#Microgravity
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

For years, I have wondered what a fish swimming in microgravity would look like. Finally, my curiosity has been rewarded. Here is a sphere of water in microgravity, complete with a fish. Personally, I am impressed that, despite the fish’s best efforts, the surface tension of the water is strong enough to keep it confined. This may not bode well for microgravity swimming pools at space hotels. (Video credit: IRPI LLC, source)
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Small Tissue Chips in Space a Big Leap Forward for Research
Tissue chips, thumb-drive sized devices that contain human cells in a 3D matrix, represent a giant leap in science.
They can test cells’ response to:
•stresses
•drugs
•genetic changes
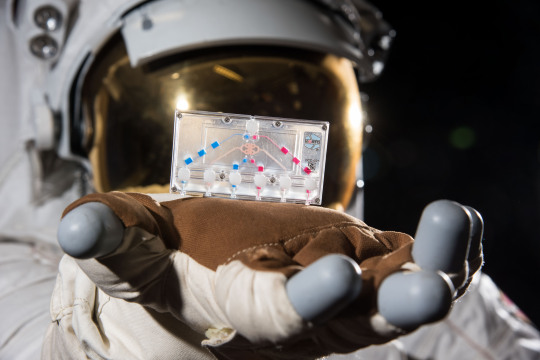
The Tissue Chips in Space initiative seeks to better understand the role of microgravity on human health and disease and to translate that understanding to improved human health on Earth.
This series of investigations to test tissue chips in microgravity aboard the International Space Station is planned through a collaboration between the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) at the National Institutes for Health (NIH) and the National Laboratory in partnership with NASA.

Many of the changes in the human body caused by microgravity resemble the onset and progression of diseases associated with aging on Earth, but in space, changes occur much faster. Scientists may be able to use tissue chips in space to model changes that take months or years to happen on Earth.
A tissue chip needs three properties, according to Lucie Low, scientific program manager at NCATS. “It has to be 3D,” she explained. “It must have multiple different types of cells, and it must have microfluidic channels. Essentially, you get a functional unit of what human tissues are like, outside of the body,” said Low.
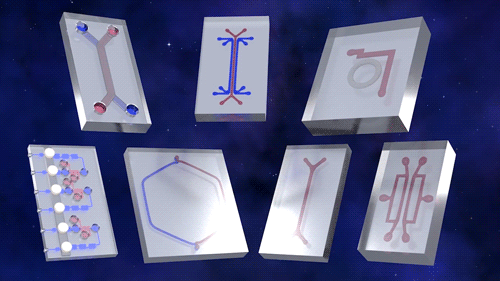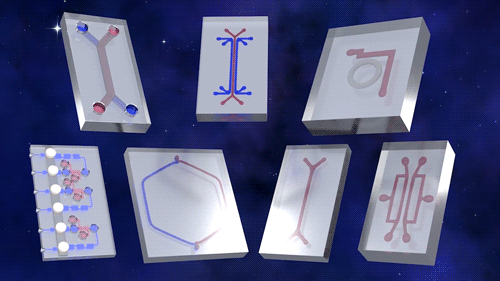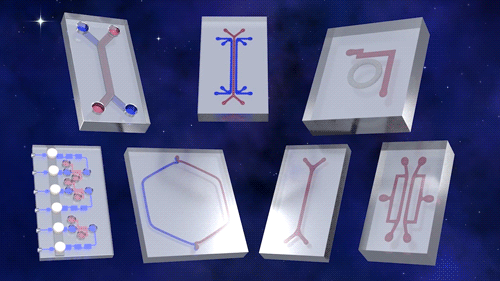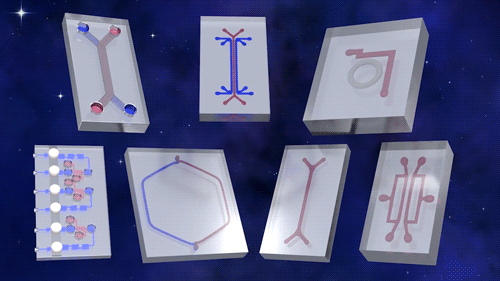
As accurate models of the structure and function of human organs, tissue chips provide a model for predicting whether a drug, vaccine or biologic agent is safe in humans more quickly and effectively than current methods.
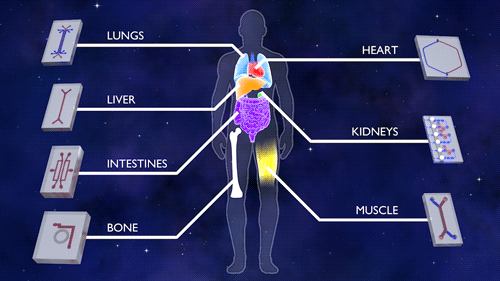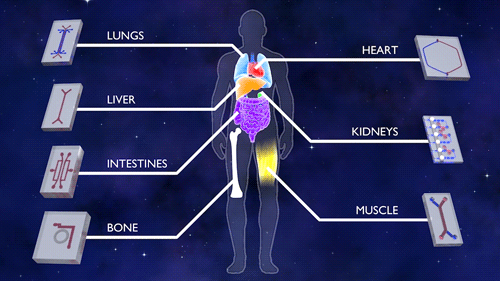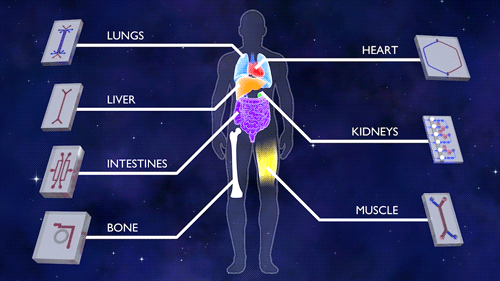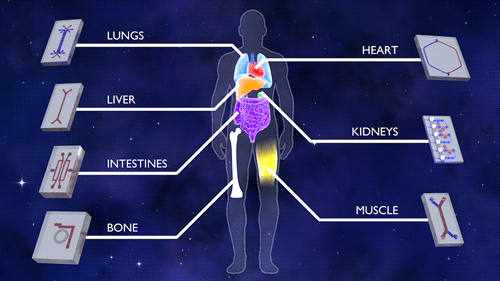
This first phase of Tissue Chips in Space includes five investigations. An investigation of immune system aging is planned for launch on the SpaceX CRS-16 flight, scheduled for mid-November. The other four, scheduled to launch on subsequent flights, include lung host defense, the blood-brain barrier, musculoskeletal disease and kidney function. This phase tests the effects of microgravity on the tissue chips and demonstrates the capability of the automated system.
All five investigations make a second flight about 18 months later to confirm use of the model, such as testing potential drugs on the particular organs. Four more projects are scheduled for launch in summer 2020, including two on engineered heart tissue to understand cardiovascular health, one on muscle wasting and another on gut inflammation.
Ultimately, the technology could allow astronauts going into space to take along personalized chips that could be used to monitor changes in their bodies and to test possible countermeasures and therapies. That would be a major leap forward in keeping astronauts healthy on missions to deep space!
youtube
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo

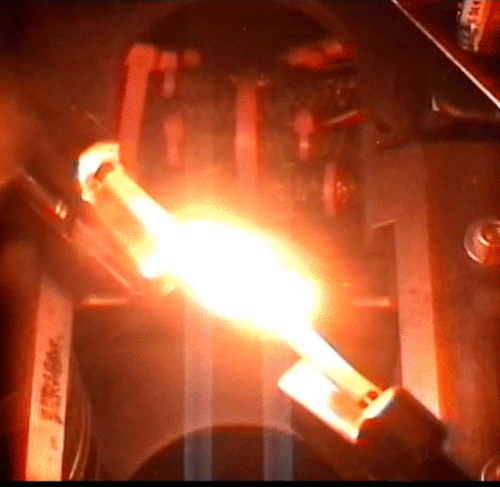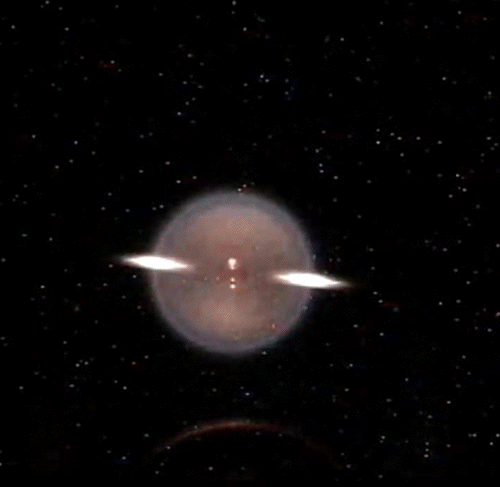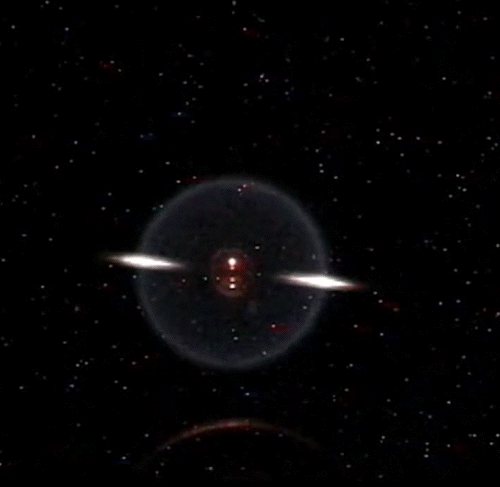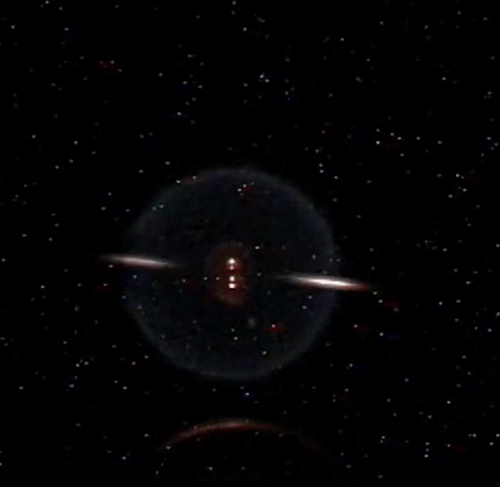

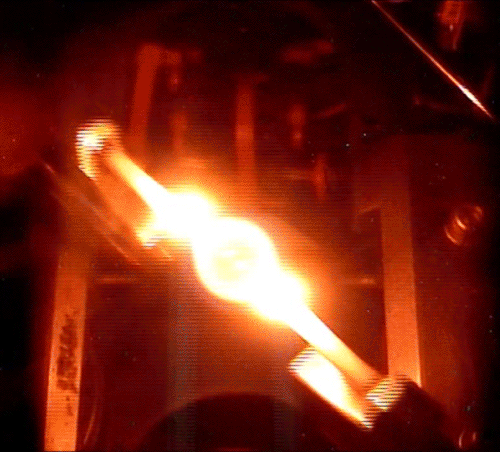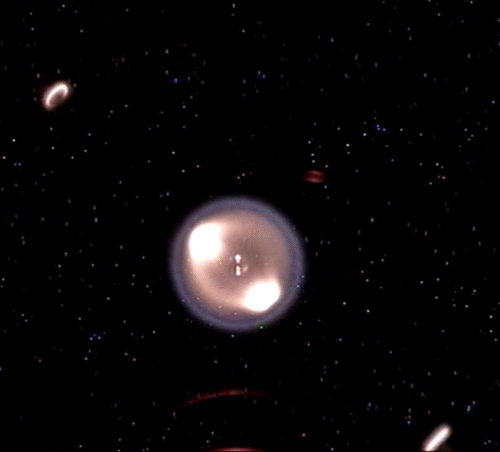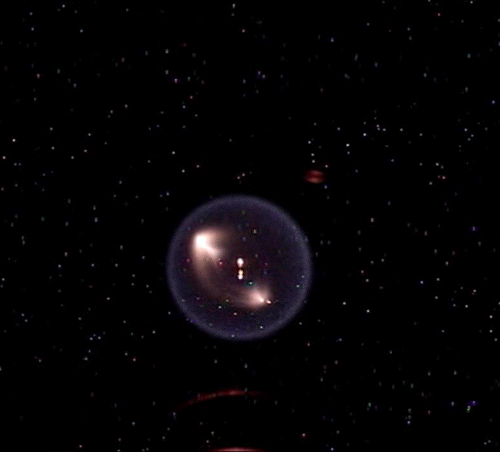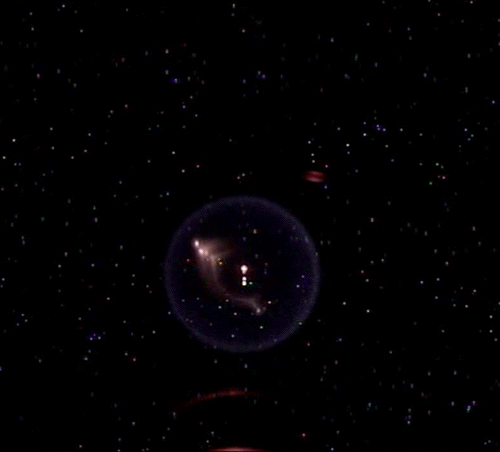
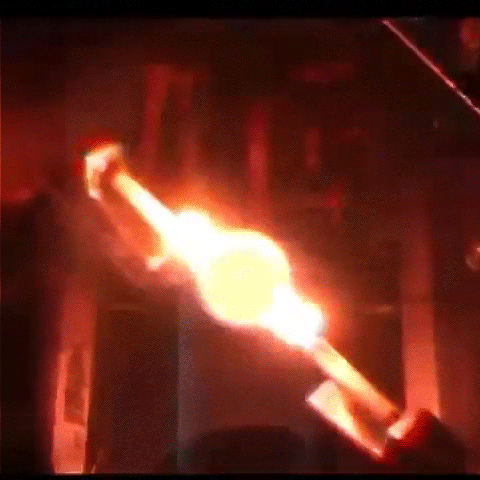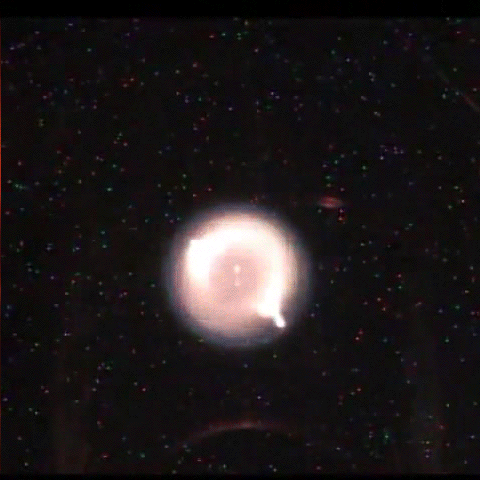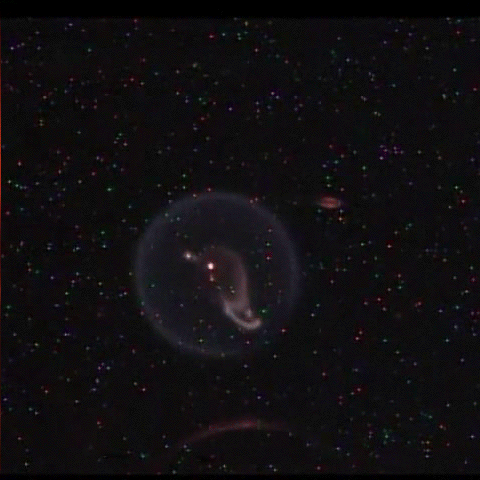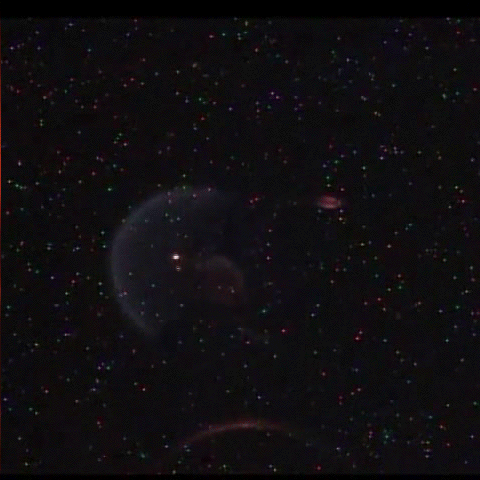
Fundamental Studies in Droplet Combustion and FLame EXtinguishment in Microgravity (FLEX-2)
The Flame Extinguishment - 2 (FLEX-2) experiment is the second experiment to fly on the ISS which uses small droplets of fuel to study the special spherical characteristics of burning fuel droplets in space. The FLEX-2 experiment studies how quickly fuel burns, the conditions required for soot to form, and how mixtures of fuels evaporate before burning. Understanding how fuels burn in microgravity could improve the efficiency of fuel mixtures used for interplanetary missions by reducing cost and weight. It could also lead to improved safety measures for manned spacecraft.
More information: here
Credit: Reid Wiseman/NASA
#Astronomy#ISS#FLEX-2#microgravity#science#physics#flame#fuel combustion#space#gif#NASA#plasma#fire#experiment
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Water Droplet Orbiting a Needle in Space
“This experiment was performed back in 2012 by astronaut Don Pettit on board the International Space Station (ISS) as part of NASA's Science off the Sphere series. And although the set-up may look a lot like a strangely shaped planetary system, the physics here is a little different, because it's the effect of static electric forces, rather than gravitational pull, that's keeping the droplets in orbit.“
This happens because our awesome astronaut rubbed the polyethylene needle with paper to create an electric charge, (similar to rubbing a balloon on your head..) which “captures” the water droplet in an orbit. In the absence of gravity the potential force of the charge keeps the water droplet in orbit.
Here’s an explanation from the astronaut himself. It’s awesome.
VIDEO.
Neat! :D
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo

If you put a bunch of snakes on a plane (for science), you're subjecting them to microgravity. When you subject a cat to microgravity, it rolls over in an attempt to land on its feet. This isn't necessarily true with every animal. Some snakes, for example, seem to attack their own bodies.
Read why here, by Jason G. Goldman at io9.
EDIT from pavender: The snake in the gif is NOT attacking itself. It is "merely exhibiting a coiling response in an effort to regain their sense of grounding."
398 notes
·
View notes
Photo

“Four sequential video frames of the rat snake...in microgravity.” Reptiles in microgravity. Zoological science. 1993.
348 notes
·
View notes
Photo

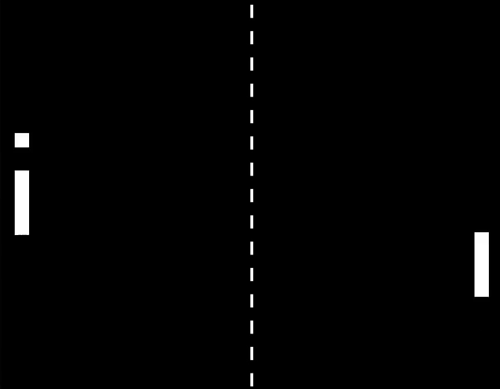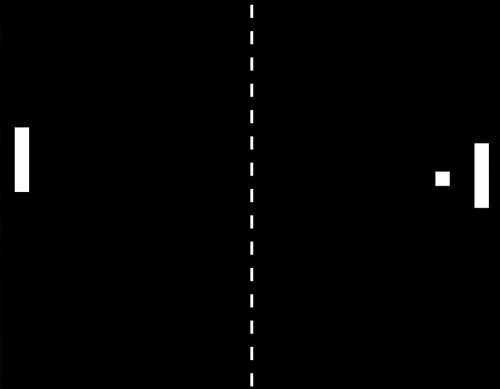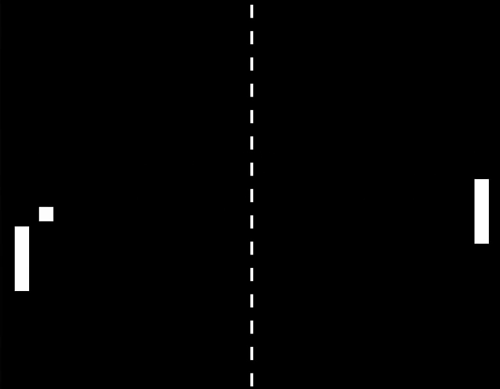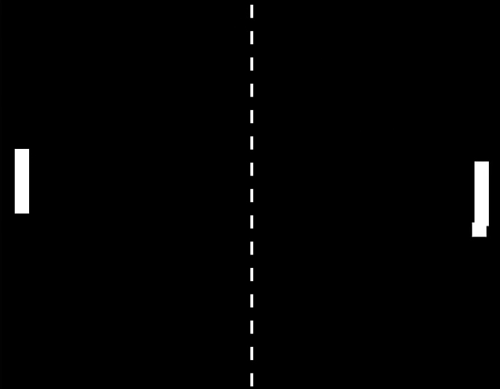
In zero gravity, ping pong becomes real-life pong, because with no gravity to alter its course, the ball just keeps travelling straight in the same direction.
Watch the video of Kevin Fong trying to play ping pong in space.
345 notes
·
View notes
Photo

How a flame burns in microgravity.
Video taken during an experiment performed at NASA's Glenn Microgravity Drop Facility.
326 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The microgravity environment of space is an excellent place to investigate fluid properties. In particular, surface tension and capillary action appear more dramatic in space because gravitational effects are not around to overwhelm them. In this animation, astronaut Don Petit injects a jet of air into a large sphere of water. Some of the water's reaction is similar to what occurs on Earth when a drop falls into a pool; the jet of air creates a cavity in the water, which quickly inverts into an outward-moving jet of water. In this case, the jet is energetic enough to eject a large droplet. Meanwhile, the momentum, or inertia, from the air jet and subsequent ejection causes a series of waves to jostle the water sphere back and forth. Surface tension is strong enough to keep the water sphere intact, and eventually surface tension and viscosity inside the sphere will damp out the oscillations. You can see the video in full here. (Image credit: Don Petit/Science off the Sphere)
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

Two rings to shear them all!
This GIF shows a drop of insulin solution contained by surface tension in the Ring Sheared Drop device as part of an experiment conducted aboard the International Space Station. The device pins a drop of liquid between two rings and rotates one while keeping the other stationary to create shear flow, or a difference in velocity between adjacent liquid layers. Researchers used the device to study protein aggregates called amyloid fibrils, which may be related to diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and type 2 diabetes.
Scientists investigating the mechanisms of certain diseases on Earth must contend with the forces of gravity and the interaction between liquids and solid containers. These forces differ from such interfaces in the body, such as those in arteries and brain tissue, and can affect results. The Ring Sheared Drop investigation team developed a device that uses surface tension rather than a solid container to hold liquids, something possible only in microgravity!
Fluid extracted after each run will return to Earth aboard a Dragon capsule on September 30 so researchers can determine the extent of protein fibril formation, study their structure, and compare both to what happens in ground-based controls. Results could improve the fundamental understanding of how amyloid fibrils form and are transported, as well as the effects of shear at fluid interfaces relevant to conditions in the body.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#space#science#microgravity#NASA#International Space Station#research#health#medicine#experiments#gif
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo
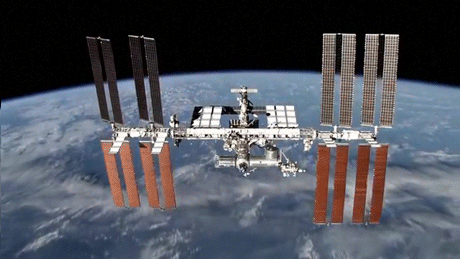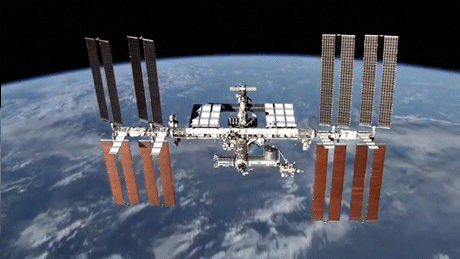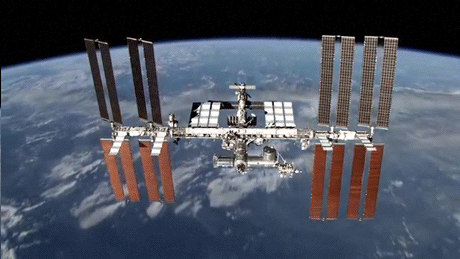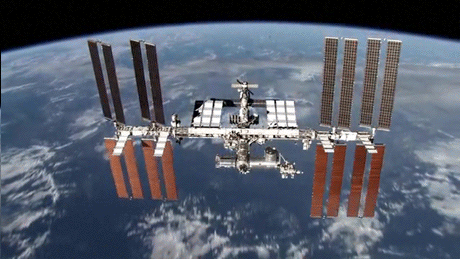
15 Years of the International Space Station
The first International Space Station component, the Russian Zarya module, was launched in November 1998. In the 15 years since, NASA and its global partners have built a world class orbiting laboratory, establishing a continuous human presence in space since 2000 and paving the way for future exploration beyond.
Credit: NASA
780 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Lines of Microgravity
©Raymond P Sussmann
215 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Three South Carolina high school students designed a science experiment that's going to be carried out on the International Space Station.
#spacex#microgravity#iss#science#water#space#orbit#falcon 9#dragon#student#competition#experiment#crs-10
204 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Flames look a little different in space. On Earth, gravity causes a candle flame to be teardrop-shaped, and carries soot to the flame's tip, making it yellow. In microgravity, where these forces are absent, the flame is spherical, soot-free, and blue: http://1.usa.gov/1u7Z9eK
194 notes
·
View notes
Photo
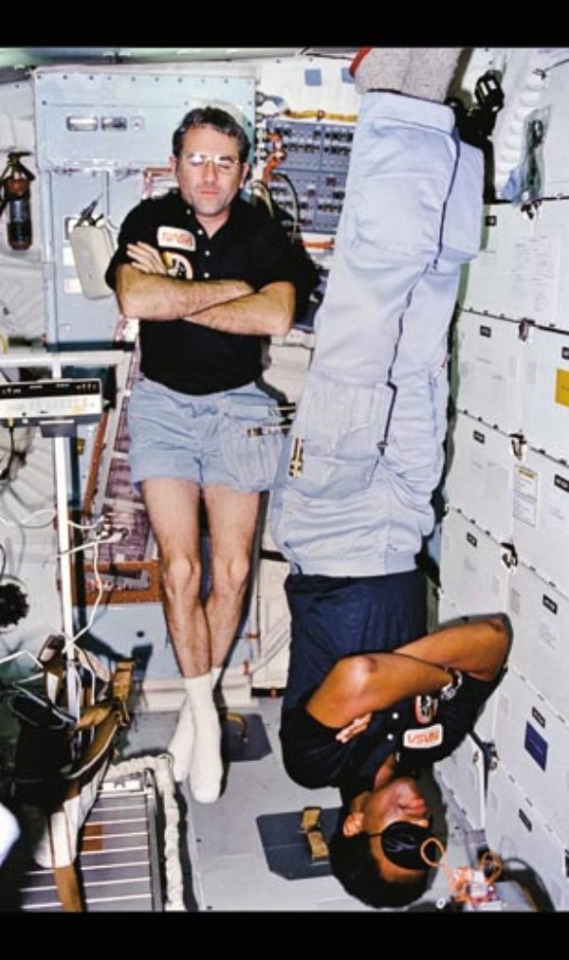

Sleeping in microgravity environment
via reddit
152 notes
·
View notes
Photo

A golden egg floating on board the Spacelab, photographed by Dutch astronaut Wubbo Ockels, 1985.
Source: DLR.
137 notes
·
View notes