Text
39 notes
·
View notes
Text




[ID: Four posters by @LizWhatsHerFace on Instagram. 1. A muscular man wearing a black respirator, a black tank top and black shorts. “Are you man enough to wear the Ellipse P100 Niosh respirator or should I call Kyle?” 2. A thin woman wearing a black N95 facemask, pink lace bralette, white fur vest, pink and white striped pants and sunglasses “Sorry I made it weird when I said my life is worth more than eating indoors at Applebees.” 3. A stacked woman wearing a white N95 facemask and a low cut white tank top “I bring a sort of wear a fuckin mask vibe to the party” 4. A photonegative woman wearing a black N95 facemask and black tshirt “Radical Covid zero extremists want your dick to keep working.” Comment by Liz at the bottom “trying some new approaches 🌈🍔”]
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Published April 26, 2024
Highlights
"Mitochondria, the cellular organelles known as the powerhouses of the cell, are central to this discussion. They play a crucial role in cellular energy production through the process of oxidative phosphorylation, in addition to their involvement in oxidative stress, apoptosis (programmed cell death), induction of cellular senescence, and the modulation of immune responses. The function of mitochondria is essential for maintaining cellular and systemic homeostasis. Disruptions in mitochondrial function can lead to a decrease in energy production, increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and initiation of inflammatory pathways, all of which can contribute to the pathophysiology of various diseases."
Mitochondrial DYSFUNCTION already proven or highly suspected in:
- Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS)
- Post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS)
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and other herpesviruses
- Chronic Q fever fatigue syndrome (QFS)
Long-lasting structural damage to mitochondria:
"During the acute phase of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 can directly interact with mitochondria, exploiting mitochondrial dynamics for virus proliferation and causing structural damage"
Persistent dysregulation of mitochondrial bioenergetics:
Viral proteins may interfere with the mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS), disrupting its normal function in the antiviral response and leading to chronic mitochondrial dysfunction
Autoimmunity triggered by COVID-19:
The immune system’s response to SARS-CoV-2 might include the development of autoantibodies that mistakenly target mitochondrial proteins, a phenomenon possibly driven by molecular mimicry
Mechanisms linking mitochondrial dysfunction to long COVID symptoms:
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is intricately linked to the diverse symptoms of long COVID through its impact on energy production, oxidative stress, immune response, metabolic processes, and vascular health. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted interventions to mitigate the effects of long COVID and improve patient outcomes."
"PRDX3 is located in the mitochondria, where it plays a key role in detoxifying hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and protecting cells from oxidative damage."
"While initial findings highlighted PRDX3’s potential in reflecting oxidative stress within mitochondria, our results specifically connect elevated PRDX3 levels to the symptom of dizziness rather than a broader range of long COVID symptoms such as fatigue."
"This points to a more nuanced understanding of PRDX3’s role, necessitating a careful interpretation of its utility as a biomarker."
Potential therapeutic implications
“Strategies to improve mitochondrial function involve a combination of pharmacological interventions, lifestyle modifications, and nutritional support." "Antioxidants, such as coenzyme Q10, MitoQ, N-acetylcysteine, resveratrol, and alpha-lipoic acid, have been suggested to reduce oxidative stress in mitochondria, thereby improving their function."
"Additionally, compounds like L-carnitine, which facilitate fatty acid transport into mitochondria for energy production, could also prove beneficial. NAD+ boosters, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), have garnered attention for their potential to enhance mitochondrial function by increasing the levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a critical coenzyme involved in cellular energy production and repair processes"
“Moreover, understanding the interaction between mitochondrial dysfunction and other pathophysiological processes in long COVID, such as immune dysregulation and endothelial dysfunction, could lead to the development of combination therapies that address multiple facets of the disease. Integrative approaches that combine pharmacological treatments with lifestyle and nutritional interventions may offer the most promise for comprehensive management of long COVID, aiming not only to alleviate symptoms but also to restore overall health and well-being.”
#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#long covid#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

Airborne norovirus? Ahem... Excuse me... "Puff cloud" norovirus?
47 notes
·
View notes
Note
i think you rbd the hot dog poll to the wrong blog haha
I wanted to spread that one around a little more 😆 the results genuinely surprised me a lil bit.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi! If you wanna tip me for the daily covid updates, feel free to throw some money at my cashapp ($Covidsafehotties) or dm me for my paypal or venmo if that works better! Thanks in advance!

194 notes
·
View notes
Text
"I can’t stop thinking about the essay No, Young Adults Should Not Live in Fear from Coronavirus by Drs. John Mandrola and Andrew Foy, two so-called “medical conservatives”. It was written on December 29th, 2020 in response to a research letter titled All-Cause Excess Mortality and COVID-19–Related Mortality Among US Adults Aged 25-44 Years, March-July 2020, which found that 4,535 COVID deaths were recorded among young adults during the pandemic’s first 5-months.
Many people were sad that 4,535 young people had died from COVID in such a short time, especially considering there had been just 4.49 million confirmed cases of COVID by the end of July 2020.
These “medical conservatives”, however, were unperturbed by thousands of dead young people. They castigated those who were concerned, decrying their “fearsome messaging.” “The infection fatality rate for young adults is quite low,” they said reassuringly. They sought to numb their readers by encouraging them to focus on the tens of millions of young adults who hadn’t died of COVID, while ignoring that the vast majority of them had yet to contract it. They wrote:
We offer four reasons why this study and OpEd do not support the claim that young adults should live in fear from the virus…
An excess of 12,000 deaths sounds bad, but Professor Don Boudreaux, from George Mason University, has noted that there are nearly 88 million people in this age group. Thus, the individual risk for a person this age is found by dividing 4,560 (the number dead from COVID19 in this study) by 88 million. This equates to a 0.0052% risk of dying from COVID19.
Of course, anything that kills young people can be made to sound trivial by dividing it by 88 million. The individual risk of dying at all is low for young people."
#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Preprint accepted April 26, 2024 (to be fully published with minor corrections soon)
“The identified knowledge gaps are significant as they impact quality of patient care. and opinions about future vaccination practice such as recommending, providing, and counseling about vaccines. Equipping students with knowledge and communication skills will enable them to be strong vaccine advocates to improve overall public health.”
Only 68%(medical students) and 55%(dental students) scored an average/above-average knowledge on COVID-19 and influenza vaccine items...
#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#long covid#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#long covid#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Preprint published April 4, 2024
Abstract
Highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses of the H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b arrived in North America in the winter of 2021/2022. These viruses have spread across the Americas causing morbidity and mortality in both wild and domestic birds as well as some mammalian species, including cattle. Many surveillance programs in wildlife as well as commercial poultry operations have detected these viruses. Here we conducted surveillance of avian species in the urban environment in New York City. We detected highly pathogenic H5N1 viruses in six samples from four different bird species and performed full genome sequencing. Sequence analysis showed the presence of multiple different genotypes. Our work highlights that the interface between animals and humans that may give rise to zoonotic infections or even pandemics is not limited to rural environments and commercial poultry operations but extends into the heart of our urban centers.
Importance
While surveillance for avian influenza viruses is often focused on migratory routes and their associated stop-over locations, or commercial poultry operations, many bird species – including migratory birds – frequent or live in urban green spaces and wetlands. This brings them into contact with a highly dense population of humans and pets providing an extensive urban animal-human interface in which the general public may have little awareness of circulating infectious diseases. This study focuses on virus surveillance at this interface, combined with culturally responsive science education and community outreach.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
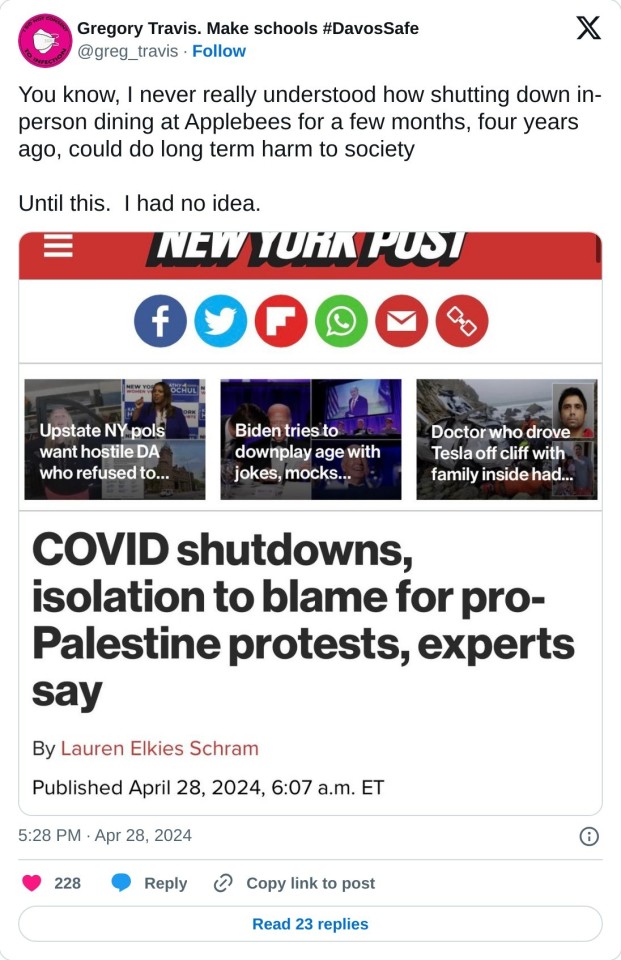
#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#long covid#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus#free palestine#palestine
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#long covid#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

A poster from the 1918-1920 flu pandemic in Japan shows germs infecting the air around a maskless man on a train. The text reads: 'Underestimated flu bacteria! Not wearing a mask is reckless!' (Public domain)
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Published April 24, 2024
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, has revealed a broader impact beyond the respiratory system, predominantly affecting the vascular system with various adverse manifestations. The infection induces endothelial dysfunction and immune system dysregulation, creating an inflammatory and hypercoagulable state. It affects both microvasculature and macrovasculature, leading to thromboembolic events, cardiovascular manifestations, impaired arterial stiffness, cerebrovascular complications, and nephropathy, as well as retinopathy—frequently observed in cases of severe illness. Evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 infection may result in persistent effects on the vascular system, identified as long-term COVID-19. This is characterized by prolonged inflammation, endotheliopathy, and an increased risk of vascular complications. Various imaging modalities, histopathological studies, and diagnostic tools such as video capillaroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging have been employed to visualize vascular alterations. This review aims to comprehensively summarize the evidence concerning short and long-term vascular alterations following COVID-19 infection, investigating their impact on patients’ prognosis, and providing an overview of preventive strategies to mitigate associated vascular complications.
Highlights
"COVID-19 has a significant impact on multiple organs, primarily through its effects on the vascular system, leading to diverse manifestations and complications."
"Patients present with various clinical complications, such as thromboembolic events, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular manifestations, nephropathy, and retinopathy."
"Several imaging techniques, histopathological studies, and diagnostic tools like video capillaroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging have been employed to visualize and study vascular alterations in these patients."
"Beyond the acute phase, SARS-CoV-2 infection can lead to persistent effects on blood vessels, known as long-term COVID-19", even after “Mild” COVID-19.
"Considering that COVID-19 infection entails a continuum of pathophysiological changes, a sterilized classification into short and long-term changes may appear simplistic."
"Early detection, appropriate medication and management, anticoagulation therapy, and vaccinations can substantially limit adverse events and improve clinical outcomes."
#mask up#covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#pandemic#covid conscious#long covid#covid is airborne#wear a mask#coronavirus
6 notes
·
View notes
