Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
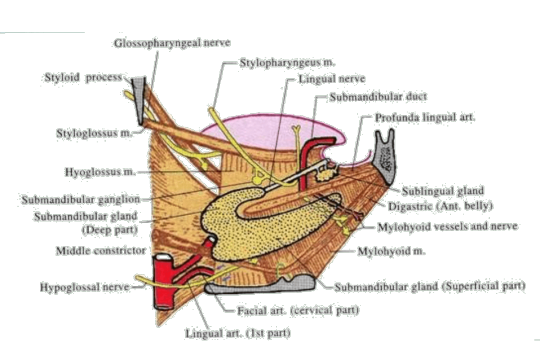
Submandibular Ganglion
Features: It is the peripheral parasympathetic ganglion. Topographically related to lingual Nerve Functionally related to chorda tympani, branch of facial Nerve It is a fusiform ganglion lies on hypoglossus, above the deep part of submandibular gland suspended from lingual Nerve by two roots. Connections of Submandibular Ganglion
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Sublingual Salivary Gland
Features: It is the Smallest salivary gland almond shaped weighs 3-4gms Situation lies above mylohyoid below the mucosa of floor of mouth medial to sublingual fossa of mandible lateral to genioglossus Relations Front – meets opposite side gland Behind – deep part of submandibular gland Above – mucous membrane of mouth Below – Mylohyoid muscle Lateral – sublingual fossa Medial –…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
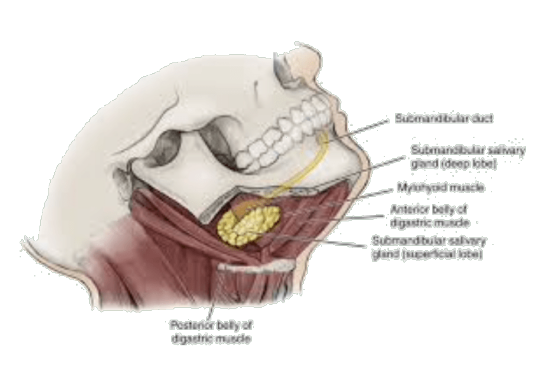
Submandibular Salivary Gland
Features large salivary gland situated in anterior part of digastric triangle size of walnut weighs about 15-20gms roughly J – shaped The posterior border of mylohyoid divides the gland into – large superficial part – small deep part Coverings: The Gland is partially enclosed between two layers of investing layer of deep cervical fascia superficial layer – covers the inferior surface…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Suprahyoid Muscles
The suprahyoid muscles are the digastric, the stylohyoid, the mylohyoid and the geniohyoid. The muscles are in following layers: 1. First layer formed by digastric and stylohyoid. 2. Second layer formed by mylohyoid 3. Third layer formed by geniohyoid and hyoglossus 4. Fourth layer formed by genioglossus Digastric Muscle has two bellies united by an intermediate…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Structures in the Anterior Median Region of the Neck
Structures in the Anterior Median Region of the Neck
Skin Superficial fascia Decussating fibres of platysma Anterior jugular Vein Jugular venous Arch Submental Lymph Nodes Terminal part of transverse Nerve Deep fascia Investing layer Above hyoid bone — splits to enclose submandibular gland Below splits to enclose suprasternal space Deep structure above hyoid bone Mylohyoid muscle Anterior belly of digastric Superficial part of…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
OTIC Ganglion
Introduction Peripheral parasympathetic ganglion Topographically related to mandibular Nerve Functionally related to glossopharyngeal Nerve Situation 2-3 mm in size Situated in infratemporal fossa Just below foramen ovale Related – laterally to mandibular Nerve Medially to tensor veli palatini Surrounds the origin to Nerve to medial pterygoid Other Connections Sensory root from…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Mandibular Nerve
Largest mixed branch of trigeminal Nerve Nerve of first pharyngeal arch Associated with Otic & submandibular ganglion Formation & Divisions Begins in middle cranial fossa Large sensory root – arises from lateral part of trigeminal ganglion – Leaves the cranial cavity through foramen ovale Small motor root Passes deep to the trigeminal ganglion Passes through foramen ovale Joins with…

View On WordPress
#auriculotemporal nerve#deep temporal nerve#inferior alveolar nerve#lingual nerve#Mandibular nerve#masseteric nerve#meningeal nerve#nerve to lateral pterygoid#nerve to medial pterygoid#nervous spinous#trigeminal neuralgia
0 notes
Text
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT
It is a Synovial joint, Condylar variety Articular Surfaces Upper articular surface Articular tubercle Anterior part of mandibular fossa Posterior non-articular part formed by tympanic plate Inferior articular surface Head of mandible Articular surface covered with fibrocartilage Joint cavity is divided into upper & lower compartments by intra-articular disc Ligaments Fibrous…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
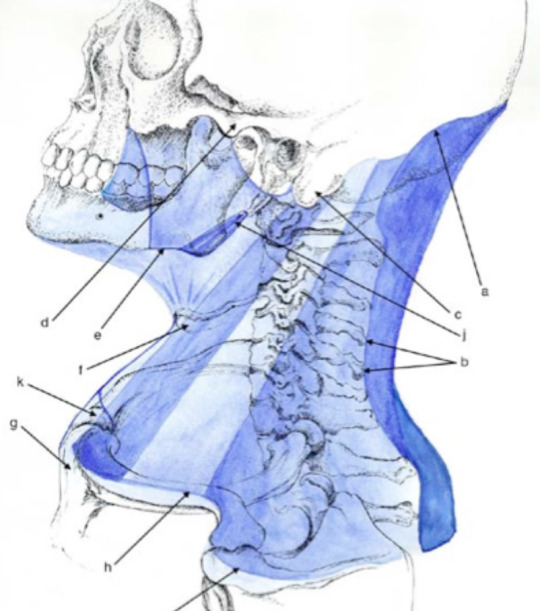
Deep Cervical Fascia/ Fascia Colli
Deep Cervical Fascia/ Fascia Colli
The deep fascia of the neck is condensed to form the following layers: 1. Investing layer 2. Pretracheal layer 3. Prevertebral layer 4. Carotid sheath 5. Buccopharyngeal fascia 6. Pharyngobasilar fascia. INVESTING LAYER It lies deep to the platysma, surrounds the neck like a collar. It forms the roof of the posterior triangle of the neck Attachments Superiorly : a. External…
View On WordPress
#carotid sheath#deep fascia#fascia colli#investing layer of deep cervical fascia#pretracheal fascia#prevertebral fascia
0 notes
Text
Lacrimal Apparatus
COMPONENTS The structures concerned with secretion and drainage of the lacrimal or tear fluid constitute the lacrimal apparatus. It is made up of the following parts: 1. Lacrimal gland and its ducts 2. Conjunctival sac. 3. Lacrimal puncta and lacrimal canaliculi. 4. Lacrimal sac. 5. Nasolacrimal duct. Lacrimal Gland It is a serous gland situated chiefly in the lacrimal fossa on the…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
Nerve Supply, Blood Supply And Lymphatic Drainage of Face
Nerve Supply, Blood Supply And Lymphatic Drainage of Face
Motor Nerve Supply The facial nerve is the motor nerve of the face. Its five terminal branches, temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical emerge from the parotid gland and diverge to supply the various facial muscles as follows. Temporal– frontalis, auricular muscles, orbicularis oculi. Zygomatic– orbicularis oculi. Buccal– muscles of the cheek and upper lip Marginal…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Face
It extends superiorly from the adolescent position of hairline, inferiorly to the chin and the base of the mandible, and on each side to the auricle. The forehead is, therefore, common to both the face and the scalp. SKIN 1 The facial skin is very vascular. Rich vascularity makes the face blush and blanch. Wounds of the face bleed profusely but heal rapidly. The results of plastic surgery on…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Ascending Tract - Lateral Spino-thalamic tract
Ascending Tract – Lateral Spino-thalamic tract
It is the main control pathway for fast pain and temperature sensations.It is formed by the axons of second order sensory neurons (Tract cells), which are located in the laminae IV to VII of spinal grey matter.They tracts receive fibres from lateral division of dorsal nerve root through the collateral and terminal branches of dorso-lateral tract of Lissauer.Axons of tract cells cross midline in…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Limbic System
The word limbus means ring, the term limbic system is applied to the parts of the cortical and subcortical structures that form a ring around the upper end of the brainstem. The limbic system was formerly called rhinencephalon because of its association to olfaction, but in human beings only a small part of it is actually concerned with smell. The limbic cortex is phylogenetically oldest part…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Reticular Formation
The reticular formation is defined as diffuse ill-defined mass of intermingled neurons and nerve fibres occupying the entire core of brainstem. The reticular formation has derived its name from its light microscopic appearance of a vague network of nerve cells and nerve fibres. It has been defined to include all areas within the brainstem (except the named nuclei and tracts) which when…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic (self-controlling) nervous system is that part of the nervous system which regulates most of the involuntary activities of the body, such as the activities of smooth muscles of bronchial tree, gut, genitourinary system, pupil, arrector pili muscles of the hair, cardiac muscle and secretion of the glands. Thus it represents the visceral component of the nervous system, hence sometimes…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
Venous Drainage of The Brain
Venous Drainage of The Brain
The veins of the brain drain into the intracranial dural venous sinuses, which eventually open into the internal jugular veins of the neck. The veins emerge from the brain, traverse the subarachnoid space, pierce the arachnoid mater and meningeal layer of dura mater to drain into the venous sinuses. The characteristic features of venous drainage of the brain are: • The venous return in the…

View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note