#Java encapsulation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Is Object-Oriented Programming in Java and Why Does It Matter?

Java is super popular in the programming world, and one of the main reasons for that is its use of object-oriented programming (OOP). So, what exactly is OOP in Java, and why should you care? OOP is a way to organize your code by grouping related data and functions into objects. This makes Java easier to work with, more organized, and simpler to update.
Key Ideas Behind Object-Oriented Programming
To get a grip on OOP in Java, you need to know four main ideas: Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstraction. These concepts help you write clean and reusable code, which is pretty important in software development today.
Encapsulation: Keeping Data Safe
Encapsulation means protecting the internal data of an object from being accessed directly. You do this using private variables and public methods. When you take a Java course in Coimbatore, you’ll learn how this helps keep your code secure and safeguards data from accidental changes.
Inheritance: Building on Existing Code
Inheritance lets a new class take on the properties of an existing class, which cuts down on code repetition and encourages reuse. Grasping this idea is key if you want to dive deeper into Java development, especially in a Java Full Stack Developer course in Coimbatore.
Polymorphism: Flexibility in Code
Polymorphism allows you to treat objects as if they are from their parent class rather than their specific class. This means you can write more flexible code that works across different cases. You’ll definitely encounter this in Java training in Coimbatore, and it’s essential for creating scalable applications.
Abstraction: Simplifying Complexity
Abstraction is all about hiding the messy details and only showing what’s necessary. For example, when you use your smartphone, you don’t need to understand how everything works inside it. Java uses abstract classes and interfaces to make things simpler, which you’ll notice in any solid Java course in Coimbatore.
Why It Matters in Real Life
So, circling back: What is OOP in Java and why is it important? Its real strength comes from making big software projects easier to manage. OOP allows multiple developers to work on their parts without stepping on each other’s toes.
OOP and Full Stack Development
Full stack developers cover both the frontend and backend. Understanding OOP in Java can make your backend logic much better. That’s why a Java Full Stack Developer Course in Coimbatore focuses on OOP right from the start.
Java and Your Career Path
If you're looking to become a software developer, getting a good handle on OOP is a must. Companies love using Java for building big applications because of its OOP focus. Joining a Java training program in Coimbatore can help you get the practical experience you need to be job-ready.
Wrapping Up: Start Your Java Journey with Xplore IT Corp
So, what is object-oriented programming in Java and why is it important? It’s a great way to create secure and reusable applications. Whether you’re interested in a Java Course in Coimbatore, a Full Stack Developer course, or overall Java training, Xplore IT Corp has programs to help you kick off your career.
FAQs
1. What are the main ideas of OOP in Java?
The key ideas are Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, and Abstraction.
2. Why should I learn OOP in Java?
Because it’s the foundation of Java and helps you create modular and efficient code.
3. Is it tough to learn OOP for beginners?
Not really! With good guidance from a quality Java training program in Coimbatore, it becomes easy and fun.
4. Do I need to know OOP for full stack development?
Definitely! Most backend work in full stack development is based on OOP, which is covered in a Java Full Stack Developer Course in Coimbatore.
5. Where can I find good Java courses in Coimbatore?
You should check out Xplore IT Corp; they’re known for offering the best Java courses around.
#Java programming#object-oriented concepts#Java syntax#Java classes#Java objects#Java methods#Java interface#Java inheritance#Java encapsulation#Java abstraction#Java polymorphism#Java virtual machine#Java development tools#Java backend development#Java software development#Java programming basics#advanced Java programming#Java application development#Java code examples#Java programming logic
0 notes
Text
Tính Đóng Gói (Encapsulation) trong Java | Khái Niệm và Ứng Dụng
Tính đóng gói (Encapsulation) là một trong bốn nguyên tắc cơ bản của lập trình hướng đối tượng (OOP) trong Java, cùng với kế thừa, đa hình và trừu tượng hóa. Đây là một khái niệm quan trọng giúp lập trình viên bảo vệ dữ liệu, tăng tính bảo mật và tạo ra mã nguồn dễ bảo trì hơn. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ cùng tìm hiểu chi tiết về tính đóng gói trong Java, cách triển khai và vai trò của nó trong việc xây dựng các ứng dụng chất lượng cao.

Tính Đóng Gói trong Java là gì?
Tính Đóng Gói trong Java là gì?
Tính đóng gói trong Java là kỹ thuật ẩn giấu chi tiết triển khai của một đối tượng và chỉ cung cấp các phương thức công khai để truy cập hoặc thay đổi dữ liệu. Điều này được thực hiện thông qua việc sử dụng các biến private và các phương thức public (getter và setter) để kiểm soát quyền truy cập vào dữ liệu.
Ví dụ, hãy tưởng tượng một chiếc hộp có khóa: bạn chỉ có thể lấy đồ bên trong qua một khe nhỏ được kiểm soát. Tính đóng gói hoạt động tương tự, đảm bảo rằng dữ liệu bên trong một lớp (class) chỉ có thể được truy cập hoặc thay đổi thông qua các phương thức được định nghĩa sẵn, giúp bảo vệ dữ liệu khỏi các truy cập không mong muốn.
Tại sao Tính Đóng Gói quan trọng?
Bảo vệ dữ liệu: Ngăn chặn việc truy cập trực tiếp vào các thuộc tính của lớp, từ đó giảm nguy cơ dữ liệu bị thay đổi ngoài ý muốn.
Tăng tính linh hoạt: Cho phép thay đổi cách triển khai bên trong lớp mà không ảnh hưởng đến các phần khác của chương trình.
Dễ bảo trì: Mã nguồn trở nên rõ ràng và dễ quản lý hơn khi các thành phần được đóng gói đúng cách.
Kiểm soát truy cập: Chỉ cho phép truy cập dữ liệu thông qua các phương thức được kiểm soát, đảm bảo tính hợp lệ của dữ liệu.

Ảnh mô tả tính đóng gói (Encapsulation) trong Java.
Cách triển khai Tính Đóng Gói trong Java
Để triển khai tính đóng gói trong Java, bạn cần tuân theo các bước sau:
Sử dụng từ khóa private cho các biến: Các thuộc tính của lớp nên được khai báo là private để ngăn chặn truy cập trực tiếp từ bên ngoài.
Cung cấp getter và setter: Sử dụng các phương thức public để truy cập (getter) hoặc thay đổi (setter) giá trị của các biến private.
Kiểm tra tính hợp lệ trong setter: Thêm logic kiểm tra để đảm bảo dữ liệu được cập nhật đúng cách.
Ví dụ minh họa
Dưới đây là một ví dụ về cách áp dụng tính đóng gói trong Java:
public class SinhVien { private String hoTen; private int tuoi; private double diemTB; // Getter cho hoTen public String getHoTen() { return hoTen; } // Setter cho hoTen public void setHoTen(String hoTen) { this.hoTen = hoTen; } // Getter cho tuoi public int getTuoi() { return tuoi; } // Setter cho tuoi với kiểm tra tính hợp lệ public void setTuoi(int tuoi) { if (tuoi > 0 && tuoi < 150) { this.tuoi = tuoi; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Tuổi không hợp lệ!"); } } // Getter cho diemTB public double getDiemTB() { return diemTB; } // Setter cho diemTB với kiểm tra tính hợp lệ public void setDiemTB(double diemTB) { if (diemTB >= 0 && diemTB <= 10) { this.diemTB = diemTB; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Điểm trung bình không hợp lệ!"); } } }
Trong ví dụ trên:
Các thuộc tính hoTen, tuoi, diemTB được khai báo là private, không thể truy cập trực tiếp từ bên ngoài.
Các phương thức get và set được sử dụng để truy cập và thay đổi dữ liệu.
Setter có logic kiểm tra tính hợp lệ của dữ liệu (ví dụ: tuổi phải nằm trong khoảng 0-150, điểm trung bình từ 0-10).

Ví dụ minh họa
Lợi ích của Tính Đóng Gói trong thực tế
Tính đóng gói mang lại nhiều lợi ích trong việc phát triển phần mềm:
Tăng tính bảo mật: Bằng cách ẩn dữ liệu, tính đóng gói ngăn chặn việc sửa đổi dữ liệu không đúng cách, đảm bảo rằng chỉ các phương thức được chỉ định mới có thể thay đổi trạng thái của đối tượng.
Giảm sự phụ thuộc: Các lớp khác không cần biết chi tiết triển khai bên trong, giúp giảm sự phụ thuộc giữa các module.
Dễ dàng nâng cấp: Lập trình viên có thể thay đổi logic bên trong lớp mà không làm ảnh hưởng đến các lớp khác sử dụng nó.
Tính tái sử dụng: Các lớp được đóng gói tốt có thể được sử dụng lại trong nhiều dự án khác nhau.
Ví dụ, trong một ứng dụng quản lý nhân sự, tính đóng gói có thể được sử dụng để bảo vệ thông tin cá nhân của nhân viên, như lương hoặc ngày sinh, chỉ cho phép truy cập thông qua các phương thức được kiểm soát.
Những lưu ý khi sử dụng Tính Đóng Gói
Mặc dù tính đóng gói mang lại nhiều lợi ích, nhưng cần lưu ý một số điểm sau để sử dụng hiệu quả:
Không lạm dụng getter và setter: Việc cung cấp getter và setter cho mọi thuộc tính có thể làm mất đi ý nghĩa của tính đóng gói. Hãy chỉ cung cấp những phương thức thực sự cần thiết.
Kiểm tra dữ liệu chặt chẽ: Trong các phương thức setter, luôn kiểm tra tính hợp lệ của dữ liệu để đảm bảo tính toàn vẹn.
Sử dụng từ khóa final khi cần: Nếu một thuộc tính không cần thay đổi sau khi khởi tạo, hãy sử dụng final để tăng tính an toàn.
Ứng dụng thực tế của Tính Đóng Gói
Tính đóng gói được sử dụng rộng rãi trong các ứng dụng Java, từ phát triển ứng dụng web, ứng dụng di động đến hệ thống quản lý doanh nghiệp. Một số ví dụ thực tế bao gồm:
Ứng dụng ngân hàng: Các thông tin như số dư tài khoản, mật khẩu được đóng gói để chỉ có thể truy cập thông qua các phương thức được xác thực.
Hệ thống quản lý sinh viên: Thông tin cá nhân của sinh viên được bảo vệ, chỉ có thể thay đổi thông qua các phương thức được định nghĩa sẵn.
Ứng dụng thương mại điện tử: Dữ liệu giỏ hàng hoặc thông tin thanh toán được đóng gói để đảm bảo an toàn.
Kết luận
Tính đóng gói trong Java là một kỹ thuật quan trọng giúp lập trình viên xây dựng mã nguồn an toàn, dễ bảo trì và tái sử dụng. Bằng cách sử dụng các biến private và các phương thức public như getter và setter, bạn có thể kiểm soát chặt chẽ việc truy cập và thay đổi dữ liệu. Hiểu và áp dụng đúng tính đóng gói sẽ giúp bạn trở thành một lập trình viên Java chuyên nghiệp hơn.
Hy vọng bài viết này đã cung cấp cho bạn cái nhìn tổng quan và chi tiết về tính đóng gói trong Java. Hãy áp dụng nó trong các dự án của bạn để thấy được sức mạnh của lập trình hướng đối tượng!
Encapsulation trong Java – Bảo vệ dữ liệu, tăng tính bảo mật và linh hoạt cho mã nguồn. Tìm hiểu cách sử dụng private, getter, setter trong thực tế. 🔎 Khám phá ngay tại: Java Highlight
0 notes
Text
Preventing Application Crashes: An Overview of Exception Handling in Java
Java development frameworks’ robust and versatile nature creates a requirement for developing applications without interruptions. Users operating within a system exhibit dissatisfaction, resulting in the loss of essential data and negative word-of-mouth releases about the product following an unanticipated shutdown or crash. Java application reliability and resilience depend on mastering the Java exception handling principles. Click to read the complete guide
#python tuple#bca course subjects#Encapsulation in Java#Constructor in java#Python tuple#Polymorphism in Java
0 notes
Text
Understanding Java Encapsulation: Benefits, Concepts, and Data Hiding Explained
Encapsulation provides several benefits that make it an essential aspect of Java programming. First, it enhances data security by restricting access to private variables.
0 notes
Text
Encapsulation in C++ : A Comprehensive Exploration
Discover the power of encapsulation in C++! 🚀 Learn how this cornerstone principle makes software robust and manageable. Dive into practical examples and unravel its essence with us at p4n.in. #cplusplus #programming #encapsulation
In the world of object-oriented programming (OOP), encapsulation is a key idea. It helps programmers make strong and easy-to-look-after software. In C++, encapsulation lets programmers bundle up data and actions in neat little packages called classes. This keeps the inside stuff hidden away from outside meddling. Here on p4n.in, this blog explores encapsulation in C++ in detail. We’ll dive into…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The Encapsulation contribute to achieving data hiding in OOP?
Encapsulation is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming (OOP) that contributes to achieving data hiding, one of the core principles of OOP. Data hiding is the idea that an object’s internal state should not be directly accessible from outside the object; instead, it should be accessed through well-defined methods or interfaces. Encapsulation is the mechanism that allows you to…
View On WordPress
#AccessModifiers#CodeSample#DataEncapsulation#DataHiding#Encapsulation#EncapsulationInJava#Java#JavaExample#ObjectOrientation#OOP#Programming
0 notes
Text
o hi i use both of them! in particular rust is my favorite programming language
rust: fast like C/C++ but memory management doesnt suck unlike C/C++
If any Haskell and or Rust fans follow me, give me 1 good reason to learn them
#ultimately it depends on what you find convincing#rust is less popular than languages like C C++ and java so if you want a job then eh#if you don't need the performance of C then sticking to higher-level OOP languages like java is fine#notably rust lacks proper inheritance (though it does have other OOP features like polymorphism & encapsulation)#so if u use inheritance a lot then thats a reason to Not use rust#rust has a couple more specific language features that i really love so lmk if u want me to expand on them#as for haskell if ur not interested in functional programming then it's probably not worth it ngl#im a massive fuckin nerd so i like it but it definitely took a LOT of effort compared to any procedural language!
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
The concept of object oriented programming explained
Object-oriented programming is a fundamental concept present in numerous programming languages such as C++, Java, JavaScript, and more. It becomes straightforward once you truly grasp it, and that's precisely what this post aims to help you achieve. So, stop your scrolling for a second and delve into this post for a thorough and clear explanation.

Understanding the Term "Object-Oriented"
To grasp OOP, let's begin by explaining the name itself: "Object-Oriented." This term signifies that OOP revolves around entities known as "objects."
What Exactly Is an Object?
An object in OOP is any entity that possesses both state and behavior. Consider a dog as an example: it has states such as color, name, and breed, while its behaviors encompass actions like wagging the tail, barking, and eating.
The reason we introduce the concept of objects in programming is to effectively represent real-world entities, a task that cannot be accomplished with conventional variables or arrays.
Classes: Abstract Forms of Objects
Now, what about classes? A class is essentially the abstract form of an object. If we take the example of a "dog," the object "Mydog" is a concrete instance, while the class "dog" represents dogs in a more general sense. Think of a class as a blueprint or template from which you can create individual objects.
Four Pillars of Object-Oriented Programming
Now that we've established the fundamentals of objects and classes. OOP is built upon four key principles:
Inheritance: Inheritance occurs when one object inherits all the properties and behaviors of a parent object. It promotes code reusability and facilitates runtime polymorphism.
Polymorphism: Polymorphism entails performing a single task in multiple ways. For instance, it can involve presenting information differently to customers or implementing different shapes like triangles or rectangles.
Abstraction: Abstraction is about concealing internal details while exposing functionality. Consider a phone call; we don't need to understand the intricate inner workings.
Encapsulation: Encapsulation involves bundling code and data into a single unit. Just like a capsule contains various medicines . In a fully encapsulated class (e.g., a Java bean), all data members are private, ensuring data integrity and controlled access.
I remember finding these images that explained these concepts using the 'Squid Game' series, and they are just perfect. So, I'm sharing them here and giving all credit to their owner :
Polymorphism , Inheritance , Encapsulation
#code#codeblr#css#html#python#studyblr#progblr#programming#comp sci#web design#web developers#web development#website design#webdev#website#tech#html css#learn to code#OOP#object oriented programming
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
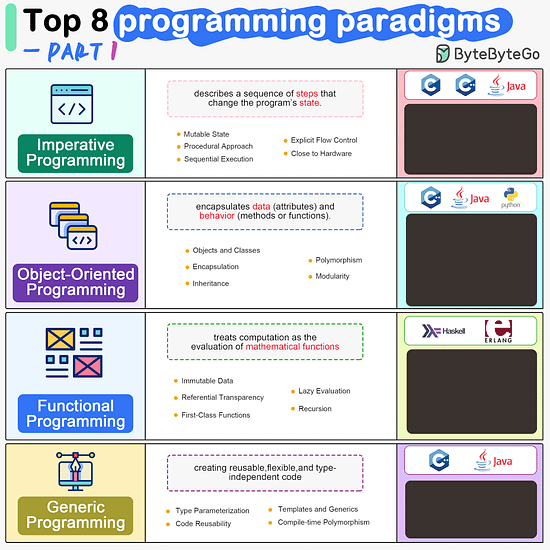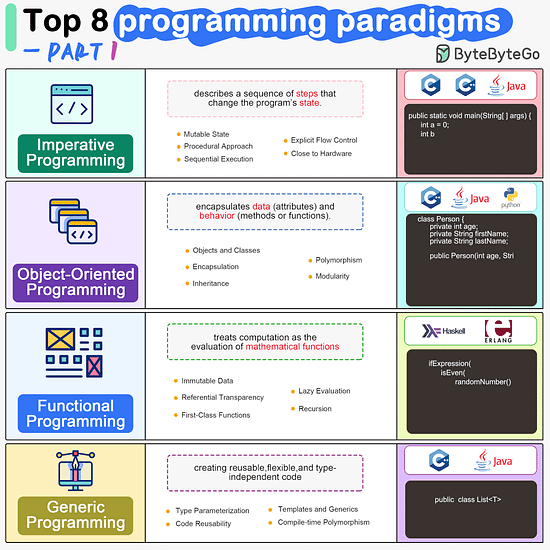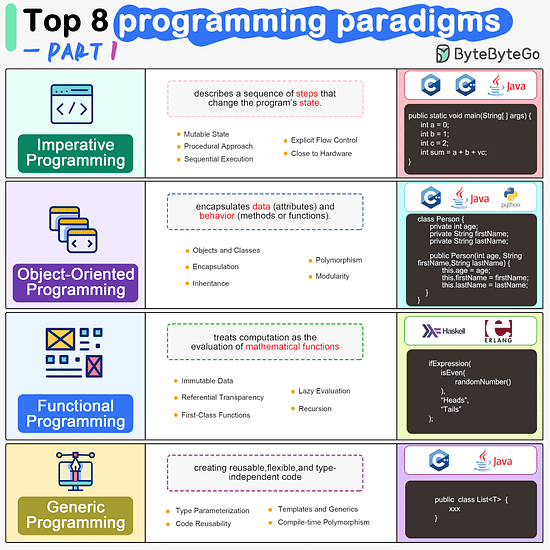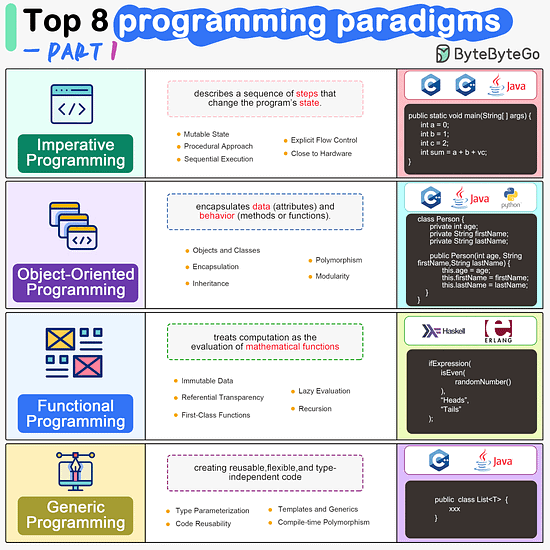
ByteByteGo | Newsletter/Blog
From the newsletter:
Imperative Programming Imperative programming describes a sequence of steps that change the program’s state. Languages like C, C++, Java, Python (to an extent), and many others support imperative programming styles.
Declarative Programming Declarative programming emphasizes expressing logic and functionalities without describing the control flow explicitly. Functional programming is a popular form of declarative programming.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Object-oriented programming (OOP) revolves around the concept of objects, which encapsulate data (attributes) and behavior (methods or functions). Common object-oriented programming languages include Java, C++, Python, Ruby, and C#.
Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) Aspect-oriented programming (AOP) aims to modularize concerns that cut across multiple parts of a software system. AspectJ is one of the most well-known AOP frameworks that extends Java with AOP capabilities.
Functional Programming Functional Programming (FP) treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and emphasizes the use of immutable data and declarative expressions. Languages like Haskell, Lisp, Erlang, and some features in languages like JavaScript, Python, and Scala support functional programming paradigms.
Reactive Programming Reactive Programming deals with asynchronous data streams and the propagation of changes. Event-driven applications, and streaming data processing applications benefit from reactive programming.
Generic Programming Generic Programming aims at creating reusable, flexible, and type-independent code by allowing algorithms and data structures to be written without specifying the types they will operate on. Generic programming is extensively used in libraries and frameworks to create data structures like lists, stacks, queues, and algorithms like sorting, searching.
Concurrent Programming Concurrent Programming deals with the execution of multiple tasks or processes simultaneously, improving performance and resource utilization. Concurrent programming is utilized in various applications, including multi-threaded servers, parallel processing, concurrent web servers, and high-performance computing.
#bytebytego#resource#programming#concurrent#generic#reactive#funtional#aspect#oriented#aop#fp#object#oop#declarative#imperative
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
anyway, while we're on the subject of music discs, i wanna talk about the name.
while very iconic, i'm not sure the term 'music discs' truly encapsulates all that they are. on bedrock edition (and older versions of java edition), they are internally referred to as 'records', which i think does a better job. it has a double meaning.
like, yeah, the discs are records as in music, but some of them are also records as in... records. records of past events. recordings of horrors and atrocities.
.
interestingly, a lot of the newer ones seem to be both at the same time. discs like otherside and creator feel like someone took an event and used it as inspiration for music. they might not have been able to record the event itself, but they would record what it felt like.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Encapsulation in Java – A Complete Guide
Learn everything about Encapsulation in Java with Scientech Easy's beginner-friendly guide. Understand how encapsulation helps in data hiding, improves code maintainability, and secures your Java applications. This comprehensive article covers its real-world use, syntax, and practical examples to help you grasp the concept easily. Perfect for students and developers looking to strengthen their OOP fundamentals.Scientech Easy for clear explanations and step-by-step learning on Java programming topics. Start mastering encapsulation today!

#bca course subjects#python tuple#Interface in Java#Encapsulation in Java#Method overriding in Java#Polymorphism in Java#Constructor in java
0 notes
Note
Experience with rust thus far
Rust is great! I've been working with it off and on for around a year and change now, and I have no complaints.
It's a very... sane language. At no point have I looked at a language feature and thought "wow that's a hack", which has been my experience with almost every other imperative language to that point. (Java, C, C#, JavaScript, Python, etc.) There are a few features I think it's currently lacking, but most of them are present in the nightly branch. (I'm a big fan of let_chains and const_fn_floating_point_arithmetic, among others.)
Library support via Cargo is great, no complaints, and I love how easy doc comments are to write, it makes for an almost Elisp level of good documentation.
I've written a few non-trivial applications, like a breakout clone and a flappy bird-esque thing, and while I ditched good practices for the sake of implementation efficiency (both projects were more about learning libraries than the final product) Rust's nature makes it really easy to refactor from copy-paste spaghetti hell into clean, encapsulated, maintainable code.
I also love how anal-retentive the compiler is. Again, Rust is a very sane language. I do not want to be writing Raku, where there are a thousand "basically correct" ways to do the same thing. I want constraints, and I want them strict. I want to be able to express to the compiler not just what I want a piece of code to do, but what I don't want it to do as well. We're all human! We're gonna mess up! I want it to be easy to tell that I've messed up! (Looking at you, python, with your assignment equals declaration bullshit. Typoing a variable name should not be permitted.)
Overall it's just great. When it comes to writing applications I'd pick no other language. (Except maybe D. Too bad nobody supports D...)
#ive probably missed some stuff here#but thats the general picture#my thoughts#programming#rustlang#thanks for the ask!#your thoughts
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Java Data Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Java, one of the most widely used programming languages, is known for its portability, security, and rich set of features. At the core of Java programming are data types, which define the nature of data that can be stored and manipulated within a program. Understanding data types is crucial for effective programming, as they determine how data is stored, how much memory it occupies, and the operations that can be performed on that data.
What are Data Types?
In programming, data types specify the type of data that a variable can hold. They provide a way to classify data into different categories based on their characteristics and operations. Java categorizes data types into two main groups:
1. Primitive Data Types
2. Reference Data Types
Why Use Data Types?
1. Memory Management: Different data types require different amounts of memory. By choosing the appropriate data type, you can optimize memory usage, which is particularly important in resource-constrained environments.
2. Type Safety: Using data types helps catch errors at compile time, reducing runtime errors. Java is a statically typed language, meaning that type checks are performed during compilation.
3. Code Clarity: Specifying data types makes the code more readable and understandable. It allows other developers (or your future self) to quickly grasp the intended use of variables.
4. Performance Optimization: Certain data types can enhance performance, especially when dealing with large datasets or intensive calculations. For example, using int instead of long can speed up operations when the range of int is sufficient.
5. Defining Operations: Different data types support different operations. For example, you cannot perform mathematical operations on a String data type without converting it to a numeric type.
When and Where to Use Data Types?
1. Choosing Primitive Data Types:
Use int when you need a whole number without a decimal, such as counting items.
Use double for fractional numbers where precision is essential, like financial calculations.
Use char when you need to store a single character, such as a letter or symbol.
Use boolean when you need to represent true/false conditions, like in conditional statements.
2. Choosing Reference Data Types:
Use String for any textual data, such as names, messages, or file paths.
Use Arrays when you need to store multiple values of the same type, such as a list of scores or names.
Use Custom Classes to represent complex data structures that include multiple properties and behaviors. For example, a Car class can encapsulate attributes like model, year, and methods for actions like starting or stopping the car.
1. Primitive Data Types
Primitive data types are the most basic data types built into the Java language. They serve as the building blocks for data manipulation in Java. There are eight primitive data types:
Examples of Primitive Data Types
1. Byte Example
byte age = 25; System.out.println(“Age: ” + age);
2. Short Example
short temperature = -5; System.out.println(“Temperature: ” + temperature);
3. Int Example
int population = 1000000; System.out.println(“Population: ” + population);
4. Long Example
long distanceToMoon = 384400000L; // in meters System.out.println(“Distance to Moon: ” + distanceToMoon);
5. Float Example
float pi = 3.14f; System.out.println(“Value of Pi: ” + pi);
6. Double Example
double gravitationalConstant = 9.81; // m/s^2 System.out.println(“Gravitational Constant: ” + gravitationalConstant);
7. Char Example
char initial = ‘J’; System.out.println(“Initial: ” + initial);
8. Boolean Example
boolean isJavaFun = true; System.out.println(“Is Java Fun? ” + isJavaFun);
2. Reference Data Types
Reference data types, unlike primitive data types, refer to objects and are created using classes. Reference data types are not defined by a fixed size; they can store complex data structures such as arrays, strings, and user-defined classes. The most common reference data types include:
Strings: A sequence of characters.
Arrays: A collection of similar data types.
Classes: User-defined data types.
Examples of Reference Data Types
1. String Example
String greeting = “Hello, World!”; System.out.println(greeting);
2. Array Example
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; System.out.println(“First Number: ” + numbers[0]);
3. Class Example
class Car { String model; int year;
Car(String m, int y) { model = m; year = y; } }
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Car car1 = new Car(“Toyota”, 2020); System.out.println(“Car Model: ” + car1.model + “, Year: ” + car1.year); } }
Type Conversion
In Java, type conversion refers to converting a variable from one data type to another. This can happen in two ways:
1. Widening Conversion: Automatically converting a smaller data type to a larger data type (e.g., int to long). This is done implicitly by the Java compiler.
int num = 100; long longNum = num; // Widening conversion
2. Narrowing Conversion: Manually converting a larger data type to a smaller data type (e.g., double to int). This requires explicit casting.
double decimalNum = 9.99; int intNum = (int) decimalNum; // Narrowing conversion
Conclusion
Understanding data types in Java is fundamental for effective programming. It not only helps in managing memory but also enables programmers to manipulate data efficiently. Java’s robust type system, consisting of both primitive and reference data types, provides flexibility and efficiency in application development. By carefully selecting data types, developers can optimize performance, ensure type safety, and maintain code clarity.
By mastering data types, you’ll greatly enhance your ability to write efficient, reliable, and maintainable Java programs, setting a strong foundation for your journey as a Java developer.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Software Technical Interview Review List
Data Structures
Arrays (and Java List vs ArrayList)
String
Stack
Queue
LinkedList
Algorithms
Sorting (Bubblesort, Mergesort, Quicksort)
Recursion & Backtracking
Linear and Binary Search
String/Array algos
Tree traversal
Dynamic Programming
Graph algos (DFS, BFS, Dijksta's and Kruskals)
OOP fundamentals
Polymorphism
Inheritance
Encapsulation
Data abstraction
SOLID and GRASP
Explanations & example questions:
Strings and Arrays [ 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 ]
Stacks and Queues [ 1 | 2 ]
LinkedList [ 1 | 2 ]
Sorting & searching [ 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 ]
Recursion and Backtracking [ 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 ]
Dynamic Programming [ 1 | 2 | 3 | 4]
Graphs [ 1 | 2 | 3 ]
Tree [ 1 | 2 ]
General DS&A info and questions [ 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 ]
OOP review & questions [ 1 | 2 | 3 ]
#ive been procrastinating this coding assessment for my interview so bad 😭😭#im just scared of messing up cause i need this internship#But its due soon so im really buckling down now >:)#object oriented programming#algorithms#data structures#software engineering#ref#resource#mypost
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering Java: Your Comprehensive Guide to Programming Excellence
Embarking on the journey of mastering Java is akin to entering a realm of endless possibilities. Java, a versatile and widely-utilized programming language, offers a broad spectrum of applications, from crafting web and mobile applications to powering robust enterprise systems. Whether you are a novice in the realm of coding or a seasoned programmer looking to broaden your skill set, the path to proficiency in Java is an exciting one.

In this comprehensive guide, we will be your guiding light through the intricacies of Java, starting from the foundational basics and progressing to the more advanced aspects of the language. Our objective is to equip you with the knowledge and skills that form a robust and unshakable foundation for your journey into the vibrant world of Java. Fasten your seatbelt as we embark on this exhilarating exploration, charting a course that will empower you to thrive in the ever-evolving landscape of software development.
Here's a 8-step guide to effectively learn Java
Step 1: Setting Up Your Development Environment
Your journey to becoming a proficient Java developer commences with setting up your development environment. The essential components are the Java Development Kit (JDK) and an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA. These tools aren't just convenient; they're the gears that will drive your Java programming endeavors. They streamline the coding process, provide useful features, and offer an organized workspace, making your coding experience efficient and enjoyable.
Step 2: The Foundation - Learning the Basics
With your development environment ready, it's time to delve into the fundamental building blocks of Java. Begin by acquainting yourself with data types, variables, operators, and control structures. These are the nuts and bolts of the language, and a solid grasp of these concepts is essential. You'll find an abundance of online tutorials and beginner-friendly Java books to assist you at this stage.
Step 3: Navigating the World of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
The object-oriented programming (OOP) approach is well known in Java. To harness the true power of Java, immerse yourself in the world of OOP. Understand the concepts of classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism. This knowledge forms the bedrock of Java programming and enables you to design efficient, organized, and scalable code.
Step 4: Mastering Data Structures and Algorithms
Data structures (such as arrays, lists, and sets) and algorithms are the secret sauce behind solving real-world problems efficiently. As you progress, dive into the world of data structures and algorithms. These are the tools that will empower you to handle complex tasks and optimize your code. They're your go-to assets for creating efficient and responsive applications.
Step 5: The Art of Exception Handling
Java boasts a robust exception-handling mechanism. Understanding how to handle exceptions properly is not just an add-on skill; it's a vital aspect of writing reliable code. Exception handling ensures that your code gracefully manages unexpected situations, preventing crashes and delivering a seamless user experience.
Step 6: Exploring Input and Output Operations
In this step, you'll explore the realm of input and output (I/O) operations. Mastering I/O is crucial for reading and writing files, as well as interacting with users. You'll gain the ability to build applications that can efficiently process data and communicate effectively with users.
Step 7: Conquering Multi tasking
Java's support for multi tasking is a significant advantage. Understanding how to manage threads and synchronize their actions is vital for creating concurrent applications. Multithreading is the key to developing software that can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making your applications responsive and scalable.
Step 8: Building Projects and Real-World Practice
Theory is only as valuable as its practical application. The final step involves applying what you've learned by building small projects. These projects serve as a proving ground for your skills and provide valuable additions to your portfolio. Whether it's a simple application or a more complex project, the act of building is where the real learning takes place.

As you step into this vibrant realm of Java, remember that continuous learning is the key to staying relevant and effective in the ever-evolving field of software development. Be open to exploring diverse applications, from web development to mobile apps and enterprise solutions, and never underestimate the power of hands-on practice. Building projects, no matter how small, will solidify your knowledge and boost your confidence.
In your quest to master Java, ACTE Technologies stands as a valuable ally. Their expert guidance and comprehensive training programs will sharpen your skills, boost your confidence, and pave the way for a rewarding career in software development. Whether you're embarking on your Java journey or looking to take your skills to the next level, ACTE Technologies offers the resources and support you need to thrive in the world of Java programming.
So, with Java as your trusty companion, and ACTE Technologies as your guide, the possibilities are boundless. Your journey is just beginning, and the world of software development awaits your innovation and expertise. Best of luck on your path to mastering Java!
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding Object-Oriented Programming and OOPs Concepts in Java
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a paradigm that has revolutionized software development by organizing code around the concept of objects. Java, a widely used programming language, embraces the principles of OOP to provide a robust and flexible platform for developing scalable and maintainable applications. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of Object-Oriented Programming and explore how they are implemented in Java.

Object-Oriented Programming:
At its core, Object-Oriented Programming is centered on the idea of encapsulating data and behavior into objects. An object is a self-contained unit that represents a real-world entity, combining data and the operations that can be performed on that data. This approach enhances code modularity, and reusability, and makes it easier to understand and maintain.
Four Pillars of Object-Oriented Programming:
Encapsulation: Encapsulation involves bundling data (attributes) and methods (functions) that operate on the data within a single unit, i.e., an object. This encapsulation shields the internal implementation details from the outside world, promoting information hiding and reducing complexity.
Abstraction: Abstraction is the process of simplifying complex systems by modeling classes based on essential properties. In Java, abstraction is achieved through abstract classes and interfaces. Abstract classes define common characteristics for a group of related classes, while interfaces declare a set of methods that must be implemented by the classes that implement the interface.
Inheritance: Inheritance is a mechanism that allows a new class (subclass or derived class) to inherit properties and behaviors of an existing class (superclass or base class). This promotes code reuse and establishes a hierarchy, facilitating the creation of specialized classes while maintaining a common base.
Polymorphism: Polymorphism allows objects of different types to be treated as objects of a common type. This is achieved through method overloading and method overriding. Method overloading involves defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters within a class, while method overriding allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass.
Java Implementation of OOP Concepts:
Classes and Objects: In Java, a class is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines the attributes and methods that the objects of the class will have. Objects are instances of classes, and each object has its own set of attributes and methods. Classes in Java encapsulate data and behavior, fostering the principles of encapsulation and abstraction.
Abstraction in Java: Abstraction in Java is achieved through abstract classes and interfaces. Abstract classes can have abstract methods (methods without a body) that must be implemented by their subclasses. Interfaces declare a set of methods that must be implemented by any class that implements the interface, promoting a higher level of abstraction.
Inheritance in Java: Java supports single and multiple inheritances through classes and interfaces. Subclasses in Java can inherit attributes and methods from a superclass using the extends keyword for classes and the implements keyword for interfaces. Inheritance enhances code reuse and allows the creation of specialized classes while maintaining a common base.
Polymorphism in Java: Polymorphism in Java is manifested through method overloading and overriding. Method overloading allows a class to define multiple methods with the same name but different parameters. Method overriding occurs when a subclass provides a specific implementation for a method that is already defined in its superclass. This enables the use of a common interface for different types of objects.
Final Thoughts:
Object-oriented programming and its concepts form the foundation of modern software development. Java, with its robust support for OOP, empowers developers to create scalable, modular, and maintainable applications. Understanding the principles of encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, and polymorphism is crucial for harnessing the full potential of OOPs concepts in Java. As you continue your journey in software development, a solid grasp of these concepts will be invaluable in designing efficient and effective solutions.
#javascript#javaprogramming#java online training#oops concepts in java#object oriented programming#education#technology#study blog#software#it#object oriented ontology#java course
3 notes
·
View notes