just a little spot for references that I have used or plan to use in my writing...or really anything that I think would be useful
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
writing advice for characters with a missing eye: dear God does losing an eyes function fuck up your neck. Ever since mine crapped out I've been slowly and unconsciously shifting towards holding my head at an angle to put the good eye closer to the center. and human necks. are not meant to accommodate that sorta thing.
85K notes
·
View notes
Text
Some notes on worldbuilding with carnivorous cultures:
Animals feed more people than you think. You don't kill a cow for just one steak, this is a modern kind of idea since we're removed from the actual animals we eat our meat from. In fact, slaughtering a single cow often means a feast time for possibly dozens of people. Every part of an animal can be used, and you can see this in cultures that live by ranching and transhumance.
Here, you should look at the Mongols and the people of the Eurasian Steppe, the people of the North American Plains, the people of the Pampas (fun fact; Buenos Aires was called the "carnivore city"), European and Asian cultures that practice transhumance, and those of the Arctic circle.
There are many ways to cook meat, but arguably, the most nutritious way to consume meat is in stew, as it allows you to consume all the fats of the animal and add other ingredients. In fact, mutton soup and stew historically was one of the basic meals for the for people in the Eurasian Steppe, who are one of the people with the highest meat consumption in the world.
Of course, meat spoils away easily. Fortunately, from jerky to cured meats, there are ways to prevent this. In pre-industrial and proto-industrial societies, salted meat was the main way of consumption and exporting meat. This makes salt even a more prized good.
Often, certain parts of animals like eyes, the liver, the testicles, the entrails, are considered not only cultural delicacies but as essential for vitamins and nutrients unavailable in environments such as the poles. The Inuit diet is a very strong example.
Pastures and agriculture have often competing dynamics. The lands that are ideal for mass pasture, that is, temperature wet grasslands, are also often ideal for agriculture. So pastoralism has often been in the margins of agrarian societies. This dynamic could be seen in the Americas. After the introduction of cattle and horses, the Pampas hosted semi-nomadic herdsmen, natives and criollo gauchos. The introduction of wire eventually reduced this open territory, converting it into intense agriculture, and traditional ranching was displaced to more "marginal" land less suitable for agriculture. Similar processes have happened all over the world.
This also brings an interesting question to explore. Agriculture is able to feed more people by density. What about species that DON'T do agriculture, because they're completely carnivorous? The use of what human civilization considers prime agricultural land will be different. They will be able to support much higher population densities than pastoralism.
Pastoral human populations have developed lactase persistance to be able to feed on dairy products even in adulthood. This mutation has happened all over the world, presumably with different origins. In any mammalian species that domesticates other mammals such a thing would be very common if not ubiqutous, as it massively expands the diet. Milk provides hydration, and cheese, yogurth and other such products allows long lasting food sources.
What about hunting? Early humans were apex predators and we are still ones today. However, humans can eat plants, which somewhat reduces the hunting pressure on fauna (though not the pressure of agrarian expansion which can be even worse). An exclusively carnivorous species (for example some kind of cat people) would have to develop very rigid and very complex cultural behavior of managing hunting, or else they would go extinct from hunger before even managing domestication. These cultural views towards hunting have also arosen in people all over the world, so you can get a sense of them by researching it.
It is possible for pastoral nomadic people, without any agriculture, to have cities? Of course. All nomadic peoples had amazing cultures and in Eurasia, they famously built empires. But they traded and entered conflicts with agrarian societies, too. They weren't isolated. Most of nomadic societies were defined by trade with settled ones.
The origin of human civilization and agriculture is still debated. It would be probably completely different for a non-human carnivorous society. One possible spark would be ritual meeting points (such as the historical Gobleki Tepe) or trade markets growing into permanent cities. But in general, pastoralism, hunting and ranching favors low-density populations that would be quite different.
Fishing, on the other hand, is a reliable source of protein and promotes settled cities. One can imagine acquaculture would be developed very early by a civilization hungry for protein.
Other possibilities of course are the raising of insects and mushrooms, both very uncommonly explored in fiction besides passing mentions.
Of course, most carnivorous species have some limited consumption of plant matter and many herbivores are oportunistic predators. The main thing to ask here is what the daily meal is here. For most human agrarian cultures, it's actually grain (this is where the word meal comes from). What about species that cannot live with a grain-based diet? You will find that many things people take for granted in agrarian society would be completely different.
As I always say: the most important question you can ask is "where does the food comes from?"
I hope you found these comments interesting and useful! I would love to do a better post once I'm able to replace my PC (yes, I wrote this all in a phone and I almost went insane). If you like what I write and would love to see more worldbuilding tips, consider tipping my ko-fi and checking my other posts. More elaborate posts on this and other subjects are coming.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
In which my uncle is the best de facto parent of a queer kid ever
It’s Pride, and also the first anniversary of my uncle’s death, so I want to type up a story about him. (NB: my aunt, his wife, is equally cool, but she’d want this story to be about him too.) So here goes.
I skipped town when I was 16. Nothing interesting about that part; just standard queer kid in a conservative place in the 1990s stuff. I’d just gotten my driver’s license (this took a while; I’m good at other things), it was the beginning of summer break, and my parents had recently bought a new car and were planning to fix up their old one to sell. In the meantime, the old car (whom I’d named Harold Godwinson because one of his headlights kept exploding) was sitting all by himself in a corner of the driveway, and I thought he might be down for a little adventure. So, one night, I threw some stuff in my backpack (documents, journals, a few changes of clothes, my $235 in babysitting cash) and snuck out after everyone else in the house had gone to sleep.
Harold Godwinson and I hit the highway. The thing about him was that he started shaking violently at speeds over 57 mph, but in fairness so did I – I’d driven on the interstate in driver’s ed, but, like, twice, and for 5 minutes at a time instead of several consecutive hours – so we made a good pair. We were lucky enough (seriously: I cannot stress enough how lucky we were in this) to have a destination in mind, and we reached it just as the sun was coming up.
My uncle was in the kitchen making breakfast for my aunt, who’s not a morning person, and he did not look surprised at all to see me coming up the path with my luggage. He met me at the door and said, “Well, hey there babygirl, we were just thinking you might want to come and stay with us for a while, and I’m so glad you read our minds.” I ate my aunt’s breakfast and then faceplanted in the attic bedroom while he called my parents to tell them where I was and that I’d be staying. (I could hear the yelling even through the adrenaline crash; I think that’s the only time I ever heard my uncle yell and, believe me, I did a LOT of dumb shit in front of him over the years.)
The next week my uncle and I went out to run an errand. I’d thought we were just going to the hardware store – we were forever putting up shelves together – but instead we drove 45 minutes to the state’s only “alternative” (plausible-deniability term for “gay and lesbian”) bookstore. He walked me inside, poked his head into every room while I watched, confused, from the entrance hall, and then came back over. “Okay, babygirl. Here’s a twenty, you should, uhhhhhh, buy yourself some, uhhhhhh, alternative books. Back in one hour, I gotta go to the grocery.” At this point he looked around and realized that the cashier (who, I was about to learn, was permanently cosplaying Mo from Dykes to Watch Out For) and a nice middle-aged lesbian couple were trying very hard not to stare at him. He bowed slightly toward them, said “Ladies,” and then backed out the door in what might have been the most awkward little shuffle ever.
“Your dad is really sweet,” said the cashier. I didn’t bother correcting her.
16K notes
·
View notes
Text
Disabilities that You Should Consider Representing in Your Writing More… part 1
[large text: Disabilities that You Should Consider Representing in Your Writing More… part 1]
While all disabilities are underrepresented in basically all sorts of media, it’s hard to not notice the trend in what disabilities make up the majority of representation. It’s especially visible when having a blog like this, where we can see what disabilities writers even consider including in their writing, and which ones never come up.
One in four people are disabled. With eight billion people alive it means there’s a lot of disabled people, and a lot of reasons why they are disabled in the first place - but this diversity is rarely represented, even on this blog, and anyone who has been following for a while has probably noticed that fact.
To be blunt: there are disabilities other than “amputee” and “(otherwise invisibly disabled) mobility aid user”. Does that mean that it’s wrong to write either of those? Of course not, and we don’t want to imply that it is. Does it mean that when you are deciding on what to give your character, you should think beyond just those two? Absolutely. Disability is a spectrum with thousands of things in it - don’t limit yourself for no reason and embrace the diversity that’s built into it instead.
This is, simply, a list of common disabilities. This is just a few of them, as this is part one of presumably many (or, at least three as of right now). By “common” we rather arbitrarily decided on “~1% or more” - so at least 1 in 100 people has the disabilities below, which is a lot. Featuring!: links that you should click, sources of the % that are mostly just medical reports and might be hard to read, and quick, very non-exhaustive explanations to give you a basic idea of what these are.
Intellectual disability (about 1.5%) Intellectual disability is a condition we have written about at length before. It’s a developmental disability that affects things such as conceptualization, language, problem-solving, or social and self-care skills. ID can exist on its own or be a part of another condition, like Down Syndrome, Congenital Iodine Deficiency, or Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. This post covers a lot of basic information that you might need. We have an intellectual disability tag that you can look through!
Cancer survivors (5.4% in the US, about 0.55% worldwide) A cancer survivor is a pretty self-explanatory term. There is a lot of types of cancer and some of them are very common while others are very rare, which makes this a very diverse category. Cancers also have different survival rates. While not every survivor will have disabling symptoms, they definitely happen. Most of the long-term side effects are related to chemotherapy, radiation, and other medication, especially if they happened in children. They can include all sorts of organ damage, osteoporosis, cognitive problems, sensory disabilities, infertility, and increased rate of other cancers. Other effects include removal of the affected area, such as an eye, a spleen, breasts, or the thyroid gland, each of which will have different outcomes. Cancer, and cancer treatments, can also result in PTSD.
Diabetes (about 8.5%, ~95% of that are type 2) Diabetes is a group of endocrine conditions that cause hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) for various reasons depending on the type. The vast majority of people have type 2 diabetes, which can cause fatigue, poor healing, or feeling thirsty or hungry. A diabetic person will use insulin when needed to help manage their blood sugar levels. There are many complications related to diabetes, from neuropathy, to retinopathy, and chronic kidney disease, and there's a lot of disabilities that coexist with diabetes in general! You might want to check out the #how to write type 1 diabetes tag by @type1diabetesinfandom!
Disabling vision loss (about 7.5%) Blindness and low vision are a spectrum, ranging from total blindness (around 10% of legally blind people) to mild visual impairment. Blindness can be caused by countless things, but cataracts, refractive errors, and glaucoma are the most common. While cataracts cause the person to have a clouded pupil (not the whole eye!) blind eyes usually look average, with strabismus or nystagmus being exceptions to that fairly often (but not always). Trauma isn't a common cause of blindness, and accidents are overrepresented in fiction. A blind person can use a white cane, a guide dog or horse, or both. Assistive solutions are important here, such as Braille, screenreaders, or magnifying glasses. We have a blindness tag that you can look through, and you might want to check out @blindbeta and @mimzy-writing-online.
Psoriasis (about 2-4%) Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition with multiple subtypes; it can cause intense itching, pain, and general discomfort, and often carries social stigma. It’s an autoimmune and non-contagious disability that affects the skin cells, resulting in raised patches of flaky skin covered with scales. It often (30%) leads to a related condition, psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain, tenderness, and fatigue, among other things.
Stroke survivors (0.5-1%) A stroke survivor is a person who has survived any kind of stroke (ischemic, hemorrhagic, etc.). While the specific symptoms often depend on the exact location on where the stroke happened, signs such as hemiplegia, slurred speech, vision problems, and cognitive changes are common in most survivors to some degree. When someone has a stroke as a baby, or before they are born, it can result in cerebral palsy, epilepsy, and other disabilities. We have a brain injury tag that you can look through!
Noonan Syndrome (about 0.1-1% - mild is 1%, severe 0.1%) Noonan Syndrome is a disability that is almost never mentioned in any context, but certainly not around the topic of writing disabled characters. It’s a congenital condition that can cause cardiomyopathy, chronic joint pain, hypermobility, short stature, facial differences such as ptosis, autism, and various lymphatic problems among other things. Some people with Noonan Syndrome might use mobility aids to help with their joint pain.
Hyperthyroidism (about 1.2%) Hyperthyroidism is a condition of the endocrine system caused by hormone overproduction that affects metabolism. It often results in irritability, weight loss, heat intolerance, tremors, mood swings, or insomnia. Undertreated hyperthyroidism has a rare, but extremely dangerous side effect associated with it called a thyroid storm, which can be fatal if untreated.
Hypothyroidism (>5%) Hypothyroidism is an endocrine condition just as hyperthyroidism is, and it causes somewhat opposite symptoms. Due to not producing enough thyroid hormones, it often causes fatigue, depression, hair loss, weight gain, and a frequent feeling of being cold. It’s often comorbid with other autoimmune disabilities, e.g. vitiligo, chronic autoimmune gastritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Extreme hypothyroidism can also be potentially fatal because of a condition known as Myxedema coma (or “crisis”), which is also rare.
Deafblindness (about 0.2-2%) Being DeafBlind is often considered to be an extremely rare disability, but that’s not really the case. DeafBlindness on its own isn’t a diagnosis - it can be caused by a wide range of things, with CHARGE syndrome (congenital), Usher syndrome (born deaf, becomes blind later in life), congenital rubella, and age-related deafness and blindness being some of the most common reasons. DeafBlindness is a wide spectrum, the vast majority of DeafBlind people aren’t fully blind and deaf, and they can use various ways of communication. Some of these could be sign language (tactile or not), protactile, the deafblind manual, oral speech (aided by hearing aids or not), the Lorm alphabet, and more. You can learn more about assistive devices here! Despite what various media like to tell you, being DeafBlind isn’t a death sentence, and the DeafBlind community and culture are alive and thriving - especially since the start of the protactile movement. We have a DeafBlindness tag that you can look through!
It’s probably worth mentioning that we have received little to no asks in general for almost all the disabilities above, and it’s certainly not due to what mods answer for - majority of our inbox is amputee-related, and we haven’t had mods that answer those for somewhere around four years now. Our best guess is that writers don’t realize how many options they have and just end up going for the same things over and over.
Only representing “cool” disabilities that are “not too much while having a particular look/aura/drama associated” isn’t what you should aim for. Disabled people just exist, and all of us deserve to be represented, including those whose disabilities aren’t your typical “cool design” or “character inspo”. Sometimes we are just regular people, with disabilities that are “boring” or “too much”, and don’t make for useful plot points.
mod Sasza (with huge thank yous to mod Sparrow, Rot, and Virus for their contributions with research and data!)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Resources For Writing Deaf, Mute, or Blind Characters
Despite the fact that I am not deaf, mute, or blind myself, one of the most common questions I receive is how to portray characters with these disabilities in fiction.
As such, I’ve compiled the resources I’ve accumulated (from real life deaf, mute, or blind people) into a handy masterlist.
Deaf Characters:
Deaf characters masterpost
Deaf dialogue thread
Dialogue with signing characters (also applies to mute characters.)
A deaf author’s advice on deaf characters
Dialogue between deaf characters
Mute Characters
Life as a Mute
My Silent Summer: Life as a Mute
What It’s Like Being Mute
21 People Reveal What It’s Really Like To Be Mute
I am a 20 year old Mute, ask me anything at all!
Blind Characters:
The 33 Worst Mistakes Writers Make About Blind Characters.
@referenceforwriters masterpost of resources for writing/playing blind characters.
The youtube channel of the wonderful Tommy Edison, a man blind from birth with great insight into the depiction of blind people and their lives.
An Absolute Write thread on the depiction of blind characters, with lots of different viewpoints and some great tips.
And finally, this short, handy masterpost of resources for writing blind characters.
Characters Who Are Blind in One Eye
4 Ways Life Looks Shockingly Different With One Eye
Learning to Live With One Eye
Adapting to the Loss of an Eye
Adapting to Eye Loss and Monocular Vision
Monocular Depth Perception
Deaf-Blind Characters
What Is It Like To Be Deafblind?
Going Deaf and Blind in a City of Noise and Lights
Deaf and Blind by 30
Sarita is Blind, Deaf, and Employed (video)
Born Deaf and Blind, This Eritrean American Graduated Harvard Law School (video)
A Day of a Deaf Blind Person
Lesser Known Things About Being Deafblind
How the Deaf-Blind Communicate
Early Interactions With Children Who Are Deaf-Blind
Raising a DeafBlind Baby
If you have any more resources to add, let me know! I’ll be adding to this post as I find more resources.
I hope this helps, and happy writing! <3
119K notes
·
View notes
Text
Injury angst for writing dummies.
Hospitals and injury are always such a staple of angst fics, but 9 times out of 10 the author has clearly never been in an emergency situation and the scenes always come off as over-dramatized and completely unbelievable. So here’s a crash course on hospital life and emergencies for people who want authenticity. By someone who spends 85% of her time in a hospital.
Emergency Departments/Ambulances.
Lights and sirens are usually reserved for the actively dying. Unless the person is receiving CPR, having a prolonged seizure or has an obstructed airway, the ambulance is not going to have lights and sirens blaring. I have, however, seen an ambulance throw their lights on just so they can get back to the station faster once. Fuckers made me late for work.
Defibrillators don’t do that. You know, that. People don’t go flying off the bed when they get shocked. But we do scream “CLEAR!!” before we shock the patient. Makes it fun.
A broken limb, surprisingly, is not a high priority for emergency personnel. Not unless said break is open and displaced enough that blood isn’t reaching a limb. And usually when it’s that bad, the person will have other injuries to go with it.
Visitors are not generally allowed to visit a patient who is unstable. Not even family. It’s far more likely that the family will be stuck outside settling in for a good long wait until they get the bad news or the marginally better news. Unless it’s a child. But if you’re writing dying children in your fics for the angst factor, I question you sir.
Unstable means ‘not quite actively dying, but getting there’. A broken limb, again, is not unstable. Someone who came off their motorbike at 40mph and threw themselves across the bitumen is.
CPR is rarely successful if someone needs it outside of hospital. And it is hard fucking work. Unless someone nearby is certified in advanced life support, someone who needs CPR is probably halfway down the golden tunnel moving towards the light.
Emergency personnel ask questions. A lot of questions. So many fucking questions. They don’t just take their next victim and rush off behind the big white doors into the unknown with just a vague ‘WHAT HAPPENED? SHE HIT HER HEAD?? DON’T WORRY SIR!!!’ They’re going to get the sir and ask him so many questions about what happened that he’s going to go cross eyed. And then he’s going to have to repeat it to the doctor. And then the ICU consultant. And the police probably.
In a trauma situation (aka multiple injuries (aka car accident, motorbike accident, falling off a cliff, falling off a horse, having a piano land on their head idfk you get the idea)) there are a lot of people involved. A lot. I can’t be fucked to go through them all, but there’s at least four doctors, the paramedics, five or six nurses, radiographers, surgeons, ICU consultants, students, and any other specialities that might be needed (midwives, neonatal transport, critical retrieval teams etc etc etc). There ain’t gonna be room to breathe almost when it comes to keeping someone alive.
Emergency departments are a life of their own so you should probably do a bit of research into what might happen to your character if they present there with some kind of illness or injury before you go ahead and scribble it down.
Wards
Nurses run them. No seriously. The patient will see the doctor for five minutes in their day. The nurse will do the rest. Unless the patient codes.
There is never a defibrillator just sitting nearby if a patient codes.
And we don’t defibrillate every single code.
If the code does need a defibrillator, they need CPR.
And ICU.
They shouldn’t be on a ward.
There are other people who work there too. Physiotherapists will always see patients who need rehab after breaking a limb. Usually legs, because they need to be shown how to use crutches properly.
Wards are separated depending on what the patient’s needs are. Hospitals aren’t separated into ICU, ER and Ward. It’s usually orthopaedic, cardiac, neuro, paediatric, maternity, neonatal ICU, gen surg, short stay surg, geriatric, palliative…figure out where your patient is gonna be. The care they get is different depending on where they are.
ICU.
A patient is only in ICU if they’re at risk of active dying. I swear to god if I see one more broken limb going into ICU in a fic to rank up the angst factor I’m gonna shit. It doesn’t happen. Stop being lazy.
Tubed patients can be awake. True story. They can communicate too. Usually by writing, since having a dirty great tube down the windpipe tends to impede ones ability to talk.
The nursing care is 1:1 on an intubated patient. Awake or not, the nurse is not gonna leave that room. No, not even to give your stricken lover a chance to say goodbye in private. There is no privacy. Honestly, that nurse has probably seen it all before anyway.
ICU isn’t just reserved for intubated patients either. Major surgeries sometimes go here post-op to get intensive care before they’re stepped down. And by major I mean like, grandpa joe is getting his bladder removed because it’s full of cancer.
Palliative patients and patients who are terminal will not go to ICU. Not unless they became terminally ill after hitting ICU. Usually those ones are unexpected deaths. Someone suffering from a long, slow, gradually life draining illness will probably go to a general ward for end of life care. They don’t need the kind of intensive care an ICU provides because…well..they’re not going to get it??
Operations.
No one gets rushed to theatre for a broken limb. Please stop. They can wait for several days before they get surgery on it.
Honestly? No one gets ‘rushed’ to theatre at all. Not unless they are, again, actively dying, and surgery is needed to stop them from actively dying.
Except emergency caesarians. Them babies will always get priority over old mate with the broken hip. A kid stuck in a birth canal and at risk of death by pelvis is a tad more urgent than a gall stone. And the midwives will run. I’ve never seen anyone run as fast as a midwife with a labouring woman on the bed heading to theatres for an emergency caesar.
Surgery doesn’t take as long as you think it does. Repairing a broken limb? Two hours, maybe three tops. Including time spent in recovery. Burst appendix? Half an hour on the table max, maybe an hour in recovery. Caesarian? Forty minutes or so. Major surgeries (organs like kidneys, liver and heart transplants, and major bowel surgeries) take longer.
You’re never going to see the theatre nurses. Ever. They’re like their own little community of fabled myth who get to come to work in their sweatpants and only deal with unconscious people. It’s the ward nurse who does the pick up and drop offs.
Anyway there’s probably way, way more that I’m forgetting to add but this is getting too long to keep writing shit. The moral of the story is do some research so you don’t look like an idiot when you’re writing your characters getting injured or having to be in hospital. It’s not Greys Anatomy in the real world and the angst isn’t going to be any more intense just because you’re writing shit like it is.
Peace up.
56K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey! Are there blacksmiths in your story? I'm a hobbyist blacksmith and I'm here to help!
Blacksmithing is one of those things that a lot of people get wrong because they don't realize it stuck around past the advent of the assembly line. Here's a list of some common misconceptions I see and what to do instead!
Not all blacksmiths are gigantic terrifying muscly guys with beards and deep voices. I am 5'8, skinny as a twig, have the muscle mass of wet bread, and exist on Tumblr. Anybody who is strong enough to pick up a hammer and understands fire safety can be a blacksmith.
You can make more than just swords with blacksmithing. Though swords are undeniably practical, they're not the only things that can be made. I've made candle holders, wall hooks, kebab skewers, fire pokers, and more. Look up things other people have made, it's really amazing what can be done.
"Red-hot" is actually not that hot by blacksmith terms. when heated up, the metal goes from black, to red, to orange, to yellow, to white. (for temperature reference, I got a second degree burn from picking up a piece of metal on black heat) The ideal color to work with the metal is yellow. White is not ideal at all, because the metal starts sparking and gets all weird and lumpy when it cools. (At no point in this process does the metal get even close to melting. It gets soft enough to work with, but I have never once seen metal become a liquid.)
Blacksmithing takes fucking forever. Not even taking into account starting the forge, selecting and preparing metal, etc. etc. it takes me around an hour to make one (1) fancy skewer. The metals blacksmiths work with heat up and cool down incredibly fast. When the forge is going good, it only takes like 20 seconds to get your metal hot enough to work with, but it takes about the same time for it to cool down, sometimes even less.
As long as you are careful, it is actually stupidly easy to not get hurt while blacksmithing. When I picked up this hobby I was like "okay, cool! I'm gonna make stuff, and I'm gonna end up in the hospital at some point!" Thus far, the latter has yet to occur. I've been doing this for nearly a year. I have earned myself a new scar from the aforementioned second degree burn, and one singe mark on my jeans. I don't even wear gloves half the time. Literally just eye protection, common sense, and fast reflexes and you'll probably be fine. (Accidents still happen of course, but I have found adequate safety weirdly easy to achieve with this hobby)
A forge is not a fire. The forge is the thing blacksmiths put their metal in to heat it up. It starts as a small fire, usually with newspaper or something else that's relatively small and burns easily, which we then put in the forge itself, which is sort of a fireplace-esque thing (there's a lot of different types of forge, look into it and try to figure out what sort of forge would make the most sense for the context you're writing about) and we cover it with coal, which then catches fire and heats up. The forge gets really hot, and sometimes really bright. Sometimes when I stare at the forge for too long it's like staring into the sun. The forge is also not a waterfall of lava, Steven Universe. It doesn't work like that, Steven Universe.
Welding and blacksmithing are not the same thing. They often go hand-in-hand, but you cannot connected two pieces of metal with traditional blacksmithing alone. There is something called forge welding, where you heat your metal, sprinkle borax (or the in-universe equivalent) on it to prevent the metal from oxidizing/being non-weldable, and hammer the pieces together very quickly. Forge welding also sends sparks flying everywhere, and if you're working in a small space with other blacksmiths, you usually want to announce that you're welding before you do, so that everyone in a five-foot radius can get out of that five-foot radius. You also cannot just stuck some random pebbles into the forge and get a decent piece of metal that you can actually make something with, Steven Universe. It doesn't work like that, Steven Universe.
Anvils are really fucking heavy. Nothing else to add here.
Making jewelry is not a blacksmithing thing unless you want jewelry made of steel. And it will be very ugly if you try. Blacksmithing wasn't invented to make small things.
If there's anything here I didn't mention, just ask and I'll do my best to answer.
38K notes
·
View notes
Text
October 15th is white cane awareness day! White canes are an important mobility tool for the blind and low vision, but did you know they're so much more than just one type of cane?
Blind people have been using canes and staffs to navigate independently for centuries, but it was only in the 1930s that the concept of a white cane was widely introduced as a symbol for blindness. A man named James Briggs who lost his sight after an accident claimed to have invented it in 1921 after painting his cane white so drivers could better see it while he was crossing the street, and from there the idea spread across Europe and North America while being promoted by blind organizations .
There are different types of canes for different uses. Long canes, also called mobility or probing canes, are what you typically think of when you imagine a white cane user. They go up to at least your chest height or taller and are used for probing in front of you. They are helpful for people with a lot of trouble navigating.
Guide canes are shorter, more lightweight canes that can be used to poke at obstacles or judge curbs, but they don't provide the same tactile feedback as long canes. They are helpful for people with a bit of trouble navigating.
Identification or symbol canes are even smaller sticks that are normally held off the ground. Their only purpose is for signaling to others that you have low vision, and can't be used for obstacle detection. They are helpful for people who don't struggle that much with navigating but still need recognition or assistance in public .
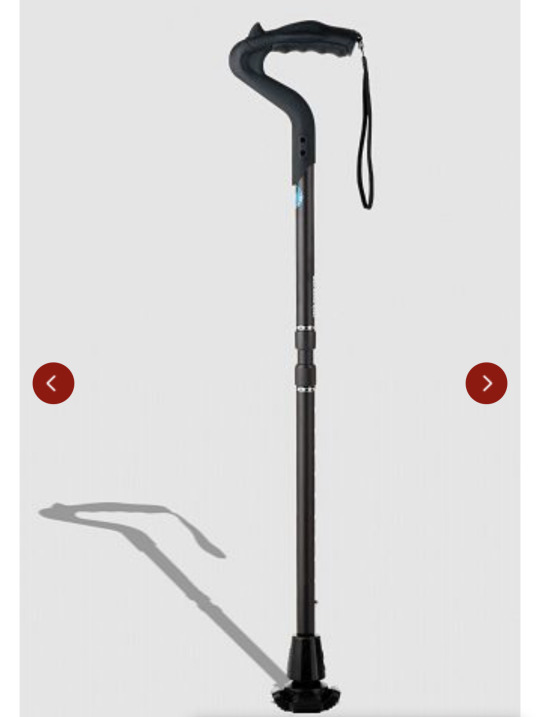
Some people with mobility disabilities and low vision will also use a support cane/walking stick that is painted white for identification!
Here are pictures of a long cane, guide cane, identification cane, and white support cane respectively:
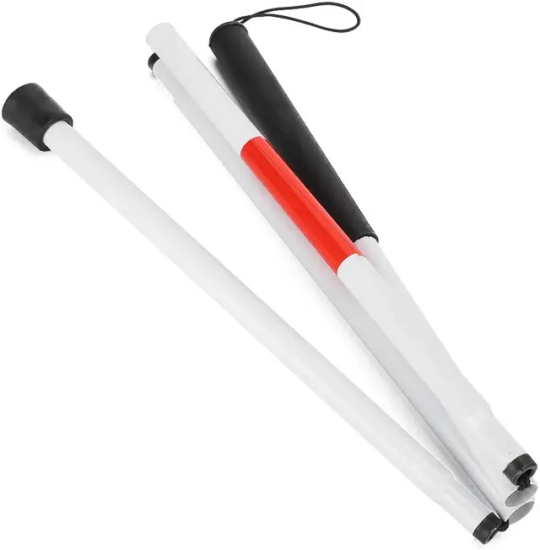
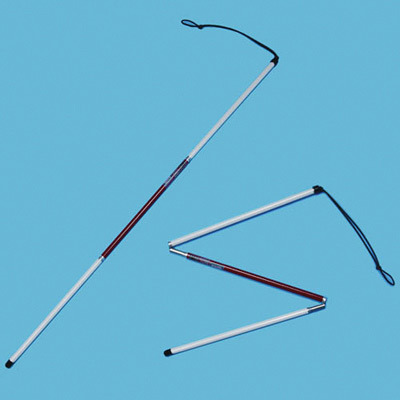




The colour of your cane can have meaning too, but they are not hard and fast rules and vary by region. In North America, fully white canes signal total blindness. Canes with a red segment signal partial sight. Canes with multiple red stripes signal DeafBlindness.
Regionally, the fully white cane is more common in Europe, and the red and white cane is more common in North America no matter your vision level. Fully blind people in cold areas like Canada may use the red and white cane so it's easier to spot in the snow. They also come in fun colours that mean nothing but encourage people to use their canes more ! I have one in a marigold yellow colour because yellow is my favourite.
The white cane is a wonderful tool, but it's also a powerful symbol of blind independence and adaption. Now you know more about the white cane and what they represent!
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Resources For Writing Deaf, Mute, or Blind Characters
Despite the fact that I am not deaf, mute, or blind myself, one of the most common questions I receive is how to portray characters with these disabilities in fiction.
As such, I’ve compiled the resources I’ve accumulated (from real life deaf, mute, or blind people) into a handy masterlist.
Deaf Characters:
Deaf characters masterpost
Deaf dialogue thread
Dialogue with signing characters (also applies to mute characters.)
A deaf author’s advice on deaf characters
Dialogue between deaf characters
Mute Characters
Life as a Mute
My Silent Summer: Life as a Mute
What It’s Like Being Mute
21 People Reveal What It’s Really Like To Be Mute
I am a 20 year old Mute, ask me anything at all!
Blind Characters:
The 33 Worst Mistakes Writers Make About Blind Characters.
@referenceforwriters masterpost of resources for writing/playing blind characters.
The youtube channel of the wonderful Tommy Edison, a man blind from birth with great insight into the depiction of blind people and their lives.
An Absolute Write thread on the depiction of blind characters, with lots of different viewpoints and some great tips.
And finally, this short, handy masterpost of resources for writing blind characters.
Characters Who Are Blind in One Eye
4 Ways Life Looks Shockingly Different With One Eye
Learning to Live With One Eye
Adapting to the Loss of an Eye
Adapting to Eye Loss and Monocular Vision
Monocular Depth Perception
Deaf-Blind Characters
What Is It Like To Be Deafblind?
Going Deaf and Blind in a City of Noise and Lights
Deaf and Blind by 30
Sarita is Blind, Deaf, and Employed (video)
Born Deaf and Blind, This Eritrean American Graduated Harvard Law School (video)
A Day of a Deaf Blind Person
Lesser Known Things About Being Deafblind
How the Deaf-Blind Communicate
Early Interactions With Children Who Are Deaf-Blind
Raising a DeafBlind Baby
If you have any more resources to add, let me know! I’ll be adding to this post as I find more resources.
I hope this helps, and happy writing! <3
119K notes
·
View notes
Text
Resources For Writing Deaf, Mute, or Blind Characters
Despite the fact that I am not deaf, mute, or blind myself, one of the most common questions I receive is how to portray characters with these disabilities in fiction.
As such, I’ve compiled the resources I’ve accumulated (from real life deaf, mute, or blind people) into a handy masterlist.
Deaf Characters:
Deaf characters masterpost
Deaf dialogue thread
Dialogue with signing characters (also applies to mute characters.)
A deaf author’s advice on deaf characters
Dialogue between deaf characters
Mute Characters
Life as a Mute
My Silent Summer: Life as a Mute
What It’s Like Being Mute
21 People Reveal What It’s Really Like To Be Mute
I am a 20 year old Mute, ask me anything at all!
Blind Characters:
The 33 Worst Mistakes Writers Make About Blind Characters.
@referenceforwriters masterpost of resources for writing/playing blind characters.
The youtube channel of the wonderful Tommy Edison, a man blind from birth with great insight into the depiction of blind people and their lives.
An Absolute Write thread on the depiction of blind characters, with lots of different viewpoints and some great tips.
And finally, this short, handy masterpost of resources for writing blind characters.
Characters Who Are Blind in One Eye
4 Ways Life Looks Shockingly Different With One Eye
Learning to Live With One Eye
Adapting to the Loss of an Eye
Adapting to Eye Loss and Monocular Vision
Monocular Depth Perception
Deaf-Blind Characters
What Is It Like To Be Deafblind?
Going Deaf and Blind in a City of Noise and Lights
Deaf and Blind by 30
Sarita is Blind, Deaf, and Employed (video)
Born Deaf and Blind, This Eritrean American Graduated Harvard Law School (video)
A Day of a Deaf Blind Person
Lesser Known Things About Being Deafblind
How the Deaf-Blind Communicate
Early Interactions With Children Who Are Deaf-Blind
Raising a DeafBlind Baby
If you have any more resources to add, let me know! I’ll be adding to this post as I find more resources.
I hope this helps, and happy writing! <3
119K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing and drawing amputee characters: Not every amputee wears prosthetics (and that's ok)
Not every amputee wears prosthetics, and not doing so is not a sign that they've "given up".
It's a bit of a trope that I've noticed that when an amputee, leg amputees in particular, don't wear prosthetics in media its often used as a sign that they've given up hope/stopped trying/ are depressed etc. If/when they start feeling better, they'll start wearing their prosthetics again, usually accompanied by triumphant or inspiring music (if it's a movie). The most famous example of this is in Forest Gump, Where Dan spends most of the movie after loosing his legs wishing he'd died instead. He does eventually come around, and him finally moving from his wheelchair to prosthetics is meant to highlight this.

The thing is, it's not that it's unrealistic - in fact my last major mental health spiral was started because one of my prosthetics was being a shit and wouldn't go on properly, despite fitting perfectly at the prosthetist's the day before. I'm not going to use my legs when I'm not in a good headspace, but the problem is, this is the only time non-prosthetic using amputees ever get representation: to show how sad they are. Even if that's not what the creator/writer necessarily intended, audiences will often make that assumption on their own unless you're very careful and intentional about how you frame it, because it's what existing media has taught them to expect.
But there are lots of reasons why someone might not use prosthetics:
they might not need them: this is more common in arm amputees because of how difficult it can be to use arm prosthetic, especially above-elbow prosthetics. Most folks learn how to get on without them pretty well. In fact, most of the arm amputees I know don't have prosthetics, or only have them for specific tasks (e.g. I knew a girl who had a prosthetic hand made specifically for rowing, but that's all she used it for).
Other mobility aids just work better for them: for me, I'm faster, more manoeuvrable and can be out for longer when I'm in my wheelchair than I ever could on my prosthetics. Youtube/tik tok creator Josh Sundquist has said the same thing about his crutches, he just feels better using them than his prosthetic. This isn't the case for everyone of course, but it is for some of us. Especially people with above-knee prosthetics, in my experience.
Other disabilities make them harder to use: Some people are unable to use prosthetics due to other disabilities, or even other amputations. Yeah, as it turns out, a lot of prosthetics are only really designed for single-limb amputees. While they're usable for multi-limb amps, they're much harder to use or they might not be able to access every feature. For example, the prosthetic knee I have has the ability to monitor the walk cycle of the other leg and match it as close as possible - but that only works if you have a full leg on the other side. Likewise, my nan didn't like using her prosthetic, as she had limited movement in her shoulders that meant she physically couldn't move her arms in the right way to get her leg on without help.
Prosthetics are expensive in some parts of the world: not everyone can afford a prosthetic. My left prosthetic costs around $5,000 Australian dollars, but my right one (the above knee) cost $125,000AUD. It's the most expensive thing I own that I only got because my country pays for medical equipment for disabled folks. Some places subsidise the cost, but paying 10% of $125,000 is still $12,500. Then in some places, if you don't have insurance, you have to pay for that all by yourself. Even with insurance you still have to pay some of it depending on your cover. Arm prosthetics are even more expensive. Sure, both arms and legs do have cheaper options available, but they're often extremely difficult to use. You get what you pay for.
they aren't suitable for every type of environment: Prosthetics can be finicky and modern ones can be kind of sensitive to the elements. My home town was in a coastal lowland - this means lots of beaches and lots of swamp filled with salty/brackish water. The metals used in prosthetics don't hold up well in those conditions, and so they would rust quicker, I needed to clean them more, I needed to empty sand out of my foot ALL THE TIME (there always seemed to be more. It was like a bag of holding but it was just sand). Some prosthetics can't get wet at all. There were a few amputees who moved to the area when I was older who just didn't bother lol. It wasn't worth the extra effort needed for the maintenance.
People have allergies to the prosthetic material: This is less of a problem in the modern day, but some people are allergic to the materials their prosthetics are made from. You can usually find an alternative but depending on the type of allergy, some people are allergic to the replacements too.
Some people just don't like them.
There's nothing wrong with choosing to go without a prosthetic. There's nothing wrong with deciding they aren't for you. It doesn't make you a failure or sad or anything else. Using or not using prosthetics is a completely morally neutral thing.
Please, if you're writing amputees, consider if a prosthetic really is the best mobility aid for your character and consider having your characters go without, or at least mix it up a bit.
For example, Xari, one of the main characters in my comic, uses prosthetics unsupported and with crutches, and uses a wheelchair. They alternate between them throughout the story.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Reminder that associating hair length with gender is not a culturally universal concept and that many indigenous folks in North America don’t cut their hair for cultural reasons that have nothing to do with gender.
Reminder that a native guy should be allowed to wear his hair in long braids without people calling it gender nonconformity or saying he’s breaking gender norms, because hair length has nothing to do with his gender norms.
Reminder that a queer native woman should be allowed to wear her hair long without being automatically read as femme presenting, that she can be butch with long hair, because long hair is not associated with femininity in her culture.
Reminder that many native folks cut their hair for solemn reasons, usually mourning, and remarking on it as a reflection of personal style or gender presentation can be deeply disrespectful. No, she didn’t just get a fierce butch haircut - she cut her hair because someone died. No, he didn’t cave to a gender conforming haircut - he cut his hair because someone died.
Reminder that this is not universally practiced by native folks and, like all cultural practices, some people are more strict in their adherence than others.
24K notes
·
View notes
Text
That post about writing motorcycle scenes I've been meaning to write
Riding a bike is one of those things that’s a very physical experience, so if you haven’t ridden, then there’s a lot you will naturally not be aware of. I love motorcycle scenes in stories, but over the years I’ve noticed that scenes written by non-riders almost always make the same mistakes. They’re ubiquitous in fact, to the point that if you haven’t been there to learn the contrary yourself, it’s natural to assume that’s how it actually works.
The first thing to know about motorcycles is that when driving, the motorcycle performs as an extension of you. It’s almost cybernetic, the way your mass and balance fuse with the machine’s, the way it transmutes your sense of your surroundings and the surface you’re driving on, and the sense of the bike itself and how it’s performing.
Most notably, the driver’s center of gravity becomes the central steering mechanism. At speeds faster than around 10 mph, the driver steers primarily through shifting their center of balance. If you want to turn left, you lean your body left. You’re actually tilting yourself and the motorcycle to take curves and corners.
When carrying a passenger, then, the passenger needs to shift their center of gravity along with the driver’s. It’s like taking the ‘follower’ position in partner dancing. You lean WITH them; not less, because then your weight counters theirs and they end up not turning (which can be highly bad if, say, the road does not go that way), and not more, because then the bike could tip right over.
Being a good passenger on a bike is not a huge learning curve for most people, but there is a learning curve. And some people have more of a knack for it than others. Some people are natural back-seat drivers, for whatever reason overly pushy, eager, demanding, or determined that they know better than you, and have a habit of making it hard on the driver. I’ve had people tell me they hate riding pillion even if they’re good at it, because they don’t like how out-of-control it feels. I detest it myself, in fact; I’d far rather be driving, and it’s a constant struggle for me to just follow along and behave myself.
This means, though, that carrying a passenger who weighs significantly more than you can be a tricky business. I weigh about 110, and when carrying a rider weighing significantly more than that, it’s awfully easy to crash if the passenger tries to back-seat steer. (A way to mitigate this, especially for new passengers, is to simply take 15 minutes or so to bump around quiet local roads at low speeds so that the driver and passenger can familiarize themselves a bit with minimal risk to themselves.)
Now, undoubtedly the #1 most-committed mistake I see from almost everybody who writes about motorcycles (and for that matter, a lot of unsuspecting new passengers try it in real life) is the ‘wrapping arms around the driver’s waist’ business. It’s so common that this line is practically required by law when somebody’s writing a motorcycle scene, but seriously: DON’T DO THAT. <–The all caps there is not for shaming; it’s for emphasizing the safety issues. It’s not only uncomfortable for the driver, it’s potentially dangerous. It makes it hard to steer, hard to breathe comfortably, and easy to get jerked off balance and into a crash.
In a similar vein, holding onto the driver via grabbing their clothing is ill-advised. This can lead to getting jerked off balance, having seams dig in painfully, and being choked by fabric.
What to do instead: The rider sitting pillion should brace their hands on either side of the driver’s waist.
I know, if you’re in it for the sexual tension, this sounds less sexy, but I’m here to tell you that’s a filthy lie. A passenger who’s sitting properly is basically molded onto the driver’s back. Riding with/being a passenger on a bike is a startlingly intimate experience. There’s a lot of trust and teamwork involved, which takes place at a kinesthetic level. It feels a lot like dancing, as I said before, or maybe partnered sports, where the collaboration is happening at a physical, bone-deep level that often skips right past the conscious intellect.
Now, sometimes (you may’ve seen this on the road) you’ll have passengers who prefer to hang onto a part of the bike–bits of the frame, maybe, or a ‘sissy bar’/seat back sticking up from the back. It’s not uncommon, but it’s a bad habit because the passenger is never quite as in-tune with the driver this way, and if something happens–a tire slips in a puddle, for example–their weight moving in the wrong direction can end up jerking the bike out of the driver’s control.
Another thing I see a lot of writers do in stories that doesn’t work in real life: unfortunately, helmets are NOT easily swappable. They’re designed to clasp the head; a well-fitted helmet should not move on your head at all, even if you shake your head hard (though it also shouldn’t be tight enough to exert uncomfortable pressure). A helmet that fits loosely is useless at best and dangerous at worst. One that’s too tight is either painful or doesn’t go on at all. It doesn’t take much difference in the size of two people’s heads for one person’s helmet to not fit the other person properly. (And even if they’re the same size, that doesn’t necessarily mean it’ll be comfortable for more than short-term wear, but hey.)
Also, the stupid things are ridiculously expensive–especially the full-face models–so most bikers aren’t lucky enough to have a bunch of extras just laying around.
Another tip, both for writing and riding: riding pillion on a sports bike (those sleek ones where the driver’s crouched and leaning forward like a race jockey) is a miserable freaking experience. On a lot of models, you’re perched up there on something that barely counts as a seat and leaves you constantly feeling like you’re about to slide off the back; your legs are pushed up into a crouch; you’re hunched like a monkey over the driver; and possibly you’ve got a scalding-hot muffler pressed up against your calf.
(Pro tip: if anybody ever invites you for a ride on their bike and you’re wearing shorts, pay attention to where the muffler’s located in relation to the foot pegs.)
Now, what is it about motorcycles that makes some of us bikers go into a lathered-up frenzy at the idea of riding? It’s because it FEELS SO DAMN ALIVE.
Look. It’s like…life these days is, well, canned. We spend a lot of our time in pods–houses, cars, subway trains–breathing tinned air, walking around on pavement or carpet… But when I’m on a bike, it’s me and a 360 degree panorama of the world, and there’s nothing between me and it. Some people get off on the risk of that, but for me it’s a matter of immersion. When I ride, I can feel the cool humid air rolling down from under a forested hillside. I can smell the road dust, the oil, the exhaust, the herby scent of weeds and wildflowers on the roadside, the river I’m driving near, the shady scent of a forest, the roadside fruit stand…and I’m not talking in that wafty, broken-up way you get if you roll the car doors down. It’s like driving into a wall of scent, crashing through one bubble after another of temperature changes and smells and sounds and sights, and I have this bike underneath me that’s rumbling and vibrating and moving like it’s part of me, and it’s just the most powerful sense I’ve ever had of being in charge of my own life and not hiding from the world. I can see it, and it can see me, and yeah, that’s a bit dangerous, but it’s also real.
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello gamers, local disabled cane user is gonna teach you how to design a cane.
Tl:dr: design a cane based on comfortability and the disability of the character
First things first, you need to know why you’re character needs a cane. Do they have chronic pain? Unhealed injury? Muscle or joint issues? Do they have poor blood circulation which makes them dizzy? Do they need the cane all the time or does their disability fluctuate? Do they use a wheelchair or a walker sometimes?
There’s a lot you should know about a characters ability/disability in order to find what type of mobility aid they should be using.
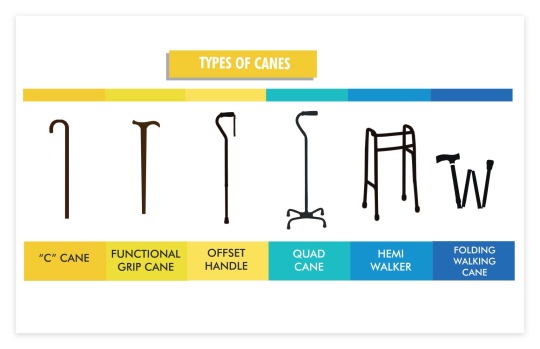
There are a bunch of different kinds of canes/crutches. The 4 on the left are crutches. The difference between canes and crutches are, crutches are meant to keep weight off your legs as much as possible, and generally you use a crutch on each arm. Canes are used for stability and you usually only use one. Folding canes are great for people who only use their cane sometimes

Great! You’ve picked either a cane or crutches for your character. I’m done right? WRONG. Cane handles.
This is probably the most important part of canes because if you have the wrong handle your wrist will die.

I gently kiss all the canes on the left, they are all very good for grip and wrist, although the middle left is designed for left or right hand so you cannot switch hands with it.
The ones on the right are also pretty good, they wouldn’t be my first choice but they are still great. The top one is also very good as it has a wristband so you can’t drop it as easily. (Trust me when I say I DROP MY CANE SO MUCH)
Sigh. The middle cane handles… the bottom one I have never actually seen but it looks like it would kill my wrist. The top one is uncomfortable for long period uses, but it is good for if you’re a shepherd. And the pimp cane… the knob cane… it’s awful. Just no. It’s hard to grip, it is unstable it’s bad it’s awful I throw it into a fire. Please don’t give your character, they don’t deserve that pain
Now you know the basic ergonomic things, there are different shafts for canes and crutches
You can really get creative with this type of thing, just as long as it looks stable enough.
Here are some good examples of pretty canes that are ergonomic and good to use! (featuring victor arcane who i adore)
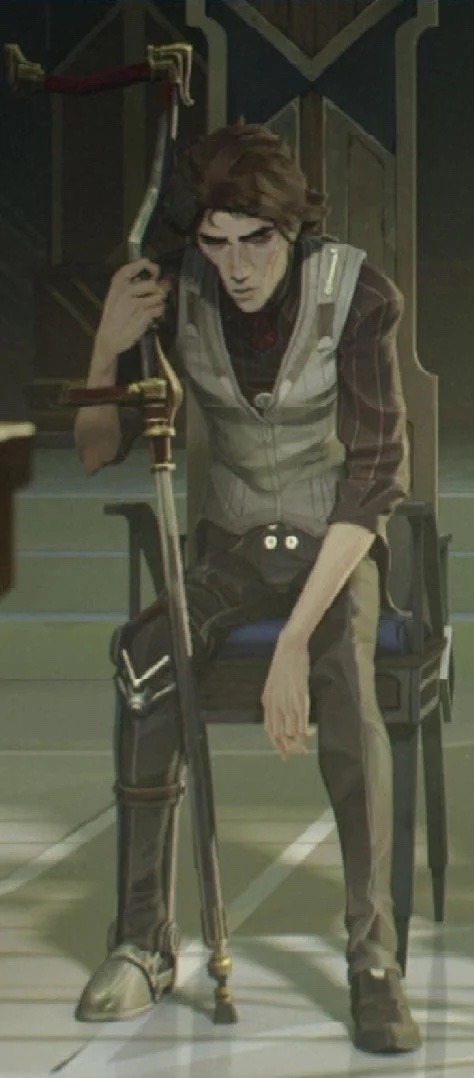
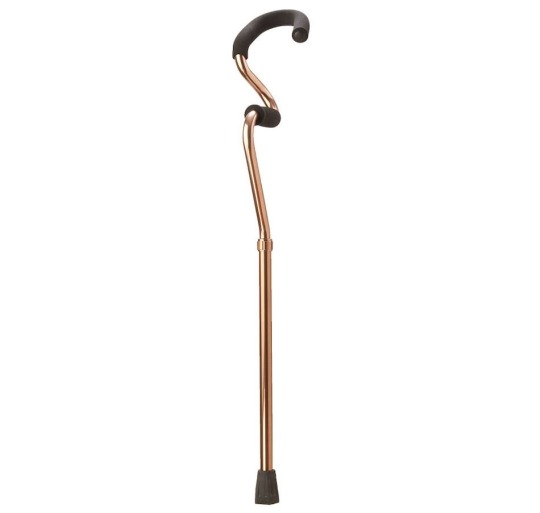



Add some cute details to the cane if you want! You can add stickers, colours, grip support. And while I love the concept of cane swords those are very unstable, if you want a cane weapon you can make it lead weighted, put knives in it. A poison vile in the shaft. Be creative.
Just some of these components are important to consider with a disabled character. There’s a lot more to consider with wheelchairs and walkers which I don’t have the experience with.
If you do have any questions my asks are always open to questions about this stuff! I’d love to help if you’re making a disabled character.
24K notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS IS THE MOST ACCURATE THING I'VE SEEN TODAY

5K notes
·
View notes
Text
I was getting pretty fed up with links and generators with very general and overused weapons and superpowers and what have you for characters so:
Here is a page for premodern weapons, broken down into a ton of subcategories, with the weapon’s region of origin.
Here is a page of medieval weapons.
Here is a page of just about every conceived superpower.
Here is a page for legendary creatures and their regions of origin.
Here are some gemstones.
Here is a bunch of Greek legends, including monsters, gods, nymphs, heroes, and so on.
Here is a website with a ton of (legally attained, don’t worry) information about the black market.
Here is a website with information about forensic science and cases of death. Discretion advised.
Here is every religion in the world.
Here is every language in the world.
Here are methods of torture. Discretion advised.
Here are descriptions of the various methods used for the death penalty. Discretion advised.
Here are poisonous plants.
Here are plants in general.
Feel free to add more to this!
194K notes
·
View notes