Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Buddhist Cross Word Puzzle

World Religions: Buddhism
1 note
·
View note
Text

Hinduism Cross Word Four Stages
0 notes
Text
Drainage

#geology 101#geo 101#geology 100#geo 100#earth science#earth#geo#rivers#drainage#drain#notes#chicken stratch#studyblr
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mineral Family tree


#family#family tree#mineral#mineral groups#crave that mineral#theyre minerals#its not a rock its a mineral#quartz#crystals#geology#geo 101#geo#science#geo science#earth science
0 notes
Text
Plutonic vs. Volcanic Textures.

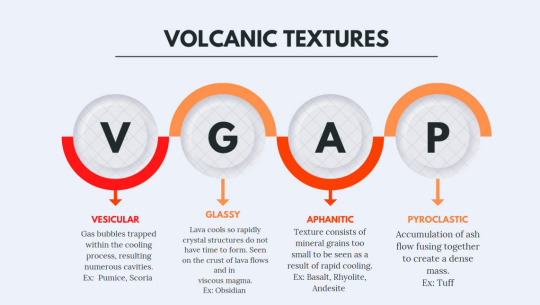
#geology 100#geo 100#geology 101#earth science#flow chart#free#worksheet#geology igneous#igneous rocks#rocks
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mafic and Felsic problem set mind maps.

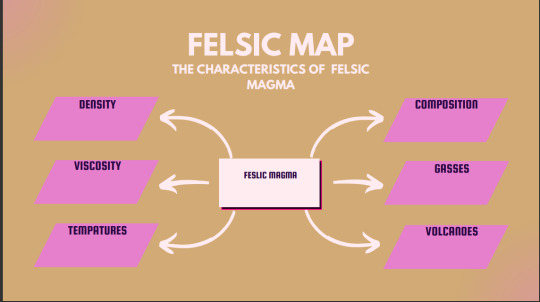
0 notes
Text
All Quizzez
Glacier And Long Term Climate Change
Arid Landscapes
Mineral Resources
Energy
Waste
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Waste Management
Puzzle Game: Waste Management Classes and Disposal Groups
Quizzez:
0 notes
Text
Masterlist
Here is a master list of links to everything I have posted regarding UNIT 3 for geology 150
Moc Essay Questions:
Glaciers and Long-Term Climate Change:
Deserts and Arid Climates:
Minerals and Resources:
Energy and the Environment:
Waste Management:
#geology#geo 150#testing#unit 3#minerals#resources#minerals and resources#arid#arid climates#glacier#glaciers#long term climate change#climate change#geology 150
0 notes
Text
Mineral Resources and Society: Mineral Deposit Origins Cross Word
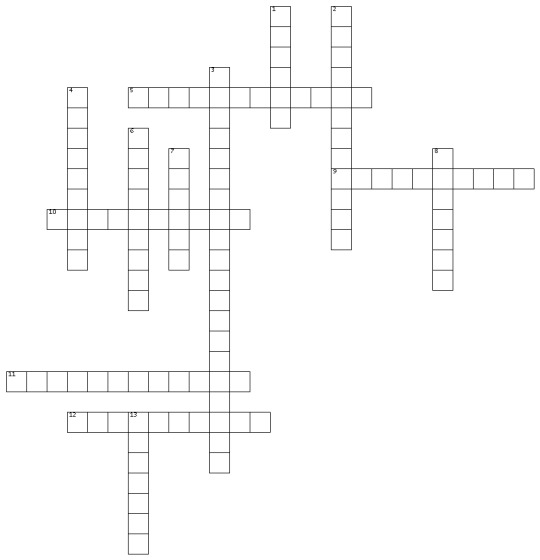
ACROSS 5. deposits left behind typically when hot fluids come into contact with cooling magma 9. Surficial precipitations are created from minerals crystalizing from water, otherwise known as 10. a result of an igneous vein experiencing a season of slow cooling which allows for large crystal growth and is a source of mineral deposits containing Be, Li 11. deposits that come from large igneous intrusions spilling mineralized veins around its border 12. last.
DOWN 1. deposits are a result of concentrated fluvial deposition 2. deposits are a result of volcanic activity producing vents near the surface, in association with MOR black smoker activity 3. the notion that mafic minerals will crystalize first and felsic minerals will 4. precipitation is formed on the ocean floor, producing nodules that are radioactive 6. evaporites saline lakes produce mineral deposits such as borax, trona, carbonates and other salts 7. _____ evaporites come in the form of gypsum, calcite, halite, and anhydrite. 8. Settling result of magma cooling. where magma chamber separates minerals based on density; following Bowen’s Reaction Series 13. chemical precipitate form as a result of ______ marine basins
Here's a fake personality test based on the Igneous Processes
I am not sure if I will be able to make a quizzez on Minerals and Resources by tonight. But will keep you updated. Everything should be done no later than Sunday Night tho.
#cross word#wordle#geology 101#geology 150#minerals#mineral resources#environmental geology#we live in a society#society#mineral origin#earth science#sceince#science#undergrad
0 notes
Text
Mock Essay Questions
DISCLAIMER: I don't know what the essay questions will be.
but I have created questions I hypothesize might be on the test. I am posting these for those who might want extra practice on their written answer techniques, as well as a personalized way of studying details on possible test material.
What is desertification? How does it affect the surrounding land? What causes the desertification of an area?
Name the five different types of deserts. Where do they form? Explain their characteristics. Be sure to give examples of each.
Explain the difference between Advancing and Receding glaciers. What are their glacial budgets?
What are the general causes of global climate change, how do they contribute to the changing of the climate? What are the major causes of global climate change today? Which ones are natural, which one are anthropogenic?
What are the evidences and consequences of global climate change? Where do we see the most impact at?
What are the different ways petroleum can be trapped? Explain the differences between Structural Traps and Stratigraphic traps? Which of the two produces more?
Describe how coal forms and its characteristics. What are some of the negative effects of using coal as an energy resource? What are the pros and cons of coal alternatives?
Name the different types of Waste Disposal methods. What are the pros and cons of each?
Describe the different types of Nuclear Waste. Which of them has the highest radioactivity? Which has the lowest? Be sure to describe where each type forms.
0 notes
Text
Long-Term Climate Change
I tried to do a quiz on this new content creation site im currently playing with, these seem more formal than quizzez but I find it less fun but I already made the quiz so oh well. However for the select all that apply, worry not. You only need to select one correct answer and it will reveal all the correct answers for that question.
UPDATE: THE ACCUMLATIVE GLACIER AND LONG TERM CLIMATE CHANGE QUIZ HAS BEEN MADE
I should have the Mineral Chapter up no later than 6pm
Unfortunately [to avoid burn out] that might be all I post for today. Stay tuned tho!
#long term climate chage#long term climate change#climate change#long ter#long term#geo 150#contempary geology#geology 150#environmental geology#environmental science
0 notes
Text
Glacial Depositional Features Word Search

Deposition Drumlin Erratic Esker Flute
Kame Kettles Moraines Outwash Till Varves
Unscramble Word Worksheet: Hidden message

0 notes
Text
Arid Lands and Desertification
Desert Association Card game
#quizzez#deserts#desert formation#more on deserts#geolgoy 150#geo 150#contempary geology#enviromental#environmental science#environmental geology#geology#earth science 150#undergrad#uni#community college#geo#sand#sand dunes
0 notes
Text
Desert Classification
>What is a polar desert:
>{perpetual snowline cover}
>{intense cold}
>{descending air}
>:[Greenland, Antarctica]:
A polar desert is a desert that experiences intense cold with little rainfall due to the descending air flow of the region, this gives it a predominant snowline. These can be seen in areas of Antarctica and Greenland.
>What is a subtropical desert?
>{largest dry expansions}
>{subsiding air from global air circulation}
>:[[T R A D E W I N D ]]:
>:[Sahara, Australia]:
A subtropical desert deserts are a result of subsiding air from global air circulations. The daily temperatures in these areas vary, all the while experiencing little to no precipitation. These are known as the largest dry expansions. Latitudes between 20˚ and 40˚ are most likely to experience these conditions, such as that of the Sahara and Australia. Also due to their location they are also known as Trade wind deserts.
>What is a Mid-Latitude Desert?
>{mountain genesis}
> {related to a global rain shadow effect}
> :{{Deep within continental interior, remote from the influence of an ocean}}:
>:[Gobi, Asian Deserts]:
A Mid-Latitude Desert is a desert that consists of semiarid grasslands that are a result of a global orographic effect in which the land is not impacted by ocean air influence and rests deep in the interior of a continent. Such deserts can be seen in Asia such as the Gobi desert.
>What is a Rain-Shadow Desert?
>inland desert
>relatively close to ocean
>result of rain shadow: when moist air deposits rain on the upward side of a mountain and dry air accumulates on the leeward side.
>:[ Great Basin Deserts, Mojave]:
A Rain-Shadow Desert is a desert that is a result of rain shadow where the moist water deposits rain on the upward side of a mountain and dry air accumulates on the leeward side. Such deserts can be found throughout the Great Basins and in the Mojave.
>What are coastal deserts?
>adjacent to cold eastern boundary currents
>affected by upwelling
> costal margins may experience wet fog
>inland air experiences intense evaporation
>:[Atacama,Chile}:
A Coastal Desert is a desert that exists near eastern boundary currents in which upwelling takes place. Although their coastal margins experience wet fogs, the more inland the air moves, the more evaporation the air experiences; this leaves behind extremely dry air, the driest of all the deserts. This is the case with Atacama, Chile.
#desert#geology 101#earth science#science#geology150#contempary geology#enviormentalism#enviroment#geography#stem#earth science 100#earth science 150#upper geology#geology 150#geo#geoscience#undergrad
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unit 2: testing material
Plate Tectonics
Geologic Time
Earthquakes
Structural
#structural geology#unit 2#plate tectonics#geology 101#earth science 1010#earthscience101#geology100#earth science 100#earth#science#earth science#science 101#science 100#university#earthquakes
0 notes
Text
Chapters 6-10
Chapter 6: Soils
Chapter 7: Mass Wasting
Chapter 8: Freshwater
Chapter 9: Hydrologic Hazards
Chapter 10: Coasts and Beaches
Chapter 10: Tsunamis and ENSO
#geology#geo 150#geological hazards#geology 150#geological disasters#contempary geology#weather#natural disasters#disasters#tsnumai#floods#midigation#lake pollution#the block brochure: welcome to the soil 4#soils#mollisol#aridisol#oxisol#mechanical weathering#erosion#deposition
0 notes