Planet 3D explores aesthetics, theory, immersive environments, innovation, and body and brain interfaces as they relate to artistic practices in new and emerging media. Ellen Pearlman received her PhD from the the School of Creative Media, Hong Kong City University.
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Control The Social Life of Mice With Light
Using just optogenetic light scientists at NorthWestern University changed the social behavior of mice.
youtube
For the first time ever, Northwestern engineers and neurobiologists have wirelessly programmed -- and then deprogrammed -- mice to socially interact with one another in real time. The advancement is thanks to a first-of-its-kind ultraminiature, wireless, battery-free and fully implantable device that uses light to activate neurons. This is the same tech used for wireless payments. Interesting.
This paper represents the first time we've been able to achieve wireless, battery-free implants for optogenetics with full, independent digital control over multiple devices simultaneously in a given environment," said Northwestern bioelectronics pioneer John A. Rogers, who led the technology development. "Brain activity in an isolated animal is interesting, but going beyond research on individuals to studies of complex, socially interacting groups is one of the most important and exciting frontiers in neuroscience. We now have the technology to investigate how bonds form and break between individuals in these groups and to examine how social hierarchies arise from these interactions."
"As they move around, the fibers tugged in different ways," Rogers said. "As expected, these effects changed the animal's patterns of motion. One, therefore, has to wonder: What behavior are you actually studying? Are you studying natural behaviors or behaviors associated with a physical constraint?"
When mice were physically near one another in an enclosed environment, Kozorovitskiy's team wirelessly synchronously activated a set of neurons in a brain region related to higher order executive function, causing them to increase the frequency and duration of social interactions. Desynchronizing the stimulation promptly decreased social interactions in the same pair of mice. In a group setting, researchers could bias an arbitrarily chosen pair to interact more than others.
"We didn't actually think this would work," Kozorovitskiy said. "To our knowledge, this is the first direct evaluation of a major long-standing hypothesis about neural synchrony in social behavior."

You have to pay for the paper, but it is here,
Which begs the question. Can mice become best friends?
youtube
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
If You Say Circle, I Will Walk In A Circle.
2

An example of the sentence “A person walks in a circle” and the language output of an animated pose of a stick figure walking in a circle - Image Carnegie Mellon
Two researchers from Carnegie Mellon made a natural language application that does an animation of a verbal description. They invented a language called “Joint Language to Pose” or JL2P which is a neural architecture that uses 3D pose data with human sentences. The first idea is to use it for movie script pose generation. The animation works with joints like the wrist, or the hip point or neck, or elbow, these kinds of structures. Verbs and adverbs describe the action and speed/acceleration of the action; nouns and adjectives describe locations and directions. They have to be mapped to small movements and then stitched together.

Encoding each movement of the model with math symbols.
The researchers were able to show that show their model generated more accurate and natural animations from natural language sentences than other data driven models.
That’s quite a leap.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Do Player Pianos, IBM Punchcards, Telepathy and Elon Musk’s Neuralink Have In Common?
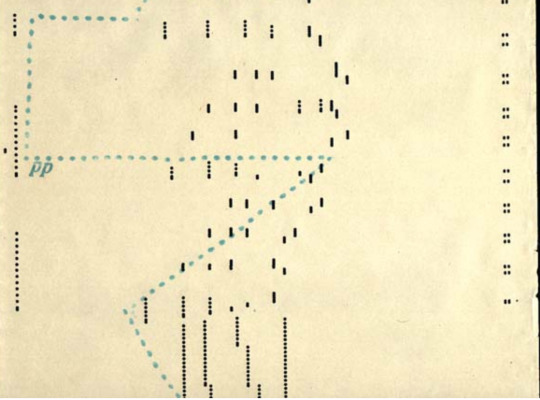
This is a player piano punch sheet or score taken from a rolled up drum. The holes make the keys move. It is a very simple pattern that translates into musical notes.

This is a decoding of “neural spikes” according to scientists at Elon Musk’s brain computer company Neuralink. The spikes are pictured in single boxes, and many spikes when they fire make a pattern. From that pattern you can begin to decode thought. According to Neuralink, “Everything you hear or think is all action potentials, its action spikes and it feels so real, it feels very real.”

This is an early IBM computer punch card, and the basic pattern recognition of the presence or absence of holes in predefined patterns led to everything we know today about computers. Though IBM introduced the first cards in 1928, they had already been in use to ‘program’ cloth in the Jacquard loom in 1804, making gorgeous silks and tapestries.

I think we are basically back in the same position as we were when IBM first made the computer punch card in 1928 in terms of brain research and decoding thought. Neuralink is putting together elements in brain research that 100 years from now, or even 50 years from now will have tremendous repercussions. The company did not invent all of the aspects of technology it is using to put things together, but they did improve upon existing tech and brought it all together.
THE SURGICAL ROBOT

The Neuralink robot doing an implantation
Neuralink works by extracting electrical signals from neurons. In order to do that it has to implant extremely thin wires in the brain to access and read those signals onto a nanochip. Before it can do that, it has to make a precision surgical robot machine operated by neuroscientists to insert the wires - so it did. Apparently there was some DARPA money thrown into the mix somewhere along the way. The robotic surgeon has to implant tiny wires in between blood vessels and neurons, not on them. This can only be achieved through microscopes and nanometer precision. The implant needle is 24 microns small. Tiny threads are about 1/10 of a human hair, which is about the same size as a neuron. The needle to implant the wire is 24 microns small. You can open the skull, insert the threads, put in a tiny chip, and then glue the skull shut. The chip functions as a wireless bluetooth signal.
THE WIRES
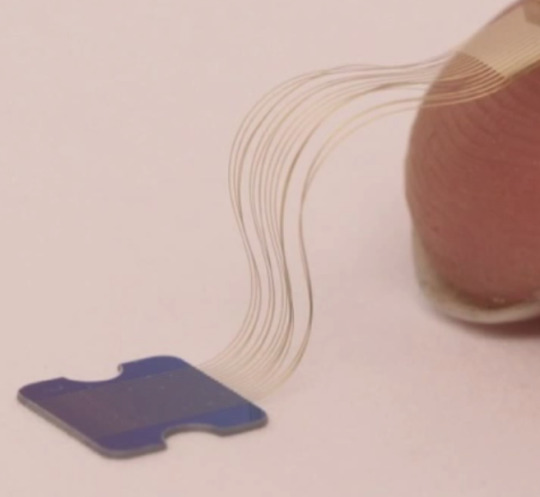
This picture shows thin nano threads pasted onto a fingertip. The thinness of this wire is the big issue DARPA was trying to solve with Moldavian wire from Paradromics, that I previously blogged about in 2017, but Musk beat them to the punch. He wrote about his breakthroughs here.
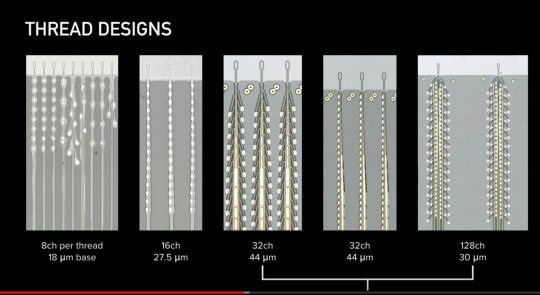
This is the different new design of the threads called a “linear edge”, which are made of layered polymers. They are so are super duper thin they can’t bee seen with a human eye, so they need the special robot that inserts the threads onto the surface of the brain. Another reason is the brain’s surface moves with inhalation and exhalation, and the robot can account for this natural movement. The wires and chip have to record the output from neurons. They are micro fabricated as precisely as the size of an electron beam. It is important to separate the signal to noise ratio in the chips, as they work with nanometer sizes of light. A new design. 350 nanometers,is smaller than visible light.
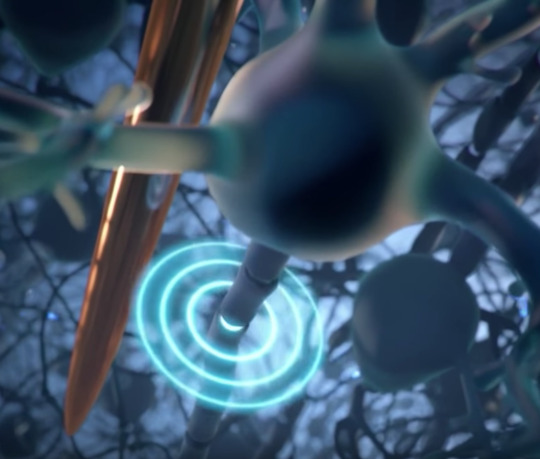

This image is the crux of how Neuralink acquires the signal. Here you see the neuron sending out an electrical spike and a thread next to it picking up the impulse. The electrical spike is the bulls eye. The copper colored needle is actually the implanted wire thread. You need to be 60 microns away or less to read the signals, so you really need to be under the skull. This is a graphic representation
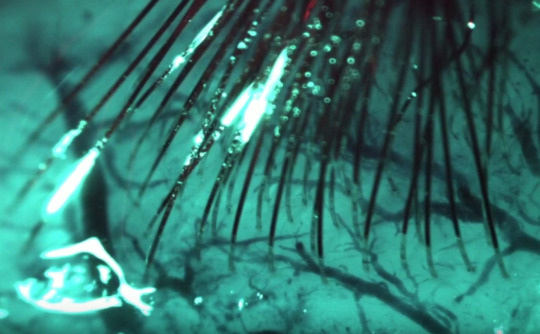
This is a photo of the real thing, with lots of wires precision implanted into brain tissue. If you look really closely you will see they skirt around the blood vessels and neuron branches, but don’t touch any of them. Its sort of like an amazing game of darts, but the goal is to miss the bull’s eye of the vessels.
HISTORY OF IMPLANT CHIPS

This is a short history of brain research about making chips to implant in the brain. At this point the Utah array is still the most used implant chip in academia. Neuralinks chips are way, way faster and smaller. Their research builds on a century of neuroscience research and a decade of neuro engineering research. More advanced applications with advanced innovations will follow.
CHIPS AND PODS
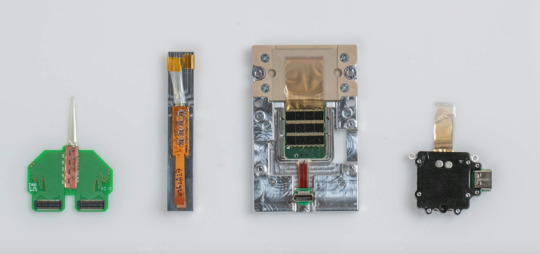
These are early iterations of chips and devices made by Neurlink. Looks like Arduino 101, more or less.

The N1 sensor - the beginning of the sophisticated bean sized implant that goes into the skull and contains the chips.

The actual chips are made on super thin nano wafers in a hermetic environment so there is no dust. They are also super duper thin. A 4 x 4 millimeter chip has a thousand electrodes,and implanting up to 10 chips is feasible. At this point the best FDA approved chip implant for Parkinsons Disease only has 10 electrodes. The Neuralink chips read and write, and are 1000 times more powerful than what is publicly approved. They will get better with newer versions.

Shades of Cyborg Neil Harbisson and his Eyeborg! The Neuralink implant with four chips receive information from the threads, and sends them to an output area for batteries and firmware.

This is the size of the output piece, like an earphone.You can upgrade the firmware on the pod on the ear, it is not the actual implant but connects to it. It will be controlled through an iPhone app. Probably Android as well.
SIGNAL PROCESSING

Waves of neural spikes from an array from implanted threads that are being read out on a computer. monitor The color screen shows the brain at work, and traces of electrodes from single threads. Each trace is a voltage waveform in time. If you focus on one trace, it shows voltage deflections, or spikes per wave. It occurs when a neuron has an action potential, because that is the core information that is recorded. Then the algorithm is decoded, which means capturing the intended information. You just have to think about something and build up the decoding data from that information or thought, and you can begin to interpret movement, memory, and many other different types of experiences.
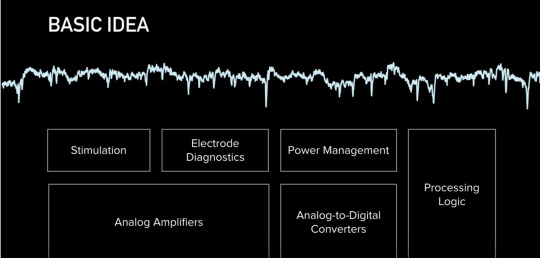
This is a basic diagram of signal processing from the chip - how they get the stuff out of the wires and threads to actually show the spikes. Neuralink said “Everything we care about is contained in the statistics of spikes (inside the brain).” So it goes back to the basic IBM punchcards, or the player piano drum roll - decipher the pattern and you decipher the thought.

Here is their basic logic analogue to digital conversion that is necessary to change action potential spikes to computer code..Calling Alvin Lucier, John Cage, Nam June Paik, David Rosenboom, Richard Teitelbaum - or Duh, this has been going on with the brain, changing analog to digital since 1965 in the music world.
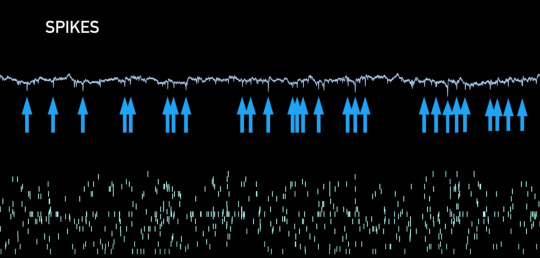
Spike rasters in the brain - The top is the brainwave spikes pointed at by the blue arrows, and the bottom is the beginning of pattern recognition of individual neurons. There should be one pixel per electrode. They are on-chip spike detectors. The methods for detection are thresholding signals or directly characterizing the shape. The Neuralink scientists claim they can identify different neurons from same electrode based on their shape. The engineers had to modify the algorithms and scale them to compress neural data up to 200 times. It takes only 900 nano seconds to compute the signal, faster than the brain knows that the signal even occurred. They can also stimulate any combination of up to 64 channels

One good use of this in the next few years is creating visual feedback for the blind by targeting the visual cortex to create an image better than a dot matrix image - or computer vision basics meets brain wetware. The scientists want to not only read out, but read into the brain. You can read into the brain by passing a current in the electrode. This causes the cell to fire an action potential, like for cochlear implants, or a way for the eye to restore vision. You can also use this technique in the brain to restore the sense of touch or vision. The visual cortex has maps, a spatial map (orange section of the brain in graphic). If you stimulate a point in that area, a blind person sees a point of light or phosphene. The idea is you can stimulate areas of the brain in the visual cortex to resemble a dot matrix level of the world. There are also parts of the brain that control orientation, color, size and speed of moving objects, and once you figure out what they are, and where to stimulate them, you can generate a more comprehensive image that a blind person can experience. Neuralink wants a device with electrodes that are small enough, but with high density that can do better than a dot matrix image.
The first iteration of their implant will have three different types that can go from a mobile device to a mouse or keyboard on a Bluetooth signal. Neuralink needs to get FDA approval. Right now they are working on patients with complete paralysis so it is for serious neurological needs, and idea is to make it really safe.
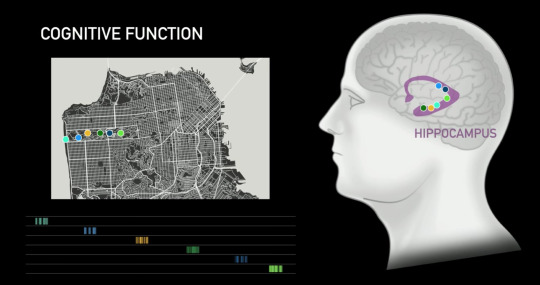
Who needs Google maps when you can tap into someone’s brain algorithm in their Hippocampus which contains spatial orientation. Here is a rendition of someone who really knows San Francisco, and they can send you pattern signals as you wander through the park and direct you telepathically - voila!
THE PURPOSE
Musk gave a number of reasons for his very public video presentation. The first he shamelessly admitted, was to recruit for new talent to Neuralink. He then framed the motivation of his company as wanting to solve brain ailments, spinal disorders, or catastrophic injuries like a broken neck or spine,. He admitted it won’t happen quickly, and kept mentioning the need for FDA approval. He wants to make his devices as cheap and accessible as a Lasik-like device.
“Hopefully,” he said, “AI is a benign scenario. You can chose to have a neural implant if you want, it is not a mandatory thing... We already have digital super intelligence - our access to a computer and a smart phone. The input speed in the human brain is fast, due to our vision, but the output speed is slow because we have to type information into a computer. We are constrained by human bandwidth and mechanics. “
But then he dropped the Neuralink AI bomb - that he believes that we “ultimately (will) achieve a symbiosis with artificial intelligence” (if you want it at a civilization level scale). Then he added, “two people with Neuralink could have telepathy, a new kind of communication, conceptual telepathy, it has to be consensual”.
So the new “me too” movement will concern having consensual telepathy #metooconsensualtelepathy.
*Screen shot photos all taken from publicly available Neuralink YouTube video here.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
In, Out, and About the Brain
This post looks at research in both invasive and non invasive methods for detecting what is going on inside our brains. It examines developments in speech reconstruction, health monitoring , silk brain implants, and capturing the visions of your imagination.
Speech Reconstruction
Electrodes were implanted surgically into a subject’s brain to simulate and then understand computer generated speech usually by counting from one to ten. With the help of computational neural networks, simple words were reconstructed that were 75 percent accurate just through the pattern of neurons firing. This is a very complex procedure, as information had to pass between layers of chips and human brain tissue to infer and reconstruct the sounds. The authors stated “ Reconstructing speech from the human auditory cortex creates the possibility of a speech neuroprosthetic to establish a direct communication with the brain.”

Various layering between implant, brain tissue and computation to infer speech
What was so cool about this experiment is it is accompanied by a neuroacoustic library of code and recordings using ielectroencephalography (EEG), electrocorticography (ECoG) and magnetoecnephalography (MEG).
If you click this link, or this one, you can actually hear squeaky weird reconstructed counting of one to nine, or synthesized human speech created by neurons firing in the brain through specific patterns.
Touch
In 2016 in an experiment with direct brain implantation at the University of Pittsburg, scientists put sensors in a mind-controlled robotic arm producing the sensation of touch in a paralyzed man. This let him experience subtle pressure in his own fingertips when the artificial ones were touched.

University of Pittsburgh researcher Robert Gaunt prepares Nathan Copeland for research testing.TIMOTHY BETLER/UPMC/PITT HEALTH SCIENCES VIA AP
Nathan Copeland had a broken spinal chord, so small chips were implanted in his brain to relay electrical signals that produce movement. Sensors were packed inside the prosthetics, then electrodes were implanted in Copeland’s brain at the site that controls haptic sensation. Electrically stimulating those cells worked even a decade after his accident, meaning the cells were still partially viable.
New Implant Technology
Instead of clunky electrodes and wires, thin silk, meaning all the way down to 2.5 micrometers (0.00025cm) has been developed. This means, as people in the fashion world say, that thinner is indeed better.

How silk electrodes are implanted onto the brain
Since the brain is basically wet anyway, if saline water is put on top of the implant the silk dissolves, leaving the electrodes exposed and stable, even on top of the curvy part of the brain. The silk breaks down easily, and is reabsorbed back into the body because in essence silk is a fibrous protein.

Silk dissolving on the brain like a pair of faded, bleached jeans.
But it can take a while to dissolve, so graphene, which dissoles more quickly, is also being tried out.

Graphene with electrodes sandwiched in between computer circuits
OpenWater
The most astonishing breakthroughs are continuing to occur in Mary Lou Jepsen’s OpenWater company, a company I have been tracking for a about a year and wrote about here.
Jepsen’s background is in electrical engineering and optics, and includes stints at Apple, Google, Oculus Rift and Facebook. She surmised that the medical diagnostic imaging world, dominated by fMrIs, CT Scans and PET technologies had not really been updated for decades. Using consumer electronics imagining systems and electronics, she reduce the size of an apparatus to scan the brain to about that of a thick headband.
With Jepsen’s background in imaging and optics, she understood that the body is translucent to red light, x-rays, and gamma rays. Out of all of these light sources, red light is the cheapest. but it scatters or diffracts quite a bit, and loses strength and focus. Her solution to this problem is to use holography to recapture the scattering of lightwaves, which can then be mathematically inverted to strengthen the signal. The wavelength of the light that is refocused is 1 micron, which means its possible to record it directly into a hologram. Using technology first developed by Texas Instruments in the 1990s that uses an ultrasonic ping, the light is subtlety changed, and two beams of the same color light make a holographic interference pattern. The hologram is then decoded with blasts of light at one million times a second with double stacked camera chips.

Japanese scientists also trying to figure out what you might be seeing in your brain when you are dreaming.
The brain and body can be scanned out voxel by voxel in different resolutions . Jepsen’s tests surpassed fMRIs, MRIs, all the way down to a few microns, which means they can focus through skull and brain to a single neuron. This means neuron states can be read and written using light alone, without using an invasive probe.

OpenWaters new camera, ultrasonic and laser chips
Currently the testing is going on with rats, but here is where it gets totally interesting. Jepsen brings the research back to Jack Gallants UC Berkeley Lab that I have written about in great depth over the years. She believes if the size can be brought down and the image and resolution brought up, we can look at images of thought. She also referenced the work done by Japanese dream researchers (see image above) to bring up those images that usually remain locked inside one’s head. She states a five percent false negative reading, so its pretty accurate. She also mentioned focused ultrasound surgery without incision, very Star Trekky.
Jepsen states telepathy is within reach now, and the technologies to assist that are big data and machine learning. She actually asked “what if we could dump the raw images in our brains out to each other? How do we handle being able to see each other’s thoughts and dreams?” She sees it as the “democratization of healthcare and telepathy”, a very optimistic view.

Mary Lou holding a mock up of potential Open Water headband with optical devices
#Ellen Pearlman#planet3d#new aesthetic#openwater#Mary Lou Jepsen#brain implants#Brain Hacks#speech reconstruction#brain silk
0 notes
Text
If You Can Read My Thoughts I’ll Take Your Job
As new devices are developed to ‘read’ thoughts without invasive means, AI is speeding along developing imitation newscasters. As tech monitoring moves inward towards cognition, simulation and simulacra moves outward towards artifice and puppetry.

Arnav Kapur, wearing AlterEgo selects which channel to watch on TV just by thinking about it. Looks like the History Channel won the challenge.
AlterEgo Reads Your Thoughts
A new device named “AlterEgo” developed by MIT student Arnav Kapur uses subtle neuromuscular movements on the face, known as inner articulatory muscles to interpret thought. AlterEgo describes itself as a “non-invasive, wearable, peripheral neural interface that allows humans to converse in natural language with machines, artificial intelligence assistants, services, and other people without any voice—without opening their mouth, and without externally observable movements—simply by articulating words internally”
The articulatory muscles are able to be interpreted into thought for words from the speech system. This occurs when one subconsciously forms words one sees when reading text. The device picks up very subtle myoelectrical pulses and it was painstakingly trained in the lab to interpret about 100 words, such as the numbers 1 to 9, and the words add, subtract, reply and call.
Once the device was able to pick up myoelectrical pulses, Kapur focused on developing a data set to train AlterEgo to recognize signal signatures for various words. It was a laborious process — someone had to sit in a lab wearing the device and silently speak specific words until the computer mastered them.

Going into a store Kapur is able to keep a running tab on his bill with thre prices showing up as neon green numbers on screen- photo courtesy MIT Media Lab
The device cannot read one’s mind, and can only work if the wearer chooses to have it work. The point is to give feedback to the user “through audio, via bone conduction, without disrupting the user's usual auditory perception, and making the interface closed-loop. This enables an human-computer interaction that is subjectively experienced as completely internal to the human user—like speaking to one's self.” Its a great idea to use for those who are speech impaired or paralyzed for sure.
AIs Deliver the News In China

This AI Zhang Zhao displays typical traits of humility. even though he is an English language AI, where traits of humility are rare
Using machine learning, NLG (natural language generation a sub-branch of natural language processing — NLP) and GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), researchers in China have created digital composites created from footage from human hosts that read the day’s news using synthesized voices.

Mr. Zhang’s doppleganger does not look too happy about being created just to lower production costs
Then there is Zhang’s competitor, Qui Hao also modeled thorough AI but only for Chinese language speakers

Qui Hao gets the Star Wars treatment

Hao is slightly more chunky, has no glasses and has more wing tipped ears than Zhao

Qui Hao Alpha (the real one) in front pleads with his boss (off camera) to be able to keep his job against his AI competitor (behind) because he (Alpha) has ‘richer emotions”
So will there be a scenario where you just think your thoughts and it gets translated into an AI doppleganger who says what you mean? Great for the ultimate couch potato who gets to stay and home and just think, while the AI goes off and does all the heavy lifting.
0 notes
Text
Finally - Brain Image Formation As Art

Pierre Huyghe, via Serpentine Galleries/Kamitani Lab/Kyoto University and ATR
The artist Pierre Huyghe has made, with the help of Kamitami Lab/Kyoto University and an fMRI, art works of voxel and machine learning representations of reconstructed images of how the brain perceives the world. This is a development Planet 3D has been tracking for years, and its great to see it made it into the big time.
Katami Labs in Kyoto states on their homepage, “Brain signals can be seen as “codes” that encode our mental contents. We study methods for modeling brain functions and representations using information science and technology including machine learning and artificial neural networks. Our approach is based on data-driven predictive models that relate brain data and mind states via analysis of massive neural, behavioral, and multimedia data. Using these models, we aim to understand basic principles of neural information processing, and seek to develop real-life applications such as brain–machine interfaces that exploit decoded brain information.” The newest incarnation of the lab came into existence in 2015, and this is the place Huyghe collaborated with for his works.

An image from the Kamitami lab of a swan. Love the green head.
The artist never shows the original of what the images are all about, but this type of voxel reconstruction has been around since 2011 at Jack Gallant’s Lab at UC Berkeley.
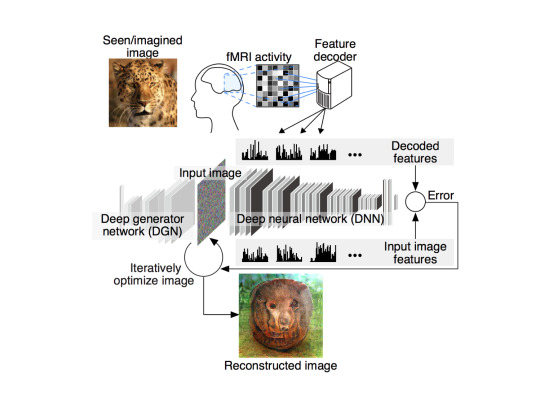
The actual steps in using an fMRI to code and decode an image according to Katami’s Lab, including the new DGN, or deep generator network
The video that shows the images over time can be accessed here - The lab says, “To reconstruct visual images, we first decoded (translated) measured brain activity patterns into deep neural network (DNN) features, then fed those decoded features to a reconstruction algorithm. Our reconstruction algorithm starts from a given initial image and iteratively optimizes the pixel values so that the DNN features of the current image become similar to those decoded from brain activity.” The actual paper written in 2017 states, “Here, we present a novel image reconstruction method, in which the pixel values of an image are optimized to make its DNN features similar to those decoded from human brain activity at multiple layers. We found that the generated images resembled the stimulus images (both natural images and artificial shapes) and the subjective visual content during imagery. While our model was solely trained with natural images, our method successfully generalized the reconstruction to artificial shapes, indicating that our model indeed ‘reconstructs’ or ‘generates’ images from brain activity, not simply matches to exemplars.”
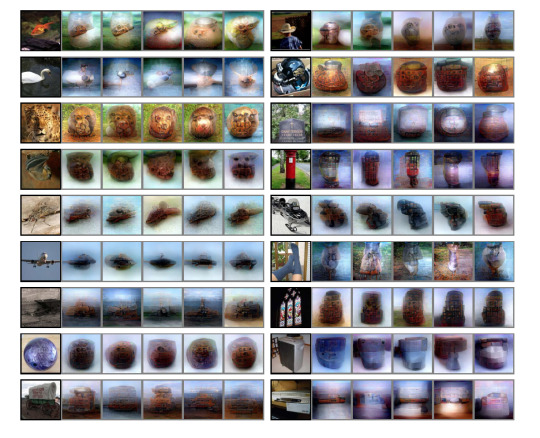
Reconstruction of learning datasets for images. The more simple the image (circle) the better the reconstruction
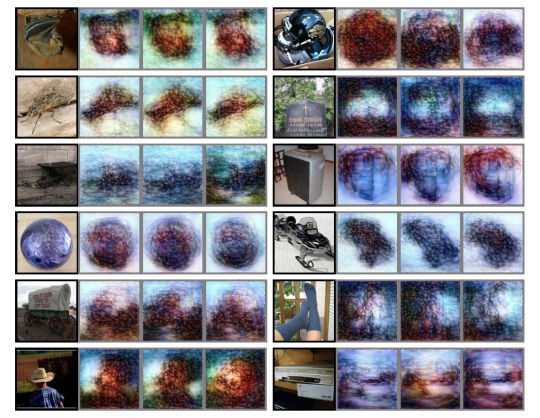

Here are the same images without the DGM (Deep Generator Network) sophisticated smoothing.
Katami’s Github it really fascinating. He gives all the data away, and anyone could theoretically emulate this if they had a nifty fMIRI, which I for one don’t.

Artificial shape reconstruction including the alphabet
What is amazing is how far they have come in emulating basic shapes and letters. Especially letters. This is what Facebook Building 8 has been going ballistic about. Now its here. So “Is There A Place In Human Consciousness Where Surveillance Cannot Go?”. Hmmmm
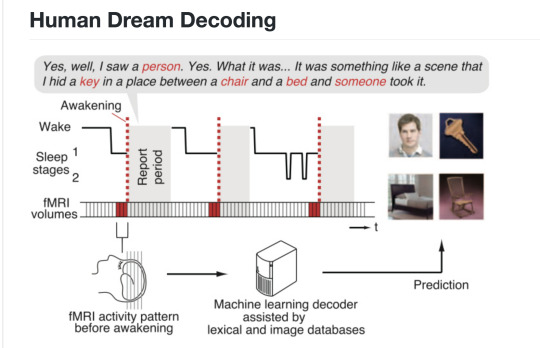
Katami’s work from 2013 in decoding images from dreams.
0 notes
Text
Hold Onto Your Memory Hat

Image from [email protected] - note the cute butterfly to make it a warm and fuzzy picture, instead of a despicable Dr. Doom-like image
DARPA wants to write in, or augment your memory code, a development they have been pursuing since 2013 with the Restoring Active Memory Program (RAM). This also includes bolstering the efforts of their collaborators. Robert Hampson, a professor at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center says that that without memory, one loses a sense of self. In a compelling experiment he was able to achieve “the first successful implementation in humans of a proof-of-concept system for restoring and improving memory function via facilitation of memory encoding using the patient's own hippocampal spatiotemporal neural codes for memory.”

Feeding back an exact pattern match of memory from Hampson’s lab
To do this, he focused on epilepsy patients, because many in that population work with therapies using electrodes already implanted in their brains to control seizures. This approach was preceded on the success of numerous animal studies demonstrating how the techniques of pattern matching neurons worked. While undergoing hospital medical procedures, the study asked patients to play video games that involved memory activities. The researchers recorded the activity of specific clusters of neurons in the hippocampus. When they tested patients using a pattern they had extracted from their very own hippocampus, not a randomized pattern, they could improve short term memory in about 35 percent of test subjects. The goal of the study is to help people with stroke, brain injury and memory loss from the diseases of aging.

The shape of neurons (green) and the synaptic connections of the neuron (white) of a zebra fish, part of ongoing research at University of Southern California on memory.
The way the study was carried out is the subjects were shown a photo with an image. After a short pause they were asked to choose the photo out of group including other random photos, as per the photo of someone choosing the monarch butterfly above. During this time span their neural patterns were recorded, focusing particularly on when they selected the correct answer. Then, after 75 minutes the subjects were shown a new set of photos, one of which included the original photos. When the subjects were stimulated with the frequency of their own patterns of correct answers, they were able to identify the correct photos with a 35 percent higher accuracy for this type of short term, episodic memory. These patterns are referred to as “spatiotemporal firing of neural ensembles”.

Figuring out MIMO Models in rats, picture from Frontiers in Neuroscience between two different rats
This is not entirely new research, as DARPA and their affiliates have already been testing it on individual humans since 2015, and research on rats in 2013 and 2011. Scientists discovered short term memory in humans was like a type of RAM computer memory. The memory is created from sensory information in the hippocampus that also includes the critiical perception of space and time. That consortium of information is held briefly, and if it is accessed again and again it becomes more of a long term memory. The neuron signal moves from a mapped section of the hippocampus called CA3 to a different section, CA1. It is by recreating the CA3 to CA1 signal that an increase in short term memory occurs. This pattern, once understood, can be recreated with an algorithm. This algorithm and process is called the MIMO model, or multi-input, multi-output nonlinear model. If you want to figure out how to make one of these MIMO models, this publication from Sweden is very helpful, but not something you can assemble on your own.
So short term memory patterns can be recorded and replicated. I can’t wait until is as easy to changing your hat as to change your memory.
0 notes
Text
OpenWater - A FloodGate Of the Mind

Mary Lou Jepsen CEO of OpnWatr does artist James Turrell - or is she really just inside a colossal, colored fMRI?
It began with musician Peter Gabriel thinking about a day in the not so distant future when the world will morph into a matrix of ‘visible thought’. He named that day “Open Water - the Internet of Visible Thought”.
Gabriel thought long and hard about this idea, referencing two sources to arrive at his conclusion. The first was the work of Berkeley professor Jack Gallant who is known for mapping visual thoughts, or what he calls the ‘semantic brain’, a topic I blogged about previously on Planet 3D here. His second source involved the work of researcher Mary Lou Jepsen, formerly of Facebook/Oculus, Google X, Intel and MIT Media labs, where she has worked for decades on LCDs and optical displays. Gabriel realized that if Gallant’s work could be enhanced with “optical techniques (and) the advantages of consumer electronics can really assert themselves, the power of AI algorithms will do the rest. This science-fiction future (of reading thoughts) is not only realisable, but because of enormous potential benefits, will inevitably be realised.”

Mary Lou Jepsen speaking at EmTech, MIT.
He suggested Jepsen create a company, which she did and graciously named ‘Openwater’ or ‘OpnWatr’, right after she resigned from Facebook. OpnWatr aims to transform cumbersome brain scan images made in enormous and expensive fMRIs into consumer sized devices. It does this through using diffuse optical tomography combined with new techniques in depth, resolution, size, and cost.
Jepsen too, was applying the research of Alexander Huth at Jack Gallant’s lab on the semantic brain, calling it ‘telepathic’. The lab’s research had also inspired the use of massive quasi-ballistic photons accelerators that Facebook Building 8′s former director Regina Durbin raved about as a new way to read the semantic brain before she bailed on FBB8 for unknown reasons, something I also covered previously in Planet 3D.
Jepsen wants to up the optical resolution of the semantic brain, making it a billion times stronger in order to track the ‘heartbeat’ of neurons themselves. To do this she had to invent special LCDs or liquid crystal displays and detectors, combining them with special infrared light sources. This process enables the body, and especially blood flow to become translucent. It is also capable of creating a hologram of the brain by inverting the infrared images through the computational process of phase conjugation. Phase conjugation is a mathematical calculation that makes the brain appear transparent down to resolutions of 1 micron. It looks at voxels of neurons, something neither an MRI nor fMRI can accomplish.

Traditional big, cumbersome fMRI machines. Totally old school.
Jepsen, a survivor of a brain tumor, is adamant that she does not want to shock, stimulate, or drill in anyone else’s brain, the opposite of what a lot of other researchers, especially those in the military are proposing for brain-to-brain communications. Instead she is making an LCD enabled ski-hat, or bandage at consumer electronics price-points. Her goal is to make it “1000 times lower in cost, a million times smaller in size” than an fMri. Her investors have given her a five percent chance of doing it, which is good enough for Mary Lou.

Typical infrared beams go through an optical device with just a few being picked up (orange line). The rest are scattered. This is old school
Using this process Jepsen is awed by the possibility of dumping dreams directly into a repository, and unequivocally states it will be used for this type of telepathy in less than 10 years. She is also acutely aware of the profound ethical and legal implications of attempting this. The issues of who can make you wear a thought revealing headset, such as law enforcement, the military, your parents, your spouse, etc., is an open question. Such a device could also be used both for healthcare, and a personal enhancement tools, and predicts the software development will take longer than the hardware development. The end product will be limited mostly by signal to noise ratio, a problem that will eventually be solved.

Image from Nature Magazine on phase conjugation speed affecting the quality of optical focusing of infrared light. Moving towards the new school.
Jepsen also looked very closely at the research in the work on optics of Dr. Lihong Wang and his team at Washington University in St. Louis. They were able to harvest not just one beam of infrared light, but all the normally scattered infra red lights to make a more comprehensive image. According to Washington University’s newsletter “The new TRUE technology combines two techniques: focused ultrasonic modulation and optical phase conjugation. Researchers use a type of mirror to record then time-reverse the ultrasound-modulated light emitted from the ultrasonic focus to achieve the best focus.” They accomplished this by using a pretty complex series of imaging and mirrors and a whole lot of mathematical computations.

How neurons actually scatter light, but now with holograms you can see them more clearly

Image from Nature Magazine better focusing of infrared light mimicking its use on types of tissues - very new school.

Using a holgraphic LCD, scattered infrared rays of light are all recaptured through a voxel (in the center) onto a detector, enhancing resolution - new school interpretations.

Putting a flashlight up to your hand in the dark to see what shines through. Very very old school.
Wang’s team used the technique on a mouse ear and got pretty good results, though all they show in the diagram below is graphs and dots. I would really like to see the EAR, of the mouse and what it looks like, not the photo of the poor little mouse’s head held down by all all those metal thingeys. Its actually a sort of fancy adaptation of putting a flashlight up to the palm of your hand in the dark.

Image from Nature Magazine - optical focusing on the little mouse’s ear. Very new school, despite what the mouse thinks.
Holograms are created from wavelengths of light and be turned into super high resolution images using with LCD chips. They can even focus the light to the size of one neuron which has previously been unobtainable. This technology could eventually replace fMri’s. Right now OpnWatr can focus at a 1000 pixels a second, but has plans to make it much faster. It turns out to be fashionable, incorporating the analytics of big data and AI software, as well as the ready made supply chain trillion dollar LCD business from China.

Pretty looking bendable LCD holographic material. The newest of the new.
The main idea is to have this product embedded in a beanie cap or for internal processes, a bandage you can wrap around your stomach. No needles, surgery, pain, invasion or mess. So seeing into your brain is coming to a movie theater near you in the not so distant future. Better get ready.

Voila - the mind reading beanie cap, or a bandage that wraps around the belly
#new aesthetic#Ellen Pearlman#planet 3d#mary lou jepsen#telepathy#FMRI#holography#openwater#Professor Jack Gallant#alexander huth
1 note
·
View note
Text
All Together Now - 1000 Brains Watching A Movie

Tiera and friend get ready to have their brains analyzed
It was only a matter of time starting from when Marion LeBorgne’s original experiment Cloud Brain, held at the Exploratorium in 2015 that dealt with live time brain data analytics went big time, but I really did not expect it to happen in just two years It has now become Intheon - NeuroTechnology, Anytime, Anywhere
It seems Tim Mullen’s well funded company Intheon, formerly known as Qusp (like the artist formerly known as Prince), which riffed off LeBorge’s breakthrough open source experiment hit pay dirt when it team up with Terra Mater Films and Fathom Events to produce MindGamers. MindGamers is a sci-fi movie about a group of students who discover a way to link minds together through a wireless neural network.

The movie MindGamers and the accompanying MindGamers neurosensors

Tim Mullen at MindGamers premier, footage courtesy VOA

Fun science experiments where someone else controls your brain forcing you to pull the trigger - Note: kids do not try this at home (MindGamers)
At the premier, 500 people in Los Angeles and in 500 in New York wore a brainwave EEG headset that let Mullen and his team at Intheon read the electrical activity inside the brains of 1000 participants simultaneously. After putting on the headset each person was given a small Android tablet to plug it into. A running app then notified the participant it was streaming their brainwaves. Cloud technology measured and recorded measure EEG patterns of focus and how it worked throughout different scenes in the movie.

Interested audience in L.A. with brain sensors watch a movie on mind control

The good old days of just watching movies in 3D without brain monitoring

Audience in N.Y. way more laid back than in L.A., watching their collective brain’s response (photo by Dan Krauss)
What was most interesting is that the government back publication Voice of America (VOA) pushed this article out with exclusive footage, and not a more traditional Hollywood source like Entertainment Tonight. Is this part of the silent but very active arms (brains) race between Facebook, Neuralink, and DARPA/IARPA or even perhaps an unknown something else?

Hot colors (red, orange) mean a big increase in focus. This correlated with a scene in the movie when a woman was going to jump off of a building. It sort of looked like the original Cloudbrain data experiment.

Cloudbrain at the Exploratorium did it first in 2015 . Here people walk around with EEG brainwave sensors while looking at their group data

Movie participant in L.A. in 2017 wondering, “where’s the free popcorn and soda they promised me?”
0 notes
Text
DARPA Throwing Money Left and Right At Brain Start Ups

According to Forbes Magazine, DARPA just laid 18.3 million on a brain start up. The lucky bride is Paradromics who are working on “Massively Parallel Neural Interfaces & Real–Time Decoding” or as they put it, “Broadband For the Brain”. Their goal is to treat the connectivity disorders of “blindness, deafness, paralysis, ALS, and amputation” and that is really great. Very laudable. Then they drop the big “if” - “So what if patients with connectivity disorders could connect their brains directly to a computer?”
Well, as the developers say themselves, its a bit of a pickle because computers work in serial processing, and brains in parallel processing.

Their idea is to take CMOS technology with microtechnology to deal with the issue of single channel vs. massively parallel channels.

Paralysis, they believe, is only a communications error., a very novel and systems analysis perspective. They will be offering “65,000, 32 kHz microwire electrodes for massively–parallel neural recordings.”
Yikes! Sounds painful. They immediately backpedal by posting “Notice: This device is not intended nor approved for human use. It is a scientific tool intended for research purposes only.” Well then, you can’t have it both ways.

A custom CMOS array of low–noise, high–speed amplifiers to which bundles of microwire electrodes are connected. Each microwire consists of a metal–in–glass fiber with an outer diameter of less than 20 µm.
Maybe its because that blue thing wit the Paradromics logo is what they want to put in your head? If you open it up it looks like this:

So from what I can figure out at this point they made a big bulky processor with some itsy thin wires and they want to stick this on people’s brains who are injured, and then connect them to external device. Basically I get it, its like version 1.0 and won’t really work but if they can miniaturize it enough, then it might work. They seemed to have sourced their main material from “an obscure Moldavan company that had developed a way to stretch hot metal and mass-produce coils of extremely thin insulated wires, just 20 microns thick.” Moldavia - wow, now that’s unique.

The core of the idea - super thin connecting wire from Moldavia
They say that their “Neural Input–Output Bus, or NIOB, will be capable of reading and stimulating brain activity from 1 million neurons with an effective data rate of > 1 Gbps.”
So the company started with a 30 something Stanford guy who is trained in nano-tech and neuro-science, they are brining in some big gun Stanford doctor surgeon, another big gun sensor guy and they are giving it a whirl.
Actually, I can’t wait to see where there goes. According to the MIT Tech Review, the DARPA money is throwing a wide net, “looking at “flexible circuits that can be layered onto the brain, sand-size wireless “neurograins,” and holographic microscopes able to observe thousands of neurons at once. “ They have also awarded money to support what they call the Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program: Brown University; Columbia University; Fondation Voir et Entendre (The Seeing and Hearing Foundation); John B. Pierce Laboratory; and the University of California, Berkeley.
Now this is where it gets dicey. Up front it sounds all very normal, but with the new appointees of our government agencies, what, exactly does this mean. According to DARPA’s own website, “The program’s first year will focus on making fundamental breakthroughs in hardware, software, and neuroscience, and testing those advances in animals and cultured cells. Phase II of the program calls for ongoing basic studies, along with progress in miniaturizations and integration, with attention to possible pathways to regulatory approval for human safety testing of newly developed devices. As part of that effort, researchers will cooperate with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to begin exploration of issues such as long-term safety, privacy, information security, compatibility with other devices, and the numerous other aspects regulators consider as they evaluate potential applications of new technologies.
The FDA is in charge of privacy and information security for these areas and devices? Really? Wow, that is going to be dodging all sorts of regulatory bullets in terms of other areas of society. Smart move.
Is this one step further into neuro control or is it only neuro rehabilitation?
#planet3D#Ellen Pearlman#new aesthetic#neuro implant#ALS#brain chip#DARPA#neurotechnology#brain implants
0 notes
Text
2018 - It’s Shaping Up To Be All About How You Feel

This is an Emoshape Affective Toy robotic doll you can construct in 10 minutes that understands your emotions.

This is a totally wired up person having all their thermal image vital signs registered in Dolby Labs. This does not take 10 minutes.
2018 is going to be the year that biometrics, robotics and consumer technology are going meet and greet all over the place.
Emoshape
Emoshape, hails itself as ‘emotions next frontier’ uses a chip with tons of processing power to work with language to generate EPU (emotional processing units). It uses a patent pending technology that creates emotional states and synthetic emotion in intelligent machines. It claims to distinguish between twelve primary emotions: anger, fear, sadness, disgust, indifference, regret, surprise, anticipation, trust, confidence, desire and joy. The emotion recognition classifiers says it achieves up to 94 percent accuracy on conversation. It does this with a microcontroller using real-time appraisal computation with reinforcement learning. An Emotional Profile Graph (EPG) computation functionality allows the AI or robot to experience 64 trillion possible distinct emotional states. Emotional stimuli is stored within the memory bank through emotional patterns or fingerprints.
64 trillion emotional states? Like I don’t have enough to worry about? What does having 64 trillion emotional states actually feel like? It exhausts me just thinking about it.

12 emotions graphed in realtime - great representations for the synesthesiac crowd.

How the colors are assigned - although I beg to synesthesiacally differ
It uses “sound waves of our consciousness” (not sure about that one). To drill down further, the Emoshape has two recognition layers that work at the sentence level and uses an form or evolution of the Ekman emotion classification, first developed in 1993. From what I have seen a lot of people are now redefining that classification, but it does give a basic structure to operate within. It then incorporates a semantic level that refers back to the Emoshape API cloud service based on Patrick Levy-Rosenthal psychobiotic evolutionary theory. I wondered what that was, so I found an article from Trends In Neuroscience which said, “Psychobiotics were previously defined as live bacteria (probiotics) which, when ingested, confer mental health benefits through interactions with commensal gut bacteria.” Interesting. The Neuroscience article goes on to say “Much psychobiotic research is based on rodent models.”

Original Chatty Cathy Mattel dolls and their wonderful wardrobes

Pull the string - and she says 11 different things!

The buffers of how the emotional stacks are weighted and assembled in Emoshape.
However, this part looks quite complex and well thought out. And the flow chart below absolutely amps it up.

But still, it all seems semantically based, like a huge taxonomy of words though there is an API for physical interaction, and a psychophysics API, which at this stage seems to mean a relationship between mental phenomenon and physical stimuli - a pretty wide net for sure .
Dolby Labs
Dolby Labs has been around since 1965, but they now place a high premium on people watching movies. This is so they can show their clients that certain colors, sounds, or frequency ranges will elicit a certain response. Neurophysiologist Poppy Crum run the labs. Affective computing is not new news, but the entertainment industry is now all over this one. Netflix and Hulu at this point use eyetrackers.

Poppy Crum at Dolby Labs
But what do these biosensors really talk about? Well, to begin with a subject is outfitted with a 10/20 brain EEG Cap.

Brainwave EEG headset being fitted on TV host Lauren Goode

Muscle detector and lie detector also being booted up. Thermal images are also captured (see beginning of post)

Raw EEG, GSR and heart rate are all displayed livetime.
Some of the things they discovered that if you are shown a huge screen with flames, your body begins to flush - and that apparently helps shape the stories.
As immersive environments or ‘mixed reality’ grows in influence, it is logical that tracking the emotional responses of users needs to move along as well.
Disney
Disney is now so all over affective emotions and measurements they have teamed with Cal Tech to start using Artificial Intelligence. They work with what they call “factorized variational autoencoders,” or FVAEs, which after observing an audience member’s face for just 10 minutes, can predict how a person will react to the rest of the movie.

It can actually work on any type of time durational data - "We are all awash in data, so it is critical to find techniques that discover patterns automatically," said Markus Gross, vice president at Disney Research. "Our research shows that deep learning techniques, which use neural networks and have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence, are effective at reducing data while capturing its hidden patterns."

Singing Christmas carols - can you pick out the unhappy one? Bonus points - Disney Research is based in.....Pittsburg - with free research trips to Disney Park
However, all is not well in Mickey/Minnie Land. British police have been employing facial recognition emotionally valanced information, and on May 31, 2017 made their first arrest ever based on analysis from the facial recognition technology. In partnership with the company NEC they were monitoring a sporting event of the Champion Leagues finals, and picked out a suspect from the random samples they just happened to be monitoring. Bet that suspect had a really unhappy facial recognition analysis.
#Raw EEG#facial recognition#planet 3d#Ellen Pearlman#new aesthetic#Dolby labs#disney research#emoshape#affective emotions
0 notes
Text
Brains and VR - Like I Didn’t See This Coming?

Halloween costume Neurable
Planet 3D has been tracking immersion and biometrics, specifically BCIs for quite a while. Using BCIs as controllers is not new news. Using BCIs for VR is not new either. But now companies are entering the commercial sphere, and that promises to be interesting. Neurable has recently launched, and its certainly ain’t pretty.

First date night Neurable with HTC Vive
Neurable says “Our approach is science-driven and cross disciplinary, incorporating elements of neuroscience, biology, statistics, machine learning and design to create the ultimate user interface. With Neurable, mixed reality can finally achieve its full potential.” Hmmm, what, exactly does that mean?
Well, they use dry electrodes, which at least saves on the cost of conductor paste or saline solution and clean up gear. It’s wireless, and according to MIT Technology Review “The startup expects to offer software tools for game development later this year, and it isn’t planning to build its own hardware; rather, Neurable hopes companies will be making headsets with sensors to support its technology in the next several years.” So they have already opted out of the hardware, which means no messy import snafus with factories and their deadlines in China.
Their headset seems to work with Event Related Potentials (ERPs) which are difficult to interpret. They are using machine learning to cut down on processing time (I would love to see the hard stats on that!) and they are trying to move away from Alpha, Beta, Theta, Delta, Gamma waves, that don’t tell you much in terms of interpretation, except that they are registering Alpha, Beta, Theta and Gamma waves. . I am not sure what their ERP is about, unless it is the old fall back of the P-300 Mermer signal that Lawrence Farwell and his cohorts in the military cooked up decades ago, when Farwell discovered that when you recognized something (like your mother) your brain spiked a recognition signal in 1/300 of a second (hence the 300 number). Actually, that is pretty much what Neurable did. Their analysis is based on a paper their founder RE Alcaide-Aguirre published in the Journal of Neural Engineering titled “Novel Hold-Release Functionality in a p-300 brain computer interface.” What this means is hold and release, or in layman’s terms start and stop accuracy selection rate was enabled in the p-300 signal - an enormous hurdle for these types of apparatuses.

Mom and Dad can I have one of these for Christmas?
Apparently Neurable also incorporates eye-tracking technology from German firm SMI, so its a one-stop shop for monitoring your vitals. The machine learning aspect is how it intends to work with the patterns of your individual vitals, as opposed to everyone else’s.
This is pointing towards a time where eye tracking, voice, movement, thought, genetics, and other factors, combined with big data and AI and wacky dictatorships and rouge military contingents t could really bring on the dystopic - or not.
0 notes
Text
Drilling Down into Facebook Building 8

Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, the California Institute of Technology, Stanford University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard University, Rice University, University of California San Francisco, UC Berkeley, Northeastern University, Princeton University, University of Waterloo (Canada), University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Arizona State University, Texas A&M University, Georgia Tech, and Virginia Tech are the universities that are now contracting with Facebook to accelerate learning into brain scanning technologies. Regina Dugan, the new director of FB8 is moving ahead so quickly on implementing this project that she has created The Sponsored Academic Research Agreement, or SARA, that allows Facebook to set up research projects within weeks or even days, rather than months. They are especially interested in neuroscience and optical remote sensing.

Regina Dugan visits her alma mater for her BA and Ma - Virginia Tech
Electrocorticography from the Johns Hopkins APL Lab, is an invasive procedure that directly observes neural processing, but the electrodes have to be implanted. fMRIs, like I wrote about in my post on the semantic brain and brain fingerprinting is still viable, but the newest research is now interested in “filtering for quasi-ballistic photons” which supposedly can scan the brain 100 times per second. I first started following the semantic brain in 2013 with my post “Memories, Dreams and Visions - New Interpretations”, but honestly had no idea at that time that DARPA and Facebook would gobble it up like gummy bears for their own purposes. As of this writing Building 8's is advertising for “brain-computer interface engineer”, “neural imaging engineer” to get their party started.

The brain as a series of 0′s and 1′s The brain as a series of 0′s and 1′s
So what is a quasi-ballastic photon? According to Inverse Innovation, “When you point a laser through your finger, it glows because the photons in the laser are deflected away from their original path. Ballistic photons are the rare few that get through your finger and exit where you originally pointed the beam. Quasi-ballistic photons are only deflected a little bit, so if you look around the edge of where the beam was supposed to exit, you can find them. If you can use quasi-ballistic photons to look at brain activity, instead of just ballistic photons, your chances get a lot better at seeing what is happening.”
This means Building 8 and especially its academic partners have to amp up the photons/physics relationship, and get down with some pretty powerful machines. Dugan states its important to use precise non-invasive sensors that don’t have signal distortion even through the hair and skull, and do it by 2019. Really? Right now QBP’s only work on mouse brains taken out of their skulls. In terms of the human animal, apparently it only works in measuring 10 strands of hair thick. So the idea is to build a new measurement QPB machine that amps that up a gazillion fold. This will be a new type of non-invasive, real time neuron imaging tech. By 2019. Good luck!
Can I have my brain back, please? Photo credit Brookhaven Lab
#Ellen Pearlman#planet 3d#new aesthetic#regina dugan#Facebook building 8#quasi-ballistic photons#BCI#FMRI
0 notes
Text
FB Building 8 - “Is there a place in human consciousness where surveillance cannot go?”

Still from “Noor - A Brain Opera” with emotions of frustration (red) and interest (yellow)
I knew it would come to this. After premiering “Noor - A Brain Opera” (Is there a place in human consciousness where surveillance cannot go?) last year, it was just announced this week former DARPA director and research scientist Regina Dugan (who had also been at Google) has joined FB to develop a non-invasive brain computer interface to decode neural activity related to speech - using, among other things research on the semantic brain.

The semantic brain, picture from Nature
The researchers plan to use optical imaging with quasi ballastic photons to create a narrow beam with a new way of detecting blood oxygen levels.

Quasi-ballistic photons - hmm, look familiar? Like in the red emotions of frustration pictured above? Picture from Facebook
Then also this week Elon Musk announced that in 2021 there will be the first human with an internet link in their head - wrong. How about Neil Harbisson and the world’s first skull transmitted painting? Musk thinks Neuralink, his new company will do it first - sorry, the art world already beat him to the punch.

Musk wants to use TCMS, or transcrainial magnetic communication which I referred to in my 2013 Planet 3D post as ‘vulcan mind meld’. Sure he has fancy Neural Dust, merged with high end mesh electronics but that is because he went out and hired another DARPA alum, Paul Merolla, who happened to work as the lead chip designer at IBM on their DARPA-funded SyNAPSE program. Its like old McDonald’s farm in the brain realm - and a DARPA here, and a DARPA there, here a DARPA, there a DARPA, everywhere a DARPA/IARPA - E I E I O.

MIT Tech Review
They will lay these chips down using biodegradable silk, which at least gives silk worms an new factory to output to. This would require neurosurgery, which is invasive. And its open to being hacked, surveilled, and having implanted malware secretly inserted (its a chip after all).

Noor: A Brain Opera
So is there a place in human consciousness where surveillance cannot go?
#planet 3d#Ellen Pearlman#new aesthetic#brain opera#Noor: A Brain Opera#surveillance#Neuro Imaging Surveillance#facebook building 8#Neil Habisson#transcranial magnetic stimulation#semantic brain#darpa#iarpa
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Neural Engineering System Design (NESD), Just In Time Info For Your Brain Gets Real

Image courtesy DARPA
Following up on my post from February 2015, a new DARPA program aims to develop an implantable neural interface able to provide unprecedented signal resolution and data-transfer bandwidth between the human brain and the digital world. The interface would serve as a translator, converting between the electrochemical language used by neurons in the brain and the ones and zeros that constitute the language of information technology. The goal is to achieve this communications link in a biocompatible device no larger than one cubic centimeter in size, roughly the volume of two nickels stacked back to back. However, on a more crude level, this sort of research has been going on for almost half a decade.
DARPA is going to invest up to 60 MILLION DOLLARS in the next four years to build out, and they are OUTSOURCING it like its a start up with security clearance. The stuff is low hanging fruit for the right research lab.

Image courtesy DARPA
All you have to do is go down the the Westin Hotel in Arlington, Virginia and check it out.
The Biological Technologies Office (BTO) of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is sponsoring Proposers Days for the potential proposer community in advance of a planned Broad Agency Announcement (BAA) for the Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) Program. The Proposers Days will be held on February 2-3, 2016 at The Westin Gateway Hotel, 801 N. Glebe Road, Arlington, VA 22203. Advanced registration is required.
The Proposers Days objectives are to:
•• Introduce the science and technology community (industry, academia, and government) to the NESD program vision and goals;
•• Facilitate interaction between investigators that may have capabilities to develop elements of interest and relevance to NESD goals; and
•• Encourage and promote teaming arrangements among organizations that have the relevant expertise, research facilities and capabilities for executing research and development responsive to the NESD program goals.
The Proposers Days will include overview presentations, teaming sessions, and a poster session where participants will be provided an opportunity to present their research.

Image courtesy DARPA
Darpa says among the program’s potential applications are devices that could compensate for deficits in sight or hearing by feeding digital auditory or visual information into the brain at a resolution and experiential quality far higher than is possible with current technology. They have a range of proposals and potential research interests already lined up.
What they really want to do is enable this: “The Neural Engineering System Design (NESD) program seeks innovative research proposals to design, build, demonstrate, and validate in animal and human subjects a neural interface system capable of recording from more than one million neurons, stimulating more than one hundred thousand neurons, and performing continuous, simultaneous full-duplex (read and write) interaction with at least one thousand neurons in regions of the human sensory cortex.”
They have further broken it down into two areas of expertise:
Technical Area 1, Neural Transducers and Algorithms, focuses on the scientific and technical advances along with their proofs of principle and function to inform and enable the final design of the NESD system.
Technical Area 2, Hardware, Prototyping, and Manufacture, focuses on the design, prototyping, integration, fabrication, and test/validation of the NESD components and overall system/platform.
If you thought simple network surveillance was not to be believed, wait until this effort blossoms into the real deal - or coming to a cortical modem movie theater near you in the not too distant future.
0 notes
Text
Facial Recognition: Just As Easy As Driving Your Car!

It’s official. New York State, and most likely other locations will match faces, cars, drivers licences and social media accounts. With non-stop cameras running 24/7 there will soon be petraflops of information collected on just about everybody coming in via bridge and tunnel to the Big Apple.
The call for proposals by the state reads:
The Authority is interested in implementing a Facial Detection System, in a free-flow highway environment, where vehicle movement is unimpeded at highway speeds as well as bumper-to-bumper traffic, and license plate images are taken and matched to occupants of the vehicles (via license plate number) with Facial Detection and Recognition methods from a gantry-based or road-side monitoring location.
Since the proposal wants to place these trackers at all seven bridges and tunnels into New York City, it gives a new meaning to the term “bridge and tunnel” or B&T, best known from the movie “Saturday Night Fever.”

John Travolta, an original B&T kinda guy - go Bay Ridge!
Although the request for proposal was put out by the Cuomo administration, its really interesting to see the links these types of technologies have to the Trump administration.

Michael Dougherty who is now part of Homeland Security stepped away from his job as CEO of the Security Identity & Biometrics Association, a lobbyist group for facial recognition technologies. Maybe that is the reason the site has not been updated since June, 2016, except for a few tweets.

Then there is John Sanders, who was the TSA's Chief Technology Officer, and jumped to the board of Evolv Technology - a company focusing on facial recognition for crowds and threats.


So get ready, because now facial recognition is going to be as easy as driving your car!

#Ellen Pearlman#planet 3d#new aesthetic#facial recognition#3d facial recognition#biometric tracking#biometrics
0 notes
Text
Now, A 360 Ballet For VR

Dancers coming right up to the camera eye
Although Blanca Li created the first dance performance for VR, the Dutch National Ballet is crowing that it has created the first ballet for VR. Yes, its a ballet for VR in 360 degrees, which is tough to put together. Called “Night Fall”, it has all performers, as well as a violinist moving up to the main camera, most likely a go-pro rig of some sorts with a dozen or so cameras, and letting an on-line viewer roll around an internet screen with a 360 degree view.

Violinist walking around playing next to performers
Its nice, but its also exhausting, as you can’t just move your head in real space, but have to drag the screen around as the ballerina plies, and then minces and trots across the stage to another location. The violinist is walking around as well, but what orients you as the viewer, oddly enough, is the spatialized patter of the dancer’s footsteps. It gives you the cues as to which way the action is going.

Dancers about to whirl off screen into another area of the 360 screen
When they whirl around and disappear ‘off camera’ that is not true. You just drag your mouse around and you can follow them as they spin in and out of the frame. What this does is it forces the viewer, who is usually in couch potato mode, to get active and drag the mouse all over the place in order to remain part of the action and not be left staring at an empty stage.
The questions here are does sitting at your computer, or even putting on a VR headset equal the same experience as standing in the middle of the theater as a real person? Is it more valuable to have the experience in VR, or in reality? Of course millions more people can see it in VR, and have an experience where they are ‘almost’ there, and of course, you would most likely never have the opportunity to actually be so up close and personal with the dancers. At this point, its a sheer tradeoff.
0 notes