header>
The <article> Element
The <article> element represents a self-contained piece of content that could be distributed independently. This could include articles, blog posts, or news stories.
Usage Example:
<article> <h2>The Rise of Semantic HTML</h2> <p>Semantic HTML is revolutionizing the way we write web content, making it more accessible and SEO-friendly...</p> </article>
The <section> Element
The <section> element defines a thematic grouping of content, generally with a heading. It is useful for dividing a document into discrete parts, each with a specific theme or purpose.
Usage Example:
<section> <h2>Benefits of Semantic HTML</h2> <p>Using semantic HTML offers numerous advantages, including enhanced accessibility and SEO...</p> </section>
Other Important Semantic Elements
<nav>: Used for navigation links.
<aside>: Represents content tangentially related to the content around it, like sidebars.
<footer>: Defines the footer for a section or page.
<main>: Specifies the primary content of a document.
<figure> and <figcaption>: Used for images, diagrams, or illustrations with captions.
Structuring a Web Page with Semantic HTML
To illustrate how semantic HTML can be used to structure a web page, let's consider a simple blog layout. Here's how you might organize the main sections:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>My Semantic Blog</title> </head> <body> <header> <h1>My Semantic Blog</h1> <nav> <ul> <li><a href="#home">Home</a></li> <li><a href="#about">About</a></li> <li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li> </ul> </nav> </header> <main> <article> <h2>Understanding Semantic HTML</h2> <p>Semantic HTML is a powerful tool for web developers...</p> </article> <section> <h2>Why Use Semantic HTML?</h2> <p>There are several compelling reasons to use semantic HTML...</p> </section> <aside> <h2>Related Articles</h2> <ul> <li><a href="#article1">The Basics of HTML</a></li> <li><a href="#article2">CSS for Beginners</a></li> </ul> </aside> </main> <footer> <p>© 2023 My Semantic Blog</p> </footer> </body> </html>
In this example, semantic elements are used to clearly delineate the different parts of the page. The <header> contains the title and navigation, <main> houses the primary content, <article> and <section> divide the content into logical units, and <aside> provides supplementary content.
Best Practices for Using Semantic HTML
Use Appropriate Tags: Choose semantic tags that accurately describe the content they enclose. Avoid using and when a more descriptive tag is available.
Organize Content Logically: Structure your HTML documents so that they are easy to read and understand, both for users and search engines.
Complement with ARIA: While semantic HTML improves accessibility, using Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) attributes can further enhance the experience for users with disabilities.
Validate Your Code: Regularly check your HTML with a validator to ensure it is well-formed and follows semantic standards.
Keep Learning: Stay updated with the latest HTML standards and best practices to continue writing accessible and efficient code.
Conclusion
Semantic HTML is an essential aspect of modern web development, offering numerous benefits for accessibility, SEO, and code maintenance. By understanding and utilizing semantic elements like <header>, <article>, and <section>, developers can create more meaningful and structured web pages. Embracing semantic HTML not only improves the user experience but also future-proofs your websites for evolving technologies.
FAQs
What is the difference between semantic and non-semantic HTML?
Semantic HTML uses tags that convey meaning about the content they enclose, such as <article> or <header>. Non-semantic HTML, like <div> or <span>, doesn't provide any information about the content's role or purpose.
Why is semantic HTML important for accessibility?
Semantic HTML helps assistive technologies, like screen readers, understand the structure of a webpage, making it easier for users with disabilities to navigate and comprehend the content.
Can I use semantic HTML tags for styling purposes?
While semantic HTML is primarily used for structuring content, it can also be styled using CSS. However, the choice of semantic tags should be based on the content's meaning, not its appearance.
How does semantic HTML benefit SEO?
Search engines use the semantic structure of a webpage to better understand its content, which can improve search engine rankings. Semantic HTML helps search engines identify key parts of a page, like headings and articles.
Is semantic HTML supported by all browsers?
Yes, modern browsers support semantic HTML. However, it's always a good practice to test your web pages across different browsers to ensure compatibility.
#SemanticHTML#HTMLBestPractices#CleanCode#AccessibleWeb#WebAccessibility#SemanticWeb#AccessibleDesign#InclusiveWeb#WebStandards#HTMLStructure#WebDevelopment#FrontendDevelopment#FrontendTips#FrontendDesign#ResponsiveDesign#UIUXDesign#UXBestPractices#UXDesign#CSSTips#JavaScriptTips#CodingStandards#CleanCoding#BestPractices#CodeQuality#CodeBetter#WebCoding#WebDevTips#ProgrammingTips#DevTips#DeveloperLife
0 notes
Text
Test-Driven Development: A Complete Guide to Better Software
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is more than just a testing strategy — it’s a philosophy that reshapes how developers write code. Instead of writing code and testing it later, TDD emphasizes testing first, ensuring that each piece of functionality is thoroughly tested from the start. This approach creates clean, reliable, and maintainable code by focusing on the requirements and expected behavior upfront.
What is Test Driven Development?
At its core, Test-Driven Development involves a simple but powerful cycle:
Red: Write a test that fails because the functionality isn't implemented yet.
Green: Write the minimum code necessary to make the test pass.
Refactor: Clean up the code without changing its behavior, knowing that the test ensures everything still works.
The Benefits of TDD:
Improved Code Quality: TDD forces developers to think through the design and requirements before writing code, leading to cleaner and more purposeful implementations.
Better Design: By considering interfaces and functionality early, developers create modular, maintainable code.
Comprehensive Test Coverage: With every piece of functionality being tested before implementation, TDD results in high test coverage, providing confidence in your code.
Faster Debugging: When tests fail, developers instantly know what’s broken, speeding up the debugging process.
Documentation Through Tests: Well-written tests act as documentation, showing the intended behavior of your code.
Best Practices for TDD Success:
Start Small: Focus on small, isolated units of functionality to begin with.
Write Meaningful Test Names: The test name should clearly describe the behavior being tested.
Test Behavior, Not Implementation: Focus on testing what your code does, not how it does it.
Keep Tests Independent: Tests should be self-contained and not rely on other tests.
TDD works wonders in web development, API development, and mobile development — helping to ensure your code works as expected, every time.
For teams looking to streamline testing and improve the development process, Keploy can support TDD practices and more.
#TestDrivenDevelopment#TDD#SoftwareDevelopment#CleanCode#CodeQuality#TestAutomation#DeveloperTools#BestPractices#SoftwareTesting#Programming#Debugging#TestDriven#SoftwareDesign#AgileDevelopment#DevelopmentProcess#Keploy#CodingTips#TechTips#CI#WebDevelopment#APIDevelopment#MobileDevelopment#TechCommunity
0 notes